Arthrobotrys mendozadegivensis sp. nov. (Fungi: Orbiliales) from Mexico: Predatory Activity and Nematocidal Activity of Its Liquid Culture Filtrates Against Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
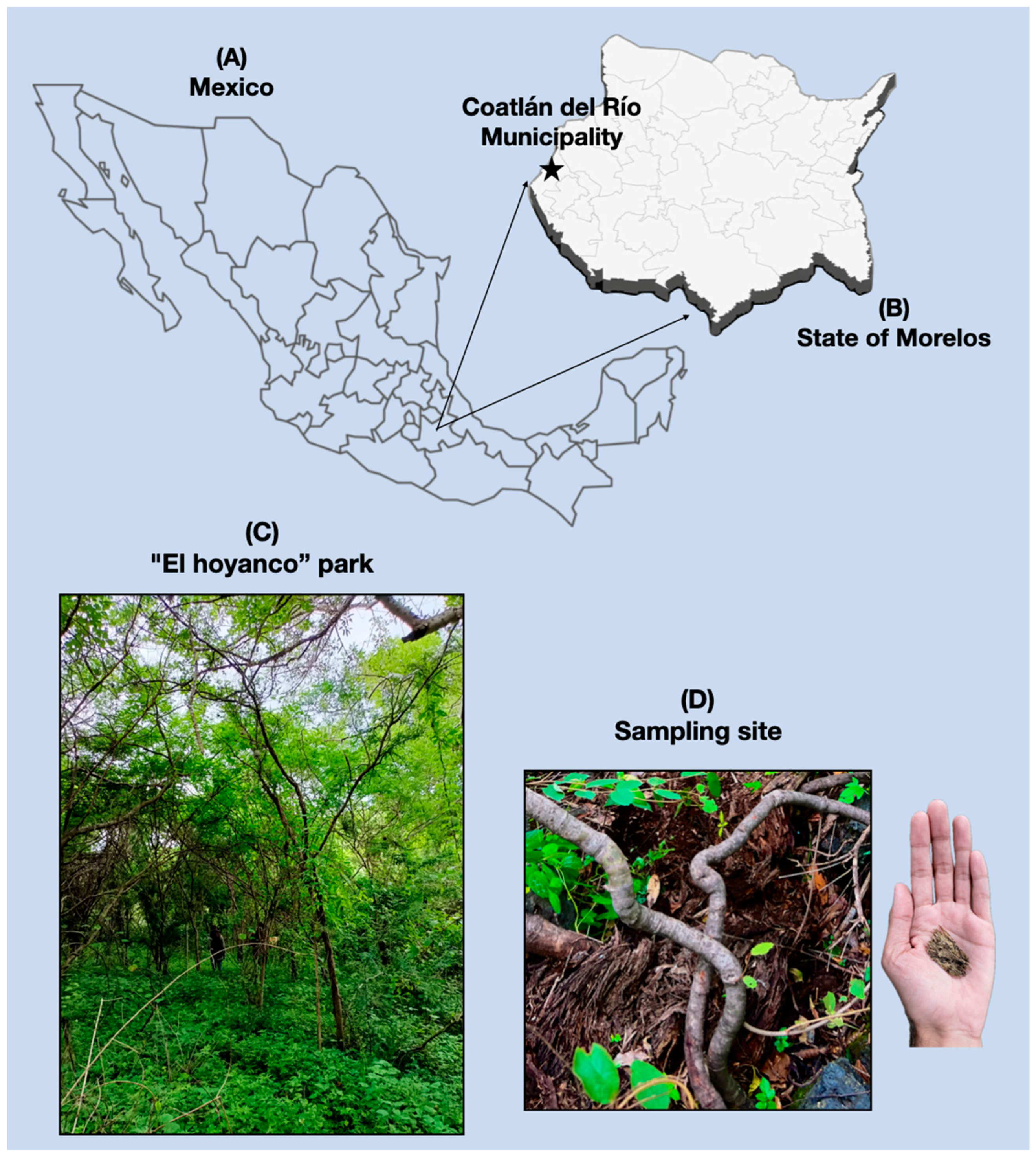
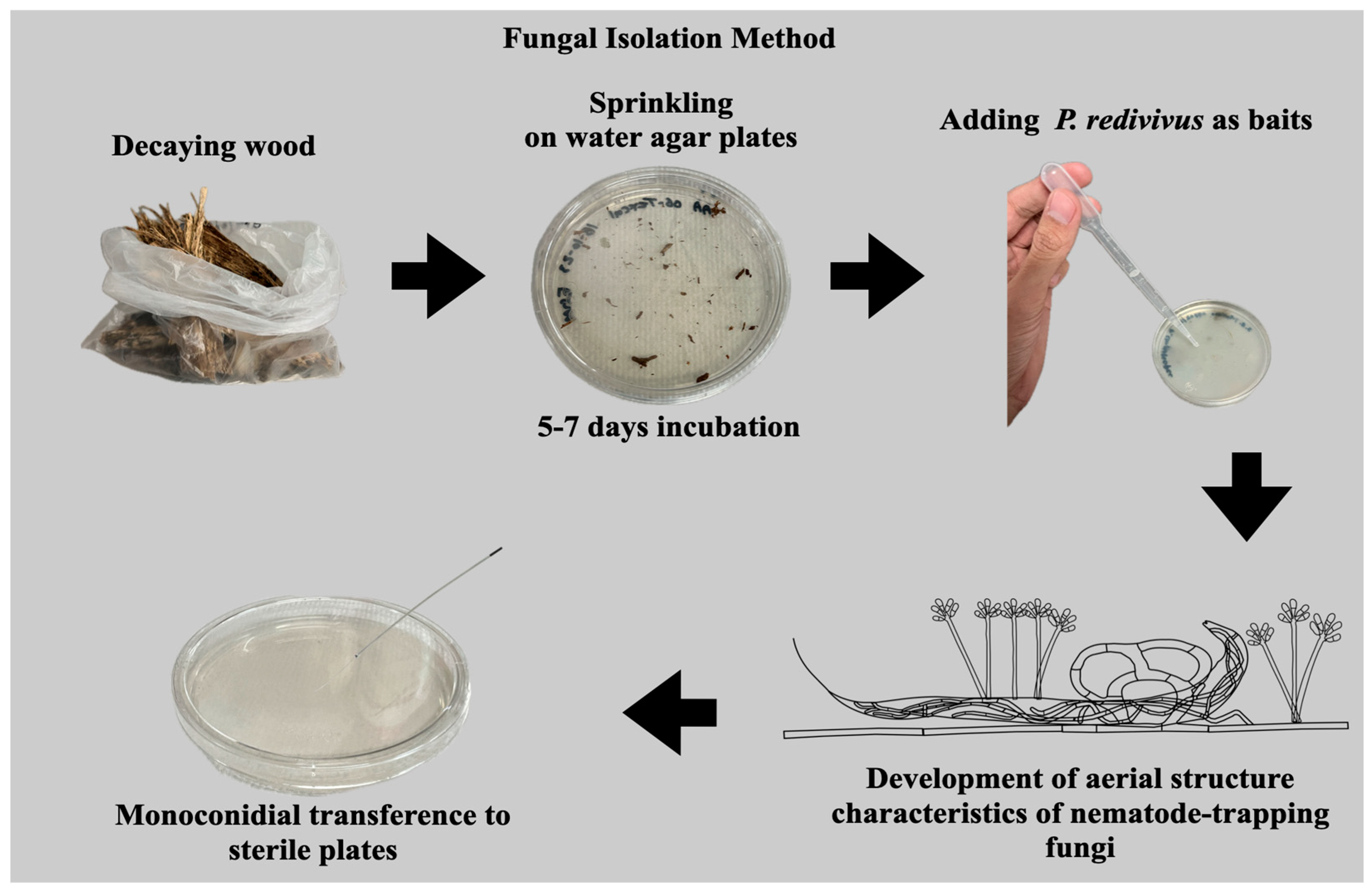
2.1. Fungal Isolation
2.2. Morphological Identification
2.3. Molecular Identification
Genomic DNA Isolation
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Predatory Activity Assessment
2.6. Production of the Fungus in Liquid Media
2.7. Obtaining Fungal Liquid Culture Filtrates
2.8. In Vitro Assessment of Nematocidal Activity of Liquid Culture Filtrates Against Haemonchus contortus Infective Larvae (L3)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
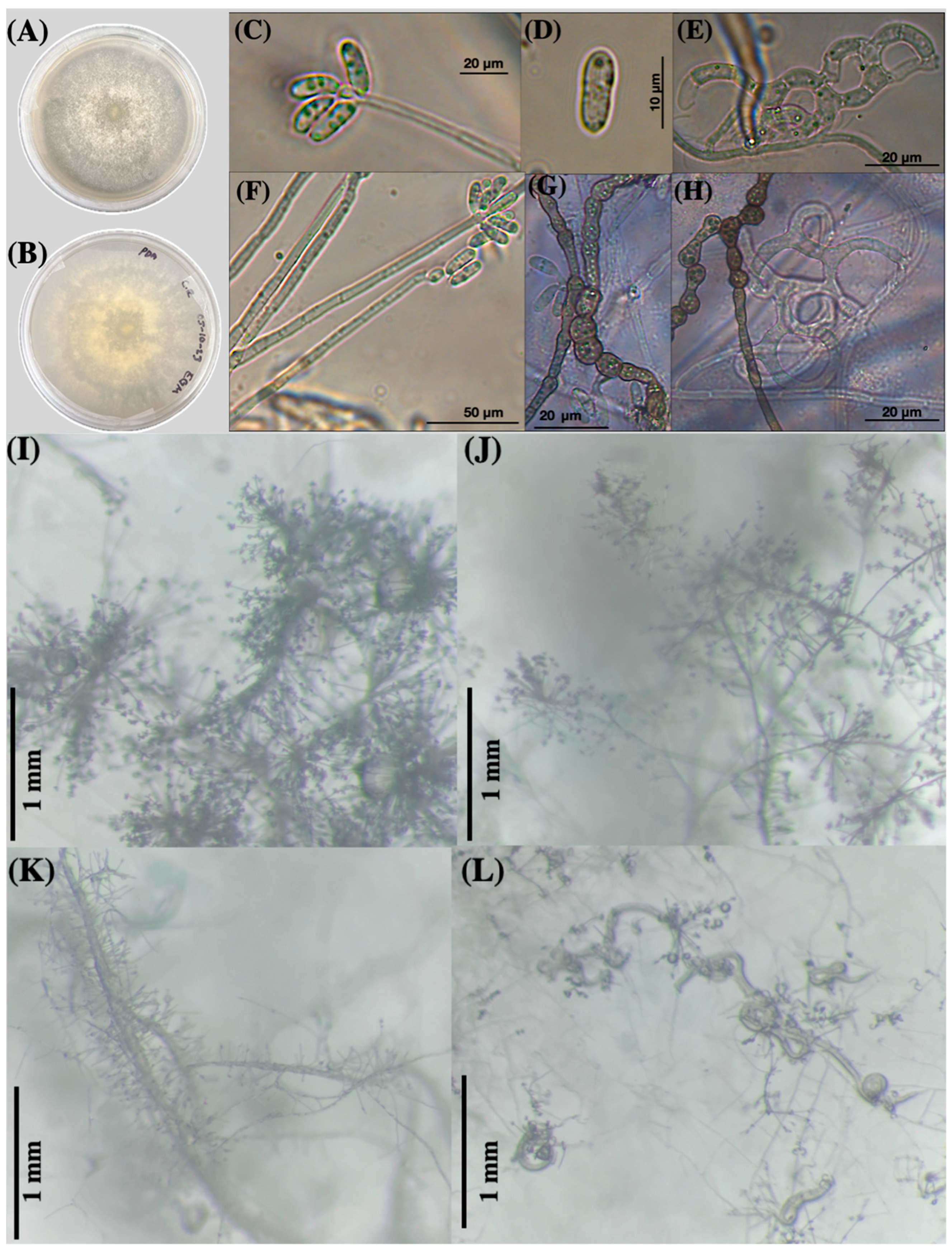
3.1. Morphological Taxonomic Identification
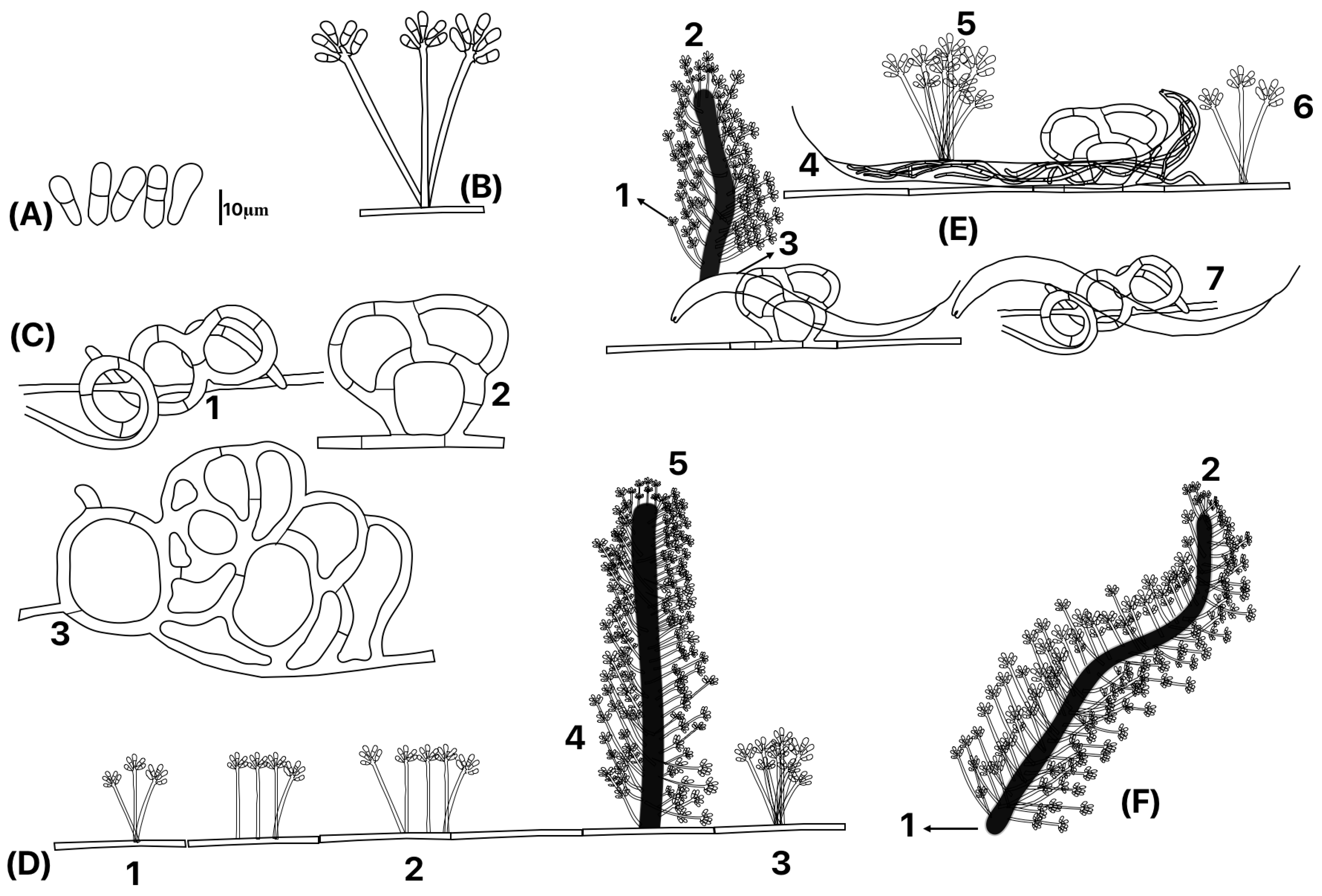
3.1.1. Macroscopic Characteristics
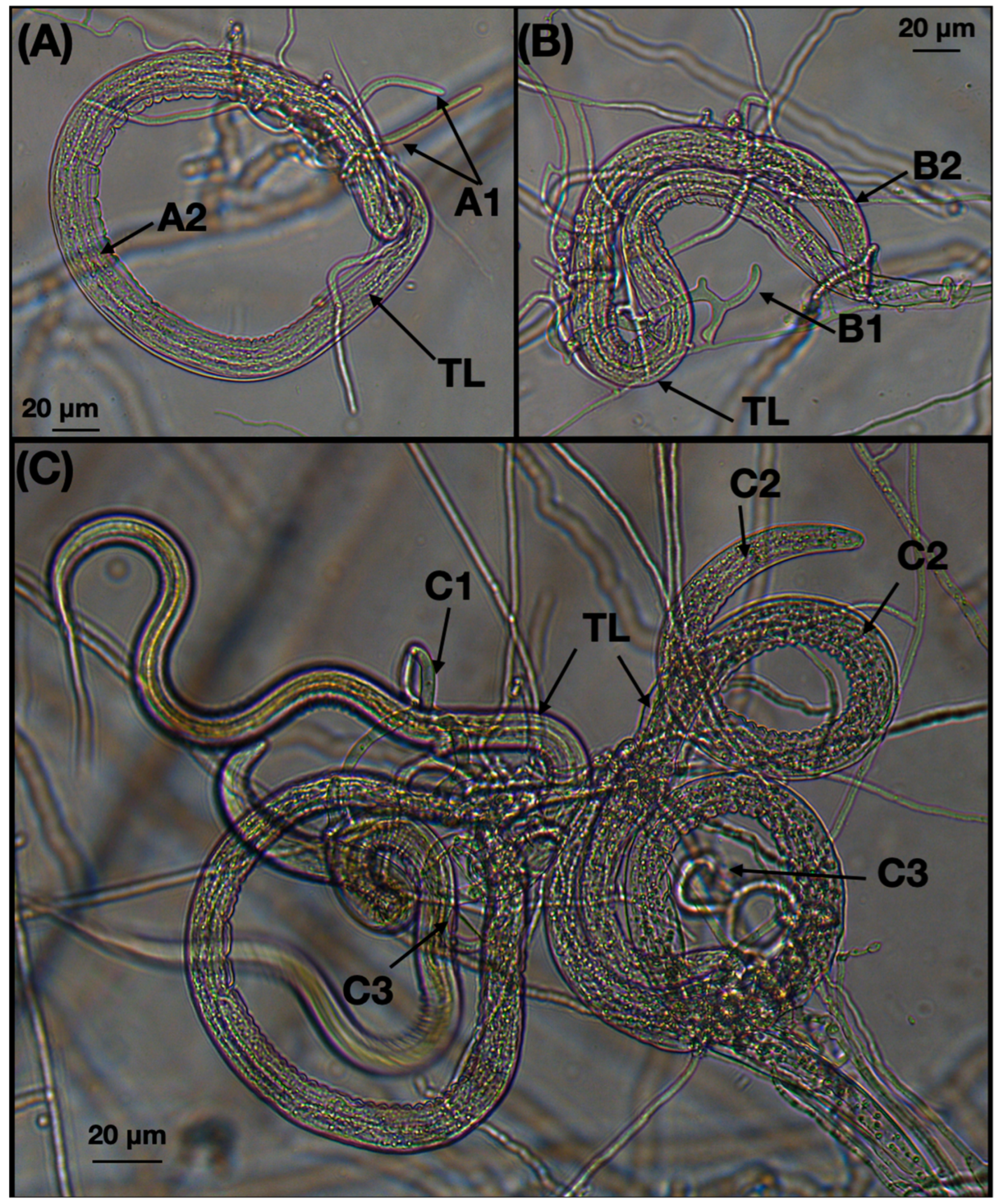
3.1.2. Microscopic Fungal Characteristics
3.2. Molecular Identification
3.3. Predatory Activity Assessment
3.4. Nematocidal Activity of Liquid Culture Filtrates of Arthrobotrys Mendozadegivensis Against Haemonchus Contortus Infective Larvae (L3) Under In Vitro Conditions
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crous, P.W.; Rong, I.H.; Wood, A.; Lee, S.; Glen, H.; Botha, W.; Slippers, B.; de Beer, W.Z.; Wingfield, M.J.; Hawksworth, D.L. How Many Species of Fungi Are There at the Tip of Africa? Stud. Mycol. 2006, 55, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda-Robertos, N.F.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Olmedo-Juárez, A.; Luna-Palomera, C.; Peralta-Torres, J.A.; López-Arellano, M.E.; Mendoza-de-Gives, P. In Vitro Predatory Activity of Nematophagous Fungi Isolated from Water Buffalo Feces and from Soil in the Mexican Southeastern. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2019, 28, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Martínez, E.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Hernández-Romano, J.; Castañeda-Ramírez, G.S.; Mendoza-de-Gives, P. Taxonomic and Biological Characterization and Predatory Activity of Four Nematophagous Fungi Isolates of Arthrobotrys Species from Tapachula, Chiapas, Mexico. Arch. Acker Pflanzenbau Bodenkd. 2023, 69, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, A.; Vera-Morales, M.; Espinoza-Lozano, F.; Castañeda-Ruiz, R.F.; Sosa del Castillo, D.; Magdama, F. Assessing the predatory activity of Arthrobotrys oligosporus strain C-2197 as biocontrol of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne spp. Bionatura 2021, 6, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swe, A.; Jeewon, R.; Pointing, S.B.; Hyde, K.D. Diversity and Abundance of Nematode-Trapping Fungi from Decaying Litter in Terrestrial, Freshwater and Mangrove Habitats. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 1695–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.F.; Bailey, F. Ecology of Nematophagous Fungi: Vertical Distribution in a Deciduous Woodland. Plant Soil 1985, 86, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, W.E.; Munir, E.; Hastuti, L.D.S.; Hartanto, A. Occurrence of nematophagous fungi in freshwater samples of Toba Lake, North Sumatra, Indonesia. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1462, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Mo, M.; Su, H.; Zhang, K. Ecology of aquatic nematode-trapping hyphomycetes in southwestern China. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 40, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.F.; Lewis Smith, R.I. The Distribution of Nematophagous Fungi in the Maritime Antarctic. Mycopathologia 1984, 85, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, H.-B.; Poinar, G.O., Jr. Some Possible Fossil Nematophagous Fungi. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1986, 87, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Yang, J. Trapping Devices of Nematode-Trapping Fungi: Formation, Evolution, and Genomic Perspectives: Trapping Devices of Nematode-Trapping Fungi. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2017, 92, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-de Gives, P. Soil-Borne Nematodes: Impact in Agriculture and Livestock and Sustainable Strategies of Prevention and Control with Special Reference to the Use of Nematode Natural Enemies. Pathogens 2022, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corda, A.K.J. Pracht-Flora Europaeischer Schimmelbildungen; G. Fleischer: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1839. [Google Scholar]
- Zopf, W.F. Zur Kenntniss der Infections-Krankheiten niederer Thiere und Pflanzen. Acad. Nat. 1888, 52, 314–376. [Google Scholar]
- Jarowaja, N. The genus Arthrobotrys Corda. Acta Myc. 1970, 6, 337–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Boonmee, S.; Bhat, J.D.; Xiao, W.; Yang, X.-Y. New Arthrobotrys Nematode-Trapping Species (Orbiliaceae) from Terrestrial Soils and Freshwater Sediments in China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayaka, A.H. Orbiliaceae from Thailand. Mycosphere 2018, 9, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In En PCR Protocols; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 315–322. ISBN 9780123721808. [Google Scholar]
- Stielow, J.B.; Lévesque, C.A.; Seifert, K.A.; Meyer, W.; Iriny, L.; Smits, D.; Renfurm, R.; Verkley, G.J.M.; Groenewald, M.; Chaduli, D.; et al. One Fungus, Which Genes? Development and Assessment of Universal Primers for Potential Secondary Fungal DNA Barcodes. Persoonia 2015, 35, 242–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, G.L. The Nematode Destroying Fungi; Editorial Lancaster Press, Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1977; 140p. [Google Scholar]
- Harirchi, S.; Rousta, N.; Varjani, S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Sampling, Preservation, and Growth Monitoring of Filamentous Fungi. In En Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 149–180. ISBN 9780323918725. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.K.; Johnson, E.M. Identification of Pathogenic Fungi: Campbell/Identification of Pathogenic Fungi; Warnock, D.W., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781444330700. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Anzúrez, G.; Olmedo-Juárez, A.; von-Son de Fernex, E.; Alonso-Díaz, M.Á.; Delgado-Núñez, E.J.; López-Arellano, M.E.; González-Cortázar, M.; Zamilpa, A.; Ocampo-Gutierrez, A.Y.; Paz-Silva, A.; et al. Arthrobotrys Musiformis (Orbiliales) Kills Haemonchus Contortus Infective Larvae (Trichostronylidae) through Its Predatory Activity and Its Fungal Culture Filtrates. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigano-Milani, M.S.; Honeycutt, R.J.; Lacey, L.A.; Assis, R.; McClelland, M.; Sobral, B.W.S. Genetic Variability of Paecilomyces Fumosoroseus Isolates Revealed by Molecular Markers. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1995, 65, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, E.; An, Z.; Liu, X. Evolution of Nematode-Trapping Cells of Predatory Fungi of the Orbiliaceae Based on Evidence from rRNA-Encoding DNA and Multiprotein Sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8379–8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Zhou, F.-P.; Xiao, W.; Boonmee, S.; Yang, X.-Y. Multilocus Phylogeny and Characterization of Five Undescribed Aquatic Carnivorous Fungi (Orbiliomycetes). J. Fungi 2024, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.P. Molecular Phylogeny and DNA Barcoding of Nematode-Trapping Hyphomycetes and Related Taxa; submitted; Yunnan University: Kunming, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Baral, H.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yu, Z.F. New Species and New Combination of Orbiliaceae from Yunnan, China; submitted; Yunnan University: Kunming, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Zhou, F.-P.; Xiao, W.; Boonmee, S.; Yang, X.-Y. Morphological and Phylogenetic Characterization of Five Novel Nematode-Trapping Fungi (Orbiliomycetes) from Yunnan, China. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masigol, H.; Rezakhani, F.; Pourmoghaddam, M.J.; Khodaparast, S.A.; Grossart, H.-P. The Introduction of Two New Species of Aquatic Fungi from Anzali Lagoon, Northern Iran. Diversity 2022, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.A.; Zhou, X.-J.; Monkai, J.; Li, F.-T.; Liu, S.-R.; Yang, X.-Y.; Wen, X.; Hyde, K.D. Two new species of nematode-trapping fungi (Dactylellina, Orbiliaceae) from burned forest in Yunnan, China. Phytotaxa 2020, 452, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich-N, J.; Despres, V.R.; Poschl, U. Global Atmospheric Diversity of Fungi: Asco- and Basidiomycota in Continental and Marine Air; submitted; Max Planck Institute for Chemistry: Mainz, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Qiao, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, C. Isolation of Arthrobotrys oligospora from soil of the Chinese Northern Tianshan Mountain slope pasture show predatory ability against Haemonchus contortus larvae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Tlalapango, J.; Mendoza-de Gives, P.; Isabel-Higuera-Piedrahita, R.; Ocampo-Gutiérrez, A.Y.; Eugenia-López-Arellano, M.; Pérez-Anzúrez, G.; Olmedo-Juárez, A.; Hernández-Romano, J.; Maza-Lopez, J.; Delgado-Núñez, E.J.; et al. Study of a Mexican Isolate of Arthrobotrys Musiformis (Orbiliales): Predatory Behavior and Nematocidal Activity of Liquid Culture Filtrates against Haemonchus Contortus (Trichostrongylidae), Protein Profile and Myco-Constituent Groups. Fungal Biol. 2023, 127, 1345–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.K.; Valadão, M.C.; Carvalho, L.M.; de Araújo, J.V.; Guimarães, M.P. In vitro nematophagous activity of predatory fungi on infective larvae of Strongyloides papillosus. Acta Vet. Bras. 2017, 11, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.-Z.; Wang, F.-H.; Wang, K.-Y.; Liu, J.-L.; Wang, B.-B.; Xu, Q.; Xue, Y.-J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Fang, W.-X.; et al. In Vitro Predatory Activity of Arthrobotrys Oligospora and after Passing through Gastrointestinal Tract of Small Ruminants on Infective Larvae of Trichostrongylides. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 177, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula Santos, C.; Padilha, T.; de Lurdes de Azevedo Rodrigues, M. Predatory activity of Arthrobotrys oligospora and Duddingtonia flagrans on pre-parasitic larval stages of cyathostominae under different constant temperatures. Cienc. Rural 2001, 31, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Gutiérrez, A.Y.; Hernández-Velázquez, V.M.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Cardoso-Taketa, A.; Zamilpa, A.; López-Arellano, M.E.; González-Cortázar, M.; Hernández-Romano, J.; Reyes-Estebanez, M.; Mendoza-de Gives, P. Morphological and Molecular Characterization, Predatory Behaviour and Effect of Organic Extracts of Four Nematophagous Fungi from Mexico. Fungal Ecol. 2021, 49, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Soares, F.E.; de Queiroz, J.H.; Braga, F.R.; Dos Santos Lima, W.; Zamprogno, T.T.; de Araújo, J.V. Proteolytic Activity of the Nematophagous Fungus Arthrobotrys Sinensis on Angiostrongylus Vasorum Larvae. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
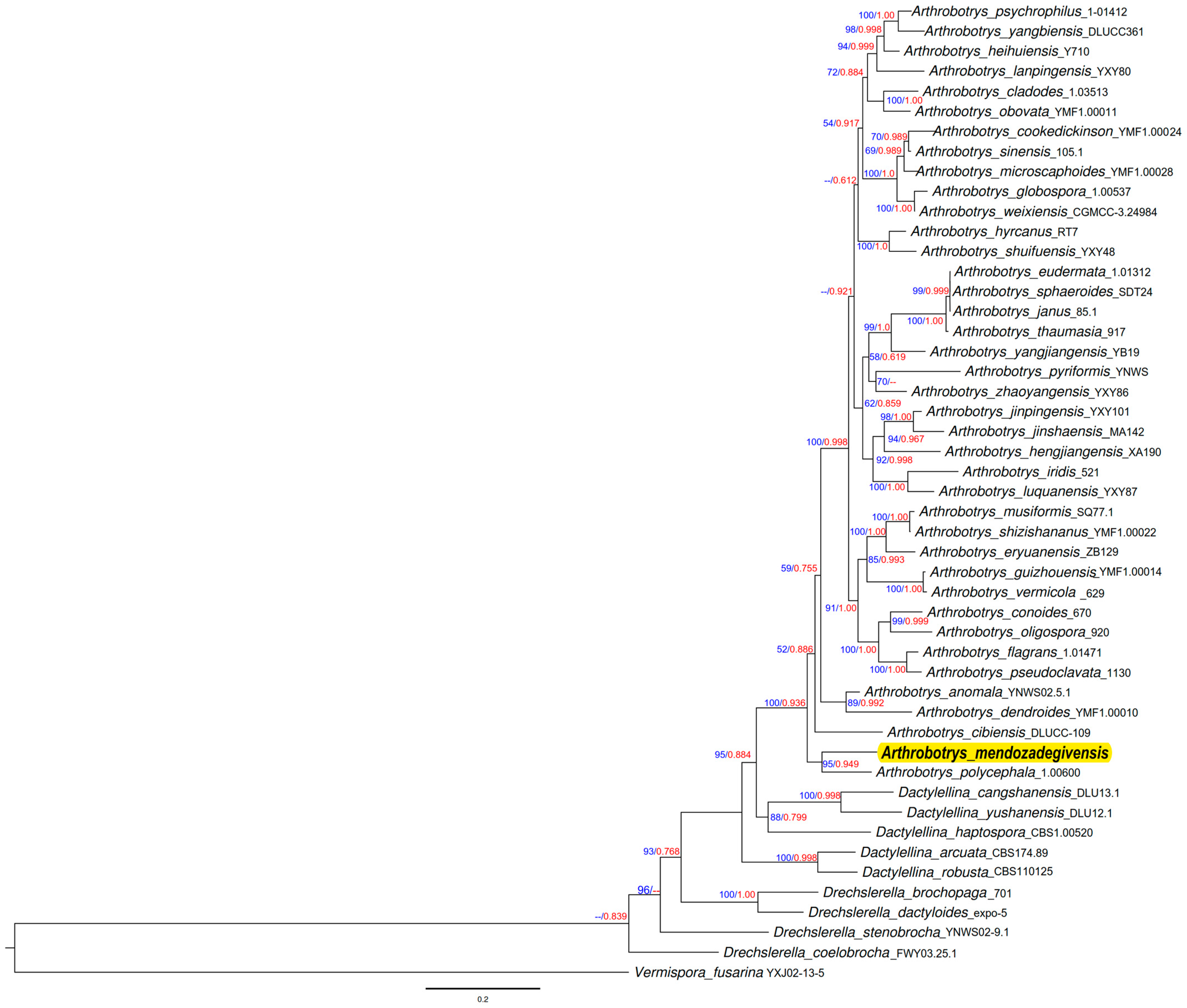
| Species | Strain Number | GenBank Accession Number | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | TEF | RPB2 | |||
| Arthrobotrys anomala | YNWS02-5-1 | AY773451 | AY773393 | AY773422.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys cibiensis | DLUCC 109 | OR880379 | OR882792 | OR882797.1 | [26] |
| Arthrobotrys cladodes | 1.03513 | MH179792 | MH179615 | MH179892.1 | [27] |
| Arthrobotrys conoides | 670 | AY773455 | AY773397 | AY773426.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys cookedickinson | YMF1.00024 | MF948393 | MF948550 | MF948474.1 | [28] |
| Arthrobotrys dendroides | YMF1.00010 | MF948388 | MF948545 | MF948469.1 | [28] |
| Arthrobotrys eryuanensis | ZB129 | MT612105 | OM850307 | OM850301 | [16] |
| Arthrobotrys eudermata | 1.01312 | MH179725 | MH179576 | MH179830.1 | [27] |
| Arthrobotrys flagrans | 1.01471 | MH179741 | MH179583 | MH179845.1 | [27] |
| Arthrobotrys globospora | 1.00537 | MH179706 | MH179562 | MH179814.1 | [27] |
| Arthrobotrys guizhouensis | YMF1.00014 | MF948390 | MF948547 | MF948471.1 | [28] |
| Arthrobotrys heihuiensis | Y710 | OR902194 | OR882786 | OR882801.1 | [16] |
| Arthrobotrys hengjiangensis | XA190 | OQ946586 | OQ989311 | OQ989301 | [29] |
| Arthrobotrys hyrcanus | RT7 | MH367058 | OP351540 | ___________ | [30] |
| Arthrobotrys iridis | 512 | AY773452 | AY773394 | AY773423.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys janus | 85-1 | AY773459 | AY773401 | AY773430.1. | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys jinpingensis | YXY101 | ON808621 | ON809552 | OR882804.1 | [16] |
| Arthrobotrys jinshaensis | MA142 | OR902197 | OR882789 | OR882804 | [26] |
| Arthrobotrys lanpingensis | YXY80 | ON808618 | ON809549 | ON809555 | [16] |
| Arthrobotrys luquanensis | YXY87 | ON808619 | ON809550 | ON809556 | [16] |
| Arthrobotrys microscaphoides | YMF1.00028 | MF948395 | MF948552 | MF948476.1 | [28] |
| Arthrobotrys musiformis | SQ77-1 | Y773469 | AY773411 | AY773440.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys obovata | YMF1.00011 | MF948389 | MF948546 | MF948470.1 | [28] |
| Arthrobotrys oligospora | 920 | AY773404 | AY773462 | AY773433.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys polycephala | 1.006 | MH179724 | MH179575 | MH179829.1 | [27] |
| Arthrobotrys pseudoclavata | 1130 | AY773446 | AY773388 | AY773417.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys psychrophila | 1.01412 | MH179727 | MH179578 | MH179832.1 | [27] |
| Arthrobotrys pyriformis | YNWS02-3-1 | AY773450 | AY773392 | AY773421.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys shizishananus | YMF1.00022 | MF948392 | MF948549 | MF948473.1 | [28] |
| Arthrobotrys shuifuensis | YXY48 | ON808617 | ON809548 | ON809554.1. | [16] |
| Arthrobotrys sinensis | 105-1 | AY773445 | AY773387 | AY773416.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys sphaeroides | SDT24 | AY773465 | AY773407 | AY773436.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys thaumasia | 917 | AY773461 | AY773403 | AY773432.1. | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys vermicola | 629 | AY773454 | AY773396 | AY773425.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys weixiensis | CGMCC 3.24984 | OQ946585 | OQ989310 | OQ989300.1 | [29] |
| Arthrobotrys yangbiensis | DLUCC 36-1 | OR880382 | OR882795 | OR882800.1 | [26] |
| Arthrobotrys yangjiangensis | YB19 | OR902196 | OR882788 | OR882803.1 | [26] |
| Arthrobotrys zhaoyangensis | YXY86 | ON808620 | ON809551 | ON809557 | [16] |
| Dactylellina arcuate | CBS 174.89 | AF106527 | DQ999852 | DQ999799.1 | [25] |
| Dactylellina cangshanensis | DLU 13-1 | MK372062 | MN915115 | MN915114.1 | [31] |
| Dactylellina haptospora | CBS 100520 | DQ999820 | DQ999850 | DQ999814.1 | [25] |
| Dactylellina robusta | CBS 110125 | DQ999821 | DQ999851 | DQ999800.1 | [25] |
| Dactylellina yushanensis | DLU12-1 | MK372061 | MN915113 | MN915112.1 | [31] |
| Drechslerella brochopaga | 701 | AY773456.1 | AY773398.1 | AY773427.1 | [25] |
| Drechslerella coelobrocha | FWY03-25-1 | AY773464.1 | AY773406.1 | AY773435.1 | [25] |
| Drechslerella dactyloides | Expo-5 | AY773463.1 | AY773405.1 | AY773434.1 | [25] |
| Drechslerella stenobrocha | YNWS02-9-1 | AY773460.1 | AY773402.1 | AY773431.1 | [25] |
| Dactylaria sp. | YNWS02-7-1 | AY773457 | AY773399 | AY773428.1 | [25] |
| Vermispora fusarina | YXJ02-13-5 | AY773447 | AY773418 | AY773418.1 | [25] |
| Arthrobotrys mendozadegivensis | INIFAP-EGM-01 | PQ649538 | PQ655528 | PQ661202 | Present study |
| Fungus | Query Cover % | Identity % | GenBank Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncultured fungus | 98 | 99.11 | GU053870.1 |
| Arthrobotrys polycephala | 98 | 93.12 | NR_160072 |
| A. polycephala | 98 | 93.12 | MH855875.1 |
| A. dendroides | 98 | 91.55 | NR_159642. |
| A. dendroides | 98 | 91.55 | MH861894.1 |
| A. ellipsospora | 98 | 91.55 | LC146721.1 |
| Media | Concentration | Dead Larvae ± SD | Total Larvae ± SD | Mortality (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CzDoxB | PBS | 1.92 ± 1.46 | 101.24 ± 11.28 | 1.9 ± 1.68 |
| NF | 4.10 ± 2.23 | 95.03 ± 19.20 | 4.31 ± 3.41 | |
| 25 | 4.31 ± 2.50 | 103.65 ± 10.65 | 4.15 ± 2.43 | |
| 50 | 7.45 ± 8.56 | 100.09 ± 13.00 | 7.44 ± 8.68 | |
| 100 | 33.34 ± 15.49 | 95.49 ± 14.41 | 34.91 ± 16.67 | |
| SPDB | PBS | 1.05 ± 0.63 | 77.23 ± 17.49 | 1.36 ± 0.35 |
| NF | 3.37 ± 2.5 | 97.25 ± 15.31 | 3.47 ± 2.07 | |
| 25 | 2.23 ± 1.21 | 92.66 ± 25.21 | 2.41 ± 1.82 | |
| 50 | 2.51 ± 3.39 | 92.73 ± 19.24 | 2.71 ± 2.62 | |
| 100 | 35.25 ± 16.55 | 86.18 ± 8.33 | 40.90 ± 18.66 |
| Arthrobotrys Species | Blank Nematode | Predatory Activity | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arthrobotrys oligospora | Haemonchus contortus | 76–79% | [33] |
| A. musiformis | H. contortus | 74.9% | [34] |
| A. cladodes | Strongyloidess papillosus | 99.5% | [35] |
| A. oligospora | Trichostrongylus colubriformis H. contortus | 90–99.99% | [36] |
| A. oligospora A. flagrans | H. contortus | 47.5% 41.8% | [37] |
| A. conoides | H. contortus | 75% | [38] |
| A. mendozadegivensis | H. contortus | 76.92% | (Present study) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Medina, E.; Mendoza-de Gives, P.; Pérez-Anzúrez, G.; Colinas-Picazo, A.; Bautista-García, G.A.; Alonso-Díaz, M.Á.; von Son-de Fernex, E.; López-Arellano, M.E. Arthrobotrys mendozadegivensis sp. nov. (Fungi: Orbiliales) from Mexico: Predatory Activity and Nematocidal Activity of Its Liquid Culture Filtrates Against Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae). J. Fungi 2024, 10, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120888
Gutiérrez-Medina E, Mendoza-de Gives P, Pérez-Anzúrez G, Colinas-Picazo A, Bautista-García GA, Alonso-Díaz MÁ, von Son-de Fernex E, López-Arellano ME. Arthrobotrys mendozadegivensis sp. nov. (Fungi: Orbiliales) from Mexico: Predatory Activity and Nematocidal Activity of Its Liquid Culture Filtrates Against Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae). Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(12):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120888
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Medina, Enrique, Pedro Mendoza-de Gives, Gustavo Pérez-Anzúrez, Antonio Colinas-Picazo, Génesis Andrea Bautista-García, Miguel Ángel Alonso-Díaz, Elke von Son-de Fernex, and María Eugenia López-Arellano. 2024. "Arthrobotrys mendozadegivensis sp. nov. (Fungi: Orbiliales) from Mexico: Predatory Activity and Nematocidal Activity of Its Liquid Culture Filtrates Against Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae)" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 12: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120888
APA StyleGutiérrez-Medina, E., Mendoza-de Gives, P., Pérez-Anzúrez, G., Colinas-Picazo, A., Bautista-García, G. A., Alonso-Díaz, M. Á., von Son-de Fernex, E., & López-Arellano, M. E. (2024). Arthrobotrys mendozadegivensis sp. nov. (Fungi: Orbiliales) from Mexico: Predatory Activity and Nematocidal Activity of Its Liquid Culture Filtrates Against Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae). Journal of Fungi, 10(12), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120888