Abstract
Streptococcus suis causes severe infections in both swine and humans, making it a serious threat to the swine industry and public health. Insight into the physiology and pathogenesis of S. suis undoubtedly contributes to the control of its infection. During the infection process, a wide variety of virulence factors enable S. suis to colonize, invade, and spread in the host, thus causing localized infections and/or systemic diseases. Enzymes catalyze almost all aspects of metabolism in living organisms. Numerous enzymes have been characterized in extensive detail in S. suis, and have shown to be involved in the pathogenesis and/or physiology of this pathogen. In this review, we describe the progress in the study of some representative enzymes in S. suis, such as ATPases, immunoglobulin-degrading enzymes, and eukaryote-like serine/threonine kinase and phosphatase, and we highlight the important role of various enzymes in the physiology and pathogenesis of this pathogen. The controversies about the current understanding of certain enzymes are also discussed here. Additionally, we provide suggestions about future directions in the study of enzymes in S. suis.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus suis is an important bacterial pathogen that causes a severe threat to public health and great economic losses in the pig industry worldwide []. It is associated with meningitis, septicaemia, arthritis, and other infections in swine []. A recent survey revealed that it was the most prevalent bacterial pathogen in Chinese pig farms from 2013 to 2017 []. In addition, S. suis can be transmitted to humans and cause severe infections, such as meningitis, septicemia, and streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome []. S. suis infection in human was first recorded in Denmark in 1968 []. Since then, human cases have been reported in many countries, although most of them are sporadic []. However, two large outbreaks of S. suis epidemics occurred in China in 1998 and 2005, resulting in 240 human cases with 53 deaths in total [,]. The repeated outbreaks of S. suis infections in humans have suggested that S. suis is an emerging zoonotic pathogen []. By the end of 2013, worldwide reported S. suis infections in humans reached 1642 cases []. Human cases have also been frequently reported worldwide in recent years [,,,,], suggesting that the threat of S. suis infection still exists.
S. suis possesses capsular polysaccharides (CPS) that cover on the surface of bacterial cells []. Initially, 35 serotypes (1–34, and 1/2) were described for S. suis, based on the serological reaction with its CPS []. Subsequently, serotypes 20, 22, 26, and 32–34 were proposed to be novel bacterial species, and the remaining 29 serotypes were referred to as genuine S. suis [,,,]. Globally, serotype 2 (S. suis 2) is the most predominant serotype associated with clinical S. suis infection in both swine and humans [].
In swine, the main route of S. suis infection is the upper respiratory tract, yet the gastrointestinal tract cannot be excluded as a secondary route. In China and in Western countries, small skin injuries are considered to be the main route of S. suis infection in humans, while in Southeast Asian countries, the gastrointestinal tract (consumption of contaminated pork by-products) seems to be the main route [,].
During the infection process, a wide variety of virulence-associated factors enable S. suis to colonize, invade, and spread in the host, thus causing localized infections and/or systemic diseases [,]. Enzymes function as catalysts that catalyze almost all aspects of metabolism in living organisms. It has been well established that many enzymes are involved in the pathogenesis of S. suis []. Moreover, some enzymes play important roles in bacterial physiology, even though they are not virulence-associated factors. In this review, we emphasize the role of some representative enzymes in the physiology and pathogenesis of S. suis (Table 1), and we also discuss the controversies about the current understanding of certain enzymes.

Table 1.
Characterization of some representative enzymes in Streptococcus suis.
2. ATPases
Recently, we identified two P-type ATPases (CopA and PmtA) that function as metal efflux pumps in S. suis [,]. In certain Gram-positive bacteria, copA is a component of the cop operon that is a copper-responsive system [,]. Although not arranged as an operon in S. suis, copA expression is significantly upregulated when the bacterium is treated with copper. In line with this result, CopA protects S. suis against bactericidal effects conferred by copper through copper efflux []. While pmtA expression is induced by ferrous iron, cobalt, and nickel, the ΔpmtA mutant exhibits impaired growth under ferrous iron, ferric iron, cobalt, and zinc excess conditions. Compared with the wild-type (WT) and complementation strains, ΔpmtA also accumulates higher levels of iron and cobalt, and is more sensitive to streptonigrin, a ferrous iron-activated antibiotic. The addition of manganese could alleviate the growth defect of ΔpmtA under ferrous iron and cobalt excess conditions. Furthermore, PmtA is involved in the tolerance to oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide []. Despite the homologs of CopA and PmtA having been shown to be required for bacterial virulence [,,,], these two ATPases have exhibited no obvious role in the pathogenesis of S. suis [,,]. Thus, it is necessary to study even well-characterized genes in different species.
In addition to CopA and PmtA, another ATPase, MsmK, has been identified in S. suis [,]. Similar to its homologs in Streptococcus pneumoniae [], MsmK is required for the utilization of multiple carbohydrates, such as raffinose, melibiose, and maltotetraose in S. suis []. Deletion of msmK results in a longer chain length, decreased hemolytic activity, and an impaired ability to tolerate osmotic and oxidative stresses []. The ΔmsmK mutant also exhibited reduced survival in mouse blood, increased susceptibility to macrophages, and an attenuated ability to colonize the mouse brain [,]. These results clearly demonstrated that MsmK contributes to the pathogenesis of S. suis.
3. Immunoglobulin-Degrading Enzymes
Immunoglobulins (Igs) are important components of the host immune defense system. Based on the differences in their heavy chains, Igs are divided into five classes, including IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE. In S. suis, two Ig-degrading enzymes, i.e., IdeSsuis and IgdE, have been extensively characterized [,,,,]. IdeSsuis is a novel IgM-degrading enzyme that can degrade IgM but neither IgG nor IgA. IdeSsuis is host-specific, since it specifically cleaves porcine IgM, but not IgM from six other investigated species []. Vaccination of piglets with recombinant IdeSsuis elicited specific immunity that led to the efficient killing of S. suis in porcine blood, and thus, protected piglets against S. suis infection []. In addition, IgM cleavage activity of IdeSsuis is involved in complement evasion, although it does not seem to be critical for the virulence of S. suis in piglets [,]. IgdE is a novel IgG-degrading protease that targets the hinge region of porcine IgG. Similar to IdeSsuis, only porcine IgG can be a substrate of IgdE. Therefore, this enzyme is also host-specific. The IgG proteolytic activity is present in all S. suis strains investigated, and specific antibodies against IgdE were detectable in piglet serum []. These findings suggest that IgdE is expressed during infection; thus, it is a putative virulence factor and a potential vaccine candidate.
Another Ig-degrading enzyme, i.e., IgA1 protease, has been reported to cleave human IgA1 []. This enzyme has also been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis of S. suis and to serve as a protective antigen [,]. However, IgA1 protease activity was not detected in three S. suis strains in another study []. Recently, the enzyme was demonstrated to be ZmpC, a zinc metalloprotease in S. suis. Moreover, ZmpC is not a critical virulence factor, as it has no role in adherence to porcine bronchial epithelial cells or colonization of the upper respiratory tract of pigs [].
4. Eukaryote-Like Serine/Threonine Kinase and Phosphatase
The eukaryote-like serine/threonine kinases and phosphatases (eSTKs/eSTPs) have important roles in the physiology and pathogenesis of Streptococci []. In S. suis, eSTK is involved in bacterial morphology, stress tolerance, and pathogenesis [,,]. The eSTK-deletion mutant exhibits much longer chain length and increased cell size [,]. Subsequent research revealed that DivIVA, a substrate of eSTK, is involved in cell division regulation []. The morphological differences between the WT strain and the mutant might be due to the different phosphorylation levels of DivIVA in these two strains. The mutant displayed impaired growth when cultured under stress conditions, including high temperature, high osmolarity, acidic pH, and oxidative stresses []. In line with these phenotypes, seven metabolic pathways were significantly repressed in the mutant []. The involvement of eSTK in S. suis pathogenesis has been demonstrated by the following findings: firstly, the mutant showed a decreased ability to adhere to and invade cells, and had reduced survival in pig whole blood [,]; secondly, the ability of the mutant to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) was reduced []; thirdly, virulence of the mutant was attenuated in both murine and pig infection models; finally, the expression of some virulence-associated genes were down-regulated in the mutant [,]. These findings suggest that in S. suis, eSTK participates in multiple steps of the infection process.
eSTP has been identified as a putative virulence factor of S. suis serotype 9 by suppressing subtractive hybridization. Furthermore, the eSTP gene was present in most of the virulent strains, but absent in the avirulent strain. In S. suis 9, the eSTP-defective mutant exhibited decreased adherence to HEp-2 cells, reduced survival in pig whole blood, and attenuated virulence in the murine infection model. Consistent with these results, the expression of a few genes involved in adhesion and virulence was down-regulated in the mutant []. As has been observed in S. suis 9, deletion of eSTP attenuated the virulence of S. suis 2 in a murine infection model. However, the eSTP mutant of S. suis 2 displayed an enhanced ability to adhere to HEp-2 and bEnd.3 cells, to survive in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells, and to resist reactive oxygen species. The role of eSTP in cell adhesion and immune evasion seems to be contradictory between S. suis 2 and 9. Given that eSTP shares high level of homology between S. suis 2 and 9 [], further studies should be performed to determine whether the opposite conclusions are attributable to the different serotypes.
5. Subtilisin-Like Serine Proteases
The subtilisin-like serine protease-1 (SspA-1) was identified by screening a S. suis 2 genomic expression library using convalescent-phase pig sera []. Later, SspA-1 was identified as an effector secreted by the type IV secretion system (T4SS) of S. suis 2 by using a shotgun proteomics approach and western blot analysis []. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis demonstrated that SspA-1 expression in vivo was markedly higher than that in vitro, indicating that SspA-1 might be involved in S. suis virulence []. Consistent with this speculation, the SspA-1 knockout mutant exhibited attenuated virulence in both murine and pig infection models [,]. Compared with the WT strain, the mutant induced much lower levels of interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin 12p70 in mice; treatment of THP-1 cells with purified recombinant SspA-1 resulted in massive production of these cytokines. These results suggested that SspA-1 plays an important role as a trigger of proinflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, the reaction of SspA-1 with convalescent-phase pig sera revealed that SspA-1 might be a protective antigen. As expected, immunization of mice with SspA-1 elicited a specific immune response, producing a SspA-1 specific antibody that protected mice against S. suis infection [].
The subtilisin-like serine protease-2 (SspA-2) was identified by screening a S. suis mutant library to isolate mutants deficient in proteinase activity. The sspA-2 gene was present in all detected S. suis strains, including serotype 2 and other serotypes []. Different from SspA-1, the secretion of SspA-2 was not affected by T4SS []. A contribution of SspA-2 to the pathogenesis of S. suis has been revealed by several lines of evidence. Firstly, the recombinant SspA-2 displayed toxicity against brain microvascular endothelial cells. Secondly, SspA-2 could react with convalescent-phase pig sera, suggesting that it is expressed during infection []. Thirdly, the SspA-2 inactive mutant was more susceptible to killing by human whole blood. Fourthly, mice infected with the mutant had a lower mortality rate than those infected with the WT strain []. Finally, SspA-2 induced a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages, which might promote meningitis [].
6. Superoxide Dismutase and NADH Oxidase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD), usually coupled with a metal cofactor, can catalyze the reaction of superoxide to oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, and it is involved in oxidative stress resistance and virulence in many bacterial species []. In S. suis, manganese, instead of iron, is required for the activity of SOD []. The sod gene deletion mutant loses its SOD activity, and it is more sensitive to hydrogen peroxide and paraquat-induced oxidative stress. The mutant also shows decreased survival in RAW264.7 macrophages, attenuated virulence in mice, and an impaired ability to colonize the tissues of mice []. Subsequently, further studies demonstrated that the involvement of SOD in anti-autophagic responses was mediated by the scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in infected macrophages []. Superoxide dismutase appeared to be regulated by the two-component system Ihk/Irr and the SpxA1 regulator in S. suis, since expression of the sod gene was significantly down-regulated in the Ihk/Irr and spxA1 deletion mutants [,].
NADH oxidase (Nox) can catalyze the reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide or water, combined with the oxidation of NADH to NAD+ in bacteria []. In Streptococcus mutans, there are two nox genes, i.e., nox-1 and nox-2, which encode a hydrogen peroxide-forming Nox-1 and a water-forming Nox-2, respectively []. However, only one Nox, either Nox-1 or Nox-2, is present in many other bacterial species. For example, Mycoplasma bovis possesses Nox-1 [], whereas Streptococcus pneumoniae, Group B Streptococcus, and Streptococcus sanguinis possess Nox-2 [,,]. In S. suis, a homolog of Nox-2 was identified to be regulated by the SpxA1 regulator []. The nox gene deletion mutant displayed reduced tolerance to oxidative stress induced by environmental oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and SIN-1. Deletion of nox resulted in attenuated virulence in S. suis in both murine and pig infection models []. Very recently, in vivo transcriptome analysis and coinfection experiments further confirmed the involvement of Nox in S. suis virulence []. In addition, it was demonstrated that the enzymatic activity of Nox contributed significantly to oxidative stress resistance, and to a lesser extent, to the virulence of S. suis []. Given that Nox of S. pneumoniae elicits a protective immune response in mice, S. suis Nox may have vaccine potential.
7. Nucleases
Two nucleases, i.e., SsnA and EndAsuis, have been intensively studied in S. suis [,,,,]. SsnA possesses a secretion signal peptide sequence at the N-terminus and a cell wall anchoring motif (LPKTG) at the C-terminus [,]. In accordance with its structure, SsnA is cell-wall located, with a portion secreted into the supernatant []. SsnA targets single- and double-stranded linear DNA, and its activity is dependent on Ca2+ and Mg2+ [,]. Reverse transcription-PCR analysis showed that the ssnA gene is expressed throughout the S. suis growth stages and western blotting revealed that SsnA is expressed during infection. Results from different research teams all demonstrated that SsnA plays a role in the pathogenesis of S. suis. Fontaine et al. showed that most of the S. suis field strains isolated from internal organs displayed a nuclease phenotype, whereas less than half of the surface isolates exhibited the same phenotype []. Consistently, comparative proteomics analysis revealed that SsnA is expressed in a virulent S. suis 9 strain, but is absent in an avirulent strain []. Haas et al. found that a DNase-deficient mutant, in which transposon Tn917 was inserted into the ssnA gene, exhibited attenuated virulence in an amoeba model and induced lower levels of cytokines and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in a macrophage model []. de Buhr et al. demonstrated that SsnA is involved in the degradation of human and porcine neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), thus protecting S. suis against the antimicrobial activity mediated by NETs []. Recently, Li et al. confirmed the role of SsnA in S. suis virulence. The ssnA deletion mutant showed markedly decreased adherence to and invasion of HEp-2 cells. Deletion of ssnA in S. suis led to attenuated virulence in a CD1 mouse infection model []. The recombinant SsnA protein could elicit a significant immune response in mice and pigs. However, only mice were protected against S. suis challenge [,].
EndAsuis is a novel nuclease of S. suis that showed a high level of homology to the pneumococcal endonuclease A. EndAsuis is cell membrane-anchored, and its activity could not be detected in the supernatant. In contrast to SsnA, the activity of EndAsuis is dependent on Mg2+, but not on Ca2+. Interestingly, although EndAsuis is involved in the degradation of NETs, the endAsuis deletion mutant exhibited no significant difference in resistance to the antimicrobial activity mediated by neutrophils or NETs compared to the parent strain []. Further studies are necessary to elucidate the role of EndAsuis in the pathogenesis of S. suis.
8. Enolase
Enolase of S. suis has attracted a lot of attention since it was first identified. Enolase could bind to extracellular matrix components, including fibronectin, plasminogen, fibrinogen, and laminin [,,,], which further promotes S. suis adhesion to and invasion of host cells. Moreover, the involvement of enolase in S. suis adhesion to host cells has been clearly demonstrated using various methods [,,,,]. Through interactions with human fibrinogen, enolase contributes to S. suis resistance to phagocytosis by neutrophils, thus enhancing S. suis survival in human blood []. In addition, S. suis enolase plays a role in disrupting the integrity of the blood-brain barrier by inducing interleukin-8 release []. Very recently, enolase of S. suis was identified to be a pig and human IgG-binding protein, and the two binding domains in the C-terminal exhibited specificity to interact with pig and human IgGs [].
While there is no debate about the role of enolase in the pathogenesis of S. suis, the subcellular localization and vaccine potential of enolase appear to be strongly controversial. Feng et al. showed that S. suis enolase is a cell surface protein using multiple approaches, whereas Esgleas et al. reported that enolase is present in the supernatant, cell wall, and cytoplasm [,]. Recently, Liu et al. showed that enolase was significantly increased in both secreted and surface-associated fractions of the prsA deletion mutant []. Based on these results, we speculate that after synthesis in the cell, enolase can be transported to the cell surface of S. suis, with a portion secreted to the supernatant. It is worth noting that studies carried out by different research teams obtained opposite results regarding the protective ability of enolase against S. suis infection in mice, despite a strong antibody response being induced following immunization with this protein [,,,]. Considering that these studies were conducted using a mouse infection model, further studies using the natural host of S. suis (pig) are still required.
9. S-ribosylhomocysteinase (LuxS)
LuxS is one of the enzymes required for the production of autoinducer-2 (AI-2, a signal molecule involved in quorum sensing), although the transcription level of luxS is not correlated with AI-2 production [,]. In S. suis, expression of luxS is positively regulated by small RNA rss04 []. The functions of LuxS in the physiology and pathogenesis of S. suis have been extensively studied. Figure 1 shows the gene regulation and functions of LuxS in S. suis. Deletion of luxS in S. suis led to various phenotypic changes, including impaired growth, decreased biofilm formation and hemolytic activity, reduced adherence to epithelial cells, thinner capsular, enhanced resistance to hydrogen peroxide, and increased susceptibility to fluoroquinolones [,,]. The luxS deletion mutant also displayed attenuated virulence in both zebrafish and piglet infection models. The contribution of LuxS to the pathogenicity of S. suis might be partly due to its positive regulation of several virulence-associated genes [,]. The involvement of S. suis LuxS in the resistance to fluoroquinolones is mediated by regulating the fluoroquinolone efflux pump SatAB [].
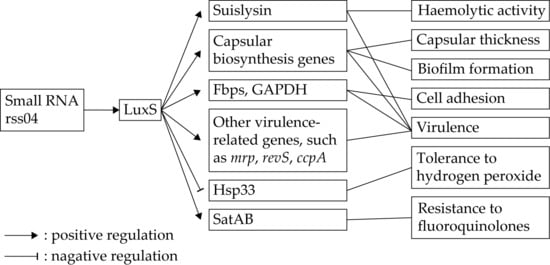
Figure 1.
Gene regulation and functions of S-ribosylhomocysteinase (LuxS) in S. suis. LuxS is positively regulated by small RNA rss04. LuxS regulates the expression of multiple genes associated with various phenotypes of S. suis.
10. Peptidyl Isomerase PrsA
The peptidyl isomerase PrsA is a potential substrate of the type IV-like secretion system (T4SS) in S. suis. Deletion of the T4SS component VirD4 resulted in significant down-regulation of PrsA in secreted proteins upon exposure to hydrogen peroxide. PrsA exhibited significant cytotoxicity to bEnd.3 cells and induced production of proinflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 cells []. It has also been demonstrated that PrsA is expressed in intracellular, surface-associated and secreted proteins. The prsA gene is highly conserved among S. suis strains, and immunization with PrsA induced antibody responses in mice and conferred protection against both S. suis 2 and S. suis 9 challenges []. Recently, the role of PrsA in the pathogenesis of S. suis has been partly elucidated. Deletion of prsA resulted in increased chain length, decreased growth, enhanced adhesion to but weakened invasion of host epithelial cells, reduced survival in RAW264.7 cells and pig whole blood, and attenuated virulence in mice. Suilysin, a virulence factor involved in the hemolytic activity of S. suis, was markedly reduced in surface-associated and secreted proteins of the prsA gene deletion mutant. In contrast, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and enolase, two adhesion-associated factors of S. suis, were significantly increased []. These results suggested that PrsA could be involved in the secretion of selected virulence factors, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of S. suis.
11. (p)ppGpp Synthetases
The alarmones guanosine tetraphosphate and guanosine pentaphosphate, collectively termed (p)ppGpp, are involved in the regulation of growth and stress responses in bacteria. (p)ppGpp synthetases play a key role in controlling the cellular levels of (p)ppGpp []. There are two (p)ppGpp synthetases, i.e., RelA and RelQ, in S. suis. Simultaneous deletion of RelA and RelQ resulted in different phenotypes and attenuated pathogenicity compared to the wild type S. suis strain. The mutant exhibited a longer chain, a reduced ability to adhere to and invade HEp-2 cells, decreased resistance to blood killing and phagocytosis by THP-1 cells, attenuated virulence in mice, and ensured easier clean-up in mouse tissues. Moreover, the expression of several virulence factors was down-regulated in the mutant, suggesting that (p)ppGpp synthetases could modulate virulence genes expression in S. suis []. Zhang et al. further explored the role of individual (p)ppGpp synthetases in the stringent response induced by glucose starvation. The results showed that only RelA plays a role in the adaptation to glucose starvation. Transcriptome analysis revealed that RelA is involved in the regulation of protein synthesis, DNA replication, cell division and growth, cell wall/membrane biogenesis, carbohydrate transport, glycolysis, and carbon catabolite in S. suis []. Recently, it was shown that the CodY regulator could bind to the promoter of relA in a manner independent of GTP, and the expression of relA was positively regulated by CodY in S. suis [].
12. Conclusions
S. suis remains one of the most severe swine bacterial pathogens and it is a serious threat to public health. Understanding of the physiology and pathogenesis of S. suis undoubtedly contributes to the control of its infections. This review highlights the role of various enzymes in the physiology and pathogenesis of S. suis. Many enzymes have a role, either confirmed or potential, in the physiology and pathogenesis of S. suis, despite only some representative enzymes being introduced here. It should be noted that previous studies were mainly carried out in S. suis 2. Since some enzymes are present in various serotypes of S. suis, further investigation of these enzymes in other serotypes of S. suis should be performed. For certain enzymes, the controversial results obtained from different teams need to be clarified. Given that enzymes play important roles in a wide variety of intracellular processes, a promising approach is to design novel antimicrobial drugs targeted to certain enzymes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z.; investigation, C.Z., M.W., M.J., and M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.W., M.J., and M.C.; supervision, C.Z.; project administration, C.Z.; funding acquisition, C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31802210), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M630615), and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (18KJB230007).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, Z.R.; Wang, Q.P.; Chen, X.G.; Li, A.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Streptococcus suis: An emerging zoonotic pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ku, X.; Yu, X.; Sun, Q.; Wu, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Tang, X.; He, Q. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibilities of bacterial pathogens in Chinese pig farms from 2013 to 2017. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, H.F.; Nghia, H.D.; Taylor, W.; Schultsz, C. Streptococcus suis: An emerging human pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e151. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Jing, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Zu, R.; Luo, L.; et al. Human Streptococcus suis outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Guo, J.; Cheng, C.; Gu, B. Human infection caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in China: Report of two cases and epidemic distribution based on sequence type. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Ma, C.; Li, C.H. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis due to Streptococcus suis in a 12-year-old girl A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e15136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayanakorn, A.; Katip, W.; Lee, L.H.; Oberdorfer, P. Endophthalmitis with bilateral deafness from disseminated Streptococcus suis infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e228501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, A.; Knausz, M.; Schmidt, P. Special case of purulent meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis. Case report. Orv. Hetil. 2019, 160, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yanase, T.; Morii, D.; Kamio, S.; Nishimura, A.; Fukao, E.; Inose, Y.; Honma, Y.; Kitahara, N.; Yokozawa, T.; Chang, B.; et al. The first report of human meningitis and pyogenic ventriculitis caused by Streptococcus suis: A case report. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis virulence factors: Are they all really critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, R.; Gottschalk, M.; Boudreau, M.; Lebrun, A.; Henrichsen, J. Description of six new capsular types (29-34) of Streptococcus suis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1995, 7, 405–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.E.; Gottschalk, M.; Brousseau, R.; Harel, J.; Hemmingsen, S.M.; Goh, S.H. Biochemical analysis, cpn60 and 16S rDNA sequence data indicate that Streptococcus suis serotypes 32 and 34, isolated from pigs, are Streptococcus orisratti. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 107, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien le, H.T.; Nishibori, T.; Nishitani, Y.; Nomoto, R.; Osawa, R. Reappraisal of the taxonomy of Streptococcus suis serotypes 20, 22, 26, and 33 based on DNA-DNA homology and sodA and recN phylogenies. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, R.; Maruyama, F.; Ishida, S.; Tohya, M.; Sekizaki, T.; Osawa, R. Reappraisal of the taxonomy of Streptococcus suis serotypes 20, 22 and 26: Streptococcus parasuis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohya, M.; Arai, S.; Tomida, J.; Watanabe, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Katsumi, M.; Ushimizu, M.; Ishida-Kuroki, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Uzawa, Y.; et al. Defining the taxonomic status of Streptococcus suis serotype 33: The proposal for Streptococcus ruminantium sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3660–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Calzas, C.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Initial steps of the pathogenesis of the infection caused by Streptococcus suis: Fighting against nonspecific defenses. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 3772–3799. [Google Scholar]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Segura, M.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, M.; Lu, T.; Gao, M.; Li, L. CopA Protects Streptococcus suis against copper toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, M.; Gao, M.; Lu, T.; Li, L.; Zhou, P. PmtA functions as a ferrous iron and cobalt efflux pump in Streptococcus suis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.F.; Gao, T.; Liu, W.Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.W.; Teng, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. MsmK, an ATPase, contributes to utilization of multiple carbohydrates and host colonization of Streptococcus suis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.F.; Liu, W.Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Gao, T.; Zheng, L.L.; Qiu, D.X.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. The involvement of MsmK in pathogenesis of the Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seele, J.; Singpiel, A.; Spoerry, C.; von Pawel-Rammingen, U.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. Identification of a novel host-specific IgM protease in Streptococcus suis. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seele, J.; Beineke, A.; Hillermann, L.M.; Jaschok-Kentner, B.; von Pawel-Rammingen, U.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. The immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis, IdeSsuis, is involved in complement evasion. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungelrath, V.; Weisse, C.; Schutze, N.; Muller, U.; Meurer, M.; Rohde, M.; Seele, J.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Kirschfink, M.; Beineke, A.; et al. IgM cleavage by Streptococcus suis reduces IgM bound to the bacterial surface and is a novel complement evasion mechanism. Virulence 2018, 9, 1314–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoerry, C.; Seele, J.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G.; von Pawel-Rammingen, U. Identification and characterization of IgdE, a novel IgG-degrading protease of Streptococcus suis with unique specificity for porcine IgG. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7915–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Mu, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Han, L.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Identification and characterization of IgA1 protease from Streptococcus suis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.D.; Mu, X.F.; Chen, B.; Han, L.; Chen, H.C.; Jin, M.L. IgA1 protease contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bek-Thomsen, M.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M. Occurrence and evolution of the paralogous zinc metalloproteases IgA1 protease, ZmpB, ZmpC, and ZmpD in Streptococcus pneumoniae and related commensal species. mBio 2012, 3, e00303-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumesnil, A.; Auger, J.P.; Roy, D.; Votsch, D.; Willenborg, M.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Park, P.W.; Grenier, D.; Fittipaldi, N.; Harel, J.; et al. Characterization of the zinc metalloprotease of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.; Ni, Y.; Yu, Z.; Mao, A.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wen, L.; Li, B.; et al. Contribution of eukaryotic-type serine/threonine kinase to stress response and virulence of Streptococcus suis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Tan, M.; Dong, M.; Liu, W.; Gao, T.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, R. The eukaryote-like serine/threonine kinase STK regulates the growth and metabolism of zoonotic Streptococcus suis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, L.; Weiyi, L.; Yu, M.; Hong, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhe, M.; Hongjie, F. The serine/threonine protein kinase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 affects the ability of the pathogen to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Cell Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, M.; Lu, C. The novel virulence-related gene stp of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 strain contributes to a significant reduction in mouse mortality. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 51, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, J.; Fan, P.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.; Fang, W. A serine/threonine phosphatase 1 of Streptococcus suis type 2 is an important virulence factor. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, P.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Teng, L.; Zhou, M.; Bei, W.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Identification of a cell wall-associated subtilisin-like serine protease involved in the pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 48, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Li, M.; Rao, X.; Yao, X.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y.; Tang, J.; Hu, F.; et al. Subtilisin-like protease-1 secreted through type IV secretion system contributes to high virulence of Streptococcus suis 2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27369. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifait, L.; de la Cruz Dominguez-Punaro, M.; Vaillancourt, K.; Bart, C.; Slater, J.; Frenette, M.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. The cell envelope subtilisin-like proteinase is a virulence determinant for Streptococcus suis. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifait, L.; Vaillancourt, K.; Gottschalk, M.; Frenette, M.; Grenier, D. Purification and characterization of the subtilisin-like protease of Streptococcus suis that contributes to its virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifait, L.; Grenier, D. The SspA subtilisin-like protease of Streptococcus suis triggers a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages through a non-proteolytic mechanism. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, W.; Lu, Z.Y.; Fang, W.H. Inactivation of the sodA gene of Streptococcus suis type 2 encoding superoxide dismutase leads to reduced virulence to mice. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.H.; Shen, H.X.; Tang, Y.L.; Fang, W.H. Superoxide dismutase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 plays a role in anti-autophagic response by scavenging reactive oxygen species in infected macrophages. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Ren, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Shi, G.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Bei, W. Contribution of NADH oxidase to oxidative stress tolerance and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Virulence 2017, 8, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, J.; Bossers-de Vries, R.; Harders-Westerveen, J.; Buys, H.; Ruuls-van Stalle, L.M.F.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Zaccaria, E.; Tommassen, J.; Wells, J.M.; Smith, H.E.; et al. In vivo transcriptomes of Streptococcus suis reveal genes required for niche-specific adaptation and pathogenesis. Virulence 2019, 10, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.; Bonifait, L.; Vaillancourt, K.; Charette, S.J.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. Characterization of DNase activity and gene in Streptococcus suis and evidence for a role as virulence factor. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Buhr, N.; Neumann, A.; Jerjomiceva, N.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Baums, C.G. Streptococcus suis DNase SsnA contributes to degradation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and evasion of NET-mediated antimicrobial activity. Microbiology 2014, 160, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cai, R.J.; Li, C.L.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Yang, D.X. Deletion of ssnA attenuates the pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis and confers protection against serovar 2 strain challenge. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Buhr, N.; Stehr, M.; Neumann, A.; Naim, H.Y.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Baums, C.G. Identification of a novel DNase of Streptococcus suis (EndAsuis) important for neutrophil extracellular trap degradation during exponential growth. Microbiology 2015, 161, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esgleas, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Hancock, M.A.; Harel, J.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Gottschalk, M. Isolation and characterization of alpha-enolase, a novel fibronectin-binding protein from Streptococcus suis. Microbiol-SGM 2008, 154, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lu, H.; Qi, J.X.; Lu, G.W.; Gao, G.F. An octamer of enolase from Streptococcus suis. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pian, Y.Y.; Wang, P.P.; Liu, P.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.L.; Xu, B.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Y.Q. Proteomics identification of novel fibrinogen-binding proteins of Streptococcus suis contributing to antiphagocytosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, H.Z.; Du, D.C.; Yu, Y.F.; Ma, C.F.; Jiao, F.F.; Yao, H.C.; Lu, C.P.; Zhang, W. Identification of novel laminin- and fibronectin-binding proteins by far-western blot: Capturing the adhesins of Streptococcus suis type 2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, A.; Xu, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Large-scale identification of bacteria-host crosstalk by affinity chromatography: Capturing the interactions of Streptococcus suis proteins with host cells. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5163–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Chen, B.; Mu, X.; Li, R.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Identification and characterization of a novel protective antigen, enolase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.J.; Pan, X.Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, X.F.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Z.Q.; Ge, J.C.; Zheng, F.; et al. Streptococcus suis enolase functions as a protective antigen displayed on the bacterial cell surface. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.T.; Liu, J.F.; Xia, X.J.; Sun, C.J.; Feng, X.; Gu, J.M.; Du, C.T.; et al. Enolase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 enhances blood-brain barrier permeability by inducing IL-8 release. Inflammation 2016, 39, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fu, Y.; Guo, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W. Identification of novel pig and human immunoglobulin G-binding proteins and characterization of the binding regions of enolase from Streptococcus suis serotype 2. AMB Express 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Lu, C. Functional analysis of luxS in Streptococcus suis reveals a key role in biofilm formation and virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Zheng, F.; Li, M.; Liao, H.; Mao, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, D.; et al. Functional definition of LuxS, an autoinducer-2 (AI-2) synthase and its role in full virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Gong, S.; Dong, X.; Mao, C.; Yi, L. LuxS/AI-2 system is involved in fluoroquinolones susceptibility in Streptococcus suis through overexpression of efflux pump SatAB. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 233, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Roles of the putative type IV-like secretion system key component VirD4 and PrsA in pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis type 2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Liao, X.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Peptidyl isomerase PrsA is surface-associated on Streptococcus suis and offers cross-protection against serotype 9 strain. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Jiang, X.; Liao, X.; Yue, M.; Li, X.; Fang, W. PrsA contributes to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 pathogenicity by modulating secretion of selected virulence factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Su, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Xiao, R.; Teng, M.; Tan, M.; Zhou, R. (p)ppGpp synthetases regulate the pathogenesis of zoonotic Streptococcus suis. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 191, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Luo, Q.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Tucker, A.; Shao, H.; Zhou, R. The roles of RelA/(p)ppGpp in glucose-starvation induced adaptive response in the zoonotic Streptococcus suis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrakul, K.; Loo, C.Y.; Hughes, C.V.; Ganeshkumar, N. Role of a Streptococcus gordonii copper-transport operon, copYAZ, in biofilm detachment. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 19, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solioz, M.; Abicht, H.K.; Mermod, M.; Mancini, S. Response of gram-positive bacteria to copper stress. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 15, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquethamy, S.F.; Khorvash, M.; Pederick, V.G.; Whittall, J.J.; Paton, J.C.; Paulsen, I.T.; Hassan, K.A.; McDevitt, C.A.; Eijkelkamp, B.A. The Role of the CopA copper efflux system in Acinetobacter baumannii virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafeeq, S.; Yesilkaya, H.; Kloosterman, T.G.; Narayanan, G.; Wandel, M.; Andrew, P.W.; Kuipers, O.P.; Morrissey, J.A. The cop operon is required for copper homeostasis and contributes to virulence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 81, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, H.L.; Patel, S.J.; Arguello, J.M.; Helmann, J.D. The Listeria monocytogenes Fur-regulated virulence protein FrvA is an Fe(II) efflux P1B4-type ATPase. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 100, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWal, A.R.; Makthal, N.; Pinochet-Barros, A.; Helmann, J.D.; Olsen, R.J.; Kumaraswami, M. Iron efflux by PmtA is critical for oxidative stress resistance and contributes significantly to Group A Streptococcus virulence. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00091-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, C.; Aten, A.E.; Woodiga, S.A.; King, S.J. Identification of an ATPase, MsmK, which energizes multiple carbohydrate ABC transporters in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4193–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seele, J.; Hillermann, L.M.; Beineke, A.; Seitz, M.; von Pawel-Rammingen, U.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. The immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis, Ide(Ssuis), is a highly protective antigen against serotype 2. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Zhao, J.Q.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.M.; Han, L.; Xie, C.Y.; Zhou, R.; Jin, M.L.; Zhang, A.D. Characterization of IgA1 protease as a surface protective antigen of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patenge, N.; Fiedler, T.; Kreikemeyer, B. Common regulators of virulence in streptococci. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 368, 111–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.; Fan, W.W.; Li, C.L.; Wu, Q.Q.; Hongfen, H.F.; Hui, D.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, X.H.; Wang, C.J.; Cao, X.R.; et al. Streptococcus suis DivIVA protein is a substrate of Ser/Thr kinase STK and involved in cell division regulation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzman, S.S.; Culotta, V.C. Chemical warfare at the microorganismal level: A closer look at the superoxide dismutase enzymes of pathogens. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niven, D.F.; Ekins, A.; Al-Samaurai, A.A.W. Effects of iron and manganese availability on growth and production of superoxide dismutase by Streptococcus suis. Can. J. Microbiol. 1999, 45, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.M.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, Q.H.; Xuan, C.L.; Zheng, B.W.; Tang, J.Q.; Yan, J.H.; Zhang, J.R.; Li, M.; Cheng, H.; et al. The two-component system Ihk/Irr contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strain 05ZYH33 through alteration of the bacterial cell metabolism. Microbiol-SGM 2012, 158, 1852–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.K.; Xu, J.L.; Li, J.Q.; Hu, L.H.; Xia, J.D.; Fan, J.Y.; Guo, W.N.; Chen, H.C.; Bei, W.C. Two Spx regulators modulate stress tolerance and virulence in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108197. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.H.; Elrami, F.; Kong, F.X.; Kitten, T.; Xu, P. Involvement of NADH oxidase in competition and endocarditis virulence in Streptococcus sanguinis. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Poole, L.B.; Shimada, M.; Sato, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Kamio, Y. Functions of two types of NADH oxidases in energy metabolism and oxidative stress of Streptococcus mutans. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5940–5947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.F.; Guo, Y.S.; He, C.F.; Khan, F.A.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, H.C.; et al. Mycoplasma bovis NADH oxidase functions as both a NADH oxidizing and O2 reducing enzyme and an adhesin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auzat, I.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Le Bras, G.; Dos Santos, D.; Ogunniyi, A.D.; Le Thomas, I.; Garel, J.R.; Paton, J.C.; Trombe, M.C. The NADH oxidase of Streptococcus pneumoniae: Its involvement in competence and virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Pargade, V.; Lamberet, G.; Gaudu, P.; Thomas, F.; Texereau, J.; Gruss, A.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Poyart, C. The Group B Streptococcus NADH oxidase Nox-2 is involved in fatty acid biosynthesis during aerobic growth and contributes to virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 772–785. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, M.C.; Perez-Casal, J.; Willson, P.J. Investigation of a novel DNase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 774–781. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Comparative proteome analysis of secreted proteins of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 isolates from diseased and healthy pigs. Microbial. Pathog. 2008, 45, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Gascon, L.; Cardoso-Toset, F.; Tarradas, C.; Gomez-Laguna, J.; Maldonado, A.; Nielsen, J.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Rodriguez-Ortega, M.J.; Luque, I. Characterization of the immune response and evaluation of the protective capacity of rSsnA against Streptococcus suis infection in pigs. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 47, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Gascon, L.; Cardoso-Toset, F.; Amarilla, P.S.; Tarradas, C.; Carrasco, L.; Olaya-Abril, A.; Jimenez-Munguia, I.; Rodriguez-Ortega, M.J.; Luque, I. A new recombinant SsnA protein combined with aluminum hydroxide protects mouse against Streptococcus suis. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6992–6999. [Google Scholar]
- Esgleas, M.; Dominguez-Punaro, M.D.; Li, Y.Y.; Harel, J.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Gottschalk, M. Immunization with SsEno fails to protect mice against challenge with Streptococcus suis serotype 2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumesnil, A.; Martelet, L.; Grenier, D.; Auger, J.P.; Harel, J.; Nadeau, E.; Gottschalk, M. Enolase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV protein sub-unit vaccines are not protective against a lethal Streptococcus suis serotype 2 challenge in a mouse model of infection. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 448. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.G.; Lu, C.P. Detection of autoinducer-2 and analysis of the profile of luxS and pfs transcription in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, H.; Cheng, X.; Lu, C. Overexpression of luxS cannot increase autoinducer-2 production, only affect the growth and biofilm formation in Streptococcus suis. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 924276. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Tang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Dai, J.; Lai, L.; Lu, C.; Yao, H.; Fan, H.; Wu, Z. Streptococcus suis small RNA rss04 contributes to the induction of meningitis by regulating capsule synthesis and by inducing biofilm formation in a mouse infection model. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauryliuk, V.; Atkinson, G.C.; Murakami, K.S.; Tenson, T.; Gerdes, K. Recent functional insights into the role of (p)ppGpp in bacterial physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Su, Z.; Feng, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, T.; Shao, H.; Zhou, R. Co-regulation of CodY and (p)ppGpp synthetases on morphology and pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 223–225, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).