Clinical Case of Feline Leishmaniosis: Therapeutic Approach and Long-Term Follow-Up
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsachev, I.; Kyriazis, I.D.; Boutsini, S.; Karagouni, E.; Dotsika, E. First report of canine visceral leishmaniasis in Bulgaria. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2010, 34, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tánczos, B.; Balogh, N.; Király, L.; Biksi, I.; Szeredi, L.; Gyurkovsky, M.; Scalone, A.; Fiorentino, E.; Gramiccia, M.; Farkas, R. First record of autochthonous canine leishmaniasis in Hungary. Vector-Born Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mircean, V.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Mircean, M.; Bolfa, P.; Györke, A.; Mihalca, A.D. Autochthonous canine leishmaniasis in Romania: Neglected or (re)emerging? Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ready, P.D. Threats and risks of phlebotomine sand fly-borne diseases becoming established in Germany and northern Europe: Preparedness for integrated control and prevention. Nova Acta Leopold. 2017, 411, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Svobodová, V.; Svoboda, M.; Friedlaenderova, L.; Drahotsky, P.; Bohacova, E.; Baneth, G. Canine leishmaniosis in three consecutive generations of dogs in Czech Republic. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 237, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalca, A.D.; Cazan, C.D.; Sulesco, T.; Dumitrache, M.O. A historical review on vector distribution and epidemiology of human and animal leishmaniosis in Eastern Europe. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.; Benelli, G.; Panarese, R.; Iatta, R.; Furlanello, T.; Beugnet, F.; Zatelli, A.; Otranto, D. Leishmania infantum and Dirofilaria immitis infections in Italy, 2009–2019: Changing distribution patterns. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maroli, M.; Pennisi, M.G.; Gramiccia, M.; Di Muccio, T.; Khouri, C.; Lo Giudice, S. First report of experimental Leishmania infection in Phlebotomus perniciosus fed on a cat with natural acquired leishmaniosis in Italy. Parassitologia 2007, 48, 332. [Google Scholar]
- Abbate, J.M.; Arfuso, F.; Napoli, E.; Gaglio, G.; Giannetto, S.; Latrofa, M.S.; Otranto, D.; Brianti, E. Leishmania infantum in wild animals in endemic areas of southern Italy. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 67, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.; Schalling, H.; Persichetti, F.; Pennisi, M.G. New epidemiological aspects of animal leishmaniosis in Europe: The role of vertebrate hosts other than dogs. Pathogens 2021, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.; González, E.; Iriso, A.; Marco, E.; Alegret, A.; Fúster, F.; Molina, R. Detection of Leishmania infantum and identification of blood meals in Phlebotomus perniciosus from a focus of human leishmaniasis in Madrid, Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2453–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.; González, E.; Martín-Martín, I.; Hernández, S.; Molina, R. Could wild rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) be reservoirs for Leishmania infantum in the focus of Madrid, Spain? Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 28, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Cardoso, L.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Koutinas, A.; Miró, G.; Oliva, G.; Solano-Gallego, L. Leishvet update and recommendations on feline leishmaniosis. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brianti, E.; Falsone, L.; Napoli, E.; Gaglio, G.; Giannetto, S.; Pennisi, M.G.; Priolo, V.; Latrofa, M.S.; Tarallo, V.D.; Solari Basano, F.; et al. Prevention of feline leishmaniosis with an imidacloprid 10%/flumethrin 4.5% polymer matrix collar. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otranto, D.; Napoli, E.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Tarallo, V.D.; Greco, G.; Lorusso, E.; Gulotta, L.; Falsone, L.; Basano, F.S.; et al. Feline and canine leishmaniosis and other vector-borne diseases in the Aeolian Islands: Pathogen and vector circulation in a confined environment. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 236, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brianti, E.; Celi, N.; Napoli, E.; Abbate, J.M.; Arfuso, F.; Gaglio, G.; Iatta, R.; Giannetto, S.; Gramiccia, M.; Otranto, D. Treatment and long-term follow up of a cat with leishmaniosis. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baneth, G.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Zuberi, A.; Zipori-Barki, N.; Orshan, L.; Kleinerman, G.; Shmueli-Goldin, A.; Bellaiche, M.; Leszkowicz-Mazuz, M.; Salant, H. Leishmania infection in cats and dogs housed together in an animal shelter reveals a higher parasite load in infected dogs despite a greater seroprevalence among cats. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gallego, A.; Bernabe, L.F.; Dalmau, A.; Esteban-Saltiveri, D.; Font, A.; Leiva, M.; Ortuňez-Navarro, A.; Peňa, M.T. Feline leishmaniosis: Diagnosis, treatment, and outcome in 16 cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.; Gomes, J.; Cristóvão, J.; Nunes, M.; Martines, A.; Rebêlo, E.; Campino, C. Feline Leishmania infection in a canine leishmaniasis endemic region, Portugal. Vet. Parsitol. 2010, 174, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, F.; Albanese, F.; Gattuso, S.; Randone, A.; Fileccia, I.; Dedola, C.; Ibba, F.; Ottaiano, P.; Brianti, E. Skin Lesions in Feline Leishmaniosis: A Systematic Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervàs, J.; De Lara, F.C.M.; Sdnchez-lsarria, M.A.; Pellicer, S.; Carrasco, L.; Castillo, J.A.; Gòmez-Villamandos, J.C. Two cases of feline visceral and cutaneous leishmaniosis in Spain. J. Feline Med. Surg. 1999, 1, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Venza, M.; Reale, S.; Vitale, F.; Lo Giudice, S. Case report of leishmaniasis in four cats. Vet. Res. Commun. 2004, 28, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, P.; Alves-Pimenta, S.; Barros, J.; Barbosa, P.; Rodrigues, A.; Pereira, M.J.; Maltez, L.; Gama, A.; Cristovao, J.M.; Campino, L.; et al. Feline leishmaniosis in Portugal: 3 cases (year 2014). Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2015, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.; Maia, C. Leishmania infection in cats and feline leishmaniosis: An updated review with a proposal of a diagnosis algorithm and prevention guidelines. In Current Research in Parasitology & Vector-Borne Diseases 1; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; p. 100035. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.; Cristovao, J.M.; Vilhena, H.; Martins, A.; Cachola, P.; Henriques, J.; Coimbra, M.; Catarino, A.; Lestinova, T.; Spitzova, T.; et al. Antibody response to Phlebotomus perniciosus saliva in cats naturally exposed to phlebotomine sand flies is positively associated with Leishmania infection. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, M.; Lloret, A.; Pena, T.; Roura, X. Therapy of ocular and visceral leishmaniasis in a cat. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2005, 8, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Durão, J.; Rebelo, E.; Peleteiro, M.; de Jesus Correia, J.M.; Simões, G. First case of leishmaniosis in domestic cat (Felis catus domesticus) detected in Portugal (Sesimbra). Rev. Port. Cienc. Vet. 1994, 511, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, R.; Santos, M.; Malhão, F.; Pereira, R.; Fernandes, A.C.; Montenegro, L.; Roccabianca, P. Pancytopenia in a cat with visceral leishmaniasis. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 38, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.; Sousa, C.; Ramos, C.; Cristóvão, J.M.; Faísca, P.; Campino, L. First case of leishmaniosis caused by Leishmania infantum genotype E in a cat with a concurrent nasal squamous cell carcinoma. JFMS Open Rep. 2015, 1, 2055116915593969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, M.A.; Marques, C.; Santos, M.; Duarte, A.; Pissarra, H.; Carreira, L.M.; Gomes, L.; Valério-Bolas, A.; Tavares, L.; Santos-Gomes, G.; et al. Successful treatment of feline leishmaniosis using a combination of allopurinol and N-methyl-glucamine antimoniate. JFMS Open Rep. 2016, 2, 2055116916630002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brianti, E.; Napoli, E.; Gaglio, G.; Falsone, L.; Giannetto, S.; Solari Basano, F.; Nazzari, R.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Tarallo, V.D.; et al. Field Evaluation of Two Different Treatment Approaches and Their Ability to Control Fleas and Prevent Canine Leishmaniosis in a Highly Endemic Area. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatta, R.; Furlanello, T.; Colella, V.; Tarallo, V.D.; Latrofa, M.S.; Brianti, E.; Trerotoli, P.; Decaro, N.; Lorusso, E.; Schunack, B.; et al. A nationwide survey of Leishmania infantum infection in cats and associated risk factors in Italy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 15, e0007594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa-Val, A.P.; Coura, F.M.; Barbieri, J.M.; Diniz, L.; Sampaio, A.; Reis, J.K.P.; Lopes-bueno, B.; Ferreira-Gontijo, C.M. Serological study of feline leishmaniasis and molecular detection of Leishmania infantum and Leishmania braziliensis in cats (Felis catus). Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Persichetti, M.F. Feline leishmaniosis: Is the cat a small dog? Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 15, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Hartmann, K.; Lloret, A.; Addie, D.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Hosie, M.J.; et al. Leishmaniosis in cats: ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcondes, M.; Hirata, K.Y.; Vides, J.P.; Sobrinho, L.S.V.; Azevedo, J.S.; Vieira, T.S.W.J.; Vieira, R.F.C. Infection by Mycoplasma spp., feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukemia virus in cats from an area endemic for visceral leishmaniasis. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.B.S.; Portela, R.A.; Arruda, L.F.B.; Ferreira, J.S.; Souto, E.P.F.; Araújo, A.L.; Madeira, M.F.; Dantas, A.F.M.; Melo, M.A. Natural infection by Leishmania infantum in domestic cats (Felis catus) in a municipality of moderate transmission in the Brazilian semi-arid region. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, e016620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocholle, E.; Reyes-Gomez, E.; Giacomo, A.; Delaunay, P.; Hasseine, L.; Marty, P. A case of feline leishmaniasis in the south of France. Parasite 2012, 19, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hervas, J.; Chacon-Manrique De Lara, F.; Lopez, J.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Guerrero, M.J.; Moreno, A. Granulomatous (pseudotumoral) iridociclitis associated with leishmaniasis in a cat. Vet. Rec. 2020, 149, 624–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, R.O.; Pereira, H.; Cartaxeiro, C.; Delgado, E.; Peleteiro, M.C.; Pereira Fonseca, I. Granulomatous rhinitis secondary to feline leishmaniosis: Report of an unusual presentation and therapeutic complications. JFMS Open Rep. 2018, 4, 2055116918811374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Abramo, F.; Barsotti, P.; Leva, S.; Gramiccia, M.; Ludovisi, A.; Mancianti, F. Feline leishmaniosis due to Leishmania infantum in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Miró, G.; Koutinas, A.; Cardoso, L.; Pennisi, M.G.; Ferrer, L.; Bourdeau, P.; Oliva, G.; Baneth, G. LeishVet guidelines for the practical management of canine leishmaniosis. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Montserrrat-Sangra, S.; Ordeix, L.; Martínez-Orellana, P. Leishmania infantum-specific production of IFN-γ and IL-10 in stimulated blood from dogs with clinical leishmaniosis. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rüfenacht, S.; Sager, H.; Mueller, N.; Schaerer, V.; Heier, A.; Welle, M.M.; Roosje, P.J. Two cases of feline leishmaniasis in Switzerland. Vet. Rec. 2005, 156, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.; Valente, J.; Parreira, R.; Cristovao, J.M.; Azinheira, S.; Campino, L.; Maia, C. An unusual case of feline leishmaniosis with involvement of the mammary glands. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2019, 37, 2017–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuir-Baraja, A.E.; Ruiz, M.P.; Garijo, M.M.; Llobat, L. Feline Leishmaniosis: An Emerging Public Health Problem. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Persichetti, M.F.; Migliazzo, A.; De Majo, M.; Iannelli, N.M.; Vitale, F. Feline leishmaniosis: Clinical signs and course in 14 followed up cases. In Proceedings of the LXX Convegno SISVet, Palermo, Italy, 13–16 June 2016; pp. 166–167. [Google Scholar]
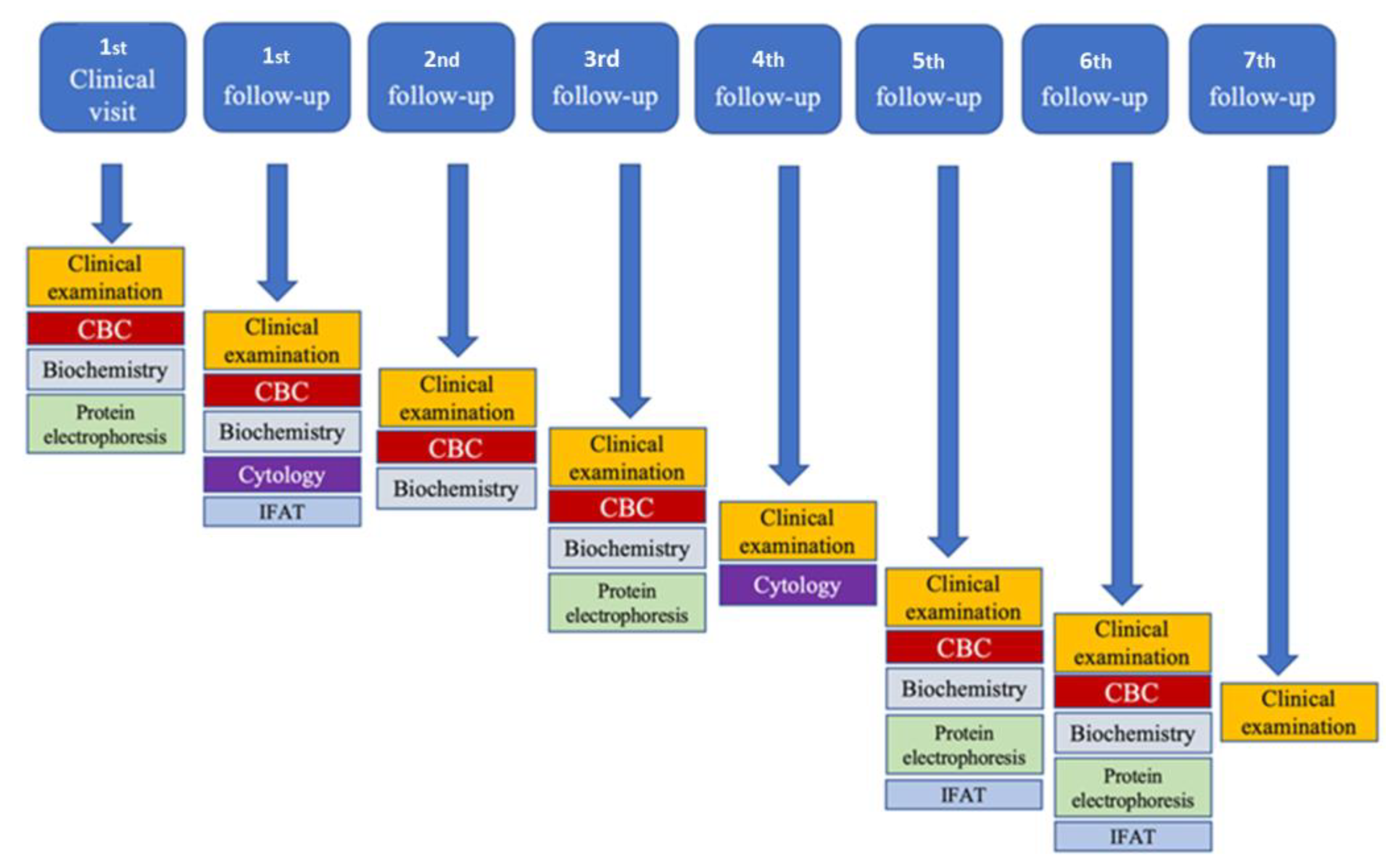
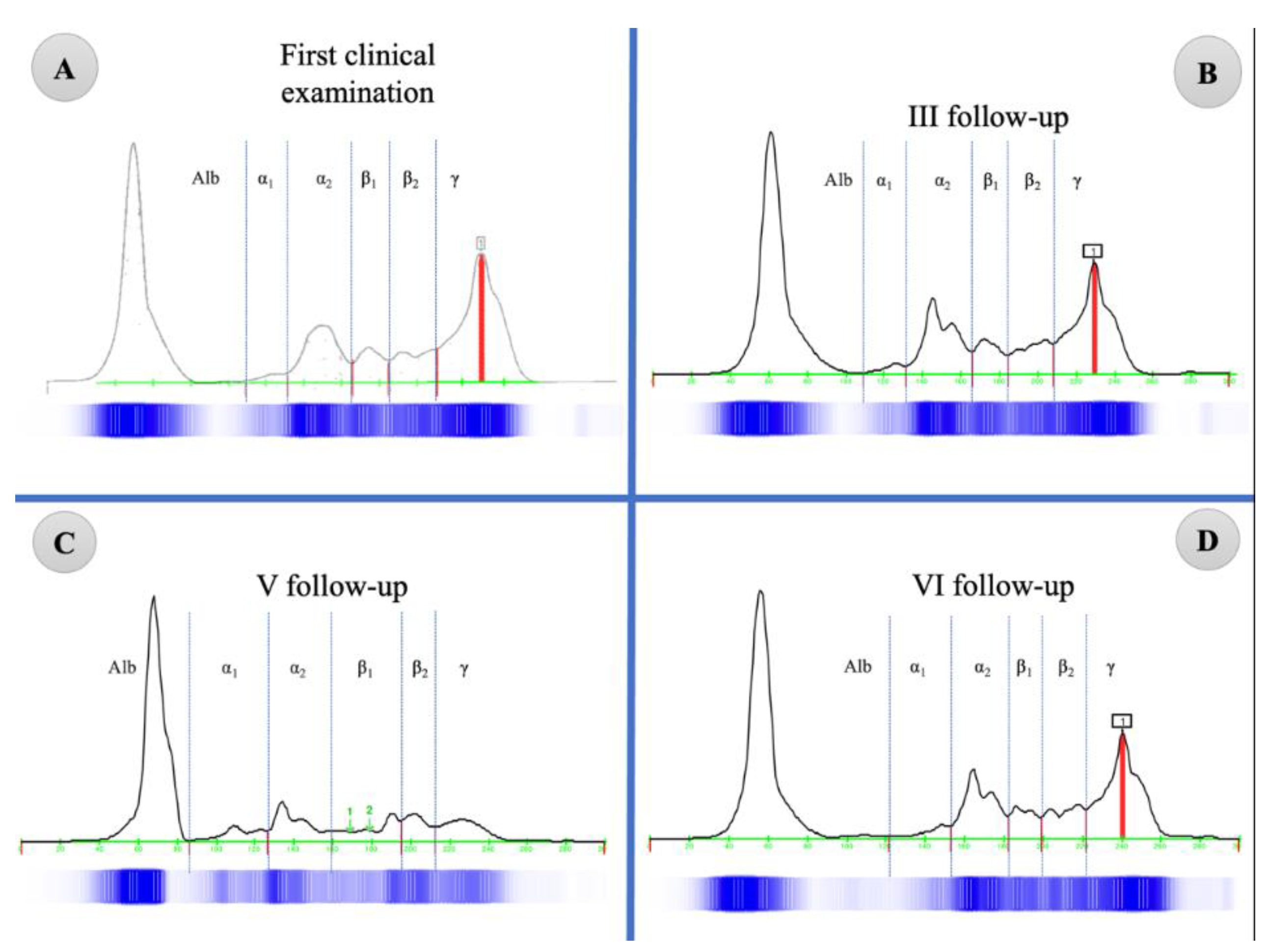
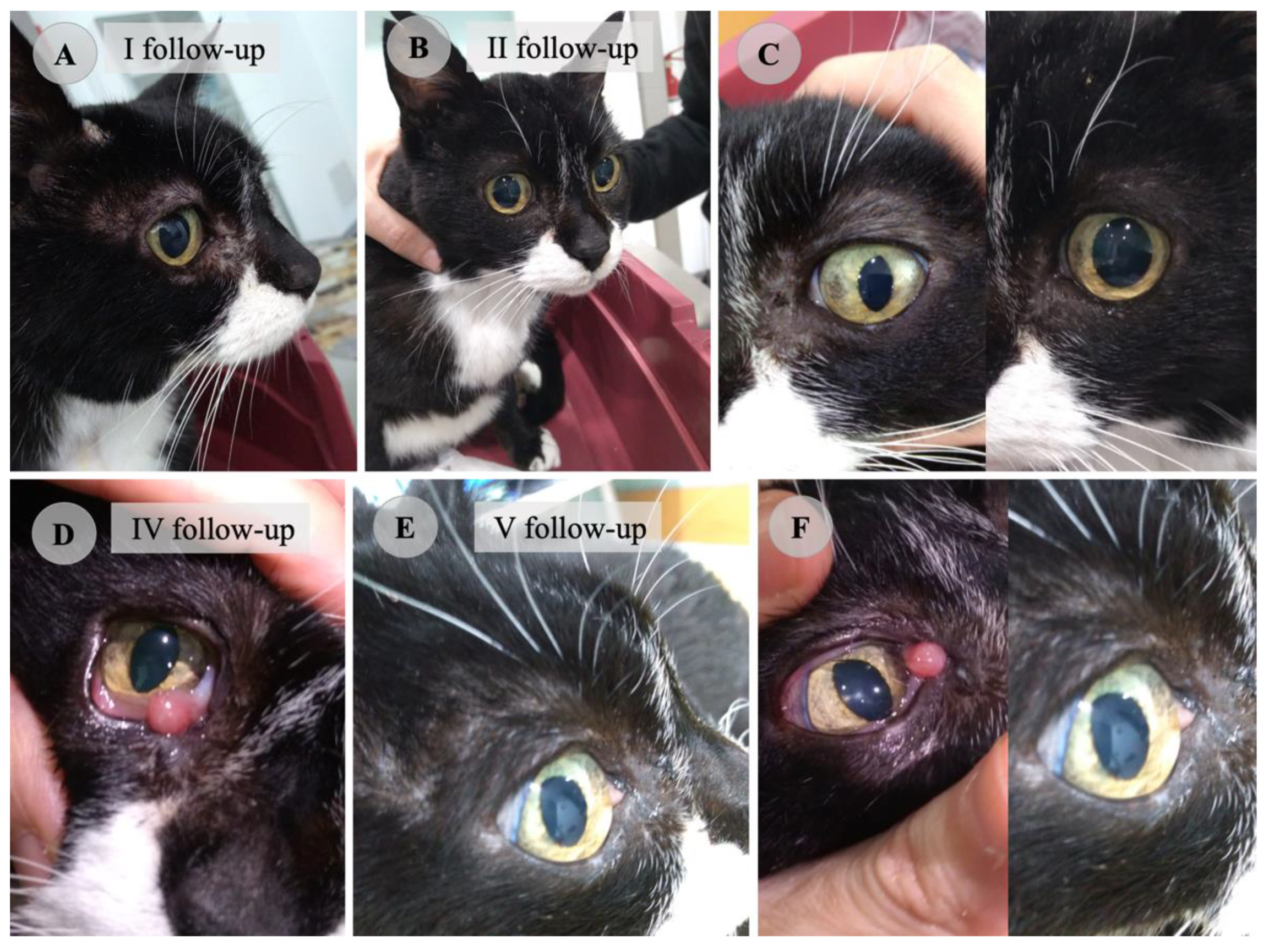
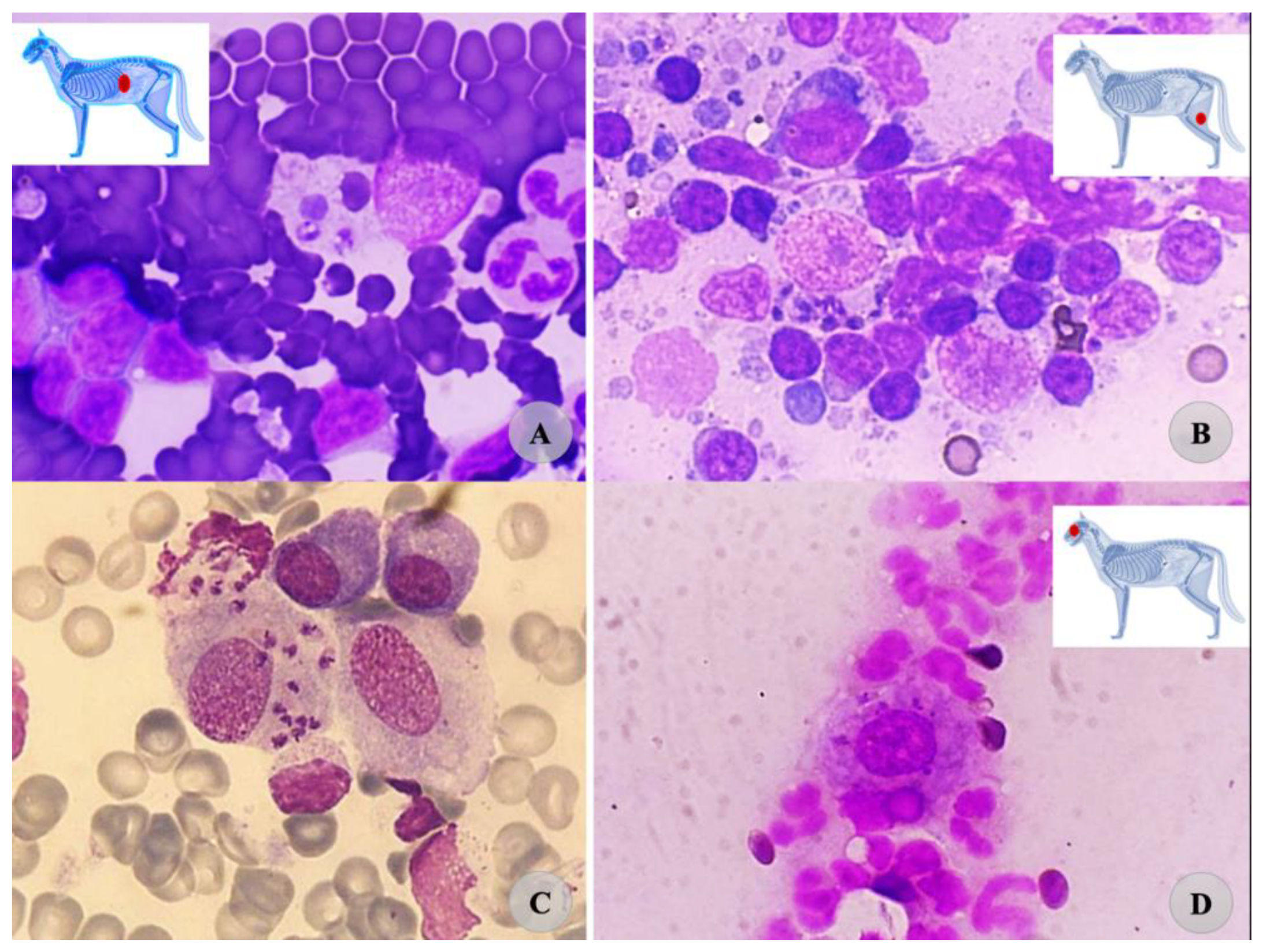
| Parameter | Reference Range | Unit | First Visit | I Follow-Up | II Follow-Up | III Follow-Up | V Follow-Up | Vi Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | 6.00–19.00 | 103/uL | 6.53 | 27.1 + | 72.6 + | 4.91 | 4.49 | 4.90 |
| Neutrophils | 2.50–12.00 | 103/uL | 4.21 | --- | --- | 2.40 | 2.50 | 2.60 |
| Lymphocytes | 2.20–8.00 | 103/uL | 2.11 | 12.57 | 64.3 | 2.31 | 2.1 | 3.1 |
| Monocytes | 0.20–1.00 | 103/uL | 0.15 | --- | --- | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| Eosinophils | 0.20–1.50 | 103/uL | 0.05 | --- | --- | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.0 |
| Basophils | 0.00–0.10 | 103/uL | 0.01 | --- | --- | 0.00 | 0.9 | 0.0 |
| RBC | 5.00–10.10 | 106/uL | 7.14 | 5.43 | 5.18 | 6.97 | 7.78 | 7.64 |
| HGB | 8.0–15.0 | g/dL | 11.3 | 8.8 | 12.4 | 10.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 |
| HTC | 25.0–45.0 | % | 39.1 | 34.7 | 41.8 | 35.6 | 36 | 37.4 |
| MCV | 41.0–45.0 | fL | 54.8 + | 60.0 + | 67.7 + | 51.1 + | 46 + | 49.0 + |
| MCH | 13.0–17.0 | Pg | 15.8 | 13.05 | 20 | 14.8 | 14 | 14.0 |
| MCHC | 31.0–36.0 | g/dL | 28.9 | 24.4 | 29.6 | 28.9 | 30.3 | 28.6 |
| PLT | 150–500 | 106/uL | 23 − | 100 − | 198 | 84 − | 146 − | 97 − |
| Parameter | Reference Range | Unit | First Visit | I Follow-Up | II Follow-Up | III Follow-Up | V Follow-Up | VI Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azotemia | 10.0–30.0 | mg/dL | 62 + | 41 + | 84 + | 80 + | 12 * | 66 + |
| Creatinine | <1.5 | mg/dL | 2.2 + | 2.3 + | 3.8 + | 3.3 + | 0.7 * | 3.5 + |
| Urea/Creatinine | 28.2 | 17.8 | 22.1 | --- | 17.1 | 18.9 | ||
| Total cholesterol | 90.0–200.0 | mg/dL | 109 | --- | 143.6 | 164 | 228 * | 148 |
| AST | <80 | UI/L | 30 | --- | 32 | 45 | 32 | |
| ALT | <80 | UI/L | 47 | --- | 94 | 80 | 140 | 65 |
| Total bilirubin | <0.6 | mg/dL | 0.48 | --- | 0.42 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.20 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | <200 | UI/L | 33 | --- | 35 | 57 | 4479 * | 87 |
| Total protein | 5.3–7.9 | g/dL | 6.7 | --- | 7.87 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.3 |
| Globulin | mg/dL | 4.1 | 4.66 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 3.5 | ||
| Albumin | 2.1–3.4 | g/dL | 2.6 | --- | 3.21 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 2.8 |
| A/G | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Parameter | Reference Range | Unit | First Visit | I Follow-Up | II Follow-Up | III Follow-Up | V Follow-Up | VI Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin | 44.0–56.0 | % | 39.9 | --- | --- | 43.2 | 55.6 | 44.4 |
| Alpha 1 | 2.7-5.0 | % | 1.5 | --- | --- | 1.90 | 5.8 | 2.4 |
| Alpha 2 | 6.3–12.5 | % | 13.8 | --- | --- | 16.50 | 12.0 | 14.2 |
| Beta 1 | 2.0–8.0 | % | 5.9 | --- | --- | 5.70 | 9.3 | 5.6 |
| Beta 2 | 7.0–11.5 | % | 7.6 | --- | --- | 7.50 | 6.9 | 8.0 |
| Gamma | 12.0–22.00 | % | 32.3 | --- | --- | 26.60 | 10.4 | 25.4 |
| Albumin | 2.1–3.4 | g/dL | 2.6 | --- | --- | 2.90 | 3.1 | 2.8 |
| Alpha 1 | 0.1–0.6 | g/dL | 0.1 | --- | --- | 0.10 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Alpha 2 | 0.3–1.3 | g/dL | 0.9 | --- | --- | 1.00 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Beta 1 | 0.3–0.7 | g/dL | 0.4 | --- | --- | 0.40 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Beta 2 | 0.2–1.3 | g/dL | 0.5 | --- | --- | 0.50 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Gamma | 0.8–1.5 | g/dL | 2.2 | --- | --- | 1.80 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| Total protein | g/dL | 6.68 | --- | --- | 6.70 | 5.58 | 6.28 | |
| Alb/Glob rate | >0.9 | 0.64 | --- | --- | 0.76 | 1.25 | 0.86 | |
| IFAT Leishmania | --- | 1:1280 | --- | 1:1280 | 1:640 | 1:320 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Napoli, E.; De Benedetto, G.; Fazio, C.; La Russa, F.; Gaglio, G.; Brianti, E. Clinical Case of Feline Leishmaniosis: Therapeutic Approach and Long-Term Follow-Up. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080400
Napoli E, De Benedetto G, Fazio C, La Russa F, Gaglio G, Brianti E. Clinical Case of Feline Leishmaniosis: Therapeutic Approach and Long-Term Follow-Up. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(8):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080400
Chicago/Turabian StyleNapoli, Ettore, Giovanni De Benedetto, Cristina Fazio, Francesco La Russa, Gabriella Gaglio, and Emanuele Brianti. 2022. "Clinical Case of Feline Leishmaniosis: Therapeutic Approach and Long-Term Follow-Up" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 8: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080400
APA StyleNapoli, E., De Benedetto, G., Fazio, C., La Russa, F., Gaglio, G., & Brianti, E. (2022). Clinical Case of Feline Leishmaniosis: Therapeutic Approach and Long-Term Follow-Up. Veterinary Sciences, 9(8), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080400







