Preparation and Application of Clostridium perfringens Alpha Toxin Nanobodies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Recombinant CPA Protein
2.2. Screening and Preparation of CPA Nanobodies
2.3. Evaluation of CPA-VHH Characteristics
2.4. Neutralization of CPA-VHH on Phospholipase C and Erythrocyte Hemolyticity
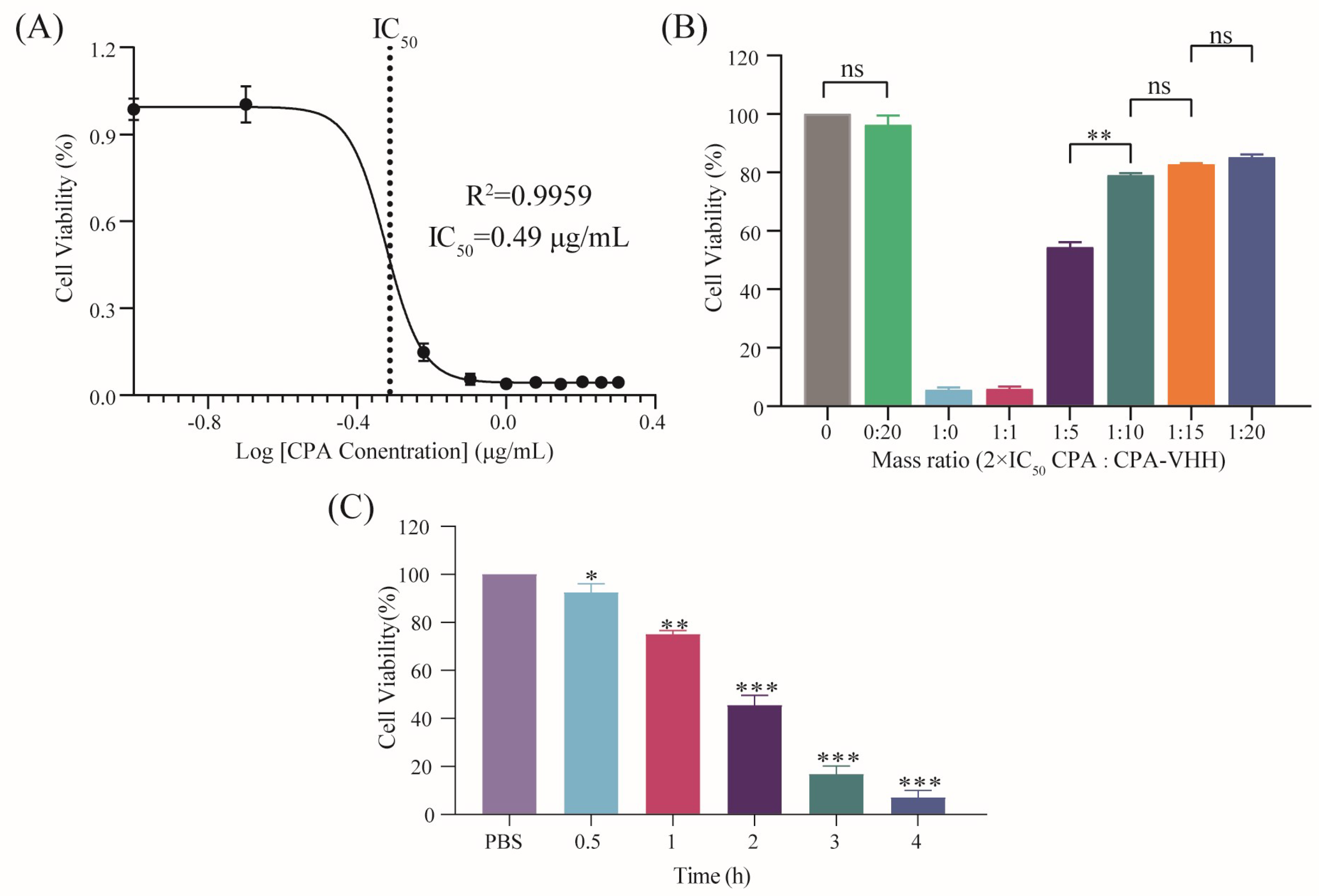
2.5. Determination of the Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) of CPA in Vero Cells
2.6. Investigation of CPA-VHH’s Neutralizing Effect on CPA in Vero Cells
2.7. Determination of Median Lethal Dose (LD50) for CPA
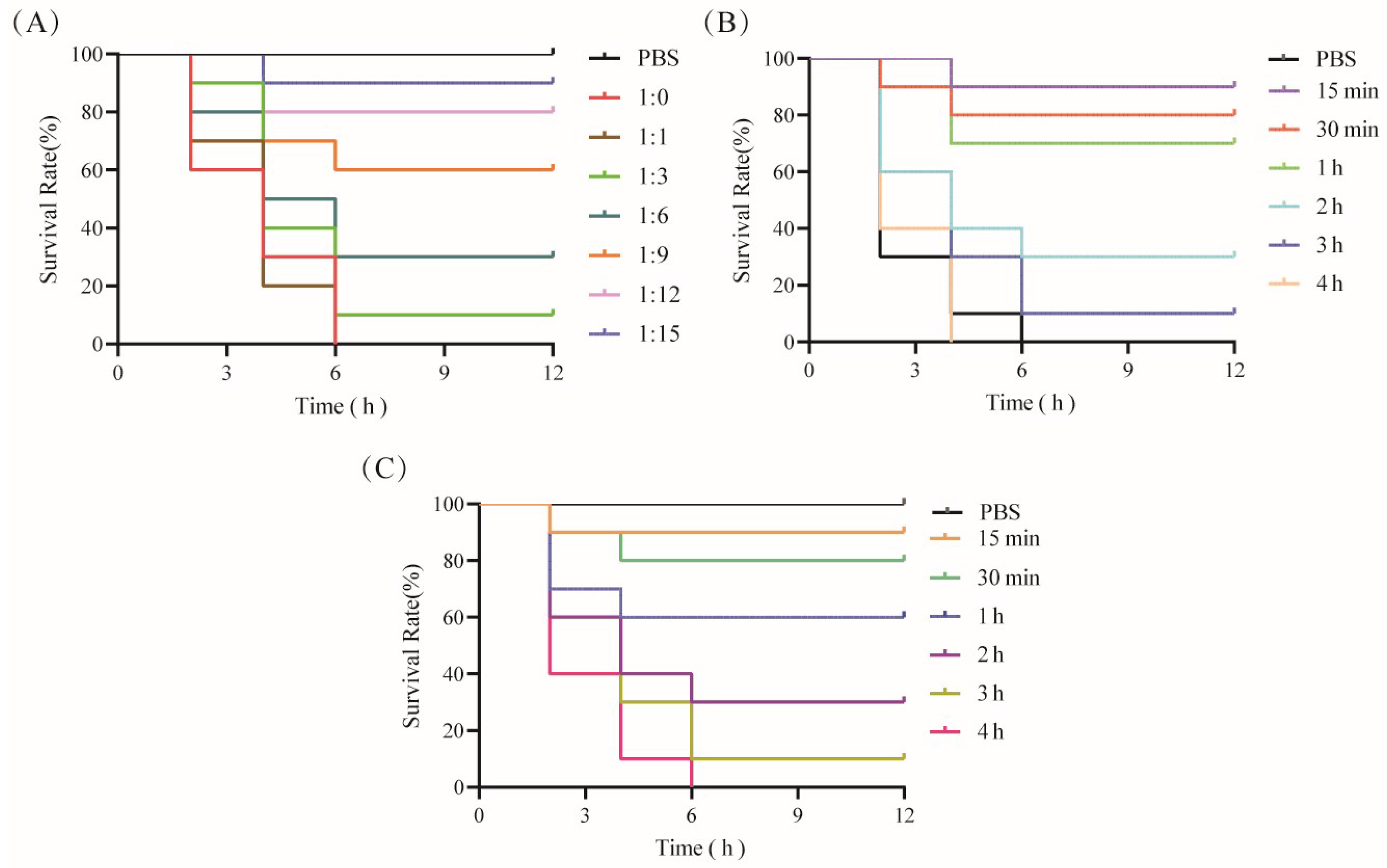
2.8. Biological Effects of CPA-VHH in Mice Exposed to CPA
2.9. Total RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.10. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
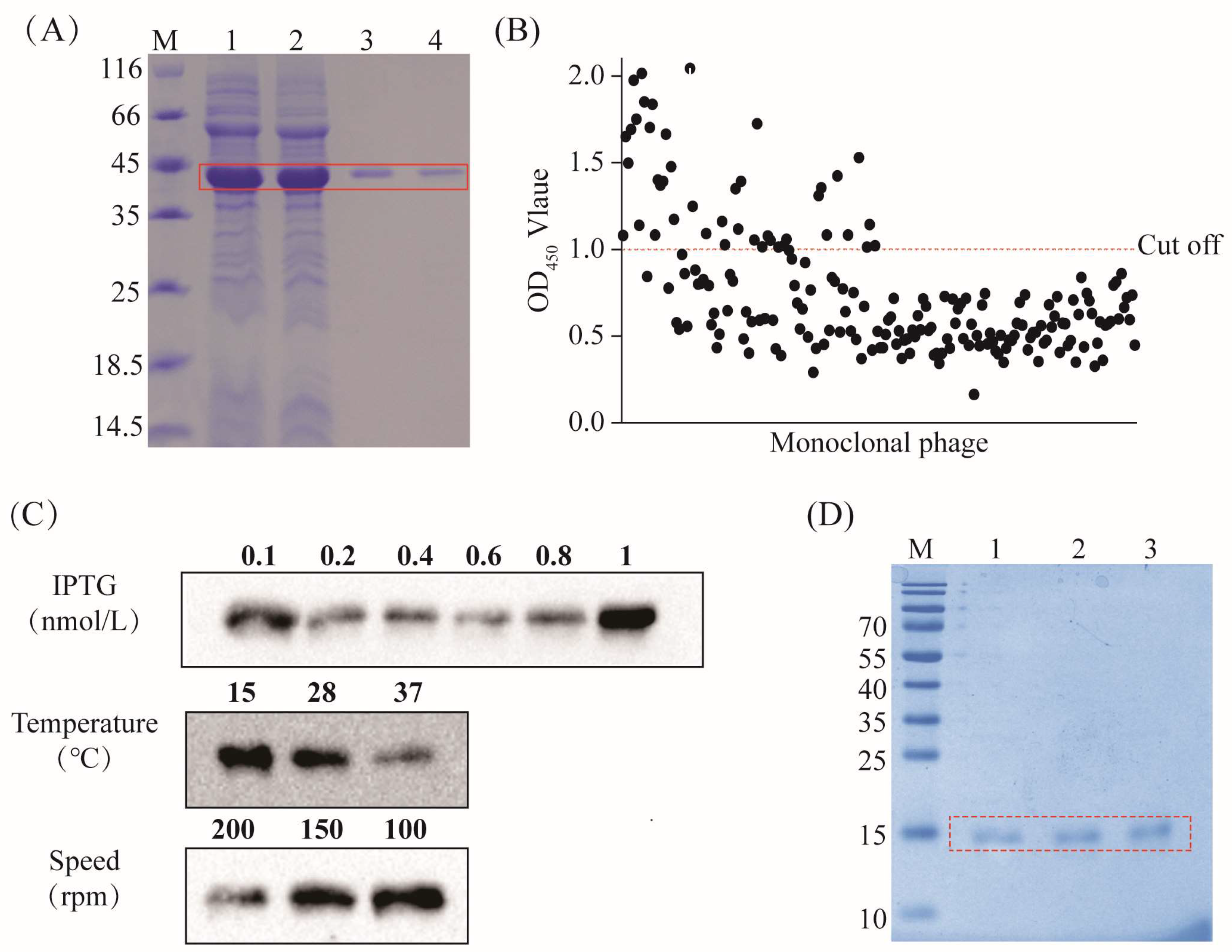
3.1. Preparation of CPA Recombinant Protein and CPA-VHH
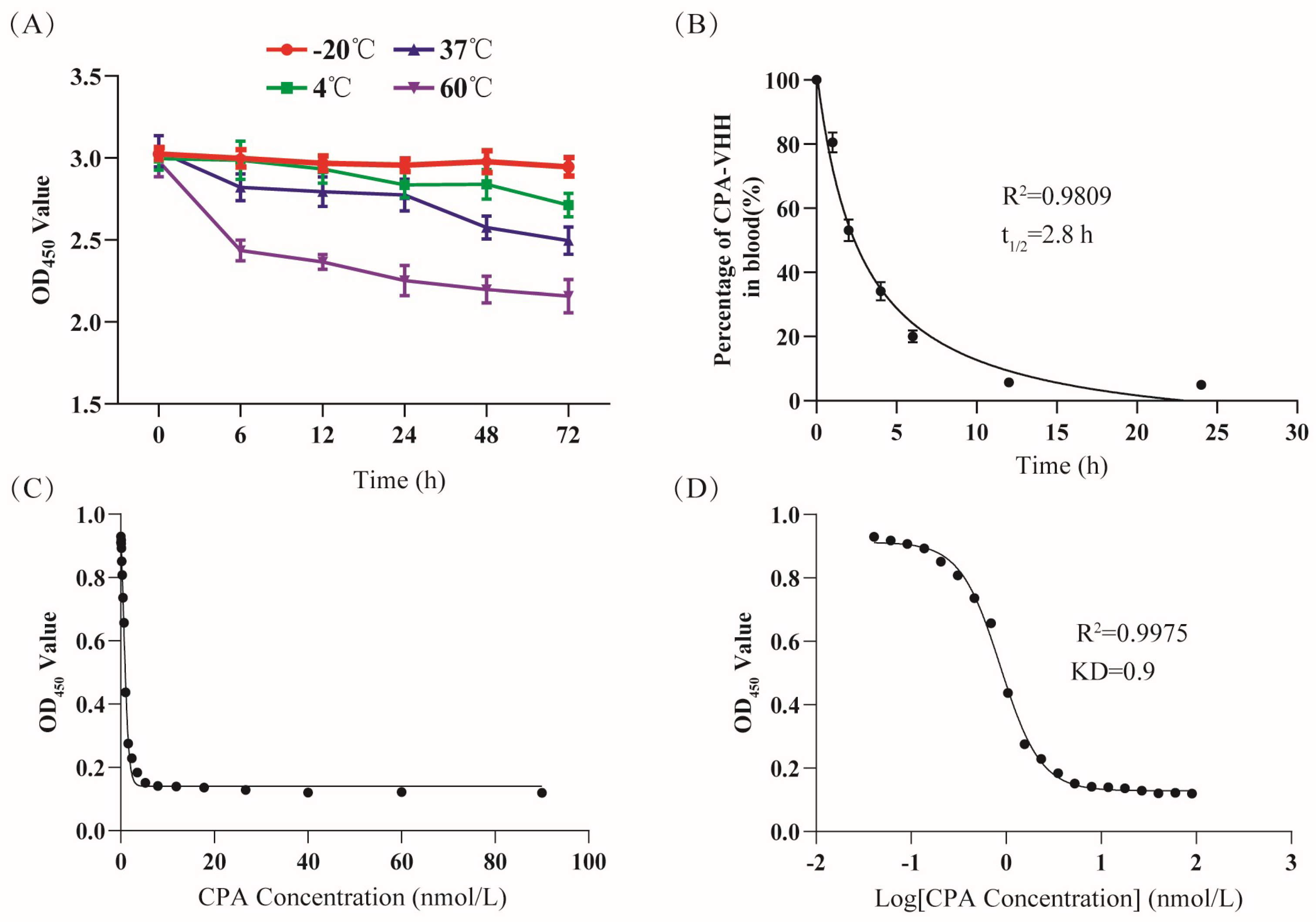
3.2. Evaluation of CPA-VHH Characteristics
3.3. Neutralizing Effect of CPA-VHH on Phospholipase C and Erythrocyte Hemolyticity
3.4. Neutralizing Effect of CPA-VHH on CPA in Vero Cells
3.5. Effects of CPA-VHH in Terms of Neutralization of CPA and Prevention and Treatment of Infection with CPA in Mice
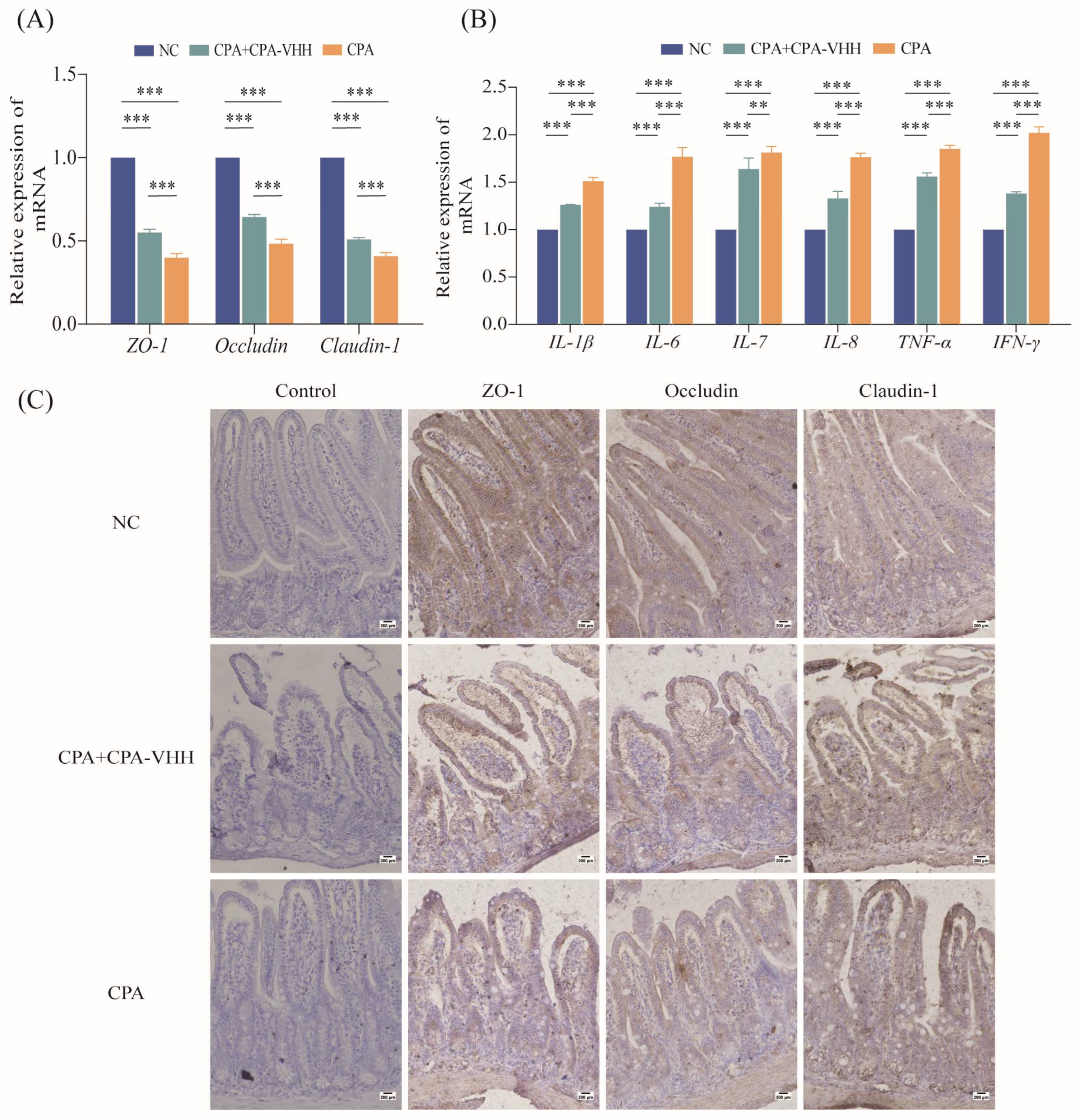
3.6. Protective Effect of CPA-VHH on Intestinal Mucosa during CPA Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grenda, T.; Jarosz, A.; Sapała, M.; Grenda, A.; Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. Clostridium perfringens—Opportunistic Foodborne Pathogen, Its Diversity and Epidemiological Significance. Pathogens 2023, 12, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulliver, E.L.; Adams, V.; Marcelino, V.R.; Gould, J.; Rutten, E.L.; Powell, D.R.; Young, R.B.; D’adamo, G.L.; Hemphill, J.; Solari, S.M.; et al. Extensive genome analysis identifies novel plasmid families in Clostridium perfringens. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, E.; Valgaeren, B.R.; Pardon, B.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Deprez, P.R.; Van Immerseel, F. Rethinking the role of alpha toxin in Clostridium perfringens-associated enteric diseases: A review on bovine necro-haemorrhagic enteritis. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, F.A.; Freedman, J.C.; Shrestha, A.; Theoret, J.R.; Garcia, J.; Awad, M.M.; Adams, V.; Moore, R.J.; Rood, J.I.; McClane, B.A. Towards an understanding of the role of Clostridium perfringens toxins in human and animal disease. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Bansal, M.; Alenezi, T.; Almansour, A.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Vaccines Using Clostridium perfringens Sporulation Proteins Reduce Necrotic Enteritis in Chickens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, K.K.; Songer, J.G. Necrotic enteritis in chickens: A paradigm of enteric infection by Clostridium perfringens type A. Anaerobe 2009, 15, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rood, J.I.; Adams, V.; Lacey, J.; Lyras, D.; McClane, B.A.; Melville, S.B.; Moore, R.J.; Popoff, M.R.; Sarker, M.R.; Songer, J.G.; et al. Expansion of the Clostridium perfringens toxin-based typing scheme. Anaerobe 2018, 53, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiu, R.; Hall, L.J. An update on the human and animal enteric pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, M.; Terao, Y.; Sakurai, J.; Nagahama, M. Membrane-binding mechanism of Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin. Toxins 2015, 7, 5268–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyburn, A.L.; Sheedy, S.A.; Ford, M.E.; Williamson, M.M.; Awad, M.M.; Rood, J.I.; Moore, R.J. Alpha-toxin of Clostridium perfringens is not an essential virulence factor in necrotic enteritis in chickens. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6496–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, M.; Kabura, M.; Takagishi, T.; Suzue, A.; Tominaga, K.; Urano, S.; Nagahama, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; et al. Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin recognizes the GM1a-TrkA complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 33070–33079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hammers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hammers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Deschacht, N.; Muyldermans, S. A case of convergence: Why did a simple alternative to canonical antibodies arise in sharks and camels? PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, D. Nanobodies: The potential application in bacterial treatment and diagnosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 214, 115640–115651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. Applications of Nanobodies. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 9, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesniak, W.G.; Chu, C.; Jablonska, A.; Azad, B.B.; Zwaenepoel, O.; Zawadzki, M.; Lisok, A.; Pomper, M.G.; Walczak, P.; Gettemans, J.; et al. PET imaging of distinct brain uptake of a nanobody and similarly-sized PAMAM dendrimers after intra-arterial administration. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovčevska, I.; Muyldermans, S. The Therapeutic Potential of Nanobodies. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kang, G.; Yuan, H.; Cao, X.; Huang, H.; de Marco, A. Research Progress and Applications of Multivalent, Multispecific and Modified Nanobodies for Disease Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 838082–838089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Yang, X.; Xie, S.; Zhong, D.; Lin, X.; Ding, Z.; Duan, S.; Mo, F.; Liu, A.; Yin, S.; et al. A new PD-1-specific nanobody enhances the antitumor activity of T-cells in synergy with dendritic cell vaccine. Cancer Lett. 2021, 522, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Avila, D.; Hughes, M.; Hughes, A.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A new antigen receptor gene family that undergoes rearrangement and extensive somatic diversification in sharks. Nature 1995, 374, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural single-domain antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbabi Ghahroudi, M.; Desmyter, A.; Wyns, L.; Hamers, R.; Muyldermans, S. Selection and identification of single domain antibody fragments from camel heavy-chain antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1997, 414, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, P.; Zinner, K.; Mücke, N.; Bartoschik, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Hoheisel, J.D. The structural basis of nanobody unfolding reversibility and thermoresistance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontermann, R.E. Strategies for extended serum half-life of protein therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Jiao, X.; Liu, X.F. Prevalence of serogroups and virulence factors of Escherichia coli strains isolated from pigs with postweaning diarrhoea in eastern China. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 103, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, S.; Oda, M.; Matsuda, H.; Ikari, S.; Sakurai, J. Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin activates the sphingomyelin metabolism system in sheep erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12181–12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, M.; Matsuno, T.; Shiihara, R.; Ochi, S.; Yamauchi, R.; Saito, Y.; Imagawa, H.; Nagahama, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Sakurai, J. The relationship between the metabolism of sphingomyelin species and the hemolysis of sheep erythrocytes induced by Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, J.; Ochi, S.; Tanaka, H. Regulation of Clostridium perfringens alpha-toxin-activated phospholipase C in rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, S.T.; Hunter, J.H.; Taylor, A.E. Regulation of tight-junction permeability during nutrient absorption across the intestinal epithelium. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1995, 15, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Enteric Pathogens and Their Toxin-Induced Disruption of the Intestinal Barrier through Alteration of Tight Junctions in Chickens. Toxins 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Itoh, M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zou, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y. Resveratrol alleviates fumonisin-induced intestinal cytotoxicity by modulating apoptosis, tight junction, and inflammation in IPEC-J2 porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Possemiers, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Guiot, Y.; Everard, A.; Rottier, O.; Geurts, L.; Naslain, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Lambert, D.M.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009, 58, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y. Effects of dietary L-tryptophan supplementation on intestinal response to chronic unpredictable stress in broilers. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.G.; Simpson, L.J.; Ferreira, A.-M.; Rustagi, A.; Roque, J.; Asuni, A.; Ranganath, T.; Grant, P.M.; Subramanian, A.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; et al. Cytokine profile in plasma of severe COVID-19 does not differ from ARDS and sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Hirano, T.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990, 4, 2860–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggiolini, M.; Clark-Lewis, I. Interleukin-8, a chemotactic and inflammatory cytokine. FEBS Lett. 1992, 307, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Knapp, M.; Lang, I.; Köhler, G. Interleukin 8 (IL-8)—A universal biomarker? Int. Arch. Med. 2010, 3, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y. Inflammatory responses to a Clostridium perfringens type A strain and α-toxin in primary intestinal epithelial cells of chicken embryos. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| ZO-1-F | GCCGCTAAGAGCACAGCAA |
| ZO-1-R | GCCCTCCTTTTAACACATCAGA |
| Occludin-F | TTGAAAGTCCACCTCCTTACAGA |
| Occludin-R | CCGGATAAAAAGAGTACGCTGG |
| Claudin-1-F | GCCTTGATGGTAATTGGCATCC |
| Claudin-1-R | GGCCACTAATGTCGCCAGAC |
| IL-1β-F | TTCAGGCAGGCAGTATCACTC |
| IL-1β-R | GAAGGTCCACGGGAAAGACAC |
| IL-6-F | TCCAGTTGCCTTCTTGGGAC |
| IL-6-R | GACAGGTCTGTTGGGAGTGG |
| IL-7-F | TTCCTCCACTGATCCTTGTTCT |
| IL-7-R | AGCAGCTTCCTTTGTATCATCAC |
| IL-8-F | ATGCCCTCTATTCTGCCAGAT |
| IL-8-R | GTGCTCCGGTTGTATAAGATGAC |
| TNF-α-F | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT |
| TNF-α-R | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG |
| INF-γ-F | ATGAACGCTACACACTGCATC |
| INF-γ-R | CCATCCTTTTGCCAGTTCCTC |
| β-actin-F | TTGCTGACAGGATGCAGAAG |
| β-actin-R | ACATCTGCTGGAAGGTGGAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Gao, S.; Fan, R. Preparation and Application of Clostridium perfringens Alpha Toxin Nanobodies. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080381
Jia Q, Ren H, Zhang S, Yang H, Gao S, Fan R. Preparation and Application of Clostridium perfringens Alpha Toxin Nanobodies. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(8):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080381
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Qiong, Hongrui Ren, Shuyin Zhang, Haoyu Yang, Shuaipeng Gao, and Ruiwen Fan. 2024. "Preparation and Application of Clostridium perfringens Alpha Toxin Nanobodies" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 8: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080381
APA StyleJia, Q., Ren, H., Zhang, S., Yang, H., Gao, S., & Fan, R. (2024). Preparation and Application of Clostridium perfringens Alpha Toxin Nanobodies. Veterinary Sciences, 11(8), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080381





