Protective Effects of Bacillus subtilis HH2 against Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Beagles
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Preparation of Probiotic Bacterial Strain
2.3. Animal and Experimental Design
2.4. Clinical Investigations
2.5. Indicator Detection of Intestinal Immunity and Intestinal Barrier
2.6. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.7. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
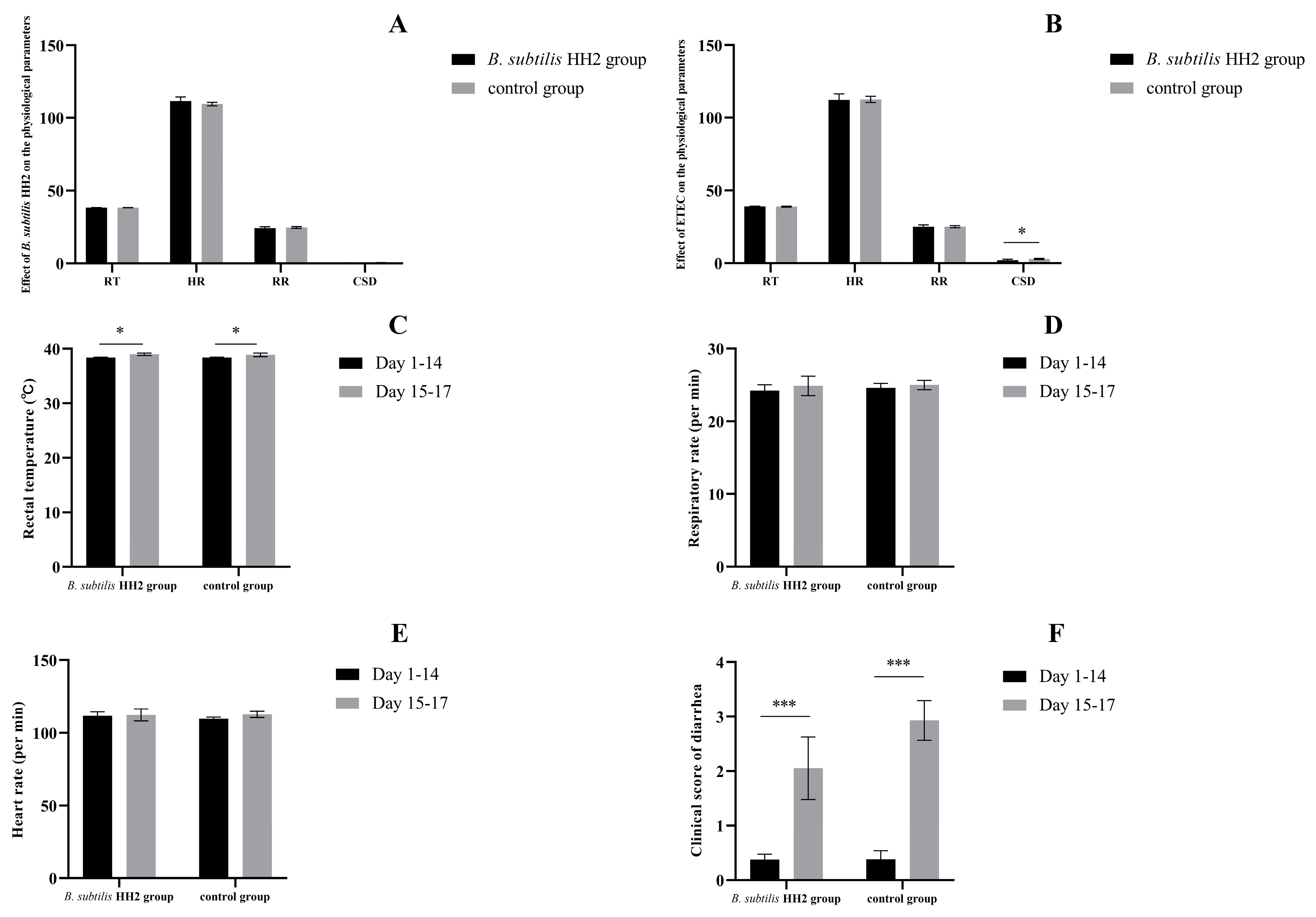
3.1. Effects of B. subtilis HH2 and ETEC on Beagles
3.2. Serum DAO Activity and D-LA Concentration
3.3. Serum Concentrations of IgG, IgA, and IgM
3.4. Assessment of Sequence Data
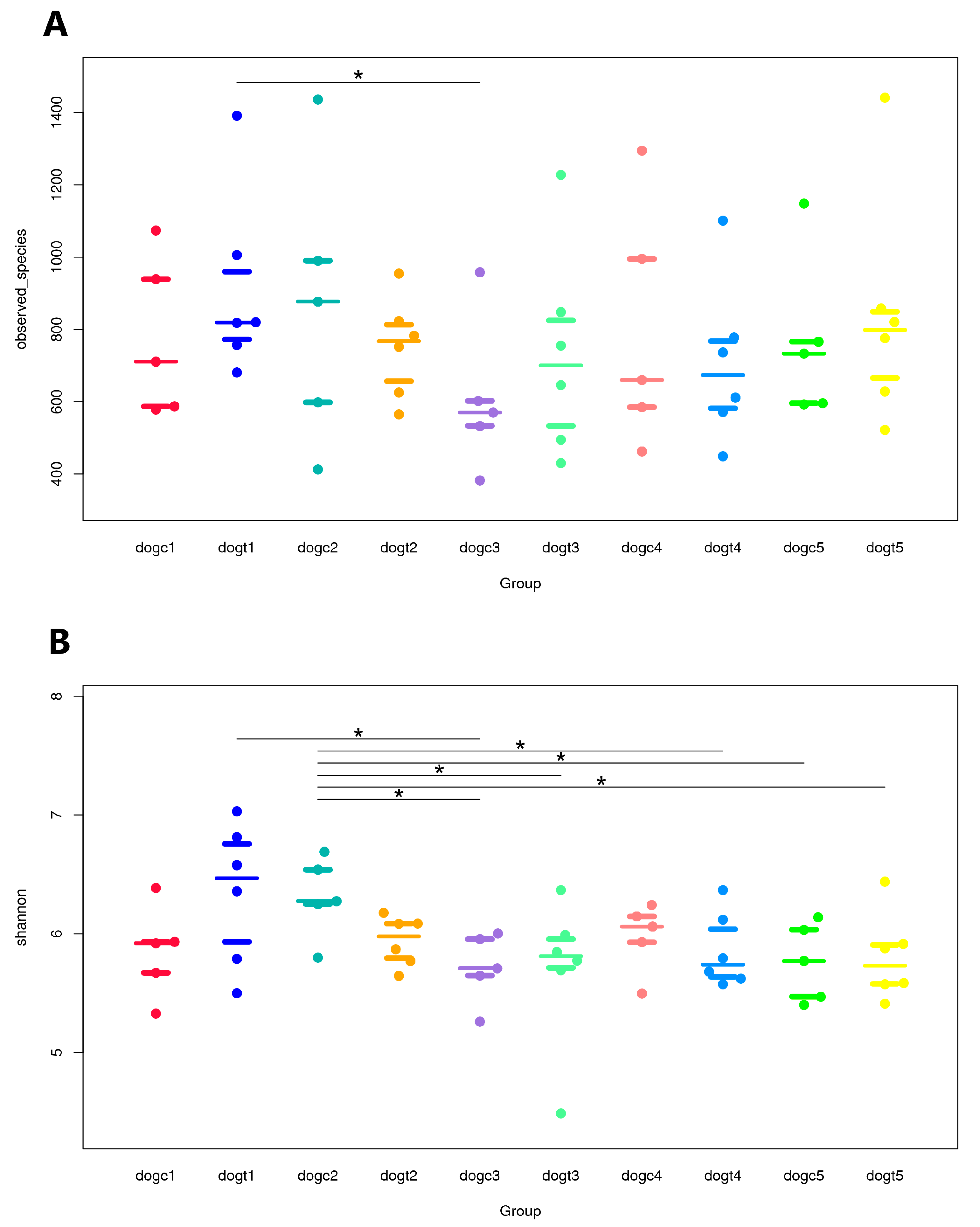
3.5. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analysis
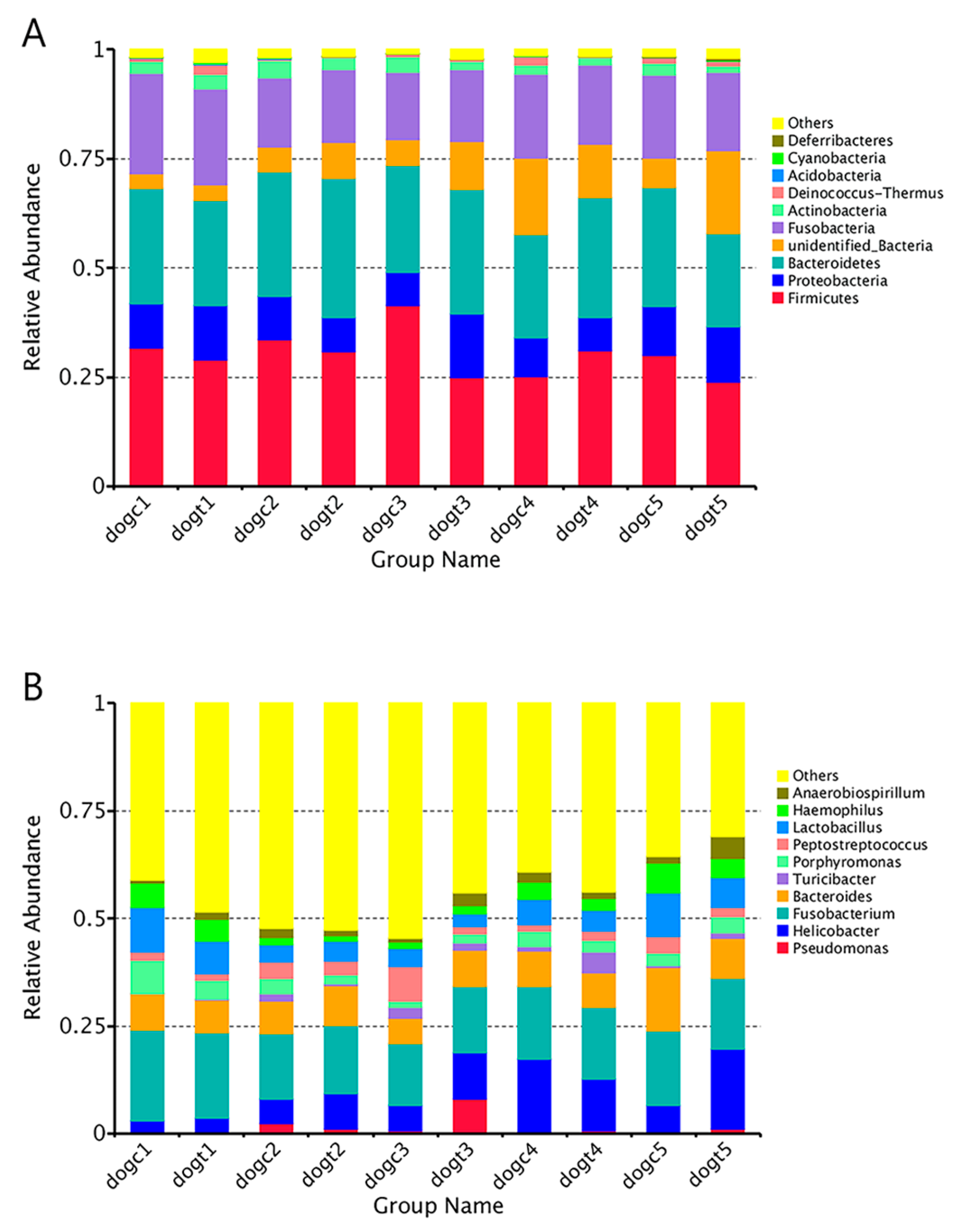
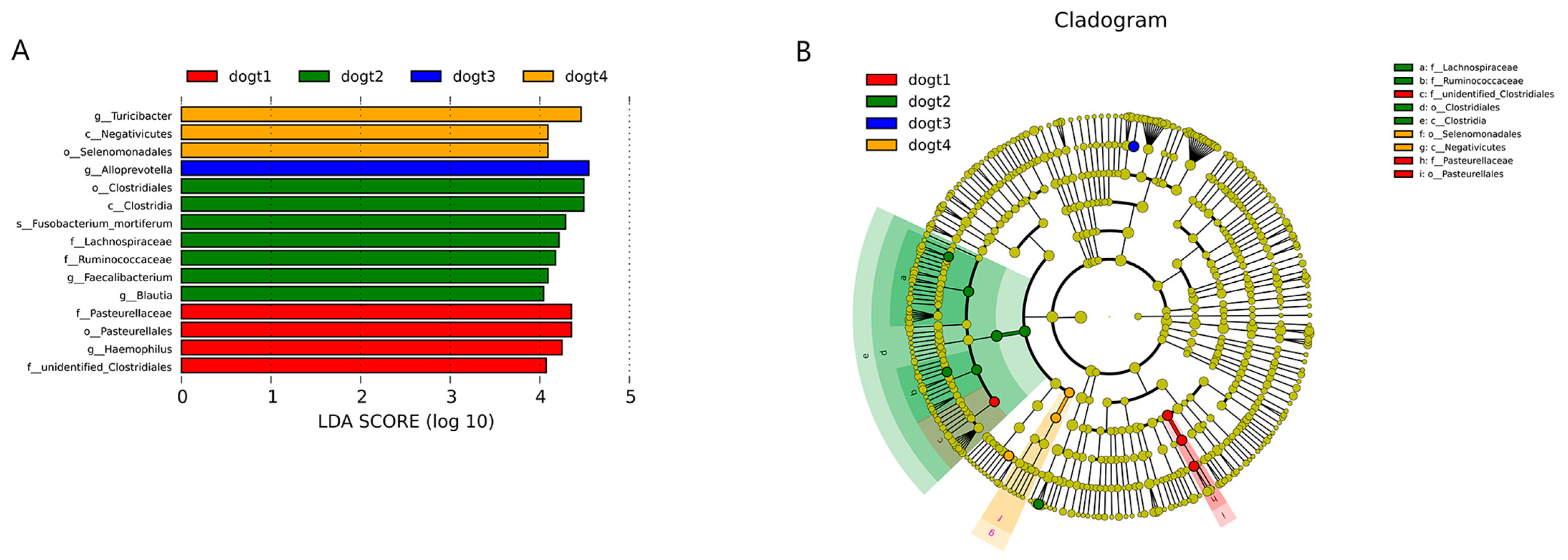
3.6. Community Composition Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagy, B.; Fekete, P.Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in veterinary medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2005, 295, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, P.; Cowieson, A.; Fru, F.; Steinert, R.; Kluenter, A.-M.; Verlhac Trichet, V. Gastrointestinal functionality in animal nutrition and health: New opportunities for sustainable animal production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, S.; Di, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Gut health benefit and application of postbiotics in animal production. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambo, M.T.; Chang, X.; Liu, D. The Recent Trend in the Use of Multistrain Probiotics in Livestock Production: An Overview. Animals 2021, 11, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Tu, W.J.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, M.L.; Fang, R.D.; Jiang, S. Bacillus subtilis inhibits intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating gut flora and related metabolites in laying hens. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 16, 100474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Lan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, G.; Yang, C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immunity, short chain fatty acid production, antioxidant capacity, and cecal microflora in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Niu, H.; Sun, M.; Miao, X.; Jin, X.; Xu, X.; Yanping, C.; Mei, H.; Wang, J.; Da, L.; et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis natto JLCC513 on gut microbiota and intestinal barrier function in obese rats. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 3634–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.H.B.; Nielsen, B.; Boll, E.J.; Skjøt-Rasmussen, L.; Wellejus, A.; Jørgensen, L.; Lauridsen, C.; Canibe, N. Functional in vitro screening of probiotic strains for inoculation of piglets as a prophylactic measure towards Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 180, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudan, S.; Flick, R.; Nong, L.; Li, J. Potential Probiotic Bacillus subtilis Isolated from a Novel Niche Exhibits Broad Range Antibacterial Activity and Causes Virulence and Metabolic Dysregulation in Enterotoxic E. coli. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.; Zohra, R.R.; Tarar, O.M.; Qader, S.A.U.; Aman, A. Screening, purification and characterization of thermostable, protease resistant Bacteriocin active against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.; Hegazi, E.; Nassef, E.; Habotta, O.A.; Gewaily, M.S. The optimized inclusion level of Bacillus subtilis fermented Azolla pinnata in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diets: Immunity, antioxidative status, intestinal digestive enzymes and histomorphometry, and disease resistance. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Effects of Bacillus subtilis UBT-MO2 on growth performance, relative immune organ weight, gas concentration in excreta, and intestinal microbial shedding in broiler chickens. Livest. Sci. 2013, 155, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudan, S.; Zhan, X.; Li, J. A Novel Probiotic Bacillus subtilis Strain Confers Cytoprotection to Host Pig Intestinal Epithelial Cells during Enterotoxic Escherichia coli Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0125721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhao, J.; Guo, T.; Kong, J. Probiotic Bacillus subtilis LF11 Protects Intestinal Epithelium against Salmonella Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 837886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z. Probiotic Bacillus subtilis CW14 reduces disruption of the epithelial barrier and toxicity of ochratoxin A to Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2019, 126, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liang, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Yang, L. Natural products from Bacillus subtilis with antimicrobial properties. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinno, C.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis or antibiotics modified intestinal microbiome of weaned pigs under enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1064328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; He, Y.; Xiong, X.; Ehrlich, A.; Li, X.; Raybould, H.; Atwill, E.R.; Maga, E.A.; Jørgensen, J.; Liu, Y. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis influenced intestinal health of weaned pigs experimentally infected with a pathogenic E. coli. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo Santano, N.; Juncker Boll, E.; Catrine Capern, L.; Cieplak, T.M.; Keleszade, E.; Letek, M.; Costabile, A. Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial and Mucus Induction Properties of Selected Bacillus Strains against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Li, P.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Q. Bacillus subtilis inhibition of enterotoxic Escherichia coli-induced activation of MAPK signaling pathways in Caco-2 cells. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Kim, K.; Kovanda, L.; Jinno, C.; Song, M.; Chase, J.; Li, X.; Tan, B.; Liu, Y. Bacillus subtilis: A potential growth promoter in weaned pigs in comparison to carbadox. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, Z.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Feng, F.; Lan, J.; et al. Cellulose-dependent expression and antibacterial characteristics of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis HH2 isolated from the giant panda. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Su, H.; Luo, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Transcriptional regulation and adaptation to a high-fiber environment in Bacillus subtilis HH2 isolated from feces of the giant panda. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Fu, H.; et al. Bacillus subtilis HH2 ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by modulating gut microbiota composition and improving intestinal barrier function in rabbit model. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 74, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, B.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Pan, K.; Jing, B.; et al. Assessment the role of some Bacillus strains in improvement rex rabbits resistance against ETEC challenge. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 165, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, R.B.; Johnson, J.; Pierce, N.F.; Keren, D.F.; Yardley, J.H. Challenge of dogs with live enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and effects of repeated challenges on fluid secretion in jejunal Thiry-Vella loops. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 134, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jergens, A.E.; Schreiner, C.A.; Frank, D.E.; Niyo, Y.; Ahrens, F.E.; Eckersall, P.D.; Benson, T.J.; Evans, R. A scoring index for disease activity in canine inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterer, S.; Strohmeyer, K.; Kruse, B.D.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Treatment of aseptic dogs with hemorrhagic gastroenteritis with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid: A prospective blinded study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Vidal, E.; Castillejos, L.; López-Colom, P.; Rivero Urgell, M.; Moreno Muñoz, J.A.; Martín-Orúe, S.M. Evaluation of the Probiotic Strain Bifidobacterium longum subsp. Infantis CECT 7210 Capacities to Improve Health Status and Fight Digestive Pathogens in a Piglet Model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, S.; Ishii, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Abe, S.; Ono, Y.; Sekimizu, K. Lactobacillus paraplantarum 11-1 Isolated from Rice Bran Pickles Activated Innate Immunity and Improved Survival in a Silkworm Bacterial Infection Model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, H.; Wang, B.; Sun, Q.; Fu, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, W. Probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC06 Induces Autophagy to Protect against Pathogens in Macrophages. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, W.; Hou, Q.; Kwok, L.Y.; Laga, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Oral Administration of Compound Probiotics Improved Canine Feed Intake, Weight Gain, Immunity and Intestinal Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, F.; Hou, Q.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Metagenomic analysis revealed beneficial effects of probiotics in improving the composition and function of the gut microbiota in dogs with diarrhoea. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Yu, B.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.; Yan, H.; He, J. Protective effect of sialyllactose on the intestinal epithelium in weaned pigs upon enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 11627–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yu, B.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.; Mao, X.; Luo, J.; Yan, H.; He, J. Agrobacterium sp. ZX09 β-Glucan Attenuates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Disruption of Intestinal Epithelium in Weaned Pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Ji, S.; Yu, G.; Jia, P.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on jejunal integrity, redox status, and microbial composition of intrauterine growth restriction suckling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.F.; Boris, S.; Barbés, C. Probiotic properties of human lactobacilli strains to be used in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; Galdeano, C.M.; Chaves, S.; Perdigón, G. Oral Administration of L. Casei CRL 431 Increases Immunity in Bronchus and Mammary Glands. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2005, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, E.M.; Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Carmuega, E.; Weill, R.; Bibas Bonet, M.E.; Perdigón, G. Probiotic fermented milk consumption modulates the allergic process induced by ovoalbumin in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumachi, K.; Aoki, R.; Ohmori, H.; Saeki, M.; Kawashima, T. Effect of fermented liquid diet prepared with Lactobacillus plantarum LQ80 on the immune response in weaning pigs. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2009, 3, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Li, C.L.; Wang, J.; Qi, G.H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, S.G. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus subtilis, as an Alternative to Antibiotics, on Growth Performance, Serum Immunity, and Intestinal Health in Broiler Chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 786878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Feng, G.; Ke, H. Role of Clostridium butyricum, Bacillus subtilis, and algae-sourced β-1,3 glucan on health in grass turtle. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 131, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.T. Effects of Bacillus subtilis natto on performance and immune function of preweaning calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5851–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-p.; Yang, L.; Tang, X.-S.; Cai, L.; Liu, G.; Kong, X.; Blachier, F.; Yin, Y. Dietary supplementation with high-dose Bacillus subtilis or Lactobacillus reuteri modulates cellular and humoral immunities and improves performance in weaned piglets. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2011, 9, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W. Probiotics modulate the gut microbiota composition and immune responses in patients with atopic dermatitis: A pilot study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2119–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, H.F.; Rasmussen, S.H.; Asiller, Ö.; Lied, G.A. Probiotics in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueiro, A.Y.; Raizel, R.; Bonvini, A.; Tirapegui, J.; Rogero, M.M. Probiotics for inflammatory bowel diseases: A promising adjuvant treatment. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, S.; Artzi, D.M.; Aabenhus, R. Probiotics for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Outpatients-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, M.; Paulson, J.N.; Chakraborty, S.; Astrovskaya, I.; Lindsay, B.R.; Li, S.; Bravo, H.C.; Harro, C.; Parkhill, J.; Walker, A.W.; et al. Individual-specific changes in the human gut microbiota after challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and subsequent ciprofloxacin treatment. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Feng, B.; Hu, Y.; Mu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H. Escherichia coli O(101)-induced diarrhea develops gut microbial dysbiosis in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tsai, T.; Wei, X.; Zuo, B.; Davis, E.; Rehberger, T.; Hernandez, S.; Jochems, E.J.M.; Maxwell, C.V.; Zhao, J. Effect of Lactylate and Bacillus subtilis on Growth Performance, Peripheral Blood Cell Profile, and Gut Microbiota of Nursery Pigs. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.; Phungviwatnikul, T.; de Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S. Nutrient digestibility and fecal characteristics, microbiota, and metabolites in dogs fed human-grade foods. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.D.; Young, W.; Maclean, P.H.; Cookson, A.L.; Bermingham, E.N. Metagenomic insights into the roles of Proteobacteria in the gastrointestinal microbiomes of healthy dogs and cats. MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 7, e00677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zou, C.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Preventive Effect of Depolymerized Sulfated Galactans from Eucheuma serra on Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Caused Diarrhea via Modulating Intestinal Flora in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.T.; Xin, Z.; Hua, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, R.X.; Yang, Y.L.; Xie, R.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, J.K. Comparative assessment of gut microbial composition and function in patients with Graves’ disease and Graves’ orbitopathy. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.A.; Burkholder, K.M. Application of prebiotics and probiotics in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Luo, R.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Shen, L.; Cao, S.; et al. Protective Effects of Bacillus subtilis HH2 against Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Beagles. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070432
Yang J, Zhang X, Zhou Z, Li C, Luo R, Liu H, Fu H, Zhong Z, Shen L, Cao S, et al. Protective Effects of Bacillus subtilis HH2 against Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Beagles. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(7):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070432
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jinpeng, Xinyue Zhang, Ziyao Zhou, Caiwu Li, Run Luo, Haifeng Liu, Hualin Fu, Zhijun Zhong, Liuhong Shen, Suizhong Cao, and et al. 2023. "Protective Effects of Bacillus subtilis HH2 against Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Beagles" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 7: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070432
APA StyleYang, J., Zhang, X., Zhou, Z., Li, C., Luo, R., Liu, H., Fu, H., Zhong, Z., Shen, L., Cao, S., Luo, Y., Li, D., & Peng, G. (2023). Protective Effects of Bacillus subtilis HH2 against Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Beagles. Veterinary Sciences, 10(7), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070432






