Beyond White-Nose Syndrome: Mitochondrial and Functional Genomics of Pseudogymnoascus destructans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pangenome Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes in Leotiomycetes
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis
2.4. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes
2.5. Functional Annotation of Pseudogymnoascus destructans
3. Results
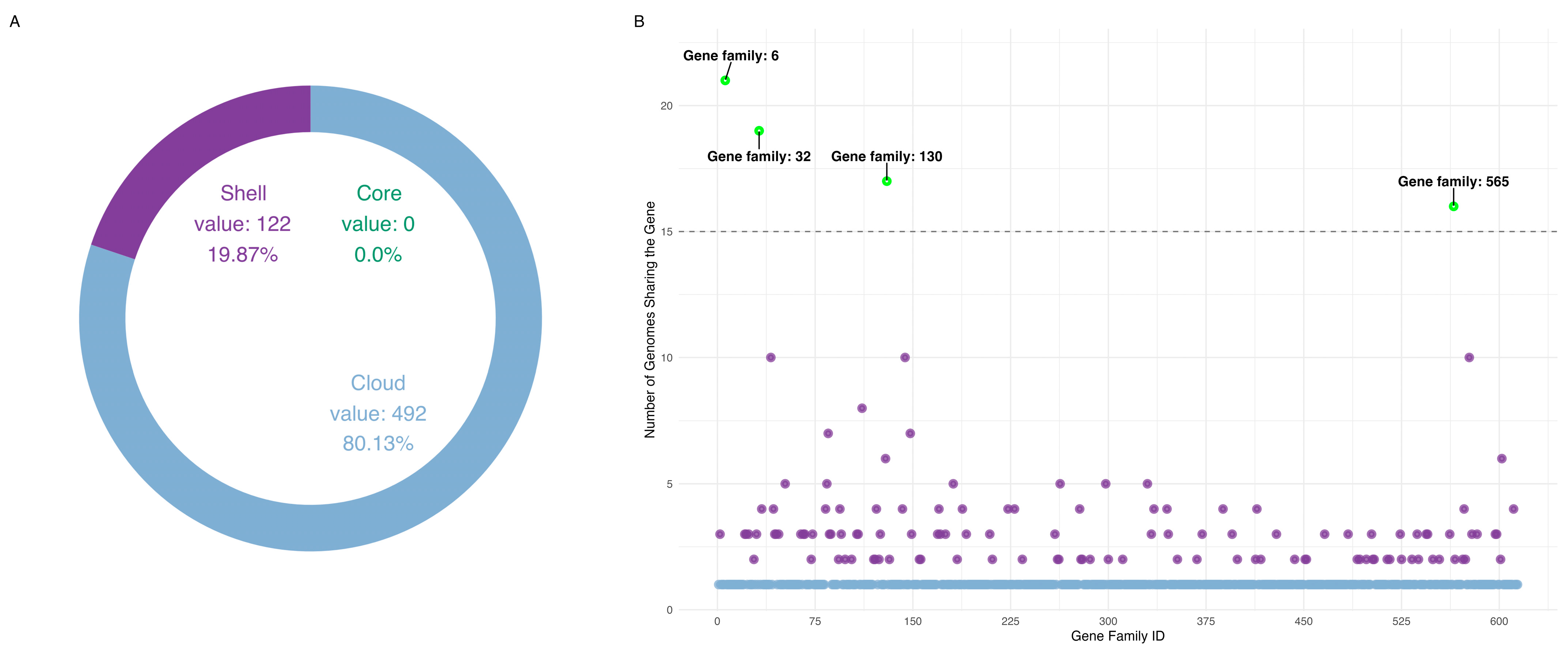
3.1. Pangenome Composition
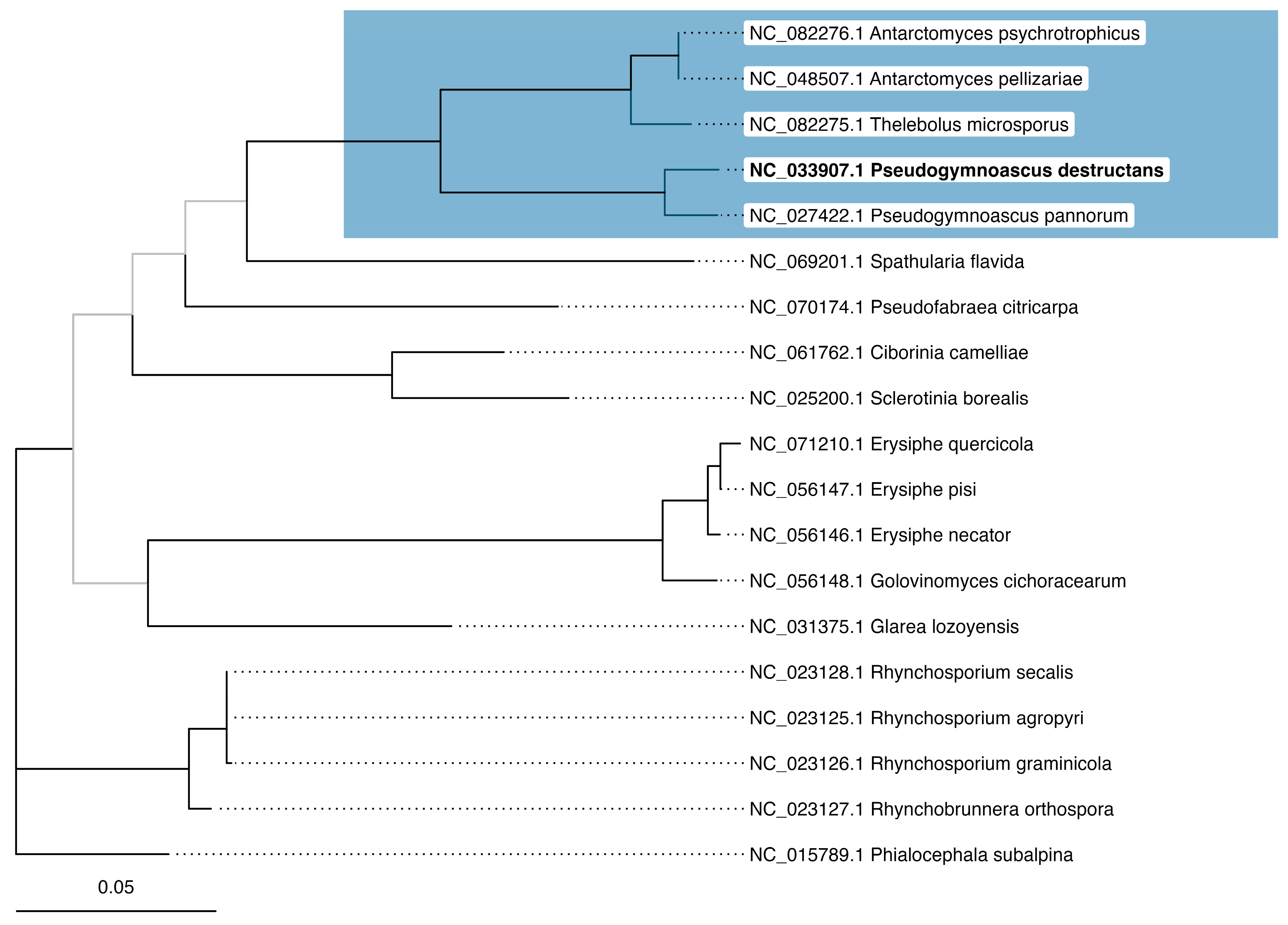
3.2. Phylogenetic Inference
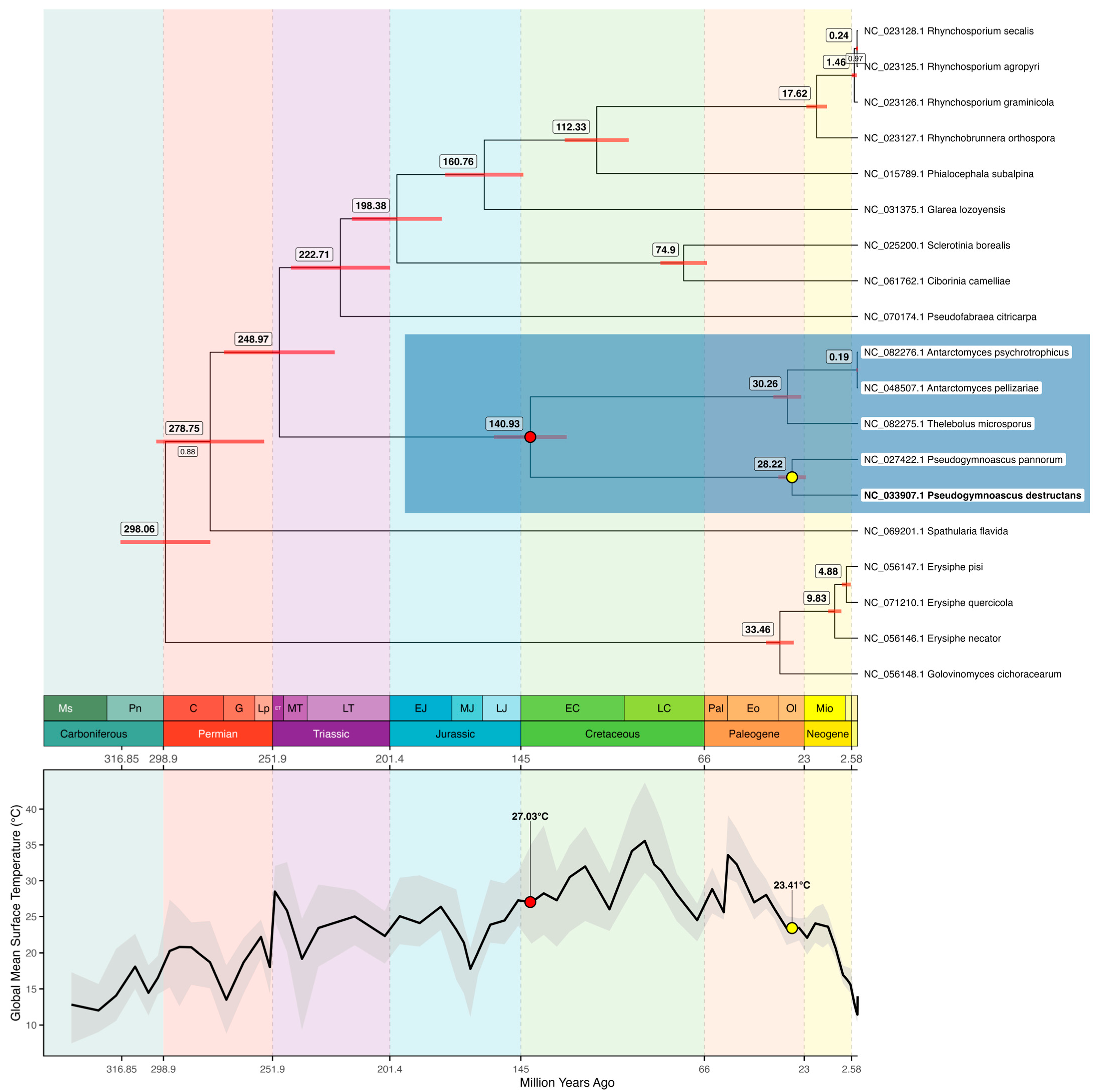
3.3. Bayesian Evolutionary Inference
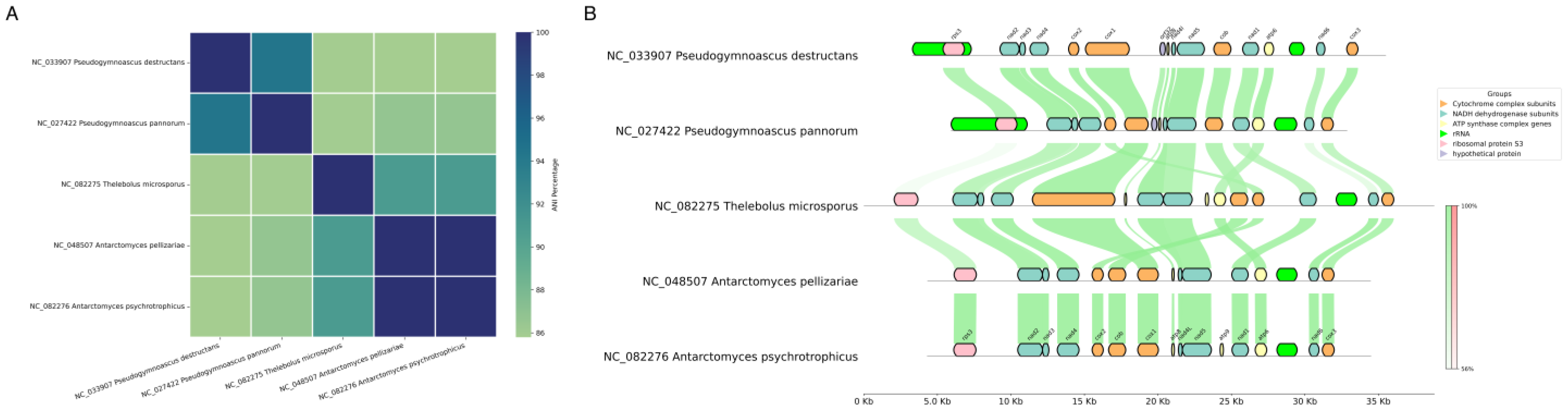
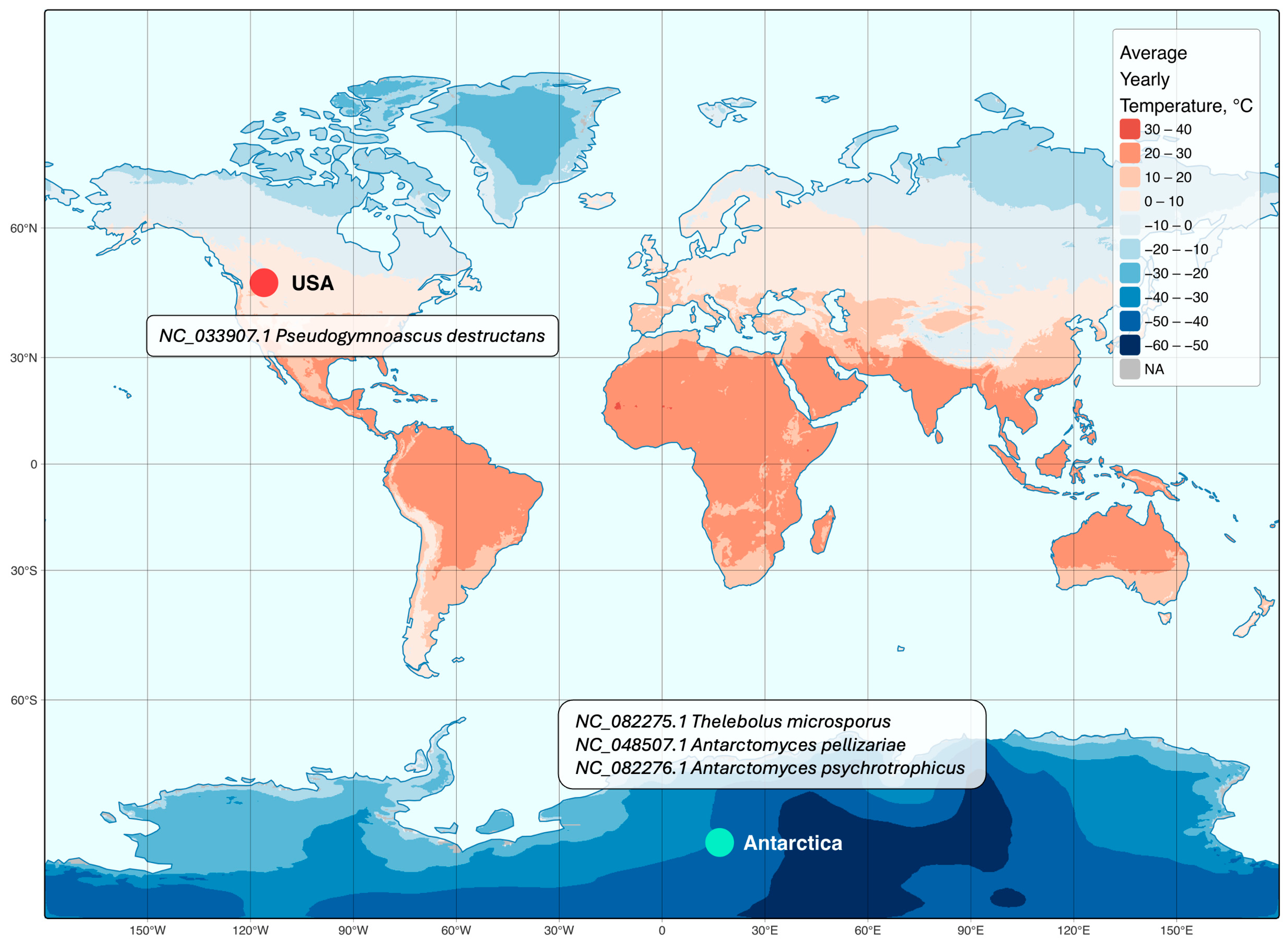
3.4. Mitochondrial Genomic Comparison
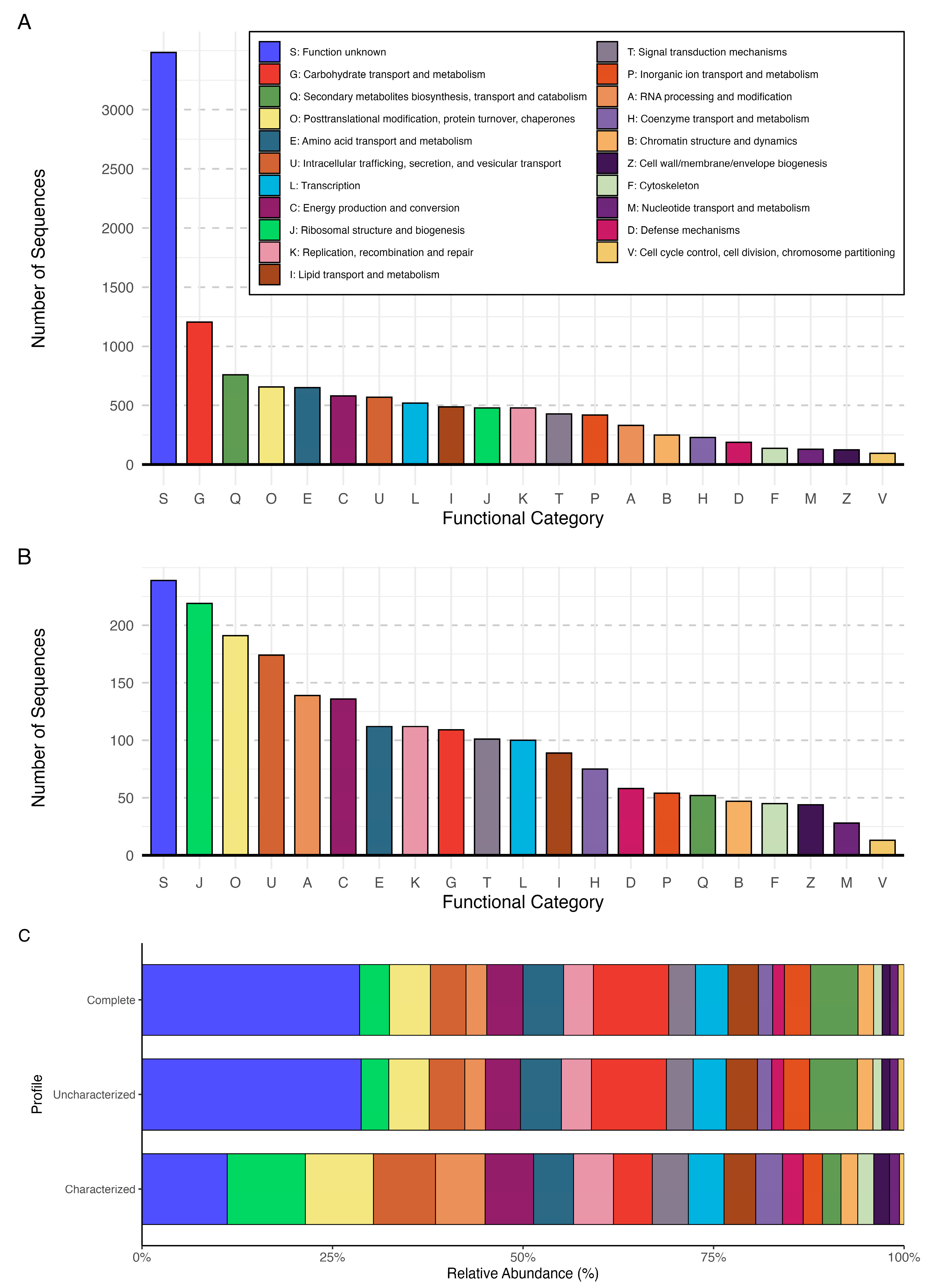
3.5. Functional Profile of Pseudogymnoascus destructans
3.5.1. Information Storage and Processing
3.5.2. Cellular Processes and Signaling
3.5.3. Metabolism
3.5.4. Poorly Characterized Categories
3.5.5. Comparison to Previously Characterized and Uncharacterized Proteins Dataset
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WNS | White-Nose Syndrome |
| ML | Maximum Likelihood |
| PCGs | Protein-coding genes |
| ESS | Effective sample sizes |
| MCC | Maximum clade credibility |
| GMST | Global mean surface temperature |
| ANI | Average Nucleotide Identity |
| COG | Clusters of Orthologous Genes |
| Ms | Mississippian epoch |
| Pn | Pennsylvanian epoch |
| C | Cisuralian epoch |
| G | Guadalupian epoch |
| Lp | Lopingian epoch |
| ET | Early Triassic epoch |
| MT | Middle Triassic epoch |
| LT | Late Triassic epoch |
| EJ | Early Jurassic epoch |
| MJ | Middle Jurassic epoch |
| LJ | Late Jurassic epoch |
| EC | Early Cretaceous epoch |
| LC | Late Cretaceous epoch |
| Pal | Paleocene epoch |
| Eo | Eocene epoch |
| Ol | Oligocene epoch |
| Mio | Miocene epoch |
| MRCA | Most recent common ancestor |
| Mya | Million years ago |
| HPD | Highest posterior density |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| NADH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
References
- Kasso, M.; Balakrishnan, M. Ecological and Economic Importance of Bats (Order Chiroptera). ISRN Biodivers. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Fráncel, L.A.; García-Herrera, L.V.; Losada-Prado, S.; Reinoso-Flórez, G.; Sánchez-Hernández, A.; Estrada-Villegas, S.; Lim, B.K.; Guevara, G. Bats and Their Vital Ecosystem Services: A Global Review. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.L.; Reichard, J.D.; Coleman, J.T.H.; Weller, T.J.; Thogmartin, W.E.; Reichert, B.E.; Bennett, A.B.; Broders, H.G.; Campbell, J.; Etchison, K.; et al. The Scope and Severity of White-Nose Syndrome on Hibernating Bats in North America. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langwig, K.E.; Frick, W.F.; Bried, J.T.; Hicks, A.C.; Kunz, T.H.; Kilpatrick, A.M. Sociality, Density-Dependence and Microclimates Determine the Persistence of Populations Suffering from a Novel Fungal Disease, White-Nose Syndrome. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, C.L.; Davis, A.D.; Herzog, C. The Evolution of a Bat Population with White-Nose Syndrome (WNS) Reveals a Shift from an Epizootic to an Enzootic Phase. Front. Zool. 2019, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, E.G. The Economic Impacts of Ecosystem Disruptions: Costs from Substituting Biological Pest Control. Science 2024, 385, eadg0344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyt, J.R.; Kilpatrick, A.M.; Langwig, K.E. Ecology and Impacts of White-Nose Syndrome on Bats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.; Gourlay, C.W. Editorial: Mitochondrial Function and Dysfunction in Pathogenic Fungi. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1506684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, R.; Franco, M.E.E.; Bartel, L.C.; Martinez Alcántara, V.; Saparrat, M.C.N.; Balatti, P.A. Fungal Mitogenomes: Relevant Features to Planning Plant Disease Management. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Fu, R.; Wang, J.; Xiong, C.; Fan, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhang, H.; Lu, D. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Pathogenic Fungus Scytalidium Auriculariicola (Leotiomycetes) and Insights into Its Phylogenetics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drees, K.P.; Palmer, J.M.; Sebra, R.; Lorch, J.M.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.-C.; Bok, J.W.; Keller, N.P.; Blehert, D.S.; Cuomo, C.A.; et al. Use of Multiple Sequencing Technologies To Produce a High-Quality Genome of the Fungus Pseudogymnoascus destructans, the Causative Agent of Bat White-Nose Syndrome. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00445-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D.; et al. Reference Sequence (RefSeq) Database at NCBI: Current Status, Taxonomic Expansion, and Functional Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kans, J. Entrez Direct: E-Utilities on the Unix Command Line. In Entrez Programming Utilities Help [Internet]; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, A.; Rocha, E.P.C. PanACoTA: A Modular Tool for Massive Microbial Comparative Genomics. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2021, 3, lqaa106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. MMseqs2 Enables Sensitive Protein Sequence Searching for the Analysis of Massive Data Sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnici, V.; Chicco, D. Seven Quick Tips for Gene-Focused Computational Pangenomic Analysis. BioData Min. 2024, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, P.; Stadler, P.F.; Lechner, M. Proteinortho6: Pseudo-Reciprocal Best Alignment Heuristic for Graph-Based Detection of (Co-)Orthologs. Front. Bioinform. 2023, 3, 1322477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian Phylogenetic and Phylodynamic Data Integration Using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Fernandez, J. A Practical Guide to Design and Assess a Phylogenomic Study. Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14, evac129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguileta, G.; de Vienne, D.M.; Ross, O.N.; Hood, M.E.; Giraud, T.; Petit, E.; Gabaldón, T. High Variability of Mitochondrial Gene Order among Fungi. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beimforde, C.; Feldberg, K.; Nylinder, S.; Rikkinen, J.; Tuovila, H.; Dörfelt, H.; Gube, M.; Jackson, D.J.; Reitner, J.; Seyfullah, L.J.; et al. Estimating the Phanerozoic History of the Ascomycota Lineages: Combining Fossil and Molecular Data. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 78, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, E.J.; Tierney, J.E.; Lunt, D.J.; Montañez, I.P.; Huber, B.T.; Wing, S.L.; Valdes, P.J. A 485-Million-Year History of Earth’s Surface Temperature. Science 2024, 385, eadk3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High Throughput ANI Analysis of 90K Prokaryotic Genomes Reveals Clear Species Boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.P. Flattening the Earth: Two Thousand Years of Map Projections; TAschenbuchausgabe; The University of Chicago Press: London, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-0-226-76747-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-Mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mölder, F.; Jablonski, K.P.; Letcher, B.; Hall, M.B.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.H.; Sochat, V.; Forster, J.; Lee, S.; Twardziok, S.O.; Kanitz, A.; et al. Sustainable Data Analysis with Snakemake. F1000Res 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, M.; Andreeva, A.; Florentino, L.C.; Chuguransky, S.R.; Grego, T.; Hobbs, E.; Pinto, B.L.; Orr, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Ponamareva, I.; et al. InterPro: The Protein Sequence Classification Resource in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D444–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaba, S.; Kumari, A.; Medema, M.; Kaushik, R. Pan-Genome Analysis and Ancestral State Reconstruction of Class Halobacteria: Probability of a New Super-Order. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spremulli, L.L. The Protein Biosynthetic Machinery of Mitochondria. In Encyclopedia of Cell Biology; Bradshaw, R.A., Stahl, P.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 545–554. ISBN 978-0-12-394796-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Z.; Su, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, T. Comparative Mitochondrial Genomics of Thelebolaceae in Antarctica: Insights into Their Extremophilic Adaptations and Evolutionary Dynamics. IMA Fungus 2024, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, M.J.; Badrane, H.; Ferea, T.; Adams, J.; Brown, P.O.; Rosenzweig, F.; Botstein, D. Characteristic Genome Rearrangements in Experimental Evolution of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16144–16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudet, D.; Terrat, Y.; Halary, S.; de la Providencia, I.E.; Hijri, M. Mitochondrial Genome Rearrangements in Glomus Species Triggered by Homologous Recombination between Distinct mtDNA Haplotypes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 1628–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, A.I.; Putintseva, Y.A.; Simonov, E.P.; Biriukov, V.V.; Oreshkova, N.V.; Pavlov, I.N.; Sharov, V.V.; Kuzmin, D.A.; Anderson, J.B.; Krutovsky, K.V. Mobile Genetic Elements Explain Size Variation in the Mitochondrial Genomes of Four Closely-Related Armillaria Species. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losada, L.; Pakala, S.B.; Fedorova, N.D.; Joardar, V.; Shabalina, S.A.; Hostetler, J.; Pakala, S.M.; Zafar, N.; Thomas, E.; Rodriguez-Carres, M.; et al. Mobile Elements and Mitochondrial Genome Expansion in the Soil Fungus and Potato Pathogen Rhizoctonia Solani AG-3. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 352, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsushima, A.; Gan, P.; Kumakura, N.; Narusaka, M.; Takano, Y.; Narusaka, Y.; Shirasu, K. Genomic Plasticity Mediated by Transposable Elements in the Plant Pathogenic Fungus Colletotrichum Higginsianum. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demené, A.; Laurent, B.; Cros-Arteil, S.; Boury, C.; Dutech, C. Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus. Peer Community J. 2022, 2, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavirta, H.; Oksanen, I.; Kuuskeri, J.; Mäkelä, M.; Laine, P.; Paulin, L.; Lundell, T. Mitochondrial Genome of Phlebia Radiata Is the Second Largest (156 Kbp) among Fungi and Features Signs of Genome Flexibility and Recent Recombination Events. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Shakya, V.P.S.; Idnurm, A. Exploring and Exploiting the Connection between Mitochondria and the Virulence of Human Pathogenic Fungi. Virulence 2018, 9, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderone, R.; Li, D.; Traven, A. System-Level Impact of Mitochondria on Fungal Virulence: To Metabolism and Beyond. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15, fov027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcila-Galvis, J.E.; Arango, R.E.; Torres-Bonilla, J.M.; Arias, T. The Mitochondrial Genome of a Plant Fungal Pathogen Pseudocercospora Fijiensis (Mycosphaerellaceae), Comparative Analysis and Diversification Times of the Sigatoka Disease Complex Using Fossil Calibrated Phylogenies. Life 2021, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.M.; Onetto, C.A.; Borneman, A.R. Adaptation During the Shift from Entomopathogen to Endosymbiont Is Accompanied by Gene Loss and Intensified Selection. Genome Biol. Evol. 2024, 16, evae251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, T.M.; Hilario, H.O.; de Brito, G.A.M.; Moreira, R.G.; Furtado, C.; de Menezes, G.C.A.; Rosa, C.A.; Rosa, L.H.; Franco, G.R. Whole-Genome Sequencing of the Endemic Antarctic Fungus Antarctomyces Pellizariae Reveals an Ice-Binding Protein, a Scarce Set of Secondary Metabolites Gene Clusters and Provides Insights on Thelebolales Phylogeny. Genomics 2020, 112, 2915–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stchigel, A.M.; Cano, J.; Mac Cormack, W.; Guarro, J. Antarctomyces Psychrotrophicus Gen. et Sp. Nov., a New Ascomycete from Antarctica. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.; DeFiglio, H.; Chaturvedi, S. Phenotype Profiling of White-Nose Syndrome Pathogen Pseudogymnoascus destructans and Closely-Related Pseudogymnoascus pannorum Reveals Metabolic Differences Underlying Fungal Lifestyles. F1000Res 2018, 7, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidoro-Ayza, M.; Lorch, J.M.; Klein, B.S. The Skin I Live in: Pathogenesis of White-Nose Syndrome of Bats. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormerod, K.L.; Morrow, C.A.; Chow, E.W.L.; Lee, I.R.; Arras, S.D.M.; Schirra, H.J.; Cox, G.M.; Fries, B.C.; Fraser, J.A. Comparative Genomics of Serial Isolates of Cryptococcus Neoformans Reveals Gene Associated With Carbon Utilization and Virulence. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2013, 3, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ene, I.V.; Bennett, R.J.; Anderson, M.Z. Mechanisms of Genome Evolution in Candida Albicans. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 52, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Ghosh, K.K.; Chakrabortty, S.; Gulyás, B.; Padmanabhan, P.; Ball, W.B. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in Infection and Immunity. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meteyer, C.U.; Dutheil, J.Y.; Keel, M.K.; Boyles, J.G.; Stukenbrock, E.H. Plant Pathogens Provide Clues to the Potential Origin of Bat White-Nose Syndrome Pseudogymnoascus destructans. Virulence 2022, 13, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.M.; Drees, K.P.; Foster, J.T.; Lindner, D.L. Extreme Sensitivity to Ultraviolet Light in the Fungal Pathogen Causing White-Nose Syndrome of Bats. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Al-Harrasi, A. Fungal Genomes: Suffering with Functional Annotation Errors. IMA Fungus 2021, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davy, C.M.; Donaldson, M.E.; Bandouchova, H.; Breit, A.M.; Dorville, N.A.S.; Dzal, Y.A.; Kovacova, V.; Kunkel, E.L.; Martínková, N.; Norquay, K.J.O.; et al. Transcriptional Host-Pathogen Responses of Pseudogymnoascus destructans and Three Species of Bats with White-Nose Syndrome. Virulence 2020, 11, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, A.; Xu, J. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the White-Nose Syndrome Pathogen, Pseudogymnoascus destructans. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2017, 2, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twort, V.G.; Laine, V.N.; Field, K.A.; Whiting-Fawcett, F.; Ito, F.; Reiman, M.; Bartonicka, T.; Fritze, M.; Ilyukha, V.A.; Belkin, V.V.; et al. Signals of Positive Selection in Genomes of Palearctic Myotis-Bats Coexisting with a Fungal Pathogen. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popov, I.V.; Todorov, S.D.; Chikindas, M.L.; Venema, K.; Ermakov, A.M.; Popov, I.V. Beyond White-Nose Syndrome: Mitochondrial and Functional Genomics of Pseudogymnoascus destructans. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080550
Popov IV, Todorov SD, Chikindas ML, Venema K, Ermakov AM, Popov IV. Beyond White-Nose Syndrome: Mitochondrial and Functional Genomics of Pseudogymnoascus destructans. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(8):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080550
Chicago/Turabian StylePopov, Ilia V., Svetoslav D. Todorov, Michael L. Chikindas, Koen Venema, Alexey M. Ermakov, and Igor V. Popov. 2025. "Beyond White-Nose Syndrome: Mitochondrial and Functional Genomics of Pseudogymnoascus destructans" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 8: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080550
APA StylePopov, I. V., Todorov, S. D., Chikindas, M. L., Venema, K., Ermakov, A. M., & Popov, I. V. (2025). Beyond White-Nose Syndrome: Mitochondrial and Functional Genomics of Pseudogymnoascus destructans. Journal of Fungi, 11(8), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080550






