Reproductive Disorders and Leptospirosis: A Case Study in a Mixed-Species Farm (Cattle and Swine)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.1.1. Cattle: Reproductive Performance
2.1.2. Cattle Sample Size
2.1.3. Pigs
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Strain and Culture Conditions
2.4. Serum Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
2.5. Diagnostic Real-Time PCR for Leptospirosis
2.6. Diagnostic Real-Time PCR for Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) and Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV)
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Farm at the Time of Study
- Cattle herd: 107 animals with age and sex distribution as indicated in Table 1, Holstein–Friesian breed. On average, 50 lactating cows;
- Sow unit: 140 animals. Record-keeping of the sanitary parameters in this herd was not provided.
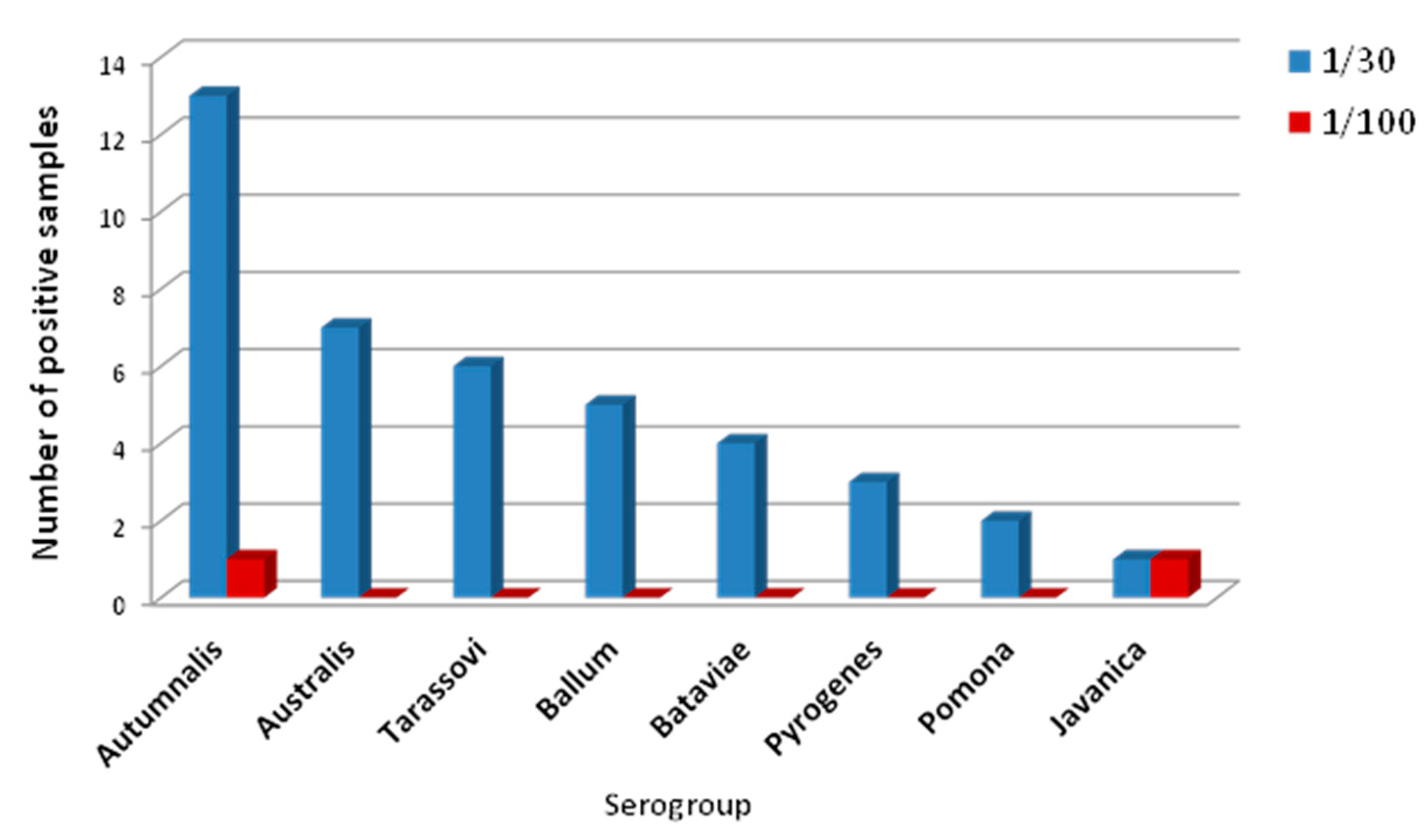
3.2. Seroprevalence and Bacteriology of Leptospira within the Cattle Population
3.3. Seroprevalence of Leptospira Antibodies in Sows
3.4. Carriage of Leptospira in Aborted Piglets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fornazari, F.; da Silva, R.C.; Richini-Pereira, V.B.; Beserra, H.E.; Luvizotto, M.C.; Langoni, H. Comparison of conventional PCR, quantitative PCR, bacteriological culture and the Warthin Starry technique to detect Leptospira spp. in kidney and liver samples from naturally infected sheep from Brazil. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 90, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Boer, K.R.; Goeijenbier, M.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; Wagenaar, J.F.P.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Establishment of Valid Laboratory Case Definition for Human Leptospirosis. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2012, 3, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, K.C.; Greig, D.J.; Alt, D.P.; Galloway, R.L.; Hornsby, R.L.; Palmer, L.J.; Soper, J.; Wu, Q.; Zuerner, R.L.; Gulland, F.M.; et al. Asymptomatic and chronic carriage of Leptospira interrogans serovar Pomona in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamond, C.; Martins, G.; Loureiro, A.P.; Pestana, C.; Lawson-Ferreira, R.; Medeiros, M.A.; Lilenbaum, W. Urinary PCR as an increasingly useful tool for an accurate diagnosis of leptospirosis in livestock. Vet. Res. Commun. 2014, 38, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. Leptospirosis. In OIE Terrestrial Manual 2014; OIE: Paris, France, 2014; Chapter 2.1.9. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, A.M.; Callanan, J.J.; Nally, J.E. Review paper: Host-pathogen interactions in the kidney during chronic leptospirosis. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayral, F.C.; Bicout, D.J.; Pereira, H.; Artois, M.; Kodjo, A. Distribution of Leptospira serogroups in cattle herds and dogs in France. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard, R.A.; Gee, J.E.; Wilkins, P.P.; McCaustland, K.; Hoffmaster, A.R. Detection of pathogenic Leptospira spp. through TaqMan polymerase chain reaction targeting the LipL32 gene. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 64, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothikumar, N.; Cromeans, T.L.; Robertson, B.H.; Meng, X.J.; Hill, V.R. A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.; Riera, P.; Sitjà, M.; Fang, Y.; Oliveira, S.; Maldonado, J. Simultaneous detection and genotyping of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) by real-time RT-PCR and amplicon melting curve analysis using SYBR Green. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 85, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, G.S.; Murray, R.D.; Dobson, H.; Montgomery, J.; Ellis, W.A. Reduced conception rates in dairy cattle associated with serological evidence of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo infection. Vet. Rec. 1996, 139, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.C.; Souza, G.N.; Lilenbaum, W. Influence of leptospirosis on reproductive performance of sows in Brazil. Theriogenology 2006, 66, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, G.S.; Murray, R.D.; Ellis, W.A. Reproductive performance of dairy herds infected with Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo relative to the year of diagnosis. Vet. Rec. 1996, 138, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, W.A. Animal leptospirosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 99–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellis, W.A.; O’Brien, J.J.; Bryson, D.G.; Mackie, D.P. Bovine leptospirosis: Some clinical features of serovar hardjo infection. Vet. Rec. 1985, 117, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, W.A.; O’Brien, J.J.; Neill, S.D.; Hanna, J. Bovine leptospirosis: Serological findings in aborting cows. Vet. Rec. 1982, 110, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappel, R.J.; Millar, B.D.; Adler, B.; Hill, J.; Jeffers, M.J.; Jones, R.T.; McCaughan, C.J.; Mead, L.J.; Skilbeck, N.W. Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo is not a major cause of bovine abortion in Victoria. Aust. Vet. J. 1989, 66, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, B.; de la Pena Moctezuma, A. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, B.R.; Narduche, L.; Oliveira, C.S.; Martins, G.; Lilenbaum1, W. Molecular demonstration of intermittent shedding of Leptospira in cattle and sheep and its implications on control. Cienc. Rural 2017, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Bauer, N.E.; Rodgers, S.; Bazan, L.R.; Mesenbrink, B.T.; Gidlewski, T. Antibodies to Various Zoonotic Pathogens Detected in Feral Swine (Sus scrofa) at Abattoirs in Texas, USA. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliabue, S.; Figarolli, B.M.; D’Incau, M.; Foschi, G.; Gennero, M.S.; Giordani, R.; Natale, A.; Papa, P.; Ponti, N.; Scaltrito, D.; et al. Serological surveillance of Leptospirosis in Italy: Two-year national data (2010–2011). Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miraglia, F.; Moreno, L.Z.; Morais, Z.M.; Langoni, H.; Shimabukuro, F.H.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Hartskeerl, R.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Moreno, A.M. Characterization of Leptospira interrogans serovar Pomona isolated from swine in Brazil. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2015, 9, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, P.S.; Libonati, H.; Lilenbaum, W. A systematic review of leptospirosis on dogs, pigs, and horses in Latin America. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, A.; Rodriguez, V.; Mattar, S.; Arrieta, G. Leptospirosis in pigs, dogs, rodents, humans, and water in an area of the Colombian tropics. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2014, 46, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Khong, N.V.; Xuan, H.N.; Nghia, V.B.; Nguyen-Viet, H.; Grace, D. Sero-prevalence of specific Leptospira serovars in fattening pigs from 5 provinces in Vietnam. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, T. A review of leptospirosis in farm animals in Portugal. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1998, 17, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre-Fontaine, G. Leptospirosis in domestic animals in France: Serological results from 1988 to 2007. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2016, 35, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercovich, Z.; Spek, C.W.; Comvalius-Adriaan, I. The occurrence of antibodies to various Leptospira serotypes in swine in The Netherlands in the period 1975–1980. Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd. 1983, 108, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.; van Treeck, U.; Lierz, M.; Espelage, W.; Zota, L.; Sarbu, A.; Czerwinski, M.; Sadkowska-Todys, M.; Avdicová, M.; Reetz, J.; et al. Resurgence of field fever in a temperate country: An epidemic of leptospirosis among seasonal strawberry harvesters in Germany in 2007. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.L.; Smythe, L.D.; Craig, S.B.; Weinstein, P. Climate change, flooding, urbanisation and leptospirosis: Fuelling the fire? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledien, J.; Sorn, S.; Hem, S.; Huy, R.; Buchy, P.; Tarantola, A.; Cappelle, J. Assessing the performance of remotely-sensed flooding indicators and their potential contribution to early warning for leptospirosis in Cambodia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frawley, A.A.; Schafer, I.J.; Galloway, R.; Artus, A.; Ratard, R.C. Notes from the Field: Postflooding Leptospirosis—Louisiana, 2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 1158–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Age | Male | Female | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Younger than 6 months | 0 | 9 | 9 |
| Between 6 and 12 months | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Between 12 and 24 months | 0 | 21 | 21 |
| Older than 24 months | 1 | 74 | 75 |
| Total | 1 | 106 | 107 |
| Fœtuses | 1st Litter | 2nd Litter | Ct or Average Ct | Range (Min-Max) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |||
| Bacteriology | |||||||||||
| Kidneys | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | 35.7 | 34.4–38.0 |
| Liver | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | 38.6 | NA |
| Spleen | nc | nc | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | 32.5 | 30.9–33.4 |
| Lungs | nc | nc | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 38.4 | NA |
| Serology | |||||||||||
| MAT 12 | 1/30 Ballum, Javanica, Australis, Autumnalis, Tarassovi | 1/10 Ballum, Javanica, Australis, Autumnalis, Tarassovi | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | NA | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mori, M.; Bakinahe, R.; Vannoorenberghe, P.; Maris, J.; De Jong, E.; Tignon, M.; Marin, M.; Desqueper, D.; Fretin, D.; Behaeghel, I. Reproductive Disorders and Leptospirosis: A Case Study in a Mixed-Species Farm (Cattle and Swine). Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040064
Mori M, Bakinahe R, Vannoorenberghe P, Maris J, De Jong E, Tignon M, Marin M, Desqueper D, Fretin D, Behaeghel I. Reproductive Disorders and Leptospirosis: A Case Study in a Mixed-Species Farm (Cattle and Swine). Veterinary Sciences. 2017; 4(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMori, Marcella, Raïssa Bakinahe, Philippe Vannoorenberghe, Jo Maris, Ellen De Jong, Marylène Tignon, Martine Marin, Damien Desqueper, David Fretin, and Isabelle Behaeghel. 2017. "Reproductive Disorders and Leptospirosis: A Case Study in a Mixed-Species Farm (Cattle and Swine)" Veterinary Sciences 4, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040064





