Changes in Serum Lipid Profiles among Canine Patients Suffering from Chronic Hepatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assawarachan, S.N.; Maneesaay, P.; Thengchaisri, N. A descriptive study of the histopathologic and biochemical liver test abnormalities in dogs with liver disease in Thailand. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 84, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bexfield, N. Canine Idiopathic Chronic Hepatitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 47, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldervaart, J.H.; Favier, R.P.; Penning, L.C.; van den Ingh, T.S.; Rothuizen, J. Primary hepatitis in dogs: A retrospective review (2002–2006). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, C.R.; Center, S.A.; Cullen, J.M.; Penninck, D.G.; Richter, K.P.; Twedt, D.C.; Watson, P.J. ACVIM consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic hepatitis in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1173–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.D.G.; Barrie, J. Lipoprotein metabolism and hyperlipidaemia in the clog and cat: A review. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1993, 34, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Sun, R.Z.; Wang, D.; Gong, M.Z.; Su, X.P.; Yi, F.; Peng, Z.W. Increased Hepatic Fatty Acids Uptake and Oxidation by LRPPRC-Driven Oxidative Phosphorylation Reduces Blood Lipid Levels. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, H.N. Lipoprotein physiology. Endocrinol. Meta.b Clin. N. Am. 1998, 27, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.; Graziani, M.S.; Jarausch, J.; Bruton, D.; Cobbaert, C.; Cole, T.G.; Colella, F.; Lefevre, F.; Gillery, P.; Haas, B.; et al. A new liquid homogeneous assay for HDL cholesterol determination evaluated in seven laboratories in Europe and the United States. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1999, 37, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Steiner, J.M. Lipid metabolism and hyperlipidemia in dogs. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Steiner, J.M. Canine hyperlipidaemia. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 56, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Nitzan-Kaluski, D.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. Prevalence of primary non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a population-based study and its association with biochemical and anthropometric measures. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2006, 26, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.E. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.L.; Turek, B.J.; Brown, D.C.; Bradley, C.; Callahan Clark, J. Cholangitis and Cholangiohepatitis in Dogs: A Descriptive Study of 54 Cases Based on Histopathologic Diagnosis (2004–2014). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allerton, F.; Swinbourne, F.; Barker, L.; Black, V.; Kathrani, A.; Tivers, M.; Henriques, T.; Kisielewicz, C.; Dunning, M.; Kent, A. Gall bladder mucoceles in Border terriers. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kweon, O.K.; Kim, W.H. Associations between serum leptin levels, hyperlipidemia, and cholelithiasis in dogs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Ingh, T.S.G.A.M.; Van Winkle, T.; Cullen, J.M.; Charles, J.A.; Desmet, V.J. Morphological Classification of Parenchymal Disorders of the Canine and Feline Liver. In WSAVA Standards for Clinical and Histological Diagnosis of Canine and Feline Liver Diseases; Rothuizen, J., Bunch, S.E., Charles, J.A., Cullen, J.M., Desmet, V.J., Szatmari, V., Twedt, D.C., van den Ingh, T.S.G.A.M., van Winkle, T., Washabau, R.J., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Assawarachan, S.N.; Chuchalermporn, P.; Maneesaay, P.; Thengchaisri, N. Evaluation of hepatobiliary ultrasound scores in healthy dogs and dogs with liver diseases. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasumi, K.; Kashiwado, N.; Okada, Y.; Sawamura, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Iwazaki, E.; Mori, N.; Yamamoto, I.; Arai, T. Age effects on plasma cholesterol and triglyceride profiles and metabolite concentrations in dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Al-Shali, K.Z.; Hegele, R.A. Hypertriglyceridemia: Its etiology, effects and treatment. Cmaj 2007, 176, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, C.E.; Schaefer, E.J.; Taam, L.A.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Lindgren, F.T.; Albers, J.J.; Jones, E.A.; Brewer, H.B., Jr. Lipoprotein abnormalities in primary biliary cirrhosis. Association with hepatic lipase inhibition as well as altered cholesterol esterification. Gastroenterology 1985, 89, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Felin, R.; Lambrecht, J.; Agostini, B.; Wieland, H.; Rost, W.; Seidel, D. Hypertriglyceridaemia secondary to liver disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 4, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, R.J. Functional activities of hepatic lipoprotein receptors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1986, 48, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisclair, J.; Doré, M.; Beauchamp, G.; Chouinard, L.; Girard, C. Characterization of the inflammatory infiltrate in canine chronic hepatitis. Vet. Pathol. 2001, 38, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, N.; Harry, D.S.; Pearson, A.J. The hypercholesterolaemia of obstructive jaundice. Gut 1975, 16, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Danielsson, B.; Ekman, R.; Johansson, B.G.; Petersson, B.G. Plasma lipoprotein changes in experimental cholestasis in the dog. Clin. Chim. Acta 1977, 80, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, M.S. Evaluation of hyperlipidemias in dogs and cats. Semin. Vet. Med. Surg. Small Anim. 1992, 7, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuang, J.H.; Shieh, C.S.; Chang, N.K.; Chen, W.J.; Lo, S.K. Metabolic effect of parenteral nutrition in dogs with obstructive jaundice. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1995, 14, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walli, A.K.; Seidel, D. Role of lipoprotein-X in the pathogenesis of cholestatic hypercholesterolemia. Uptake of lipoprotein-X and its effect on 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and chylomicron remnant removal in human fibroblasts, lymphocytes, and in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomhoff, J.P.; Holme, R.; Ostrem, T. Plasma cholesterol esterification and plasma lipoproteins in bile-duct-ligated dogs. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1978, 13, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, L.W.; Forstner, B.; Schneglberger, S.; Muckenhuber, M.; Eigenbauer, E.; Scheiner, B.; Mandorfer, M.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T. Patterns and prevalence of dyslipidemia in patients with different etiologies of chronic liver disease. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.E.; Hostutler, R.A. A laboratory diagnostic approach to hepatobiliary disease in small animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2013, 43, 1209–1225, v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, E.; Angulo, P. Hepatitis C and steatosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2007, 38, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, P.A.; Cobble, M.E. Hypertriglyceridemia: The importance of identifying patients at risk. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 128, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsunai, M.; Kanemoto, H.; Fukushima, K.; Fujino, Y.; Ohno, K.; Tsujimoto, H. The association between gall bladder mucoceles and hyperlipidaemia in dogs: A retrospective case control study. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center, S.A. Interpretation of liver enzymes. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 37, 297–333, vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Levinski, M.D.; Steiner, J.M. Serum liver enzyme activities in healthy Miniature Schnauzers with and without hypertriglyceridemia. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 232, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonkers, I.J.; Smelt, A.H.; Princen, H.M.; Kuipers, F.; Romijn, J.A.; Boverhof, R.; Masclee, A.A.; Stellaard, F. Fish oil increases bile acid synthesis in male patients with hypertriglyceridemia. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bexfield, N.H.; Buxton, R.J.; Vicek, T.J.; Day, M.J.; Bailey, S.M.; Haugland, S.P.; Morrison, L.R.; Else, R.W.; Constantino-Casas, F.; Watson, P.J. Breed, age and gender distribution of dogs with chronic hepatitis in the United Kingdom. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Hurvitz, A.I.; Lieberman, P.H. Canine hepatic neoplasms: A clinicopathologic study. Vet. Pathol. 1980, 17, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Hurvitz, A.I.; Lieberman, P.H.; Johnson, G.F. Canine hepatocellular carcinoma. Vet. Pathol. 1981, 18, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepesy, L.M.; Center, S.A.; Randolph, J.F.; Warner, K.L.; Erb, H.N. Vacuolar hepatopathy in dogs: 336 cases (1993–2005). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
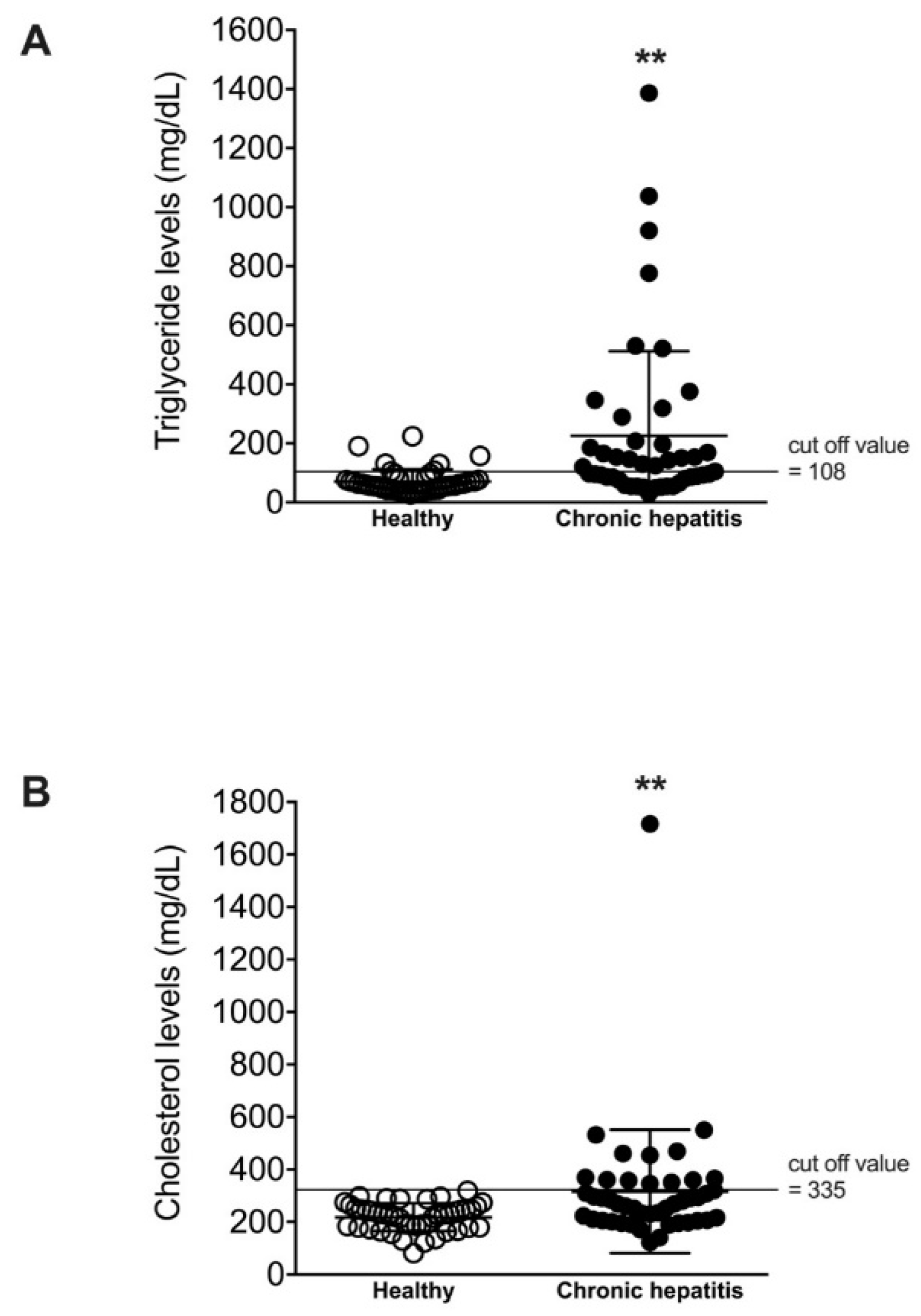
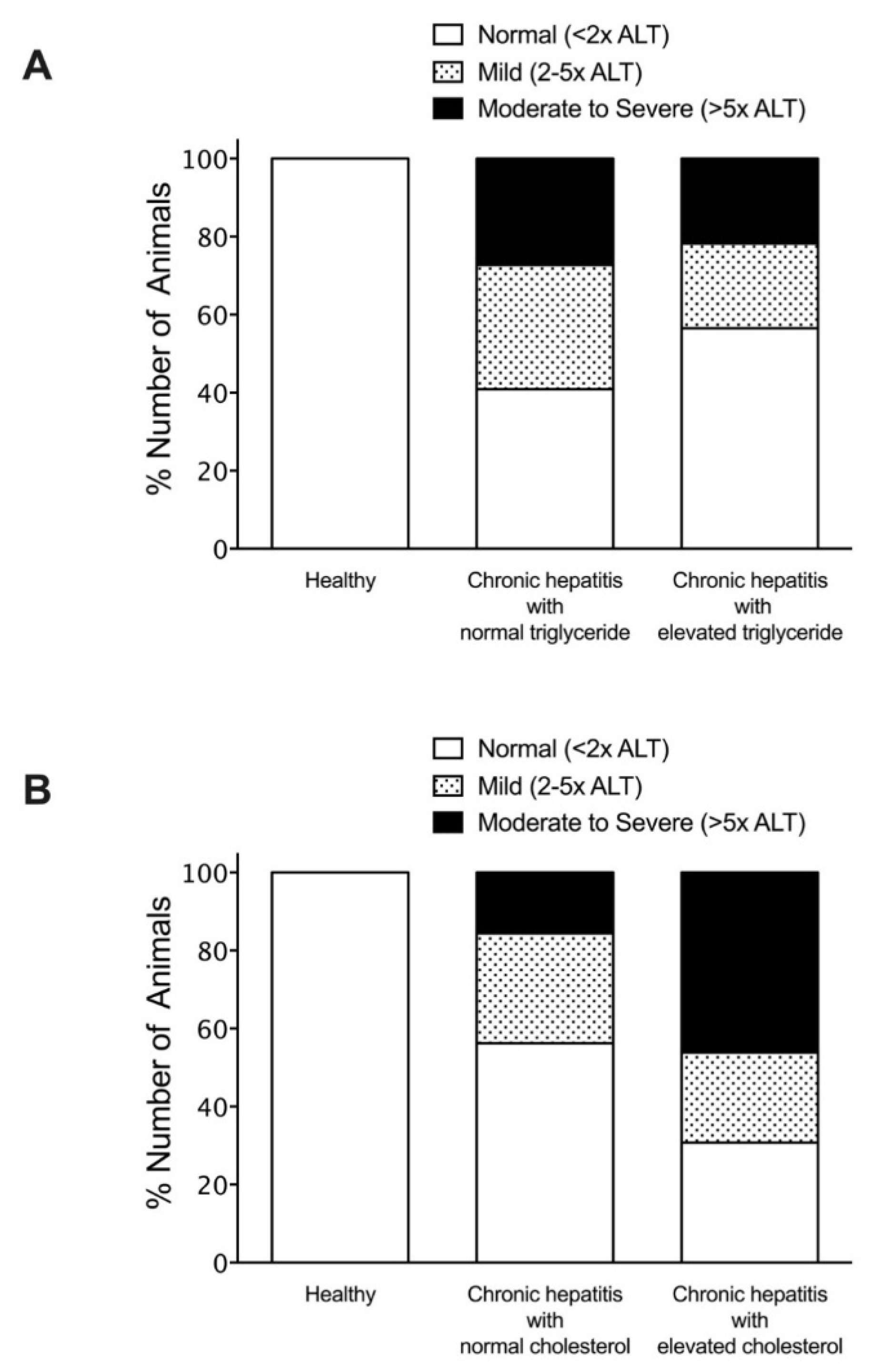
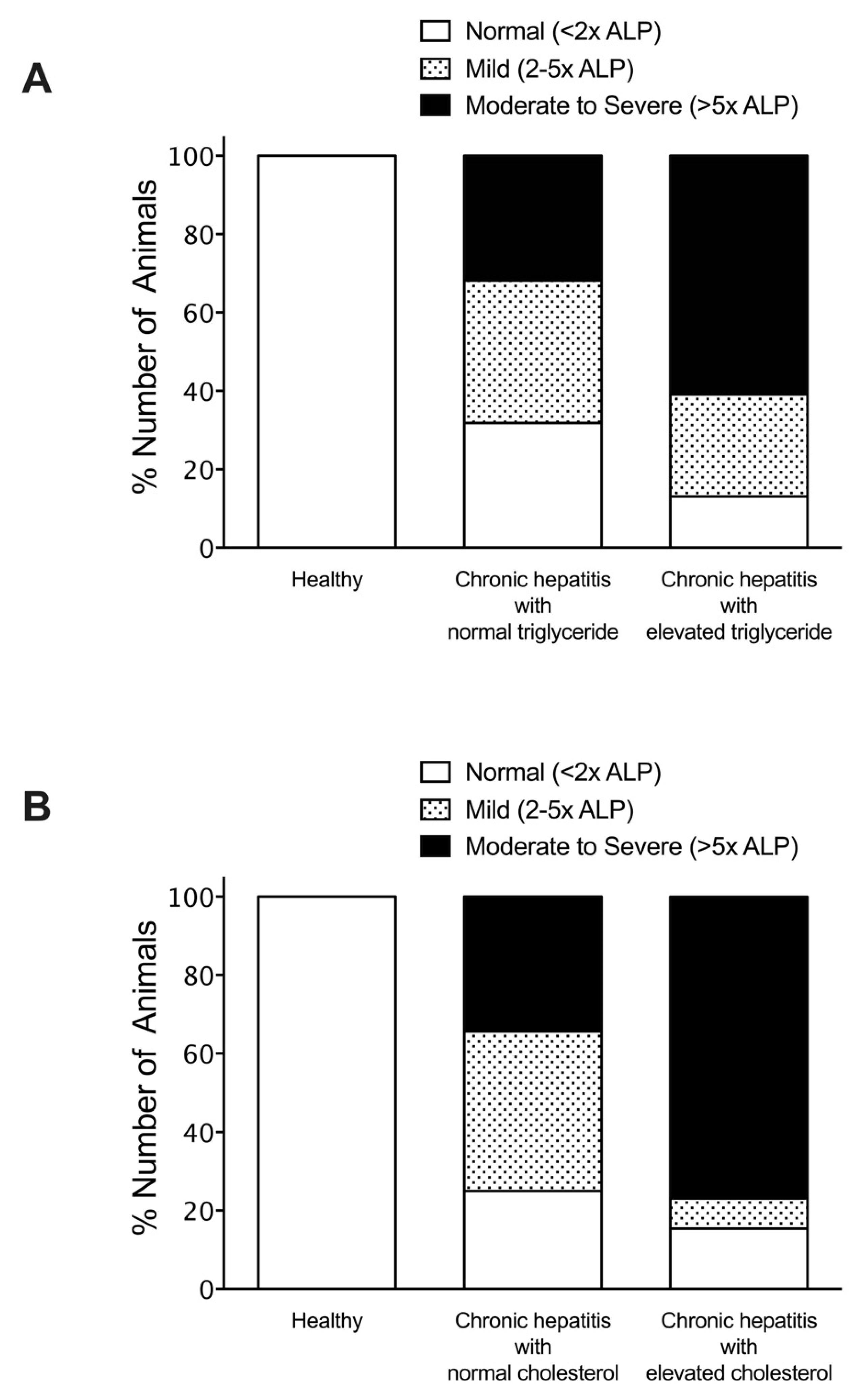
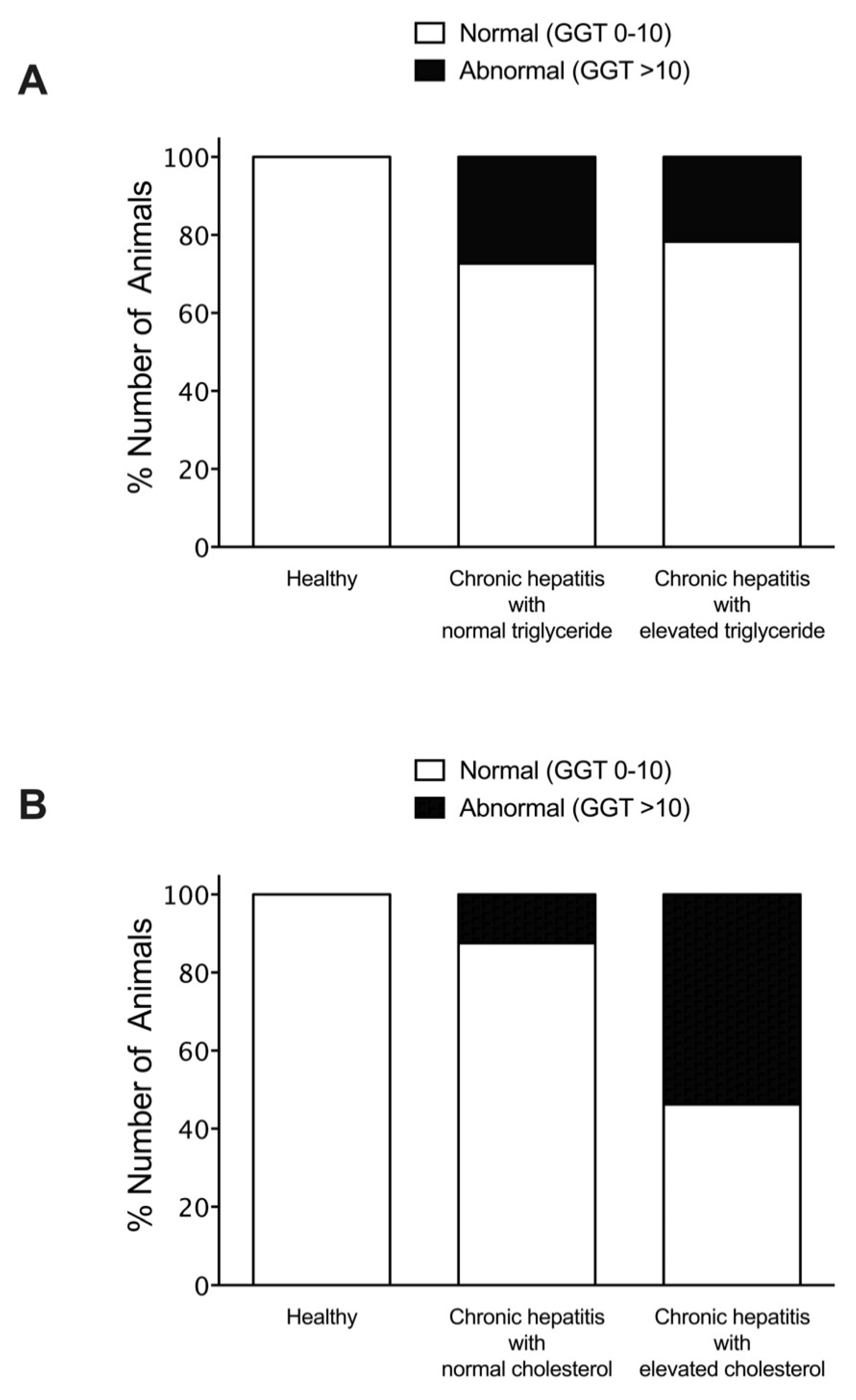
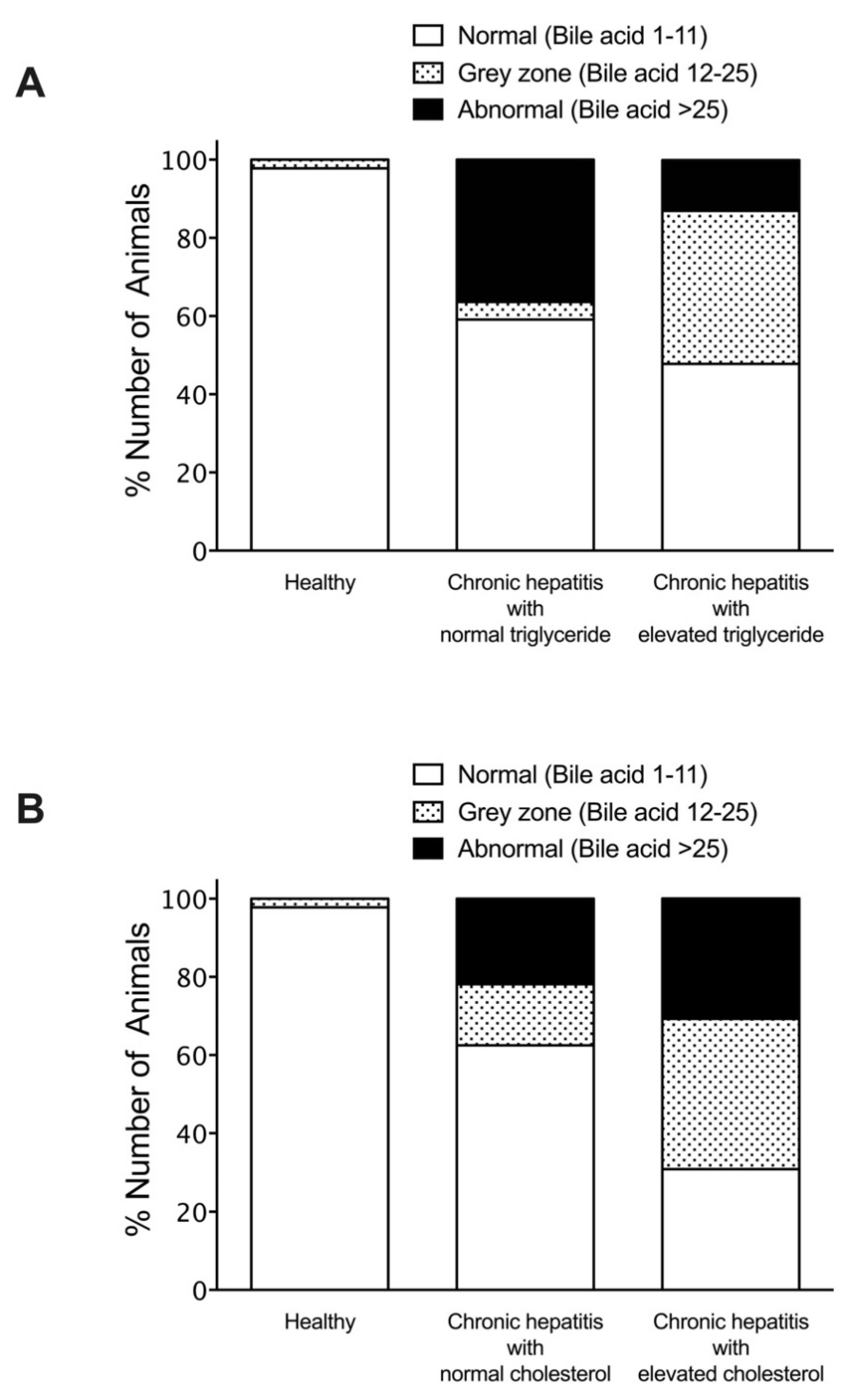
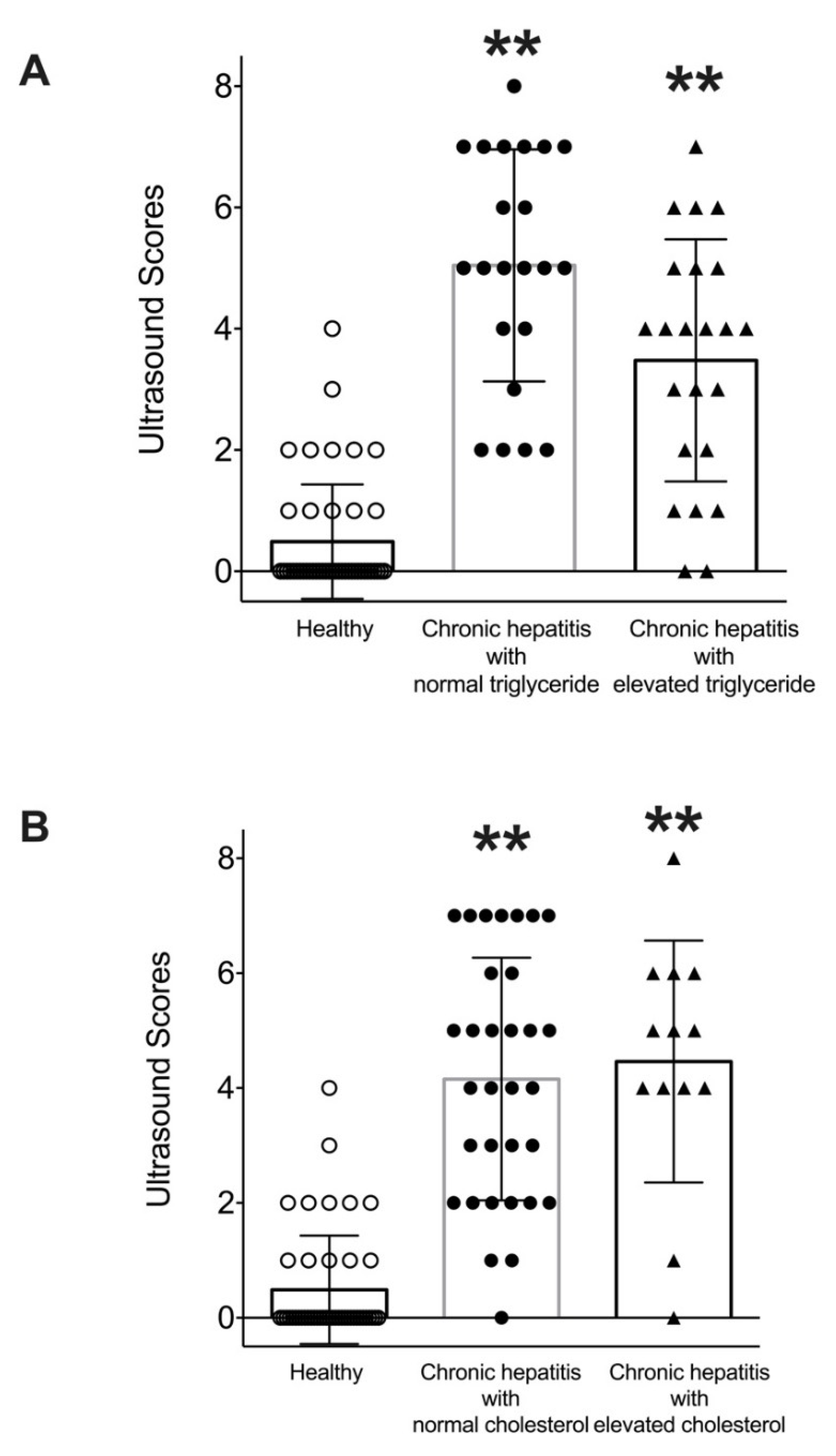
| Parameters | Healthy | Liver Disease |
|---|---|---|
| N | 45 | 45 |
| Bodyweight (kg, mean ± SD) | 23.6 ± 16.4 | 12.4 ± 9.4 ** |
| 9-point BCS (mean ± SD) | 6.2 ± 1.6 | 6.8 ± 1.8 |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 5.1 ± 2.8 | 10.1 ± 3.6 ** |
| Sex (N) | ||
| Male | 24 | 21 |
| Female | 21 | 24 |
| Size (N) | ||
| Small | 17 | 28 |
| Medium | 3 | 13 |
| Large | 25 | 4 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 70.9 ± 40.9 | 225.5 ± 286.5 ** |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 218.0 ± 52.7 | 316.3 ± 234.8 ** |
| ALT (IU/L, mean ± SD) | 37.7 ± 12.2 | 361.4 ± 735.3 ** |
| ALP (IU/L, mean ± SD) | 36.0 ± 16.7 | 1020.5 ± 1946.3 ** |
| GGT (IU/L, mean ± SD) | 2.5 ± 1.6 | 14.7 ± 33.7 * |
| Bile acid (µmol/L, mean ± SD) | 5.5 ± 2.3 | 13.8 ± 10.0 ** |
| Hyperlipidemia | Healthy | Chronic Hepatitis |
|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | |
| Normal lipid levels | 40 (88.9%) | 17 (37.8%) |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (11.1%) |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 5 (11.1%) | 15 (33.3%) |
| Both hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia | 0 (0.0%) | 8 (17.8%) |
| ALT | ALP | GGT | Bile Acid | Cholesterol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triglyceride | 0.0016 | 0.2582 * | −0.0325 | 0.0855 | 0.2442 * |
| Cholesterol | 0.8287 ** | 0.8436 ** | 0.5640 ** | 0.3310 ** | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assawarachan, S.N.; Chuchalermporn, P.; Maneesaay, P.; Thengchaisri, N. Changes in Serum Lipid Profiles among Canine Patients Suffering from Chronic Hepatitis. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100221
Assawarachan SN, Chuchalermporn P, Maneesaay P, Thengchaisri N. Changes in Serum Lipid Profiles among Canine Patients Suffering from Chronic Hepatitis. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(10):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100221
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssawarachan, Sathidpak Nantasanti, Piyathip Chuchalermporn, Phudit Maneesaay, and Naris Thengchaisri. 2021. "Changes in Serum Lipid Profiles among Canine Patients Suffering from Chronic Hepatitis" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 10: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100221
APA StyleAssawarachan, S. N., Chuchalermporn, P., Maneesaay, P., & Thengchaisri, N. (2021). Changes in Serum Lipid Profiles among Canine Patients Suffering from Chronic Hepatitis. Veterinary Sciences, 8(10), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8100221





