Synbiotic-IgY Therapy Modulates the Mucosal Microbiome and Inflammatory Indices in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Animals
2.3. Synbiotic/IgY Supplement
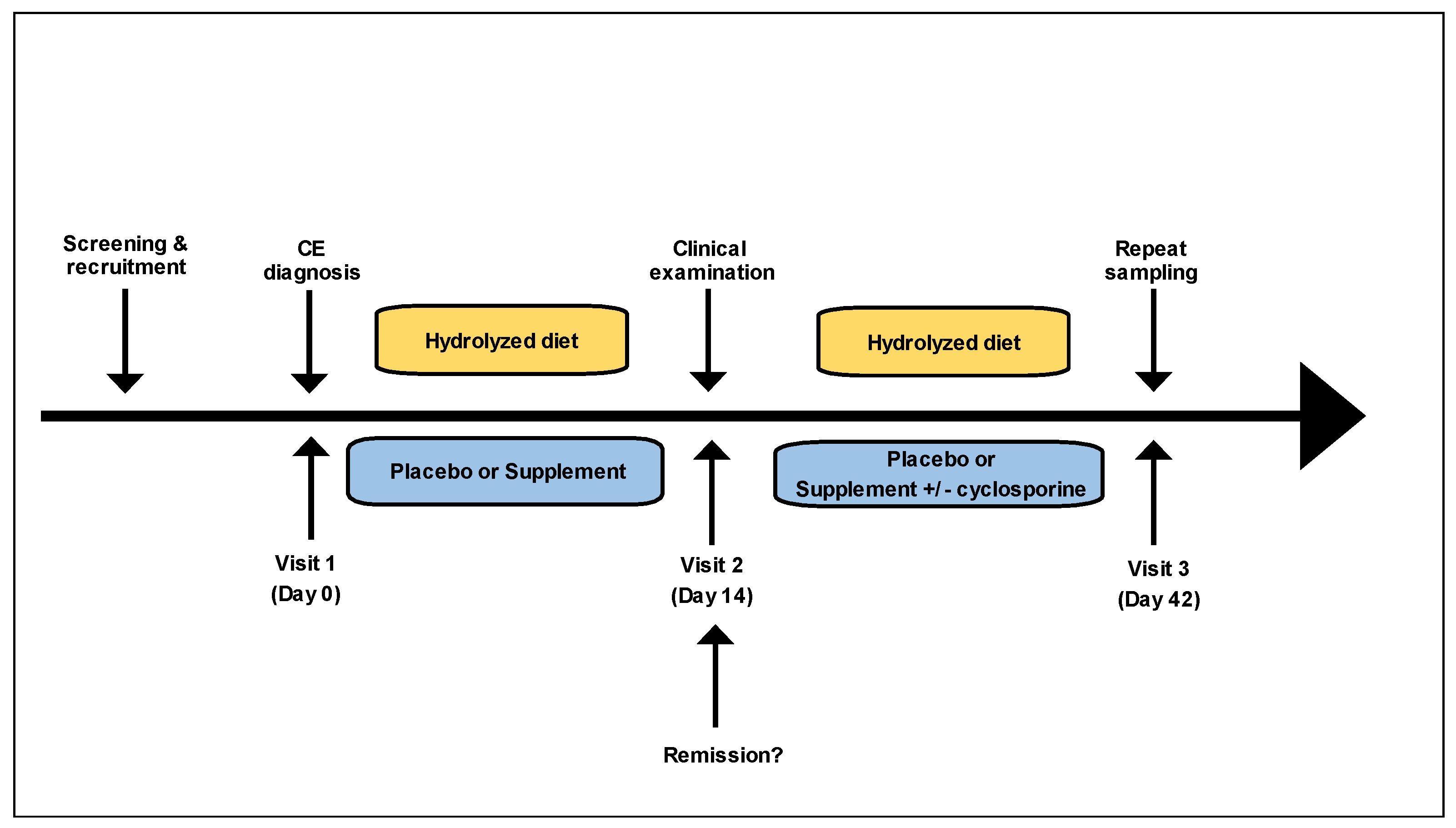
2.4. Study Design
2.5. Disease Activity Indices
2.6. Mucosal Microbiota
2.7. Biomarkers of Inflammation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
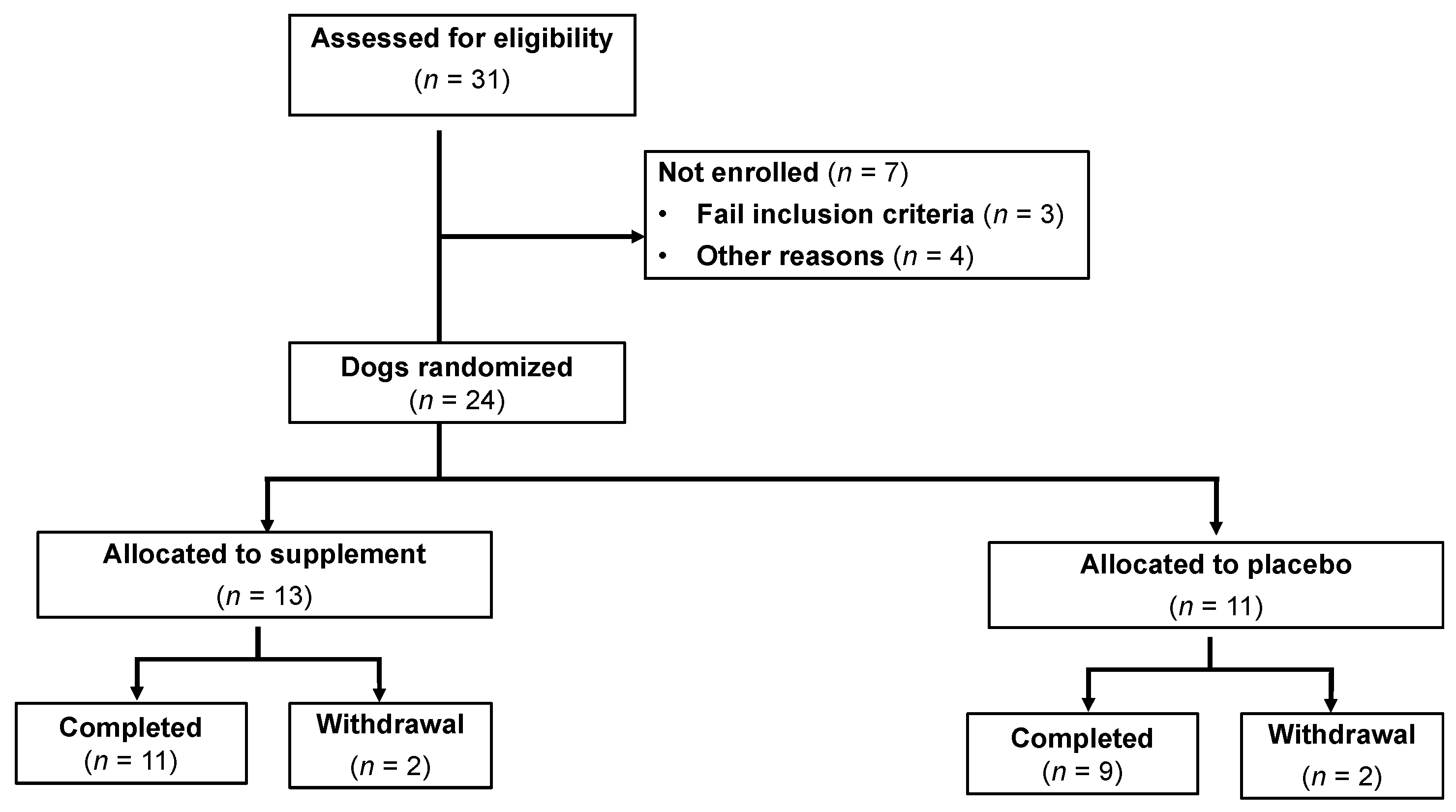
3.1. Animals—Baseline Characteristics
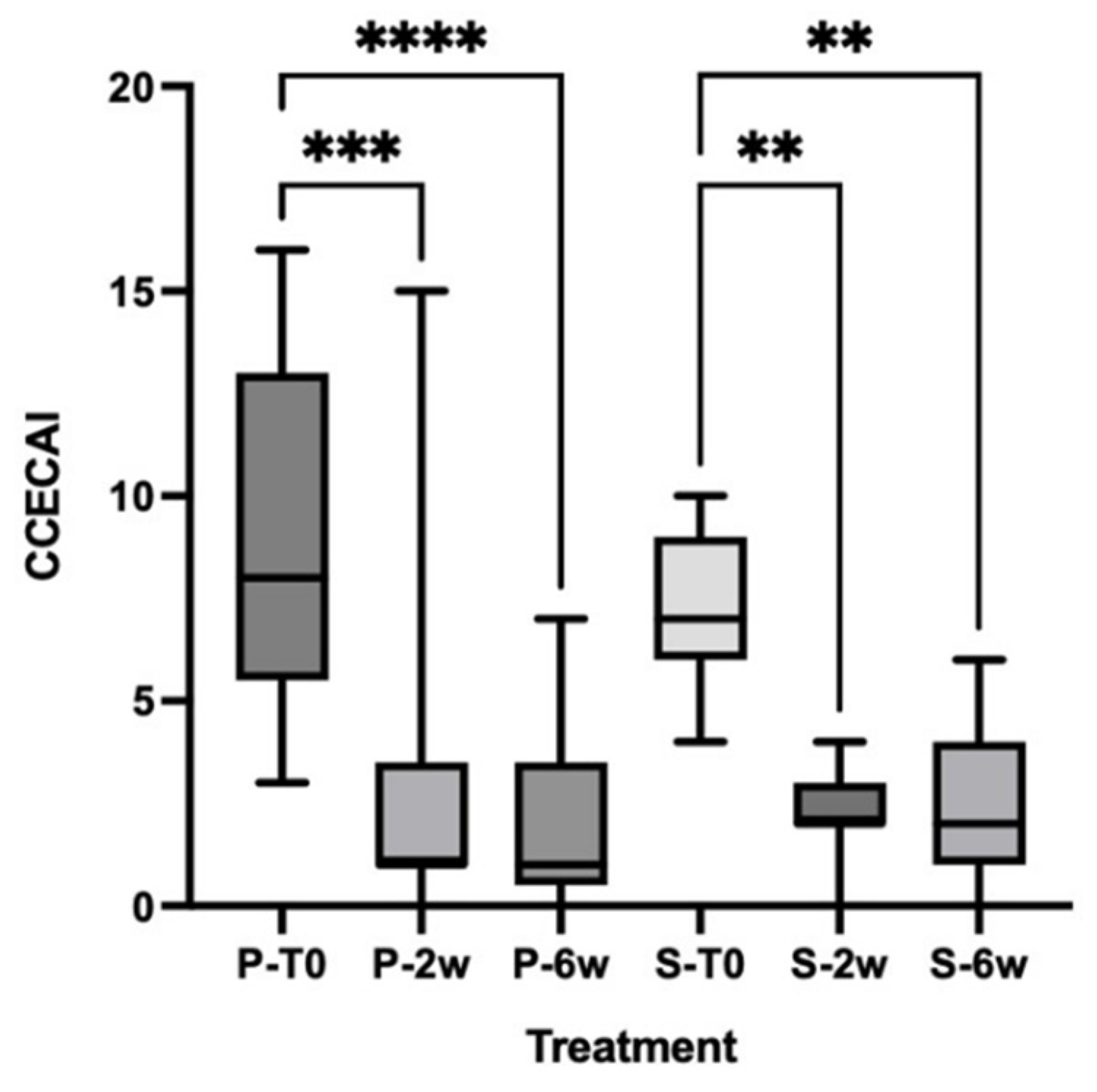
3.2. Clinical Scores
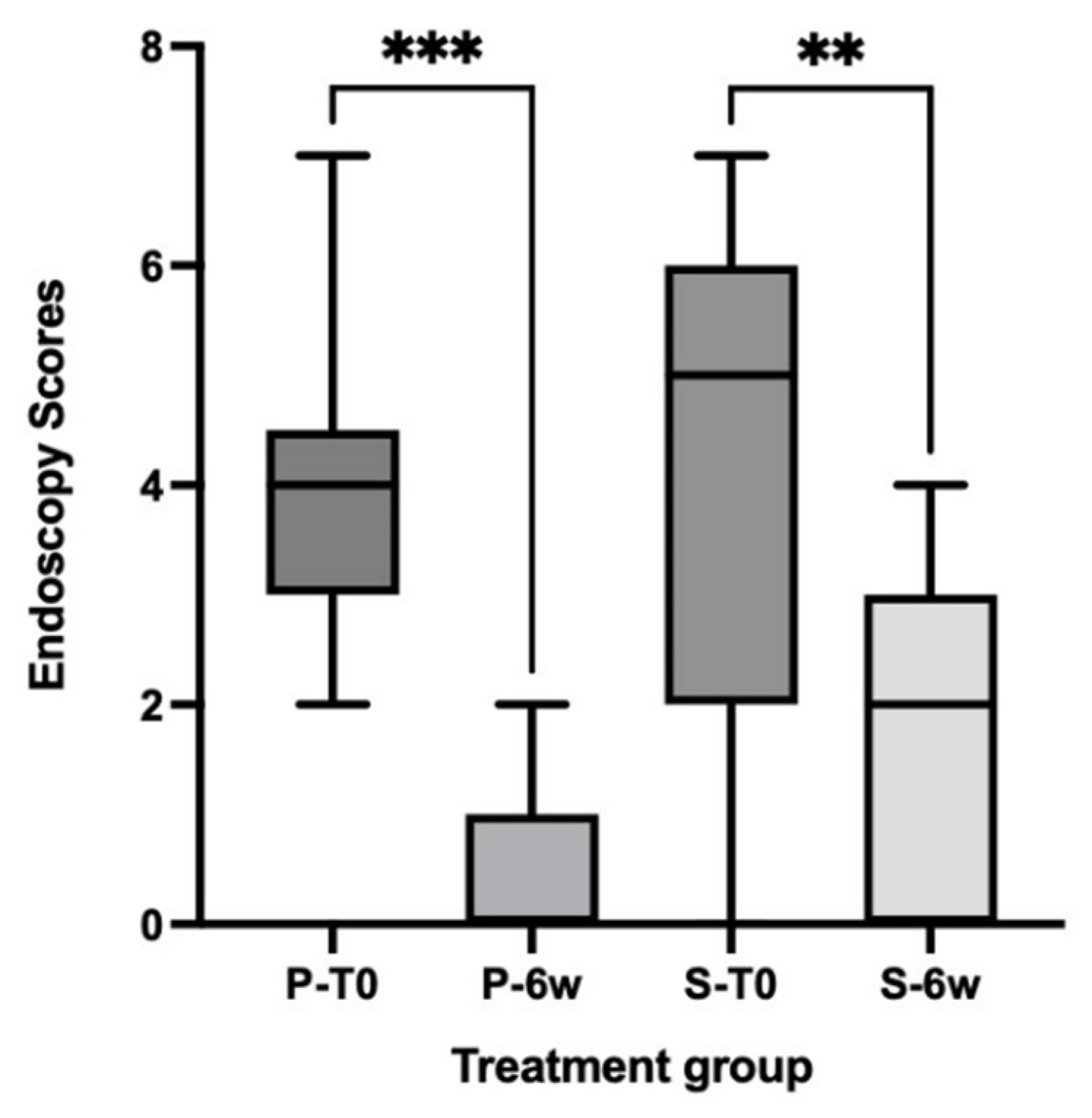
3.3. Simple Endoscopic Score
3.4. Histologic Findings
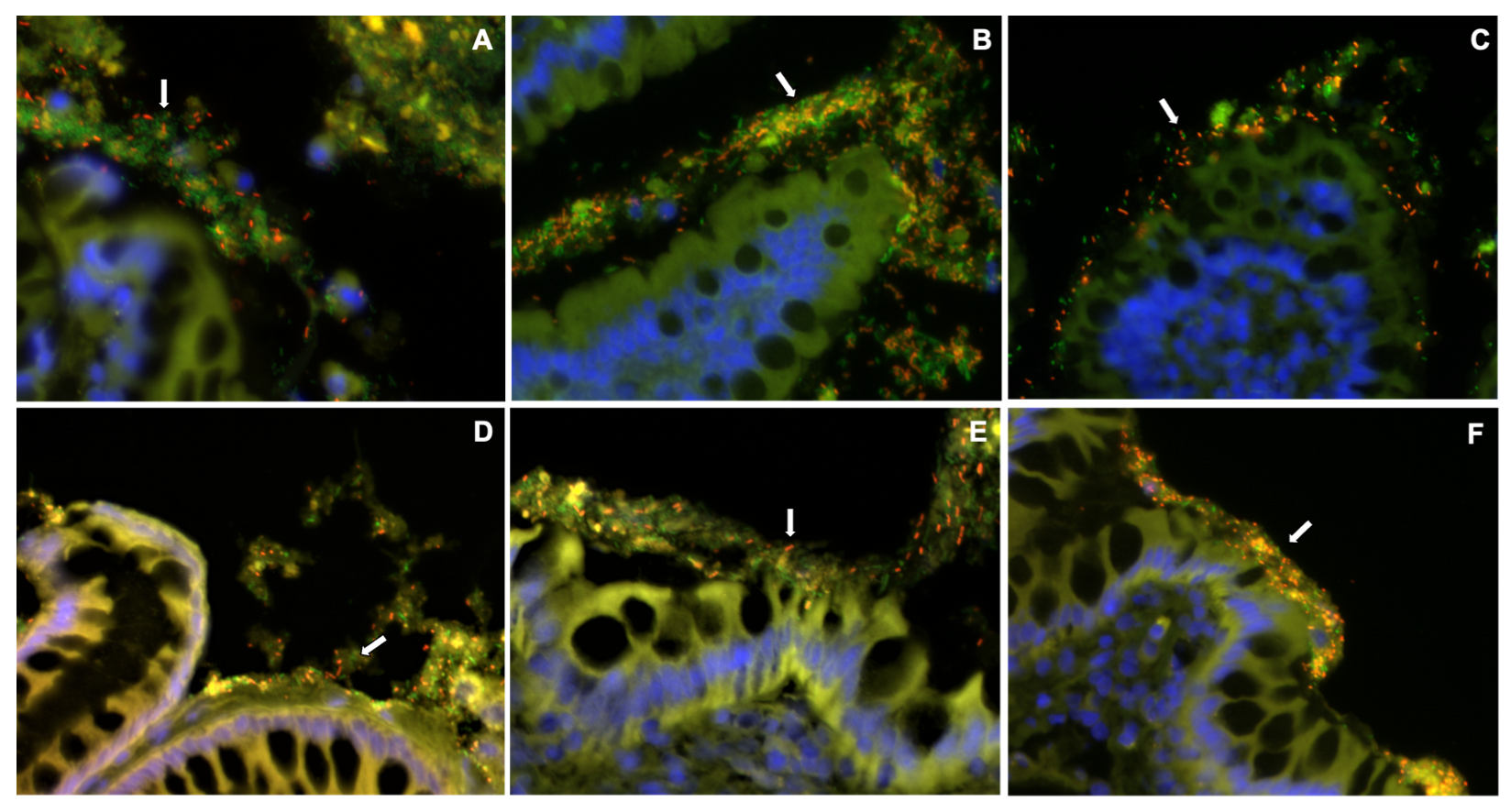
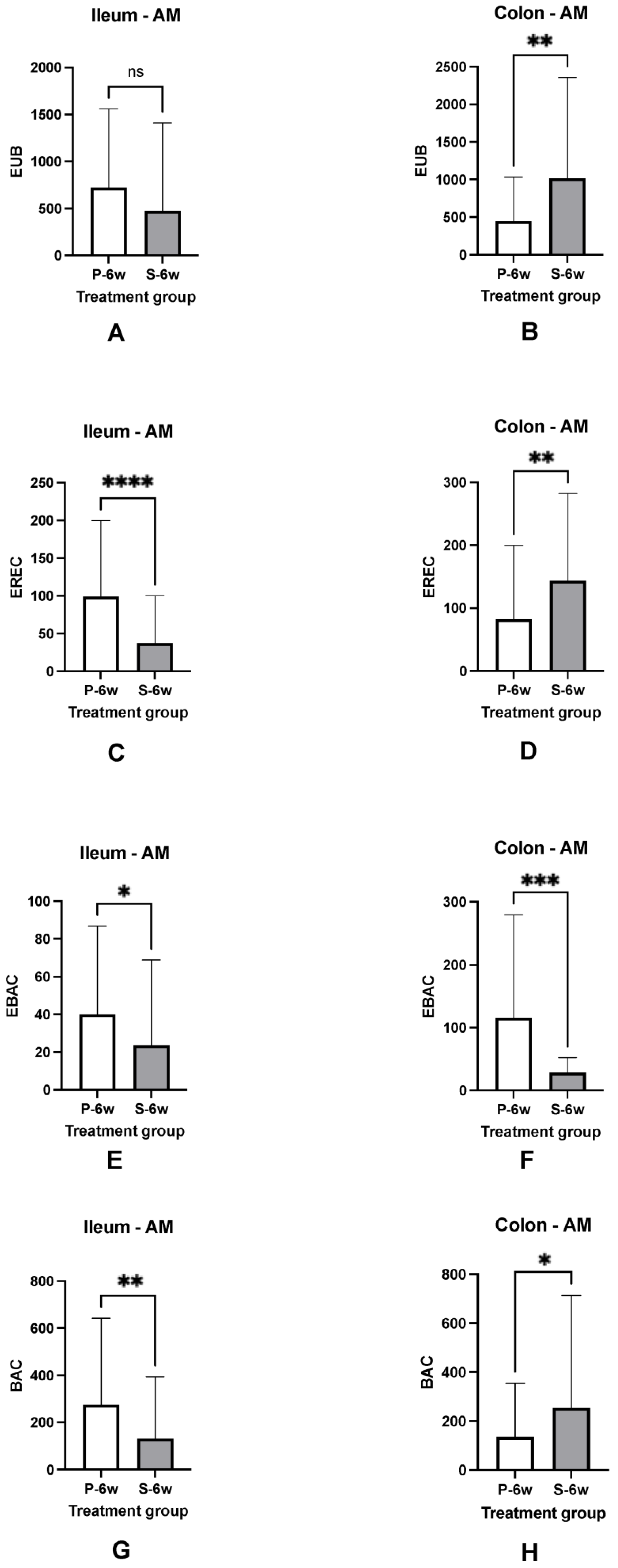
3.5. Mucosal Microbiota
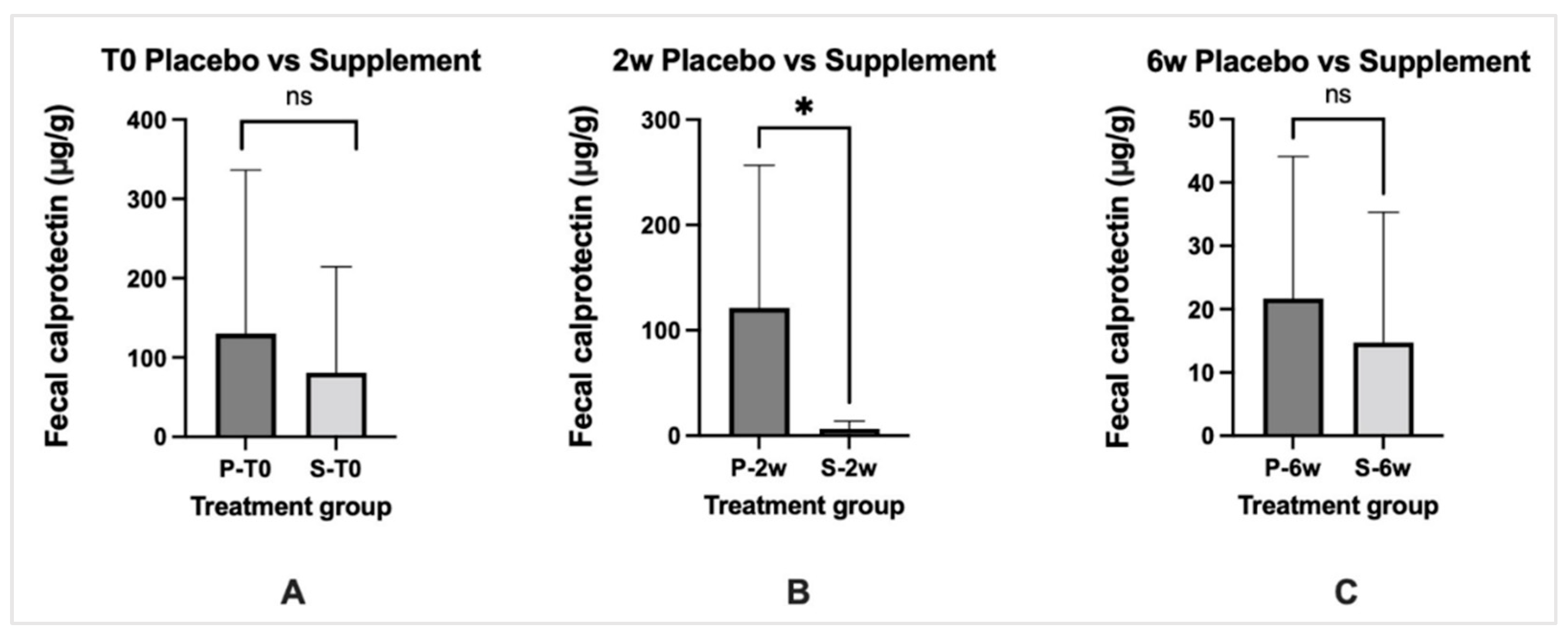
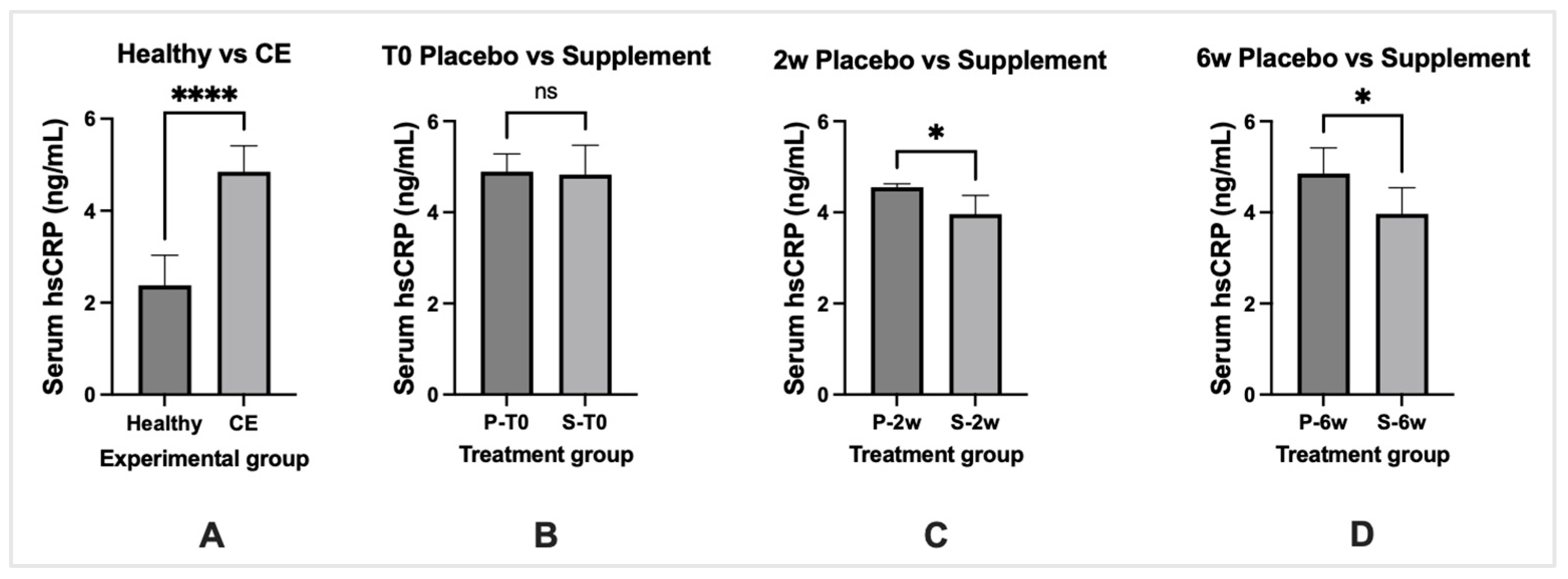
3.6. Biomarkers of Inflammation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jergens, A.E.; Heilmann, R.M. Canine chronic enteropathy—Current state-of-the-art and emerging concepts. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 923013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenspach, K. Clinical immunology and immunopathology of the canine and feline intestine. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathrani, A.; House, A.; Catchpole, B.; Murphy, A.; German, A.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. Polymorphisms in the Tlr4 and Tlr5 Gene Are Significantly Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in German Shepherd Dogs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.W.; Jergens, A.E. Pitfalls and progress in the diagnosis and management of canine inflammatory bowel disease. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, K.; Wieland, B.; Grone, A.; Gaschen, F. Chronic enteropathies in dogs: Evaluation of risk factors for negative outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandigers, P.J.; Biourge, V.; van den Ingh, T.S.; Ankringa, N.; German, A.J. A randomized, open-label, positively-controlled field trial of a hydrolyzed protein diet in dogs with chronic small bowel enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandrieux, J.R. Inflammatory bowel disease versus chronic enteropathy in dogs: Are they one and the same? J. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 57, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, F.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Galiazzo, G.; Vecchiato, C.G.; Pinna, C.; Biagi, G.; Pietra, M. Effect of an extruded animal protein-free diet on fecal microbiota of dogs with food-responsive enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, M.; Steiner, J.M.; Fosgate, G.T.; Zentek, J.; Hartmann, S.; Kohn, B. Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs-Retrospective Study in 136 Cases. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandrieux, J.R.S.; Mansfield, C.S. Chronic Enteropathy In Canines: Prevalence, Impact And Management Strategies. Vet. Med. 2019, 10, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Schmitz, S.S.; Allenspach, K.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Furlanello, T.; Gavazza, A.; Marchegiani, A.; Unterer, S.; et al. Proposal for rational antibacterial use in the diagnosis and treatment of dogs with chronic diarrhoea. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 61, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudinsky, A.J.; Parker, V.J.; Winston, J.; Cooper, E.; Mathie, T.; Howard, J.P.; Bremer, C.A.; Yaxley, P.; Marsh, A.; Laxalde, J.; et al. Randomized controlled trial demonstrates nutritional management is superior to metronidazole for treatment of acute colitis in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 260 (Suppl. S3), S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Guard, B.C.; Blake, A.B.; Ackermann, M.; Webb, C.; Hill, S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Long-Term Recovery of the Fecal Microbiome and Metabolome of Dogs with Steroid-Responsive Enteropathy. Animals 2021, 11, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiri, A.; Owlia, P.; Rasooli, I.; Salimian, J.; Derakhshanifar, E.; Aghajani, Z.; Abdollahi, S.; Khalili, S.; Talei, D.; Eslam, E.D. Specific egg yolk immunoglobulin as a promising non-antibiotic biotherapeutic product against Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.S.; Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Reimer, R.A.; Reid, G.; Verbeke, K.; Scott, K.P.; Holscher, H.D.; Azad, M.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerian Córdoba Park Hotel. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. Prevention 2001, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, S.S. Value of Probiotics in Canine and Feline Gastroenterology. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 171–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, R.B.; Wu, G.D. Roles for Intestinal Bacteria, Viruses, and Fungi in Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Therapeutic Approaches. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 327–339.e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Duysburgh, C.; Rakebrandt, M.; Marzorati, M. Dried yeast cell walls high in beta-glucan and mannan-oligosaccharides positively affect microbial composition and activity in the canine gastrointestinal tract in vitro. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Samardzic, K.; Wallach, M.; Frumkin, L.R.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Immunoglobulin Y for Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Van Nguyen, S.; Icatlo, F.C., Jr.; Umeda, K.; Kodama, Y. Oral passive IgY-based immunotherapeutics: A novel solution for prevention and treatment of alimentary tract diseases. Hum. Vaccines Immunother 2013, 9, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Schubert, A.; Zajac, J.; Dyck, T.; Oelkrug, C. IgY antibodies in human nutrition for disease prevention. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slovak, J.E.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Otoni, C.; Morrison, J.; Deitz, K.; LeVine, D.; Jergens, A.E. Development and validation of an endoscopic activity score for canine inflammatory bowel disease. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jergens, A.E.; Evans, R.B.; Ackermann, M.; Hostetter, J.; Willard, M.; Mansell, J.; Bilzer, T.; Wilcock, B.; Washabau, R.; Hall, E.J.; et al. Design of a simplified histopathologic model for gastrointestinal inflammation in dogs. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Atherly, T.; Guard, B.; Rossi, G.; Wang, C.; Mosher, C.; Webb, C.; Hill, S.; Ackermann, M.; Sciabarra, P.; et al. Randomized, controlled trial evaluating the effect of multi-strain probiotic on the mucosal microbiota in canine idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassmann, E.; White, R.; Atherly, T.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Khoda, S.; Mosher, C.; Ackermann, M.; Jergens, A. Alterations of the Ileal and Colonic Mucosal Microbiota in Canine Chronic Enteropathies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.I.; Binder, B.J.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W.; Devereux, R.; Stahl, D.A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, A.H.; Harmsen, H.J.; Raangs, G.C.; Jansen, G.J.; Schut, F.; Welling, G.W. Variations of bacterial populations in human feces measured by fluorescent in situ hybridization with group-specific 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3336–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, W.; Amann, R.; Ludwig, W.; Vancanneyt, M.; Schleifer, K.H. Application of a suite of 16S rRNA-specific oligonucleotide probes designed to investigate bacteria of the phylum cytophaga-flavobacter-bacteroides in the natural environment. Microbiology 1996, 142 Pt 5, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, L.K.; Lan, F.; Kristensen, C.S.; Hobolth, P.; Molin, S.; Krogfelt, K.A. Spatial distribution of Escherichia coli in the mouse large intestine inferred from rRNA in situ hybridization. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5191–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.J.; Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007, 448, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A.; Putignani, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Cocca, S.; Angeletti, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Tripiciano, C.; Dalla Piccola, B.; Cicala, M.; Guarino, M.P.L. Gut mucosal-associated microbiota better discloses inflammatory bowel disease differential patterns than faecal microbiota. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Palculict, B.; Allenspach, K.; Steiner, J.M.; Van House, A.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial communities imbalances in the small intestine of dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Dowd, S.E.; Wilke, V.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E. 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals bacterial dysbiosis in the duodenum of dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Xenoulis, P.G.; Paddock, C.G.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E. Molecular analysis of the bacterial microbiota in duodenal biopsies from dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enderle, L.L.; Köller, G.; Heilmann, R.M. Verification of the fCAL turbo immunoturbidimetric assay for measurement of the fecal calprotectin concentration in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Vet. Lab. Diagn. Inc 2022, 34, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, K.; Culverwell, C.; Chan, D. Long-term outcome in dogs with chronic enteropathies: 203 cases. Vet. Rec. 2016, 178, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honneffer, J.B.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S. Microbiota alterations in acute and chronic gastrointestinal inflammation of cats and dogs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16489–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.W.; Dogan, B.; Rishniw, M.; Goldstein, R.E.; Klaessig, S.; McDonough, P.L.; German, A.J.; Yates, R.M.; Russell, D.G.; Johnson, S.E.; et al. Adherent and invasive Escherichia coli is associated with granulomatous colitis in boxer dogs. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4778–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Minamoto, T.; Isaiah, A.; Sattasathuchana, P.; Buono, A.; Rangachari, V.R.; McNeely, I.H.; Lidbury, J.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Fecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations and dysbiosis in dogs with chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Otoni, C.C.; Steelman, S.M.; Buyukleblebici, O.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Alteration of the fecal microbiota and serum metabolite profiles in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary Modulation of the Human Colonic Microbiota: Introducing the Concept of Prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.; Pengo, G.; Caldin, M.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Steiner, J.M.; Cohen, N.D.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Comparison of microbiological, histological, and immunomodulatory parameters in response to treatment with either combination therapy with prednisone and metronidazole or probiotic VSL#3 strains in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.; Henrich, M.; Neiger, R.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. Stimulation of duodenal biopsies and whole blood from dogs with food-responsive chronic enteropathy and healthy dogs with Toll-like receptor ligands and probiotic Enterococcus faecium. Scand. J. Immunol. 2014, 80, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, S.; Glanemann, B.; Garden, O.A.; Brooks, H.; Chang, Y.M.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. A prospective, randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled pilot study on the effect of Enterococcus faecium on clinical activity and intestinal gene expression in canine food-responsive chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Guard, B.C.; Steiner, J.M.; Gaschen, F.P.; Olson, E.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K.; Salavati Schmitz, S.; Suchodolski, J.S. Administration of a Synbiotic Containing Enterococcus faecium Does not Significantly Alter Fecal Microbiota Richness or Diversity in Dogs with and without Food-Responsive Chronic Enteropathy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, S.; Fracassi, F.; Bresciani, F.; Galuppi, R.; Diana, A.; Linta, N.; Bettini, G.; Morini, M.; Pietra, M. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in dog with chronic enteropathies: Double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Travis, S.P. Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel diseases: A systematic review. Gut 2012, 61, 1619–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.; Palmer, R.; Travis, S. Mucosal healing as a target of therapy for colonic inflammatory bowel disease and methods to score disease activity. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. North Am. 2014, 24, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sancho, M.; Rodriguez-Franco, F.; Sainz, A.; Mancho, C.; Rodriguez, A. Evaluation of clinical, macroscopic, and histopathologic response to treatment in nonhypoproteinemic dogs with lymphocytic-plasmacytic enteritis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Berghoff, N.; Mansell, J.; Grützner, N.; Parnell, N.K.; Gurtner, C.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Association of fecal calprotectin concentrations with disease severity, response to treatment, and other biomarkers in dogs with chronic inflammatory enteropathies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jergens, A.E.; Crandell, J.; Morrison, J.A.; Deitz, K.; Pressel, M.; Ackermann, M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Evans, R. Comparison of oral prednisone and prednisone combined with metronidazole for induction therapy of canine inflammatory bowel disease: A randomized-controlled trial. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otoni, C.C.; Heilmann, R.M.; García-Sancho, M.; Sainz, A.; Ackermann, M.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E. Serologic and fecal markers to predict response to induction therapy in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeire, S.; Van Assche, G.; Rutgeerts, P. Laboratory markers in IBD: Useful, magic, or unnecessary toys? Gut 2006, 55, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikoff, M.R.; Denson, L.A. Role of fecal calprotectin as a biomarker of intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, B.; Fürnrohr, B.G.; Vyse, T.J. C-reactive protein in rheumatology: Biology and genetics. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Grellet, A.; Allenspach, K.; Lecoindre, P.; Day, M.J.; Priestnall, S.L.; Toresson, L.; Procoli, F.; Grützner, N.; Suchodolski, J.S.; et al. Association between fecal S100A12 concentration and histologic, endoscopic, and clinical disease severity in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 158, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Ackermann, M.R.; Barr, J.W.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Serum calprotectin concentrations in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Chacana, P.A.; Calzado, E.G.; Brembs, B.; Schade, R. IgY technology: Extraction of chicken antibodies from egg yolk by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 51, e3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.P.V.; van Tilburg, M.F.; Florean, E.O.P.T.; Guedes, M.I.F. Egg yolk antibodies (IgY) and their applications in human and veterinary health: A review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhen, Y.; Thacker, P.A.; Wang, L.; Shi, M.; Zhao, J.; Zong, Y.; Wang, N.; et al. Chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY) modulate the intestinal mucosal immune response in a mouse model of Salmonella typhimurium infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro-Guajardo, M.; Díaz-González, F.; Álvarez-Lobos, M.; Paredes-Sabja, D. Characterization of Chicken IgY Specific to Clostridium difficile R20291 Spores and the Effect of Oral Administration in Mouse Models of Initiation and Recurrent Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Suzuki, H.; Masaoka, T.; Kurabayashi, K.; Ishii, H.; Kitajima, M.; Nomoto, K.; Hibi, T. Effect of Dietary Anti-Urease Immunoglobulin Y on Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mongolian Gerbils. Helicobacter 2005, 10, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Nomura, S.; Masaoka, T.; Goshima, H.; Kamata, N.; Kodama, Y.; Ishii, H.; Kitajima, M.; Nomoto, K.; Hibi, T. Effect of dietary anti-Helicobacter pylori-urease immunoglobulin Y on Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharm. 2004, 20 (Suppl. 1), 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Galila, E.; Isoda, R.; Umeda, K.; Nguyen, V.; Kodama, Y. Effect of passive immunization by anti-gingipain IgY on periodontal health of dogs. Vet. Sci. Dev. 2011, 1, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathy, J.; Karthika, S.; Sentila, R.; Michael, A. In vitro evaluation of the efficacy of chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY) generated against Propionibacterium acnes. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, L.C.; Baldissera, M.D.; Grando, T.H.; Gressler, L.T.; Capeleto Dde, M.; de Sa, M.F.; de Jesus, F.P.; dos Santos, A.G., Jr.; Anciuti, A.N.; Colonetti, K.; et al. Production, purification and therapeutic potential of egg yolk antibodies for treating Trypanosoma evansi infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 204, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, A.I.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Sung, C.-H.; Hittmair, K.M.; Richter, B.; Burgener, I.A. Microbial dysbiosis and fecal metabolomic perturbations in Yorkshire Terriers with chronic enteropathy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, Y.; Ogino, H.; Tanaka, M.; Ihara, E.; Fukaura, K.; Nishioka, K.; Chinen, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakayama, J.; Kang, D.; et al. Mucosa-associated gut microbiota reflects clinical course of ulcerative colitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.M.; Musavian, H.S.; Butt, T.M.; Ingvorsen, C.; Thysen, A.H.; Brix, S. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma-associated Proteobacteria, but not commensal Prevotella spp., promote Toll-like receptor 2-independent lung inflammation and pathology. Immunology 2015, 144, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaretta, P.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Jergens, A.E.; Steiner, J.M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Cook, A.K.; Hanifeh, M.; Spillmann, T.; Kilpinen, S.; Syrjä, P.; et al. Bacterial Biogeography of the Colon in Dogs With Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 57, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Martins, R.; Sullivan, M.C.; Friedman, E.S.; Misic, A.M.; El-Fahmawi, A.; De Martinis, E.C.P.; O’Brien, K.; Chen, Y.; Bradley, C.; et al. Diet-induced remission in chronic enteropathy is associated with altered microbial community structure and synthesis of secondary bile acids. Microbiome 2019, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dog. | Breed | Age (years) | Weight (kg.) | Sex | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shih Tzu | 10.9 | 5.9 | FS | Supplement |
| 2 | Labrador Retriever | 8.9 | 41.7 | MC | Placebo |
| 3 | Cardigan Welsh Corgi | 9.1 | 14.5 | F | Placebo |
| 4 | Great Pyrenees | 2.2 | 29.0 | MC | Supplement |
| 5 | Pembroke Welsh Corgi | 12.4 | 10.2 | FS | Placebo |
| 6 | Labrador Retriever | 5.9 | 33.0 | M | Supplement |
| 7 | Vizsla | 3.9 | 18.4 | FS | Supplement |
| 8 | Yorkshire Terrier | 5.8 | 6.8 | MC | Supplement |
| 9 | Boston Terrier | 13.0 | 8.6 | FS | Supplement |
| 10 | Mongrel | 1.1 | 19.4 | MC | Supplement |
| 11 | German Shepherd Dog | 4.7 | 51.0 | MC | Supplement |
| 12 | Norwegian Elkhound | 4.2 | 25.2 | M | Placebo |
| 13 | Cavalier King Charles | 11.7 | 7.3 | FS | Placebo |
| 14 | Pitbull | 7.3 | 21.4 | MC | Placebo |
| 15 | Bichon Frise | 5.1 | 5.3 | MC | Supplement |
| 16 | Great Dane | 5.0 | 38.0 | MC | Placebo |
| 17 | Mongrel | 1.1 | 36.0 | FS | Supplement |
| 18 | Mongrel | 2.3 | 46.1 | MC | Supplement |
| 19 | Boxer | 4.1 | 21.1 | MC | Placebo |
| 20 | Bernese Mountain Dog | 4.0 | 21.4 | FS | Placebo |
| Parameter | Placebo Group (n = 9) | Supplement Group (n = 11) | Wilcoxon Statistic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age (years) Range | 7.3 (4.1–12.4) | 4.7 (1–12.9) | p > 0.05 |
| Median Weight (kg.) Range | 21.4 (7.3–41.7) | 19.4 (5.3–51) | p > 0.05 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 5 (56) | 7 (64) | p > 0.05 |
| Median disease duration (mo.) Range | 11 (2–36) | 6 (1–42) | p > 0.05 |
| Median CCECAI Range | 8 (3–16) | 7 (4–10) | p > 0.05 |
| Number of PLE dogs Median serum albumin Range | 1 1.4 g/dL * (1.3–2.3 g/dL) | 3 1.5 g/dL (1.3–2.6 g/dL) | p > 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahoo, D.K.; Allenspach, K.; Mochel, J.P.; Parker, V.; Rudinsky, A.J.; Winston, J.A.; Bourgois-Mochel, A.; Ackermann, M.; Heilmann, R.M.; Köller, G.; et al. Synbiotic-IgY Therapy Modulates the Mucosal Microbiome and Inflammatory Indices in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010025
Sahoo DK, Allenspach K, Mochel JP, Parker V, Rudinsky AJ, Winston JA, Bourgois-Mochel A, Ackermann M, Heilmann RM, Köller G, et al. Synbiotic-IgY Therapy Modulates the Mucosal Microbiome and Inflammatory Indices in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahoo, Dipak Kumar, Karin Allenspach, Jonathan P. Mochel, Valerie Parker, Adam Joseph Rudinsky, Jenessa A. Winston, Agnes Bourgois-Mochel, Mark Ackermann, Romy M. Heilmann, Gabor Köller, and et al. 2023. "Synbiotic-IgY Therapy Modulates the Mucosal Microbiome and Inflammatory Indices in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010025
APA StyleSahoo, D. K., Allenspach, K., Mochel, J. P., Parker, V., Rudinsky, A. J., Winston, J. A., Bourgois-Mochel, A., Ackermann, M., Heilmann, R. M., Köller, G., Yuan, L., Stewart, T., Morgan, S., Scheunemann, K. R., Iennarella-Servantez, C. A., Gabriel, V., Zdyrski, C., Pilla, R., Suchodolski, J. S., & Jergens, A. E. (2023). Synbiotic-IgY Therapy Modulates the Mucosal Microbiome and Inflammatory Indices in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Veterinary Sciences, 10(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010025











