Monitoring of Chemical Changes in Coffee Beans during the Roasting Process Using Different Roasting Technologies with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
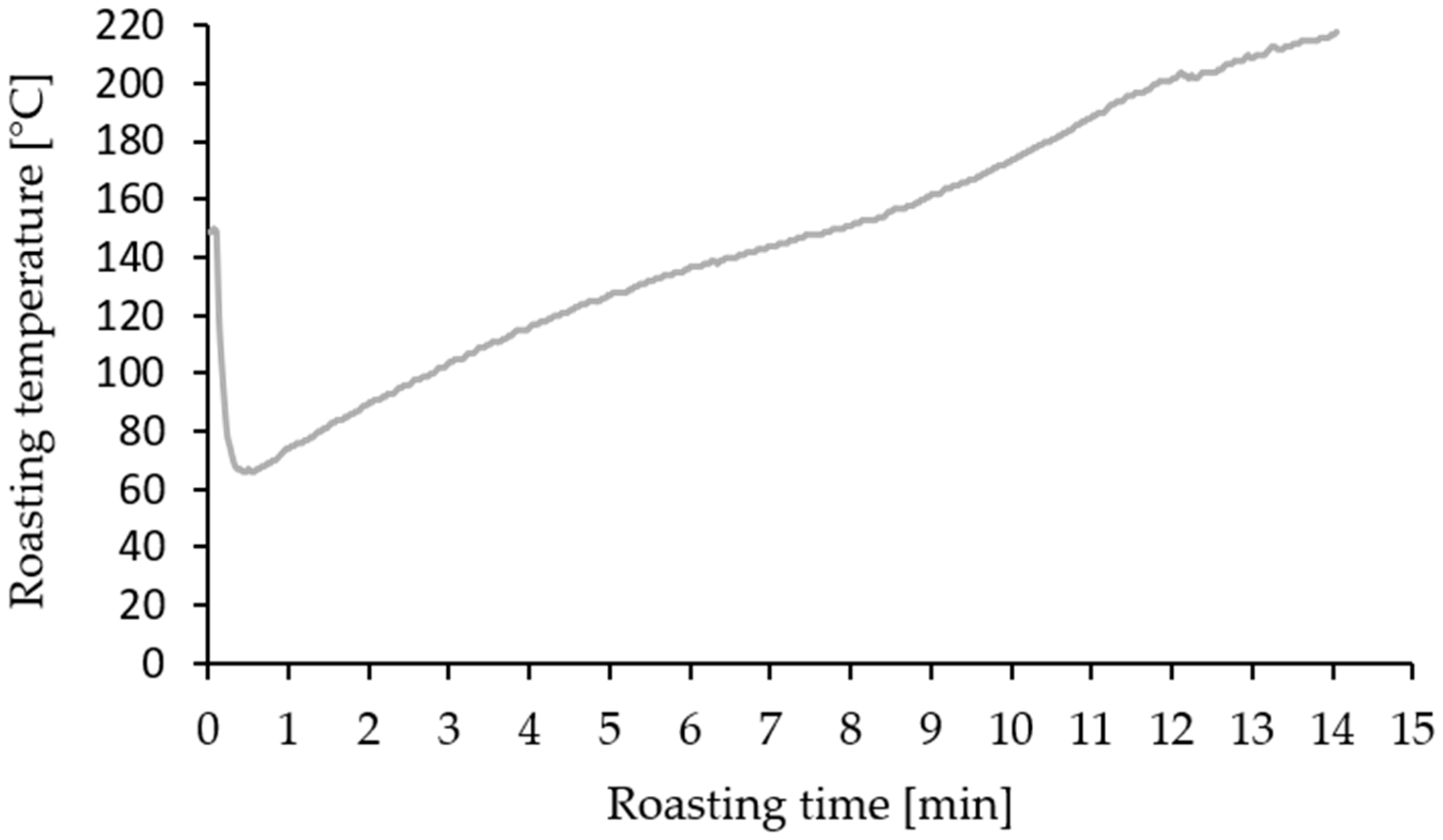
2.3. Roasting Process
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Moisture Content
2.4.2. Sample Preparation for NMR Spectroscopy
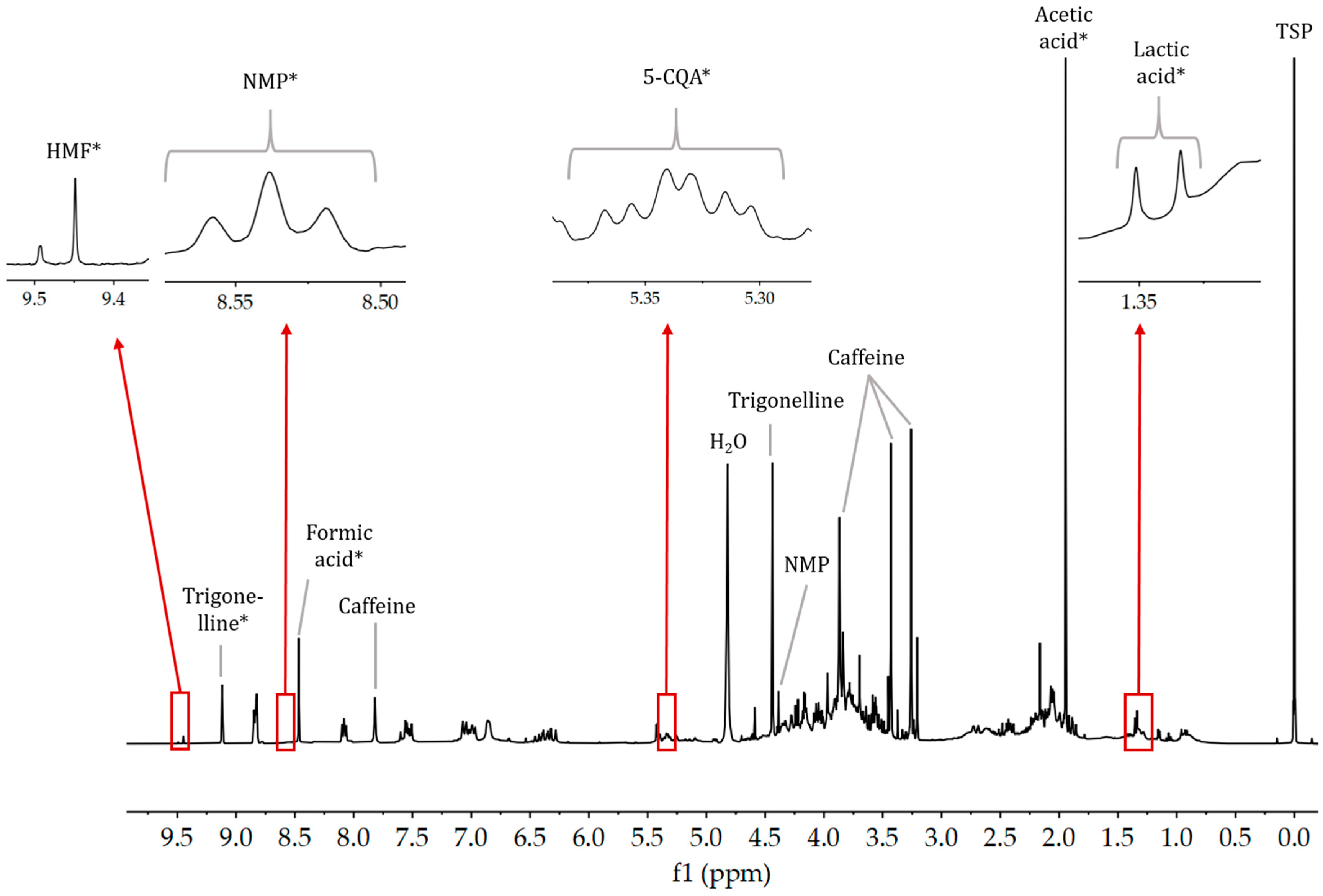
2.4.3. NMR Spectroscopy
2.4.4. NMR Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Moisture Content
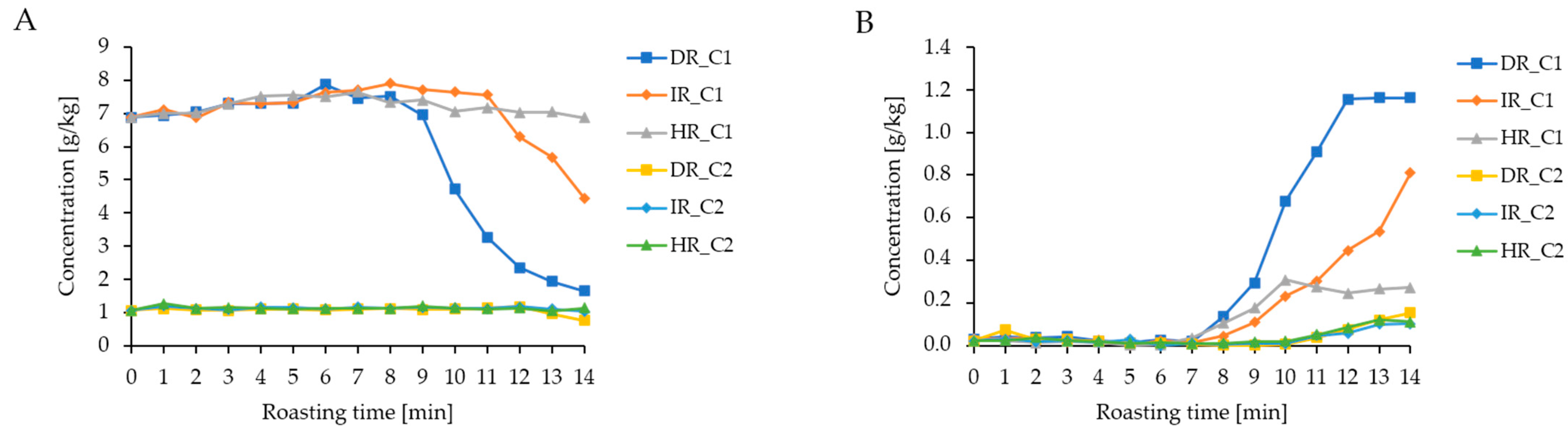
3.2. NMR Analysis of Coffee Fat Extracts
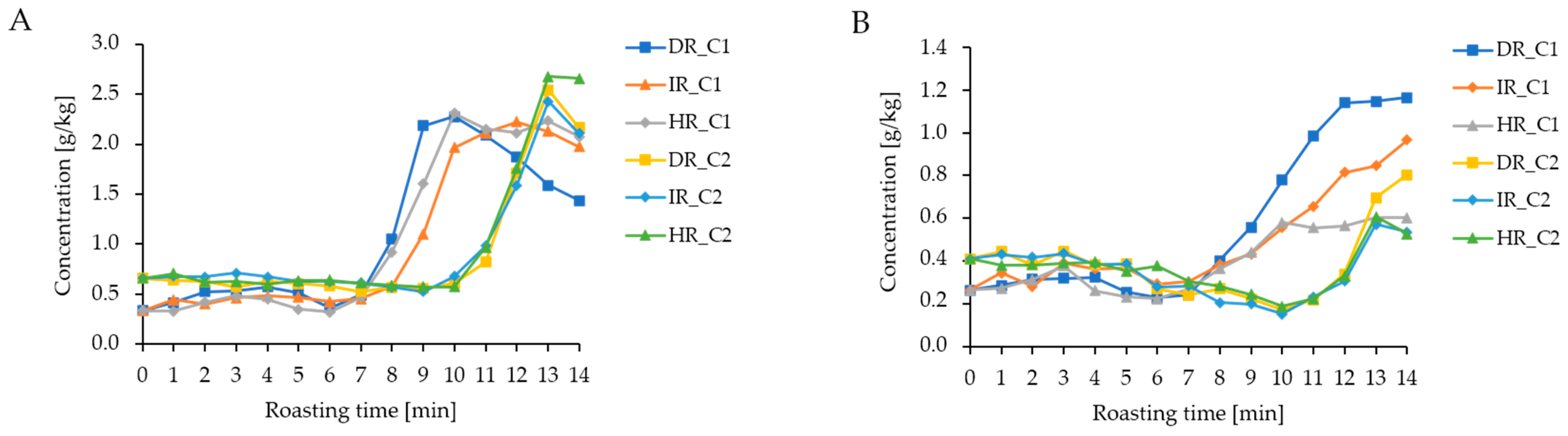
3.3. NMR Analysis of Aqueous Coffee Extracts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Coffee Organization. Coffee Market Report: Septmber 2021. Available online: http://www.ico.org/documents/cy2020-21/cmr-0921-e.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Wang, X.; Lim, L.-T. Effect of roasting conditions on carbon dioxide degassing behavior in coffee. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, A.; Cevoli, C.; Alessandrini, L.; Romani, S. Numerical modeling of heat and mass transfer during coffee roasting process. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, B. The Craft and Science of Coffee; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780128035207. [Google Scholar]
- Bolka, M.; Emire, S. Effects of coffee roasting technologies on cup quality and bioactive compounds of specialty coffee beans. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 6120–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Tanokura, M. Coffee in Health and Disease Prevention: Chapter 10: Chemical Changes in the Components of Coffee Beans during Roasting, 1st ed.; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Schwarz, S.; Teipel, J.; Hegmanns, M.; Kuballa, T.; Walch, S.G.; Breitling-Utzmann, C.M. Potential antagonistic effects of acrylamide mitigation during coffee roasting on furfuryl alcohol, furan and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Toxics 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.J.; Vitzthum, O.G. Coffee: Recent Developments; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 0632055537. [Google Scholar]
- Lire, W.H. Review on health benefit and risk of coffee consumption. Med. Aromat. Plants 2017, 06, 1000301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, N.; Franke, H.; Schwarz, S.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Risk Assessment of Trigonelline in Coffee and Coffee By-Products. Molecules 2023, 28, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Hochkogler, C.M.; Lang, R.; Bytof, G.; Lantz, I.; Hofmann, T.; Somoza, V. N-methylpyridinium, a degradation product of trigonelline upon coffee roasting, stimulates respiratory activity and promotes glucose utilization in HepG2 cells. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, M.; Moon, J.-K.; Jang, H.W.; Shibamoto, T. Role of degradation products of chlorogenic acid in the antioxidant activity of roasted coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preedy, V.R. Coffee in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9780124095175. [Google Scholar]
- IARC Working Group. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Furfuryl alcohol. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks. Hum. 2019, 119, 83–113. [Google Scholar]
- National Toxicology Program. NTP technical report on the toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of 5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furfural (CAS No. 67-47-0) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies). Natl. Toxicol. Program Tech. Rep. Ser. 2010, 554, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ruosi, M.R.; Cordero, C.; Cagliero, C.; Rubiolo, P.; Bicchi, C.; Sgorbini, B.; Liberto, E. A further tool to monitor the coffee roasting process: Aroma composition and chemical indices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11283–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febvay, L.; Hamon, E.; Recht, R.; Andres, N.; Vincent, M.; Aoudé-Werner, D.; This, H. Identification of markers of thermal processing (“roasting”) in aqueous extracts of Coffea arabica L. seeds through NMR fingerprinting and chemometrics. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, A.; Paulis, T.d.; Trugo, L.C.; Martin, P.R. Effect of roasting on the formation of chlorogenic acid lactones in coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endeshawa, H.; Belay, A. Optimization of the roasting conditions to lower acrylamide content and improve the nutrient composition and antioxidant properties of Coffea arabica. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.P.; Antoniosi Filho, N.R.; Lião, L.M.; Flores, I.S. Evaluation of the metabolic profile of arabica coffee via NMR in relation to the time and temperature of the roasting procedure. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2021, 31, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.R.; Viegas, O.; Páscoa, R.N.M.J.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Lopes, J.A. In-line monitoring of the coffee roasting process with near infrared spectroscopy: Measurement of sucrose and colour. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggenstoss, J.; Poisson, L.; Kaegi, R.; Perren, R.; Escher, F. Coffee roasting and aroma formation: Application of different time-temperature conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5836–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampa, A.; Renzi, G.; Taglienti, A.; Sequi, P.; Valentini, M. Studies on coffee roasting process by means of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Food Qual. 2010, 33, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catelani, T.A.; Santos, J.R.; Páscoa, R.N.M.J.; Pezza, L.; Pezza, H.R.; Lopes, J.A. Real-time monitoring of a coffee roasting process with near infrared spectroscopy using multivariate statistical analysis: A feasibility study. Talanta 2018, 179, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, R. Radiation Grill. Patent WO2017097780A1, 15 June 2017. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2017097780A1/en (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Holzgrabe, U. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy in pharmaceutical applications. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2010, 57, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Roy, R. Quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2012, 35, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaru, A.O.; Scharinger, A.; Rajcic de Rezende, T.; Teipel, J.; Kuballa, T.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Validation of a Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Screening Method for Coffee Quality and Authenticity (NMR Coffee Screener). Foods 2020, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kuballa, T.; Mushtakova, S.P. Standardless multicomponent qNMR analysis of compounds with overlapped resonances based on the combination of ICA and PULCON. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Kohl-Himmelseher, M.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Determination of the purity of pharmaceutical reference materials by 1H NMR using the standardless PULCON methodology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teipel, J.C.; Hausler, T.; Sommerfeld, K.; Scharinger, A.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kuballa, T. Application of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy as spirit drinks screener for quality and authenticity control. Foods 2020, 9, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, P.; Haarala, J.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Niemitz, M.; Laatikainen, R. Strategies for organic impurity quantification by 1H NMR spectroscopy: Constrained total-line-shape fitting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.C.E.; Faria-Machado, A.F.d.; Mercadante, A.Z.; Bragagnolo, N.; Benassi, M.d.T. Roasting process affects the profile of diterpenes in coffee. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, K.; Kölling-Speer, I. The lipid fraction of the coffee bean. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 18, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouchi, A.; Murkovic, M. Formation kinetics of furfuryl alcohol in a coffee model system. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Matei, M.F.; Golon, A.; Witt, M.; Kuhnert, N. Understanding the fate of chlorogenic acids in coffee roasting using mass spectrometry based targeted and non-targeted analytical strategies. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Furihata, K.; Koda, M.; Hu, F.; Miyakawa, T.; Tanokura, M. Roasting process of coffee beans as studied by nuclear magnetic resonance: Time course of changes in composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginz, M.; Balzer, H.H.; Bradbury, A.G.W.; Maier, H.G. Formation of aliphatic acids by carbohydrate degradation during roasting of coffee. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2000, 211, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Typek, R. Transformation of chlorogenic acids during the coffee beans roasting process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.; Paulis, T.d.; Moreira, D.P.; Trugo, L.C.; Martin, P.R. Chlorogenic acids and lactones in regular and water-decaffeinated arabica coffees. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amelio, N.; Fontanive, L.; Uggeri, F.; Suggi-Liverani, F.; Navarini, L. NMR reinvestigation of the caffeine–chlorogenate complex in aqueous solution and in coffee brews. Food Biophys. 2009, 4, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkovic, M.; Bornik, M.-A. Formation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (HMF) and 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furoic acid during roasting of coffee. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Caffeine-Containing Coffee Sample | Decaffeinated Coffee Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roasting Time [min] | DR [%] | IR [%] | HR [%] | DR [%] | IR [%] | HR [%] |
| 0 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 9.4 |
| 1 | 9.4 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 9.2 |
| 2 | 8.9 | 8.4 | 9.1 | 8.5 | 8.6 | 8.9 |
| 3 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 8.3 |
| 4 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 8.1 |
| 5 | 7.2 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 7.5 |
| 6 | 5.9 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 7.6 |
| 7 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 5.8 | 6.8 |
| 8 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 4.6 | 6.0 | 5.7 | 6.6 |
| 9 | 3.4 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 5.5 | 5.1 | 6.1 |
| 10 | 2.4 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 5.3 | 4.9 | 5.5 |
| 11 | 2.6 | 4.0 | 3.2 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 4.7 |
| 12 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 3.2 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 4.5 |
| 13 | 2.3 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 3.3 |
| 14 | 1.9 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.7 | 3.2 | 3.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gottstein, V.; Krumbügel, K.; Kuballa, T.; Schwarz, S.; Walch, E.; Walch, P.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Monitoring of Chemical Changes in Coffee Beans during the Roasting Process Using Different Roasting Technologies with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Beverages 2023, 9, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9040087
Gottstein V, Krumbügel K, Kuballa T, Schwarz S, Walch E, Walch P, Lachenmeier DW. Monitoring of Chemical Changes in Coffee Beans during the Roasting Process Using Different Roasting Technologies with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Beverages. 2023; 9(4):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9040087
Chicago/Turabian StyleGottstein, Vera, Katrin Krumbügel, Thomas Kuballa, Steffen Schwarz, Enrico Walch, Pascal Walch, and Dirk W. Lachenmeier. 2023. "Monitoring of Chemical Changes in Coffee Beans during the Roasting Process Using Different Roasting Technologies with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy" Beverages 9, no. 4: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9040087
APA StyleGottstein, V., Krumbügel, K., Kuballa, T., Schwarz, S., Walch, E., Walch, P., & Lachenmeier, D. W. (2023). Monitoring of Chemical Changes in Coffee Beans during the Roasting Process Using Different Roasting Technologies with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Beverages, 9(4), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9040087








