A Three-Year Study on the Nutritional Composition and Occurrence of Mycotoxins of Corn Varieties with Different Transgenic Events Focusing on Poultry Nutrition
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Classification of Corn Types
2.2. Field Experiments
2.3. Quantification of Mycotoxins via High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS)
2.3.1. Chemical Reagents
2.3.2. Aflatoxins (AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, and AFG2)
2.3.3. Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone
2.3.4. Fumonisins (FB1 and FB2)
2.3.5. Parameters of Method Performance
2.4. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Nutritional Predictions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
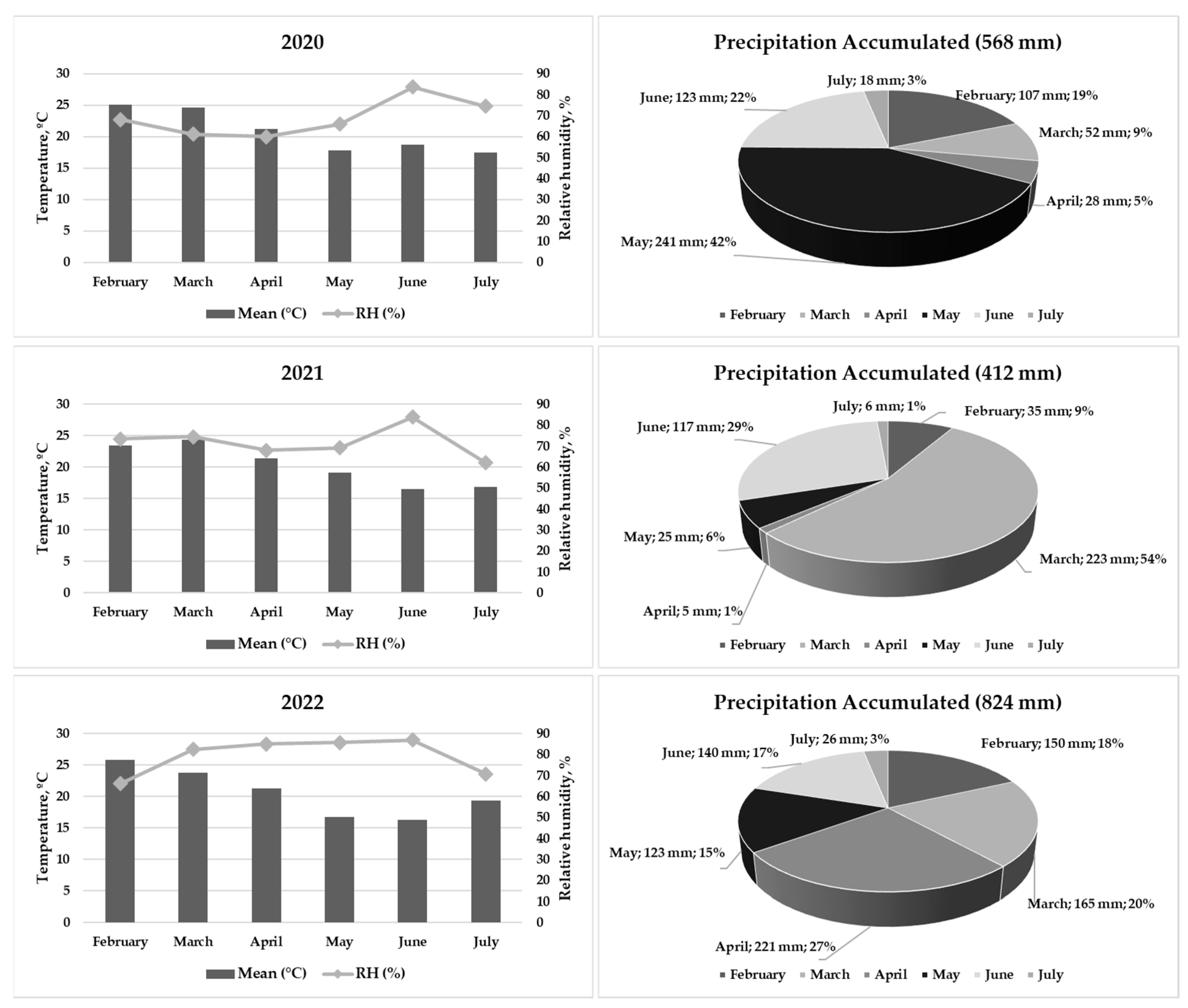
3.1. Meteorological Data
3.2. Damaged Grains, Crop Yield, and Mycotoxin Contamination
3.3. Proximal Composition and Phosphorus Values
3.4. Amino Acids and Metabolizable Energy for Poultry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Available online: https://ipad.fas.usda.gov/cropexplorer/cropview/commodityView.aspx?cropid=0440000 (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- CONAB. Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. Available online: https://www.conab.gov.br/info-agro/safras/graos/boletim-da-safra-de-graos (accessed on 18 September 2023).
- EMBRAPA. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Levantamento de Cultivares de Milho Para o Mercado de Sementes: Safra 2020/2021. Available online: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/225301/1/Doc-263-Levantamento-cultivares-milh-2020-2021.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- EMBRAPA. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Disponibilidade de Cultivares de Milho Para o Mercado de Sementes do Brasil: Safra 2021/2022. Available online: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/237270/1/Documentos-268-Disponibilidade-de-cultivares-de-milho-para-o-mercado-safra-2021-2022.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- EMBRAPA. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Cultivares de Milho Para Safra 2022/2023. Available online: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/doc/1150188/1/Documentos-272-Cultivares-de-milho-para-safra-2022-2023.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Cowieson, A.J. Factors that affect the nutritional value of maize for broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2005, 119, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.; Lundy, E. Nutritional properties and feeding value of corn and its coproducts. In Corn: Chemistry and Technology; Serna-Saldivar, S.O., Ed.; AACC International Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2019; pp. 633–659. ISSN 978-0-12-811971-6. [Google Scholar]
- Eyng, C.; Nunes, R.V.; Pozza, P.C.; Pozza, M.; Nunes, C.G.V.; Navarini, F.C.; Silva, W.T.M. Composição química e valores energéticos de cultivares de milho para 362 aves. Rev. Bras. Saúde Prod. 2009, 10, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, C.T.; Vidal, J.K.; Tyska, D.; Mallmann, A.O.; Madalosso, T.; Mallmann, C.A. Assessment of field traits, nutrient composition and digestible amino acids of corns with different endosperm textures for poultry and swine. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 295, 115510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardon, P.J. Mycotoxins: Risks in Plant, Animal, Human Systems; Council for Agricultural: Ames, IA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bryden, W.L. Mycotoxin contamination of the feed supply chain: Implications for animal productivity and feed security. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 173, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, G.P.; Arias, S.; Taschl, I.; Gruber-Dorninger, C. Mycotoxins in corn: Occurrence, impacts, and management. Chem. Technol. 2019, 9, 235–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Rocha, A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Mallmann, C.A. Natural mycotoxin contamination of maize (Zea mays L.) in the South region of Brazil. Food Control 2017, 73, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyska, D.; Mallman, A.O.; Vidal, J.K.; Simões, C.T.; Mallmann, C.A. Nearinfrared spectroscopy to assess mycotoxins contamination and nutritional composition of maize marketed in South America, years 2020–2021. World Mycot. J. 2022, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Naehrer, K.A. Three-Year Survey on the Worldwide Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Feedstuffs and Feed. Toxins 2012, 4, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wielogórska, E.; Macdonald, S.; Elliot, C.T. A review of the efficacy of mycotoxin detoxifying agents used in feed in light of changing global environment and legislation. World Mycot. J. 2016, 9, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL; MAPA. Ministério De Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Instrução Normativa 60/2011. Available online: http://sistemasweb.agricultura.gov.br/sislegis/action/detalhaAto.do?method=visualizarAtoPortalMapa&chave=1739574738 (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Mallmann, C.A.; Tyska, D.; Almeida, C.A.A.; Oliveira, M.; Gressler, L.T. Mycotoxicological monitoring of breakfast and infant cereals marketed in Brazil. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 331, 108628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Buttinger, G.; Krska, R. Rapid simultaneous determination of major type A- and B-trichothecenes as well as zearalenone in maize by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1062, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.M.; Filho, A.C. Linear relationships between agronomic and nutritional traits in transgenic genotypes of maize. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saath, K.C.O.; Fachinello, A.L. Crescimento da Demanda Mundial de Alimentos e Restrições do Fator Terra no Brasil. Rev. Econ. Sociol. Rural 2017, 56, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Durán, D.; Perez, J.F.; González-Ortiz, G.; Villagómez-Estrada, S.; Bedford, M.R.; Graham, H.; Sola-Oriol, D. Growth performance and total tract digestibility in broiler chickens fed different corn hybrids. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallmann, A.O.; Dilkin, P.; Vidal, J.K.; Meinerz, G.R.; Oliveira, M.S.; Mallmann, C.A. Influência da qualidade micotoxicológica e nutricional de híbridos de milho no custo da ração de frangos de corte. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2019, 71, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, C.T.; Vidal, J.K.; Silva, C.R.; Sarturi, J.A.; Laber, I.F.; Madalosso, T.; Mallmann, C.A. A two-year study on the occurrence and concentration of mycotoxins in corn varieties with different endosperm textures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBRAPA. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Relação Com o Clima na Produção de Milho. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/agencia-de-informacao-tecnologica/cultivos/milho/pre-producao/caracteristicas-da-especie-e-relacoes-com-o-ambiente/relacoes-com-o-clima (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- EMBRAPA. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Milho: 500 Perguntas–500 Respostas. Available online: https://mais500p500r.sct.embrapa.br/view/pdfs/90000022-ebook-pdf.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Monsanto. VT PRO3. Available online: https://www.agro.bayer.com.br/conteudos/milho-vtpro4-e-mais-tecnologia (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Corteva Agriscience. PowerCore Ultra. Available online: https://www.corteva.com.br/produtos-e-servicos/tecnologias/powercore-ultra-pwu.html (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Syngenta. Agrisure Viptera 3. Available online: https://portal.syngenta.com.br/sementes/agrisure-viptera-3 (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Ono, E.Y.S.; Silva, M.; Hashimoto, E.H.; Vizoni, E.; Kawamura, O.; Sugiura, Y.; Hirooka, E.Y. Mycotoxicological quality evaluation of corn samples used by processing industries in the Northern region of Paraná State, Brazil. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 25, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonissen, G.; Immerseel, F.V.; Pasmans, F.; Janssens, G.P.J.; Baere, S.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Su, S.; Wong, E.A.; Meulenaer, B.; Verlinden, M.; et al. Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Fumonisins Alter the Extrinsic Component of Intestinal Barrier in Broiler Chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10846–10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Haque, M.A.; Shi, Q.; Fu, Q.; He, C. Contamination with Fumonisin B and Deoxynivalenol Is a Threat to Egg Safety and Contributes to Gizzard Ulcerations of Newborn Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 676671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Iglesias, L.; Malvar, R.A.; Garzón, R.; Rosell, C.M.; Revilla, P. Nutritional Value of Whole Maize Kernels from Diverse Endosperm Types and Effects on Rheological Quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi, A.; Gholami, A.; Barzegari, M. Corn (Zea mays L.) Growth, Yield and Nutritional Properties Affected by Fertilization Methods and Micronutrient Use. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2021, 15, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, V.; Oliveira, V.; Gewehr, C.E. The effect of corn kernel texture and alpha-amylase addition in performance and digestibility of diets for weaned pigs. Cienc. Rural. 2011, 41, 2014–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vieira, R.O.; Rodrigues, P.B.; Freitas, R.T.F.; Nascimento, G.A.J.; Silva, E.L.; Hespanhol, R. Composição química e energia metabolizável de híbridos de milho para frangos de corte. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2007, 36, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| 2020 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Item | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | Agrisure® Viptera 3 | SEM | p-Value |
| Damaged grains, % | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.034 | 0.6283 |
| Crop yield, kg/ha | 9029 a | 8591 b | 8767 ab | 85.81 | 0.0411 |
| Total aflatoxins 1 (µg/kg) | 1.49 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.393 | 0.3518 |
| Deoxynivalenol (µg/kg) | <LOQ 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| Total fumonisins 2 (µg/kg) | 1180 a | 280.8 b | 8.33 b | 94.22 | 0.0001 |
| Zearalenone (µg/kg) | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| 2021 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Item | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | SEM | p-Value | |
| Damaged grains, % | 1.66 a | 0.75 b | 0.134 | 0.0005 | |
| Crop yield, kg/ha | 5085 a | 4166 b | 127.2 | 0.0002 | |
| Total aflatoxins (µg/kg) | 0.256 | 0.194 | 0.054 | 0.5705 | |
| Deoxynivalenol (µg/kg) | 21.75 | 19.00 | 7.634 | 0.8591 | |
| Total fumonisins (µg/kg) | 1657 a | 414.0 b | 190.0 | 0.0008 | |
| Zearalenone (µg/kg) | 11.80 | 1.56 | 2.728 | 0.0717 | |
| 2022 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Item | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | SEM | p-Value | |
| Damaged grains, % | 2.23 | 3.35 | 0.363 | 0.1304 | |
| Crop yield, kg/ha | 9411 a | 8806 b | 107.8 | 0.0045 | |
| Total aflatoxins (µg/kg) | 0.800 | 0.580 | 0.178 | 0.5491 | |
| Deoxynivalenol (µg/kg) | 138.8 b | 481.0 a | 70.28 | 0.0147 | |
| Total fumonisins (µg/kg) | 2566 a | 990.6 b | 317.2 | 0.0127 | |
| Zearalenone (µg/kg) | 131.7 | 345.5 | 57.57 | 0.0766 | |
| 2020 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Variable | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | Agrisure® Viptera 3 | SEM | p-Value |
| Crude protein, % | 8.21 | 8.44 | 8.44 | 0.046 | 0.0603 |
| Crude fiber, % | 2.12 a | 2.03 b | 2.09 ab | 0.014 | 0.0104 |
| Ash, % | 1.14 | 1.15 | 1.13 | 0.006 | 0.3168 |
| Ether extract, % | 4.03 a | 3.77 b | 3.69 b | 0.030 | 0.0001 |
| Total P, mg/kg | 1965 | 1959 | 1963 | 13.11 | 0.9761 |
| Phytic P, mg/kg | 1474 | 1469 | 1472 | 9.83 | 0.9750 |
| 2021 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Variable | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | SEM | p-Value | |
| Crude protein, % | 9.29 b | 10.02 a | 0.082 | 0.0001 | |
| Crude fiber, % | 1.99 | 2.00 | 0.021 | 0.8422 | |
| Ash, % | 1.19 b | 1.27 a | 0.008 | 0.0001 | |
| Ether extract, % | 3.75 a | 3.58 b | 0.033 | 0.0113 | |
| Total P, mg/kg | 2012 b | 2094 a | 15.70 | 0.0084 | |
| Phytic P, mg/kg | 1509 b | 1571 a | 11.78 | 0.0084 | |
| 2022 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Variable | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | SEM | p-Value | |
| Crude protein, % | 7.95 b | 8.87 a | 0.093 | 0.0001 | |
| Crude fiber, % | 1.96 | 1.91 | 0.022 | 0.3069 | |
| Ash, % | 1.19 b | 1.23 a | 0.009 | 0.0326 | |
| Ether extract, % | 3.70 a | 3.36 b | 0.038 | 0.0001 | |
| Total P, mg/kg | 1970 b | 2045 a | 18.83 | 0.0480 | |
| Phytic P, mg/kg | 1477 b | 1533 a | 14.14 | 0.0483 | |
| 2020 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Variable | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | Agrisure® Viptera 3 | SEM | p-Value |
| Total Met + Cys, % | 0.354 | 0.359 | 0.363 | 0.0015 | 0.0700 |
| Dig 1. Met + Cys, % | 0.326 | 0.331 | 0.334 | 0.0014 | 0.0915 |
| Total Lys, % | 0.231 | 0.230 | 0.231 | 0.0009 | 0.8598 |
| Dig. Lys, % | 0.210 | 0.210 | 0.211 | 0.0008 | 0.9845 |
| Total Thr, % | 0.291 | 0.298 | 0.299 | 0.0015 | 0.0954 |
| Dig. Thr, % | 0.259 | 0.265 | 0.266 | 0.0013 | 0.1082 |
| Total Trp, % | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.062 | 0.0002 | 0.7187 |
| Dig. Trp, % | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.0001 | 0.1465 |
| Total Arg, % | 0.379 | 0.383 | 0.385 | 0.0017 | 0.4068 |
| Dig. Arg, % | 0.338 | 0.341 | 0.342 | 0.0014 | 0.4358 |
| Total Val, % | 0.390 | 0.399 | 0.401 | 0.0020 | 0.0808 |
| Dig. Val, % | 0.371 | 0.380 | 0.378 | 0.0019 | 0.1122 |
| Total Ile, % | 0.281 b | 0.290 a | 0.291 a | 0.0018 | 0.0338 |
| Dig. Ile, % | 0.276 b | 0.285 a | 0.288 a | 0.0017 | 0.0376 |
| Total Leu, % | 1.021 b | 1.064 a | 1.070 a | 0.0079 | 0.0252 |
| Dig. Leu, % | 0.950 b | 0.990 a | 0.995 a | 0.0074 | 0.0255 |
| Total His, % | 0.241 | 0.246 | 0.246 | 0.0011 | 0.1089 |
| Dig. His, % | 0.233 | 0.238 | 0.239 | 0.0011 | 0.0677 |
| Total Phe, % | 0.386 b | 0.412 a | 0.414 a | 0.0029 | 0.0269 |
| Dig. Phe, % | 0.368 b | 0.383 a | 0.386 a | 0.0027 | 0.0193 |
| AMEn 2, kcal/kg | 3340 a | 3330 b | 3326 b | 1.4952 | 0.0007 |
| 2021 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Variable | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | SEM | p-Value | |
| Total Met + Cys, % | 0.367 b | 0.384 a | 0.0029 | 0.0043 | |
| Dig. Met + Cys, % | 0.334 b | 0.350 a | 0.0026 | 0.0025 | |
| Total Lys, % | 0.242 b | 0.251 a | 0.0014 | 0.0030 | |
| Dig. Lys, % | 0.213 b | 0.221 a | 0.0013 | 0.0020 | |
| Total Thr, % | 0.321 b | 0.345 a | 0.0028 | 0.0001 | |
| Dig. Thr, % | 0.277 b | 0.297 a | 0.0023 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Trp, % | 0.064 b | 0.067 a | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | |
| Dig. Trp, % | 0.053 b | 0.057 a | 0.0005 | 0.0016 | |
| Total Arg, % | 0.406 b | 0.426 a | 0.0028 | 0.0004 | |
| Dig. Arg, % | 0.361 b | 0.379 a | 0.0025 | 0.0004 | |
| Total Val, % | 0.430 b | 0.462 a | 0.0036 | 0.0001 | |
| Dig. Val, % | 0.400 b | 0.430 a | 0.0034 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Ile, % | 0.319 b | 0.347 a | 0.0031 | 0.0001 | |
| Dig. Ile, % | 0.307 b | 0.333 a | 0.0029 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Leu, % | 1.169 b | 1.288 a | 0.0137 | 0.0001 | |
| Dig. Leu, % | 1.076 b | 1.185 a | 0.0127 | 0.0001 | |
| Total His, % | 0.256 b | 0.272 a | 0.0020 | 0.0002 | |
| Dig. His, % | 0.244 b | 0.257 a | 0.0019 | 0.0005 | |
| Total Phe, % | 0.453 b | 0.498 a | 0.0052 | 0.0001 | |
| Dig. Phe, % | 0.417 b | 0.459 a | 0.0048 | 0.0001 | |
| AMEn, kcal/kg | 3328 a | 3317 b | 1.8655 | 0.0014 | |
| 2022 | |||||
| Transgenic Technology | |||||
| Variable | VT PRO3® | PowerCore® ULTRA | SEM | p-value | |
| Total Met + Cys, % | 0.349 b | 0.367 a | 0.0038 | 0.0226 | |
| Dig. Met + Cys, % | 0.310 b | 0.338 a | 0.0034 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Lys, % | 0.240 | 0.248 | 0.0016 | 0.1480 | |
| Dig. Lys, % | 0.209 b | 0.217 a | 0.0015 | 0.0071 | |
| Total Thr, % | 0.285 b | 0.304 a | 0.0032 | 0.0014 | |
| Dig. Thr, % | 0.241 b | 0.266 a | 0.0020 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Trp, % | 0.060 b | 0.063 a | 0.0004 | 0.0117 | |
| Dig. Trp, % | 0.050 | 0.051 | 0.0002 | 0.0909 | |
| Total Arg, % | 0.371 b | 0.388 a | 0.0033 | 0.0089 | |
| Dig. Arg, % | 0.325 b | 0.348 a | 0.0029 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Val, % | 0.381 b | 0.407 a | 0.0041 | 0.0017 | |
| Dig. Val, % | 0.347 b | 0.386 a | 0.0038 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Ile, % | 0.278 b | 0.309 a | 0.0036 | 0.0014 | |
| Dig. Ile, % | 0.260 b | 0.295 a | 0.0035 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Leu, % | 0.983 b | 1.088 a | 0.0171 | 0.0017 | |
| Dig. Leu, % | 0.873 b | 1.021 a | 0.0151 | 0.0001 | |
| Total His, % | 0.239 b | 0.248 a | 0.0025 | 0.0012 | |
| Dig. His, % | 0.220 b | 0.239 a | 0.0024 | 0.0001 | |
| Total Phe, % | 0.388 b | 0.427 a | 0.0063 | 0.0017 | |
| Dig. Phe, % | 0.356 b | 0.401 a | 0.0060 | 0.0001 | |
| AMEn, kcal/kg | 3329 a | 3311 b | 1.9347 | 0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vidal, J.K.; Simões, C.T.; Mallmann, A.O.; Tyska, D.; Pereira, H.V.; Mallmann, C.A. A Three-Year Study on the Nutritional Composition and Occurrence of Mycotoxins of Corn Varieties with Different Transgenic Events Focusing on Poultry Nutrition. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020097
Vidal JK, Simões CT, Mallmann AO, Tyska D, Pereira HV, Mallmann CA. A Three-Year Study on the Nutritional Composition and Occurrence of Mycotoxins of Corn Varieties with Different Transgenic Events Focusing on Poultry Nutrition. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(2):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020097
Chicago/Turabian StyleVidal, Juliano Kobs, Cristina Tonial Simões, Adriano Olnei Mallmann, Denize Tyska, Helder Victor Pereira, and Carlos Augusto Mallmann. 2024. "A Three-Year Study on the Nutritional Composition and Occurrence of Mycotoxins of Corn Varieties with Different Transgenic Events Focusing on Poultry Nutrition" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 2: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020097
APA StyleVidal, J. K., Simões, C. T., Mallmann, A. O., Tyska, D., Pereira, H. V., & Mallmann, C. A. (2024). A Three-Year Study on the Nutritional Composition and Occurrence of Mycotoxins of Corn Varieties with Different Transgenic Events Focusing on Poultry Nutrition. Veterinary Sciences, 11(2), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020097






