Lyssavirus Antibody Detection in Cave-Dwelling Bats on Cat Ba Island, Vietnam: Implications for Zoonotic Surveillance
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Detection of Lyssavirus-Specific Antibodies Using the PLATELIA RABIES II Kit
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ROC Curve Analysis for Diagnostic Validation
3.2. Serological Survey of Cat Ba Cave-Dwelling Bats
3.3. Sex-Related Intraspecies Differences
4. Discussion
4.1. Serological Evidence of Lyssavirus Circulation
4.2. Bats as Asymptomatic Reservoirs
4.3. Analysis of Sex-Related and Species-Specific Differences
4.4. Ecological Factors and Potential for Lyssavirus Transmission in Cave Environments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgin, C.J.; Colella, J.P.; Kahn, P.L.; Upham, N.S. How Many Species of Mammals Are There? J. Mammal. 2018, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasso, M.; Balakrishnan, M. Ecological and Economic Importance of Bats (Order Chiroptera). ISRN Biodivers. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.M.C.C.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; da Silva e Souza, K.; Gouveia, S.F.; Villalobos, F. Geographic Variation in the Relationship between Large-Scale Environmental Determinants and Bat Species Richness. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Cobo, J.; López-Roig, M. Bats and Emerging Infections: An Ecological and Virological Puzzle. In Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Infections. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Rezza, G., Ippolito, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 972, pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.L.; Schountz, T.; Wang, L.-F. Antiviral Immune Responses of Bats: A Review. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brussel, K.; Holmes, E.C. Zoonotic Disease and Virome Diversity in Bats. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 52, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Niezgoda, M.; Carroll, D.S.; Keeler, N.; Hossain, M.J.; Breiman, R.F.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rupprecht, C.E. Lyssavirus Surveillance in Bats, Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Noguchi, A.; Nguyen, D.V.; Ngo, G.C.; Thong, V.D.; Olowokure, B.; Inoue, S. Bat Lyssaviruses, Northern Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardena, P.S.; Marston, D.A.; Ellis, R.J.; Wise, E.L.; Karawita, A.C.; Breed, A.C.; McElhinney, L.M.; Johnson, N.; Banyard, A.C.; Fooks, A.R. Lyssavirus in Indian Flying Foxes, Sri Lanka. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba Villarroel, P.M.; Gumpangseth, N.; Songhong, T.; Yainoy, S.; Monteil, A.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Missé, D.; Wichit, S. Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonotic Viral Diseases in Southeast Asia: One Health Challenge. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1141483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furey, N.M.; Mackie, I.J.; Racey, P.A. Bat Diversity in Vietnamese Limestone Karst Areas and the Implications of Forest Degradation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 1821–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, V.D.; Denzinger, A.; Van Sang, N.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Thanh, H.T.; Loi, D.N.; Van Nha, P.; Van Viet, N.; Tien, P.D.; Tuanmu, M.-N.; et al. Bat Diversity in Cat Ba Biosphere Reserve, Northeastern Vietnam: A Review with New Records from Mangrove Ecosystem. Diversity 2021, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, N.K.; Taylor-Robinson, A.W. Combatting Rabies Outbreaks in Vietnam: High Time to Enforce Restrictions on Dog Meat Farming, a Key Source of Transmission. IJID Reg. 2024, 13, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Rupprecht, C.E. Bat Lyssaviruses. In Bats and Viruses: A New Frontier of Emerging Infectious Diseases; Wang, L., Cowled, C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015; pp. 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olival, K.J.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, L.-F.; Field, H.E.; Daszak, P. Are Bats Exceptional Viral Reservoirs? In New Directions in Conservation Medicine: Applied Cases of Ecological Health; Aguirre, A.A., Ostfeld, R., Daszak, P., Eds.; Oxford Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 195–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hayman, D.T.S.; Bowen, R.A.; Cryan, P.M.; McCracken, G.F.; O’Shea, T.J.; Peel, A.J.; Gilbert, A.; Webb, C.T.; Wood, J.L.N. Ecology of Zoonotic Infectious Diseases in Bats: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, K.L.; Hamel, L.; Alhmoud, N.; Ali, S.; Bilgin, R.; Sidamonidze, K.; Urushadze, L.; Karesh, W.; Olival, K.J. Bat Research Networks and Viral Surveillance: Gaps and Opportunities in Western Asia. Viruses 2019, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important Reservoir Hosts of Emerging Viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racey, P.A. The Uniqueness of Bats. In Bats and Viruses: A New Frontier of Emerging Infectious Diseases; Wang, L.-F., Cowled, C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, M.; Yovel, Y. Revising the Paradigm: Are Bats Really Pathogen Reservoirs or Do They Possess an Efficient Immune System? iScience 2022, 25, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiflu, A.B. The Immune Escape Strategy of Rabies Virus and Its Pathogenicity Mechanisms. Viruses 2024, 16, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lin, S.; Yuan, X.; Shu, S.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, F.; Chen, Z.; He, B.; Li, J.; et al. Structures of Two Lyssavirus Glycoproteins Trapped in Pre- and Post-Fusion States and the Implications on the Spatial-Temporal Conformational Transition along with PH-Decrease. PLoS Pathog. 2025, 21, e1012923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Tachedjian, M.; Wynne, J.W.; Boyd, V.; Cui, J.; Smith, I.; Cowled, C.; Ng, J.H.J.; Mok, L.; Michalski, W.P.; et al. Contraction of the Type I IFN Locus and Unusual Constitutive Expression of IFN-α in Bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2696–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondet, V.; Le Baut, M.; Le Poder, S.; Le’cu, A.; Petit, T.; Wedlarski, R.; Duffy, D.; Le Roux, D. Constitutive IFNa Protein Production in Bats. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 735866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Sui, B.; Zhao, L. Rabies Lyssavirus. In Veterinary Virology of Domestic and Pet Animals; Wang, L., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.P.; Nel, L.H. Lyssaviruses and the Fatal Encephalitic Disease Rabies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 786953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.M.Y.; Halim, A.F.N.A.; Ahmad, D.; Ramly, N.; Hassan, M.R.; Syed Abdul Rahim, S.S.; Saffree Jeffree, M.; Omar, A.; Hidrus, A. Rabies in Southeast Asia: A Systematic Review of Its Incidence, Risk Factors and Mortality. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e066587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beran, G.W.; Nocete, A.P.; Elvina, O. Epidemiological and Control Studies on Rabies in the Philippines. Southeast Asian J. Med. Public Health 1972, 3, 433–445. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization, Rabies 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rabies (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Wang, L.-F.; Breed, A.C. The Role of Bats as Reservoir Hosts of Emerging Neuroviruses. In Neurotropic Viral Infections, 2nd ed.; Reiss, C.S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 403–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-C.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lee, M.-S.; Tu, Y.-C.; Chang, J.C.; Wu, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ting, L.J.; Tsai, K.R.; Cheng, M.C.; et al. Lyssavirus in Japanese Pipistrelle, Taiwan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-C.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lee, F.; Tu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Chang, J.-C.; Hsu, W.-C. Novel Bat Lyssaviruses Identified by Nationwide Passive Surveillance in Taiwan, 2018–2021. Viruses 2022, 14, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayman, D.T.S.; Fooks, A.R.; Marston, D.A.; Garcia-R, J.C. The Global Phylogeography of Lyssaviruses—Challenging the “Out of Africa” Hypothesis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.L.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Bányai, K.; Bào, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briand, F.-X.; Briese, T.; et al. Taxonomy of the Order Mononegavirales: Update 2016. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Turmelle, A.; Kuzmin, I.V.A. Perspective on Lyssavirus Emergence and Perpetuation. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyard, A.C.; Fooks, A.R. Rabies and Rabies-Related Lyssaviruses. In Oxford Textbook of Zoonoses: Biology, Clinical Practice, and Public Health Control, 2nd ed.; Palmer, S.R., Soulsby, L., Torgerson, P.R., Brown, D.W.G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 650–680. [Google Scholar]
- Fooks, A.R.; Shipley, R.; Markotter, W.; Tordo, N.; Freuling, C.M.; Müller, T.; McElhinney, L.M.; Banyard, A.C.; Rupprecht, C.E. Renewed Public Health Threat from Emerging Lyssaviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Suo, X.; Duan, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Q.A. Customized Novel Blocking ELISA for Detection of Bat-Origin Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03930-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guito, J.C.; Prescott, J.B.; Arnold, C.E.; Amman, B.R.; Schuh, A.J.; Spengler, J.R.; Sealy, T.K.; Harmon, J.R.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Kulcsar, K.A.; et al. Asymptomatic Infection of Marburg Virus Reservoir Bats Is Explained by a Strategy of Immunoprotective Disease Tolerance. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyssaguet, M.; Dacheux, L.; Audry, L.; Compoint, A.; Morize, J.L.; Blanchard, I.; Bourhy, H. Multicenter Comparative Study of a New ELISA, PLATELIATM RABIES II, for the Detection and Titration of Anti-Rabies Glycoprotein Antibodies and Comparison with the Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test (RFFIT) on Human Samples from Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated People. Vaccine 2007, 25, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugelo, A.; Hampson, K.; McElhinney, L.M.; Lankester, F. Evaluation of an IELISA for Detection and Quantification of Rabies Antibodies in Domestic Dog Sera. Vaccine 2023, 41, 6565–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servat, A.; Feyssaguet, M.; Blanchard, I.; Morize, J.L.; Schereffer, J.L.; Boue, F.; Cliquet, F. A quantitative indirect ELISA to monitor the effectiveness of rabies vaccination in domestic and wild carnivores. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 318, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimal, S.; Ojha, K.C.; Chaisowwong, W.; Shah, Y.; Pant, D.K.; Sirimalaisuwan, A. Detection of virus-neutralising antibodies and associated factors against rabies in the vaccinated household dogs of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, V.; Bowen, R.A.; Davis, A.D.; Rupprecht, C.E.; O’shea, T.J. Rabies in a captive colony of big brown bats (Eptesicus fuscus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, D.K.A.; Favaro, A.B.B.D.B.D.C.; Carvalho, C.D.; Picolo, M.R.; Hernandez, J.C.B.; Lot, M.S.; Albas, A.; Araújo, D.B.; André Pedro, W.; Queiroz, L.H. Rabies surveillance in bats in Northwestern State of São Paulo. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidlova, V.; Zukal, J.; Brichta, J.; Anisimov, N.; Apoznański, G.; Bandouchova, H.; Bartonička, T.; Berková, H.; Botvinkin, A.D.; Heger, T.; et al. Active Surveillance for Antibodies Confirms Circulation of Lyssaviruses in Palearctic bats. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundarova, H.; Ostoich, P.; Alexieva, I.; Neov, B.; Ivanova-Aleksandrova, N.; Emilova, R.; Georgieva, I.; Kirov, K.; Bednarikova, S.; Zukalova, K.; et al. ELISA Detection of European Lyssaviruses in Bulgarian Cave-dwelling Bats. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2024, Supplement 20, 161–166. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Shope, R.E. Rabies-Related Viruses. J. Biol. Med. 1982, 55, 271–275. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- OIE. Standard Operating Procedure for OIE Validation and Certification of Diagnostic Assays. 2007. Available online: http://www.oie.int/vcda/eng/en_fichier_SOP.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Welch, R.J.; Anderson, B.L.; Litwin, C.M. An evaluation of two commercially available ELISAs and one in-house reference laboratory ELISA for the determination of human anti-rabies virus antibodies. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.R.; Arora, B.; Chhuttani, P.N.; Broor, S.; Choudhury, S.; Joshi, R.M.; Ray, S.D. Rabies Virus Infection of a Flying Fox Bat, Pteropus policephalus in Chandigarh, Northern India. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1980, 32, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.C.; Lawhaswasdi, K.; Vick, W.E.; Stanton, J.S. Isolation of Rabies Virus from Fruit Bats in Thailand. Nature 1967, 216, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynes, J.-M.; Molia, S.; Audry, L.; Hout, S.; Ngin, S.; Walston, J.; Bourhy, H. Serologic Evidence of Lyssavirus Infection in Bats, Cambodia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2231–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguin, P.M.; Murray-Lillibridge, K.; Miranda, M.E.G.; Smith, J.S.; Calaor, A.B.; Rupprecht, C.E. Serologic Evidence of Lyssavirus Infections among Bats, the Philippines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.S.; Peck, A.J.; Omar, M. The Importance of Malaysian Bats in the Transmission of Oral Disease. Med. J. Malaya 1969, 24, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Turmelle, A.S.; Jackson, F.R.; Green, D.; McCracken, G.F.; Rupprecht, C.E. Host Immunity to Repeated Rabies Virus Infection in Big Brown Bats. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2360–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Busse, P.; Pelz, G.; Dolch, D.; Teubner, J.; Encarnação, J.A.; Mühle, R.-U.; Fischer, M.; Hoffmann, B.; et al. Twenty Years of Active Bat Rabies Surveillance in Germany: A Detailed Analysis and Future Perspectives. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Shrivastava, N.; Sheikh, N.P.; Singh, P.K.; Jha, H.C.; Parmar, H.S. Rabies Vaccines: Journey from Classical to Modern Era. Vet. Vacc. 2025, 4, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarría, J.E.; Banyard, A.C.; McElhinney, L.M.; Fooks, A.R. Current Rabies Vaccines Do Not Confer Protective Immunity against Divergent Lyssaviruses Circulating in Europe. Viruses 2019, 11, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Cobo, J.; Amengual, B.; Abellán, C.; Bourhy, H. European Bat Lyssavirus Infection in Spanish Bat Populations. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellenberg, G.J.; Audry, L.; Rønsholt, L.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Bruschke, C.J.M.; Bourhy, H. Presence of European Bat Lyssavirus RNAs in Apparently Healthy Rousettus Aegyptiacus Bats. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Setien, A.; Loza-Rubio, E.; Salas-Rojas, M.; Brisseau, N.; Cliquet, F.; Pastoret, P.P.; Rojas-Dotor, S.; Tesoro, E.; Kretschmer, R. Salivary Excretion of Rabies Virus by Healthy Vampire Bats. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Morón, S.; Juste, J.; Ibáñez, C.; Ruiz-Villamor, E.; Avellón, A.; Vera, M.; Echevarría, J.E. Endemic Circulation of European Bat Lyssavirus Type 1 in Serotine Bats, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, R.V. Cryptogenic Rabies, Bats, and the Question of Aerosol Transmission. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2002, 39, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.; Phillpotts, R.; Fooks, A.R. Airborne Transmission of Lyssaviruses. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schountz, T.; Baker, M.L.; Butler, J.; Munster, V. Immunological Control of Viral Infections in Bats and the Emergence of Viruses Highly Pathogenic to Humans. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 01098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, R.; Wright, E.; Selden, D.; Wu, G.; Aegerter, J.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C. Bats and Viruses: Emergence of Novel Lyssaviruses and Association of Bats with Viral Zoonoses in the EU. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, S.; Rapin, N.; Misra, V. Immune System Modulation and Viral Persistence in Bats: Understanding Viral Spillover. Viruses 2019, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korytár, Ľ.; Ondrejková, A.; Drážovská, M.; Zemanová, S.; Prokeš, M. Serological Survey of Lyssaviruses in Synanthropic Bats and Human Exposure to Bats in Slovakia. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2022, 29, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, G.S.; Carter, G.; Bohn, K.M.; Caspers, B.; Chaverri, G.; Farine, D.; Günther, L.; Kerth, G.; Knörnschild, M.; Mayer, F.; et al. Kinship, Association, and Social Complexity in Bats. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2019, 73, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoss, S.; Becker, N.I.; Otto, M.S.; Czirják, G.Á.; Encarnação, J.A. Effect of Sex and Reproductive Status on the Immunity of the Temperate Bat Myotis Daubentonii. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 94, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willoughby, A.; Phelps, K.; Olival, K. A Comparative Analysis of Viral Richness and Viral Sharing in Cave-Roosting Bats. Diversity 2017, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, D.G. Bat Rabies and Other Lssavirus Infections, 1st ed.; USGS: Reston, Virginia, USA, 2009; Volume 68, pp. 32–38.

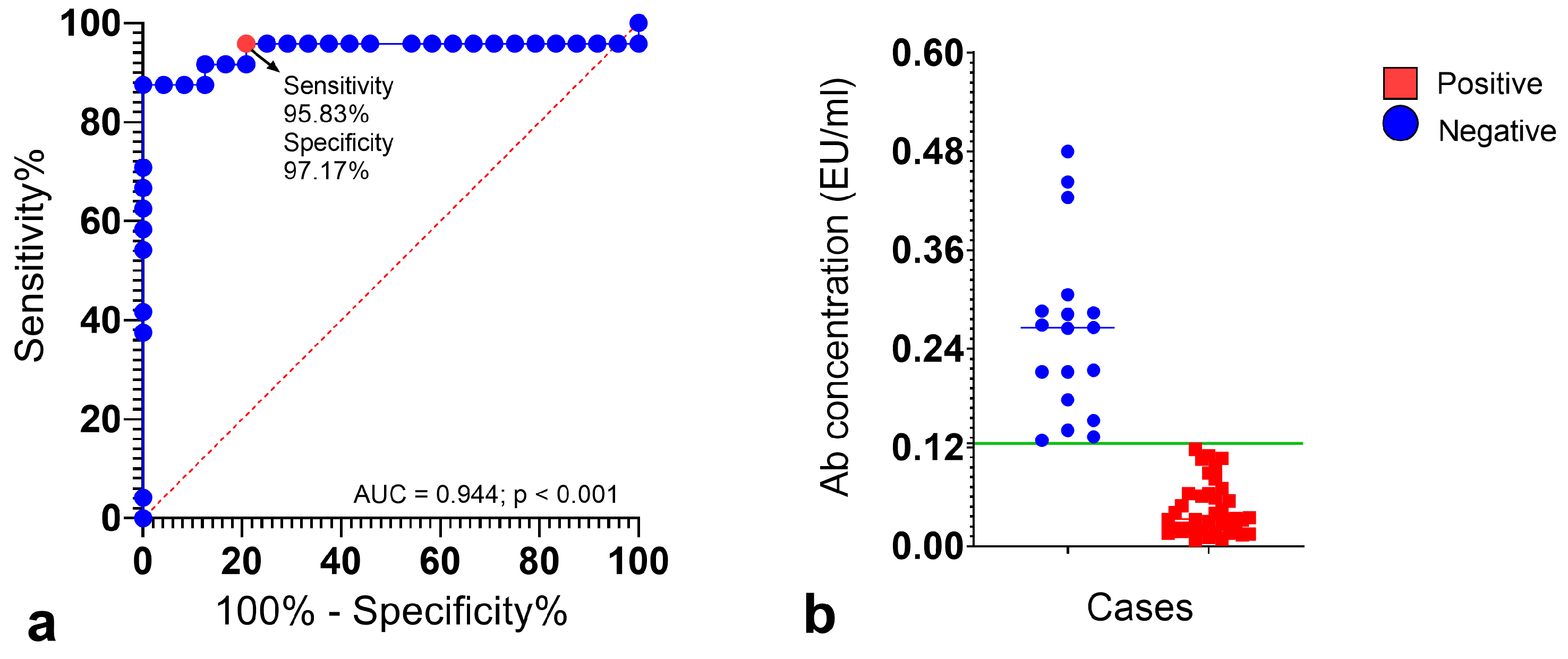

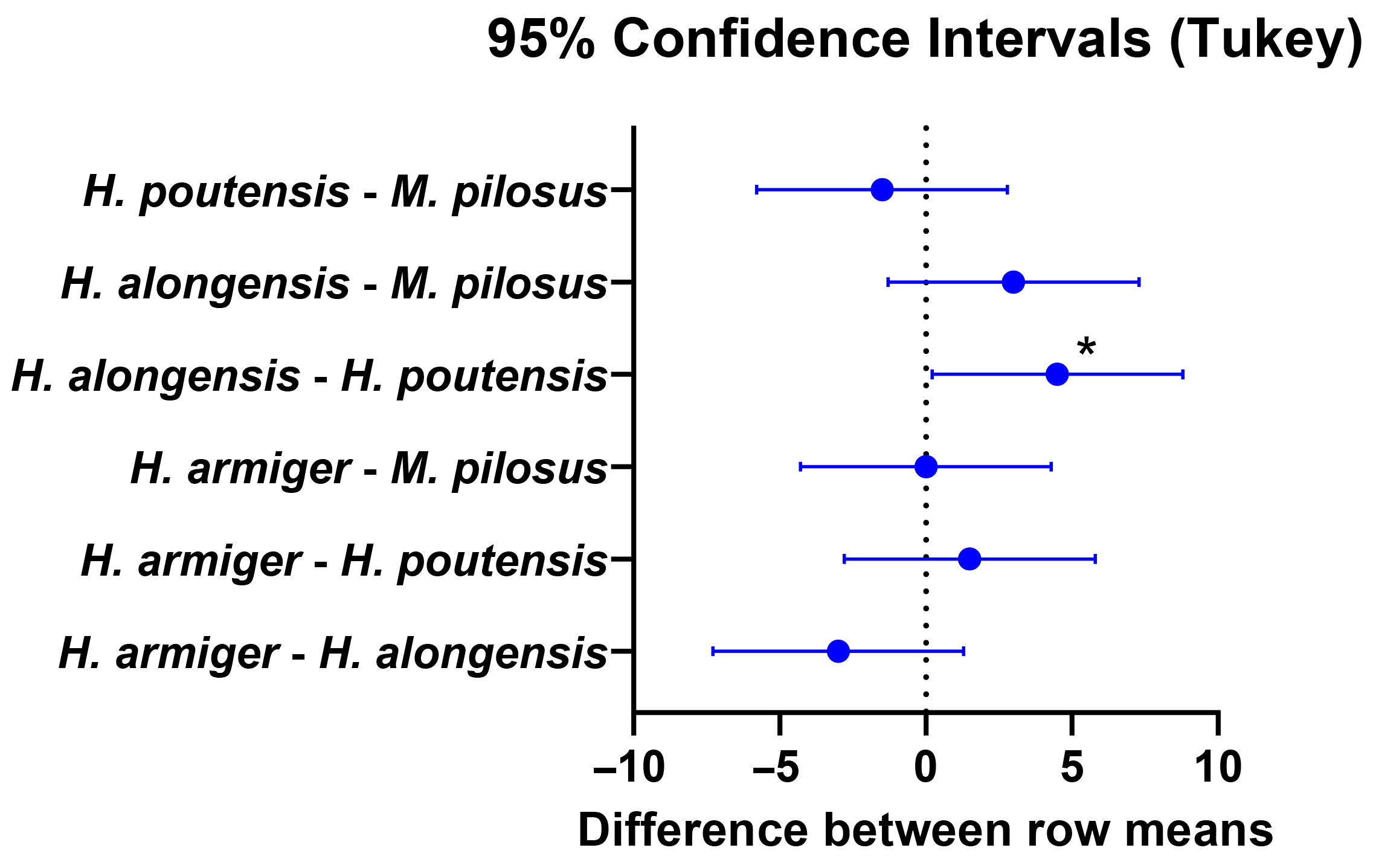
| Species | Females | Males | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Npos/Ntotal | Positives (%) (95% CI) | Npos/Ntotal | Positives (%) (95% CI) | Npos/Ntotal | Positives (%) (95% CI) | |
| H. armiger | 0/18 | 0% (0–17.59) | 4/18 | 22.22% (9.001–45.21) | 4/18 | 22.22% (9.001–45.21) |
| H. alongensis | 4/7 | 57.14% (25.05–84.18) | 6/11 | 45.45% (21.27–1.99) | 10/18 | 50% (29.03–70.97) |
| H. poutensis | 0/6 | 0% (0–43.53) | 1/12 | 8.33% (1.49–35.39) | 1/18 | 5.55% (0.98–25.76) |
| M. pilosus | 1/1 | 100% (20.66–100) | 3/5 | 60% (23.07–88.24) | 4/6 | 66.66% (30–90.32) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dundarova, H.; Chassovnikarova, T.; Todorova, N.; Beltcheva, M.; Aleksieva, I.; Luong, N.T.; Thong, V.D. Lyssavirus Antibody Detection in Cave-Dwelling Bats on Cat Ba Island, Vietnam: Implications for Zoonotic Surveillance. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070654
Dundarova H, Chassovnikarova T, Todorova N, Beltcheva M, Aleksieva I, Luong NT, Thong VD. Lyssavirus Antibody Detection in Cave-Dwelling Bats on Cat Ba Island, Vietnam: Implications for Zoonotic Surveillance. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(7):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070654
Chicago/Turabian StyleDundarova, Heliana, Tsenka Chassovnikarova, Nadezhda Todorova, Michaela Beltcheva, Iliana Aleksieva, Nguyen Thanh Luong, and Vu Dinh Thong. 2025. "Lyssavirus Antibody Detection in Cave-Dwelling Bats on Cat Ba Island, Vietnam: Implications for Zoonotic Surveillance" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 7: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070654
APA StyleDundarova, H., Chassovnikarova, T., Todorova, N., Beltcheva, M., Aleksieva, I., Luong, N. T., & Thong, V. D. (2025). Lyssavirus Antibody Detection in Cave-Dwelling Bats on Cat Ba Island, Vietnam: Implications for Zoonotic Surveillance. Veterinary Sciences, 12(7), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070654







