Assessing the Impacts of Different Levels of Nano-Selenium on Growth Performance, Serum Metabolites, and Gene Expression in Heat-Stressed Growing Quails
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Green Synthesis of Nano-Se
2.2. Quail Husbandry and Housing
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measurement of Growth Performance, and Assessment of Carcass Traits Indices
2.5. Sampling
2.6. Samples Analyses
2.6.1. Blood Analysis
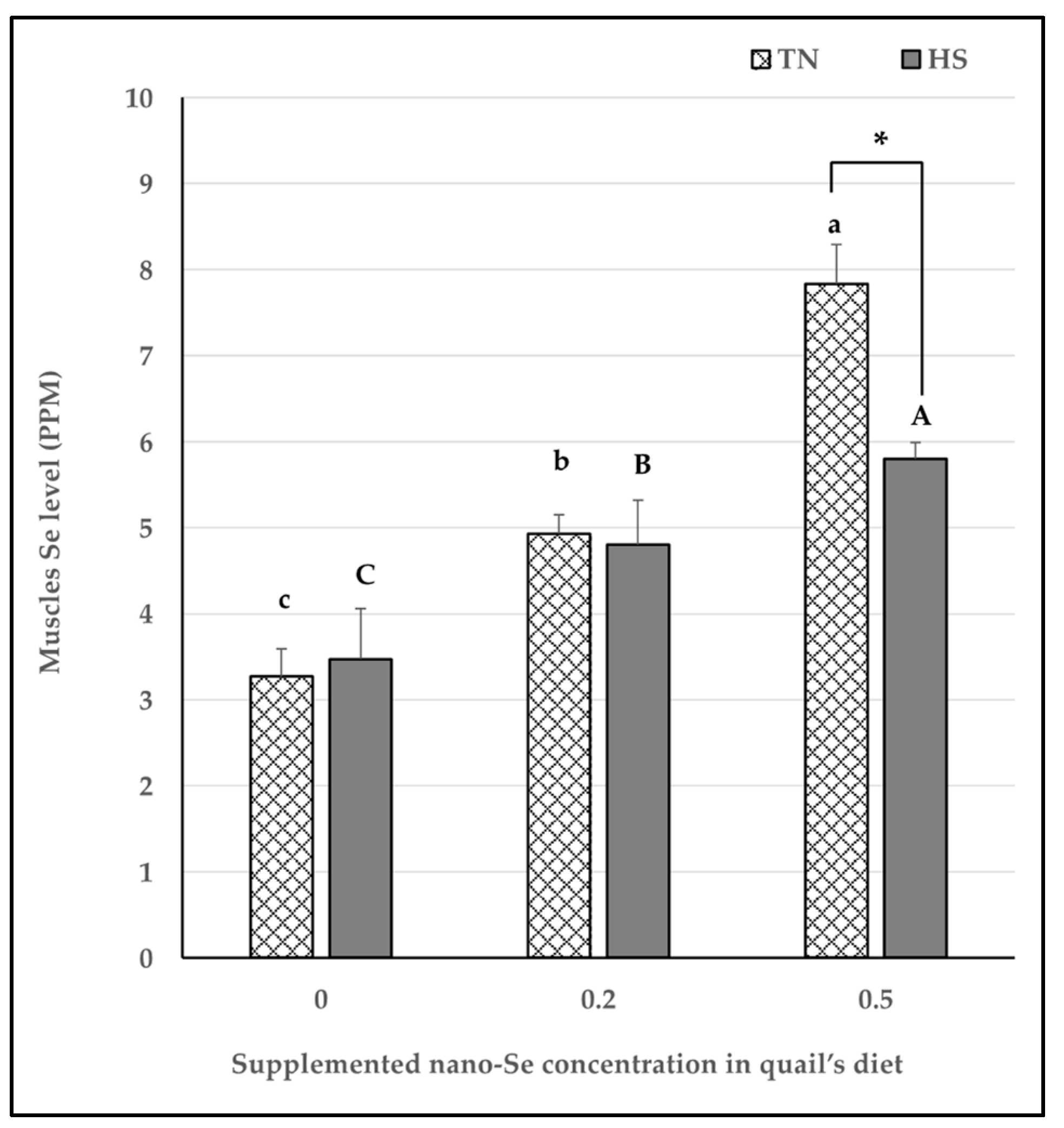
2.6.2. Tissue Se Levels Analysis
2.6.3. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.6.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Performance Characteristics
3.2. Carcass Traits
3.3. Antioxidant Indices
3.4. Gene Expression Profile of Growth Performance, Immune, and Antioxidant Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huss, D.; Poynter, G.; Lansford, R. Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) as a laboratory animal model. Lab. Anim. 2008, 37, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatoo, M.I.; Saxena, A.; Deepa, P.M.; Habeab, B.P.; Devi, S.; Jatav, R.S. Role of trace elements in animals: A review. Vet. World 2013, 6, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazalah, A.A.; Abdel-Hamid, A.E.; Asmaa, M.A.; Asmaa, E. Impact of selenium sources on productive and physiological performance of broilers. Egypt. Poult. Sci. Vol. 2020, 40, 577–597. [Google Scholar]
- Labunskyy, V.M.; Hatfield, D.L.; Gladyshev, V.N. Selenoproteins Molecular Pathways and Physiological Roles. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 739–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurai, P.F.; Karadas, F.; Pappasa, C.; Sparks, N.H.C. Effect of organic selenium in quail diet on its accumulation in tissues and transfer to the progeny. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayman, M.P. Food-chain selenium and human health: Emphasis on intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P.; Winther, K.H.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Cold, F.; Thvilum, M.; Stranges, S.; Guallar, E.; Cold, S. Effect of long-term selenium supplementation on mortality: Results from a multiple-dose, randomised controlled trial. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium intake, status, and health: A complex relationship. Hormones 2020, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wareth, A.A.A.; Muhammad Mobashar, A.S.; Abu Bakkar, S. Jojoba Seed Oil as Feed Additive for Sustainable Broiler Meat Production under Hot Climatic Condition. Animals 2022, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, S.; Sultana, F.; Chowdhury, S.D.; Roy, B.C. Response of heat-stressed commercial broilers to dietary supplementation of organic chromium. J. Agri. Vet. Sci. 2016, 9, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfiky, A.A.; Enab, A.A.; Zanaty, G.A.; Morsy, A.S.; Sewalem, H.Z. Productive performance and egg quality traits of laying hens fed on diets treated with nano-selenium under hot desert conditions. Menoufia J. Anim. Poult. Fish Prod. 2021, 5, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, T.; Senthilkumar, S.; Deepa, K.; Amutha, R. Nutritional management to alleviate heat stress in broilers. Inter. J. Sci. Enviro. 2015, 4, 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Shirsat, S.; Kadam, A.; Mane, R.S.; Jadhav, V.V.; Zate, M.K.; Naushad, M.; Kim, K.H. Protective role of biogenic selenium nanoparticles in immunological and oxidative stress generated by enrofloxacin in broiler chicken. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8845–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelyhe, C.; Mézes, M. Myths and Facts about the Effects of Nano Selenium in Farm Animals—Mini-review. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2013, 2, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Marković, R.; Ćirić, J.; Drljačić, A.; Šefer, D.; Jovanović, I.; Jovanović, D.; Milanović, S.; Trbović, D.; Radulović, S.; Baltić, M.Ž. The Effects of Dietary Selenium-yeast Level on Glutathione Peroxidase Activity, Tissue Selenium Content, Growth Performance, and Carcass and Meat Quality of Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2861–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ahmadian, A.; Seidavi, A.R. Effect of different levels of nano-selenium on performance, blood parameters, immunity and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. J. 2018, 6, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Loeschner, K.; Hadrup, N.; Hansen, M.; Pereira, S.A.; Gammelgaard, B.; Møller, L.H.; Mortensen, A.; Lam, H.R.; Larsen, E.H. Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of selenium following oral administration of elemental selenium nanoparticles or selenite in rats. Metallomics 2014, 6, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadrup, N.; Loeschner, K.; Skov, K.; Ravn-Haren, G.; Larsen, E.H.; Mortensen, A.; Lam, H.R.; Frandsen, H.L. Effects of 14-day oral low dose selenium nanoparticles and selenite in rat—As determined by metabolite pattern determination. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes: Comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoo, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, G. Green synthesis and characterization of se nanoparticles and nanorods. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2011, 7, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, N.A.; Radwan, N.L.; Youssef, S.F.; Salah Eldin, T.A.; Abo Elwafa, S. Effect of Inclusion Inorganic, Organic or Nano Selenium Forms in Broiler Diets on Growth Performance, Carcass and Meat Characteristics. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 14, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.E.; Morman, S.A.; Morrison, J.M.; Lamothe, P.J. Simultaneous Speciation of Arsenic, Selenium, and Chromium by HPLC-ICPMS; Geological Survey Open-File Report 2008-1334; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, K.; Kucuk, O. Effects of vitamin E and selenium on performance, digestibility of nutrients, and carcass characteristics of Japanese quails reared under heat stress (34 °C). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2001, 85, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ (–delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinforma. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Krejcie, R.V.; Morgan, D.W. Determining sample size for research activities. EPMEAJ 1970, 30, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.J.; Wu, C.X.; Gong, L.M.; Song, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.Y. Effects of Nano-selenium on performance, meat quality, immune function, oxidation resistance, and tissue selenium content in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; Sabic, E.; Wakwak, M.; El-Wardany, I.; El-Homosany, Y.; Mohammad, N.E. In-ovo and dietary supplementation of selenium nano-particles influence physiological responses, immunological status and performance of broiler chicks. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. 2020, 29, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Hu, M.Y.; Tang, J.; Shao, Z.F.; Li, M.H. Protective effects of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on the small intestinal mucosa in heat-stressed Wenchang chicken. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015, 25, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, G.P. Stress-induced gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction and its inflammatory effects. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87 (Suppl. 14), E101–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.A.; Najaa, M.; Zulaikha, Z.A.; Zulkifli, I.; Soleimani, A.F. Effects of heat stress on growth performance, selected physiological and immunological parameters, caecal microflora, and meat quality in two broiler strains. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari-Rostamabad, M.; Hosseini-Vashan, S.J.; Perai, A.H.; Sarir, H. Nanoselenium Supplementation of Heat-stressed Broilers: Effects on Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Blood Metabolites, Immune Response, Antioxidant Status, and Jejunal Morphology. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 178, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazraie, S.; Ghazanfarpoor, R. Effect of nano-selenium particles and sodium selenite on performance, glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase of quail under heat stress. Int. J. Rev. Life. Sci. 2015, 5, 875–882. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.S.; Wang, X.F.; Xu, T.W. Elemental selenium at nano size (nano-Se) as a potential chemopreventive agent with reduced risk of selenium toxicity: Comparison with Se-methylselenocysteine in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deep, M.H.; Daichi, I.; Tarek, A.E.; Akira, O. Effects of Dietary Nano-Selenium Supplementation on Growth Performance, Antioxidative Status, and Immunity in Broiler Chickens under Thermoneutral and High Ambient Temperature Conditions. J. Poult. Sci. 2016, 53, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahina, K.; Ondercib, M.; Sahinb, N.; Gursuc, M.F.; Khachik, F.; Kucuk, O. Effects of lycopene supplementation on antioxidant status, oxidative stress, performance and carcass characteristics in heat-stressed Japanese quail. J. Therm. Biol. 2006, 31, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, S.; Riasi, A.; Afzali, N.; Fathi Nasari, M.A. Effect of selenium and sodium bicarbonate supplementation diets on blood biochemical properties, growth performance and carcass traits of broilers in heat stress condition. Vet. J. 2011, 90, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kumbhar, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Parveen, F.; Nizamani, Z.A.; Siyal, F.A.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Gan, F.; Liu, Y.; Hamid, M.; Nido, S.A.; et al. Impacts of selenium and vitamin E supplementation on mRNA of heat shock proteins, selenoproteins and antioxidants in broilers exposed to high temperature. AMB Express 2018, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Qattan, S.Y.A.; Attia, Y.A.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Elnesr, S.S.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Madkour, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Reda, F.M. Use of Chemical Nano Selenium as Antibacterial and Antifungal Agent in Quail Diets and its Effect on Growth, Carcasses, Antioxidant, Immunity and Caecal Microbe. Animals 2021, 11, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, H.Y. Synthesis of seleniumnanoparticles in the presence of polysaccharides. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 2590–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbankova, L.; Skalickova, S.; Pribilova, M.; Ridoskova, A.; Pelcova, P.; Skladanka, J.; Horky, P. Effects of Sub-Lethal Doses of Selenium Nanoparticles on the Health Status of Rats. Toxics 2021, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Dai, W.; Hu, X.; Hong, Z. Effects of dietary glycine selenium nanoparticles on loin quality, tissue selenium retention, and serum 89. antioxidation in finishing pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 260, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, D. Antagonistic effects of nano-selenium on broilers hepatic injury induced by Cr(VI) poisoning in AMPK pathway. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41585–41595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarze, A.; Dauplais, M.; Grigoras, I.; Lazard, M.; Ha-Duong, N.T.; Barbier, F.; Blanquet, S.; Plateau, P. Extracellular production of hydrogen selenide accounts for thiol-assisted toxicity of selenite against Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8759–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyroche, G.; Saveanu, C.; Dauplais, M.; Lazard, M.; Beuneu, F.; Decourty, L.; Malabat, C.; Jacquier, A.; Blanquet, S.; Plateau, P. Sodium selenide toxicity is mediated by O2-dependent DNA breaks. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, K.; Lei, X.G. Selenium and diabetes–evidence from animal studies. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenberg, M.; Olm, E.; Hebert, C.; Björnstedt, M.; Fernandes, A.P. Selenium compounds are substrates for glutaredoxins: A novel pathway for selenium metabolism and a potential mechanism for selenium-mediated cytotoxicity. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calik, A.; Emami, N.K.; Schyns, G.; White, M.B.; Walsh, M.C.; Romero, L.F.; Dalloul, R.A. Influence of dietary vitamin E and selenium supplementation on broilers subjected to heat stress, Part II: Oxidative stress, immune response, gut integrity, and intestinal microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Pan, W.; Zhou, D. Antagonistic effect of nano-selenium on hepatocyte apoptosis induced by DEHP via PI3K/AKT pathway in chicken liver. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2021, 218, 112282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.H.; Cheng, K.; Zheng, X.C.; Ahmad, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, T. Effects of dietary supplementation with enzymatically treated Artemisia annua on growth performance, intestinal morphology, digestive enzyme activities, immunity, and antioxidant capacity of heat-stressed broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedger, M.P.; Meinhardt, A. Cytokines and the immunetesticular axis. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2003, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinteiro-Filho, W.M.; Ribeiro, A.; Ferraz-de-Paula, V.; Pinheiro, M.L.; Sakai, M.; Sá, L.R.; Ferreira, A.J.; Palermo-Neto, J. Heat stress impairs performance parameters, induces intestinal injury, and decreases macrophage activity in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.H.; Kang, D.; Park, J.; Khan, M.; Shim, K. Chronic heat stress regulates the relation between heat shock protein and immunity in broiler small intestine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibian, M.; Ghazi, S.; Moeini, M.M.; Abdolmohammadi, A. Effects of dietary selenium and vitamin E on immune response and biological blood parameters of broilers reared under thermoneutral or heat stress conditions. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, S.K.; Campos, V.L.; Leon, C.G.; Rodriguez-Lamazares, S.M.; Rojas, S.M.; Gonzalez, M.; Smith, C.; Mondaca, M.A. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles by Pantoeaagglomerans and their antioxidant activity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Chen, C. Free radical scavenging efficiency of Nano-Se in vitro. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Taylor, E.W. Size effectof elemental seleniumnanoparticles (Nano-Se) at supra nutritional levels on seleniumaccumulation and glutathione S-transferase activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, I.; Skalickova, S.; Arbab, S.; Urbankova, L.; Horky, P. Toxicological effects of nanoselenium in animals. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients | % |
|---|---|
| Yellow corn | 57.1 |
| Soybean meal | 30 |
| Corn gluten | 2 |
| Wheat bran | 7.3 |
| Soyabean oil | 0.5 |
| Limestone | 1.5 |
| Dicalcium p | 0.7 |
| Premix * | 0.3 |
| Salt | 0.3 |
| DL methionine | 0.1 |
| Lysine DL | 0.2 |
| Proximate calculated (%) ** | |
| CP% | 23.92 |
| ME, kcal/kg | 2901.6 |
| Ca% | 1.18 |
| Available P% Analyzed se content (mg/kg) | 0.7 2.32 |
| Gene | Isolation Source | Primer | Product Length (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-2 | Spleen | F: GTGCAAAGTACTGATCTTCGCC R: CTTGGTGTGTAGAGCTCGAGATG | 195 | 60 | AY613440.1 |
| IL-4 | Spleen | F: GAGAGCATCCGGATAGTGAAG R: TTCGCATAAGAGCTGGGTTC | 168 | 62 | AB559571 |
| IL-6 | Spleen | F: CAACCTCAACCTGCCCAA R: GGAGAGCTTCCTCAGGCATT′ | 85 | 60 | AB5595724 |
| IL-8 | Spleen | F: CTGAGGTGCCAGTGCATTAG R: AGCACACCTCTCTTCCATCC | 139 | 58 | AB559573 |
| SOD | Liver | F: TGGACCTCGTTTAGCTTGTG R: ACACGGAAGAGCAAGTACAGR | 126 | 62 | NM_205064.1 |
| GPX | Liver | F: TTGTAAACATCAGGGGCAAA R: TGGGCCAAGATCTTTCTGTAA | 140 | 58 | NM_001163245.1 |
| β-Actin | F: CTGGCACCTAGCACAATGAA R: CTGCTTGCTGATCCACATCT | 123 | 55 | AF199488 | |
| Environmental Temperature | TN | HS | Two Way Anova Analysis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con. of Se (mg/kg) | 0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | Temp | Conc | Inter-action | |
| IBW (g) | 68.33 ± 2.07 | 68.33 ± 1.66 | 69.16 ± 2.87 | 70.4 ± 2.42 | 70.83 ± 3.18 | 70 ± 2.46 | ns | ns | ns | |
| FBW (g) | 205.00 b ± 4.9 | 207.92 b ± 3.8 | 205.83 b ± 6.3 | 203.75 b ± 3.89 | 230.42 a ± 7.5 | 217.9 ab ± 4.5 | ** | * | * | |
| BWG(g) | 136.7 b ± 3.09 | 139.5 b ± 2.4 | 136.7 b ± 3.5 | 133.3 c ± 2.07 | 159.58 a ± 4.6 | 147.9 ab ± 2.4 | ** | ** | ** | |
| FCR | 4.57 a ± 0.12 | 4.08 bc ± 0.08 | 4.13 bc ±0.09 | 4.37 ab ± 0.24 | 3.79 c ± 0.11 | 4.07 bc ±0.06 | ** | ** | ns | |
| Parameters | Temperature | TN | HS | Tow Way Anova Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con. of Se (mg/kg) | 0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | Temp | Conc | Inter-action | |
| Dressed carcass weight | 133.3 ab ± 2.73 | 145 a ± 0.577 | 143.66 a ± 5.8 | 127.3 ab ± 5.2 | 136.3 ab ± 5.7 | 117.3 b ± 3.5 | * | * | * | |
| Liver % | 1.96 ± 0.22 | 1.69 ± 0.34 | 2.5 ± 0.17 | 2.02 ± 0.16 | 2.5 ± 0.13 | 2.03 ± 0.03 | ns | ns | ns | |
| Heart % | 0.968 ± 0.07 | 0.875 ± 0.01 | 0.914 ± 0.08 | 0.878 ± 0.02 | 0.743 ± 0.02 | 0.859 ± 0.04 | ns | ns | ns | |
| Spleen | 0.115 ± 0.03 | 0.073 ± 0.02 | 0.123 ± 0.03 | 0.200 ± 0.05 | 0.163 ± 0.04 | 0.175 ± 0.03 | ns | ns | ns | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, R.; Salama, B.; Safhi, F.A.; Pet, I.; Pet, E.; Ateya, A. Assessing the Impacts of Different Levels of Nano-Selenium on Growth Performance, Serum Metabolites, and Gene Expression in Heat-Stressed Growing Quails. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060228
Mahmoud R, Salama B, Safhi FA, Pet I, Pet E, Ateya A. Assessing the Impacts of Different Levels of Nano-Selenium on Growth Performance, Serum Metabolites, and Gene Expression in Heat-Stressed Growing Quails. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(6):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060228
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Rania, Basma Salama, Fatmah A. Safhi, Ioan Pet, Elena Pet, and Ahmed Ateya. 2024. "Assessing the Impacts of Different Levels of Nano-Selenium on Growth Performance, Serum Metabolites, and Gene Expression in Heat-Stressed Growing Quails" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 6: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060228
APA StyleMahmoud, R., Salama, B., Safhi, F. A., Pet, I., Pet, E., & Ateya, A. (2024). Assessing the Impacts of Different Levels of Nano-Selenium on Growth Performance, Serum Metabolites, and Gene Expression in Heat-Stressed Growing Quails. Veterinary Sciences, 11(6), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060228







