Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in Women and Female Dogs: A Comparative Clinical-Pathological and Immunophenotypic Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
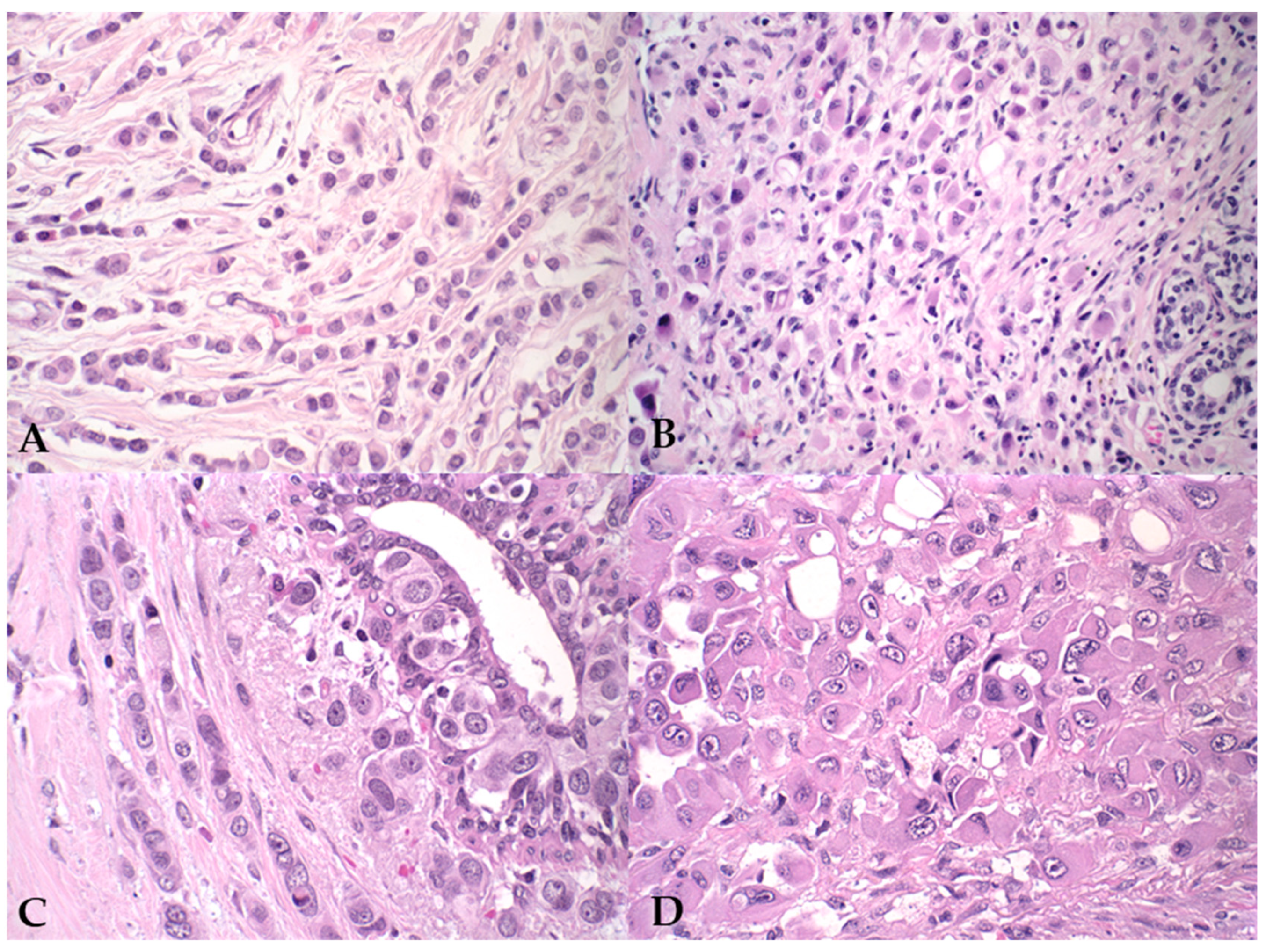
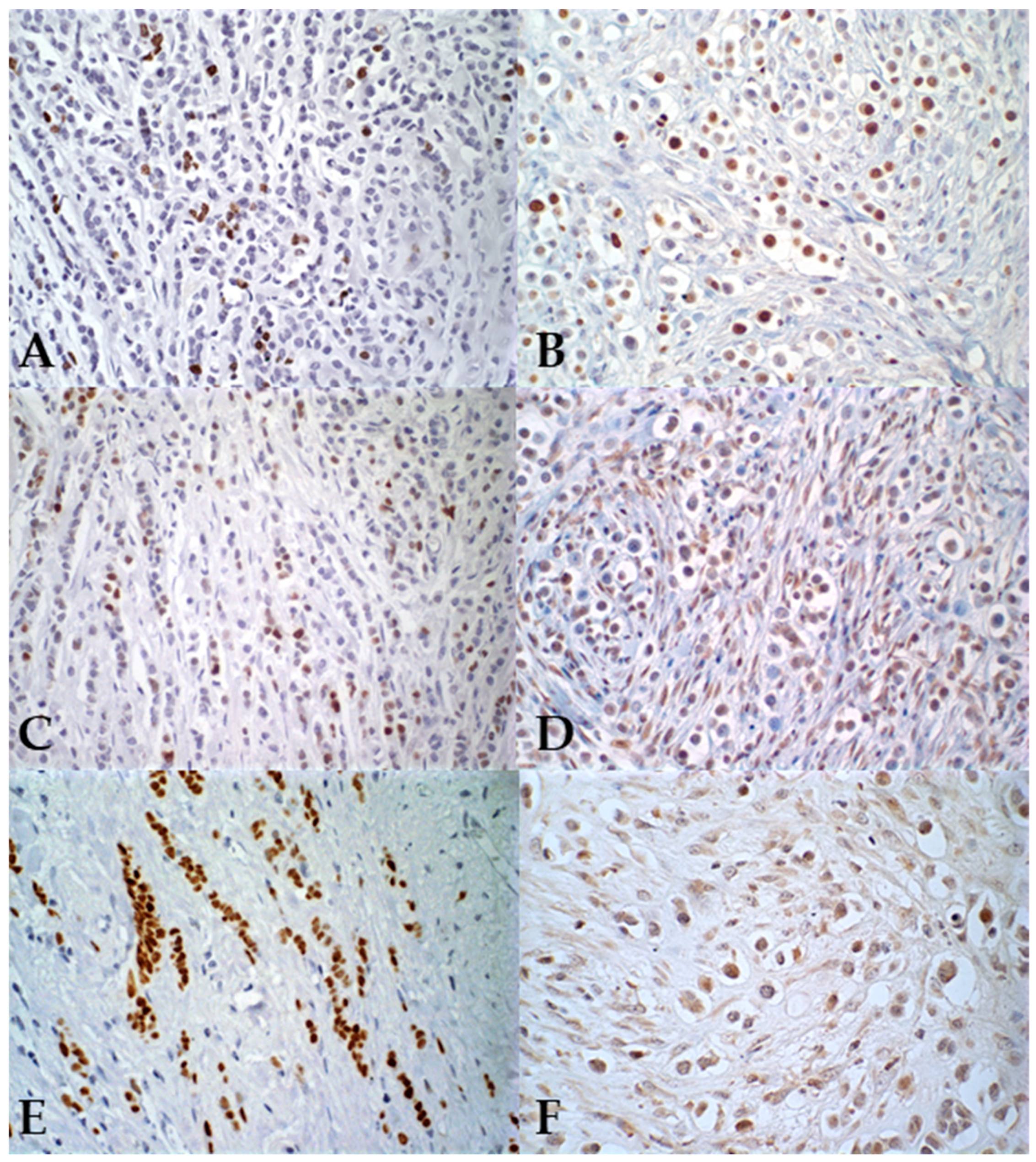
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PILC or PLC | Pleomorphic invasive lobular carcinoma |
| ILC | Invasive lobular carcinoma |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| HER-2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| LPC | Laboratory of Comparative Pathology |
| ICB–UFMG | Institute of Biological Sciences–Federal University of Minas Gerais |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| TNM | Size; regional lymph node; distant metastasis. |
| AS | Any score |
References
- Costarelli, L.; Campagna, D.; Ascarelli, A.; Cavaliere, F.; Colavito, M.H.; Ponzani, T.; Broglia, L.; La Pinta, M.; Manna, E.; Fortunato, L. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma: Is It More Similar to a Classic Lobular Cancer or to a High-Grade Ductal Cancer? Breast Cancer (Dove Med. Press) 2017, 9, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haque, W.; Arms, A.; Verma, V.; Hatch, S.; Brian Butler, E.; Teh, B.S. Outcomes of Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma versus Invasive Lobular Carcinoma. Breast 2019, 43, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segar, J.M.; Pandey, R.; Farr, K.J.; Nagle, R.; LeBeau, L.; Gonzalez, V.J.; Chalasani, P. Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics of Pleomorphic Invasive Lobular Carcinoma. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2020, 2020, 8816824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassali, G.D.; Gärtner, F.; Schmitt, F.C. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the canine mammary gland: Histopathologic and immunohistochemical features. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2002, 54, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.C.; Hicks, D.G. Diagnostic Pathology: Breast, 2nd ed.; Elsevier—Health Sciences Division: Filadélfia, PA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780323377126. [Google Scholar]
- Rakha, E.A.; van Deurzen, C.H.M.; Paish, E.C.; Macmillan, R.D.; Ellis, I.O.; Lee, A.H.S. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: Is It a Prognostically Significant Pathological Subtype Independent of Histological Grade? Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasola, C.E.; Chen, J.J.; Jensen, K.C.; Allison, K.H.; Horst, K.C. Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast. Breast J. 2018, 24, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, R.A.; Krings, G.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Mamounas, M.E.; Fahrner-Scott, K.; Wong, J.; Alvarado, M.; Ewing, C.; Esserman, L.J.; Rugo, H. Mitotic Score and Pleomorphic Histology in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: Impact on Disease-Free Survival. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 181, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolik, D.; Caduff, R.; Varga, Z. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: Its Cell Kinetics, Expression of Oncogenes and Tumour Suppressor Genes Compared with Invasive Ductal Carcinomas and Classical Infiltrating Lobular Carcinomas: Pleomorphic Lobular Breast Carcinoma. Histopathology 2001, 39, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoguchi, A.; Sakai, T.; Okuda, M.; Minehata, K.; Yazawa, M.; Ishizaka, T.; Watari, T.; Nishimura, R.; Sasaki, N.; Hasegawa, A.; et al. Aberrations of the P53 Tumor Suppressor Gene in Various Tumors in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.-C.; Lakhani, S.R.; Simpson, P.T. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: Molecular Pathology and Clinical Impact. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wronski, J.G.; Nunes, M.M.; Viscone, É.A.; Oliveira, E.A.; Figueiredo, M.d.S.; Cassali, G.D.; Nakagaki, K.Y.R. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma in a Cat: Clinical, Histopathological, and Immunohistochemical Characterization. Rev. Bras. Med. Vet. 2025, 47, e001725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressel, L.; Millanta, F.; Poli, A. Canine Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland: Morphological and Immunohistochemical Characterizations of Three Cases. J. Comp. Pathol. 2011, 144, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, G.; Santilli, J.; Cintra, P.; Calazans, S.; Ribeiro-Silva, A. Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of pleomorphic lobular mammary carcinoma in a female dog. Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 13, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, B.S.; Monteiro, L.N.; Colodel, M.M.; Figueiroa, F.C.; Nonogaki, S.; Rocha, R.M.; Rocha, N.S. Cytohistological and Immunohistochemical Features of a Mammary Invasive Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma in a Dog. Comp. Clin. Path. 2012, 21, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Assis, M.J.M.H.; Silva, L.P.; Machado, M.C.d.A.; Nascimento, N.A.; Damasceno, K.A.; Cassali, G.D.; Lima,, A.E. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the mammary gland in female dog subject to chemotherapy with carboplatin—Case report. Braz. J. Vet. Med. 2016, 38, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Cassali, G.; Jark, P.; Gamba, C.; Damasceno, K.; Estrela-Lima, A.; Nardi, A.; Ferreira, E.; Horta, R.; Firmo, B.; Sueiro, F.; et al. Consensus regarding the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of canine and feline mammary tumors—2019. Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 13, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, S.R.; International Agency for Research on Cancer; Ellis, I.O.; Schnitt, S.J. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012; ISBN 9789283224334. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, L.N.; World Health Organization; Veterinary Public Health Unit; WHO Collaborating Center for Comparative Oncology. TNM Classification of Tumours in Domestic Animals; Owen, L.n., Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980.
- Elston, C.W.; Ellis, I.O. Pathological Prognostic Factors in Breast Cancer. I. The Value of Histological Grade in Breast Cancer: Experience from a Large Study with Long-Term Follow-Up. Histopathology 1991, 19, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.C.; Campos, C.B.; Teixeira, S.V.; Bertagnolli, A.C.; Lavalle, G.E.; Cassali, G.D. Epidemiological, clinical and pathological evaluation of overall survival in canines with mammary neoplasms. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2018, 70, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.O.; Leung, S.C.Y.; Rimm, D.L.; Dodson, A.; Acs, B.; Badve, S.; Denkert, C.; Ellis, M.J.; Fineberg, S.; Flowers, M.; et al. Assessment of Ki67 in Breast Cancer: Updated Recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; Dowsett, M.; Allred, D.C.; Hagerty, K.L.; Badve, S.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Francis, G.; Goldstein, N.S.; Hayes, M.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Guideline Recommendations for Immunohistochemical Testing of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors in Breast Cancer (Unabridged Version). Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, e48–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 1364–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, A.; Alves, A.; Schmitt, F. Identification of Molecular Phenotypes in Canine Mammary Carcinomas with Clinical Implications: Application of the Human Classification. Virchows Arch. 2008, 453, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmegeed, S.M.; Mohammed, S. Canine Mammary Tumors as a Model for Human Disease. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8195–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monhollen, L.; Morrison, C.; Ademuyiwa, F.O.; Chandrasekhar, R.; Khoury, T. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma: A Distinctive Clinical and Molecular Breast Cancer Type: Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma. Histopathology 2012, 61, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Kalinowski, L.; Simpson, P.T.; Lakhani, S.R. Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: The Increasing Importance of This Special Subtype. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay-Schultz, J.; Sartorius, C.A. Steroid Hormones, Steroid Receptors, and Breast Cancer Stem Cells. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2015, 20, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoerri, M.; Guscetti, F.; Hartnack, S.; Boos, A.; Oei, C.; Balogh, O.; Nowaczyk, R.M.; Michel, E.; Reichler, I.M.; Kowalewski, M.P. Endocrine Control of Canine Mammary Neoplasms: Serum Reproductive Hormone Levels and Tissue Expression of Steroid Hormone, Prolactin and Growth Hormone Receptors. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bonfiglio, R.; Di Pietro, M.L. The Impact of Oral Contraceptive Use on Breast Cancer Risk: State of the Art and Future Perspectives in the Era of 4P Medicine. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 72, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Gama, A.; Seixas, F.; Faustino-Rocha, A.I.; Lopes, C.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F.; Medeiros, R.; Oliveira, P.A. Mammary Glands of Women, Female Dogs and Female Rats: Similarities and Differences to Be Considered in Breast Cancer Research. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenskjöld, A.; Fohlin, H.; Fornander, T.; Löfdahl, B.; Skoog, L.; Stål, O. Progesterone Receptor Positivity Is a Predictor of Long-Term Benefit from Adjuvant Tamoxifen Treatment of Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 160, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, W.L.F.; Lavalle, G.E.; Figueiredo, M.S.; Souza, A.G.; Bertagnolli, A.C.; Viana, F.A.B.; Paes, P.R.O.; Carneiro, R.A.; Cavalcanti, G.A.O.; Melo, M.M.; et al. Evaluation of Adverse Effects in Tamoxifen Exposed Healthy Female Dogs. Acta Vet. Scand. 2010, 52, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarli, G.; Preziosi, R.; Benazzi, C.; Castellani, G.; Marcato, P.S. Prognostic Value of Histologic Stage and Proliferative Activity in Canine Malignant Mammary Tumors. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2002, 14, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadie, J.; Nguyen, F.; Loussouarn, D.; Peña, L.; Gama, A.; Rieder, N.; Belousov, A.; Bemelmans, I.; Jaillardon, L.; Ibisch, C.; et al. Canine Invasive Mammary Carcinomas as Models of Human Breast Cancer. Part 2: Immunophenotypes and Prognostic Significance. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 167, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, L.L.; Nieto, A.I.; Pérez-Alenza, D.; Cuesta, P.; Castaño, M. Immunohistochemical Detection of Ki-67 and PCNA in Canine Mammary Tumors: Relationship to Clinical and Pathologic Variables. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1998, 10, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.; Bertagnolli, A.C.; Cavalcanti, M.F.; Schmitt, F.C.; Cassali, G.D. The Relationship between Tumour Size and Expression of Prognostic Markers in Benign and Malignant Canine Mammary Tumours. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2009, 7, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, N.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, B.B.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, M.S. Associations between the Standardized Uptake Value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT and the Prognostic Factors of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: In Comparison with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, L.; Lei, T.; Pu, T.; Wei, B.; Bu, H.; Zhang, Z. Biomarker Profile of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: Pleomorphic versus Classic Subtypes, Clinicopathological Characteristics and Prognosis Analyses. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 194, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağdıç, M.F.; Güler, O.C.; Subaşı, O.; Albayrak, Ö.; Özaslan, C. Comparison of Clinicopathological Features of Pleomorphic and Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinomas. Am. Surg. 2024, 90, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, E.; Horimoto, Y.; Arakawa, A.; Himuro, T.; Senuma, K.; Nakai, K.; Saito, M. Differences in Ki67 Expressions between Pre- and Post-Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Specimens Might Predict Early Recurrence of Breast Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 63, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.C.; Bertagnolli, A.C.; Lavalle, G.E.; Silveira, T.L.; Balabram, D.; Cassali, G.D. The prognostic significance of immunophenotypes in canine malignant mammary tumors. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2022, 74, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Choi, C.; Lee, S.M.; Zhong, X.; Hibshoosh, H.; Kalinsky, K.; Connolly, E.P. Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma: Pleomorphic versus Classical Subtype, Associations and Prognosis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Jaimes, L.; González-García, I.; Reguero-Callejas, M.E.; Pinilla-Pagnon, I.; Pérez-Mies, B.; Albarrán-Artahona, V.; Martínez-Jañez, N.; Rosa-Rosa, J.M.; Palacios, J. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast with Osteoclast-like Giant Cells: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeau, A. L’âge du Chien et celui de l’Homme. Essai de statistique sur la mortalité canine. Bull. Acad. Vet. Fr. 1953, 106, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Hogan, A.N.; Fong, S.; Licon, K.; Tsui, B.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Adams, P.D.; Carvunis, A.-R.; Bannasch, D.L.; et al. Quantitative Translation of Dog-to-Human Aging by Conserved Remodeling of the DNA Methylome. Cell Syst. 2020, 11, 176–185.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Sugiyama, M. Prognosis for Canine Malignant Mammary Tumors Based on TNM and Histologic Classification. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1996, 58, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.R.; Campos, L.C.; Ferreira, E.; Cassali, G.D. Quantitation of the Regional Lymph Node Metastatic Burden and Prognosis in Malignant Mammary Tumors of Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Manufacturer | Clone | Dilutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| PR | Dako | HPRA2 | 1:50 |
| ER | Dako | 1 D5 | 1:50 |
| KI67 | Dako | Mib-1 | 1:50 |
| E-Cadherin | Zymed (San Francisco, CA, USA) | 4 A2 C7 | 1:50 |
| Her-2 | Dako | Polyclonal | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Manufacturer | Clone | Dilutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| PR | Dako | SP2 | 1:200 |
| ER | Dako | EP1 | Ready to use |
| KI67 | Dako | Mib-1 | 1:180 |
| E-Cadherin | Bio SB inc. (Goleta, CA, USA) | EP700 Y | 1:180 |
| Her-2 | Dako | Polyclonal | 1:180 |
| Luminal A | Luminal B | Her2 Overexpressed | Triple Negative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Her2-Negative | Her2-Positive | ||||
| RE and/or RP | + | + | + | – | – |
| HER-2 | – | – | + | + | – |
| Ki67 | <20% | ≥20% | AS * | AS | AS |
| Canine PLC | Human PLC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) | 9.2 | 56.7 | |
| Tumor Size | % (n) | ||
| <3 cm | 26.9 (7) | - | |
| 3 to 5 cm | 30.8 (8) | - | |
| >5 cm | 38.5 (10) | - | |
| Not available | 3.8 (1) | - | |
| Tumor Size | % (n) | ||
| <2 cm | - | 35 (9) | |
| 2 to 5 cm | - | 38 (11) | |
| >10 cm | - | 12 (3) | |
| Not available | - | 15 (4) | |
| Breed | % (n) | ||
| Mixed breed | 30.8 (8) | ||
| Labrador | 26.6 (7) | ||
| Histological grade | % (n) | 0.0128 | |
| I | 0 | 15.4 (4) | |
| II | 65.4 (17) | 76.9 (20) | |
| III | 34.6 (9) | 7.7 (2) | |
| Lobular Carcinoma In situ | % (n) | 1.0 | |
| Absent | 92 (24) | 96 (24) | |
| Present | 8 (2) | 4 (1) | |
| Lymph Node Metastasis | % (n) | 1.0 | |
| Absent | 35 (9) | 27 (7) | |
| Present | 15 (4) | 35 (9) | |
| Not available | 50 (13) | 38 (10) | |
| Canine PLC | Human PLC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PR | <0.0001 | ||
| 100 (26/26) | 96.2 (25/26) | ||
| 0 | 3.8 (1/26) | ||
| ER | <0.0001 | ||
| 3.8 (1/26) | 100 (26/26) | ||
| 96.2 (25/26) | 0 | ||
| HER-2 | 0.49 | ||
| 100 (26/26) | 92.3 (24/26) | ||
| 0 | 7.7 (2/26) | ||
| KI67 | <0.0001 | ||
| Mean ± SD (Max–Min) % | 58.65 ± 18.81 (88.8–21.5) | 15.73 ± 8.48 (38.0–4.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, E.A.; Borges, L.A.B.; Vieira, T.C.; Santos, B.J.d.; Souza, F.R.; Nakagaki, K.Y.R.; Nunes, C.B.; Cassali, G.D. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in Women and Female Dogs: A Comparative Clinical-Pathological and Immunophenotypic Analysis. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060587
Oliveira EA, Borges LAB, Vieira TC, Santos BJd, Souza FR, Nakagaki KYR, Nunes CB, Cassali GD. Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in Women and Female Dogs: A Comparative Clinical-Pathological and Immunophenotypic Analysis. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060587
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Evelyn Ane, Lize Amanda Basaglia Borges, Thaynan Cunha Vieira, Bárbara Jaime dos Santos, Fernanda Rezende Souza, Karen Yumi Ribeiro Nakagaki, Cristiana Buzelin Nunes, and Geovanni Dantas Cassali. 2025. "Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in Women and Female Dogs: A Comparative Clinical-Pathological and Immunophenotypic Analysis" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060587
APA StyleOliveira, E. A., Borges, L. A. B., Vieira, T. C., Santos, B. J. d., Souza, F. R., Nakagaki, K. Y. R., Nunes, C. B., & Cassali, G. D. (2025). Pleomorphic Lobular Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland in Women and Female Dogs: A Comparative Clinical-Pathological and Immunophenotypic Analysis. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060587






