Changes of Cytokines in Saliva of Pigs with Streptococcus suis Infection Measured with a Multiplex Assay
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. Cytokine Validation and Measurements in Porcine Saliva
2.3. Statistical Analysis
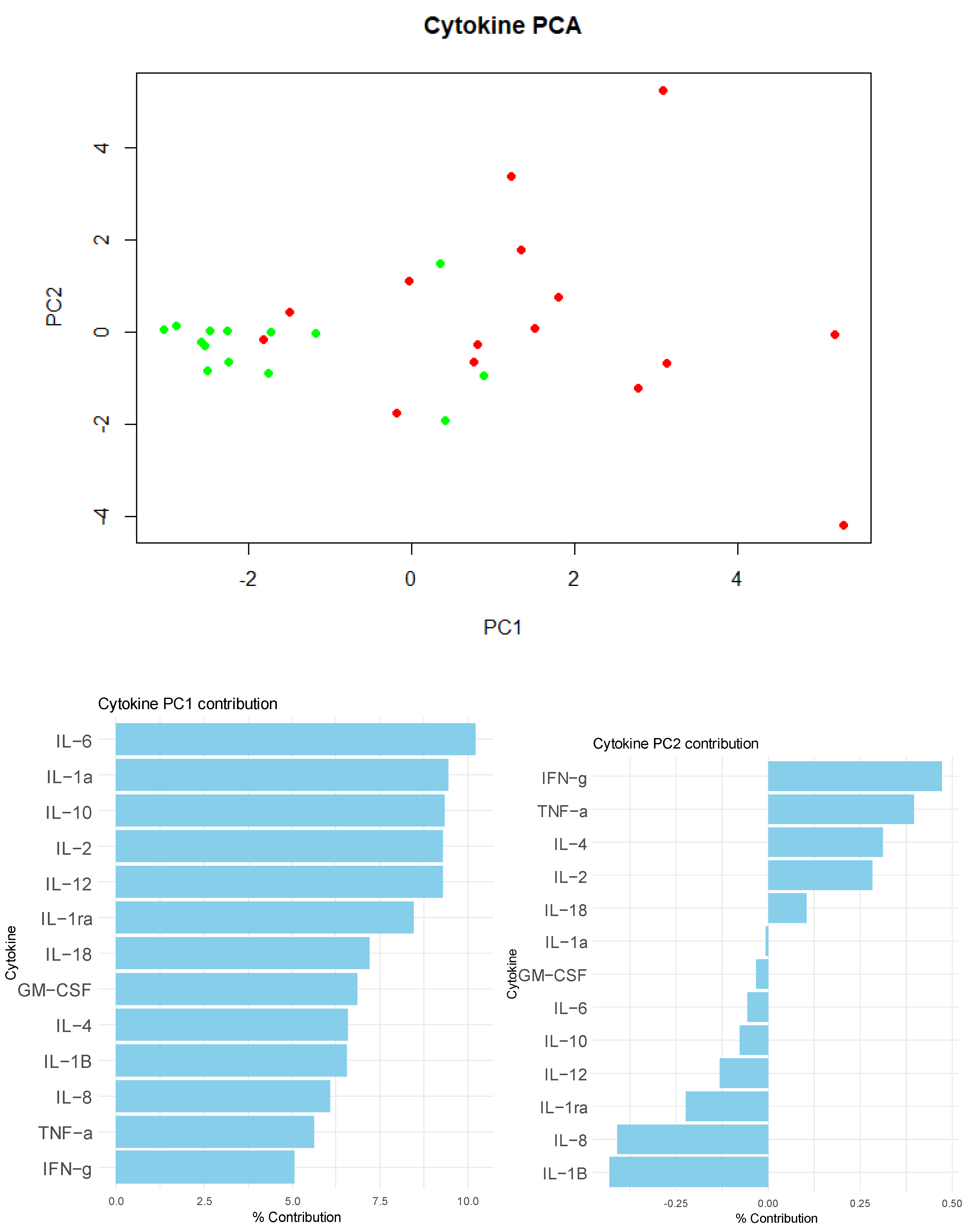
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent—An update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, C.; Varaldo, P.E.; Facinelli, B. Streptococcus suis, an emerging drug-resistant animal and human pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 16700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, D.; Poljak, Z.; Farzan, A.; Friendship, R. Factors contributing to mortality during a Streptoccocus suis outbreak in nursery pigs. Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 623. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, L.W.; Bak, H.; Nielsen, B.; Jensen, H.E.; Aalbæk, B.; Riising, H.J. Bacterial colonization and invasion in pigs experimentally exposed to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in aerosol. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2002, 49, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straw, B.E. (Ed.) Diseases of Swine, 9th ed.; Blackwell Publ: Ames, IA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, L.W.; Svensmark, B.; Elvestad, K.; Aalbaek, B.; Jensen, H.E. Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infection in pigs: New diagnostic and pathogenetic aspects. J. Comp. Pathol. 2002, 126, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Watanabe, T.; Arai, S.; Kim, H.; Tohya, M.; Ishida-Kuroki, K.; Võ, T.H.; Nguy, T.P.B.; Nakagawa, I.; Osawa, R.; et al. Characterization of pig saliva as the major natural habitat of Streptococcus suis by analyzing oral, fecal, vaginal, and environmental microbiota. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torremorell, M.; Calsamiglia, M.; Pijoan, C. Colonization of suckling pigs by Streptococcus suis with particular reference to pathogenic serotype 2 strains. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1998, 62, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Baele, M.; Chiers, K.; Devriese, L.A.; Smith, H.E.; Wisselink, H.J.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Haesebrouck, F. The gram-positive tonsillar and nasal flora of piglets before and after weaning. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena Cortes, L.C.; Leveque, R.M.; Funk, J.; Marsh, T.L.; Mulks, M.H. Development of the tonsillar microbiome in pigs from newborn through weaning. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Segura, M.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, K.; Keller, H.; Grass, G.; Minor, T.; Stueber, F.; Schroeder, S.; Putensen, C.; Paul, C.; Burger, C.; Rangger, C.; et al. Cytokines and chemokines in serum and urine as early predictors to identify septic patients on intensive care unit. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 12, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punyadeera, C.; Schneider, E.M.; Schaffer, D.; Hsu, H.Y.; Joos, T.O.; Kriebel, F.; Weiss, M.; Verhaegh, W.F.J. A biomarker panel to discriminate between systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis and sepsis severity. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock 2010, 3, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mera, S.; Tatulescu, D.; Cismaru, C.; Bondor, C.; Slavcovici, A.; Zanc, V.; Carstina, D.; Oltean, M. Multiplex cytokine profiling in patients with sepsis. APMIS 2011, 119, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Stankova, J.; Gottschalk, M. Heat-killed Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 strains stimulate tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 production by murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4646–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, M.; Vadeboncoeur, N.; Gottschalk, M. CD14-dependent and -independent cytokine and chemokine production by human THP-1 monocytes stimulated by Streptococcus suis capsular type 2. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 127, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Vanier, G.; Al-Numani, D.; Lacouture, S.; Olivier, M.; Gottschalk, M. Proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine modulation by Streptococcus suis in a whole-blood culture system. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohnstein, F.S.; Meurer, M.; de Buhr, N.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Baums, C.G.; Alber, G.; Schütze, N. Analysis of porcine pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine induction by S. suis in vivo and in vitro. Pathogens 2020, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón, J.J. Acute phase proteins, saliva and education in laboratory science: An update and some reflections. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Cerón, J.J.; Aguilar, M.D.C.; Escribano, D.; Martínez Miró, S.; López Martínez, M.J.; Ortín-Bustillo, A.; Franco-Martínez, L.; Rubio, C.; Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; et al. Basics for the potential use of saliva to evaluate stress, inflammation, immune system, and redox homeostasis in pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- López-Martínez, M.J.; Beletić, A.; Kuleš, J.; Rešetar-Maslov, D.; Rubić, I.; Mrljak, V.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Goyena, E.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; et al. Revealing the Changes in Saliva and Serum Proteins of Pigs with Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus suis: A Proteomic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, M.J.; Ornelas, M.A.S.; Amarie, R.E.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Tecles, F.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Escribano, D.; González-Bulnes, A.; Cerón, J.J.; et al. Changes in salivary biomarkers of stress, inflammation, redox status, and muscle damage due to Streptococcus suis infection in pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.R.; Segura, M.; Segalés, J.; Gottschalk, M. Review of the speculative role of co-infections in Streptococcus suis-associated diseases in pigs. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Rodriguez, M.; Shields, C.A.; Travis, O.K.; Tramel, R.W.; Baik, C.H.; Giachelli, C.A.; Tardo, G.A.; Williams, J.M.; Cornelius, D.C. Platelet Inhibition Prevents NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocchi-Rilo, M.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Aguarón-Turrientes, Á.; Roca-Martínez, E.; García-Iglesias, M.J.; Pérez-Fernández, E.; González-Fernández, A.; Herencia-Lagunar, E.; Gutiérrez-Martín, C.B. Anatomical Site, Typing, Virulence Gene Profiling, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Resistance Genes of Streptococcus suis Isolates Recovered from Pigs in Spain. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwumabua, O.; O’Connor, M.; Shull, E. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay specific for Streptococcus suis based on the gene encoding the glutamate dehydrogenase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 218, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Martinez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Teles, M.; Tort, L. Chemiluminescent assay as an alternative to radioimmunoassay for the measurement of cortisol in plasma and skin mucus of Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.W.; Kantarci, A.; LaMonte, M.J.; Andrews, C.A.; Hovey, K.M.; Falkner, K.L.; Cekici, A.; Stephens, D.; Genco, R.J.; Scannapieco, F.A.; et al. Performance of Multiplex Cytokine Assays in Serum and Saliva among Community-Dwelling Postmenopausal Women. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 59498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, P.J.; Ryder, R.R.; Todd, I.; Fairclough, L.C. ELISA in the multiplex era: Potentials and pitfalls. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Center for Vetenary Medicine Guidance for Industry Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry Bioanalytical Method Validation. FDA; 2018. FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.G.; Herrador, M.A.; Asuero, A.G. Intra-laboratory testing of method accuracy from recovery assays. Talanta 1999, 48, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Historical insights into cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, M.J.; Franco-Martínez, L.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J. Biomarkers of sepsis in pigs, horses and cattle: From acute phase proteins to procalcitonin. Anim. Heal. Res. Rev. 2022, 23, 82–99. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, L.; Barranco, I.; Parrilla, I.; Lucas, X.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H.; Roca, J. Measurable cytokine concentrations in pig seminal plasma are modified by semen handling and storage. Biology 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Smith, M.S.; Reda, D.; Suffredini, A.F.; McCoy, J.P. Multiplex bead array assays for detection of soluble cytokines: Comparisons of sensitivity and quantitative values among kits from multiple manufacturers. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2004, 61, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher-Hennings, J.; Araujo, K.P.C.; Souza, C.J.H.; Fang, Y.; Lawson, S.; Nelson, E.A.; Clement, T.; Dunn, M.; Lunney, J.K. Opportunities for bead-based multiplex assays in veterinary diagnostic laboratories. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 671–691. [Google Scholar]
- Vanier, G.; Segura, M.; Lecours, M.P.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Porcine brain microvascular endothelial cell-derived interleukin-8 is first induced and then degraded by Streptococcus suis. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 46, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueland, N.L.; Ludvigsen, J.K.; Hellerud, B.C.; Mollnes, T.E.; Skjeflo, E.W. Choice of immunoassay to evaluate porcine cytokine levels. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 230, 110129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feezor, R.J.; Oberholzer, C.; Baker, H.V.; Novick, D.; Rubinstein, M.; Moldawer, L.L.; Pribble, J.; Souza, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; Ertel, W.; et al. Molecular characterization of the acute inflammatory response to infections with gram-negative versus gram-positive bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 5803–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, M.; Lawrence, D.A.; Andersen, N.; Davidová, A.; Beran, O.; Marešová, V.; Chalupa, P. Cytokines and Chemokines as Biomarkers of Community-Acquired Bacterial Infection. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 190145. [Google Scholar]
- Surbatovic, M.; Popovic, N.; Vojvodic, D.; Milosevic, I.; Acimovic, G.; Stojicic, M.; Veljovic, M.; Jevdjic, J.; Djordjevic, D.; Radakovic, S. Cytokine profile in severe Gram-positive and Gram-negative abdominal sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11355. [Google Scholar]
| GM-CSF | IFNγ | IL-1α | IL-1β | IL-1ra | IL-2 | IL-4 | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-10 | IL-12 | IL-18 | TNF-α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linearity (R2) | High A | LLOQ | 0.382 | 0.988 | 0.998 | 0.989 | LLOQ | 0.974 | 0.982 | 1.000 | 0.917 | 0.968 | 0.980 | LLOQ |
| High B | LLOQ | 0.376 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.901 | LLOQ | 0.949 | 0.914 | 1.000 | 0.980 | 0.904 | 0.967 | LLOQ | |
| Intra-assay CV (%) | High A | 0.0 | 13.2 | 4.6 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 10.2 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 14.7 | 0.0 | 8.0 | 0.0 |
| High B | 0.0 | 7.7 | 3.5 | 7.1 | 3.3 | 0.0 | 8.7 | 14.9 | 2.7 | 13.9 | 0.0 | 5.9 | 0.0 | |
| High C | 24.7 | 14.6 | 3.9 | 4.3 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 8.1 | 3.7 | 7.5 | 8.7 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 0.0 | |
| Low A | LLOQ | 12.6 | 4.7 | 0.0 | 4.2 | 0.0 | 24.7 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | LLOQ | |
| Low B | LLOQ | 13.6 | 5.6 | 0.0 | 10.1 | 0.0 | 21.7 | 0.0 | 5.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Low C | LLOQ | 3.8 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 10.8 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Spiking recovery (%) | Saliva | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 50 + 50 | 19.5 | 50.9 | 81.1 | 50.8 | 68.7 | 75.2 | 110.7 | 67.4 | 8.9 | 82.8 | 60.7 | 76.8 | 69.0 | |
| 50 + 50 (1:2) | 37.1 | 26.2 | 113.9 | 65.7 | 79.4 | 92.6 | 82.9 | 71.1 | 13.5 | 91.6 | 74.9 | 73.0 | 95.2 | |
| 50 + 50 (1:4) | 61.0 | 59.7 | 128.2 | 80.5 | 88.3 | 109.0 | 106.1 | 80.5 | 25.9 | 93.5 | 89.3 | 80.1 | 98.7 | |
| STD | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Cytokine (ng/mL) | Median (25th, 75th Percentiles) | |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy | S. suis | |
| GM.CSF | 0.02 (0.02. 0.03) | 0.04 (0.02. 0.06) * |
| IFNγ | 0.17 (0.1125. 0.5175) | 1.16 (0.26. 2.42) * |
| IL-1α | 0.66 (0.525. 1.6575) | 2.96 (1.32. 3.99) *** |
| IL-1β | 0.16 (0.07. 0.55) | 0.39 (0.07. 0.64) *** |
| IL-1ra | 5.83 (1.91. 15.0575) | 27.61 (1.57. 61.58) |
| IL-2 | 0.025 (0.02. 0.0325) | 0.06 (0.04. 0.11) *** |
| IL-4 | 0.08 (0.0675. 0.12) | 0.32 (0.16. 0.53) *** |
| IL-6 | 0.14 (0.11. 0.335) | 0.42 (0.28. 0.7) *** |
| IL-8 | 1.95 (1.0725. 3.6775) | 4.48 (0.79. 7.74) |
| IL-10 | 0.04 (0.04. 0.06) | 0.12 (0.04. 0.19) *** |
| IL-12 | 0.02 (0.0175. 0.02) | 0.03 (0.02. 0.06) *** |
| IL-18 | 0.425 (0.3175. 0.62) | 0.94 (0.56. 1.38) ** |
| TNF-α | 0.02 (0.02. 0.02) | 0.04 (0.03. 0.08) ** |
| GM-CSF | IFNγ | IL-1α | IL-1β | IL-1ra | IL-2 | IL-4 | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-10 | IL-12 | IL-18 | TNF-α | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM.CSF | r = 0.44 p = 0.017 | r = 0.412 p = 0.027 | r = −0.151 p = 0.433 | r = 0.027 p = 0.889 | r = 0.633 p < 0.001 | r = 0.444 p = 0.016 | r = 0.507 p = 0.005 | r = −0.092 p = 0.634 | r = 0.386 p = 0.038 | r = 0.315 p = 0.096 | r = 0.364 p = 0.053 | r = 0.326 p = 0.084 | |
| IFNγ | r = 0.44 p = 0.017 | r = 0.535 p = 0.003 | r = −0.254 p = 0.184 | r = −0.041 p = 0.832 | r = 0.6 p = 0.001 | r = 0.676 p < 0.001 | r = 0.397 p = 0.033 | r = −0.264 p = 0.166 | r = 0.502 p = 0.005 | r = 0.366 p = 0.051 | r = 0.438 p = 0.018 | r = 0.614 p < 0.001 | |
| IL-1α | r = 0.412 p = 0.027 | r = 0.535 p = 0.003 | r = 0.354 p = 0.06 | r = 0.467 p = 0.011 | r = 0.646 p < 0.001 | r = 0.705 p < 0.001 | r = 0.671 p < 0.001 | r = 0.371 p = 0.047 | r = 0.735 p < 0.001 | r = 0.84 p < 0.001 | r = 0.632 p < 0.001 | r = 0.671 p < 0.001 | |
| IL-1β | r = −0.151 p = 0.433 | r = −0.254 p = 0.184 | r = 0.354 p = 0.06 | r = 0.722 p < 0.001 | r = 0.051 p = 0.793 | r = −0.024 p = 0.901 | r = 0.338 p = 0.073 | r = 0.915 p < 0.001 | r = 0.44 p = 0.017 | r = 0.585 p = 0.001 | r = 0.243 p = 0.204 | r = 0.32 p = 0.09 | |
| IL.1ra | r = 0.027 p = 0.889 | r = −0.041 p = 0.832 | r = 0.467 p = 0.011 | r = 0.722 p < 0.001 | r = 0.38 p = 0.042 | r = 0.349 p = 0.064 | r = 0.505 p = 0.005 | r = 0.63 p < 0.001 | r = 0.659 p < 0.001 | r = 0.602 p = 0.001 | r = 0.529 p = 0.003 | r = 0.359 p = 0.056 | |
| IL-2 | r = 0.633 p < 0.001 | r = 0.6 p = 0.001 | r = 0.646 p < 0.001 | r = 0.051 p = 0.793 | r = 0.38 p = 0.042 | r = 0.876 p < 0.001 | r = 0.806 p < 0.001 | r = 0.04 p = 0.836 | r = 0.653 p < 0.001 | r = 0.612 p < 0.001 | r = 0.842 p < 0.001 | r = 0.631 p < 0.001 | |
| IL-4 | r = 0.444 p = 0.016 | r = 0.676 p < 0.001 | r = 0.705 p < 0.001 | r = −0.024 p = 0.901 | r = 0.349 p = 0.064 | r = 0.876 p < 0.001 | r = 0.694 p < 0.001 | r = −0.039 p = 0.84 | r = 0.688 p < 0.001 | r = 0.604 p = 0.001 | r = 0.743 p < 0.001 | r = 0.673 p < 0.001 | |
| IL-6 | r = 0.507 p = 0.005 | r = 0.397 p = 0.033 | r = 0.671 p < 0.001 | r = 0.338 p = 0.073 | r = 0.505 p = 0.005 | r = 0.806 p < 0.001 | r = 0.694 p < 0.001 | r = 0.289 p = 0.128 | r = 0.638 p < 0.001 | r = 0.633 p < 0.001 | r = 0.87 p < 0.001 | r = 0.591 p = 0.001 | |
| IL-8 | r = −0.092 p = 0.634 | r = −0.264 p = 0.166 | r = 0.371 p = 0.047 | r = 0.915 p < 0.001 | r = 0.63 p < 0.001 | r = 0.04 p = 0.836 | r = −0.039 p = 0.84 | r = 0.289 p = 0.128 | r = 0.407 p = 0.028 | r = 0.647 p < 0.001 | r = 0.197 p = 0.305 | r = 0.393 p = 0.035 | |
| IL-10 | r = 0.386 p = 0.038 | r = 0.502 p = 0.005 | r = 0.735 p < 0.001 | r = 0.44 p = 0.017 | r = 0.659 p < 0.001 | r = 0.653 p < 0.001 | r = 0.688 p < 0.001 | r = 0.638 p < 0.001 | r = 0.407 p = 0.028 | r = 0.79 p < 0.001 | r = 0.557 p = 0.002 | r = 0.75 p < 0.001 | |
| IL-12 | r = 0.315 p = 0.096 | r = 0.366 p = 0.051 | r = 0.84 p < 0.001 | r = 0.585 p = 0.001 | r = 0.602 p = 0.001 | r = 0.612 p < 0.001 | r = 0.604 p = 0.001 | r = 0.633 p < 0.001 | r = 0.647 p < 0.001 | r = 0.79 p < 0.001 | r = 0.596 p = 0.001 | r = 0.774 p < 0.001 | |
| IL-18 | r = 0.364 p = 0.053 | r = 0.438 p = 0.018 | r = 0.632 p < 0.001 | r = 0.243 p = 0.204 | r = 0.529 p = 0.003 | r = 0.842 p < 0.001 | r = 0.743 p < 0.001 | r = 0.87 p < 0.001 | r = 0.197 p = 0.305 | r = 0.557 p = 0.002 | r = 0.596 p = 0.001 | r = 0.581 p = 0.001 | |
| TNF-α | r = 0.326 p = 0.084 | r = 0.614 p < 0.001 | r = 0.671 p < 0.001 | r = 0.32 p = 0.09 | r = 0.359 p = 0.056 | r = 0.631 p < 0.001 | r = 0.673 p < 0.001 | r = 0.591 p = 0.001 | r = 0.393 p = 0.035 | r = 0.75 p < 0.001 | r = 0.774 p < 0.001 | r = 0.581 p = 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Pardo-Marín, L.; Goyena, E.; García Manzanilla, E.; Cerón, J.J.; Franco-Martínez, L. Changes of Cytokines in Saliva of Pigs with Streptococcus suis Infection Measured with a Multiplex Assay. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040316
Muñoz-Prieto A, Pardo-Marín L, Goyena E, García Manzanilla E, Cerón JJ, Franco-Martínez L. Changes of Cytokines in Saliva of Pigs with Streptococcus suis Infection Measured with a Multiplex Assay. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040316
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Prieto, Alberto, Luis Pardo-Marín, Elena Goyena, Edgar García Manzanilla, José Joaquín Cerón, and Lorena Franco-Martínez. 2025. "Changes of Cytokines in Saliva of Pigs with Streptococcus suis Infection Measured with a Multiplex Assay" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040316
APA StyleMuñoz-Prieto, A., Pardo-Marín, L., Goyena, E., García Manzanilla, E., Cerón, J. J., & Franco-Martínez, L. (2025). Changes of Cytokines in Saliva of Pigs with Streptococcus suis Infection Measured with a Multiplex Assay. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040316








