Monitoring of Paenibacillus larvae in Lower Austria through DNA-Based Detection without De-Sporulation: 2018 to 2022
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Beekeepers and Sampling under the Voluntary Monitoring Program
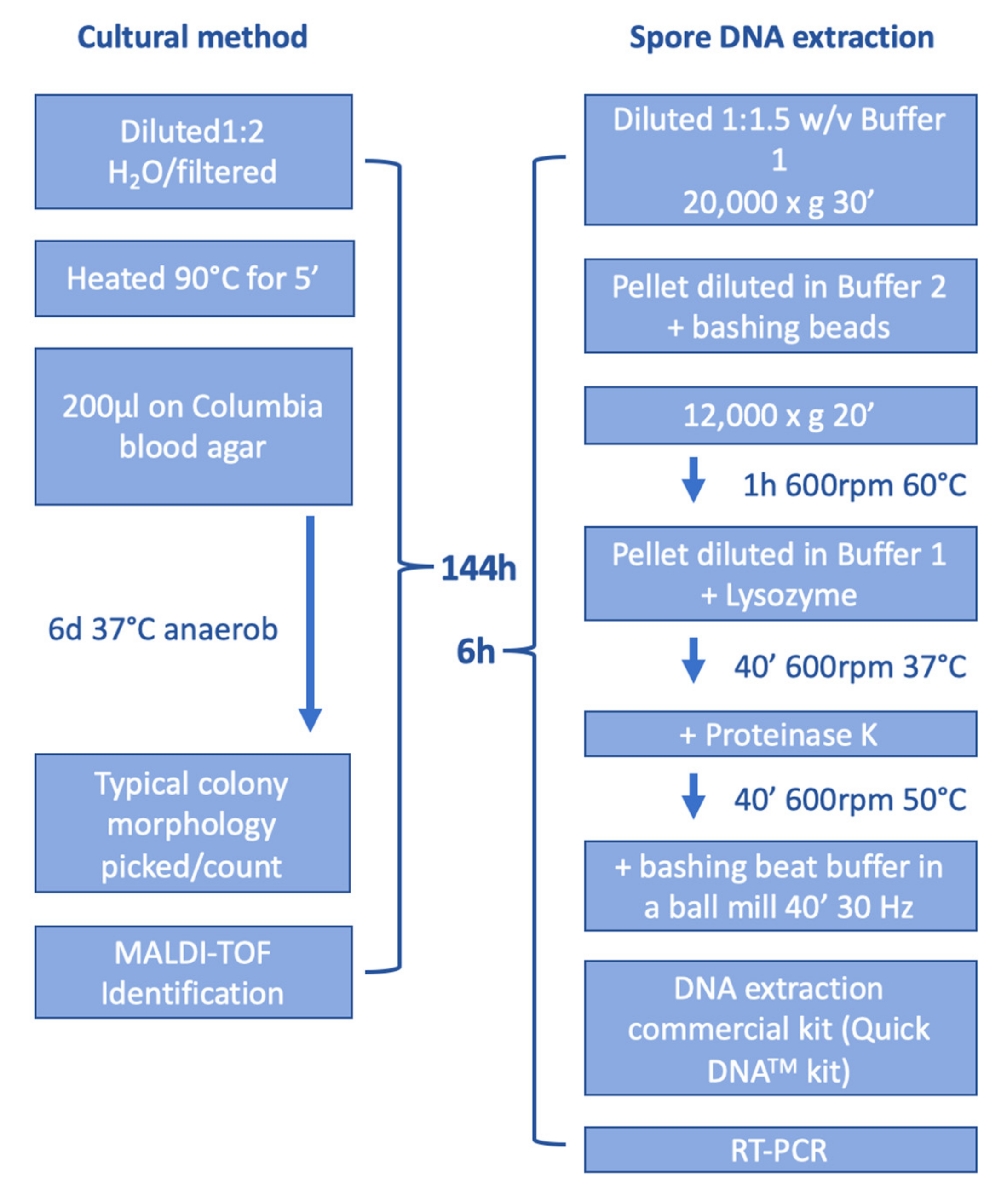
2.2. Cultural Detection of P. larvae
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Real-Time-PCR (RT-PCR)
2.5. Classification of Results
2.6. Statistical Calculation of a CT-Value Using RT-PCR and Colony Counts and Sensitivity and Specificity
2.7. Prevalence of P. larvae
3. Results
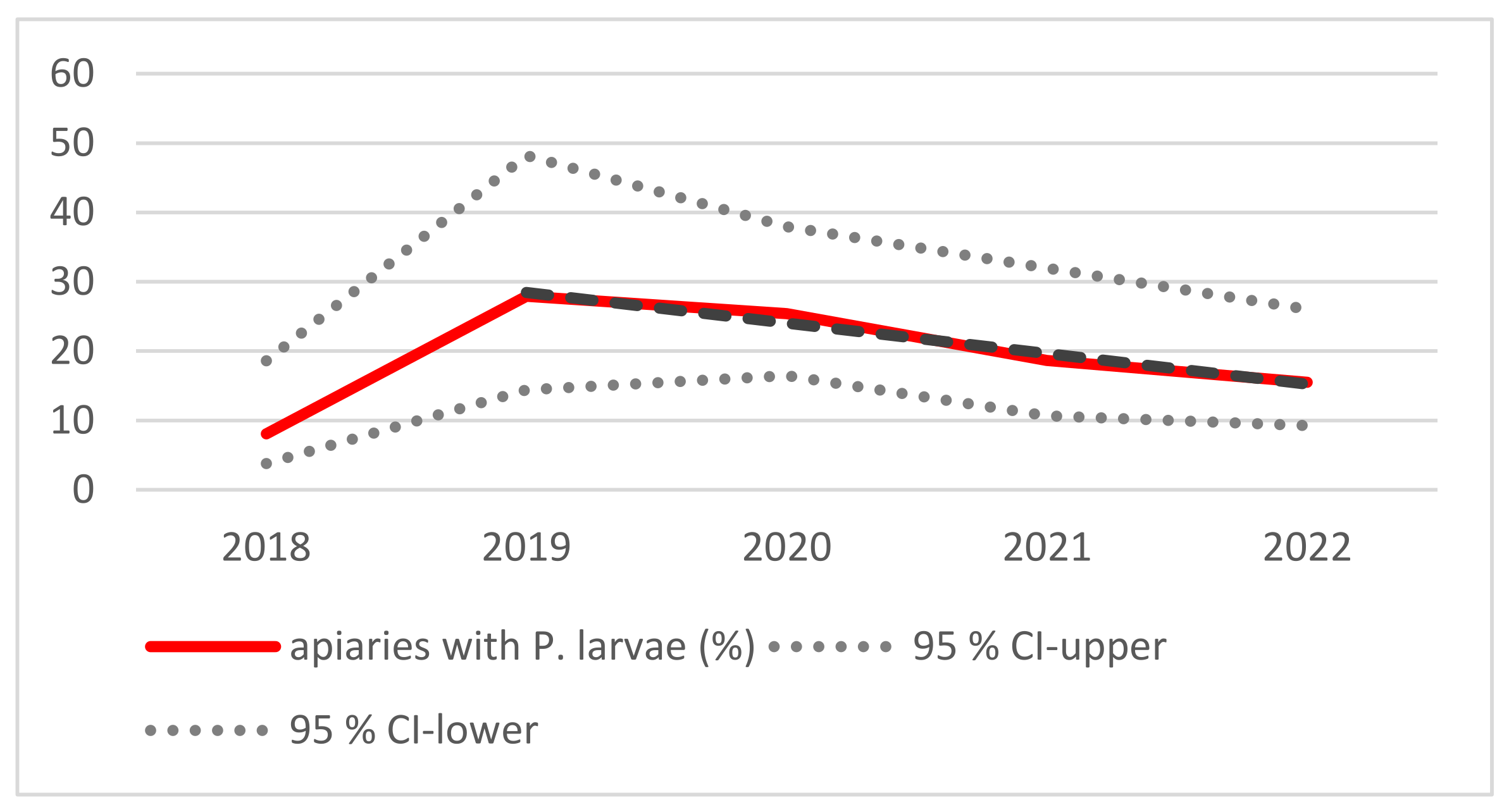
3.1. Monitoring
3.2. Sensitivity and Specificity of the RT-PCR Detection Method
3.3. Detection Limit with and without De-Coating
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebeling, J.; Knispel, H.; Hertlein, G.; Fünfhaus, A.; Genersch, E. Biology of Paenibacillus larvae, a deadly pathogen of honey bee larvae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 7387–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppinga, L.; Fünfhaus, A.; Aupperle, H.; Genersch, E. American foulbrood. In Diagnostic Colour Atlas of Bee Pathology, 1st ed.; Aupperle, H., Genersch, E., Eds.; Laboklin: Bad Kissingen, Germany, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Riessberger-Gallé, U.; von der Ohe, W.; Crailsheim, K. Adult honeybee’s resistance against Paenibacillus larvae larvae, the causative agent of the American foulbrood. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2001, 77, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, R.M.; Perry, J.H.; Houten, A.T. The effect of drifting honey bees on the spread of American foulbrood infections. J. Apic. Res. 1994, 33, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornitzky, M.A.Z. The spread of Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae in an apiary. J. Apic. Res. 1998, 37, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, A.; Korpela, S.; Fries, I. The distribution of Paenibacillus larvae spores in adult bees and honey and larval mortality, following the addition of American foulbrood diseased brood or spore-contaminated honey in honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 99, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseman, L. How long can spores of American foulbrood live? Am. Bee J. 1961, 101, 298–299. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, I.; Camazine, S. Implications of horizontal and vertical pathogen transmission for honey bee epidemiology. Apidologie 2001, 32, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillard, M.; Charriere, J.D.; Belloy, L. Distribution of Paenibacillus larvae spores inside honey bee colonies and its relevance for diagnosis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 99, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, D.C.; Alippi, A.M.; Brown, M.; Evans, J.D.; Feldlaufer, M.; Gregorc, A.; Hornitzky, M.; Pernal, S.F.; Schuch, D.M.; Titera, D.; et al. Diagnosis of American foulbrood in honey bees: A synthesis and proposed analytical protocols. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, B.; Low, M.; Forsgren, E. An integrated management strategy to prevent outbreaks and eliminate infection pressure of American foulbrood disease in a commercial beekeeping operation. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 167, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von der Ohe, W.; Dustmann, J.H. Efficient prophylactic measures against American Foulbrood by bacteriological analysis for spore contamination. Am. Bee J. 1997, 137, 603–606. [Google Scholar]
- Kušar, D.; Papić, B.; Zajc, U.; Zdovc, I.; Golob, M.; Žvokelj, L.; Knific, T.; Avberšek, J.; Ocepek, M.; Pislak Ocepek, M. Novel TaqMan PCR Assay for the Quantification of Paenibacillus larvae Spores in Bee-Related Samples. Insects 2021, 12, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beims, H.; Janke, M.; von der Ohe, W.; Steinert, M. Rapid identification and genotyping of the honeybee pathogen Paenibacillus larvae by combining culturing and multiplex quantitative PCR. Open Vet. J. 2020, 10, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, B.; Antúnez, K.; Piccini, C.; Zumino, P. DNA extraction and PCR detection of Paenibacillus larvae spores from naturally contaminated honey and bees using spore-decoating and freeze-thawing techniques. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.S. The Origins of Logistic Regression, Tinbergen Institute Discussion Paper. 2002. TI 2002-119/4. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.360300 (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Sachs, L. Angewandte Statistik, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 347–350, 433, 618–621. [Google Scholar]
- Zabrodski, M.W.; DeBruyne, J.E.; Wilson, G.; Moshynskyy, I.; Sharafi, M.; Wood, S.C.; Kozii, I.V.; Thebeau, J.; Klein, C.D.; Medici de Mattos, I.; et al. Comparison of individual hive and apiary-level sample types for spores of Paenibacillus larvae in Saskatchewan honey bee operations. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinkraus, K.H.; Morse, R.A. American foulbrood incidence in some US and Canadian honeys. Apidiologie 1992, 23, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.; Reinecke, A.; Sibum, N.; Fünfhaus, A.; Aumeier, P.; Otten, C.; Genersch, E. A comparison of different matrices for the laboratory diagnosis of the epizootic American foulbrood of honey bees. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, S.; Galletti, G.; Carpana, E.; Palminteri, S.; Bosi, F.; Loglio, G.; Carra, E. Powdered Sugar Examination as a Tool for the Assessment of Paenibacillus larvae Infection Levels in Honey Bee Colonies. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 853707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsgren, E.; Laugen, A.T. Prognostic value of using bee and hive debris samples for the detection of American foulbrood disease in honey bee colonies. Apidologie 2014, 45, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohorecka, K.; Skubida, M.; Bober, A.; Zdańska, D. Screening of Paenibacillus larvae spores in apiaries from Eastern Poland. Nationwide survey. Part, I. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribani, A.; Utzeri, V.J.; Taurisano, V.; Fontanesi, L. Honey as a Source of Environmental DNA for the Detection and Monitoring of Honey Bee Pathogens and Parasites. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setlow, P. Observations on research with spores of Bacillales and Clostridiales species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusenova, N.; Parvanova, P.; Stanilova, S. Detection of Paenibacillus larvae spores in honey by conventional PCR and its potential for American Foulbrood control. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2019, 22, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Amadoro, C.; Ruberto, A.; Ricchiuti, L. Evaluation of Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Paenibacillus larvae Targeted Assays and Definition of Optimal Conditions for Its Detection/Quantification in Honey and Hive Debris. Insects 2018, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, S.; Carpana, E.; Bergomi, P.; Galetti, G. Detection and quantification of Paenibacillus larvae spores in samples of bees, honey and hive debris as a tool for American foulbrood risk assessment. Bull. Insectol. 2018, 71, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Crudele, S.; Ricchiuti, L.; Ruberto, A.; Rossi, F. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) vs culture-dependent detection to assess honey contamination by Paenibacillus larvae. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling time | 21.03–12.04 * | 17.04–14.05 | 31.03–22.04 | 11.03–15.04 | 22.02–06.04 |
| Samples | 155 | 111 | 139 | 155 | 206 |
| Beekeepers | 62 | 43 | 63 | 59 | 71 |
| CT-Value Range | Number of Samples | Culture Positive % |
|---|---|---|
| (23.0–31.2) | 9 | 100 |
| (31.2–33.9) | 10 | 100 |
| (33.9–35.9) | 8 | 62.5 |
| (35.9–37.9) | 7 | 28.6 |
| (37.9–38.6) | 7 | 14.3 |
| (38.6–43.2) | 8 | 25.0 |
| (45) | 31 | 0.0 |
| Year | Number of Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No Spores | Low Spore Content | High Spore Content | |
| 2018 | 143 | 4 | 8 |
| 2019 | 98 | 13 | 0 |
| 2020 | 116 | 20 | 3 |
| 2021 | 146 | 18 | 1 |
| 2022 | 206 | 12 | 5 |
| CT-Value | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Value | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Estimated Value | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |
| 35 | 0.793 | 0.655 | 0.931 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 36 | 0.828 | 0.690 | 0.966 | 0.941 | 0.863 | 1.000 |
| 37 | 0.862 | 0.724 | 0.966 | 0.902 | 0.823 | 0.980 |
| 38 | 0.897 | 0.759 | 1.000 | 0.824 | 0.706 | 0.922 |
| 39 | 0.931 | 0.828 | 1.000 | 0.725 | 0.588 | 0.843 |
| Sample | Colony Count | CT-Value Using De-Coating | CT-Value without De-Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3795/1 | 10 | 31.2 | 29.8 |
| 3795/2 | 2 | 33.9 | 34.2 |
| 4/22 | 0 | 35.3 | 35.3 |
| 32/22 | 53 | 26.3 | 26.5 |
| 57/22 | 0 | 37.9 | 39.2 |
| 58/22 | 2 | 34.0 | 33.0 |
| 60/22 | 14 | 30.6 | 32.3 |
| 185/22 | 1 | 33.9 | 32.8 |
| 3796/2 | 2 | 33.8 | 32.1 |
| RSK-16-07-21 | 26 | 31.0 | 40.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilhelm, E.; Korschineck, I.; Sigmund, M.; Paulsen, P.; Hilbert, F.; Rossmanith, W. Monitoring of Paenibacillus larvae in Lower Austria through DNA-Based Detection without De-Sporulation: 2018 to 2022. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030213
Wilhelm E, Korschineck I, Sigmund M, Paulsen P, Hilbert F, Rossmanith W. Monitoring of Paenibacillus larvae in Lower Austria through DNA-Based Detection without De-Sporulation: 2018 to 2022. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(3):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030213
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilhelm, Elfriede, Irina Korschineck, Michael Sigmund, Peter Paulsen, Friederike Hilbert, and Wigbert Rossmanith. 2023. "Monitoring of Paenibacillus larvae in Lower Austria through DNA-Based Detection without De-Sporulation: 2018 to 2022" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 3: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030213
APA StyleWilhelm, E., Korschineck, I., Sigmund, M., Paulsen, P., Hilbert, F., & Rossmanith, W. (2023). Monitoring of Paenibacillus larvae in Lower Austria through DNA-Based Detection without De-Sporulation: 2018 to 2022. Veterinary Sciences, 10(3), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030213






