Enhancing Agricultural Productivity in Dairy Cow Mastitis Management: Innovations in Non-Antibiotic Treatment Technologies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Mastitis-Related Pathogens in Dairy Cows
2.1. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
2.2. Streptococcus spp.
2.3. Escherichia coli (E. coli)
2.4. Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae)
2.5. Update on Drug Resistance
3. Non-Antibiotic Applications
3.1. Vaccines
3.2. Herbal Treatment
3.3. Phage Therapy
3.4. Probiotics
4. Emerging Technologies for Next-Generation Therapies
4.1. Modification of Cow Mammary Cells by Gene Editing Technology
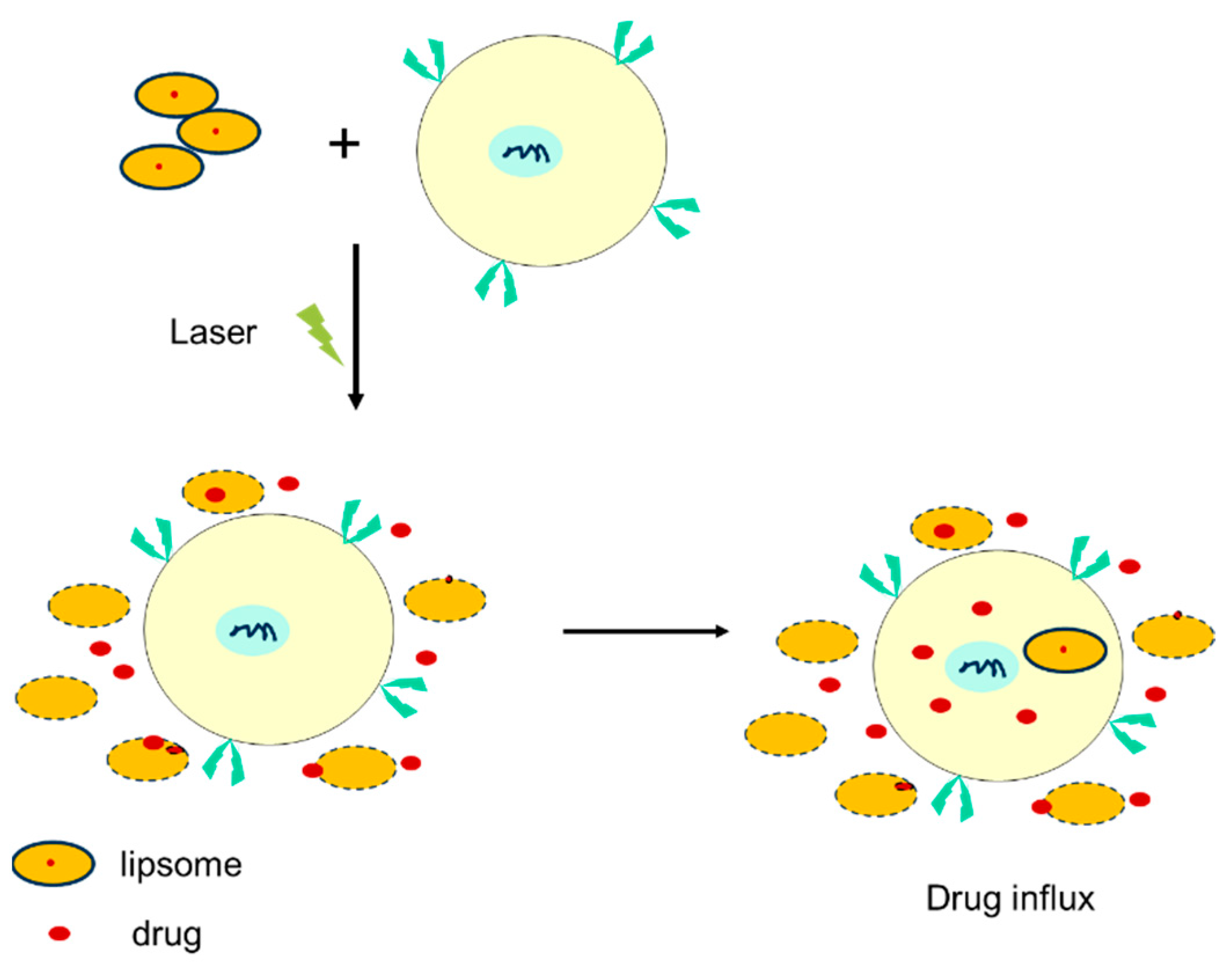
4.2. Nanotechnology and Drug-Delivery Systems
4.3. Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5. The Balance Between Treatment Efficacy and Resistance
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olde Riekerink, R.G.; Barkema, H.W.; Kelton, D.F.; Scholl, D.T. Incidence rate of clinical mastitis on Canadian dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krömker, V.; Leimbach, S. Mastitis treatment-Reduction in antibiotic usage in dairy cows. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52 (Suppl. 3), 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Arnold, L.M.; Stowe, C.J.; Harmon, R.J.; Bewley, J.M. Estimating US dairy clinical disease costs with a stochastic simulation model. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1472–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, E.; Dhuyvetter, K.C.; Overton, M.W. The cost of clinical mastitis in the first 30 days of lactation: An economic modeling tool. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 122, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, N.; Fu, Y. Role of Liver X Receptor in Mastitis Therapy and Regulation of Milk Fat Synthesis. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2019, 24, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Fang, Z.; Mu, T.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y. Application of Metabolomics in Diagnosis of Cow Mastitis: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 747519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, S.N.; Mpatswenumugabo, J.P.M.; Ntampaka, P.; Nandi, S.; Cullor, J.S. A one health framework to advance food safety and security: An on-farm case study in the Rwandan dairy sector. One Health 2023, 16, 100531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhylkaidar, A.; Oryntaev, K.; Altenov, A.; Kylpybai, E.; Chayxmet, E. Prevention of Bovine Mastitis through Vaccination. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.; Pickering, A.C.; Rocha, L.S.; Aguilar, A.P.; Fabres-Klein, M.H.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.A.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; de Oliveira Barros Ribon, A. Diversity and pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus from bovine mastitis: Current understanding and future perspectives. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duse, A.; Persson-Waller, K.; Pedersen, K. Microbial Aetiology, Antibiotic Susceptibility and Pathogen-Specific Risk Factors for Udder Pathogens from Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows. Animals 2021, 11, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, A.M.; Liski, E.; Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Pathogen-specific production losses in bovine mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9493–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wusiman, M.; Zuo, J.; Yu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wang, M.; Nie, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, W.; et al. Molecular characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae in clinical bovine mastitis in 14 provinces in China. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 49, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, D.B.; Mellata, M. Escherichia coli Mastitis in Dairy Cattle: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 928346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, V.K.C.; Costa, G.M.D.; Guimarães, A.S.; Heinemann, M.B.; Lage, A.P.; Dorneles, E.M.S. Relationship between virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from bovine mastitis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabelitz, T.; Aubry, E.; van Vorst, K.; Amon, T.; Fulde, M. The Role of Streptococcus spp. in Bovine Mastitis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainard, P.; Foucras, G.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Watts, J.L.; Koop, G.; Middleton, J.R. Knowledge gaps and research priorities in Staphylococcus aureus mastitis control. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaatout, N.; Ayachi, A.; Kecha, M. Staphylococcus aureus persistence properties associated with bovine mastitis and alternative therapeutic modalities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1102–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kløve, D.C.; Jensen, V.F.; Astrup, L.B. First Finding of a Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) t304/ST6 from Bovine Clinical Mastitis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Roshan, M.; Vats, A.; Behera, M.; Gautam, D.; Rajput, S.; Rana, C.; De, S. Evaluation of Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Forming Potential of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolates from Bovine Suspected with Mastitis. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, V.; Petzl, W.; Huber-Schlenstedt, R.; Gangl, A.; Sorge, U.S. Antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Streptococcus canis in quarter milk samples from Bavaria, Southern Germany, between 2012 and 2022. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 8452–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotti, C.; Cicotello, J.; Suarez Archilla, G.; Neder, V.; Alvarado Lucero, W.; Calvinho, L.; Signorini, M.; Camussone, C.; Zbrun, M.V.; Molineri, A.I. Antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus uberis isolated from bovine mastitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 164, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, F.; Ding, X. Ascorbic Acid-Mediated Modulation of Antibiotic Susceptibility of Major Bovine Mastitis Pathogens. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 7363–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Leite, R.F.; Tomazi, T.; Rall, V.L.M.; Santos, M.V. Association between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus uberis causing clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 12030–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, J.; He, F.; Kastelic, J.P.; Deng, Z.; Han, B. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies dysgalactiae Isolated From Bovine Mastitis in China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 751863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenni, M.; Lupo, A.; Madec, J.Y. Antimicrobial Resistance in Streptococcus spp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 10.1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohmeier, L.; Jander, S.; Koy, M.; Macías, L.; Meyerholz, M.M.; Engelmann, S.; Hoedemaker, M.; Kuehn, C.; Schuberth, H.-J.; Seyfert, H.M.; et al. Divergent genotype in Holstein heifers influences initial Staphylococcus aureus shedding after experimentally induced mastitis. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini, A.E.J.; van den Borne, B.H.P.; Wall, S.K.; Wellnitz, O.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Spadavecchia, C. Experimentally induced subclinical mastitis: Are lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid eliciting similar pain responses? Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boireau, C.; Cazeau, G.; Jarrige, N.; Calavas, D.; Madec, J.Y.; Leblond, A.; Haenni, M.; Gay, É. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from mastitis in dairy cattle in France, 2006–2016. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9451–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, X.; Yan, K.; Jiang, L.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z. PK/PD integration and pharmacodynamic cutoff of cefquinome against cow mastitis due to Escherichia coli. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 45, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wen, C.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Luo, Z.; Chen, W.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Outbreaks of Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Mastitis in Chinese Dairy Farms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0299722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddam, S.; Khan, M.; Jamal, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Slama, P.; Horky, P. Multidrug resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae reservoir and their capsular resistance genes in cow farms of district Peshawar, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Feng, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhou, M.; Hou, S.; Wang, G.; Hao, H.; et al. Epidemiology, Environmental Risks, Virulence, and Resistance Determinants of Klebsiella pneumoniae From Dairy Cows in Hubei, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, M.; Nobrega, D.B.; Barkema, H.W.; Xu, S.; Li, M.; Kastelic, J.P.; Shi, Y.; Han, B.; Gao, J. Genetic diversity and molecular epidemiology of outbreaks of Klebsiella pneumoniae mastitis on two large Chinese dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartor, Y.H.; Abd El-Aziz, N.K.; Gharieb, R.M.A.; El Damaty, H.M.; Enany, S.; Soliman, E.A.; Abdellatif, S.S.; Attia, A.S.A.; Bahnass, M.M.; El-Shazly, Y.A.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated From Bovine Mastitis and Raw Milk: The First Emergence of Colistin mcr-10 and Fosfomycin fosA5 Resistance Genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae in Middle East. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 770813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.S.; de Moura Souza, R.; Lima Moreira, J.P.; Gonzalez, A.G.M. Antimicrobial resistance of Enterobacteriaceae and Staphylococcus spp. isolated from raw cow’s milk from healthy, clinical and subclinical mastitis udders. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 227, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidaroos, N.H.; Algammal, A.M.; Mohamaden, W.I.; Alenzi, A.M.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; El-Mahallawy, H.S.; Eid, H.M.; Algwad, A.A.; Asfor, S.A.; et al. Virulence traits, agr typing, multidrug resistance patterns, and biofilm ability of MDR Staphylococcus aureus recovered from clinical and subclinical mastitis in dairy cows. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhital, B.; Chuang, S.T.; Hsieh, J.C.; Hsieh, M.H.; Chiang, H.I. Prevalence, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Major Mastitis Pathogens Isolated from Taiwanese Dairy Farms. Antibiotics 2023, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, H.; Mörk, M.J.; Larsson, M.; Waller, K.P. Vaccination against Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in two Swedish dairy herds. Acta Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.J.; Mallard, B.A.; Burton, J.L.; Schukken, Y.H.; Grohn, Y.T. Association of Escherichia coli J5-specific serum antibody responses with clinical mastitis outcome for J5 vaccinate and control dairy cattle. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schukken, Y.H.; Bronzo, V.; Locatelli, C.; Pollera, C.; Rota, N.; Casula, A.; Testa, F.; Scaccabarozzi, L.; March, R.; Zalduendo, D.; et al. Efficacy of vaccination on Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci intramammary infection dynamics in 2 dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5250–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freick, M.; Frank, Y.; Steinert, K.; Hamedy, A.; Passarge, O.; Sobiraj, A. Mastitis vaccination using a commercial polyvalent vaccine or a herd-specific Staphylococcus aureus vaccine. Results of a controlled field trial on a dairy farm. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. G. Grosstiere Nutztiere 2016, 44, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaas, I.C.; Zadoks, R.N. An update on environmental mastitis: Challenging perceptions. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65 (Suppl. 1), 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, G.; Yadlin, N.; Lubashevsy, E.; Ezra, E.; Glickman, A.; Chaffer, M.; Winkler, M.; Saran, A.; Trainin, Z. Development of a Staphylococcus aureus vaccine against mastitis in dairy cows. II. Field trial. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2003, 93, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.S.; Moon, J.S.; Kang, H.M.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, B.S.; Koo, H.C.; Park, Y.H. Protective effects of recombinant staphylococcal enterotoxin type C mutant vaccine against experimental bovine infection by a strain of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from subclinical mastitis in dairy cattle. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.J.; Breen, J.E.; Payne, B.; White, V.; Green, M.J. An investigation of the efficacy of a polyvalent mastitis vaccine using different vaccination regimens under field conditions in the United Kingdom. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perruchot, M.H.; Gondret, F.; Robert, F.; Dupuis, E.; Quesnel, H.; Dessauge, F. Effect of the flavonoid baicalin on the proliferative capacity of bovine mammary cells and their ability to regulate oxidative stress. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X. Matrine and baicalin inhibit apoptosis induced by Panton-Valentine leukocidin of Staphylococcus aureus in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Yuan, F.W.; Liang, T.; Liang, X.C.; Luo, Y.R.; Jiang, M.; Qing, S.Z.; Zhang, W.M. Baicalin inhibits Escherichia coli isolates in bovine mastitic milk and reduces antimicrobial resistance. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güran, M.; Çakıral, K.; Teralı, K.; Kandemir, T.; Şanlıtürk, G.; Öcal, M.M.; Nagiyev, T.; Köksal, F. Meropenem in combination with baicalein exhibits synergism against extensively drug resistant and pan-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in vitro. Pathog. Dis. 2023, 81, ftad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Shen, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X. Baicalein Suppresses NLRP3 and AIM2 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis in Macrophages Infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis via Induced Autophagy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0471122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Feng, J.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Tan, C. Baicalein Ameliorates Streptococcus suis-Induced Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Q. Baicalein Inhibits the Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm and the LuxS/AI-2 System in vitro. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 2861–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbab, S.; Ullah, H.; Bano, I.; Li, K.; Ul Hassan, I.; Wang, W.; Qadeer, A.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of in vitro antibacterial effect of essential oil and some herbal plant extract used against mastitis pathogens. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Miao, J. Application of Chlorogenic acid as a substitute for antibiotics in Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli-induced mastitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Kong, X.F.; Wang, D.Y. Selection of component drug in activating blood flow and removing blood stasis of Chinese herbal medicinal formula for dairy cow mastitis by hemorheological method. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, T.S.; Fussieger, C.; Theodoro, H.; Silveira, S.; Pauletti, G.F.; Ely, M.R.; Lunge, V.R.; Streck, A.F. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus chromogenes isolated from bovine mastitis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacic, G. Intramammary Propolis Formulation for Subclinical Mastitis Prevention and Treatment in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Vet. Anim. Res. 2016, 3, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Jin, X.L.; Shen, X.G.; Sun, L.P.; Wu, L.M.; Wei, J.Q.; Marcucci, M.C.; Hu, F.L.; Liu, J.X. Effects of Chinese Propolis in Protecting Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells against Mastitis Pathogens-Induced Cell Damage. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8028291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.J.; Pacan, J.C.; Carson, M.E.; Leslie, K.E.; Griffiths, M.W.; Sabour, P.M. Efficacy and pharmacokinetics of bacteriophage therapy in treatment of subclinical Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in lactating dairy cattle. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2912–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatek, M.; Parasion, S.; Mizak, L.; Gryko, R.; Bartoszcze, M.; Kocik, J. Characterization of a bacteriophage, isolated from a cow with mastitis, that is lytic against Staphylococcus aureus strains. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.S.; Eller, M.R.; Duarte, V.S.; Pereira, Â.L.; Silva, C.C.; Mantovani, H.C.; Oliveira, L.L.; Silva Ede, A.; De Paula, S.O. Use of phages against antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 3930–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, M.; Keary, R.; McAuliffe, O.; Ross, R.P.; O’Mahony, J.; Coffey, A. Bacteriophage-Derived Peptidase CHAP(K) Eliminates and Prevents Staphylococcal Biofilms. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 625341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Du, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Xie, J.; Zhao, R.; Tong, Y.; Qiu, S.; et al. Phage-delivered sensitisation with subsequent antibiotic treatment reveals sustained effect against antimicrobial resistant bacteria. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6310–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R. Probiotics in human medicine. Gut 1991, 32, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, R.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiménez, E.; Marín, M.L.; Olivares, M.; Boza, J.; Jiménez, J.; Fernández, L.; Xaus, J.; et al. The commensal microflora of human milk: New perspectives for food bacteriotherapy and probiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitching, M.; Mathur, H.; Flynn, J.; Byrne, N.; Dillon, P.; Sayers, R.; Rea, M.C.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. A Live Bio-Therapeutic for Mastitis, Containing Lactococcus lactis DPC3147 with Comparable Efficacy to Antibiotic Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, N.; Kermanshahi, R.; Yakhchali, B.; Sattari, T. Antagonistic activity of probiotic lactobacilli against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 420, 2169–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Shandilya, U.K.; Sharma, A.; Mallikarjunappa, S.; Guo, J.; Mao, Y.; Meade, K.G.; Karrow, N.A. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of TLR4 modulates Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis cell lysate-induced inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 11135–11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, R.; Chaudhary, P.; De, S. CRISPR/cas9 cassette targeting Escherichia coli (bla)CTX-M specific gene of mastitis cow milk origin can alter the antibiotic resistant phenotype for cefotaxime. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, Y.; Qu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L. dCas9-guided demethylation of the AKT1 promoter improves milk protein synthesis in a bovine mastitis mammary gland epithelial model induced by using Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Biol. Int. 2024, 48, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.G.; Park, J.H.; Khang, D. Sonodynamic and Acoustically Responsive Nanodrug Delivery System: Cancer Application. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 11767–11788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Teng, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, P.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Liang, X.J.; Ou, C. Biomimetic Grapefruit-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Safe and Targeted Delivery of Sodium Thiosulfate against Vascular Calcification. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 24773–24789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, M.; Kot, M.; Lange, A.; Kalińska, A.; Gołębiewski, M.; Jaworski, S. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, and Physical Properties of Selected Nano-Complexes in Bovine Udder Inflammatory Pathogen Control. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2024, 17, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Song, Y.; Petrovski, K.; Eats, P.; Trott, D.J.; Wong, H.S.; Page, S.W.; Perry, J.; Garg, S. Development of intramammary delivery systems containing lasalocid for the treatment of bovine mastitis: Impact of solubility improvement on safety, efficacy, and milk distribution in dairy cattle. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.E.; Elmasry, I.H.; Lebda, M.A.; El-Karim, D.; Hagar, M.; Ebied, S.K.M.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Rizk, N.I.; Ghamry, H.I.; Shukry, M.; et al. Characterization and antioxidant activity of nano-formulated berberine and cyperus rotundus extracts with anti-inflammatory effects in mastitis-induced rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.K.; Tripathi, C.B.; Saraf, S.A.; Ansari, M.N.; Saeedan, A.S.; Aldosary, S.; Rajinikanth, P.S.; Kaithwas, G. Alpha-linolenic acid based nano-suspension protect against lipopolysaccharides induced mastitis by inhibiting NFκBp65, HIF-1α, and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway in albino Wistar rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 377, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. The Smart Drug Delivery System and Its Clinical Potential. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1306–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangabad, P.S.; Mirkiani, S.; Shahsavari, S.; Masoudi, B.; Masroor, M.; Hamed, H.; Jafari, Z.; Taghipour, Y.D.; Hashemi, H.; Karimi, M.; et al. Stimulus-responsive liposomes as smart nanoplatforms for drug delivery applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.A.; Deitcher, S.R. Marqibo® (vincristine sulfate liposome injection) improves the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vincristine. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavlovich, A.; Singh, A.; Blumenthal, R.; Puri, A. A novel class of photo-triggerable liposomes containing DPPC:DC(8,9)PC as vehicles for delivery of doxorubcin to cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Wang, L.; Brey, E.M.; Uribe, G.R.; Tang, L. Smart Nanoparticles for Chemo-Based Combinational Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, P.; Hou, Y.; Ning, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Gao, M. “Smart” Nanoprobes for Visualization of Tumor Microenvironments. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C.; Emanuelson, U. Mastitis control in Swedish dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 6883–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.W.; Eidman, V.R.; Reneau, J.K. Animal health and management and their impact on economic efficiency. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.L.; Hogan, J.S. Environmental mastitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1993, 9, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Outcome | Target | Effect Size | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Increased IgG | S. aureus, E. coli | Moderate to significant | Leitner [43] Wilson [39]. |
| 2 | Reduced mastitis severity | S. aureus, E. coli | Modest to significant | Schukken [40] Chang [44] |
| 3 | Improved milk-yield | E. coli | Variable; not always statistically significant | Bradley [45] Freick [41] |
| 4 | Limited efficacy | Environmental pathogens | Inconsistent or null | Landin [38] Freick [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Liao, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Enhancing Agricultural Productivity in Dairy Cow Mastitis Management: Innovations in Non-Antibiotic Treatment Technologies. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070662
Jiang L, Li Q, Liao H, Liu H, Wang Z. Enhancing Agricultural Productivity in Dairy Cow Mastitis Management: Innovations in Non-Antibiotic Treatment Technologies. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(7):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070662
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Lijie, Qi Li, Huiqing Liao, Hourong Liu, and Zhiqiang Wang. 2025. "Enhancing Agricultural Productivity in Dairy Cow Mastitis Management: Innovations in Non-Antibiotic Treatment Technologies" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 7: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070662
APA StyleJiang, L., Li, Q., Liao, H., Liu, H., & Wang, Z. (2025). Enhancing Agricultural Productivity in Dairy Cow Mastitis Management: Innovations in Non-Antibiotic Treatment Technologies. Veterinary Sciences, 12(7), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070662






