Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2a and Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype D in Growing Pigs Suffering from Respiratory Disease
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Presentation and Sample Collection
2.2. Viral Detection by PCR
2.3. Virus Isolation and Identification
2.4. Viral Genome Amplification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Bacterial Isolation and Culture
2.6. Bacterial Catalase and Biochemical Tests
2.7. Identification of Bacterial Species Based on 16S rDNA Sequences
2.8. PCR Identification of Bacterial Species and Capsular Serotypes
2.9. Pathogenicity Test of the Isolated Bacteria
3. Results
3.1. PCV2 Nucleic Acid Was Detected in the Tissue
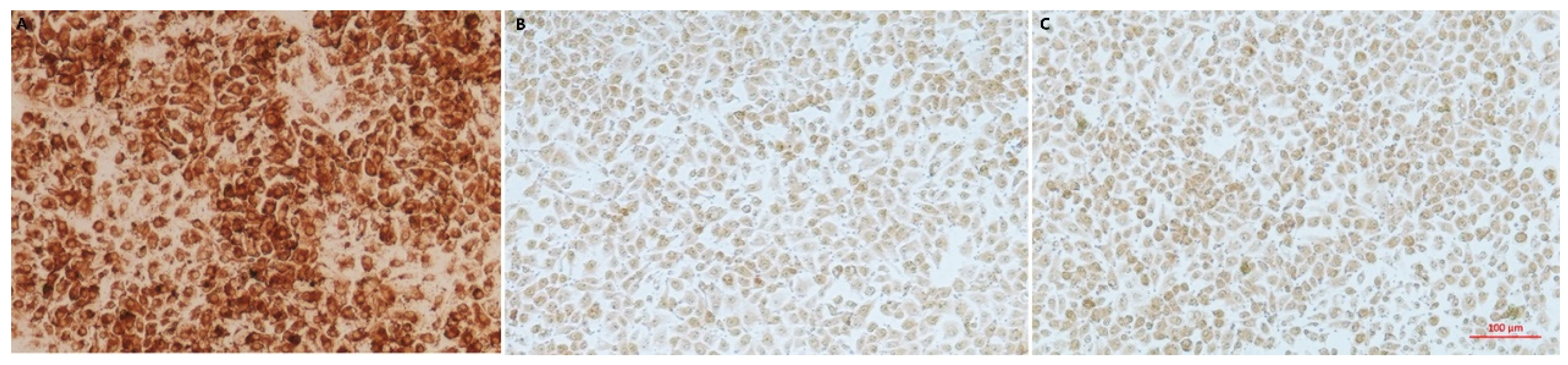
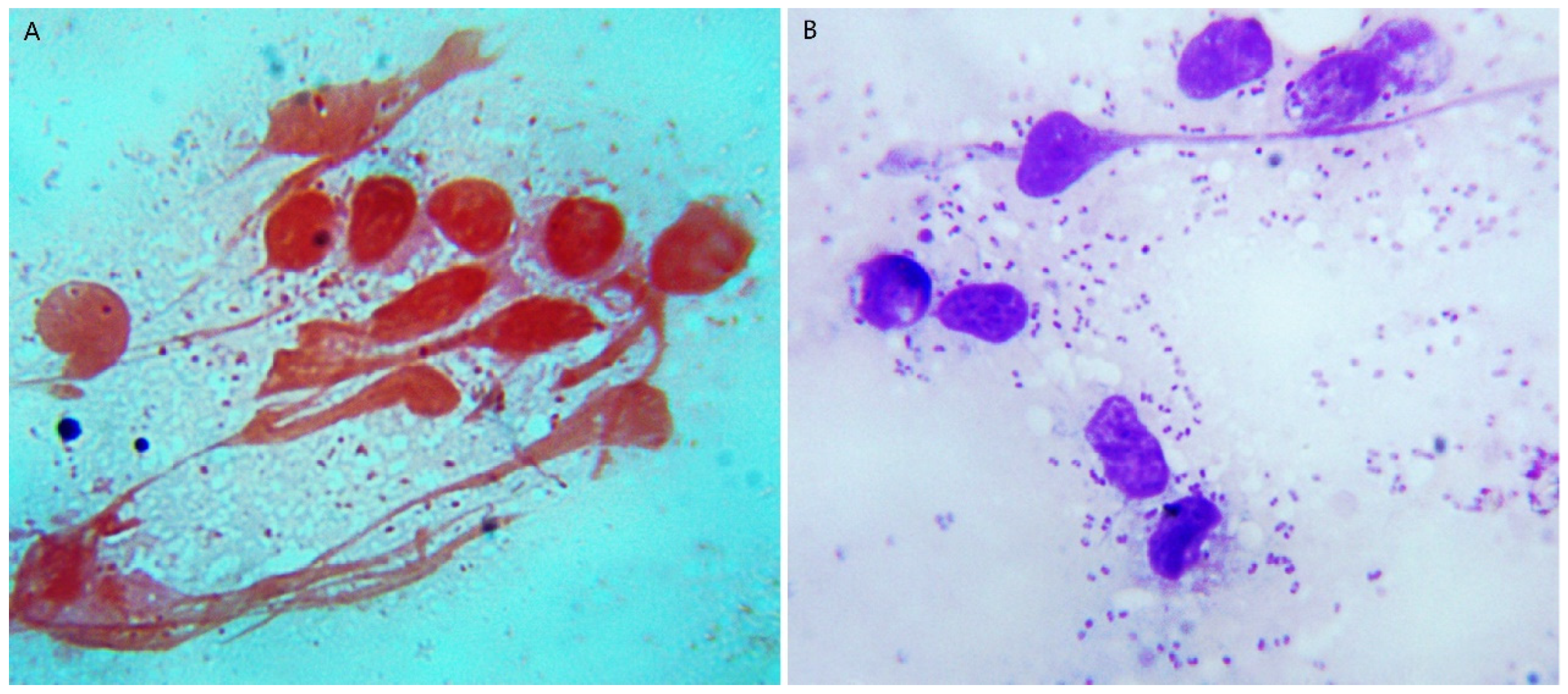
3.2. The PCV2 Strain Was Isolated from the Tissue
3.3. Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Tree of the PCV2 Isolate
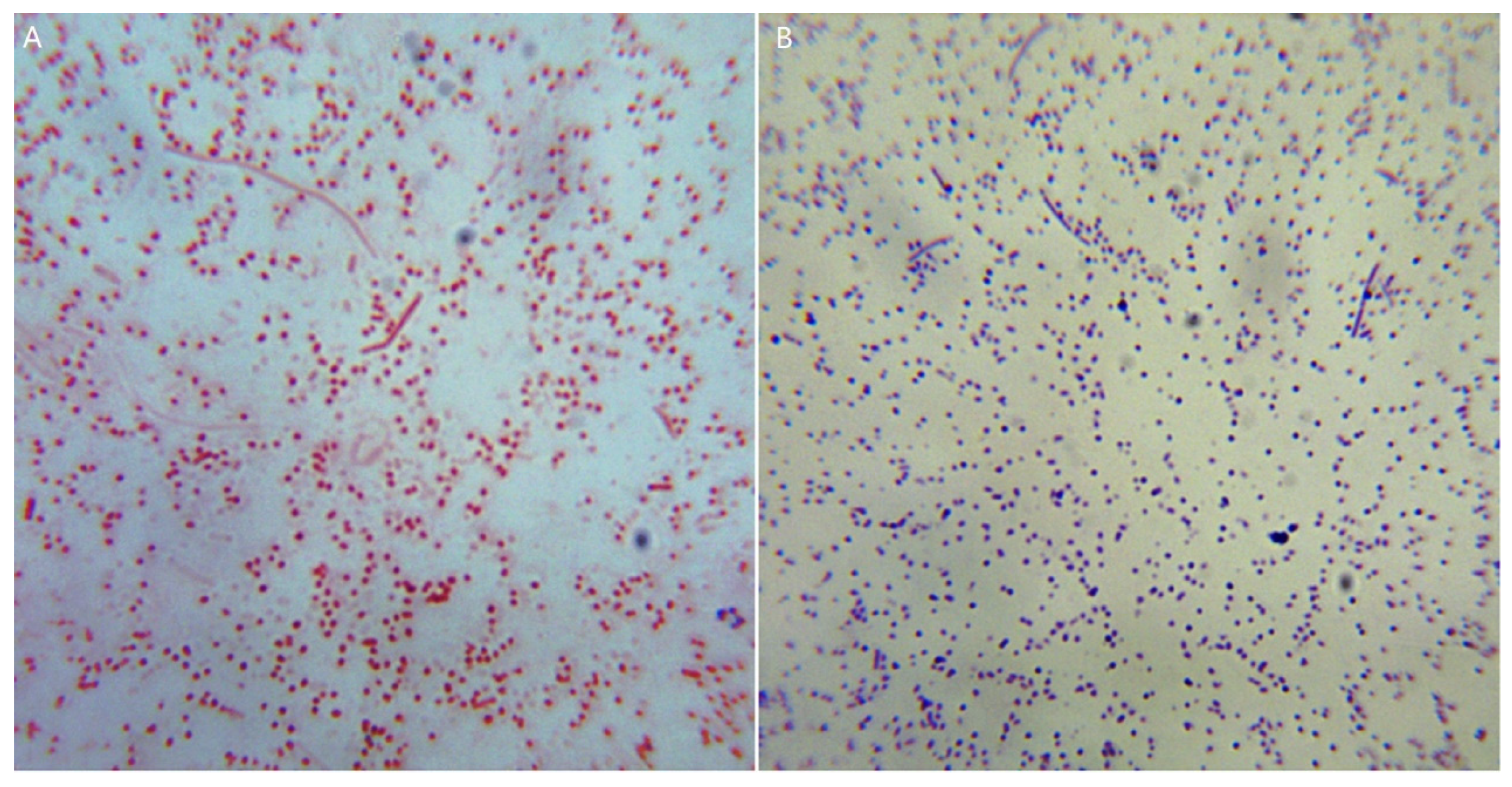
3.4. Characteristics of Bacterial Culture and Morphology
3.5. Biochemical Characteristics of Bacteria
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Isolated Bacteria Based on 16S rDNA Sequences
3.7. Species and Capsular Serotype of the Isolated Bacteria
3.8. Pathogenicity of the Isolated Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosario, K.; Breitbart, M.; Harrach, B.; Segales, J.; Delwart, E.; Biagini, P.; Varsani, A. Revisiting the taxonomy of the family Circoviridae: Establishment of the genus Cyclovirus and removal of the genus Gyrovirus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekarainen, T.; Segales, J. Porcine circovirus 2 immunology and viral evolution. Porcine Health Manag. 2015, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, C. A review of porcine circovirus 2-associated syndromes and diseases. Vet. J. 2005, 169, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Opriessnig, T.; Langohr, I. Current state of knowledge on porcine circovirus type 2-associated lesions. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Opriessnig, T.; Halbur, P.G. Concurrent infections are important for expression of porcine circovirus associated disease. Virus Res. 2012, 164, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Ren, L. Co-Infection of Swine with Porcine Circovirus Type 2 and Other Swine Viruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, C.; Charleston, M.A.; Duffy, S.; Shapiro, B.; Holmes, E.C. Insights into the evolutionary history of an emerging livestock pathogen: Porcine circovirus 2. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12813–12821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franzo, G.; Segales, J. Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV-2) genotype update and proposal of a new genotyping methodology. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208585. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; Hao, F.; Xu, L.; Guo, K. Genetic Diversity and Prevalence of Porcine Circovirus Type 2 in China During 2000–2019. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 788172. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, F.; Mi, S.; Luo, Q.; Guo, H.; Tu, C.; Zhu, G.; Gong, W. Retrospective study of porcine circovirus type 2 infection reveals a novel genotype PCV2f. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Wahaab, A.; Shi, K.; Mustafa, B.E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, K.; et al. Molecular Epidemic Characteristics and Genetic Evolution of Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (PCV2) in Swine Herds of Shanghai, China. Viruses 2022, 14, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, C. Porcine respiratory disease complex: Interaction of vaccination and porcine circovirus type 2, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Vet. J. 2016, 212, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saade, G.; Deblanc, C.; Bougon, J.; Marois-Crehan, C.; Fablet, C.; Auray, G.; Belloc, C.; Leblanc-Maridor, M.; Gagnon, C.A.; Zhu, J.; et al. Coinfections and their molecular consequences in the porcine respiratory tract. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Yang, B.; Yuan, X.; Shen, C.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.; Zhang, T.; Cui, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Advanced Research in Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Co-infection With Other Pathogens in Swine. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 699561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.R.; Segura, M.; Segales, J.; Gottschalk, M. Review of the speculative role of co-infections in Streptococcus suis-associated diseases in pigs. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.K.; Goyal, S.M.; Joo, H.S. Retrospective analysis of etiologic agents associated with respiratory diseases in pigs. Can. Vet. J. 2003, 44, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, S.C.; Hwang, E.K.; Park, B.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.H. Epidemiological characteristics of pulmonary pneumocystosis and concurrent infections in pigs in Jeju Island, Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 12, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vangroenweghe, F.; Thas, O. Seasonal Variation in Prevalence of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Other Respiratory Pathogens in Peri-Weaned, Post-Weaned, and Fattening Pigs with Clinical Signs of Respiratory Diseases in Belgian and Dutch Pig Herds, Using a Tracheobronchial Swab Sampling Technique, and Their Associations with Local Weather Conditions. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turni, C.; Meers, J.; Parke, K.; Singh, R.; Yee, S.; Templeton, J.; Mone, N.K.; Blackall, P.J.; Barnes, T.S. Pathogens associated with pleuritic pig lungs at an abattoir in Queensland Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2021, 99, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeris-Chacin, R.; Sponheim, A.; Fano, E.; Isaacson, R.; Singer, R.S.; Nerem, J.; Leite, F.L.; Pieters, M. Relationships among Fecal, Air, Oral, and Tracheal Microbial Communities in Pigs in a Respiratory Infection Disease Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Miller, E.; Aguayo, J.M.; Figueroa, C.F.; Nezworski, J.; Studniski, M.; Wileman, B.; Johnson, T. Genomic diversity and molecular epidemiology of Pasteurella multocida. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xi, X.; Xue, Q.; Long, T.; Xue, Y. Occurrence of Pasteurella multocida among pigs with respiratory disease in China between 2011 and 2015. Ir. Vet. J. 2017, 70, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yuan, W.; Guo, H.; Ma, Z.; Song, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Prevalence and genetic variation of porcine circovirus type 2 in Hebei, China from 2004 to 2014. Gene 2016, 586, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, O.; Ohene-Adjei, S.; Buchanan, C.; Joseph, T.; King, R.; Erickson, A.; Detmer, S.; Ambagala, A. Multiplex PCR and Microarray for Detection of Swine Respiratory Pathogens. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, C.; Mahe, D.; Blanchard, P.; Le Dimna, M.; Madec, F.; Jestin, A.; Albina, E. Identification of an immunorelevant ORF2 epitope from porcine circovirus type 2 as a serological marker for experimental and natural infection. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, R.; Sun, T.; Lu, J.; Song, Q. Isolation and characteristics of multi-drug resistant Streptococcus porcinus from the vaginal secretions of sow with endometritis. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, B.; Rajan, L.A.; Vinithkumar, N.V.; Kirubagaran, R. Novel marine actinobacteria from emerald Andaman & Nicobar Islands: A prospective source for industrial and pharmaceutical byproducts. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, K.M.; Boyce, J.D.; Chung, J.Y.; Frost, A.J.; Adler, B. Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap Loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaan, S.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Asadi Karam, M.R.; Ehsani, P.; Sardari, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Abolhassani, M.; Nikbakht Brujeni, G. Pasteurella multocida PlpE Protein Polytope as a Potential Subunit Vaccine Candidate. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 870–874. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ma, H.; He, J. Prevalence of porcine respiratory pathogens in slaughterhouses in Shanxi Province, China. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tian, R.B.; Hou, C.Y.; Li, X.S.; Zheng, L.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Chen, H.Y. Prevalence and genetic analysis of porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) and type 3 (PCV3) between 2018 and 2020 in central China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 94, 105016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissenbacher-Lang, C.; Kureljusic, B.; Nedorost, N.; Matula, B.; Schiessl, W.; Stixenberger, D.; Weissenbock, H. Retrospective Analysis of Bacterial and Viral Co-Infections in Pneumocystis spp. Positive Lung Samples of Austrian Pigs with Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dinh, P.X.; Nguyen, M.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tran, V.H.; Tran, Q.D.; Dang, K.H.; Vo, D.T.; Le, H.T.; Nguyen, N.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. Porcine circovirus genotypes and their copathogens in pigs with respiratory disease in southern provinces of Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, G.; Yoo, H.; Kim, Y.; Yang, K.; Lee, C. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of porcine circovirus type 2 on Jeju Island, South Korea, 2019-2020: Evidence of a novel intergenotypic recombinant. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Yuan, G.F.; Chen, S.J.; Dai, F.; Hou, L.S.; Fan, J.H.; Zuo, Y.Z. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) infection in Hebei Province from 2016 to 2019: A retrospective study. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.L.; Nie, L.B.; Wang, Q.; Ge, G.Y.; Li, D.L.; Ma, B.Y.; Sheng, C.Y.; Su, N.; Zong, Y.; et al. Prevalence of porcine circovirus 2 throughout China in 2015-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, I.E.; Carrasco, C.P.; Guzylack-Piriou, L.; Herrmann, B.; McNeilly, F.; Allan, G.M.; Summerfield, A.; McCullough, K.C. Subset-dependent modulation of dendritic cell activity by circovirus type 2. Immunology 2005, 115, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doster, A.R.; Subramaniam, S.; Yhee, J.Y.; Kwon, B.J.; Yu, C.H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Osorio, F.A.; Sur, J.H. Distribution and characterization of IL-10-secreting cells in lymphoid tissues of PCV2-infected pigs. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 11, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Park, I.B.; Chun, T. Open reading frame 5 protein of porcine circovirus type 2 induces RNF128 (GRAIL) which inhibits mRNA transcription of interferon-beta in porcine epithelial cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 140, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.G.; Huang, K.; Ma, D.; Du, Q.; Tong, D.; Huang, Y. Porcine circovirus type 2 infection inhibits the activation of type I interferon signaling via capsid protein and host gC1qR. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 266, 109354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.L.; Tong, D.; Huang, Y. Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Suppresses IL-12p40 Induction via Capsid/gC1qR-Mediated MicroRNAs and Signalings. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, Y.; Oh, C.; Lee, K.; Cho, K.H. Survey of porcine respiratory disease complex-associated pathogens among commercial pig farms in Korea via oral fluid method. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.S.; Pors, S.E.; Jensen, H.E.; Bille-Hansen, V.; Bisgaard, M.; Flachs, E.M.; Nielsen, O.L. An investigation of the pathology and pathogens associated with porcine respiratory disease complex in Denmark. J. Comp. Pathol. 2010, 143, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Khac, H.; Trinh, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.G.; Nguyen, X.T.; Nguyen, T.T. Prevalence of virulence factor, antibiotic resistance, and serotype genes of Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from pigs in Vietnam. Vet. World 2020, 13, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.B.; Bora, D.P.; Das, S.K.; Sharma, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Hazarika, R.A. Virulence gene profiling of porcine Pasteurella multocida isolates of Assam. Vet. World 2018, 11, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Zhou, Z.; Sergeant, M.J.; Achtman, M. A genomic overview of the population structure of Salmonella. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennart, M.; Guglielmini, J.; Bridel, S.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Jolley, K.A.; Criscuolo, A.; Brisse, S. A Dual Barcoding Approach to Bacterial Strain Nomenclature: Genomic Taxonomy of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
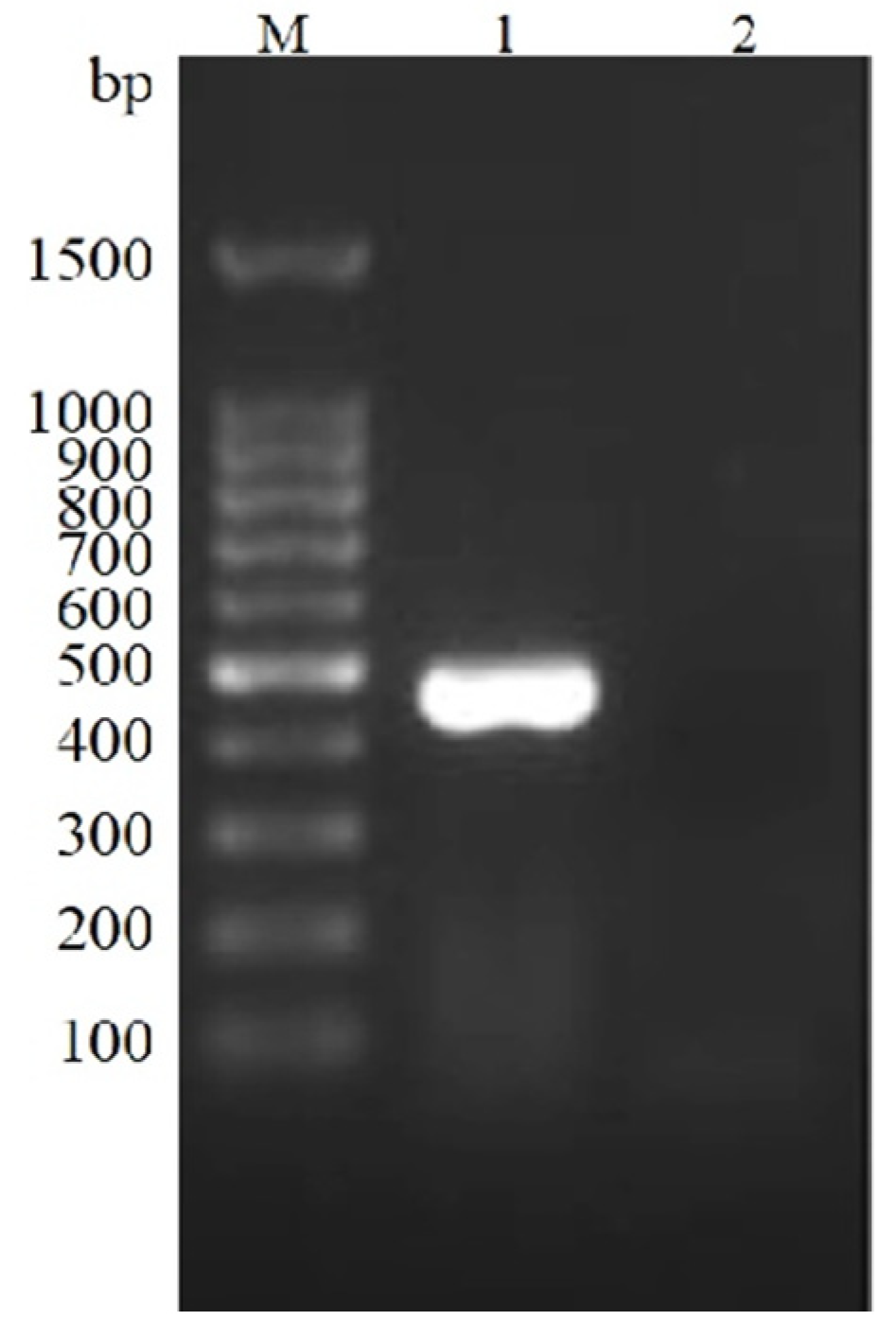


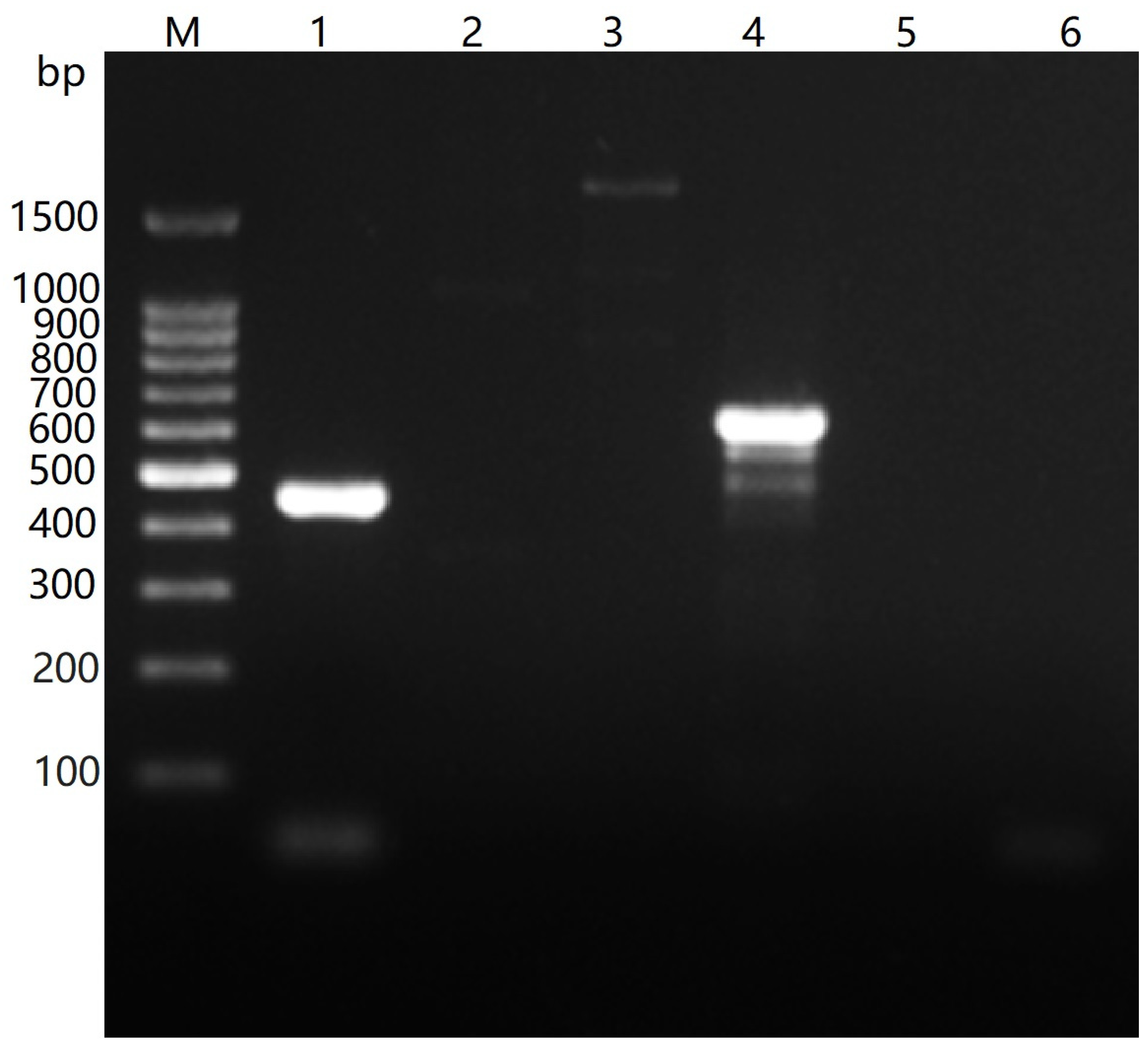
| Virus/Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | Ta (°C) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCV2/cap | PCV2_cap_U PCV2_cap_L | ACGGATATTGTAGTCCTGGT CAAGGCTACCACAGTCAGAA | 57 | 472 | This study |
| PCV2/genome | PCV2_U | GCTGGCTGAACTTTTGAAAGT | 48 | 1767 | Li et al. (2016) [23] |
| PCV2_L | AAATTTCTGACAAACGTTACA | ||||
| PCV3/cap | PCV3_cap_U PCV3_cap_L | ACATGCGAGGGCGTTTAC CACTTCTGGCGGGAACTA | 56 | 307 | This study |
| PRRSV/orf7 | orf7_U orf7_L | ATGGCCAGCCAGTCAATCAG ATGCTGAGGGTGACGTTGTG | 56 | 327 | This study |
| PRV/gE | gE_U gE_L | ACGGCGACCTCGACGGCGAC CCCGAGGCGTCGTGCAGCGT | 67 | 418 | This study |
| M.hyopneumoniae /Intergenic space | M.hyopnU | CGGTTTTATAAGAATTAGTTGCTCC | 58 | 421 | Lung et al. (2017) [24] |
| M.hyopnL | TTGGCAAGCCGCCGTCATT |
| Strain | GenBank ID | Geographic Origin | Submitted Time | Genome Size (bp) | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LG | HM038034 | Heilongjiang, China | 2010 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| JXPX-1-1 | KJ437192 | Hunan, China | 2014 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| BJ0602 | EF524540 | Beijing, China | 2007 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| SH0901 | KF850458 | Shanghai, China | 2013 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| n32na | DQ629113 | USA | 2006 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| DTC | DQ104423 | Jiangsu, China | 2005 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| BF | AF381175 | Beijing, China | 2001 | 1768 | PCV2a |
| HSH1 | DQ910866 | Hebei, China | 2006 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| K43C | DQ629118 | USA | 2006 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| Bd3-2007 | KM624031 | Hebei, China | 2014 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| XZBK | KF926650 | Henan, China | 2013 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| HB0802 | FJ608549 | Hebei, China | 2008 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| Fh19 | AY322003 | France | 2003 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| TY4 | HQ202967 | Taiwan, China | 2010 | 1767 | PCV2b |
| DK1980PMWSfree | EU148503 | Denmark | 2007 | 1767 | PCV2c |
| DK1990PMWSfree | EU148505 | Denmark | 2007 | 1767 | PCV2c |
| TJ06 | EF524539 | Tianjin, China | 2007 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| TJ | AY181946 | Tianjin, China | 2002 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| HX | KC860786 | Heilongjiang, China | 2013 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| JSTZ | JQ413808 | Jiangsu, China | 2012 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| HbTs2011 | KM624037 | Hebei, China | 2014 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| BDMC1/2016 | KY613030 | Hebei, China | 2017 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| BDAG2015 | KY569382 | Hebei, China | 2017 | 1767 | PCV2d |
| Strain | GenBank ID | Host | Organism | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | FJ463827 | chicken | P. multocida | South Korea |
| - | E05329 | - | P. multocida | Japan |
| 4074 | FJ405341 | pig | P. multocida | South Korea |
| F | CP013291 | bovine | P. multocida | China |
| 4075 | FJ405342 | goat | P. multocida | South Korea |
| Tibet-Pm1 | CP072655 | yak | P. multocida | China |
| PM-1 | CP066223 | yak | P. multocida | China |
| ATCC 43325 | NR_118749 | - | P. multocida | USA |
| LSBS1 | MN080875 | Moschus berezovskii | P. multocida | China |
| BD1643 | LC619668 | Oryctolagus cuniculus | P. multocida | Japan |
| PH40 | U57070 | bovine | P. haemolytica | USA |
| CCUG 28148 | AF224287 | - | P. haemolytica | USA |
| PH704 | U57072 | bovine | P. haemolytica | USA |
| PH2, PH8 | U57066 | sheep, bovine | P. haemolytica | USA |
| xws8 | KT588712 | pig | Glaeserellaparasuis | China |
| h1-6 | KT588715 | pig | Glaeserella parasuis | China |
| 5651 | JSVY01000046 | pig | A. pleuropneumoniae | Brazil |
| 597 | JSVX01000052 | pig | A. pleuropneumoniae | Brazil |
| Serotype | Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | KMT1 | P. ma_U P. m_L | TGCCAAAATCGCAGTCAG TTGCCATCATTGTCAGTG | 460 |
| A | hyaD-hyaC | CAPA_U CAPA_L | TGCCAAAATCGCAGTCAG TTGCCATCATTGTCAGTG | 1044 |
| B | bcbD | CAPB_U CAPB_L | CATTTATCCAAGCTCCACC GCCCGAGAGTTTCAATCC | 760 |
| D | dcbF | CAPD_U CAPD_L | TTACAAAAGAAAGACTAGGAGCCC CATCTACCCACTCAACCATATCAG | 657 |
| E | ecbJ | CAPE_U CAPE_L | TCCGCAGAAAATTATTGACTC GCTTGCTGCTTGATTTTGTC | 511 |
| F | fcbD | CAPF_U CAPF_L | AATCGGAGAACGCAGAAATCAG TTCCGCCGTCAATTACTCTG | 851 |
| Item | Reaction | Criteria of P. multocida a |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose | − b | + |
| Lactose | − | (+) d |
| Maltose | − | (−) |
| Sucrose | + c | + |
| Mannitol | + | (+) |
| Dulcitol | − | / e |
| Xylose | + | / |
| Sorbitol | + | / |
| Adonitol | − | / |
| Raffinose | − | / |
| Urease | − | − |
| Catalase | + | + |
| Indole | + | + |
| Hydrogen sulfide | + | + |
| Indole | + | + |
| Methyl red (MR) | − | / |
| Voges–Proskaurer (VP) | − | / |
| Citrate | − | / |
| Phenylalanine decarboxylase | − | / |
| Ornithine decarboxylase | − | (+) |
| Lysine decarboxylase | − | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, S.; Xu, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, K.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Song, Q. Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2a and Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype D in Growing Pigs Suffering from Respiratory Disease. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100528
Du S, Xu F, Lin Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Su K, Li T, Li H, Song Q. Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2a and Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype D in Growing Pigs Suffering from Respiratory Disease. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(10):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100528
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Shuailong, Fan Xu, Yidan Lin, Yawen Wang, Yanan Zhang, Kai Su, Tanqing Li, Huanrong Li, and Qinye Song. 2022. "Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2a and Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype D in Growing Pigs Suffering from Respiratory Disease" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 10: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100528
APA StyleDu, S., Xu, F., Lin, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Su, K., Li, T., Li, H., & Song, Q. (2022). Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2a and Pasteurella multocida Capsular Serotype D in Growing Pigs Suffering from Respiratory Disease. Veterinary Sciences, 9(10), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100528






