Isolation, Molecular, and Histopathological Patterns of a Novel Variant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Chicken Flocks in Egypt
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approve
2.2. Examination and Sampling of Chickens
2.3. Viral Isolation and Propagation in Specific Pathogen-Free Embryonated Chicken Eggs (SPF-ECE)
2.4. Real Time Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (rRT-PCR)
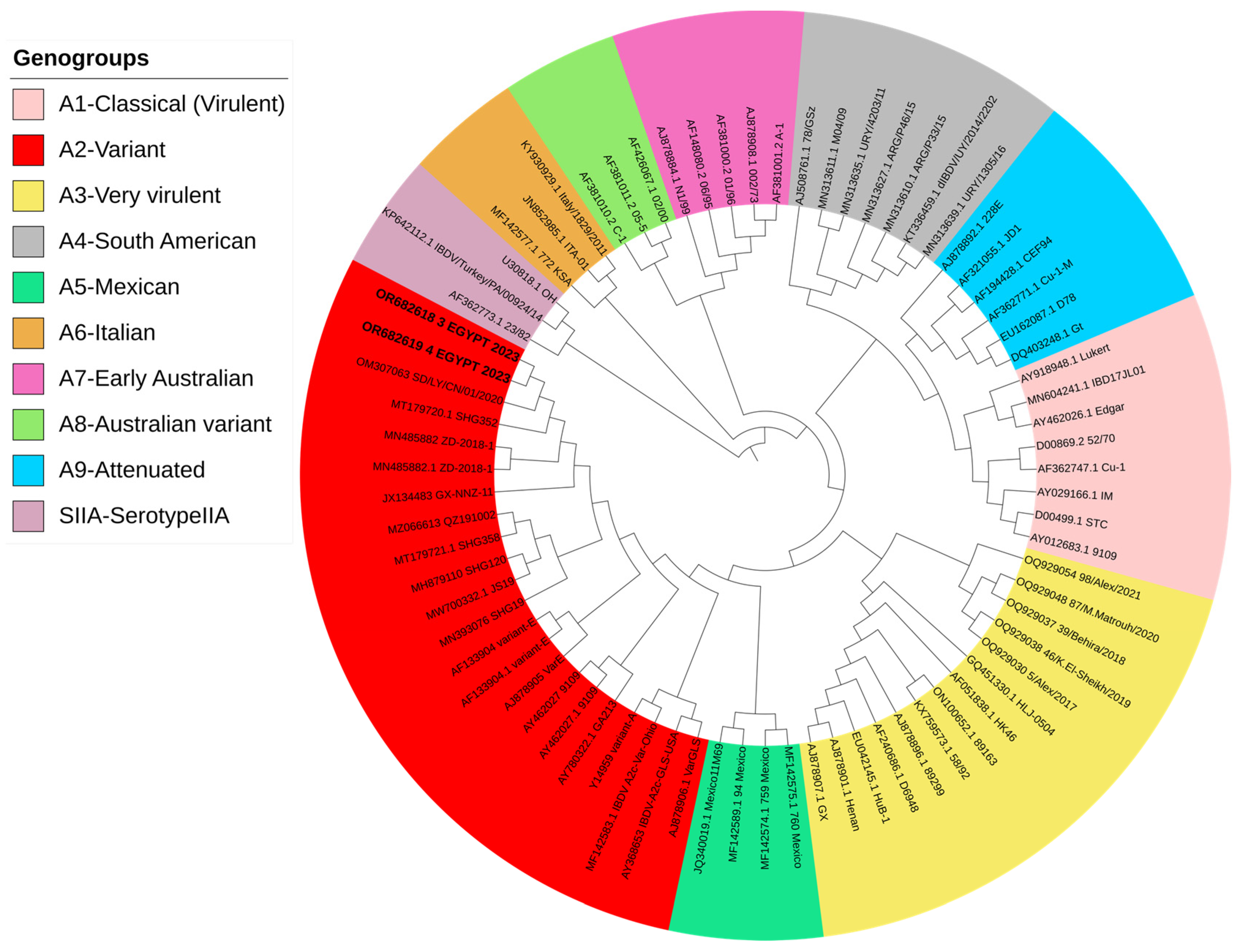
2.5. VP2 Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Tree
2.6. Histopathological Examination of Field Samples
3. Results
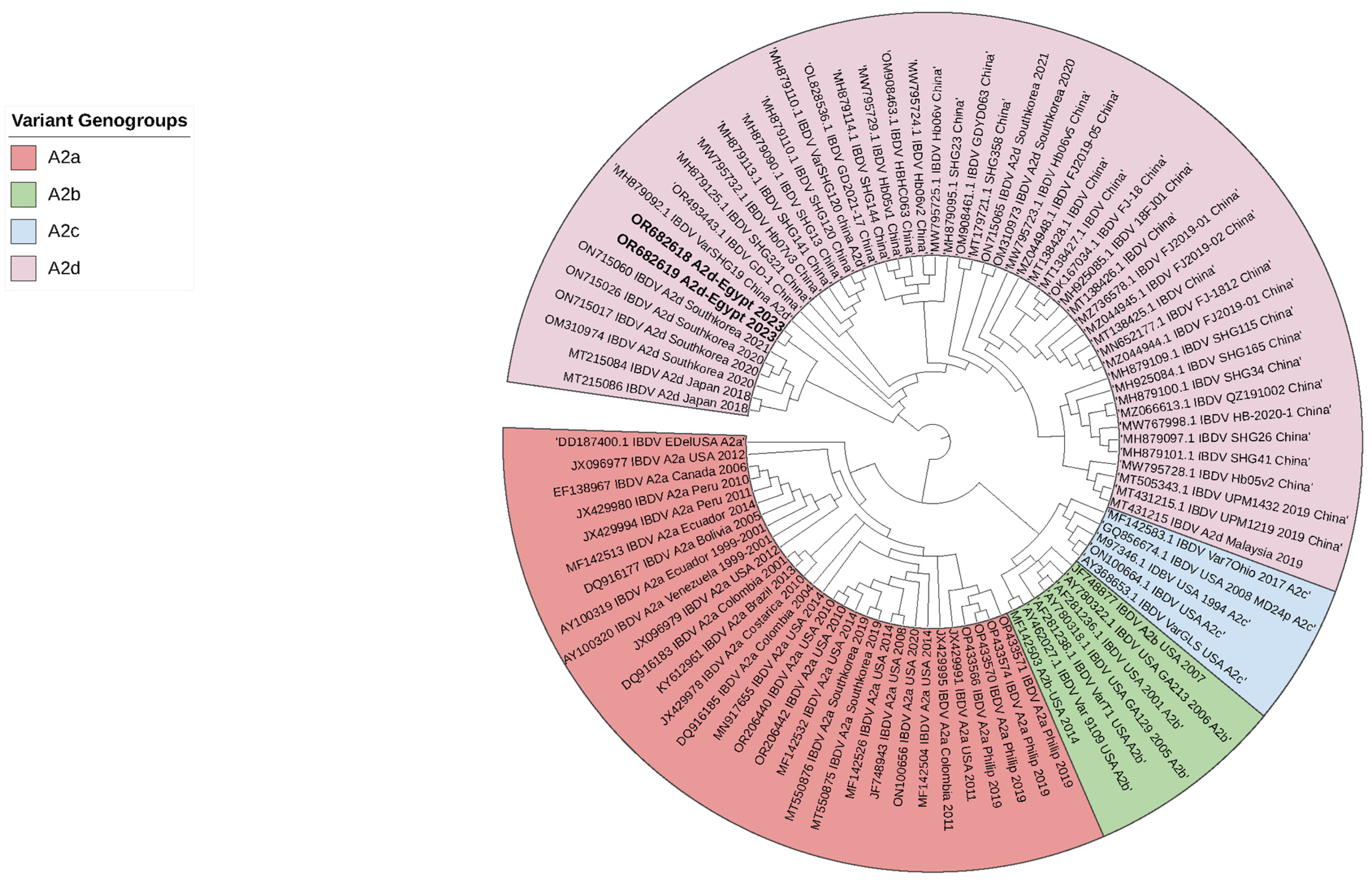
3.1. Isolation and Identification of nVarIBDV
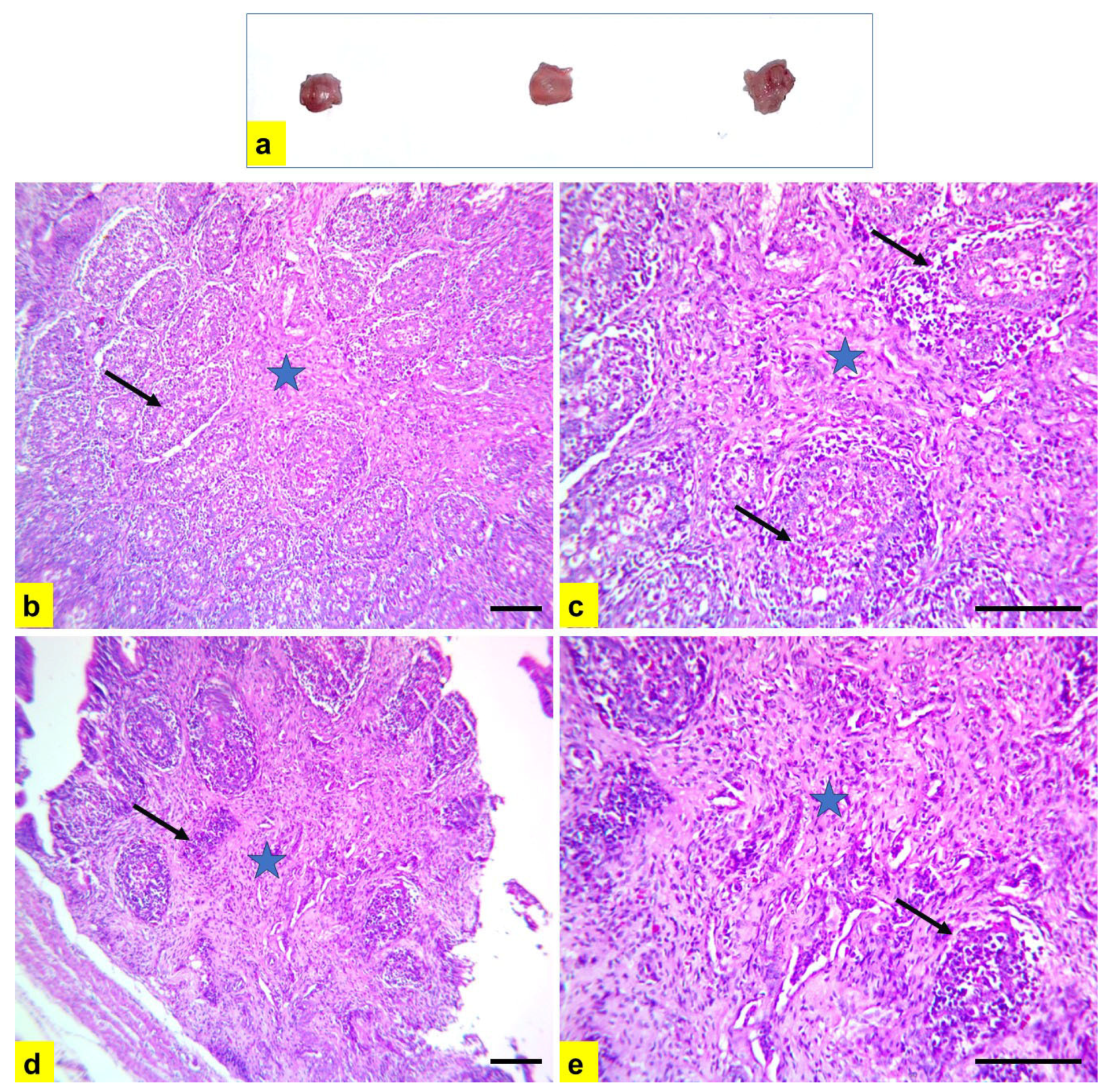
3.2. Histopathological Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eterradossi, N.; Saif, Y.M. Infectious Bursal Disease. In Diseases of Poultry; David, E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 257–283. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, A.S. An Apparently New Disease of Chickens: Avian Nephrosis. Avian Dis. 1962, 6, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchner, S.B. Infectivity of infectious bursal disease virus for embryonating eggs. Poult. Sci. 1970, 49, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, D.J.; Saif, Y.M.; Moorhead, P.D. Immunogenicity and antigenicity of infectious bursal disease virus serotypes I and II in chickens. Avian Dis. 1985, 29, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasher, H.N.; Davis, V.S. History of Infectious Bursal Disease in the U.S.A.—The First Two Decades. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettle, N.; Stuart, J.C.; Wyeth, P.J. Outbreak of virulent infectious bursal disease in East Anglia. Vet. Rec. 1989, 125, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.O.; Jackwood, D.J. Classification of infectious bursal disease virus into genogroups. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3661–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, D.J.; Schat, K.A.; Michel, L.O.; de Wit, S. A proposed nomenclature for infectious bursal disease virus isolates. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.-p.; et al. An improved scheme for infectious bursal disease virus genotype classification based on both genome-segments A and B. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Rahman, T.; Mumu, T.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Eterradossi, N.; Müller, H. A unified genotypic classification of infectious bursal disease virus based on both genome segments. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zheng, S.J. Genetic Insight into the Interaction of IBDV with Host—A Clue to the Development of Novel IBDV Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sergany, M.; Moursi, A.; Saber, M.; Mohamed, M. A preliminary investigation on the occurrence of Gumboro disease in Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 1974, 11, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, N.N.K.; Malek, G. Identification of the pathogen of Gumboro disease in Egypt. Mon. Vet. Med. 1976, 31, 106–108. [Google Scholar]
- El-Batrawi, A.M. Studies on sever outbreaks of infectious bursal disease in Egypt. In Proceedings of the 2nd Scientific Conference of the Egyptian Veterinary Poultry Association, Cairo, Egypt, 12–14 March 1990; p. 239. [Google Scholar]
- Khafagy, A.K.; El-Sawy, A.; Kouwenhoven, B.; Vieltitz, E.; Ismail, I.M.; Amer, A.A.; Sultan, H.A.; El-Gohary, A. Very virulent infectious bursal disease. Vet. Med. J. Giza. 1991, 39, 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, H.A. Studies on Infection Bursal Disease Virus in Chickens. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Mawgod, S.; Arafa, A.; Hussein, A. Molecular genotyping of the infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) isolated from broiler flocks in Egypt. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2014, 2, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhit, A.B.A. Very Virulent Form of Infectious Bursal Disease in Egypt; The third Congress of Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University: Zagazig, Egypt, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Alim, G.A.; Awad, M.H.H.; Saif, Y.M. Characterization of Egyptian field strains of infectious bursal disease virus. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.K. Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Egypt: Epidemiology, Isolation and Immunogenicity of Classic Vaccine. Vet. Res. Commun. 2004, 28, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.M.; Yousif, A.A.; Shaheed, I.B.; Mohammed, W.A.; Samy, A.M.; Reda, I.M. Re-Emergence of Very Virulent IBDV in Egypt. Int. J. Virol. 2009, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; El Zanaty, K.E.S.; Bakhit, B.M.; Safwat, M.M. Genetic Characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses Associated with Gumboro Outbreaks in Commercial Broilers from Asyut Province, Egypt. ISRN Vet. Sci. 2014, 2014, 916412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shall, N.A.; Sedeek, M.E.; El-Badawy, M.M.; Hussein, E.G.; Awad, A.M. Phylogenetic Characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) Viruses Isolated From Field Outbreaks in Chickens From Behera And Alexandria Governorates, Egypt. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 56, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ellakany, H.F.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Sayed-Ahmed, A.; Elgammal, S.; Gado, A.R.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S. Genetic point mutation inducing antigenic drift in hypervariable region of a very virulent IBDV isolate in chickens in Egypt during 2014–2016. Damanhour J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 2, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbestawy, A.R.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Ellakany, H.F.; Gado, A.R.; El-Rayes, S.H.; Salaheldin, A.H. Molecular characterization, sequence analysis, and pathogenicity of infectious bursal disease virus during 2017–2021. 2023; under publication. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, M.M.; Nassif, S.A. Studies on recent IBD field variant isolates: Genomic identification and differentiation using RT-PCR-RELP. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Vet. Med. 2005, 15, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Legnardi, M.; Poletto, F.; Talaat, S.; Selim, K.; Moawad, M.K.; Franzo, G.; Tucciarone, C.M.; Cecchinato, M.; Sultan, H. First Detection and Molecular Characterization of Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (Genotype A2dB1b) in Egypt. Viruses 2023, 15, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.M.; Kim, I.J.; Rautenschlein, S.; Yeh, H.Y. Infectious bursal disease virus of chickens: Pathogenesis and immunosuppression. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, T.P.; Morales, D.; Eterradossi, N.; Rivallan, G.; Toquin, D.; Raue, R.; Zierenberg, K.; Zhang, M.F.; Zhu, Y.P.; Wang, C.Q.; et al. Assessment of genetic, antigenic and pathogenic criteria for the characterization of Infectious bursal disease virus strain. Avian Pathol. 2004, 28, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoerr, F.J. Clinical Aspects of Immunosuppression in Poultry. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.H.; Sun, L.; Tu, K.-h.; Teng, Q.-y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, G.-z. Experimental co-infection of variant infectious bursal disease virus and fowl adenovirus serotype 4 increases mortality and reduces immune response in chickens. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organization of Animal Health (WOAH). Terrestrial Manual. Infect Bursal Disease (Gumboro Disease); Chapter 3.3.12; WOAH: Paris, France, 2024; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tomás, G.; Hernández, M.; Marandino, A.; Panzera, Y.; Maya, L.; Hernández, D.; Pereda, A.; Banda, A.; Villegas, P.; Aguirre, S.; et al. Development and validation of a TaqMan-MGB real-time RT-PCR assay for simultaneous detection and characterization of infectious bursal disease virus. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 185, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.G.; Suarez, D.L.; Seal, B.S.; Pedersen, J.C.; Senne, D.A.; King, D.J.; Kapczynski, D.R.; Spackman, E. Development of a real-time reverse-transcription PCR for detection of Newcastle disease virus RNA in clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Hoffmann, D.; Henritzi, D.; Beer, M.; Harder, T.C. Riems influenza a typing array (RITA): An RT-431 qPCR-based low density array for subtyping avian and mammalian influenza a viruses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, A.M.; Perera, C.L.; Vega, A.; Ríos, L.; Coronado, L.; Relova, D.; Frías, M.T.; Ganges, L.; Núñez, J.I.; Pérez, L.J. A duplex SYBR Green I-based real-time RT-PCR assay for the simultaneous detection and differentiation of Massachusetts and non-Massachusetts serotypes of infectious bronchitis virus. Mol. Cell Probes. 2013, 27, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günes, A.; Marek, A.; Grafl, B.; Berger, E.; Hess, M. Real-time PCR assay for universal detection and quantitation of all five species of fowl adenoviruses (FAdV-A to FAdV-E). J. Virol. Methods 2012, 183, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Dormitorio, T.; Ou, S.-C.; Giambrone, J. Detection and Differentiation of Avian Reoviruses Using SYBR-Green I-Based Two-Step Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR with Melting Curve Analysis. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimondi, A.; Pinto, S.; Olivera, V.; Dibárbora, M.; Pérez-Filgueira, M.; Craig, M.I.; Pereda, A. Comparative histopathological and immunological study of two field strains of chicken anemia virus. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, V.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvarna, S.K.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J.D. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 8th ed.; Churchill Livingstone; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.J.; Gagic, M.; Sharma, J.M. Recovery of antibody producing ability and lymphocyte repopulation of bursal follicles in chickens exposed to infectious bursal disease virus. Avian Dis. 1999, 43, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, D.H.; Saif, Y.M. Antigenic Diversity of Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses. Avian Dis. 1987, 31, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X. The Over-40-Years-Epidemic of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in China. Viruses 2022, 14, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.M.; Dohms, J.E.; Metz, A.L. Comparative pathogenesis of serotype 1 and variant serotype 1 isolates of infectious bursal disease virus and their effect on humoral and cellular immune competence of specific-pathogen-free chickens. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wu, T.; Hussain, A.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Novel variant strains of infectious bursal disease virus isolated in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 230, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, J.K.; Cloud, S.S. Isolation and characterization of variant infectious bursal disease viruses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1986, 189, 357–411. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.B. Changes in the field status of infectious bursal disease virus. Avian Pathol. 1990, 19, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van den Berg, T.P.; Meulemans, G. Acute infectious bursal disease in poultry: Protection afforded by maternally derived antibodies and interference with live vaccination. Avian Pathol. 1991, 20, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Chen, M.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Cui, H.; Pan, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Suppresses Newcastle Disease Vaccination in Broiler and Layer Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6542–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Leng, M.; Tang, S.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Chen, F.; Lin, W. Pathogenicity and molecular characterization of infectious bursal disease virus in China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Analysis of the global origin, evolution and transmission dynamics of the emerging novel variant IBDV (A2dB1b): The accumulation of critical aa-residue mutations and commercial trade contributes to the emergence and transmission of novel variants. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2832–e2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziosi, G.; Catelli, E.; Fanelli, A.; Lupini, C. Infectious bursal disease virus in free-living wild birds: A systematic review and meta-analysis of its sero-viroprevalence on a global scale. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2800–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xue, J.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, G. Phylogenetic analyses and pathogenicity of a variant infectious bursal disease virus strain isolated in China. Virus Res. 2020, 276, 197833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Hussain, A.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, H.; et al. Novel Variants of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Can Severely Damage the Bursa of Fabricius of Immunized Chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.; Rashid, H.B.; Thrusfield, M.; Welburn, S.; Bronsvoort, B.M. A Case-Control Study to Identify Risk Factors Associated with Avian Influenza Subtype H9N2 on Commercial Poultry Farms in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamed, N.; Mayahi, M.; Seifi, M.R.; Jafari, R.A. Effect of infectious bursal disease virus on pathogenicity of avian influenza virus subtype H9N2 in broiler chicks. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2013, 5, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, S.; Asasi, K.; Mohammadi, A. Natural co-infection caused by avian influenza H9 subtype and infectious bronchitis viruses in broiler chicken farms. Vet. Arh. 2010, 80, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sanousi, A.; Madbouly, H.M.; Saber, M.S.; El-Bagoury, C.F.; Abd El-Bar, N.A.; Batrawi, A.; Reda, I.M. Infectious bursal disease virus infection among Egyptian flocks. III. Antigenic characterization of IBDV by the antigen-capture ELISA (AC-ELISA) using monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Beni-Suef Vet. Res. 1994, 4, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Metwally, A.M.; Sabry, M.Z.; Samy, A.M.; Omar, M.M.; Yousif, A.A.; Reda, I.M. Direct detection of variant infectious bursal disease virus in vaccinated Egyptian broiler flocks using Antigen—Capture Elisa. Vet. Med. J. 2003, 51, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.H.; Aly, A.N.; Sultan, H.; Al-Safty, M. Transmissible viral pronventriculitis and stunting syndrome in broiler chicken in Egypt. 1. Isolation and characterized of variant infectious bursal disease virus. Vet. Med. J. 2003, 51, 445–462. [Google Scholar]
- Elkady, M.F.; Ali, A.A.; Abdel-Moneim, A.S. The role of infectious bursal disease virus in induction of proventriculitis in broiler chickens. In Proceedings of the 16th World Veterinary Poultry Association (WVPA) Congress, Marrakesh, Morocco, 8–12 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Samy, A.; Courtillon, C.; Briand, F.X.; Khalifa, M.; Selim, A.; Arafa, A.E.S.; Hegazy, A.; Eterradossi, N.; Soubies, S.M. Continuous circulation of an antigenically modified very virulent infectious bursal disease virus for fifteen years in Egypt. Infect. Gen. Evol. 2020, 78, 10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, H.G.; Haritou, M.; Failla, P.; Fahey, K.; Azad, A.A. Sequence analysis and expression of the host-protective immunogen VP2 of a variant strain of infectious bursal disease virus which can circumvent vaccination with standard type I strains. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escaffre, O.; Le Nouen, C.; Amelot, M.; Ambroggio, X.; Ogden, K.M.; Guionie, O.; Toquin, D.; Muller, H.; Islam, M.R.; Eterradossi, N. Both genome segments contribute to the pathogenicity of very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2767–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, T.; Tatar-Kis, T.; Felfoldi, B.; Jansson, D.S.; Homonnay, Z.; Banyai, K.; Palya, V. Occurrence and spread of a reassortant very virulent genotype of infectious bursal disease virus with altered VP2 amino acid profile and pathogenicity in some European countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Batrawi, A.M.; El-Kady, M.F. Studies on sever outbreaks of infectious bursal disease 3-determination of the critical age of susceptibility in maternally immune chicks. In Proceedings of the 2nd Scientific Conference of the Egyptian Veterinary Poultry Association, Cairo, Egypt, 12–14 March 1990; pp. 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bagoury, G.F.; Nada, A.F.; El-Habbaa, E.S.; Abu-Zaid, A.A. Molecular characterization of IBD virus isolated from Giza governorate, Egypt, 2014. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2015, 28, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shehata, A.A.; Sultan, H.; Halami, M.Y.; Talaat, S.; Vahlenkamp, T.W. Molecular characterization of very virulent infectious bursal disease virus strains circulating in Egypt from 2003 to 2014. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Fetouh, M.S.; Abdallah, F.M. Genetic characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses isolated from the vaccinated broiler chicken flocks in Egypt during 2015–2016. Sci. J. 2018, 21, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalefa, N.; El-Abasy, M.; Kasem, S.; Abu El-Naga, E. Molecular characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease virus (IBDV) isolated from commercial broiler chickens in Nile Delta, Egypt. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 22, 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Deng, Q.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Huang, T.; Wei, T.; Mo, M.; et al. The emerging naturally reassortant strain of IBDV (genotype A2dB3) having segment A from Chinese novel variant strain and segment B from HLJ 0504-like very virulent strain showed enhanced pathogenicity to three-yellow chickens. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e566–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Flock No. | Locality | Type of Chickens | Total No. | Age (Days) | Types and Age of IBD Vaccination Used | Mortality Rate % during 5 Days of Infection | Sample Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Valley | Commercial broiler | 40,000 | 20 | Recombinant (1 DO) and live IM (14 DO) | 0.2 | Bursa homogenate |
| 2 | New Valley | 40,000 | 13 | 0.3 | |||
| 3 | Alexandria | 12,000 | 18 | Live IM (7 DO) and IMP (14 DO) | 1 | ||
| 4 | Alexandria | 14,000 | 21 | 0.5 | |||
| 5 | Beheira | 10,000 | 17 | ICX (1 DO) and live IM (14 DO) | 1.2 | ||
| 6 | Beheira | 9000 | 20 | 1.5 | |||
| 7 | Alexandria | 15,000 | 18 | 0.4 | |||
| 8 | Beheira | 14,000 | 21 | Live IMP (14 DO) | 2 | ||
| 9 | Beheira | 10,000 | 26 | 2.1 | |||
| 10 | Alexandria | 7000 | 16 | Live IM (7 DO) and IMP (14 DO) | 1 | ||
| 11 | Alexandria | 20,000 | 18 | 2 | |||
| 12 | Beheira | 9000 | 21 | 1.4 | |||
| 13 | Beheira | 6000 | 22 | Recombinant (1 DO) and live IM (14 DO) | 1 | ||
| 14 | Beheira | 7000 | 19 | 0.9 | |||
| 15 | Alexandria | 10,000 | 25 | 0.6 | |||
| 16 | Beheira | Indigenous Balady Breed | 6000 | 49 | 0.3 | Bursa and spleen homogenate | |
| 17 | Beheira | 4500 | 35 | 2 | |||
| 18 | Beheira | 6700 | 19 | Live IM (7 DO) and IMP (14 DO) | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salaheldin, A.H.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Ellakany, H.F.; Mohamed, M.A.; Elbestawy, A.R. Isolation, Molecular, and Histopathological Patterns of a Novel Variant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Chicken Flocks in Egypt. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020098
Salaheldin AH, Abd El-Hamid HS, Ellakany HF, Mohamed MA, Elbestawy AR. Isolation, Molecular, and Histopathological Patterns of a Novel Variant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Chicken Flocks in Egypt. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(2):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020098
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalaheldin, Ahmed H., Hatem S. Abd El-Hamid, Hany F. Ellakany, Mostafa A. Mohamed, and Ahmed R. Elbestawy. 2024. "Isolation, Molecular, and Histopathological Patterns of a Novel Variant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Chicken Flocks in Egypt" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 2: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020098
APA StyleSalaheldin, A. H., Abd El-Hamid, H. S., Ellakany, H. F., Mohamed, M. A., & Elbestawy, A. R. (2024). Isolation, Molecular, and Histopathological Patterns of a Novel Variant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Chicken Flocks in Egypt. Veterinary Sciences, 11(2), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020098









