Recent Advances in Molecular Genetic Tools for Babesia
Abstract
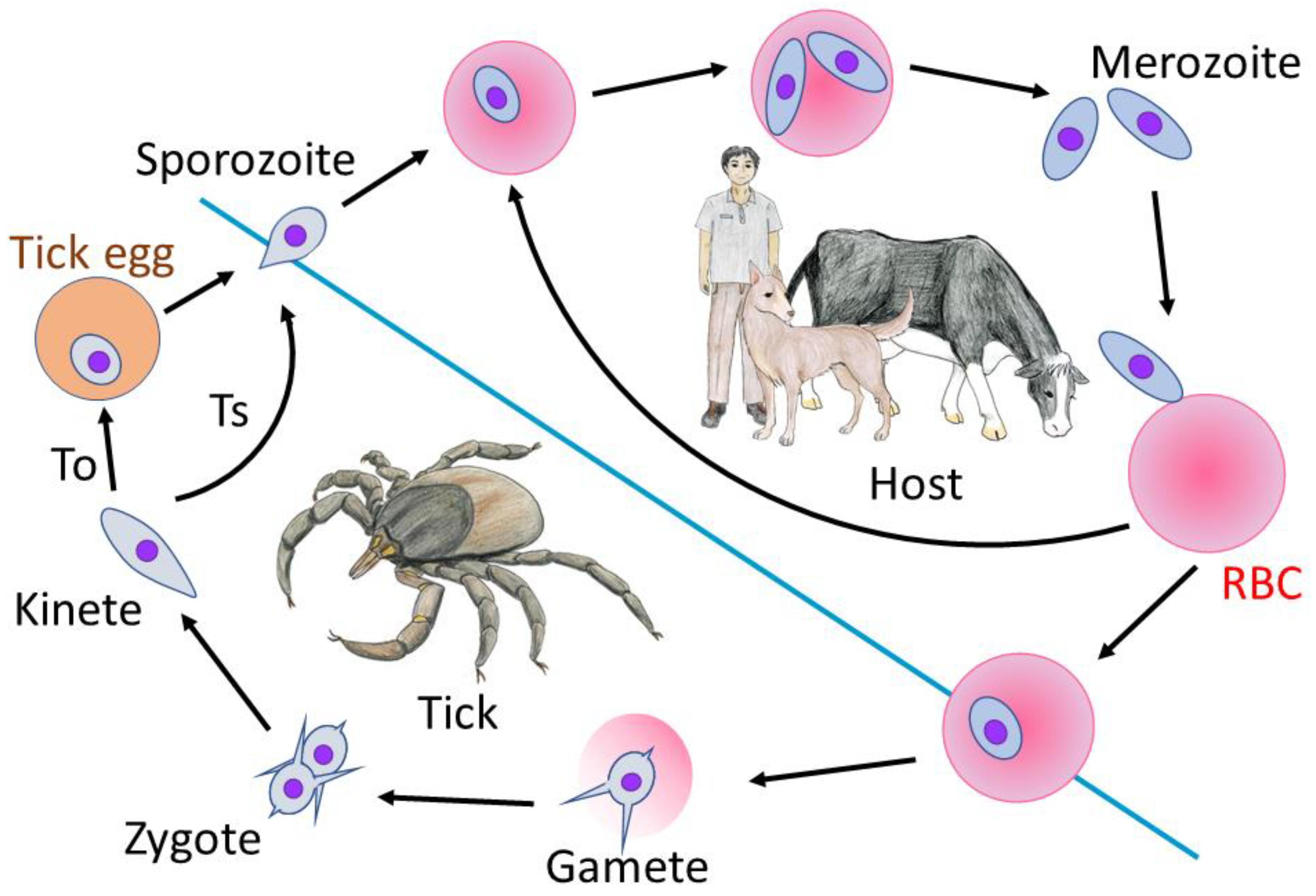
1. Introduction
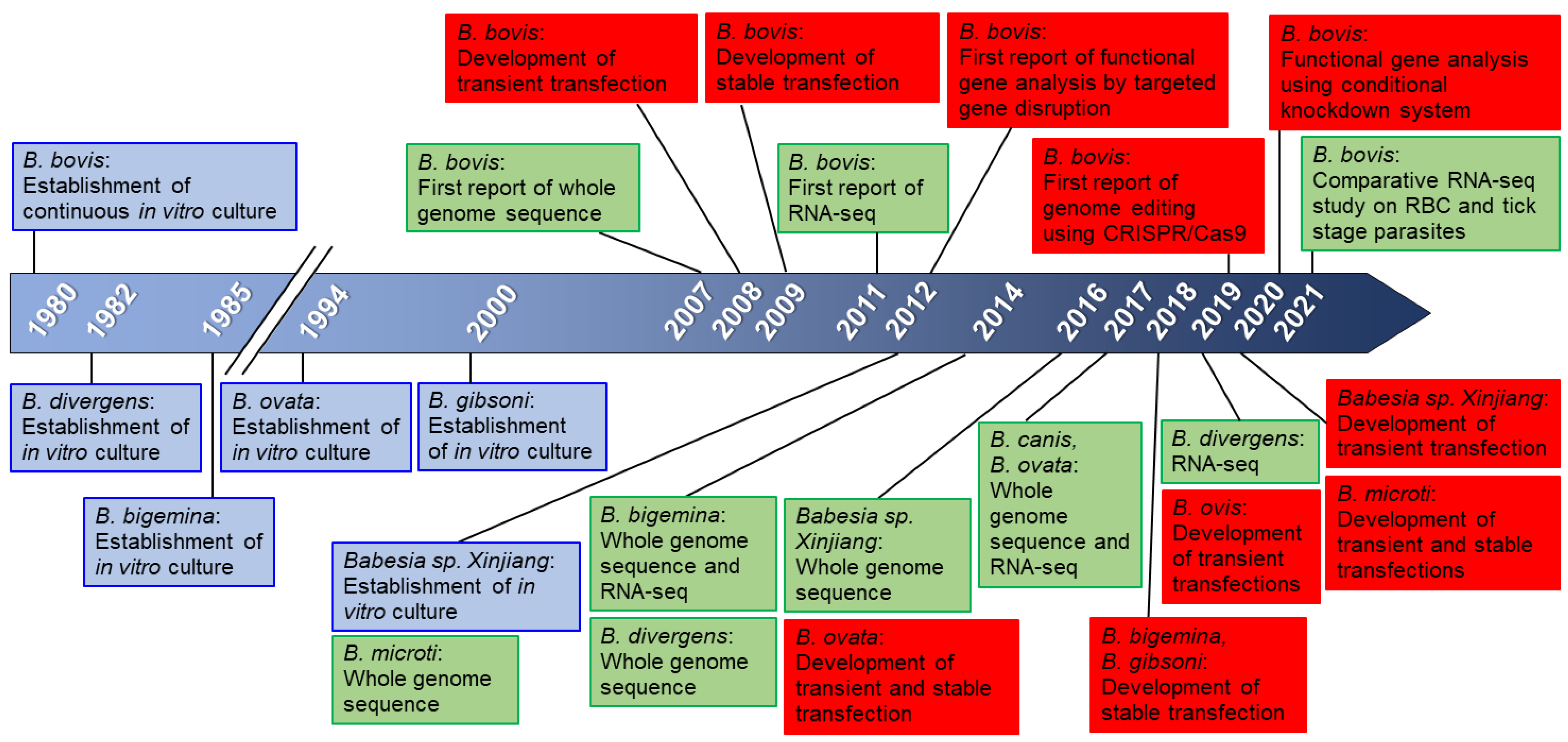
2. Genome and Genetic Tools for Babesia
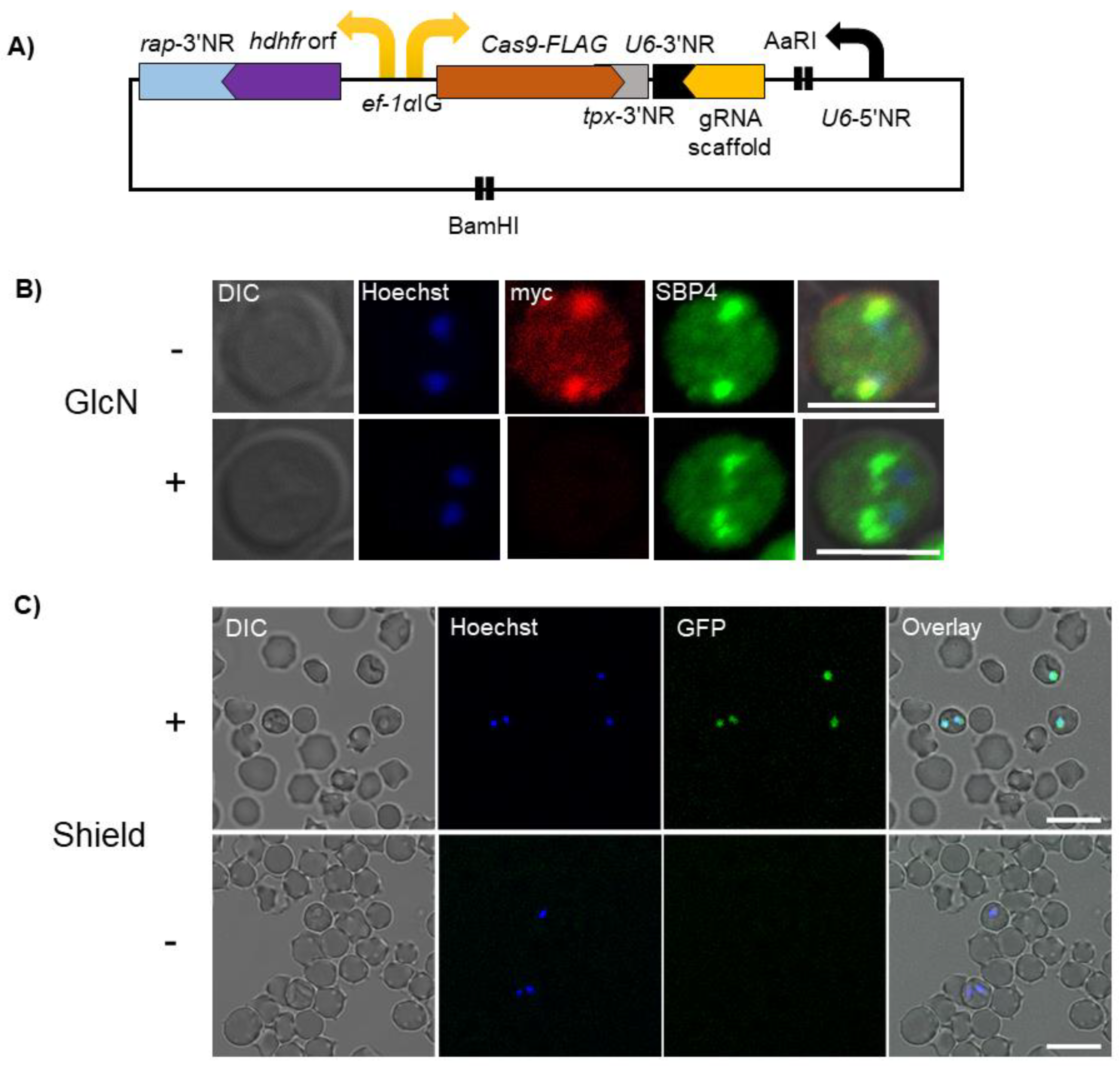
3. Genome Editing Using CRISPR/Cas9
4. Conditional Knockdown Systems
5. In Vitro Culture of Babesia and Transfection
6. Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babes, V. Sur l’he’moglobinurie bacte´rienne du boeuf. CR Acad. Sci. 1888, 107, 692–694. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, M.J.; Aguilar-Delfin, I.; Telford III, S.R.; Krause, P.J.; Persing, D.H. Babesiosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalovecka, M.; Hajdusek, O.; Sojka, D.; Kopacek, P.; Malandrin, L. The Complexity of Piroplasms Life Cycles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalovecka, M.; Sojka, D.; Ascencio, M.; Schnittger, L. Babesia Life Cycle—When Phylogeny Meets Biology. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinasamy, V.; Poole, W.A.; Bastos, R.G.; Suarez, C.E.; Cooke, B.M. Babesiosis Vaccines: Lessons Learned, Challenges Ahead, and Future Glimpses. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Sainz, Á.; Roura, X.; Peña, A.E.; Miró, G. A review of canine babesiosis: The European perspective. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keroack, C.; Elsworth, B.; Duraisingh, M.T. To kill a piroplasm: Genetic technologies to advance drug discovery and target identification in Babesia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 49, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, E.A.; Tagliamonte, M.S.; Xiao, Y.-P.; Quesada, S.; Allred, D.R. Babesia bovis Rad51 ortholog influences switching of ves genes but is not essential for segmental gene con-version in antigenic variation. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Ma, M.; Liu, A.; Du, P.; Ren, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yin, H.; Luo, J. Continuous in vitro cultivation of a recently identified Babesia that infects small ruminants in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, I.; Avarzed, A.; Tanaka, T.; Inoue, N.; Ito, M.; Omata, Y.; Saito, A.; Suzuki, N. Continuous in vitro cultivation of Babesia ovata. J. Protozool Res. 1994, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Väyrynen, R.; Tuomi, J. Continuous in Vitro Cultivation of Babesia divergens. Acta Vet. Scand. 1982, 23, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, C.; Buening, G.; Rodriquez, S.; Carson, C. Cloning of in vitro propagated Babesia bigemina. Vet. Parasitol. 1986, 22, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Ristic, M. Babesia bovis: Continuous cultivation in a microaerophilous stationary phase culture. Science 1980, 207, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhaoyong, L.V.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Lan, H.; Liu, G.; et al. Establishment of a transient transfection system for Babesia sp. Xinjiang using homologous promoters. Parasitol Res. 2021, 120, 3625–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, M.A.; El-Sayed, S.A.E.-S.; Nassif, M.; Mosqueda, J.; Xuan, X.; Igarashi, I. Assay methods for in vitro and in vivo anti-Babesia drug efficacy testing: Current progress, outlook, and challenges. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 279, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Brayton, K.; Lau, A.; Herndon, D.R.; Hannick, L.; Kappmeyer, L.; Berens, S.J.; Bidwell, S.L.; Brown, W.C.; Crabtree, J.; Fadrosh, D.; et al. Genome Sequence of Babesia bovis and Comparative Analysis of Apicomplexan Hemoprotozoa. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e148-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornillot, E.; Hadj-Kaddour, K.; Dassouli, A.; Noel, B.; Ranwez, V.; Vacherie, B.; Augagneur, Y.; Bres, V.; Duclos, A.; Randazzo, S.; et al. Sequencing of the smallest Apicomplexan genome from the human pathogen Babesia microti. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9102–9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.P.; Otto, T.; Darby, A.; Ramaprasad, A.; Xia, D.; Echaide, I.E.; Farber, M.; Gahlot, S.; Gamble, J.; Gupta, D.; et al. The evolutionary dynamics of variant antigen genes in Babesia reveal a history of genomic innovation underlying host-parasite interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7113–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, J.; Asada, M.; Hakimi, H.; Tanaka, T.Q.; Sugimoto, C.; Kawazu, S.-I. Whole-genome assembly of Babesia ovata and comparative genomics between closely related pathogens. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, G.; Korhonen, P.K.; Young, N.D.; Koehler, A.V.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, J.; Yin, H.; Gasser, R.B. Genomic resources for a unique, low-virulence Babesia taxon from China. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F. Transfection systems for Babesia bovis: A review of methods for the transient and stable ex-pression of exogenous genes. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, M.; Goto, Y.; Yahata, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Kawai, S.; Inoue, N.; Kaneko, O.; Kawazu, S.-I. Gliding Motility of Babesia bovis Merozoites Visualized by Time-Lapse Video Microscopy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, M.; Yahata, K.; Hakimi, H.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I.; Kaneko, O.; Suarez, C.E.; Kawazu, S.-I. Transfection of Babesia bovis by Double Selection with WR99210 and Blasticidin-S and Its Application for Functional Analysis of Thioredoxin Peroxidase-1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, H.; Ishizaki, T.; Kegawa, Y.; Kaneko, O.; Kawazu, S.-I.; Asada, M. Genome Editing of Babesia bovis Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System. mSphere 2019, 4, e00109-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, H.; Templeton, T.J.; Sakaguchi, M.; Yamagishi, J.; Miyazaki, S.; Yahata, K.; Uchihashi, T.; Kawazu, S.-I.; Kaneko, O.; Asada, M. Novel Babesia bovis exported proteins that modify properties of infected red blood cells. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzan, H.F.; Silva, M.G.; Davis, W.C.; Herndon, D.R.; Schneider, D.A.; Suarez, C.E. Geno- and phenotypic characteristics of a transfected Babesia bovis 6-Cys-E knockout clonal line. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.E.; Bastos, R.G.; Schneider, D.A.; Johnson, W.C.; Adham, F.K.; Davis, W.C.; Laughery, J.M.; Herndon, D.R.; Alzan, H.F.; Ueti, M.W.; et al. The Babesia bovis hap2 gene is not required for blood stage replication, but expressed upon in vitro sexual stage induction. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, I.; González, L.M.; Estrada, K.; Grande, R.; Zaballos, Á.; Lobo, C.A.; Barrera, J.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Montero, E.; Takatani, N.; et al. High-Quality Draft Genome Sequence of Babesia divergens, the Etiological Agent of Cattle and Human Babesiosis. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01168-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, R.M.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Russo, G.; Deplazes, P.; Hehl, A.B. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression and protein secretion of Babesia canis during virulent in-fection identifies potential pathogenicity factors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.O.; Kalyanaraman, A.; Echaide, I.; Palmer, G.H.; Bock, R.; Pedroni, M.J.; Rameshkumar, M.; Ferreira, M.B.; Fletcher, T.I.; McElwain, T.F. Attenuation of virulence in an apicomplexan hemoparasite results in reduced genome diversity at the popu-lation level. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, M.J.; Sondgeroth, K.S.; Gallego-Lopez, G.M.; Echaide, I.; Lau, A.O. Comparative transcriptome analysis of geographically distinct virulent and attenuated Babesia bovis strains reveals similar gene expression changes through attenuation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.M.; Estrada, K.; Grande, R.; Jiménez-Jacinto, V.; Vega-Alvarado, L.; Sevilla, E.; de la Barrera, J.; Cuesta, I.; Zaballos, A.; Bautista, J.M.; et al. Comparative and functional genomics of the protozoan parasite Babesia divergens highlighting the invasion and egress processes. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2019, 13, e0007680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueti, M.W.; Johnson, W.C.; Kappmeyer, L.S.; Herndon, D.R.; Mousel, M.R.; Reif, K.E.; Taus, N.S.; Ifeonu, O.O.; Silva, J.C.; Suarez, C.E.; et al. Comparative analysis of gene expression between Babesia bovis blood stages and kinetes allowed by improved genome annotation. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 51, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, M.; Tanaka, M.; Goto, Y.; Yokoyama, N.; Inoue, N.; Kawazu, S.-I. Stable expression of green fluorescent protein and targeted disruption of thioredoxin peroxidase-1 gene in Babesia bovis with the WR99210/dhfr selection system. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 181, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.E.; Johnson, W.C.; Herndon, D.R.; Laughery, J.; Davis, W.C. Integration of a transfected gene into the genome of Babesia bovis occurs by legitimate homologous recombination mechanisms. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2015, 202, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F. Transient transfection of purified Babesia bovis merozoites. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 118, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, C.E.; McElwain, T.F. Stable expression of a GFP-BSD fusion protein in Babesia bovis merozoites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remcho, T.P.; Guggilapu, S.D.; Cruz, P.; Nardone, G.A.; Heffernan, G.; O’Connor, R.D.; Bewley, C.A.; Wellems, T.E.; Lane, K.D. Regioisomerization of Antimalarial Drug WR99210 Explains the Inactivity of a Commercial Stock. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.G.; Knowles, D.P.; Suarez, C.E. Identification of interchangeable cross-species function of elongation factor-1 alpha promoters in Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, H.; Yamagishi, J.; Kegawa, Y.; Kaneko, O.; Kawazu, S.-I.; Asada, M. Establishment of transient and stable transfection systems for Babesia ovata. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Asada, M.; Cao, S.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Vudriko, P.; Efstratiou, A.; Hakimi, H.; Masatani, T.; Sunaga, F.; Kawazu, S.-I.; et al. Transient transfection of intraerythrocytic Babesia gibsoni using elongation factor-1 alpha promoter. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2017, 216, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, C.; Asada, M.; Hakimi, H.; Domingos, A.; Pimentel, M.; Antunes, S. Transient transfection of Babesia ovis using heterologous promoters. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ji, S.; Rizk, M.A.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Galon, E.M.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Benedicto, B.; Tumwebaze, M.A.; et al. Transient Transfection of the Zoonotic Parasite Babesia microti. Pathogens 2020, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Asada, M.; Hakimi, H.; Masatani, T.; Vudriko, P.; Lee, S.-H.; Kawazu, S.-I.; Yamagishi, J.; Xuan, X. Establishment of a stable transfection system for genetic manipulation of Babesia gibsoni. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.G.; Knowles, D.P.; Mazuz, M.L.; Cooke, B.M.; Suarez, C.E. Stable transformation of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis using a single transfection plasmid. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaijyan, D.K.; Govindasamy, K.; Singh, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Singh, A.P. Establishment of a stable transfection method in Babesia microti and identification of a novel bidirectional promoter of Babesia microti. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, E.A.; Xiao, Y.-P.; Allred, D.R. Knockout of Babesia bovis rad51 ortholog and its complementation by expression from the BbACc3 artificial chromosome platform. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzan, H.; Cooke, B.M.; Suarez, C.E. Transgenic Babesia bovis lacking 6-Cys sexual-stage genes as the foundation for non-transmissible live vaccines against bovine babesiosis. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.G.; Lau, A.O.; O’Connor, R.M.; Ueti, M.W.; Cooke, B.M.; Laughery, J.M.; Graça, T.; Madsen-Bouterse, S.; Oldiges, D.P.; Allred, D.; et al. Up-regulated expression of spherical body protein 2 truncated copy 11 in Babesia bovis is associated with reduced cytoadhesion to vascular endothelial cells. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 49, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletta, M.S.; Laughery, J.M.; Arias, L.S.L.; Ortiz, J.M.J.; Montenegro, V.N.; Petrigh, R.; Ueti, M.W.; Suarez, C.E.; Farber, M.D.; Wilkowsky, S.E. The key to egress? Babesia bovis perforin-like protein 1 (PLP1) with hemolytic capacity is required for blood stage replication and is involved in the exit of the parasite from the host cell. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A Programmable Dual-RNA-Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Symington, L.S.; Fidock, D.A. DNA Repair Mechanisms and Their Biological Roles in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Xiao, B.; Su, X.; Cui, H.; Yuan, J. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated sequential editing of genes critical for ookinete motility in Plasmodium yoelii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2016, 212, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.P.; Lindner, S.E. Ribozyme-mediated, multiplex CRISPR gene editing and CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) in rodent-infectious Plasmodium yoelii. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9555–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinzawa, N.; Nishi, T.; Hiyoshi, F.; Motooka, D.; Yuda, M.; Iwanaga, S. Improvement of CRISPR/Cas9 system by transfecting Cas9-expressing Plasmodium berghei with linear donor template. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Yin, S.; Hu, Y.; Sun, M.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, H.; Mu, J.; et al. Epigenetic editing by CRISPR/dCas9 in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 116, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konermann, S.; Lotfy, P.; Brideau, N.J.; Oki, J.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Hsu, P.D. Transcriptome Engineering with RNA-Targeting Type VI-D CRISPR Effectors. Cell 2018, 173, 665–676.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, W.C.; Nahvi, A.; Roth, A.; Collins, J.A.; Breaker, R. Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature 2004, 428, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, H.; Asada, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Kawazu, S. Isolation of viable Babesia bovis merozoites to study parasite invasion. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouLaila, M.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Rna Interfernce (Rnai) for Some Genes from Babesia Bovis. Res. J. Appl. Biotechnol. 2016, 2, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszynski, L.A.; Chen, L.-C.; Maynard-Smith, L.A.; Ooi, A.G.L.; Wandless, T.J. A Rapid, Reversible, and Tunable Method to Regulate Protein Function in Living Cells Using Synthetic Small Molecules. Cell 2006, 126, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruki, H.; Nishikawa, J.; Laemmli, U.K. The Anchor-Away Technique: Rapid, Conditional Establishment of Yeast Mutant Phenotypes. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudyba, H.M.; Cobb, D.W.; Vega-Rodríguez, J.; Muralidharan, V. Some conditions apply: Systems for studying Plasmodium falciparum protein function. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning-Ward, T.; Gilson, P.R.; Crabb, B.S. Advances in molecular genetic systems in malaria. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 13, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, J.; Flemming, S.; Reichard, N.; Soares, A.B.; Mesén-Ramírez, P.; Jonscher, E.; Bergmann, B.; Spielmann, T. A genetic system to study Plasmodium falciparum protein function. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.R.; Waters, A.P. Rapid inducible protein displacement in Plasmodiumin vivo and in vitro using knocksideways technology. Wellcome Open Res. 2017, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuepfer, E.; Napiorkowska, M.; van Ooij, C.; Holder, A.A. Generating conditional gene knockouts in Plasmodium—A toolkit to produce stable DiCre recom-binase-expressing parasite lines using CRISPR/Cas9. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetsche, B.; Volz, S.E.; Zhang, F. A split-Cas9 architecture for inducible genome editing and transcription modulation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, S.; Okamura, M.; Matsuo, T.; Kumar, S.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Host serum modifies the drug susceptibility of Babesia bovis in vitro. Parasitology 1999, 130, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk Mohamed, A.; El-Sayed Shimaa, A.; Yokoyama Naoaki, I.I. Serum-free GIT medium for short-term in vitro cultures of Babesia bigemina, Babesia divergens, and Theileria equi. J. Protozool. Res. 2017, 27, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Schrevel, J.; Grellier, P.; Rigomier, D. New approaches in in vitro cultures of Plasmodium falciparum and Babesia divergens by using serum-free medium based on human high density lipoproteins. Mem Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1992, 87 (Suppl. S3), 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, N.; Precigout, E.; Ancelin, M.-L.; Moubri, K.; Carcy, B.; Lemesre, J.L.; Vial, H.; Gorenflot, A. Continuous in vitro culture of Babesia divergens in a serum-free medium. Parasitology 1997, 115, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.A.; Millán, J.V.F.; Ueti, M.W.; Rojas-Martínez, C. Innovative Alternatives for Continuous In Vitro Culture of Babesia bigemina in Medium Free of Components of Animal Origin. Pathogens 2020, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusakisako, K.; Masatani, T.; Yada, Y.; Talactac, M.R.; Hernandez, E.P.; Maeda, H.; Mochizuki, M.; Tanaka, T. Improvement of the cryopreservation method for the Babesia gibsoni parasite by using commercial freezing media. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikano, S.; Nakada, K.; Hashiguchi, R.; Shimada, T.; Ono, K. A Short Term In vitro Cultivation of Babesia rodhaini and Babesia microti. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1995, 57, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soga, A.; Bando, H.; Ko-Ketsu, M.; Masuda-Suganuma, H.; Kawazu, S.-I.; Fukumoto, S. High efficacy in vitro selection procedure for generating transgenic parasites of Plasmodium berghei using an antibiotic toxic to rodent hosts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, S.M.; Huet, D.; Ganesan, S.M.; Huynh, M.-H.; Wang, T.; Nasamu, A.; Thiru, P.; Saeij, J.P.; Carruthers, V.B.; Niles, J.C.; et al. A Genome-wide CRISPR Screen in Toxoplasma Identifies Essential Apicomplexan Genes. Cell 2016, 166, 1423–1435.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Product | Gene ID | Targeted Method | Phenotye | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elongation factor 1-alpha (ef1-α) | BBOV_IV010620 | Knockout | Not essential for in vitro growth | [23,35,36,38] |
| Thioredoxin perxidase 1 (Tpx-1) | BBOV_II004970 | Knockout | Not essential for in vitro growth, increased sensitivity to nitrosative stress | [24,25] |
| Hap2 | BBOV_III006770 | Knockout | Not essential for in vitro growth | [28] |
| 6-Cys E | BBOV_II006640 | Knockout | Not essential for in vitro growth | [27] |
| 6-Cys A and B | BBOV_II006600, BBOV_II006610 | Double knockout | Not essential for in vitro growth | [49] |
| Thioredoxin perxidase 1 (Tpx-1) | BBOV_II004970 | Point mutation | Not essential for in vitro growth, increased sensitivity to nitrosative stress | [25] |
| Spherical Body Protein 2 (SBP2) truncated copy 11 | BBOV_III006540 | Knockin into ef1-α locus | Reduction in binding of iRBCs to endothelial cells | [50] |
| Spherical Body Protein 3 (SBP3) | BBOV_I004210 | Epitope tagging | Protein localization was confirmed with epitope tagging. | [25] |
| Rad51 | BBOV_II003540 | Knockout | Not essential for in vitro growth, increased sensitivity to methylmethane sulfonate, loss of HR-dependent integration, and reduction of in situ transcriptional switching | [9,48] |
| Multi-transmembrane protein (mtm) | BBOV_III000010, BBOV_III000060 | Episomal overexpression | Reverting blasticidin S resistance | [26] |
| VESA1-export associated protein (Bbveap) | BBOV_III004280 | Knockdown | Slow growth, abrogation of cytoadhesion | [26] |
| Perforin like protein 1 (Plp1) | BBOV_IV001370 | Knockout | Lower growth rate in vitro | [51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakimi, H.; Asada, M.; Kawazu, S.-i. Recent Advances in Molecular Genetic Tools for Babesia. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100222
Hakimi H, Asada M, Kawazu S-i. Recent Advances in Molecular Genetic Tools for Babesia. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(10):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100222
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakimi, Hassan, Masahito Asada, and Shin-ichiro Kawazu. 2021. "Recent Advances in Molecular Genetic Tools for Babesia" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 10: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100222
APA StyleHakimi, H., Asada, M., & Kawazu, S.-i. (2021). Recent Advances in Molecular Genetic Tools for Babesia. Veterinary Sciences, 8(10), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100222








