Factors Affecting the Outcome of Medical Treatment in Cats with Obstructive Ureteral Stones Treated with Tamsulosin: 70 Cases (2018–2022)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Treatment Protocol
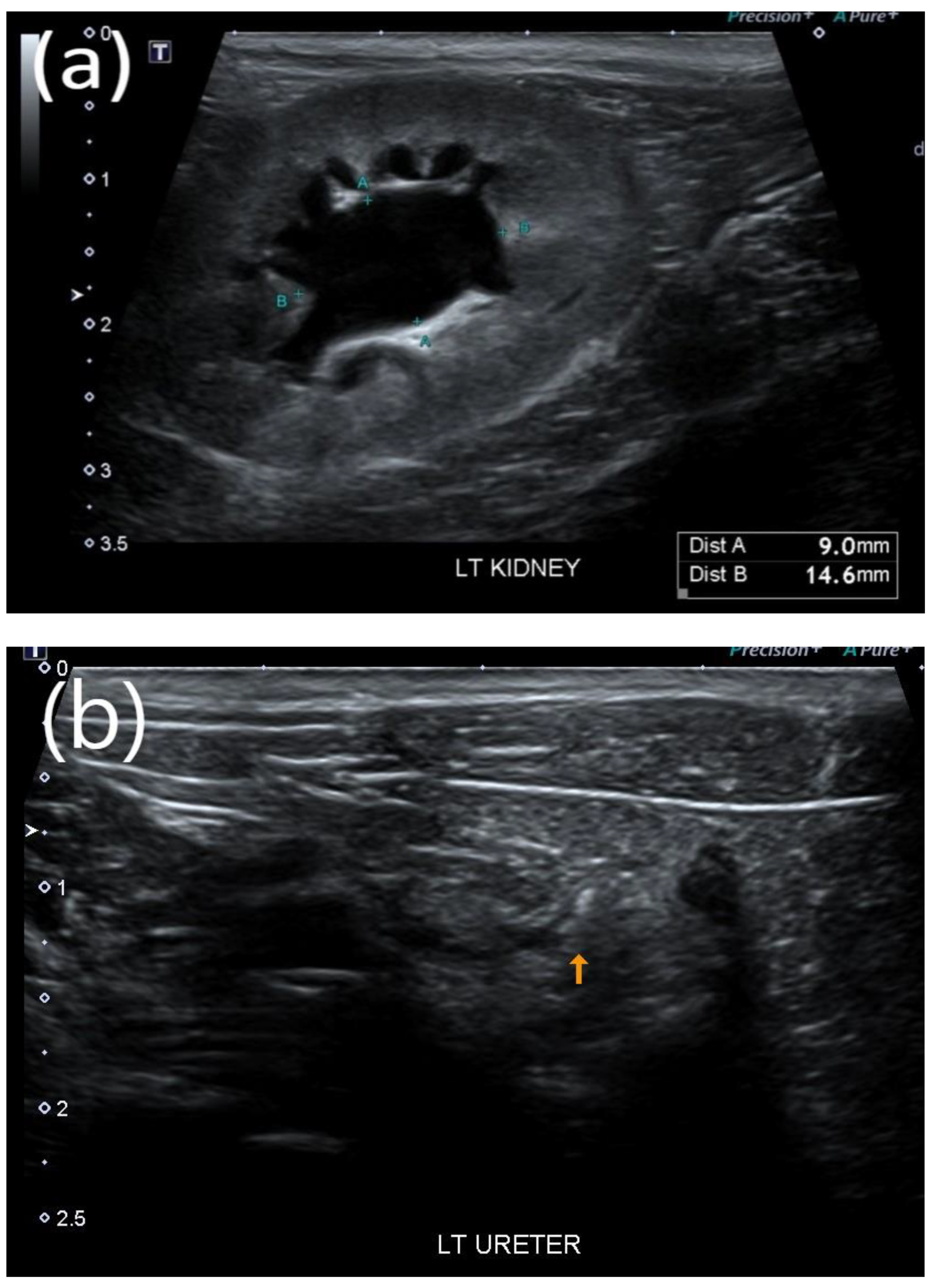
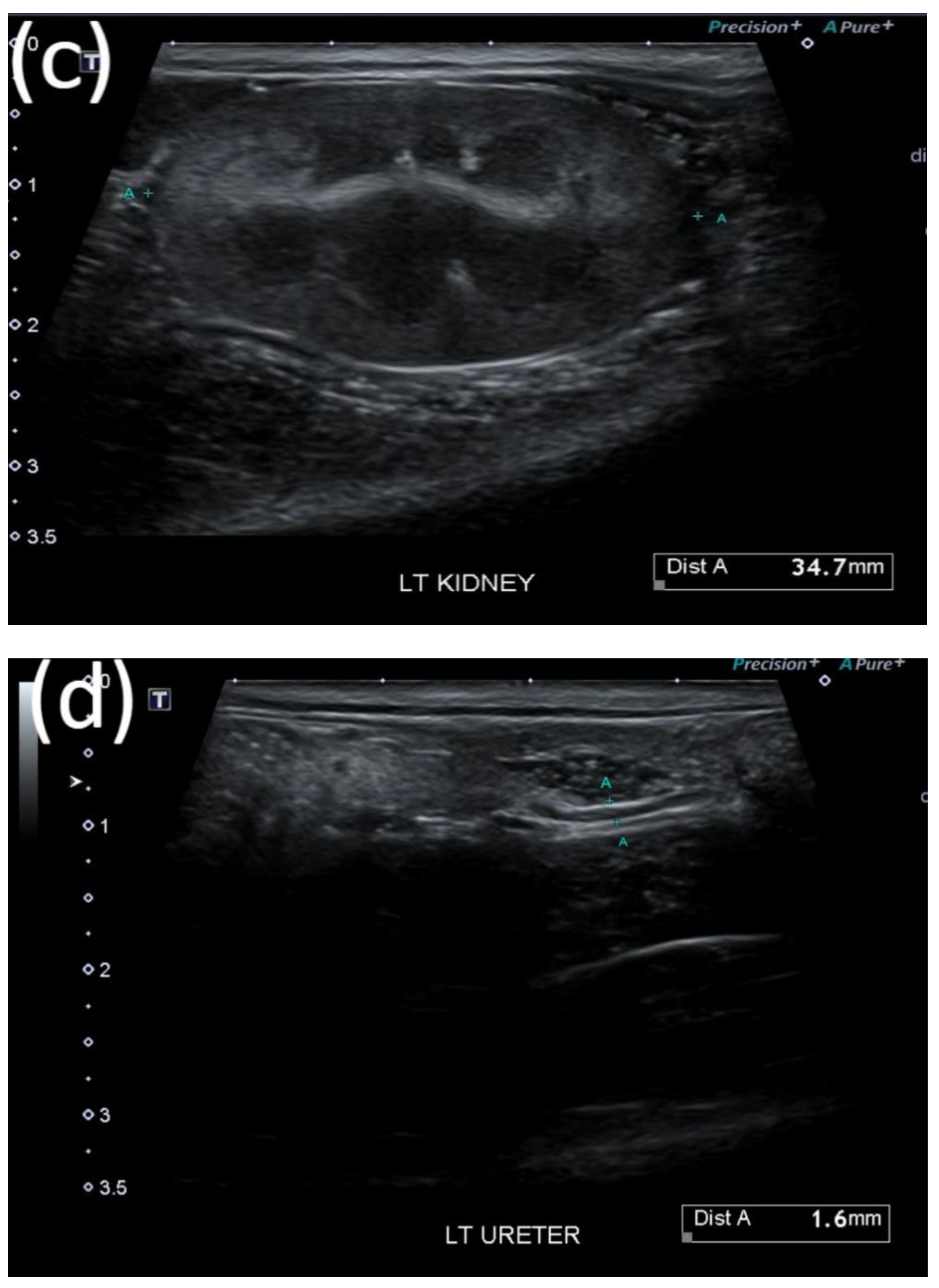
2.3. Evaluation of Treatment Response
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Diagnostic Tests
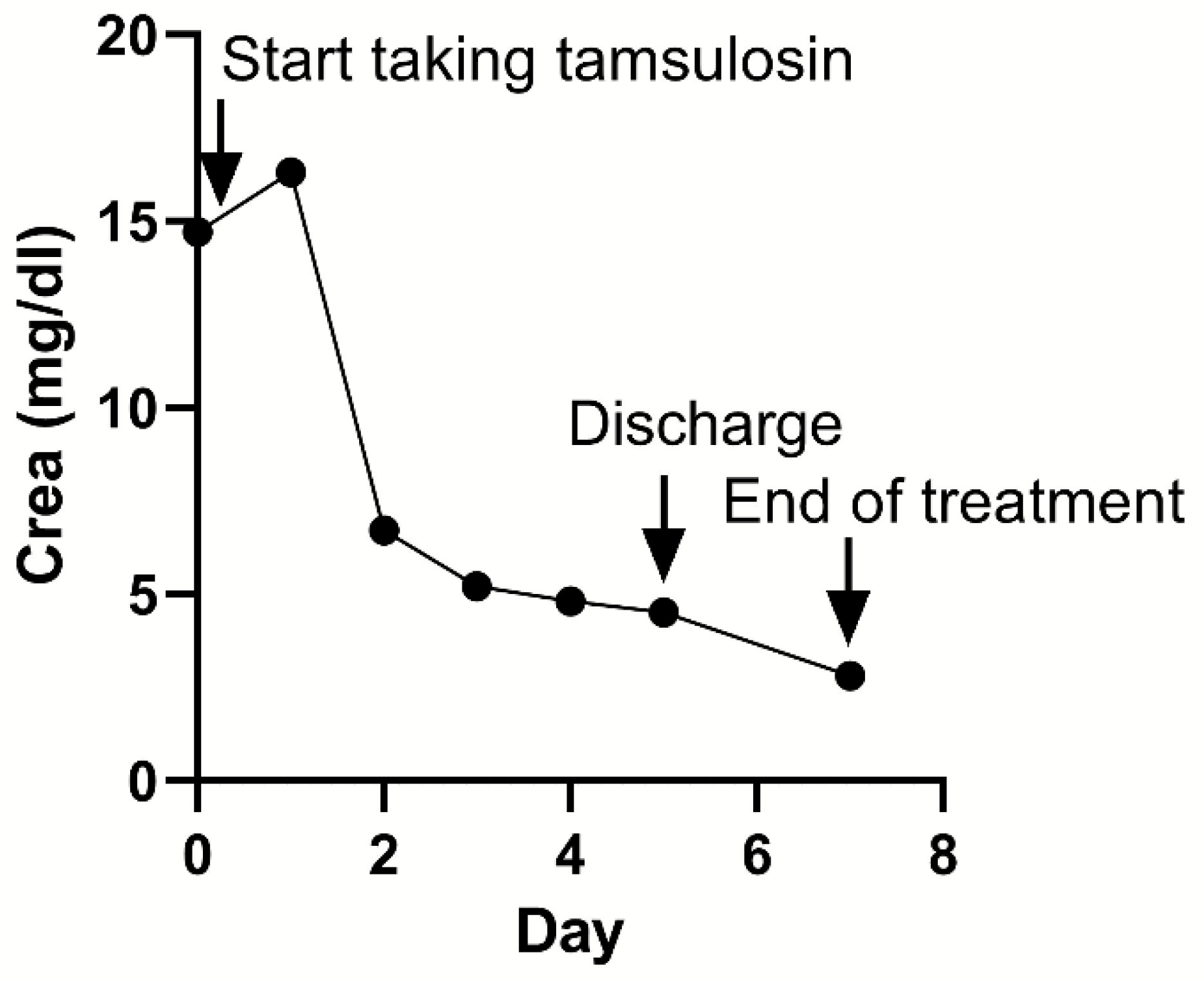
3.3. Treatment Results
3.4. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osborne, C.A.; Lulich, J.P.; Kruger, J.M.; Ulrich, L.K.; Koehler, L.A. Analysis of 451,891 canine uroliths, feline uroliths, and feline urethral plugs from 1981 to 2007: Perspectives from the Minnesota Urolith Center. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, A.B.; Westropp, J.L.; Ruby, A.L.; Kass, P.H. Evaluation of trends in urolith composition in cats: 5,230 cases (1985–2004). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 231, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyles, A.E.; Hardie, E.M.; Wooden, B.G.; Adin, C.A.; Stone, E.A.; Gregory, C.R.; Mathews, K.G.; Cowgill, L.D.; Vaden, S.; Nyland, T.G.; et al. Management and outcome of cats with ureteral calculi: 153 cases (1984–2002). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 226, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berent, A.C.; Weisse, C.W.; Todd, K.; Bagley, D.H. Technical and clinical outcomes of ureteral stenting in cats with benign ureteral obstruction: 69 cases (2006–2010). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroy, C.; Rossetti, D.; Ragetly, G.; Hernandez, J.; Poncet, C. Comparison between double-pigtail ureteral stents and ureteral bypass devices for treatment of ureterolithiasis in cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 251, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormser, C.; Clarke, D.L.; Aronson, L.R. Outcomes of ureteral surgery and ureteral stenting in cats: 117 cases (2006–2014). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2016, 248, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defarges, A.; Berent, A.; Dunn, M. New alternatives for minimally invasive management of uroliths: Ureteroliths. Compend. Contin. Educ. Vet. 2013, 35, E4. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, D.L. Feline ureteral obstructions Part 2: Surgical management. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.L. Feline ureteral obstructions Part 1: Medical management. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Alter, H.J.; Littlepage, A. A systematic review of medical therapy to facilitate passage of ureteral calculi. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2007, 50, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.; Westropp, J. Cats and calcium oxalate: Strategies for managing lower and upper tract stone disease. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berent, A.C. Ureteral obstructions in dogs and cats: A review of traditional and new interventional diagnostic and therapeutic options. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2011, 21, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, D. Plumb’s Veterinary Drug Handbook, 8th ed.; PharmaVetInc Wiley; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lulich, J.P.; Berent, A.C.; Adams, L.G.; Westropp, J.L.; Bartges, J.W.; Osborne, C.A. ACVIM small animal consensus recommendations on the treatment and prevention of uroliths in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.; Berent, A.; Weisse, C.; Langston, C.; Bagley, D. Predictors of outcome for cats with ureteral obstructions after interventional management using ureteral stents or a subcutaneous ureteral bypass device. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, P.; Tunuguntla, H.S. Long-term efficacy and safety of tamsulosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Rev. Urol. 2005, 7 (Suppl. 4), S42–S48. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, C.J.; Matheson, A.; Faulds, D.M. Tamsulosin: A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the management of lower urinary tract symptoms. Drugs Aging 2002, 19, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, P.; Evans, C.P.; Moon, T. Long-term safety and efficacy of tamsulosin for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.C.; Park, Y.Y.; Shim, B.S. Effect of tamsulosin on the expectant treatment of lower ureteral stones. Korean J. Urol. 2006, 47, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jendeberg, J.; Geijer, H.; Alshamari, M.; Cierzniak, B.; Lidén, M. Size matters: The width and location of a ureteral stone accurately predict the chance of spontaneous passage. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4775–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, C.; Aydoğdu, O.; Senocak, C.; Damar, E.; Eraslan, A.; Oztuna, D.; Bozkurt, O.F. Predictive factors for spontaneous stone passage and the potential role of serum C-reactive protein in patients with 4 to 10 mm distal ureteral stones: A prospective clinical study. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Whitaker, E.; Neilson, J.; Allen, I.E.; Stoller, M.L.; Fahimi, J. Effect of tamsulosin on stone passage for ureteral stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, 353–361.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Gabr, A.H.; Emara, A.A.; Ali, M.; Abdel-Aziz, A.S.; Alshahrani, S. Factors predicting the spontaneous passage of a ureteric calculus of ⩽10 mm. Arab J. Urol. 2015, 13, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, R.R.; Zufall, W.H. Efficacy and Safety of Alpha-Blockers for Kidney Stones in Adults. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 34, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griwan, M.S.; Singh, S.K.; Paul, H.; Pawar, D.S.; Verma, M. The efficacy of tamsulosin in lower ureteral calculi. Urol. Ann. 2010, 2, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Cat Demographics (n = 70) |
|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 8.77 years (2–16) |
| Sex | |
| Castrated males | 39 (55.7%) |
| Spayed females | 31 (44.3%) |
| Weight, median (range) | 4.25 kg (1.9–10.3) |
| Breeds | |
| Korean Short Hair | 22 |
| Siamese | 11 |
| Persian | 9 |
| Russian Blue | 7 |
| Turkish Angora | 6 |
| American Short Hair | 5 |
| Scottish Fold | 4 |
| British Short Hair | 1 |
| Munchkin | 1 |
| Ragdoll | 1 |
| Chinchilla | 1 |
| Abyssinian | 1 |
| Norwegian Forest | 1 |
| Locations of ureteral stones | |
| Upper | 26 |
| Middle | 34 |
| Lower | 26 |
| Parameter | Passage+ | Passage− | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 7.82 ± 3.32 | 9.21 ± 3.64 | 0.1321 * |
| Vertical diameter of the stone (mm) | 1.09 ± 0.29 | 1.34 ± 0.50 | 0.0301 † |
| Location, n (%) | Upper 3 (12.5%) Mid 6 (25.0%) Distal 15 (62.5%) | Upper 23 (37.1%) Mid 28 (45.2%) Distal 11 (17.7%) | 0.0002 ‡ |
| Side, n (%) | Left 12 (54.5%) Right 8 (36.4%) Bilateral 2 (9.1%) | Left 21 (43.8%) Right 13 (27.1%) Bilateral 14 (29.2%) | 0.1767 ‡ |
| Sex, n (%) | Male: 17 (77.3%) Female: 5 (22.7%) | Male: 22 (45.8%) Female: 26 (54.2%) | 0.0140 ‡ |
| Body weight (kg) | 4.16 ± 1.77 | 4.12 ± 1.41 | 0.5999 † |
| Baseline serum creatinine levels | 5.09 ± 4.14 | 7.34 ± 6.44 | 0.1338 † |
| Predictors | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.90 | 0.75–1.06 | 0.2 |
| Female sex | 0.17 | 0.04–0.59 | 0.0008 |
| Weight | 0.78 | 0.50–1.16 | 0.2 |
| Diameter | 0.24 | 0.05–0.90 | 0.056 |
| Baseline serum creatinine levels | 0.89 | 0.78–0.99 | 0.068 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chae, H.-K.; Hong, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, W.J.; Oh, S.; Ji, S.; Hong, Y.-J. Factors Affecting the Outcome of Medical Treatment in Cats with Obstructive Ureteral Stones Treated with Tamsulosin: 70 Cases (2018–2022). Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100568
Chae H-K, Hong HJ, Lee SY, Park J-H, Choi WJ, Oh S, Ji S, Hong Y-J. Factors Affecting the Outcome of Medical Treatment in Cats with Obstructive Ureteral Stones Treated with Tamsulosin: 70 Cases (2018–2022). Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(10):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100568
Chicago/Turabian StyleChae, Hyung-Kyu, Hyun Jeong Hong, Se Yoon Lee, Jung-Hoon Park, Woo Joo Choi, Seungkuk Oh, Seoyeoun Ji, and Yeon-Jung Hong. 2022. "Factors Affecting the Outcome of Medical Treatment in Cats with Obstructive Ureteral Stones Treated with Tamsulosin: 70 Cases (2018–2022)" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 10: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100568
APA StyleChae, H.-K., Hong, H. J., Lee, S. Y., Park, J.-H., Choi, W. J., Oh, S., Ji, S., & Hong, Y.-J. (2022). Factors Affecting the Outcome of Medical Treatment in Cats with Obstructive Ureteral Stones Treated with Tamsulosin: 70 Cases (2018–2022). Veterinary Sciences, 9(10), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100568






