The Effect of Pseudomonas putida on the Microbial Community in Casing Soil for the Cultivation of Morchella sextelata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
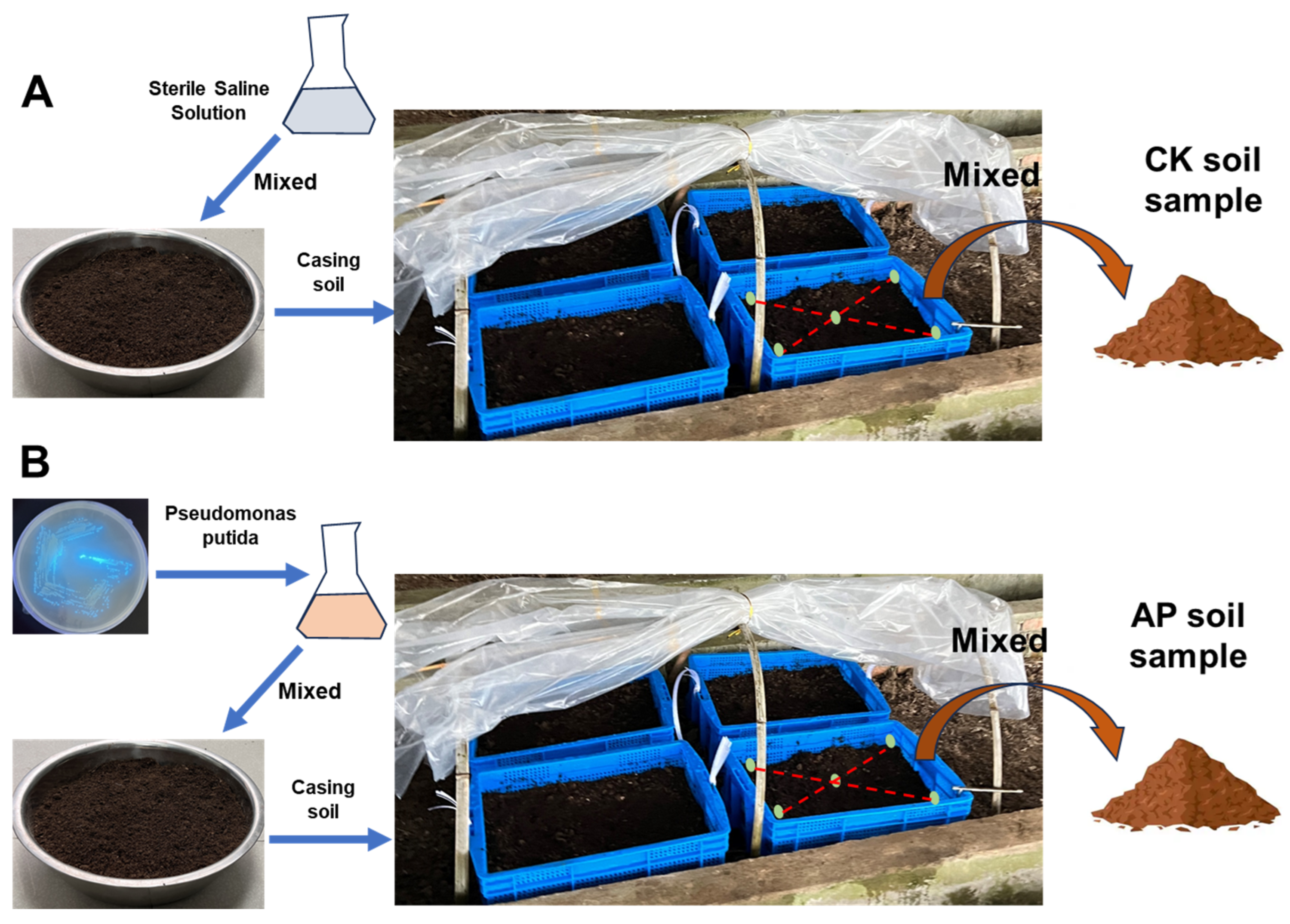
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sample Collection
2.3. Strains and Cultivation Methods
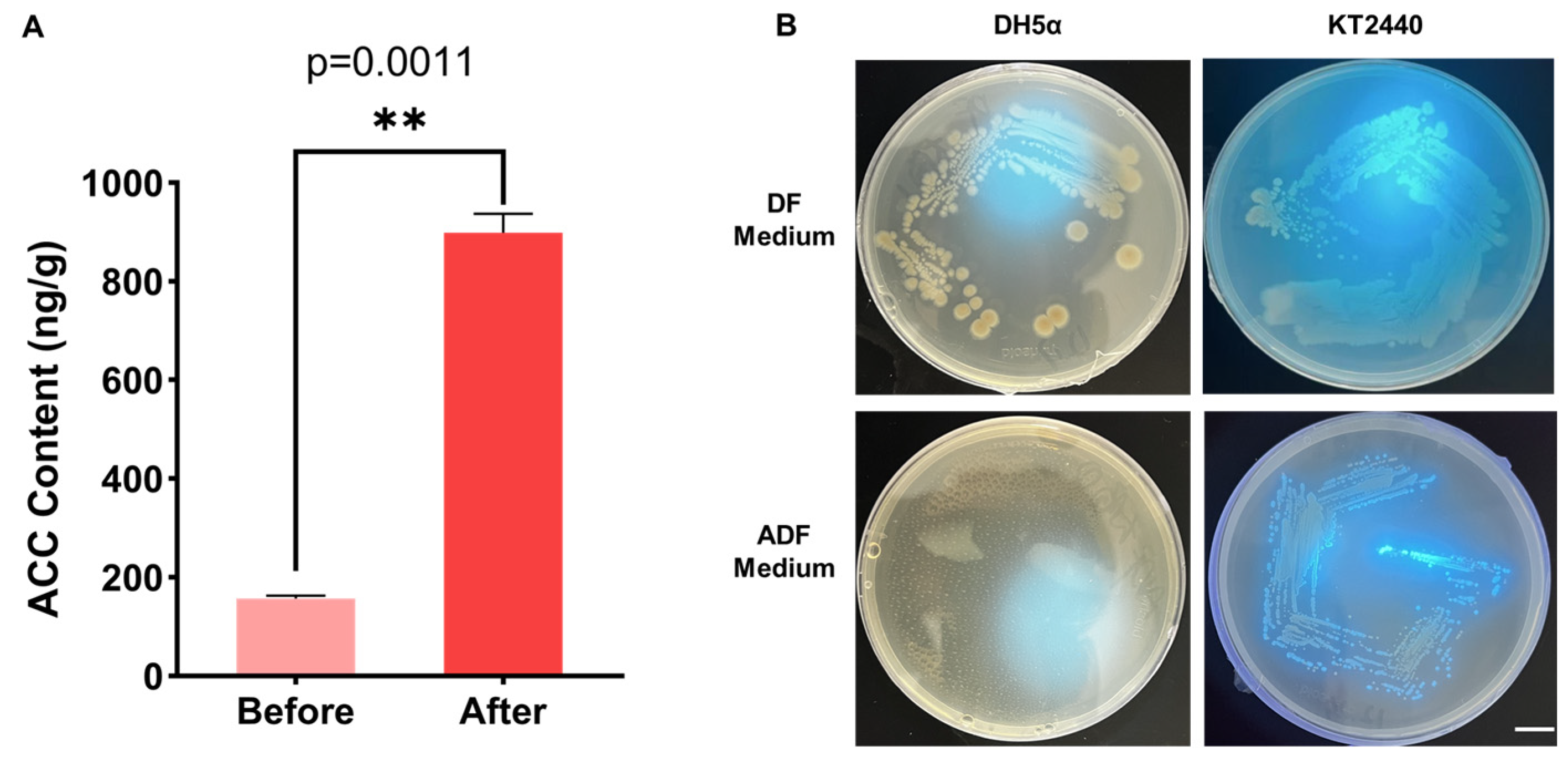
2.4. Detection of ACC Content and ACC Utilization Ability
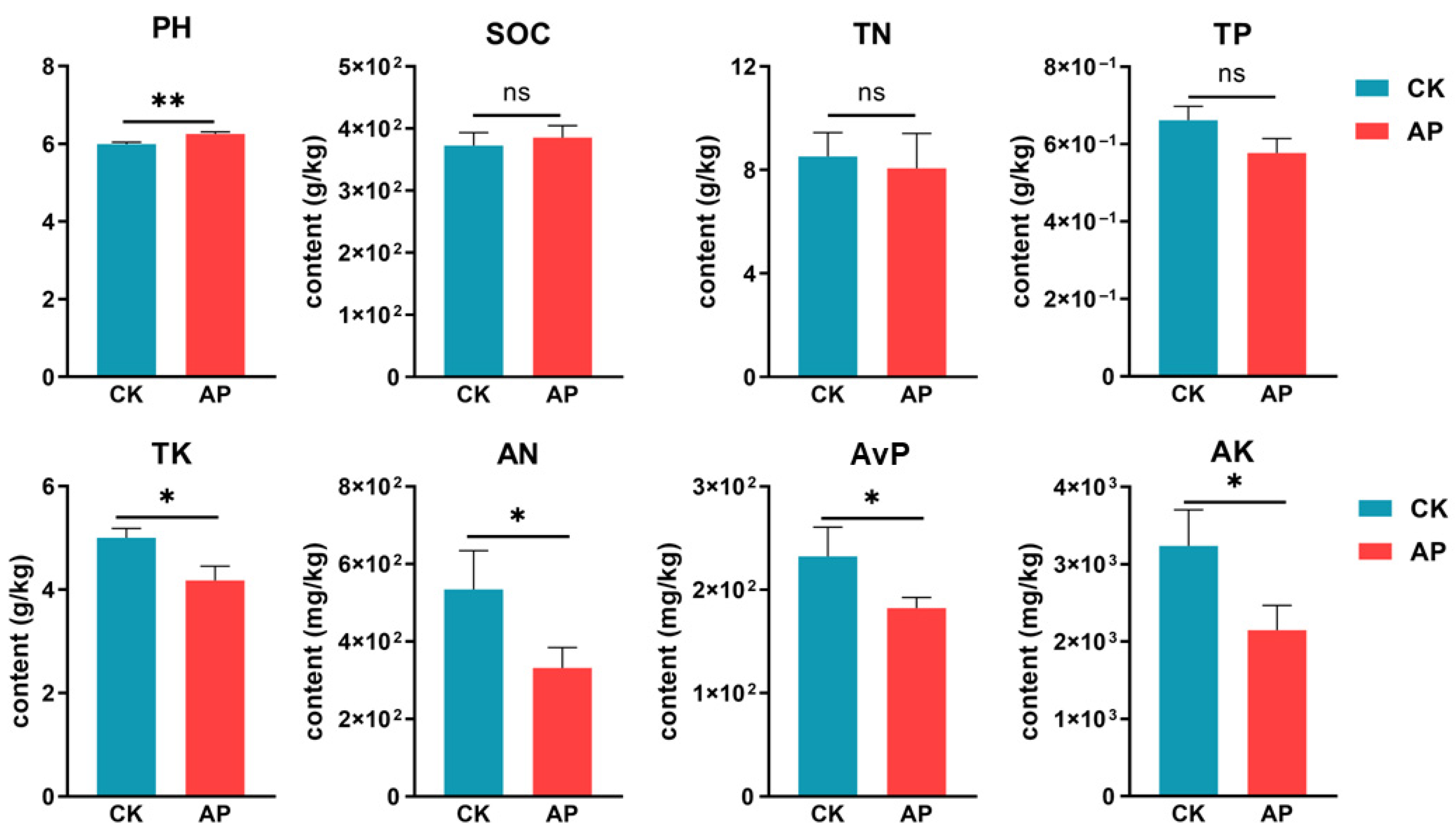
2.5. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.6. DNA Extraction
2.7. Metagenomic Sequencing and Data Processing
2.8. Taxonomic and Functional Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Changes in ACC Content and P. putida ACC Utilization Capacity
3.2. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties
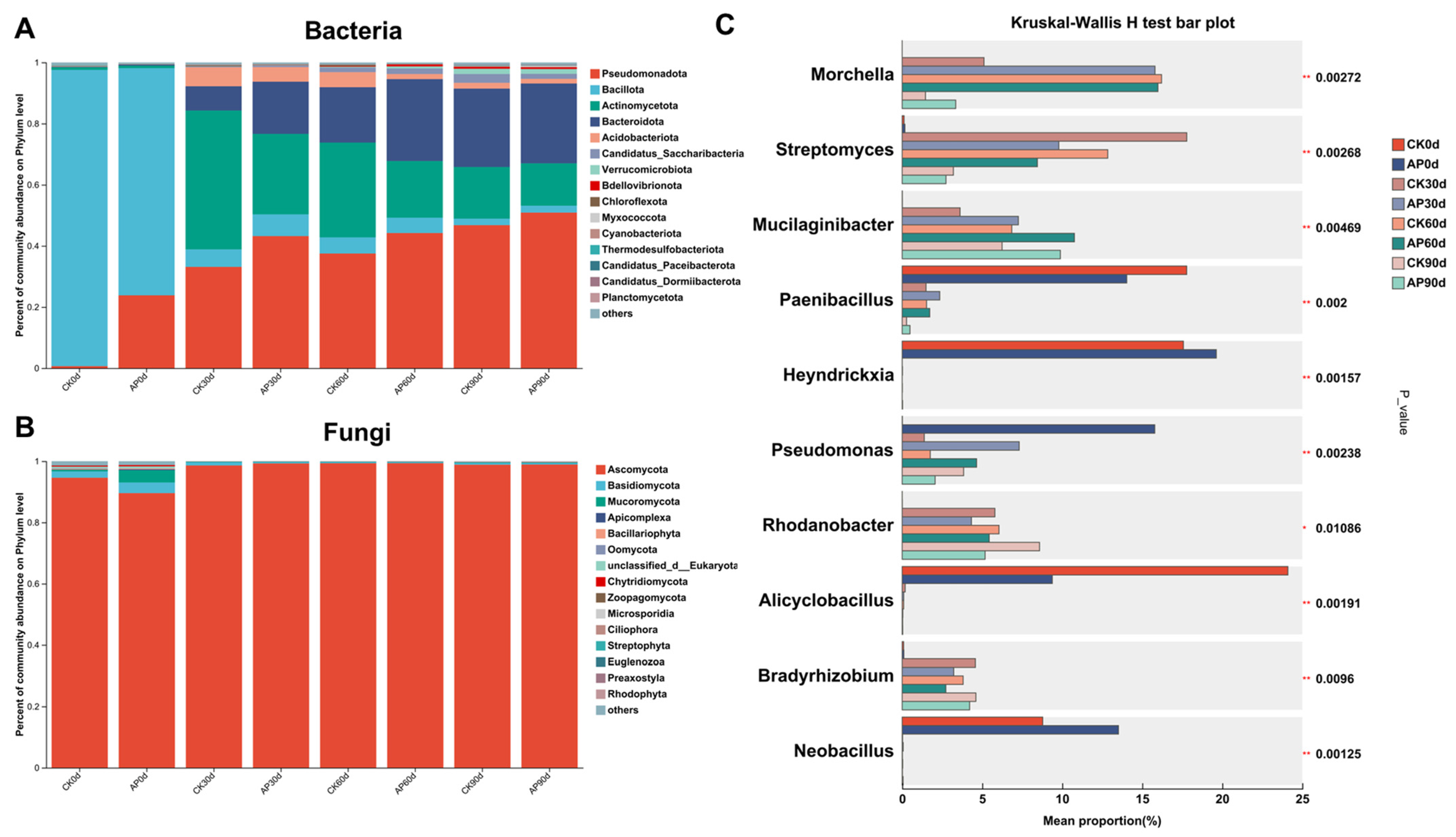
3.3. Alterations in Microbial Diversity of Casing Soil Following P. putida Inoculation
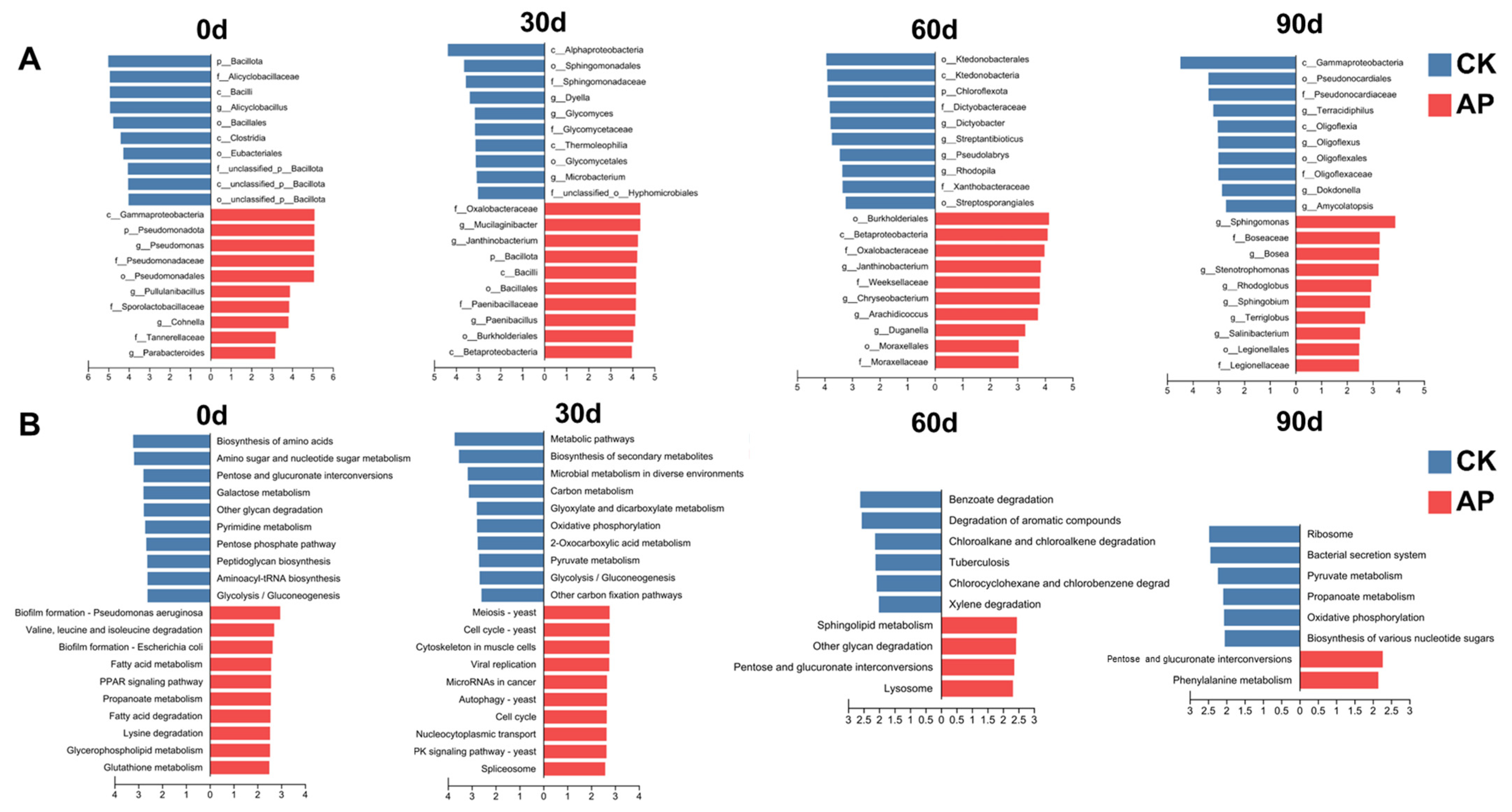
3.4. Alterations in Microbial Composition of Casing Soil Induced by P. putida Inoculation
3.5. Alteration of Microbial Functions in Casing Soil Following Pseudomonas putida Inoculation
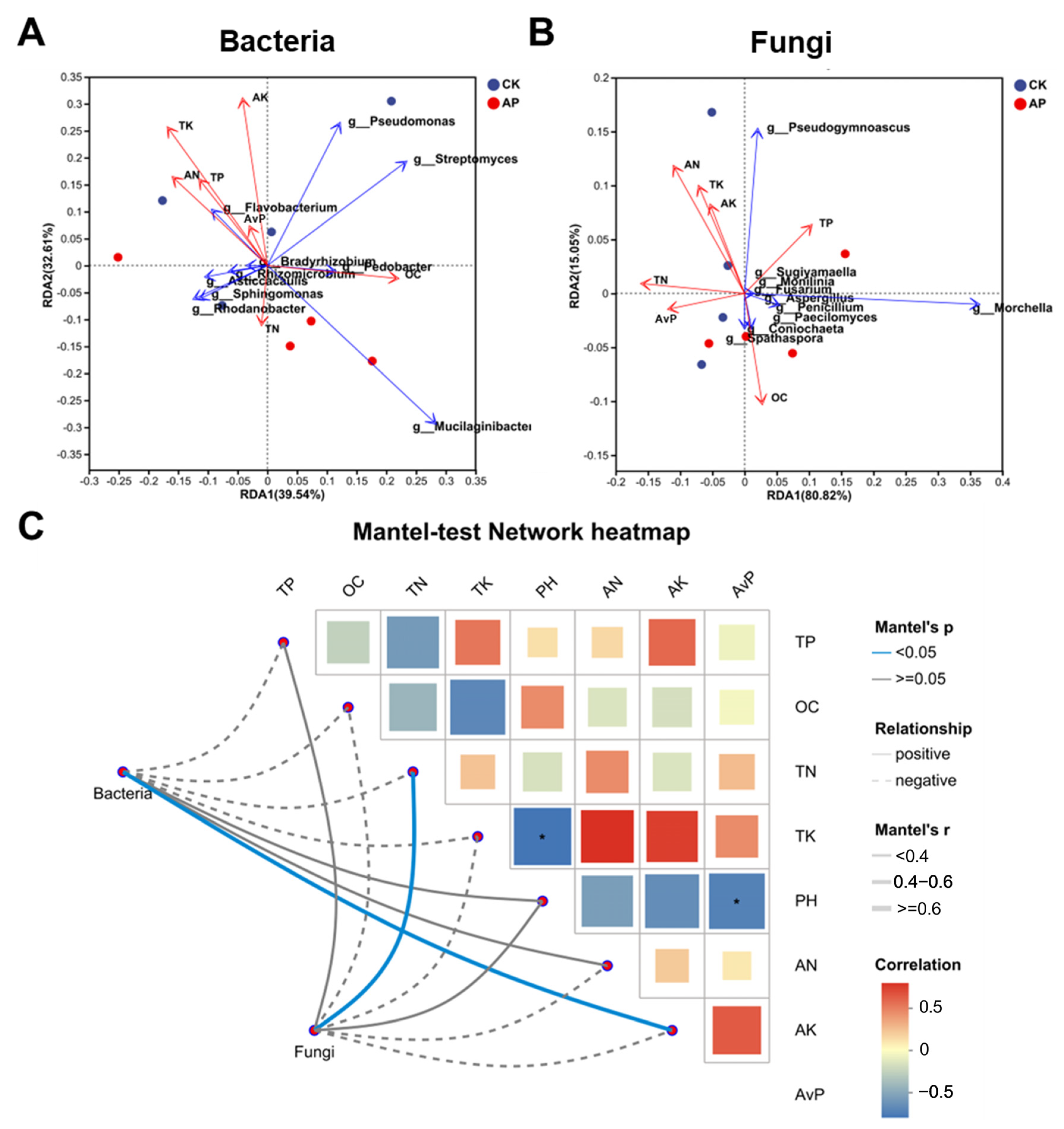
3.6. Pseudomonas putida Inoculation Alters Interactions Between Environmental Factors and Microbial Communities
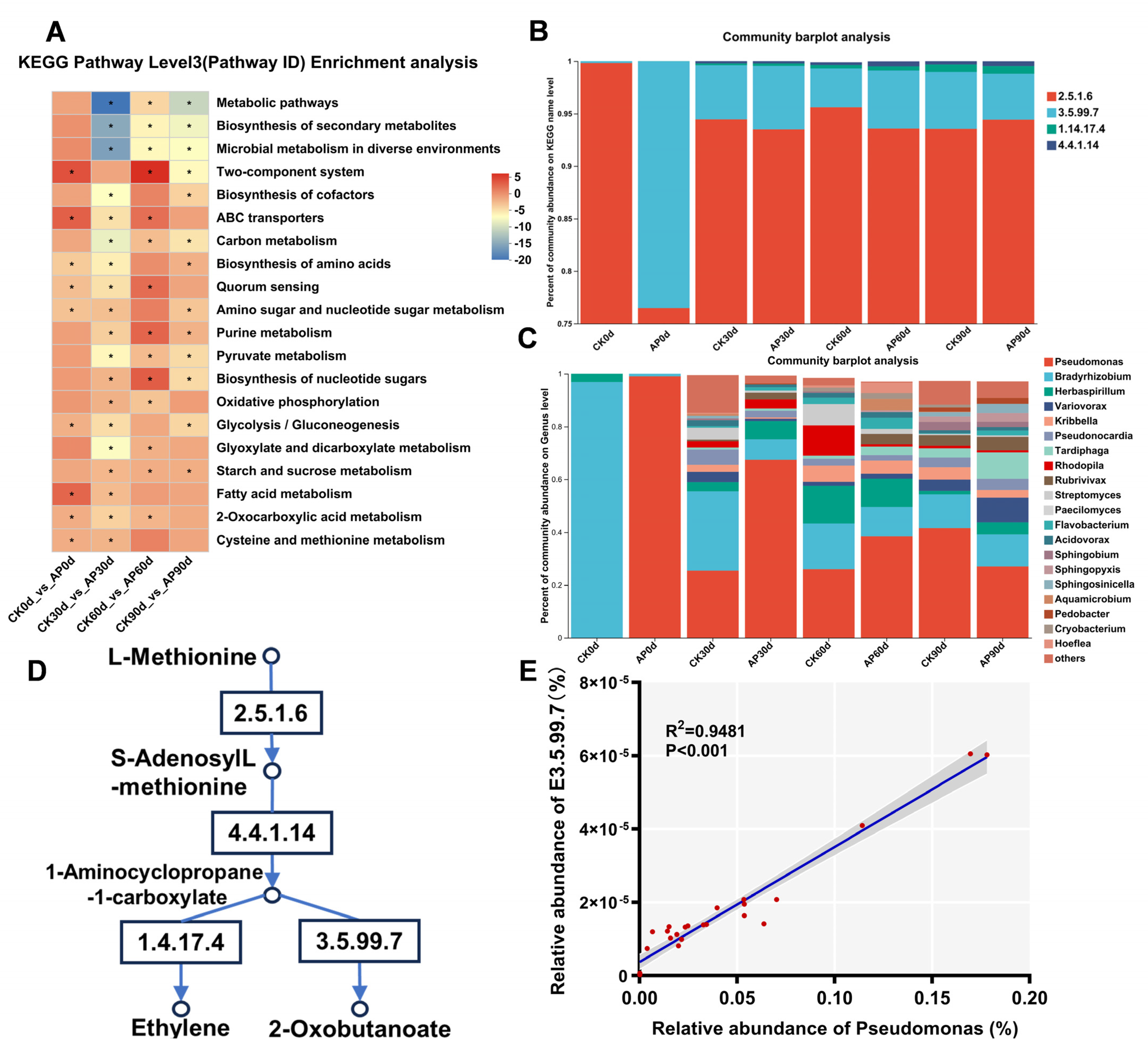
3.7. Effects of Pseudomonas putida Inoculation on KEGG- and ACC-Related Metabolic Pathways
4. Discussion
4.1. Morels Accumulate Ethylene During Their Growth Process
4.2. P. putida Affected the Microbial Composition in the Casing Soil
4.3. P. putida Affected the Microbial Functional in the Casing Soil
4.4. Effects of Pseudomonas putida on Soil Functional Genes and the ACC Metabolic Pathway
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tietel, Z.; Masaphy, S. True morels (Morchella)—Nutritional and phytochemical composition, health benefits and flavor: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Ren, S.; Zhao, J.; Cui, L.; Li, H.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, M.; Shu, L.; Li, T. Comparative analysis of the nutritional and biological properties between the pileus and stipe of Morchella sextelata. Front. Nutr. 2024, 10, 1326461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.-N.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Zhang, W.-N.; Chen, L.; Pan, W.-J.; Wu, Q.-X.; Lu, Y.-M.; Chen, Y. Characterization and immunomodulatory effect of an alkali-extracted galactomannan from Morchella esculenta. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Lin, Z. Structure and hepatoprotective activity of Usp10/NF-κB/Nrf2 pathway-related Morchella esculenta polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 303, 120453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Tan, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, W. Large-scale commercial cultivation of morels: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 4401–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Xu, J. Challenges and Strategies for Continuous Cropping of Morchella spp.: A Review. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Luo, D.; Mao, P.; Rosazlina, R.; Martin, F.; Xu, L. Decline in Morel Production upon Continuous Cropping Is Related to Changes in Soil Mycobiome. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei-Ye, L.; Hong-Bo, G.; Ke-Xin, B.; Alekseevna, S.L.; Xiao-Jian, Q.; Xiao-Dan, Y. Determining why continuous cropping reduces the production of the morel Morchella sextelata. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 903983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; He, P.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Perez-Moreno, J.; Yu, F. Large-scale field cultivation of Morchella and relevance of basic knowledge for its steady production. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; He, X. Safe production strategies for soil-covered cultivation of morel in heavy metal-contaminated soils. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Uroz, S.; Gao, T.; Li, J.; He, F.; Rosazlina, R.; Martin, F.; Xu, L. The cultivation regimes of Morchella sextelata trigger shifts in the community assemblage and ecological traits of soil bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1257905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Wei, M.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, B. Continuous cropping obstacles in fungal production: A review of mechanisms and remedial strategies. Soil Use Manag. 2025, 41, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Hu, C.; Li, C.; Guo, T.; Bao, D.; Yang, R. The roles of bacteria in casing soil during the cultivation of edible fungi. J. Biol. 2023, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, J.; Preston, G.M. Growing edible mushrooms: A conversation between bacteria and fungi. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 22, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, C.F. Microbial ecology of the Agaricus bisporus mushroom cropping process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandin, C.; Le Coq, D.; Deschamps, J.; Védie, R.; Rousseau, T.; Aymerich, S.; Briandet, R. Complete genome sequence of Bacillus velezensis QST713: A biocontrol agent that protects Agaricus bisporus crops against the green mould disease. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 278, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, A.M.; Heijboer, A.; Boschker, H.T.S.; Bonnet, B.; Lugones, L.G.; Wösten, H.A.B. Microbial biomass in compost during colonization of Agaricus bisporus. Amb. Express 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.; Lyu, M.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhong, S.; Gu, H.; Dong, J.; Dresselhaus, T.; Zhong, S. Lack of ethylene does not affect reproductive success and synergid cell death in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, T.; Shen, C.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Shen, J.; Song, A.; Qiu, L.; Ai, Y. Downregulation of ethylene production increases mycelial growth and primordia formation in the button culinary-medicinal mushroom, Agaricus bisporus (Agaricomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2016, 18, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qiu, C.; Huang, T.; Zhou, W.; Qi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shen, J.; Qiu, L. Effect of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase producing bacteria on the hyphal growth and primordium initiation of Agaricus bisporus. Fungal Ecol. 2013, 6, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Shen, C.; Li, H.; Qiu, L. 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate: A novel and strong chemoattractant for the plant beneficial rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida UW4. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R. Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol. Plant. 2003, 118, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, B.R.; Cheng, Z.; Czarny, J.; Duan, J. Promotion of plant growth by ACC deaminase-producing soil bacteria. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 119, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Kalkhove, S.I.; Lugones, L.G.; Baars, J.J.; Wösten, H.A.; Bakker, P.A. Effects of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. isolated from mushroom cultures on Lecanicillium fungicola. Biol. Control 2012, 63, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, M.; Farsi, M.; Mirshamsi Kakhki, A.; Janpoor, J. Influence of Pseudomonas putida isolateson the yield of edible white button mushroom Agaricus bisporus. J. Hortic. Sci. 2018, 32, 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, S.; Rainey, P. Phenotypic variation of Pseudomonas putida and P. tolaasii affects the chemotactic response to Agaricus bisporus mycelial exudate. Microbiology 1991, 137, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailleau, G.; Hanson, B.T.; Cravero, M.; Zhioua, S.; Hilpish, P.; Ruiz, C.; Robinson, A.J.; Kelliher, J.M.; Morales, D.; Gallegos-Graves, L.V. Associated bacterial communities, confrontation studies, and comparative genomics reveal important interactions between Morchella with Pseudomonas spp. Front. Fungal Biol. 2023, 4, 1285531. [Google Scholar]
- Benucci, G.M.N.; Longley, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Bonito, G.; Yu, F. Microbial communities associated with the black morel Morchella sextelata cultivated in greenhouses. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pion, M.; Spangenberg, J.E.; Simon, A.; Bindschedler, S.; Flury, C.; Chatelain, A.; Bshary, R.; Job, D.; Junier, P. Bacterial farming by the fungus Morchella crassipes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20132242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; He, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Wu, D. Relative roles of spatial factors, environmental filtering and biotic interactions in fine-scale structuring of a soil mite community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 79, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Tsolmon, B.; Chen, J.; Wei, W.; Lei, S.; Yang, J.; Bao, Y. The influence of transplanted trees on soil microbial diversity in coal mine subsidence areas in the Loess Plateau of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Chao, L.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X. Soil microbial community composition and co-occurrence network responses to mild and severe disturbances in volcanic areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yue, H.; Lu, J.; Li, C. Characterization of rhizobacterial strain Rs-2 with ACC deaminase activity and its performance in promoting cotton growth under salinity stress. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lu, N.; Luo, Y. Analysis of soil fertility and toxic metal characteristics in open-pit mining areas in northern Shaanxi. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ahmed, W.; Mahmood, M.; Rizwan, M.S.; Asghar, R.M.A.; Alatalo, J.M.; Imtiaz, M.; Akmal, M.; Abdelrahman, H.; Ma, J. Aquaculture sediments amended with biochar improved soil health and plant growth in a degraded soil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B. Response Mechanism of Litter to Soil Water Conservation Functions Under the Density Gradient of Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests in the Loess Plateau of the Western Shanxi Province. Plants 2025, 14, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J.-P.; Zhou, B.; Bi, B.; Xie, K.-M.; Fang, X.-J.; Wang, Y.-Z. Chemical properties of soil layers of restoration sites in phosphate mining area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2027–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, L.; Ge, X.; Cao, Y. Spatial patterns of leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry and nutrient resorption in Chinese fir across subtropical China. Catena 2021, 201, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, D.; Ren, Y.; Fu, H. Extractability of nutrients using Mehlich 3 and ammonium bicarbonate-DTPA methods for selected grassland soils of China. Plant Soil Environ. 2018, 64, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Ghosh, D.; Mohapatra, S. Modulation of polyamine biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana by a drought mitigating Pseudomonas putida strain. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 129, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, P.; Allsopp, L.P.; Filloux, A.; Llamas, M.A. The Pseudomonas putida T6SS is a plant warden against phytopathogens. ISME J. 2017, 11, 972–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Kohler, A.; Miao, R.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Tang, J.; et al. Multi-omic analyses of exogenous nutrient bag decomposition by the black morel Morchella importuna reveal sustained carbon acquisition and transferring. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3909–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhan, G.; Jia, J.; Fan, J.; Shen, Z.; Chen, L.; Sun, S. Time-course proteomics analysis and gene function validation of promoting dimorphic transition of Tremella fuciformis by Annulohypoxylon stygium extract. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, K.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; He, X.; Yu, F.; Liu, W. Spatial ratio of two fungal genotypes content of Naematelia aurantialba and Stereum hirsutum in nutritional growth substrate and fruiting bodies reveals their potential parasitic life cycle characteristics. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 22, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-H.; Bao, D.-P.; Guo, T.; Li, Y.; Ji, G.-Y.; Ji, K.-P.; Tan, Q. Bacterial profiling and dynamic succession analysis of Phlebopus portentosus casing soil using MiSeq sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wu, X.; Huang, H.; Qin, J.; Long, S.; Li, X.; Feng, B.; Qin, S. Soil chemistry, metabarcoding, and metabolome analyses reveal that a sugarcane—Dictyophora indusiata intercropping system can enhance soil health by reducing soil nitrogen loss. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1193990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yan, L.; Li, Q.; Zou, J.; Tan, H.; Tan, W.; Peng, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Dynamic succession of substrate-associated bacterial composition and function during Ganoderma lucidum growth. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.A. Ganoderma lucidum cultivation affect microbial community structure of soil, wood segments and tree roots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.; Qi, G.; Jiang, S. Effects of wine-cap Stropharia cultivation on soil nutrients and bacterial communities in forestlands of northern China. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Fan, T.; Jin, L.; Lei, P.; Shao, C.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Ren, R.; Xu, J. Soil microbial diversity and functional capacity associated with the production of edible mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata in croplands. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlofsky, E.; Zabari, L.; Bonito, G.; Masaphy, S. Changes in soil bacteria functional ecology associated with Morchella rufobrunnea fruiting in a natural habitat. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6651–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaphy, S. Biotechnology of morel mushrooms: Successful fruiting body formation and development in a soilless system. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, W. Integration of metabolomes and transcriptomes provides insights into morphogenesis and maturation in Morchella sextelata. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyoum, N.A.; Surridge, K.; Van der Linde, E.J.; Korsten, L. Microbial succession in white button mushroom production systems from compost and casing to a marketable packed product. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchia, J.; Cortese, R.; Albert, I. Investigation into the microbial community changes that occur in the casing layer during cropping of the white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Mushroom Biology and Mushroom Products (ICMBMP8), New Delhi, India, 19–22 November 2014; Volume I & II, pp. 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R.; Lal, R. Fire-Induced Changes in Soil Properties and Bacterial Communities in Rotational Shifting Cultivation Fields in Northern Thailand. Biology 2024, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Choi, D. Microbial Community Enhances Biodegradation of Bisphenol A Through Selection of Sphingomonadaceae. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive Microbial Metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yu, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.; Miao, R.; Huang, Z.; Martin, F.M.; Peng, W. Build your own mushroom soil: Microbiota succession and nutritional accumulation in semi-synthetic substratum drive the fructification of a soil-saprotrophic morel. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Chakdar, H.; Anuroopa, N.; Bagyaraj, D.J. Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Yang, X.-Y.; Wan, L.-Z.; Ren, H.-X.; Qu, L.; Guo, H.-D.; Dong, L.-L.; Lu, X.; Ren, P.-F. Influence of the casing layer on the specific volatile compounds and microorganisms by Agaricus bisporus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1154903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurak, E.; Kabel, M.A.; Gruppen, H. Carbohydrate composition of compost during composting and mycelium growth of Agaricus bisporus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, K.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y. Successional action of Bacteroidota and Firmicutes in decomposing straw polymers in a paddy soil. Environ. Microbiome 2023, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, J.; Peng, X.; Fu, Q.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, J.; Tang, L. Dynamics of organic matter and bacterial community during the composting process of food waste rich in oil with the amendment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 506, 145456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Dong, M. Study on Effects of Nitrogen Reduction with Morchella Waste Returing to Paddy Field in Rice-Morchella Rotation. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2024, 40, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.K.; Madaan, S.; Archana, G. Antibiotic producing endophytic Streptomyces spp. colonize above-ground plant parts and promote shoot growth in multiple healthy and pathogen-challenged cereal crops. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 215, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurier, S.; Corberand, T.; Lemanceau, P.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Phenazine antibiotics produced by fluorescent Pseudomonads contribute to natural soil suppressiveness to Fusarium wilt. ISME J. 2009, 3, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Ruppel, S.; Behrendt, U.; Lentzsch, P.; Müller, M.E.H. Antagonistic potential of fluorescent Pseudomonads colonizing wheat heads against mycotoxin producing alternaria and fusaria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.; Sazinas, P.; Strube, M.; Ding, L.; Dubey, S.; Shivay, Y.; Sharma, S.; Jelsbak, L. Pseudomonas is a key player in conferring disease suppressiveness in organic farming. Plant Soil 2024, 503, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifazizi, M.; Harighi, B.; Sadeghi, A. Evaluation of biological control of Erwinia amylovora, causal agent of fire blight disease of pear by antagonistic bacteria. Biol. Control 2017, 104, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kang, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Peng, W.; Martin, F.M.; Tan, H. Inoculation of the Morchella importuna mycosphere with Pseudomonas chlororaphis alleviated a soil-borne disease caused by Paecilomyces penicillatus. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2025, 61, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.O.; Yang, S.F. Ethylene biosynthesis: Identification of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid as an intermediate in the conversion of methionine to ethylene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Wen, Y.; Li, T.; Gao, Y.; Meng, F.; Qiu, L.; Ai, Y. Pseudomonas sp. UW4 acdS gene promotes primordium initiation and fruiting body development of Agaricus bisporus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Xin, L.; Zhang, L. The Effect of Pseudomonas putida on the Microbial Community in Casing Soil for the Cultivation of Morchella sextelata. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11110775
Zou R, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Chen M, Xin L, Zhang L. The Effect of Pseudomonas putida on the Microbial Community in Casing Soil for the Cultivation of Morchella sextelata. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(11):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11110775
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Ruifan, Yuping Zhang, Lili Zhang, Ming Chen, Ling Xin, and Lei Zhang. 2025. "The Effect of Pseudomonas putida on the Microbial Community in Casing Soil for the Cultivation of Morchella sextelata" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 11: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11110775
APA StyleZou, R., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, M., Xin, L., & Zhang, L. (2025). The Effect of Pseudomonas putida on the Microbial Community in Casing Soil for the Cultivation of Morchella sextelata. Journal of Fungi, 11(11), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11110775





