Antimicrobial Resistance, FlaA Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Campylobacter Isolates from Broiler Chicken Flocks in Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. FlaA Sequencing
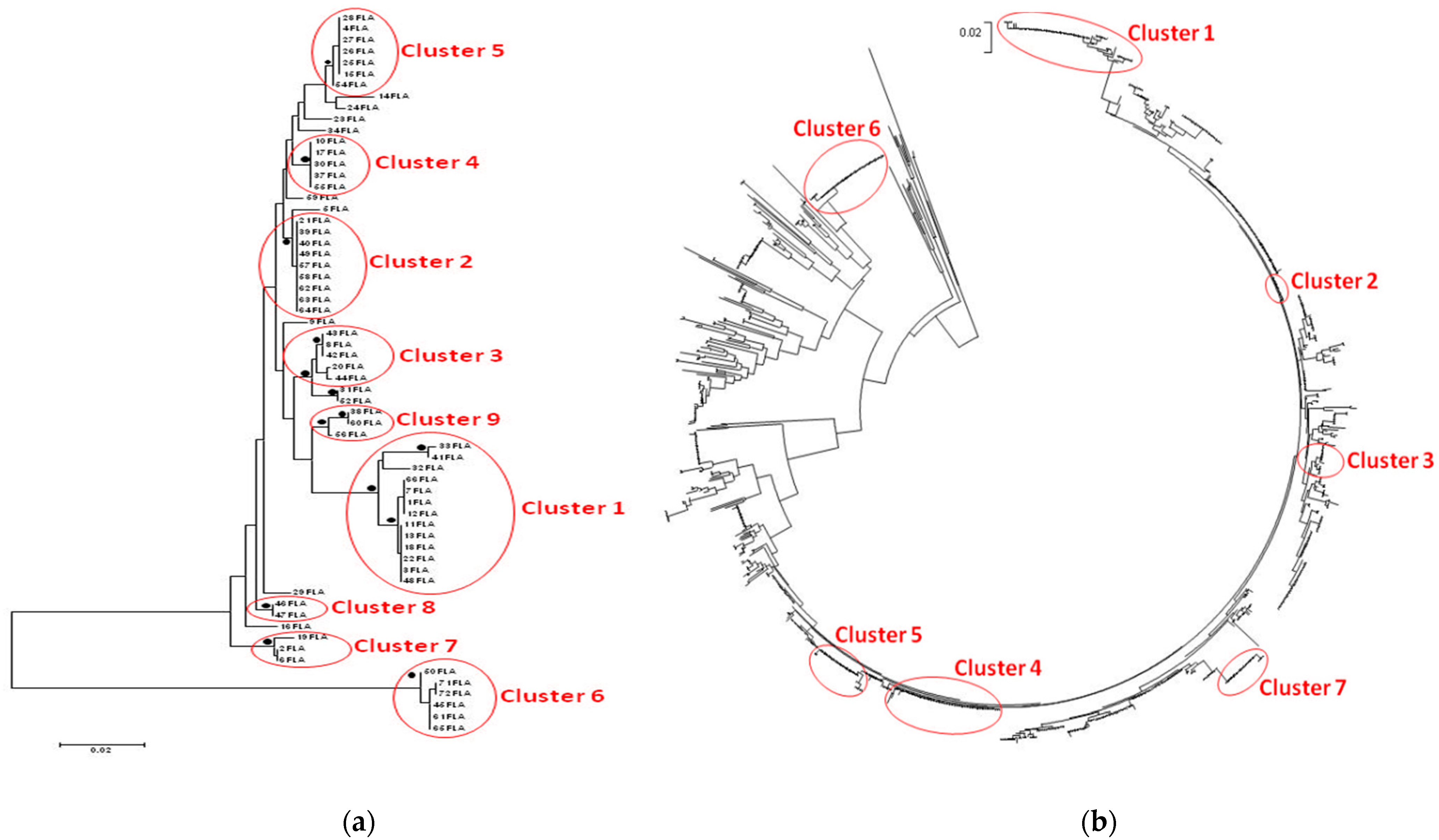
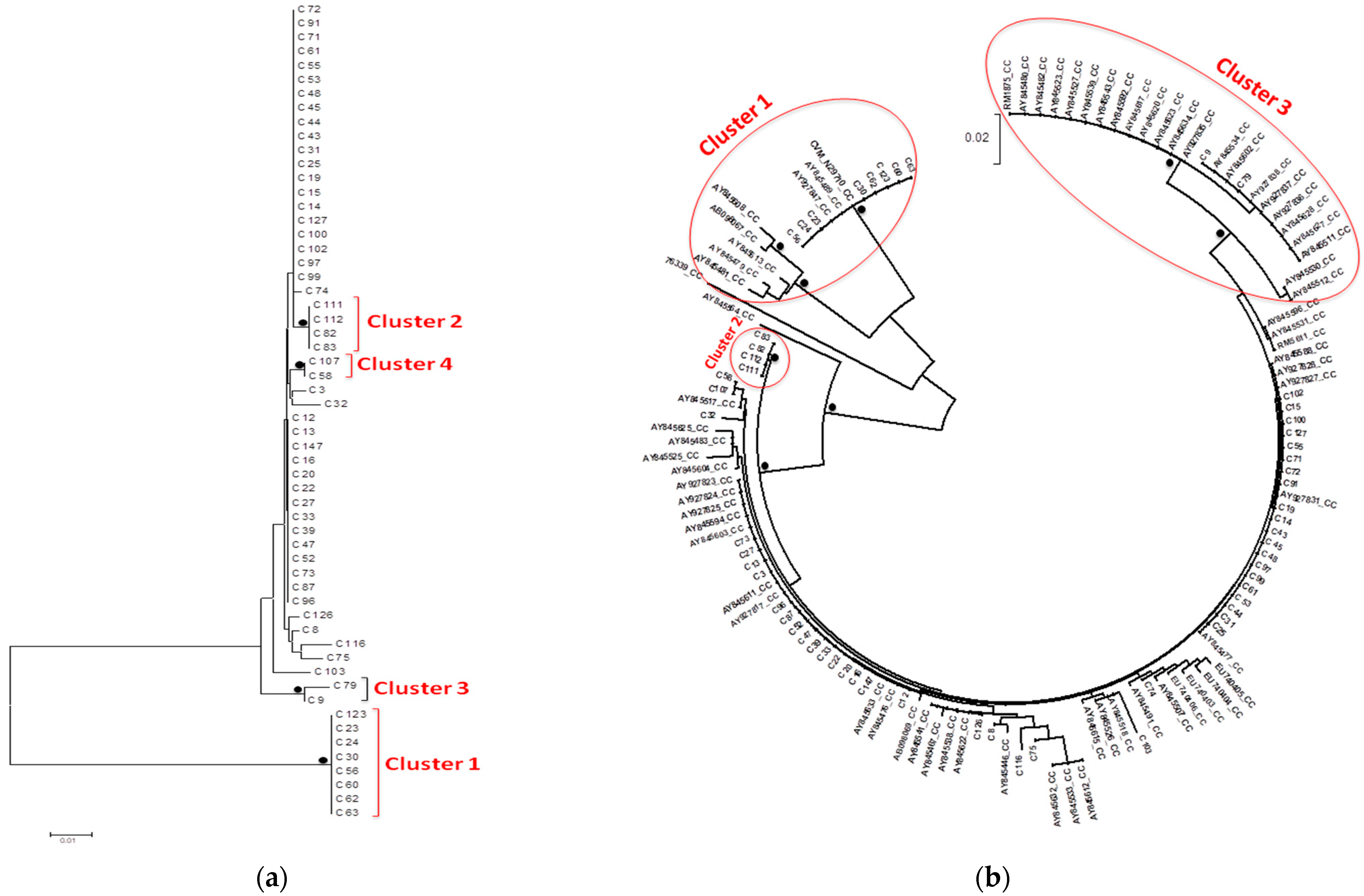
2.5. Phylogenetic Trees
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Resistance
3.2. FlaA Sequencing
3.3. Phylogenetic Trees
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natsos, G.; Koutoulis, K.C.; Sossidou, E.; Chemaly, M.; Mouttotou, N.K. Campylobacter spp. infection in humans and poultry. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2016, 67, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rossler, E.; Olivero, C.; Soto, L.P.; Frizzo, L.S.; Zimmermann, J.; Rosmini, M.R.; Sequeira, G.J.; Signorini, M.L.; Zbrun, M.V. Prevalence, genotypic diversity and detection of virulence genes in thermotolerant Campylobacter at different stages of the poultry meat supply chain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 326, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Kassem, I.I.; Shen, Z.; Lin, J.; Rajashekara, G.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter in poultry: Ecology and potential interventions. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castano-Rodriguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global epidemiology of Campylobacter infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D.; Newell, D.G. Campylobacter in poultry: Filling an ecological niche. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, D.G.; Fearnley, C. Sources of Campylobacter colonization in broiler chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeni, J.L.; Doyle, M.P. Reduction of Campylobacter jejuni colonization of chicks by cecum-colonizing bacteria producing anti-C. jejuni metabolites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q.; Meitzler, J.C.; Harr, B.S.; Morishita, T.Y.; Mohan, R. Prevalence, antigenic specificity, and bactericidal activity of poultry anti-Campylobacter maternal antibodies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3951–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreeve, J.E.; Toszeghy, M.; Pattison, M.; Newell, D.G. Sequential spread of Campylobacter infection in a multipen broiler house. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific Opinion on Quantification of the risk posed by broiler meat to human campylobacteriosis in the EU. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a Foodborne Pathogen: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hue, O.; Le Bouquin, S.; Laisney, M.J.; Allain, V.; Lalande, F.; Petetin, I.; Rouxel, S.; Quesne, S.; Gloaguen, P.Y.; Picherot, M.; et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for Campylobacter spp. contamination of broiler chicken carcasses at the slaughterhouse. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Campylobacter in broiler batches and of Campylobacter and Salmonella on broiler carcasses in the EU, 2008, Part A: Campylobacter and Salmonella prevalence estimates. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, I.; Bersimis, S.; Ioannidis, A.; Nicolaou, C.; Mitroussia-Ziouva, A.; Legakis, N.J.; Chatzipanagiotou, S. Identification and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter species isolated from animal sources. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsos, G.; Mouttotou, N.K.; Magiorkinis, E.; Ioannidis, A.; Rodi-Burriel, A.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Koutoulis, K.C. Prevalence of and risk factors for Campylobacter spp. colonization of broiler chicken flocks in Greece. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Campylobacter in broiler batches and of Campylobacter and Salmonella on broiler carcasses, in the EU, 2008; Part B: Analysis of factors associated with Campylobacter colonisation of broiler batches and with Campylobacter contamination of broiler carcasses; and investigation of the culture method diagnostic characteristics used to analyse broiler carcass samples. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. The Community Summary Report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents, antimicrobial resistance and foodborne outbreaks in the European Union in 2005. EFSA J. 2006, 94, 288. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 17, 276. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Iovine, N.M. Resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni. Virulence 2013, 4, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feye, K.M.; Shi, Z.; Pavlidis, H.O.; Kogut, M.; Ashworth, A.J.; Ricke, S.C. A historical review on antibiotic resistance of foodborne Campylobacter. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engberg, J.; Neimann, J.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aerestrup, F.M.; Fussing, V. Quinolone-resistant Campylobacter infections: Risk factors and clinical consequences. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Sahin, O.; Grover, M.; Zhang, Q. New and alternative strategies for the prevention, control, and treatment of antibiotic-resistant Campylobacter. Transl. Res. 2020, 223, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.E.; Barton, M.D.; Blair, I.S.; Corcoran, D.; Dooley, J.S.; Fanning, S.; Kempf, I.; Lastovica, A.J.; Lowery, C.J.; Matsuda, M.; et al. The epidemiology of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 6th Revision; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Colles, F.; Richardson, J.; Cody, A.J.; Elson, R.; Lawson, A.; Brick, G.; Meldrum, R.; Little, C.L.; Owen, R.J.; et al. Host association of Campylobacter genotypes transcends geographic variation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5269–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidou, V.; Ioannidis, A.; Magiorkinis, E.; Bagos, P.; Nicolaou, C.; Legakis, N.; Chatzipanagiotou, S. Multilocus sequence typing (and phylogenetic analysis) of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli strains isolated from clinical cases in Greece. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, A.; Nicolaou, C.; Legakis, N.J.; Ioannidou, V.; Papavasileiou, E.; Voyatzi, A.; Chatzipanagiotou, S. Genotyping of human Campylobacter jejuni isolates in Greece by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2006, 10, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, T.M.; Newell, D.G. Genotyping of Campylobacter spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsos, G.; Mouttotou, N.K.; Ahmad, S.; Kamran, Z.; Ioannidis, A.; Koutoulis, K.C. The genus Campylobacter: Detection and isolation methods, species identification & typing techniques. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2019, 70, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Korczak, B.M.; Zurfluh, M.; Emler, S.; Kuhn-Oertli, J.; Kuhnert, P. Multiplex strategy for multilocus sequence typing, fla typing, and genetic determination of antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates collected in Switzerland. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp. Part 1: Detection Method; [ISO 10272-1:2006]; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Meinersmann, R.J.; Helsel, L.O.; Fields, P.I.; Hiett, K.L. Discrimination of Campylobacter jejuni isolates by fla gene sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2810–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraqueza, M.J.; Martins, A.; Borges, A.C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Fernandes, M.J.; Vaz, Y.; Bessa, R.J.; Barreto, A.S. Antimicrobial resistance among Campylobacter spp. strains isolated from different poultry production systems at slaughterhouse level. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2014. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproston, E.L.; Wimalarathna, H.M.L.; Sheppard, S.K. Trends in fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thanner, S.; Drissner, D.; Walsh, F. Antimicrobial resistance in agriculture. mBio 2016, 7, e02227-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, A.O.; Isokpehi, R.D.; Thomas, B.N.; Amisu, K.O.; Obi, C.L. Human campylobacteriosis in developing countries. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, D.J.; Alm, R.A.; Burr, D.H.; Hu, L.; Kopecko, D.J.; Ewing, C.P.; Trust, T.J.; Guerry, P. Involvement of a plasmid in virulence of Campylobacter jejuni 81-176. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4384–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Kania, I.; Osek, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from poultry carcasses in Poland. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efimochkina, N.R.; Stetsenko, V.V.; Sheveleva, S.A. Formation of the resistance of Campylobacter jejuni to macrolide antibiotics. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 169, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.; Kaya, K.N.; Hancock, D.D.; Call, D.R.; Park, Y.H.; Besser, T.E. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. from cattle farms in Washington State. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlieghe, E.R.; Jacobs, J.A.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Koole, O.; Van Gompel, A. Trends of norfloxacin and erythromycin resistance of Campylobacter jejuni/Campylobacter coli isolates recovered from international travelers, 1994 to 2006. J. Travel Med. 2008, 15, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladely, S.R.; Harrison, M.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Berrang, M.E.; Englen, M.D.; Meinersmann, R.J. Development of macrolide-resistant Campylobacter in broilers administered subtherapeutic or therapeutic concentrations of tylosin. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yan, M.; Sahin, O.; Pereira, S.; Chang, Y.J.; Zhang, Q. Effect of macrolide usage on emergence of erythromycin-resistant Campylobacter isolates in chickens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Dai, M.; Wang, Y.; Peng, D.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Z. 23S rRNA mutation A2074C conferring high-level macrolide resistance and fitness cost in Campylobacter jejuni. Microb. Drug Resist. 2009, 15, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.E.; Corcoran, D.; Dooley, J.S.; Fanning, S.; Lucey, B.; Matsuda, M.; McDowell, D.A.; Megraud, F.; Millar, B.C.; O’Mahony, R.; et al. Campylobacter. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 351–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibreel, A.; Tracz, D.M.; Nonaka, L.; Ngo, T.M.; Connell, S.R.; Taylor, D.E. Incidence of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter jejuni isolated in Alberta, Canada, from 1999 to 2002, with special reference to tet(O)-mediated tetracycline resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Rivoal, K.; Houard, E.; Rose, V.; Quesne, S.; Mourand, G.; Rouxel, S.; Kempf, I.; Guillier, L.; Gauchard, F.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni from chicken meat sold in French retail outlets. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 203, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Naren, G.W.; Wu, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Dai, L.; Xia, L.N.; Luo, P.J.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.Z. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter isolates in broilers from China. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.S.; Wu, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Jeon, B.; Shen, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.Z. Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter coli isolated from pigs in two provinces of China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 146, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, P.F.; Bodeis-Jones, S.M.; Fritsche, T.R.; Jones, R.N.; Walker, R.D. Broth microdilution susceptibility testing of Campylobacter jejuni and the determination of quality control ranges for fourteen antimicrobial agents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 6136–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Potz, N.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Johnson, A.P.; Henwood, C.J.; Walker, R.A.; Varey, E.; Warner, M.; James, D.; Livermore, D.M. Reliability of routine disc susceptibility testing by the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) method. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gaudreau, C.; Girouard, Y.; Gilbert, H.; Gagnon, J.; Bekal, S. Comparison of disk diffusion and agar dilution methods for erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, and tetracycline susceptibility testing of Campylobacter coli and for tetracycline susceptibility testing of Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4475–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Morishita, T.Y.; El-Tayeb, A.B.; Ison, A.J.; Zhang, Q. Comparison of antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Campylobacter spp. by the agar dilution and the agar disk diffusion methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, K.; Kelly, L.; Madden, R.H.; Moran, L.; Carroll, C.; O’Leary, A.; Moore, J.E.; McNamara, E.; O’Mahony, M.; Fanning, S.; et al. Comparison of disc diffusion and epsilometer (E-test) testing techniques to determine antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter isolates of food and human clinical origin. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 79, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Beek, M.T.; Claas, E.C.; Mevius, D.J.; van Pelt, W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Kuijper, E.J. Inaccuracy of routine susceptibility tests for detection of erythromycin resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lehtopolku, M.; Kotilainen, P.; Puukka, P.; Nakari, U.M.; Siitonen, A.; Eerola, E.; Huovinen, P.; Hakanen, A.J. Inaccuracy of the disk diffusion method compared with the agar dilution method for susceptibility testing of Campylobacter spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. EU Protocol for Harmonised Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance in Human Salmonella and Campylobacter Isolates; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fitch, B.R.; Sachen, K.L.; Wilder, S.R.; Burg, M.A.; Lacher, D.W.; Khalife, W.T.; Whittam, T.S.; Young, V.B. Genetic diversity of Campylobacter sp. isolates from retail chicken products and humans with gastroenteritis in Central Michigan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4221–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinersmann, R.J.; Phillips, R.W.; Hiett, K.L.; Fedorka-Cray, P. Differentiation of Campylobacter populations as demonstrated by flagellin short variable region sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6368–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.G.; Elvers, K.T.; Dopfer, D.; Hansson, I.; Jones, P.; James, S.; Gittins, J.; Stern, N.J.; Davies, R.; Connerton, I.; et al. Biosecurity-based interventions and strategies to reduce Campylobacter spp. on poultry farms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8605–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis-Iversen, J.; Ridley, A.; Morris, V.; Sowa, A.; Harris, J.; Atterbury, R.; Sparks, N.; Allen, V. Persistent environmental reservoirs on farms as risk factors for Campylobacter in commercial poultry. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, N.; McKenna, A.; Richmond, A.; Ricke, S.C.; Callaway, T.; Stratakos, A.C.; Gundogdu, O.; Corcionivoschi, N. A review of the effect of management practices on Campylobacter prevalence in poultry farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battersby, T.; Whyte, P.; Bolton, D.J. The pattern of Campylobacter contamination on broiler farms; external and internal sources. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, B.; Wedderkopp, A.; Madsen, M. Thermophilic Campylobacter spp. in Danish broiler production: A cross-sectional survey and a retrospective analysis of risk factors for occurrence in broiler flocks. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.E.; Chriel, M.; Norstrom, M.; Hofshagen, M. Effect of climate and farm environment on Campylobacter spp. colonisation in Norwegian broiler flocks. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 107, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, R.; Colles, F.M.; McCarthy, N.D.; Maiden, M.C.; Sheppard, S.K. Campylobacter genotypes from poultry transportation crates indicate a source of contamination and transmission. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antimicrobial Agent | Disk Concentration (μg) | Zone Diameter Breakpoint (mm) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | I | R | ||
| Ciprofloxacin | 5 | ≥24 | 21–23 | ≤20 |
| Erythromycin | 15 | ≥16 | 13–15 | ≤12 |
| Tetracycline | 30 | ≥26 | 23–-25 | ≤22 |
| Nalidixic acid | 30 | ≥19 | 14–18 | ≤13 |
| Gentamicin | 10 | ≥15 | 13–14 | ≤12 |
| Streptomycin | 10 | ≥15 | 12–14 | ≤11 |
| Antimicrobial Agent | Caecal Samples | Neck Skin Samples | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Campylobacter Isolates 2 | % of Resistant Isolates | No. of Campylobacter Isolates 2 | % of Resistant Isolates | |||||
| S | I | R | S | I | R | |||
| Ciprofloxacin | 14 | 91 | 86.7 | 8 | 92 | 92 | ||
| Erythromycin | 97 | 8 | 7.6 | 91 | 3 | 6 | 6 | |
| Tetracycline | 22 | 2 | 81 | 77.1 | 39 | 61 | 61 | |
| Nalidixic acid | 13 | 92 | 87.6 | 9 | 2 | 89 | 89 | |
| Gentamicin | 105 | 0 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| Streptomycin | 92 | 1 | 12 | 11.4 | 93 | 7 | 7 | |
| Antimicrobial Agent | Campylobacter Jejuni | Campylobacter Coli | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Campylobacter Isolates 2 | % of Resistant Isolates | No. of Campylobacter Isolates 2 | % of Resistant Isolates | |||||
| S | I | R | S | I | R | |||
| Ciprofloxacin | 7 | 95 | 93.1 | 15 | 88 | 85.4 | ||
| Erythromycin | 94 | 8 | 7.8 | 94 | 3 | 6 | 5.8 | |
| Tetracycline | 29 | 1 | 72 | 70.6 | 32 | 1 | 70 | 68 |
| Nalidixic acid | 7 | 1 | 94 | 92.2 | 15 | 1 | 87 | 84.5 |
| Gentamicin | 102 | 0 | 103 | 0 | ||||
| Streptomycin | 90 | 1 | 11 | 10.8 | 94 | 1 | 8 | 7.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natsos, G.; Mouttotou, N.K.; Magiorkinis, E.; Ioannidis, A.; Magana, M.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Koutoulis, K.C. Antimicrobial Resistance, FlaA Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Campylobacter Isolates from Broiler Chicken Flocks in Greece. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8050068
Natsos G, Mouttotou NK, Magiorkinis E, Ioannidis A, Magana M, Chatzipanagiotou S, Koutoulis KC. Antimicrobial Resistance, FlaA Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Campylobacter Isolates from Broiler Chicken Flocks in Greece. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(5):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8050068
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatsos, George, Niki K. Mouttotou, Emmanouil Magiorkinis, Anastasios Ioannidis, Maria Magana, Stylianos Chatzipanagiotou, and Konstantinos C. Koutoulis. 2021. "Antimicrobial Resistance, FlaA Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Campylobacter Isolates from Broiler Chicken Flocks in Greece" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 5: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8050068
APA StyleNatsos, G., Mouttotou, N. K., Magiorkinis, E., Ioannidis, A., Magana, M., Chatzipanagiotou, S., & Koutoulis, K. C. (2021). Antimicrobial Resistance, FlaA Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Campylobacter Isolates from Broiler Chicken Flocks in Greece. Veterinary Sciences, 8(5), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8050068








