Coxiella burnetii (Q Fever) in Small Ruminants on Farms in North West Province, South Africa
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Sample Size Determination
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Serological Testing
2.6. DNA Extraction
2.7. PCR Detection of C. burnetii
2.8. Sequence Confirmation of C. burnetii
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
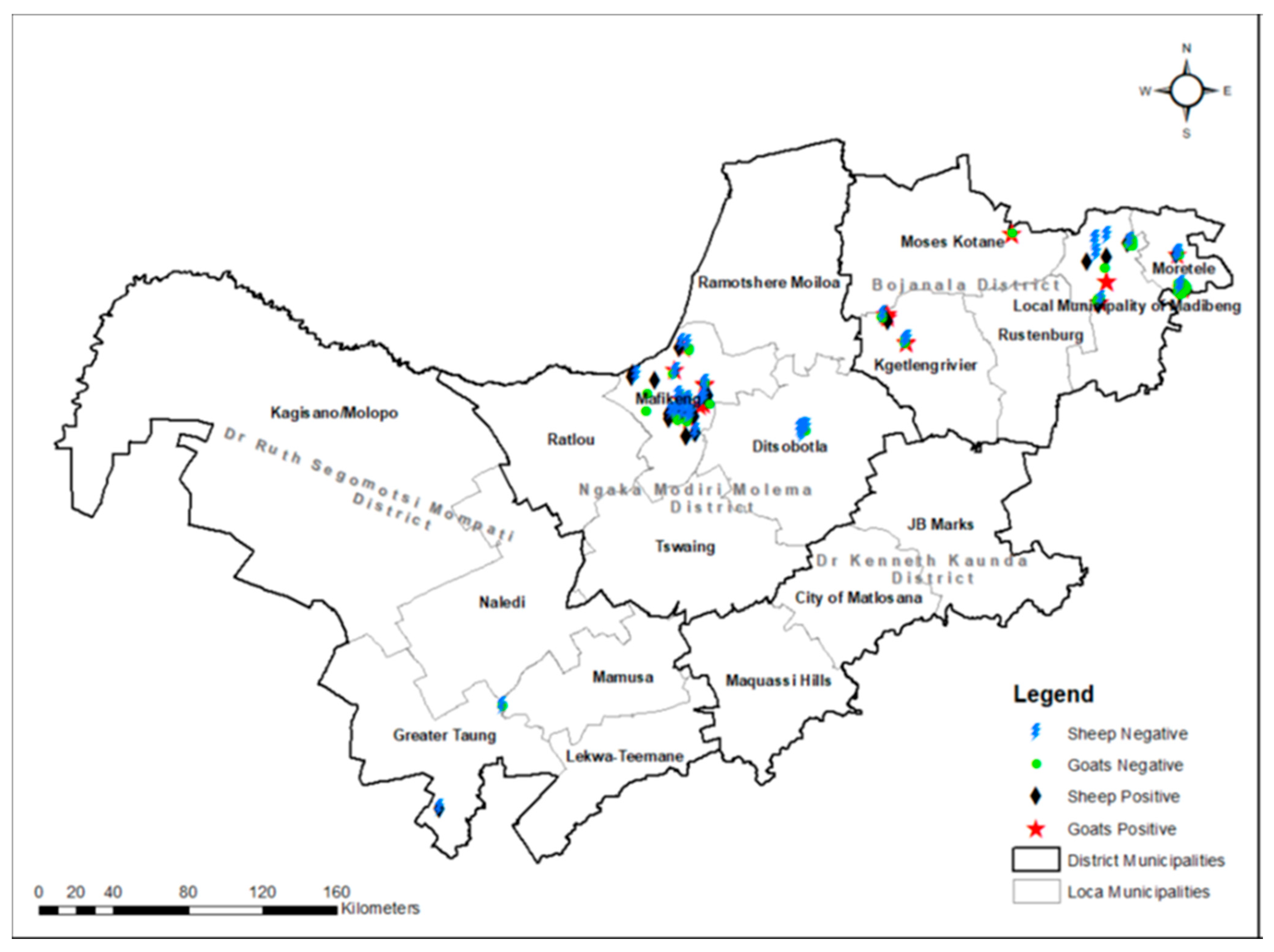
3.1. Seroprevalence of Q Fever and Risk Analysis
3.2. Molecular Detection of C. burnetii and Associated Risk Factors
3.3. Sequence Analysis of C. burnetii IS1111
3.4. Correlation Between ELISA and PCR Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sireci, G.; Badami, G.D.; Di Liberto, D.; Blanda, V.; Grippi, F.; Di Paola, L.; Guercio, A.; de la Fuente, J.; Torina, A. Recent Advances on the Innate Immune Response to Coxiella burnetii. In Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology; Frontiers Media S.A.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, E.; Raoult, D. Q fever. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 297–309. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moein, K.A.; Hamza, D.A. Rat as an overlooked reservoir for Coxiella burnetii: A public health implication. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 61, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boni, L.; Mall, S.; Msimang, V.; de Voux, A.; Rossouw, J.; Frean, J. Exposure of South African Abattoir Workers to Coxiella burnetii. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarez, A.M.; Khalili, M.; Mostafavi, E.; Esmaeili, S. Molecular detection of Coxiella burnetii infection in aborted samples of domestic ruminants in Iran. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250116. [Google Scholar]
- Honarmand, H. Q fever: An old but still a poorly understood disease. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2012, 2012, 131932. [Google Scholar]
- van Asseldonk, M.A.P.M.; Bontje, D.M.; Backer, J.A.; van Roermund, H.J.W.; Bergevoet, R.H.M. Economic aspects of Q fever control in dairy goats. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 121, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kittelberger, R.; Mars, J.; Wibberley, G.; Sting, R.; Henning, K.; Horner, G.W.; Garnett, K.M.; Hannah, M.J.; Jenner, J.A.; Pigott, C.J.; et al. Comparison of the q-fever complement fixation test and two commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of serum antibodies against coxiella burnetii (Q-fever) in ruminants: Recommendations for use of serological tests on imported animals in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2009, 57, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, H.K.; Branan, M.; Priestley, R.A.; Álvarez-Alonso, R.; Cherry, C.; Smith, C.; Urie, N.J.; Wiedenheft, A.; Bliss, C.; Marshall, K.; et al. Coxiella burnetii in domestic doe goats in the United States, 2019–2020. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1393296. [Google Scholar]
- Eibach, R.; Bothe, F.; Runge, M.; Fischer, S.F.; Philipp, W.; Ganter, M. Q fever: Baseline monitoring of a sheep and a goat flock associated with human infections. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiki, V.; Gcebe, N.; Mangena, M.L.; Ngoshe, Y.B.; Adesiyun, A.A. Prevalence and risk factors of Q fever (Coxiella burnetii) in cattle on farms of Limpopo province, South Africa. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1101988. [Google Scholar]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Knobel, D.L.; Thompson, P.N.; Wentzel, J.; Kolo, F.B.; Kolo, A.O.; Conan, A.; Simpson, G.J. Sero-Epidemiological Study of Selected Zoonotic and Abortifacient Pathogens in Cattle at a Wildlife-Livestock Interface in South Africa. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mangena, M.; Gcebe, N.; Pierneef, R.; Thompson, P.N.; Adesiyun, A.A. Q fever: Seroprevalence, risk factors in slaughter livestock and genotypes of coxiella burnetii in South Africa. Pathogens 2021, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtshali, K.; Khumalo, Z.T.H.; Nakao, R.; Grab, D.J.; Sugimoto, C.; Thekisoe, O.M.M. Molecular detection of zoonotic tick-borne pathogens from ticks collected from ruminants in four South African provinces. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 77, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Thrusfield, M. Veterinary Epidemiology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 1289. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruin, A.; Tw Van Alphen, P.; Van Der Plaats, R.Q.; Nd De Heer, L.; Reusken, C.B.; Van Rotterdam, B.J.; Janse, I. Molecular Typing of Coxiella burnetii from Animal and Environmental Matrices During Q Fever Epidemics in the Netherlands. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Andrew Dean, M.; Minn Minn Soe, M. On Academics: Openepi: A web-based epidemiologic and statistical calculator for public health. Public Health Rep. 2009, 124, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Lessons in biostatistics interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Medica 2012, 22, 276–282. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/89395 (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Magadu, R.; Thompson, P.N. Seroprevalence and factors associated with Coxiella burnetii exposure in goats in Moretele. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2023, 90, 2071. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.A.; Kaneene, J.B.; Asare-Dompreh, K.; Tasiame, W.; Mensah, I.G.; Afakye, K.; Simpson, S.V.; Addo, K. Seroprevalence of Q fever in cattle, sheep and goats in the Volta region of Ghana. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 5, 402–411. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer, B.; Luttikholt, S.; Hautvast, J.L.A.; Graat, E.A.M.; Vellema, P.; van Duynhoven, Y.T.H.P. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Q fever in goats on commercial dairy goat farms in the Netherlands, 2009–2010. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiptanui, J.; Gathura, P.B.; Kitala, P.M.; Bett, B. Seroprevalence Estimates of Q Fever and the Predictors for the Infection in Cattle, Sheep, and Goats in Nandi County, Kenya. Vet. Med. Int. 2022, 2022, 3741285. [Google Scholar]
- Adamu, G.; Kia, G.; Saidu, S.N.A.; Ejeh, F. Serosurvey and Risk Factors of Coxiella burnetii in Sheep and Goats in three agricultural zones of Borno State, Nigeria. Authorea 2022, Preprints. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.A.R.; de Castro, E.M.S.; de Oliveira, G.M.B.; Azevedo, S.S.; Peixoto, R.d.M.; Labruna, M.B.; Horta, M.C. Serological diagnosis and risk factors for Coxiella burnetii in goats and sheep in a semi-arid region of northeastern Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2018, 27, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemmer, J.; Njeru, J.; Emam, A.; El-Sayed, A.; Moawad, A.A.; Henning, K.; Elbeskawy, M.A.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Straubinger, R.K.; Neubauer, H.; et al. Q fever in Egypt: Epidemiological survey of Coxiella burnetii specific antibodies in cattle, buffaloes, sheep, goats and camels. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, T.; Muramatsu, Y.; Ueno, H.; Morita, C. Seasonal variations in the presence of antibodies against Coxiella burnetii in dairy cattle in Hokkaido, Japan. Microbiol. Immunol. 1997, 41, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangena, M.L.; Gcebe, N.; Thompson, P.N.; Adesiyun, A.A. Q fever and toxoplasmosis in South African livestock and wildlife: A retrospective study on seropositivity, sporadic abortion, and stillbirth cases in livestock caused by Coxiella burnetii. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Total Tested | Number of Positives | Prevalence (%) | Odd Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | ||||||
| Goat | 266 | 82 | 30.82 | 0.686 | 0.45–1.04 | 0.094 |
| Sheep | 155 | 61 | 39.35 | 1 | ||
| Breed | ||||||
| Boergoat | 264 | 81 | 30.68 | 1 | ||
| Dorper | 105 | 41 | 39.05 | 0.691 | 0.43–1.11 | 0.156 |
| White Dorper | 44 | 19 | 43.18 | 0.582 | 0.30–1.11 | 0.142 |
| Others | 8 | 2 | 25.00 | 1.328 | 0.26–6.72 | 0.779 a |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 395 | 134 | 33.92 | 0.969 | 0.42–2.23 | 0.887 |
| Male | 26 | 9 | 34.62 | |||
| Age category | ||||||
| 1–2 years | 65 | 27 | 41.51 | 1 | ||
| 2.5–4 years | 158 | 52 | 32.91 | 1.448 | 0.79–2.62 | 0.286 |
| >4 years | 198 | 64 | 32.32 | 1.488 | 0.83–2.64 | 0.228 |
| Farm type | ||||||
| Commercial | 38 | 13 | 34.21 | 1 | ||
| Communal | 378 | 130 | 34.39 | 0.992 | 0.49–2.00 | 0.875 |
| Semi-Commercial | 5 | 2 | 40.00 | 0.780 | 0.11–5.27 | 0.800 a |
| Season | ||||||
| Autumn | 136 | 46 | 7.44 | 1 | ||
| Spring | 197 | 65 | 7.25 | 1.038 | 0.65–1.65 | 0.968 |
| Summer | 35 | 18 | 11.31 | 0.482 | 0.23–1.02 | 0.084 |
| Winter | 53 | 14 | 5.81 | 1.424 | 0.70–2.88 | 0.420 |
| Pregnancy status | ||||||
| Not Pregnant | 400 | 133 | 33.25 | 1.825 | 0.75–4.41 | 0.264 |
| Pregnant | 21 | 10 | 47.62 | |||
| History of abortion | ||||||
| Abortion | 89 | 26 | 29.21 | 1.319 | 0.79–2.19 | 0.347 |
| No abortion | 332 | 117 | 35.24 |
| Variables | Total Tested | Number Positives | Frequency Occurrence (%) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | |||||
| Goat | 68 | 46 | 36.51 | 55.85–77.56 | 0.148 a |
| Sheep | 58 | 31 | 24.60 | 40.80–65.67 | |
| Breed | |||||
| Boergoat | 68 | 46 | 67.64 | 55.85–77.56 | 0.170 b |
| Dorper | 46 | 26 | 56.52 | 45.25–69.79 | |
| White Dorper | 12 | 5 | 41.67 | 19.33–68.05 | |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 122 | 75 | 61.47 | 52.62–69.63 | 0.669 a |
| Male | 4 | 2 | 50.00 | 15.00–85.00 | |
| Age category | |||||
| 1–2 years | 3 | 11 | 84.62 | 57.77–96.67 | 0.147 b |
| 2.5–4 years | 68 | 38 | 55.88 | 44.08–67.05 | |
| >4 years | 45 | 28 | 62.22 | 47.63–74.89 | |
| Farm type | |||||
| Communal | 6 | 2 | 33.33 | 9.67–70.00 | 0.191 a |
| Semi-Commercial | 12 | 75 | 62.50 | 53.58–70.65 | |
| District | |||||
| Bojanala | 10 | 7 | 70.00 | 39.68–89.22 | 0.097 b |
| Dr Ruth Segomotsi | |||||
| Mompati | 33 | 15 | 45.44 | 29.84–62.01 | |
| Ngaka Modiri Molema | 83 | 55 | 66.22 | 55.58–75.52 | |
| Season i | |||||
| Autumn | 38 | 28 | 73.68 | 57.99–85.03 | 0.001 b |
| Spring | 53 | 25 | 47.16 | 34.38–60.34 | |
| Summer | 16 | 15 | 93.75 | 71.67–98.89 | |
| Winter | 19 | 9 | 47.36 | 27.33–68.29 | |
| Pregnancy status | |||||
| Not Pregnant | 124 | 76 | 61.29 | 52.50–69.40 | 0.777 a |
| Pregnant | 2 | 1 | 50.00 | 9.45–90.55 | |
| History of abortion | |||||
| Abortion | 23 | 10 | 43.47 | 25.64–63.19 | 0.093 a |
| No Abortion | 103 | 67 | 65.05 | 55.45–73.56 |
| Sample ID | BLAST Result: Description of Strain | Accession Number | Percentage Similarity (%) | e-Value | Query Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-B-Madi | Coxiella burnetii strain NKH2 insertion sequence IS1111, partial sequence | MF197400.1 | 79.74 | 4.00 × 10−18 | 98% |
| S-B-Gany | Coxiella burnetii 54TI transpose gene, partial cds | MT268532.1 | 92.57 | 2.00 × 10−50 | 98% |
| G-A-Gany | Coxiella burnetii isolate Cth 974 transposase gene, partial cds | MK758121.1 | 91.95 | 1.00 × 10−48 | 96% |
| B10-8 | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transpose gene, partial cds | MT268532.1 | 86.18 | 8.00 × 10−35 | 98% |
| S-C-Stel | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT2685321.1 | 96.62 | 2.00 × 10−60 | 97% |
| S-C20-Sebo | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT2685321.1 | 89.47 | 1.00 × 10−42 | 95% |
| S-C4-Matl | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT2685321.1 | 89.26 | 5.00 × 10−42 | 97% |
| S-4A-Dith | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT2685321.1 | 91.1 | 6.00 × 10−46 | 98% |
| S-AD-Lotl | Coxiella burnetii clone GaHi12F8 insertion sequence IS1111A transposase gene, partial cds | MN094847.1 | 88.74 | 6.00 × 10−41 | 98% |
| S-H1-Kgom | Coxiella burnetii insertion sequence IS1111A transposase gene, partial cds | KU058956.1 | 89.04 | 2.00 × 10−41 | 98% |
| G-6-Mata | Coxiella burnetii clone GaHi12F8 insertion sequence IS1111A transposase gene, partial cds | MN094847.1 | 87.66 | 1.00 × 10−38 | 98% |
| S-B20-Mole | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT268532.1 | 92.67 | 6.00 × 10−51 | 97% |
| G-A2-Lotl | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT268532.1 | 93.88 | 3.00 × 10−53 | 96% |
| S-D1-Lotl | Coxiella burnetii Z3055 complete genome | LK937696.1 | 90.41 | 1.00 × 10−42 | 96% |
| G-E-Matl | Coxiella burnetii Z3055 complete genome | LK937696.1 | 89.8 | 1.00 × 10−42 | 96% |
| G-X-Masu | Coxiella burnetii isolate Cth 974 transposase gene, partial cds | MK758121.1 | 91.1 | 6.00 × 10−46 | 96% |
| G-H4-Kgom | Coxiella burnetii isolate Cth 974 transposase gene, partial cds | MK758121.1 | 88.74 | 2.00 × 10−40 | 94% |
| S-AB-Scho | Coxiella burnetii isolate INIFAP Cap01 insertion sequence IS110 transposase gene, partial cds | MT462981.1 | 88.51 | 3.00 × 10−38 | 98% |
| G-A-Rooi | Coxiella burnetii Cth 974 transposase gene, partial cds | MK758121.1 | 86.49 | 2.00 × 10−35 | 95% |
| G-C-Dith | Coxiella burnetii strain 54T1 transposase gene, partial cds | MT2685321.1 | 91.78 | 4.00 × 10−47 | 98% |
| PCR | Row Marginals | Agreement | Cohen’s Kappa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | Negative | 66 | 49 | 115 | 0.57 | 0.13 |
| Positive | 60 | 77 | 137 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosikidi, K.N.; Mphuthi, N.M.; Mangena, M.L.; Lazarus, D.D.; Sirdar, M.; Gcebe, N. Coxiella burnetii (Q Fever) in Small Ruminants on Farms in North West Province, South Africa. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040315
Mosikidi KN, Mphuthi NM, Mangena ML, Lazarus DD, Sirdar M, Gcebe N. Coxiella burnetii (Q Fever) in Small Ruminants on Farms in North West Province, South Africa. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040315
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosikidi, Katleho N., Nthabiseng Malekoba Mphuthi, Maruping L. Mangena, David D. Lazarus, Mohammed Sirdar, and Nomakorinte Gcebe. 2025. "Coxiella burnetii (Q Fever) in Small Ruminants on Farms in North West Province, South Africa" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040315
APA StyleMosikidi, K. N., Mphuthi, N. M., Mangena, M. L., Lazarus, D. D., Sirdar, M., & Gcebe, N. (2025). Coxiella burnetii (Q Fever) in Small Ruminants on Farms in North West Province, South Africa. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040315






