Resistance of Varroa destructor against Oxalic Acid Treatment—A Systematic Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
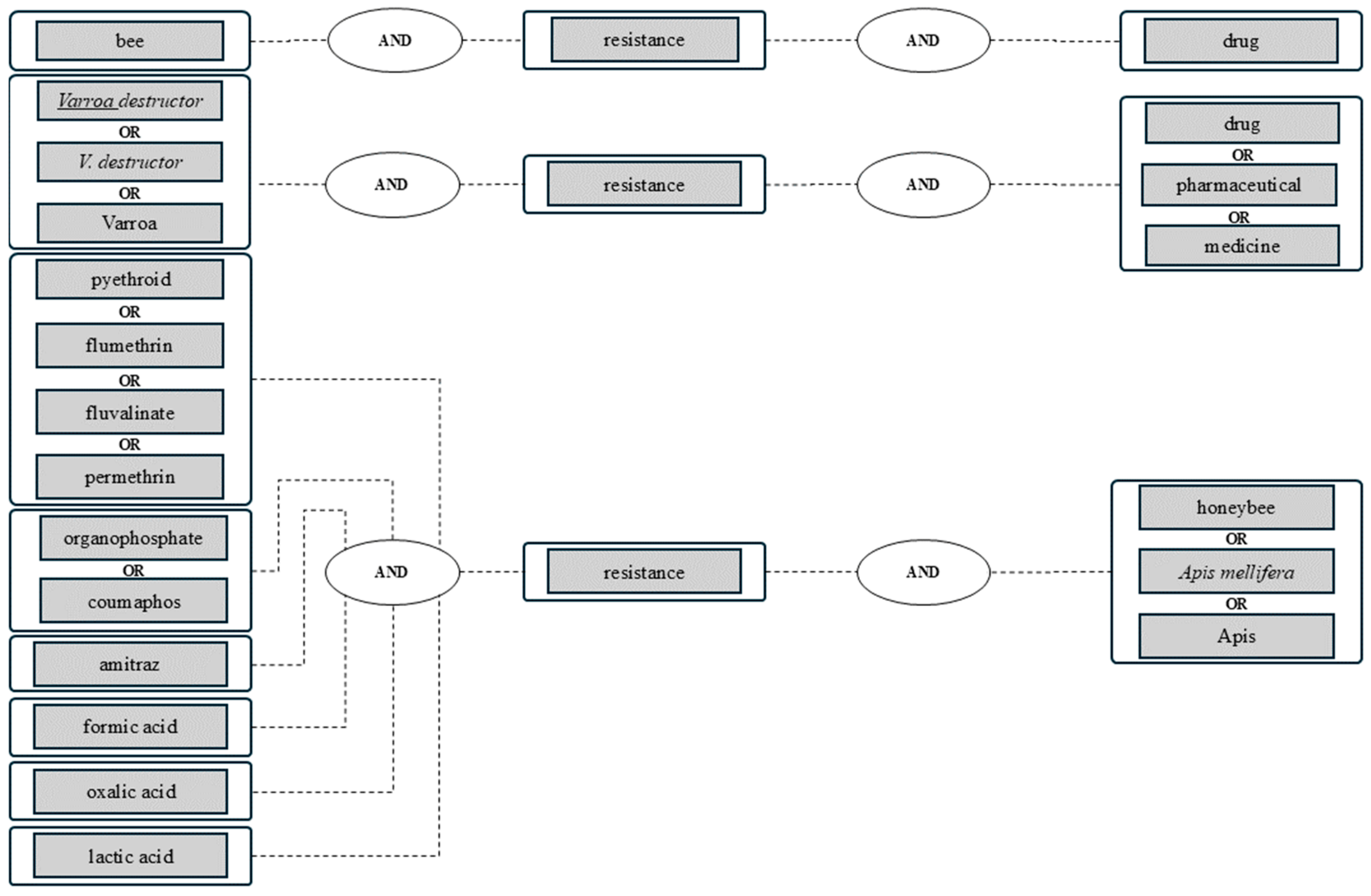
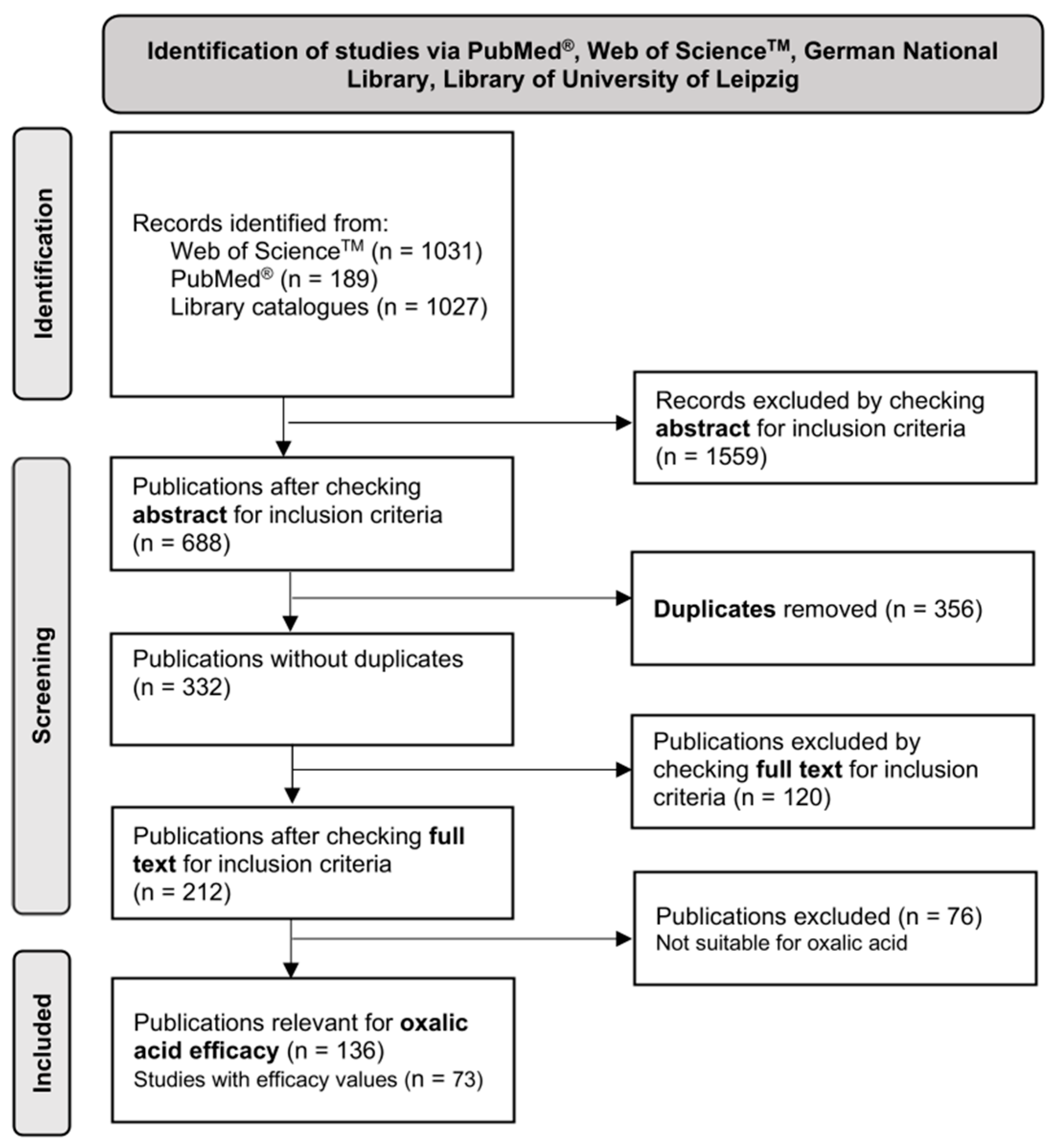
2. Materials and Methods
Data Processing
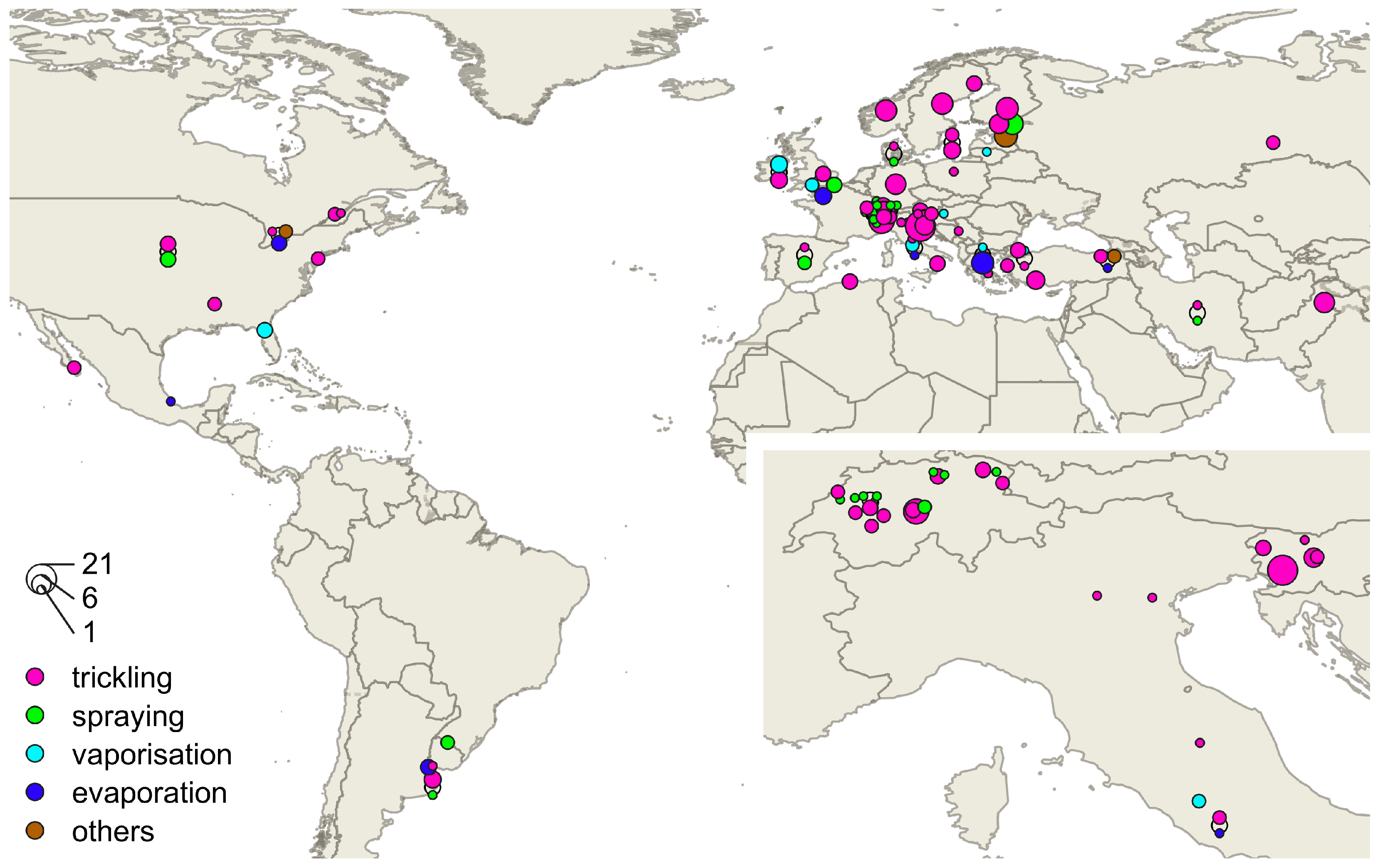
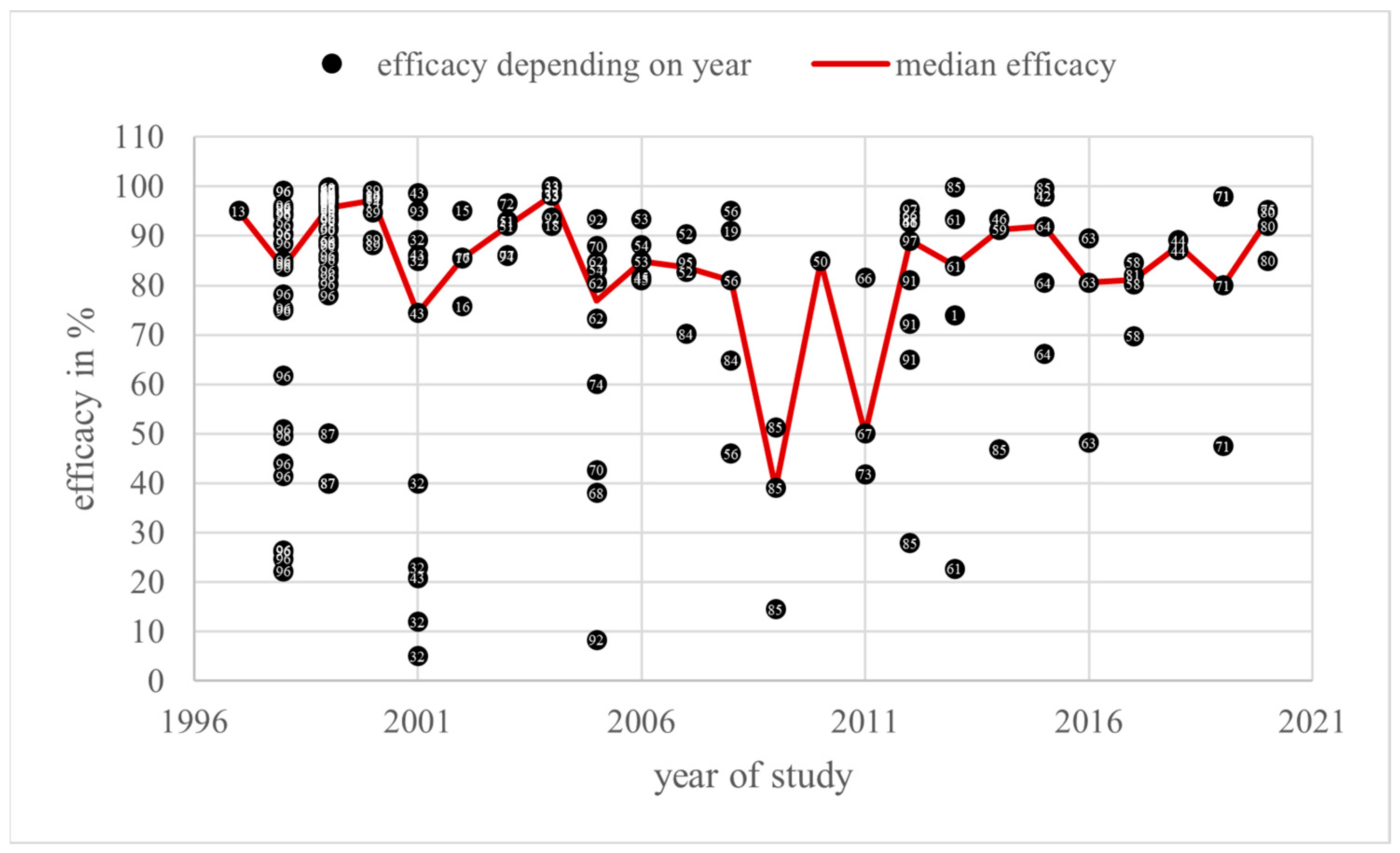
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy Measurement
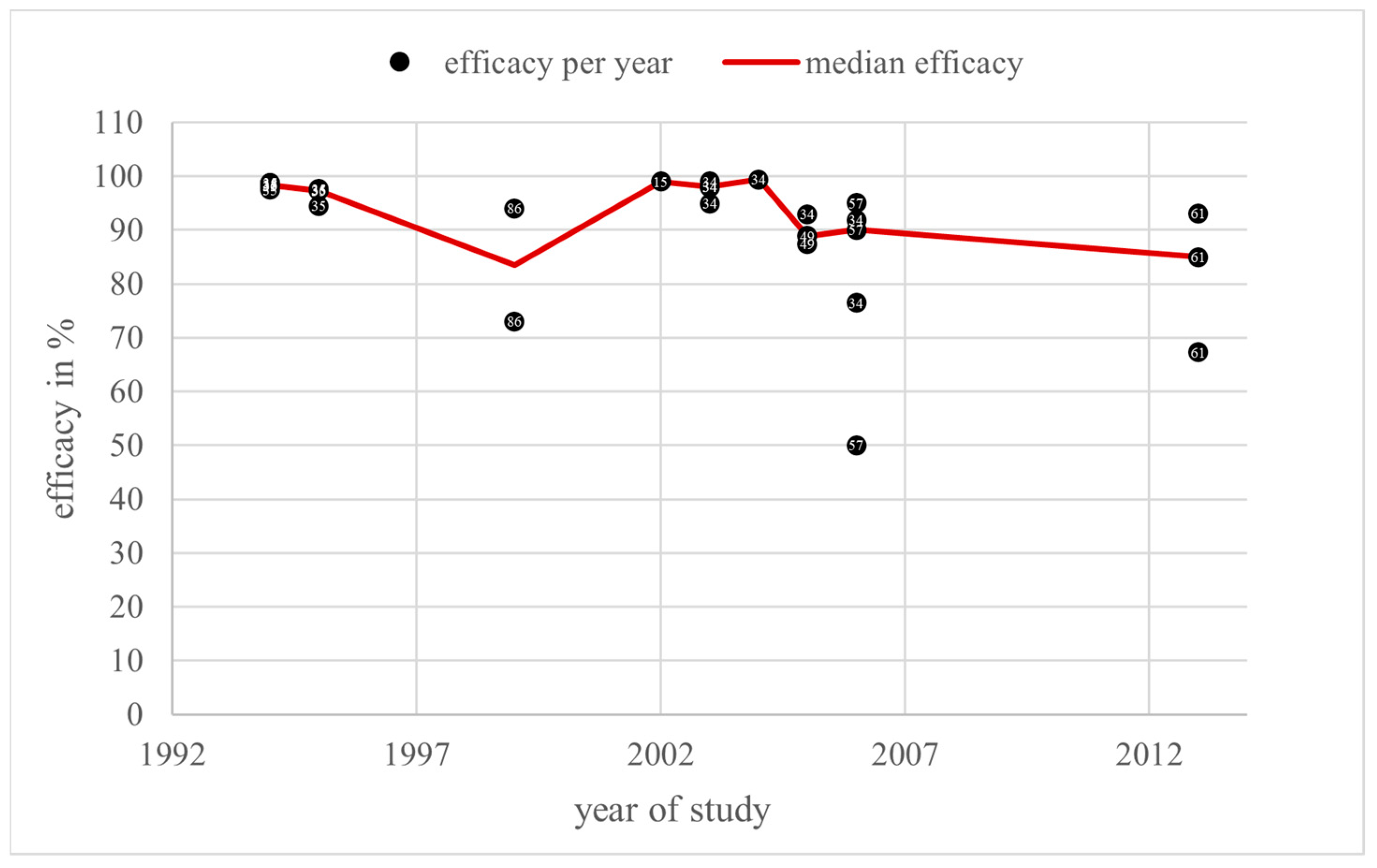
3.2. Trickling
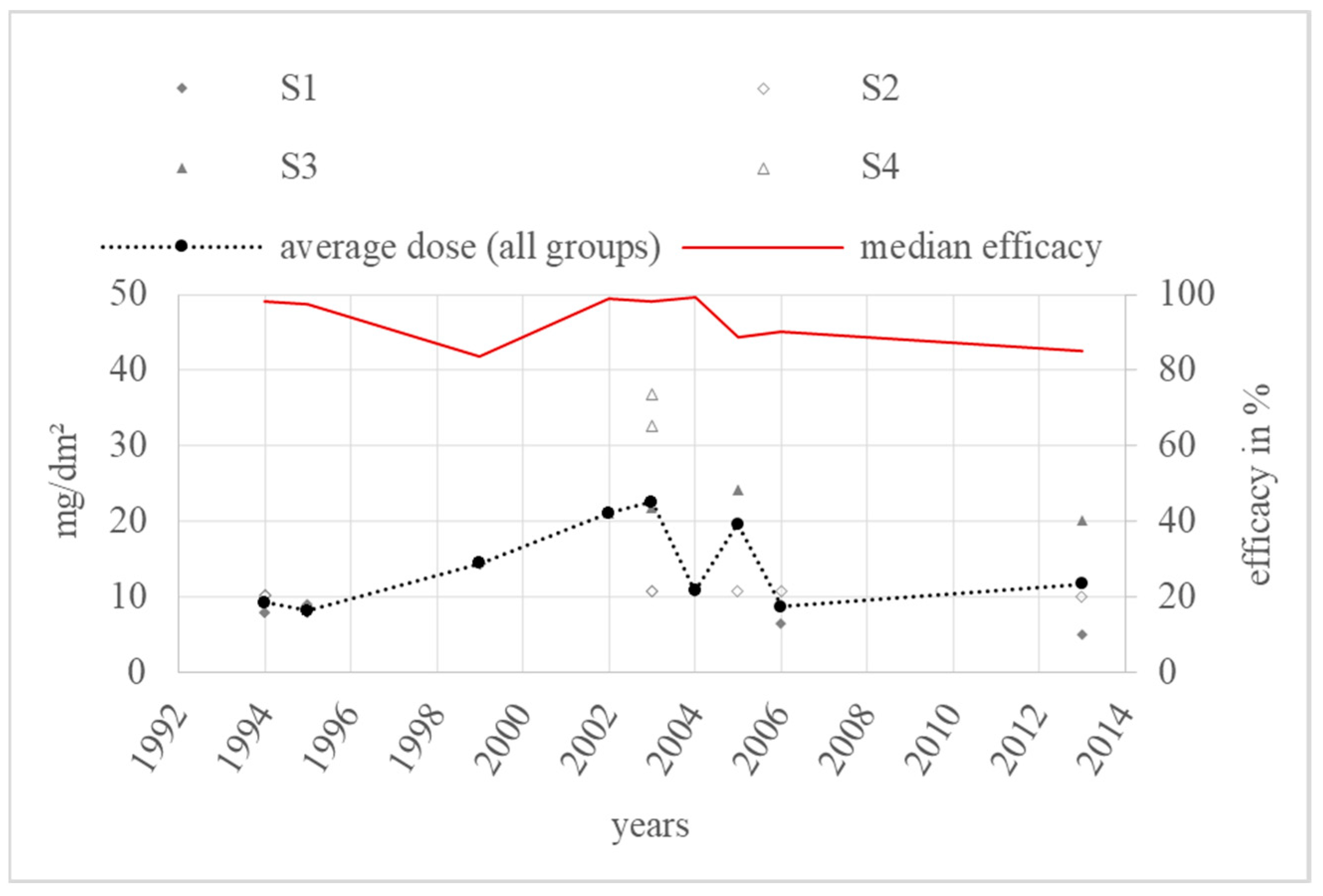
3.3. Spraying
3.4. Exchange via Direct Contact
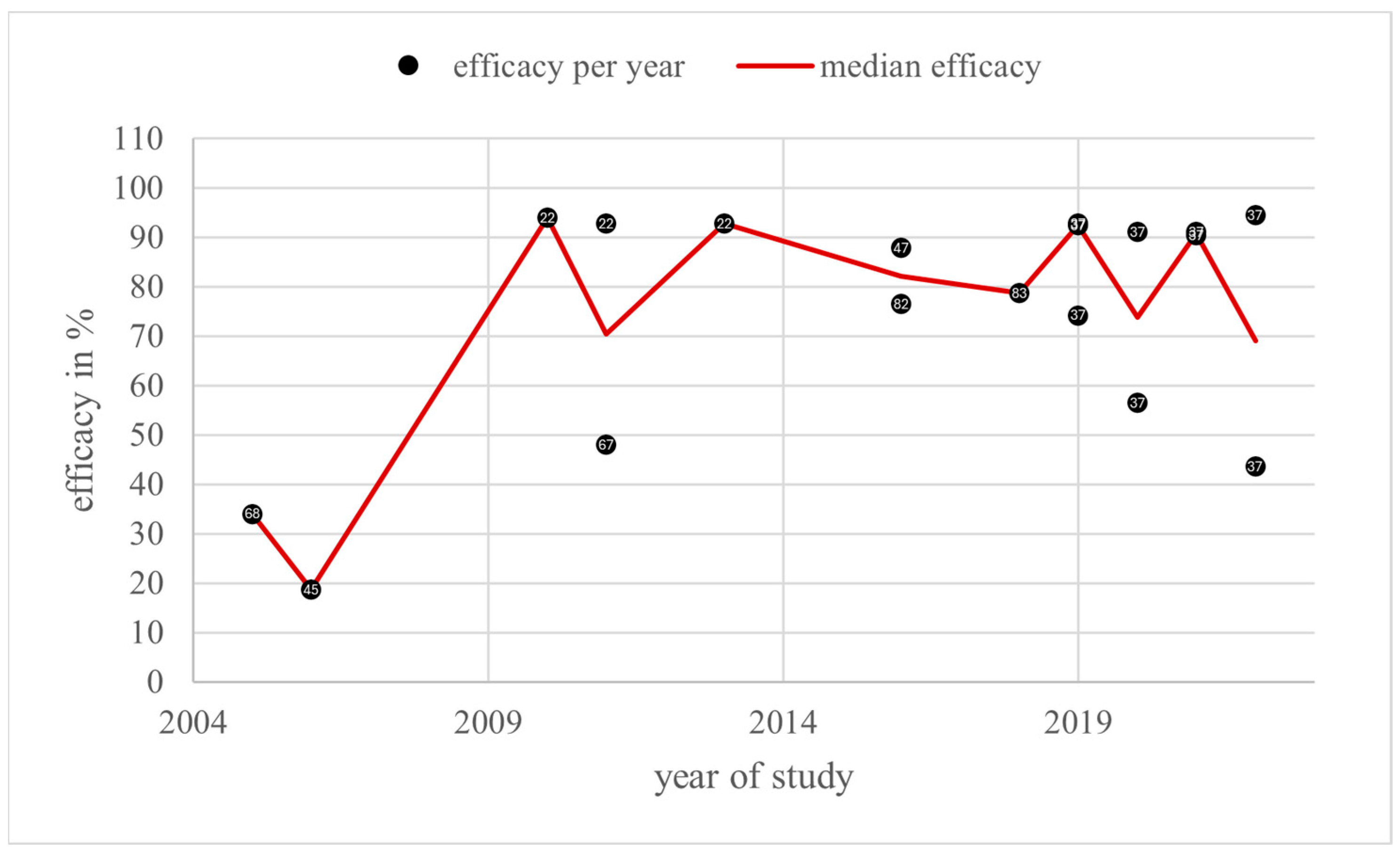
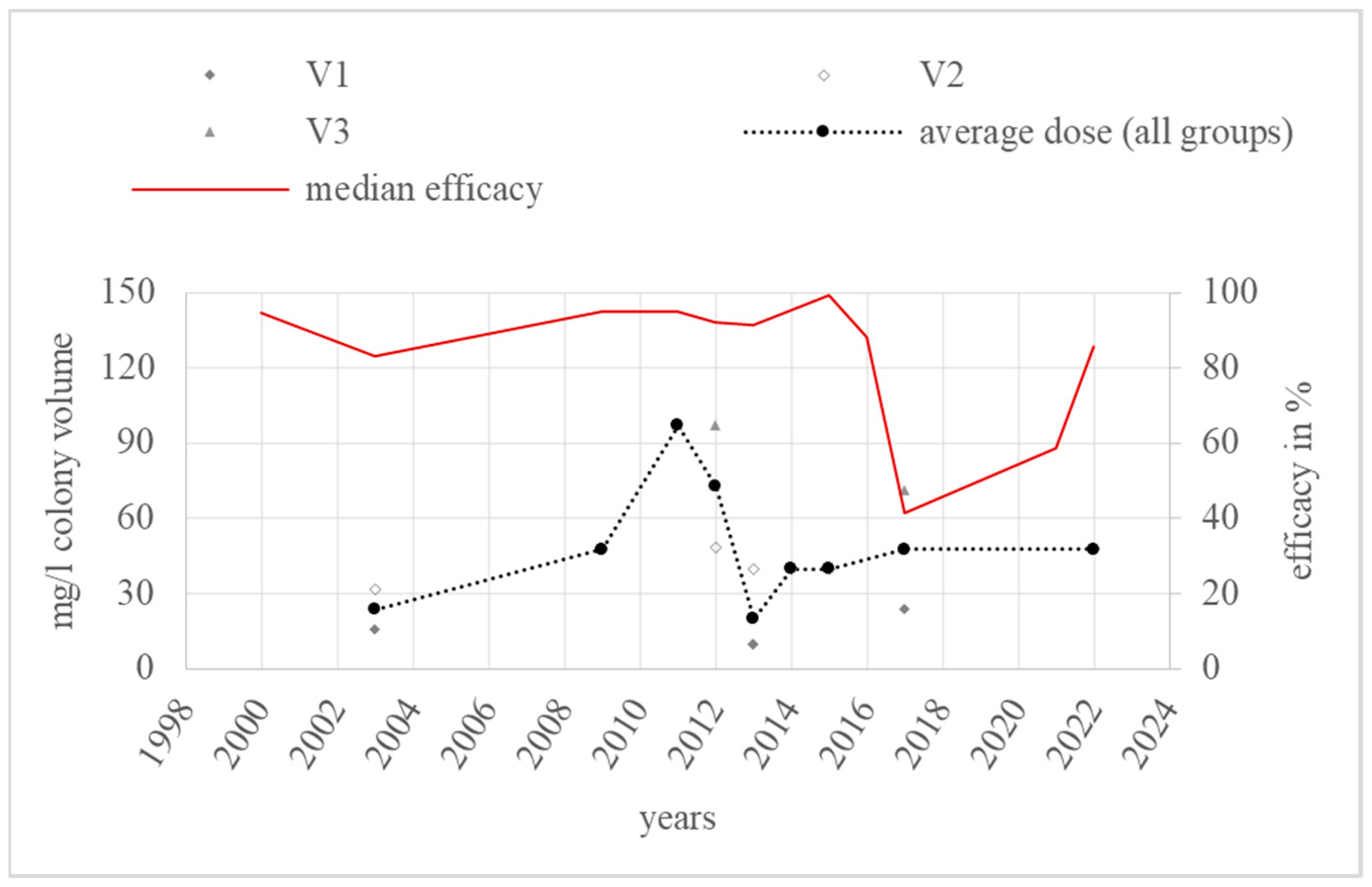
3.5. Vaporisation
3.6. Dusting
3.7. Others
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficacy Measurement
4.2. Trickling
4.3. Spraying
4.4. Exchange via Direct Contact
4.5. Vaporisation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umpiérrez, M.L.; Santos, E.; Mendoza, Y.; Altesor, P.; Rossini, C. Essential oil from Eupatorium buniifolium leaves as potential varroacide. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3389–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, T.R.; Faux, C.M. (Eds.) Honey Bee Medicine for the Veterinary Practitioner; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781119583417. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Government—Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry. Varroa destructor; 19 September 2023. Available online: https://www.agriculture.gov.au/about/news/stay-informed/communiques/varroa-destructor-19-sept-2023 (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Gallai, N.; Salles, J.-M.; Settele, J.; Vaissière, B.E. Economic valuation of the vulnerability of world agriculture confronted with pollinator decline. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitton, G.A.; Meroi Arcerito, F.; Cooley, H.; Fernández de Landa, G.; Eguaras, M.J.; Ruffinengo, S.R.; Maggi, M.D. More than sixty years living with Varroa destructor: A review of acaricide resistance. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2022, 68, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplazes, P.; Joachim, A.; Mathis, A.; Strube, C.; Taubert, A.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Zahner, H. Parasitologie für die Tiermedizin; 4. Überarbeitete Auflage; Georg Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 9783132421387. [Google Scholar]
- Gumula, E. Guideline on Veterinary Medicinal Products Controlling Varroa destructor Parasitosis in Bees; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Emmerich, I.U. Authorized medicinal products for honey bees (Apis mellifera) in Germany. Berl. Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschr. 2018, 132, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodschneider, R.; Schlagbauer, J.; Arakelyan, I.; Ballis, A.; Brus, J.; Brusbardis, V.; Cadahía, L.; Charrière, J.-D.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; et al. Spatial clusters of Varroa destructor control strategies in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 96, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, A.I.; Steinhauer, N.A.; vanEngelsdorp, D. Use of Chemical and Nonchemical Methods for the Control of Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) and Associated Winter Colony Losses in U.S. Beekeeping Operations. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagona, S.; Coppola, F.; Nanetti, A.; Cardaio, I.; Tafi, E.; Palego, L.; Betti, L.; Giannaccini, G.; Felicioli, A. Queen Caging and Oxalic Acid Treatment: Combined Effect on Vitellogenin Content and Enzyme Activities in the First Post-Treatment Workers and Drones, Apis mellifera L. Animals 2022, 12, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, K.C.; Underwood, R.M.; López-Uribe, M.M. Combined effects of oxalic acid sublimation and brood breaks on Varroa mite (Varroa destructor) and deformed wing virus levels in newly established honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 61, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutinelli, F.; Baggio, A.; Capolongo, F.; Piro, R.; Prandin, L.; Biasion, L. A scientific note on oxalic acid by topical application for the control of varroosis. Apidologie 1997, 28, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Planinc, I. The control of Varroa destructor using oxalic acid. Vet. J. 2002, 163, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, R. A comparison of two methods of applying oxalic acid for control of Varroa. J. Apic. Res. 2003, 42, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcangeli, J.; Garcia, M.d.C. Effect of Apis mellifera (Apidae) honeybee brood amount on Oxavar® acaricide efficacy against the mite Varroa destructor (Varroidae). Rev. Soc. Entomol. Argent. 2004, 63, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Enzo, M.; Patrizio, P.; Cinzia, M.; Fabio, D.P.; Francesco, A.; Livia, P.O. Oxalic acid by Varrox® to Varroa control in central Italy. Apiacata 2004, 2004, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bacandritsos, N.; Papanastasiou, I.; Saitanis, C.; Nanetti, A.; Roinioti, E. Efficacy of repeated trickle applications of oxalic acid in syrup for varroosis control in Apis mellifera: Influence of meteorological conditions and presence of brood. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Wagchoure, E.S.; Raja, S.; Sarwar, G. Control of Varroa destructor Using Oxalic Acid, Formic Acid and Bayvarol Strip in Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Colonies. Pak. J. Zool. 2012, 44, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Bubnič, J.; Moosbeckhofer, R.; Prešern, J.; Moškrič, A.; Formato, G.; Pietropaoli, M.; Gregorc, A.; Muz, M.N.; Škerl, M.I.S. Three pillars of Varroa control. Apidologie 2021, 52, 1305–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Domingues, C.; Tutun, H.; SEVİN, S. What has been done in the fight against Varroa destructor: From the past to the present. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2022, 69, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.; Tourn, E.; Negri, P.; Szawarski, N.; Marconi, A.; Gallez, L.; Medici, S.; Ruffinengo, S.; Brasesco, C.; de Feudis, L.; et al. A new formulation of oxalic acid for Varroa destructor control applied in Apis mellifera colonies in the presence of brood. Apidologie 2016, 47, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tihelka, E. Effects of synthetic and organic acaricides on honey bee health: A review. SVR 2018, 55, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS. A Free and Open Source Geographic Information System. Available online: https://www.qgis.org/de/site/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Milani, N. Activity of oxalic and citric acids on the mite Varroa destructor in laboratory assays. Apidologie 2001, 32, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howis, M.; Chorbiñski, P.; Nowakowski, P. Physical damage to the chitin plate and position of Varroa destructor on hive bottoms after use of different varroacidal treatments. Med. Weter. Vet. Med. Sci. Pract. 2012, 68, 607–611. [Google Scholar]
- Maddaloni, M.; Pascual, D.W. Isolation of oxalotrophic bacteria associated with Varroa destructor mites. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.D.; Damiani, N.; Ruffinengo, S.R.; Brasesco, M.C.; Szawarski, N.; Mitton, G.; Mariani, F.; Sammataro, D.; Quintana, S.; Eguaras, M.J. The susceptibility of Varroa destructor against oxalic acid: A study case. Bull. Insectol. 2017, 70, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Papežíková, I.; Palíková, M.; Kremserová, S.; Zachová, A.; Peterová, H.; Babák, V.; Navrátil, S. Effect of oxalic acid on the mite Varroa destructor and its host the honey bee Apis mellifera. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Toufailia, H.; Ratnieks, F.L.W. Towards integrated control of Varroa: 5) monitoring honey bee brood rearing in winter, and the proportion of Varroa in small patches of sealed brood cells. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planinc, A.G.I. Dynamics of Falling Varroa Mites in Honeybee (Apis mellifera) Colonies Following Oxalic Acid Treatments. Acta Vet. Brno 2004, 73, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gregorc, A.; Planinc, I. Using oxalic acid for varroa mite control in honey bee colonies during the beekeeping season. Slov. Vet. Res. 2004, 41, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Toomemaa, K.; Martin, A.-J.; Williams, I.H. The effect of different concentrations of oxalic acid in aqueous and sucrose solution on Varroa mites and honey bees. Apidologie 2010, 41, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdorf, A.; Charrière, J.-D.; Kilchenmann, V.; Bogdanov, S.; Fluri, P. Alternative strategy in central Europe for the control of Varroa destructor in honey bee colonies. Apiacta 2003, 38, 258–278. [Google Scholar]
- Imdorf, A.; Charriere, J.-D.; Bachofen, B. Efficiency checking of the Varroa jacobsoni control methods by means of oxalic acid. Apiacata 1997, 32, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kanelis, D.; Tananaki, C.; Liolios, V.; Rodopoulou, M.-A. Evaluation of oxalic acid with glycerin efficacy against Varroa destructor (Varroidae): A four year assay. J. Apic. Res. 2023, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsen, B.; Dodologlu, A. The Efficacy of Thymol and Oxalic Acid in Bee Cake Against Bee Mite (Varroa destructor Anderson & Trueman) in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Colonies. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2015, 21, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliano, N.P.; Ellis, M.D.; Siegfried, B.D. Acute Contact Toxicity of Oxalic Acid to Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) and Their Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Hosts in Laboratory Bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Asad, S.; Ahmad, W.; Sarwar, G.; Rafique, M.K.; Islam, N.; Qadir, Z.A.; Abiden, Z.U. Efficacy of Screen Bottom Board Tray with and without Soft Chemicals for controlling Varroa destructor in Honeybee Colonies. Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, B.; Wilde, J.; Siuda, M. Efficency of Varroa destructor management with medications used in Poland. Med. Weter. Vet. Med. Sci. Pract. 2013, 69, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorc, A.; Knight, P.R.; Adamczyk, J. Powdered sugar shake to monitor and oxalic acid treatments to control varroa mites (Varroa destructor Anderson and Trueman) in honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Poklukar, J. Rotenone and oxalic acid as alternative acaricidal treatments for Varroa destructor in honeybee colonies. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 111, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domatsky, A.N.; Domatskaya, T.F. Effectiveness of oxalic acid in varroatosis in the apiaries of Tyumen Region, Russia. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2018, 8, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Marinelli, E.; Formato, G.; Vari, G.; De Pace, F.M. Varroa control using cellulose strips soaked in oxalic acid water solution. Apiacta 2006, 41, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, A.; Mutinelli, F. Field evaluation of Maqs® and Api-Bioxal® for late summer control of Varroa mite infestation in Northeastern Italy. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 58, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaibes, S.R.R.; Arcerito, F.R.M.; Chávez-Hernández, E.; Luna-Olivares, G.; Marcangeli, J.; Eguaras, M.; Maggi, M. Control of Varroa destructor development in Africanized Apis mellifera honeybees using Aluen Cap (oxalic acid formulation). Int. J. Acarol. 2020, 46, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toufailia, H.A.; Scandian, L.; Shackleton, K.; Ratnieks, F.L. Towards integrated control of Varroa: 4) Varroa mortality from treating broodless winter colonies twice with oxalic acid via sublimation. J. Apic. Res. 2018, 57, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnino, G.L.B.; Orsi, R.d.O. Produtos naturais para o controle do ácaro Varroa destructor em abelhas africanizadas. Pesq. Agropec. Bras. 2012, 47, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, M.M. In Honey Bee Colonies (Apis mellifera L.), Usage of Different Organics Compounds and Their Effects to Colony Performance Against Varroa destructor Infestation. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2012, 18, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanghellini, M. Evaluation of selected biopesticides for the late fall control of varroa mites in a northern temperate climate. Am. Bee J. 2004, 144, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, J.; Demedio, J.; Roque, E. Eficacia Varroicida del ácido oxálico en jarabe de sacarosa por goteo. Rev. Salud Anim. 2007, 29, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Akyol, E.; Yeninar, H. Use of oxalic acid to control Varroa destructor in honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) colonies. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2009, 33, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, G.; Yucel, B. Efficacy Levels of Organic Acids are Used for Controlling Varroa (Varroa jacobsoni Qudemans) and Their Effects on Colony Development of Honey Bees (Apis mellifera L.). J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.J.; van Santen, E.; Ellis, J.D. Determining the dose of oxalic acid applied via vaporization needed for the control of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) pest Varroa destructor. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Wagchoure, E.S.; Moshin, A.U.; Raja, S.; Sarwar, G. Control of ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor in honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) colonies by using different concentrations of oxalic acid. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2012, 22, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Aliano, N.P.; Ellis, M.D. Oxalic acid: A prospective tool for reducing Varroa mite populations in package bees. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 48, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, E.; Unalan, A. Effect of oxalic acid treatment in different seasons on Varroa (Varroa destructor) population in honeybee colonies. Fresenius Environ. Bullet. 2017, 26, 3863–3867. [Google Scholar]
- Gunes, N.; Aydın, L.; Belenli, D.; Hranitz, J.M.; Mengilig, S.; Selova, S. Stress responses of honey bees to organic acid and essential oil treatments against varroa mites. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charriére, J.-D.; Imdorf, A. Oxalic acid treatment by trickling against Varroa destructor: Recommendations for use in central Europe and under temperate climate conditions. Bee World 2002, 83, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Toufailia, H.; Scandian, L.; Ratnieks, F.L.W. Towards integrated control of Varroa: 2) comparing application methods and doses of oxalic acid on the mortality of phoretic Varroa destructor mites and their honey bee hosts. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 54, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliano, N.P.; Ellis, M.D. Bee-to-bee contact drives oxalic acid distribution in honey bee colonies. Apidologie 2008, 39, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchler, R.; Uzunov, A.; Kovačić, M.; Prešern, J.; Pietropaoli, M.; Hatjina, F.; Pavlov, B.; Charistos, L.; Formato, G.; Galarza, E.; et al. Summer brood interruption as integrated management strategy for effective Varroa control in Europe. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolo, O.; Malacrinò, A.; Laudani, F.; Algeri, G.M.; Giunti, G.; Strano, C.P.; Zoccali, P.; Palmeri, V. Field efficacy of two organic acids against Varroa destructor. Entomologia 2017, 36, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, M.F.; Breen, J. Efficacy of Apilife Var® and Thymovar® against Varroa destructor as an autumn treatment in a cool climate. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, M.F.; Breen, J. The efficacy and tolerability of Api-Bioxal® as a winter varroacide in a cool temperate climate. J. Apic. Res. 2016, 55, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsen, B.; Dodologlu, A. Efficacy of Different Organic Compounds Against Bee Mite (Varroa destructor Anderson and Trueman) in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Colonies. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsen, B. The effect of three methods of application on the efficacy of thymol and oxalic acid for the fall control of the honey bee parasitic mite Varroa destructor in a northern climate. Am. Bee J. 2007, 147, 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Giovenazzo, P.; Dubreuil, P. Evaluation of spring organic treatments against Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) in honey bee Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) colonies in eastern Canada. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 55, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A. Efficacy of Oxalic Acid and Apiguard against Varroa Mites in Honeybee (Apis mellifera) Colonies. Acta Vet. Brno 2005, 74, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gregorc, A.; Planinc, I. Sustainable varroa mite (Varroa destructor) control in field conditions. Acta Vet. Brno 2022, 91, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Planinc, I. The control of Varroa destructor in honey bee colonies using the Thymol-based acaricide—Apiguard. Am. Bee J. 2005, 145, 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorc, A.; Planinc, I. Use of Thymol Formulations, Amitraz, and Oxalic Acid for the Control of the Varroa Mite in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera carnica) Colonies. J. Apic. Sci. 2012, 56, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatjina, F.; Haristos, L. Indirect effects of oxalic acid administered by trickling method on honey bee brood. J. Apic. Res. 2005, 44, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, N.M.; Glavinic, U.; Ristanic, M.; Vejnovic, B.; Stevanovic, J.; Cosic, M.; Stanimirovic, Z. Contact varroacidal efficacy of lithium citrate and its influence on viral loads, immune parameters and oxidative stress of honey bees in a field experiment. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1000944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolics, É.; Specziár, A.; Taller, J.; Mátyás, K.K.; Kolics, B. Lithium chloride outperformed oxalic acid sublimation in a preliminary experiment for Varroa mite control in pre-wintering honey bee colonies. Acta Vet. Hung. 2021, 68, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcangeli, J.A.; Garcia, M.d.C.; Cano, G.; Distefano, L.; Martin, M.L.; Quiroga, A.; Raschia, F.; Vega, C. Eficacia del Oxavar® para el Control del Ácaro Varroa destructor (Varroidae) en Colmenas de Apis mellifera (Apidae). Rev. Soc. Entomol. Argent. 2003, 62, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Marcangeli, J.; Garcia, M.d.C.; Vega, C.; Quiroga, A.; Martin, M.L.; Distefano, L.; Cano, G. Estudio sobre la Eficacia a Campo del Amivar® contra Varroa destructor (Mesostigmata: Varroidae) en Colmenas de Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Rev. Soc. Entomol. Argent. 2005, 64, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Pileckas, V.; Svirmickas, G.J.; Razmaite, V.; Paleckaitis, M. Efficacy of different ecological methods for honeybee (Apis mellifera) Varroa prevention in spring. Vet. Zootech. 2012, 59, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, Z.A.; Idrees, A.; Mahmood, R.; Sarwar, G.; Bakar, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, M.M.; Li, J. Effectiveness of Different Soft Acaricides against Honey Bee Ectoparasitic Mite Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae). Insects 2021, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, S.; Giovenazzo, P.; Fournier, V. The Use of the Predatory Mite Stratiolaelaps scimitus (Mesostigmata: Laelapidae) to Control Varroa destructor (Mesostigmata: Varroidae) in Honey Bee Colonies in Early and Late Fall. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabahi, Q.; Gashout, H.; Kelly, P.G.; Guzman-Novoa, E. Continuous release of oregano oil effectively and safely controls Varroa destructor infestations in honey bee colonies in a northern climate. Exp Appl Acarol 2017, 72, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabahi, Q.; Morfin, N.; Emsen, B.; Gashout, H.A.; Kelly, P.G.; Otto, S.; Merrill, A.R.; Guzman-Novoa, E. Evaluation of Dry and Wet Formulations of Oxalic Acid, Thymol, and Oregano Oil for Varroa Mite (Acari: Varroidae) Control in Honey Bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Colonies. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škerl, M.I.S.; Nakrst, M.; Žvokelj, L.; Gregorc, A. The acaricidal effect of flumethrin, oxalic acid and amitraz against Varroa destructor in honey bee (Apis mellifera carnica) colonies. Acta Vet. Brno 2011, 80, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomemaa, K. The synergistic effect of weak oxalic acid and thymol aqueous solutions on Varroa mites and honey bees. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 58, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higes, M.; Meana, A.; Suárez, M.; Llorente, J. Negative long-term effects on bee colonies treated with oxalic acid against Varroa jacobsoni Oud. Apidologie 1999, 30, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Planinc, I. Acaricidal effect of oxalic acid in honeybee (Apis mellifera) colonies. Apidologie 2001, 32, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Howis, M.; Chorbiñski, P.; Janiszewska, K.; Nowakowski, P. Efficacy of oxalic acid used in honeybee colonies to remove Varroa destructor mites. Med. Weter. 2011, 67, 757–759. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, I. Is the Total Amount or the Concentration of Oxalic Acid Critical for Efficacy in Varroa Mite Control? Report; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Brødsgaard, C.; Jensen, S.; Hansen, C.; Hansen, H. Spring Treatment with Oxalic Acid in Honeybee Colonies as Varroa Control; Science Report No. 6 Horticulture; CABI: Tjele, Denmark, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Adjlane, N.; Tarek, E.-O.; Haddad, N. Evaluation of Oxalic Acid Treatments against the Mite Varroa destructor and Secondary Effects on Honey Bees Apis mellifera. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 501–509. [Google Scholar]
- Girisgin, A.O.; Aydin, L. Efficacies of Formic, Oxalic and Lactic Acids Against Varroa destructor in Naturally Infested Honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) Colonies in Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2010, 16, 941–945. [Google Scholar]
- Imdorf, A.; Charriere, J.-D. Alternative varroa control. Am. Bee J. 2003, 136, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Marcangeli, J.; Perez, R.; Leveratto, D.; Guardia Lopez, A. Ensayo a campo sobre la eficacia del Colmesan® contra el ácaro Varroa destructor (Varroidae) en colmenas de Apis mellifera (Apidae). Rev. Soc. Entomol. Argent. 2004, 63, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Hernández, R.; Higes, M.; Pérez, J.L.; Nozal, M.J.; Gómez, L.; Meana, A. Short term negative effect of oxalic acid in Apis mellifera iberiensis. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 5, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanetti, A.; Büchler, R.; Charriere, J.-D.; Friesd, I.; Helland, S.; Imdorf, A.; Korpela, S.; Preben, K. Oxalic acid treatments for Varroa control (Review). Apiacta 2003, 38, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Pietropaoli, M.; Giacomelli, A.; Milito, M.; Pizzariello, M.; Gobbi, C.; Scholl, F.; Formato, G. Integrated Pest Management strategies against Varroa destructor: The use of oxalic acid combined with innovative cages to obtain the absence of brood. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 4, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Radetzki, T. Vaporisation of oxalic acid in field trial with 1509 colonies. Apiarist 2004, 1, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Andermatt BioVet GmbH. Fachinformation in Form der Zusammenfassung der Merkmale des Tierarzneimittels (Summary of Product Characteristics) OXUVAR 5.7%, 41.0 mg/mL Konzentrat zur Herstellung einer Lösung für Honigbienen Oxalsäure. 2021. Available online: https://www.andermatt-biovet.de/de-de/oxuvar-5-7-sprueh-und-traeufelbehandlung-gegen-varroa--p22890?variant=8391 (accessed on 14 July 2024).



| Group | Areal Dosage Range (mg/dm2) | Number and Share of Efficacy Values | Efficacy | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (%) | Fraction ≥ 70% | Fraction ≥ 90% | ||||
| T1 | 0–10 | 20 (10.8%) | 22.2–97.8 | 11 | 5 | [61,68,96] |
| T2 | >10–20 | 73 (39.5%) | 27.9–100 | 65 | 49 | [14,33,42,52,58,60,61,71,84,85,87,89,96] |
| T3 | >20–30 | 27 (14.6%) | 66.1–99.8 | 26 | 20 | [13,15,18,46,51,54,60,61,64,66,69,81,96] |
| T4 | >30–40 | 19 (10.2%) | 5–92.8 | 12 | 2 | [1,16,32,56,66,73,77,80,91,94] |
| T5 | >40–50 | 6 (3.2%) | 72.2–95 | 6 | 2 | [56,62,69,80,91] |
| T6 | >50 | 7 (3.8%) | 8.3–93.7 | 5 | 3 | [56,67,80,91,92] |
| Tun | Unknown; not calculable; another unit | 33 (17.8%) | 14.5–98.6 | 24 | 10 | [19,41,43,44,45,50,53,59,63,70,71,72,74,75,85,93,95,97] |
| Group | Areal Dosage Range (mg/dm2) | Number and Share of Efficacy Values | Efficacy | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (%) | Fraction ≥ 70% | Fraction ≥ 90% | ||||
| S1 | 0–10 | 9 (31.0%) | 67.3–98.3 | 8 | 7 | [34,35,36,61] |
| S2 | >10–20 | 11 (37.9%) | 73–99.42 | 11 | 9 | [34,35,61,86] |
| S3 | >20–30 | 5 (17.2%) | 87.4–99 | 5 | 3 | [15,34,49,61] |
| S4 | >30–40 | 1 (3.4%) | 98 | 0 | 1 | [34] |
| Sun | Unknown; not calculable; another unit | 3 (10.3%) | 50–95 | 2 | 2 | [57,90] |
| Group | Volume Dosage Range (mg/L) | Number and Share of Efficacy Values | Effectiveness | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (%) | Fraction ≥ 70% | Fraction ≥ 90% | ||||
| E1 | 0–400 | 6 (33.3%) | 34–78.7 | 3 | 0 | [37,67,68,82,83] |
| E2 | >400–900 | 6 (33.3%) | 90.4–94.5 | 6 | 6 | [37] |
| Eun | Unknown; not calculable; another unit | 6 (33.3%) | 18.7–94 | 4 | 3 | [22,37,45,47] |
| Group | Volume Dosage Range (mg/L) | Number and Share of Efficacy Values | Effectiveness | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (%) | Fraction ≥ 70% | Fraction ≥ 90% | ||||
| V1 | 0–30 | 5 (20%) | 30–94.2 | 4 | 2 | [17,55,61] |
| V2 | >30–60 | 8 (32%) | 41.4–99.6 | 7 | 4 | [17,37,48,55,61,65,66] |
| V3 | >60–100 | 3 (12%) | 69.3–95.1 | 2 | 2 | [55,66] |
| Vun | Unknown; not calculable; another unit | 9 (36%) | 58.7–96 | 8 | 7 | [59,63,76,98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosch, Y.; Mülling, C.; Emmerich, I.U. Resistance of Varroa destructor against Oxalic Acid Treatment—A Systematic Review. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090393
Kosch Y, Mülling C, Emmerich IU. Resistance of Varroa destructor against Oxalic Acid Treatment—A Systematic Review. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(9):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090393
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosch, Yvonne, Christoph Mülling, and Ilka U. Emmerich. 2024. "Resistance of Varroa destructor against Oxalic Acid Treatment—A Systematic Review" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 9: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090393
APA StyleKosch, Y., Mülling, C., & Emmerich, I. U. (2024). Resistance of Varroa destructor against Oxalic Acid Treatment—A Systematic Review. Veterinary Sciences, 11(9), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090393





