Phytochemical and Structural Changes of Chickpea Beverage Prepared Using Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation with Optimized Ultrasound Parameters Modelled by Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chickpea Milk Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Organic Properties
2.3.1. Reducing Sugars Content
2.3.2. Lactic Acid Content
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Phytochemical Analysis Using HPLC
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Fitting and Diagnostics for Chickpea Beverage Fermentation Parameters
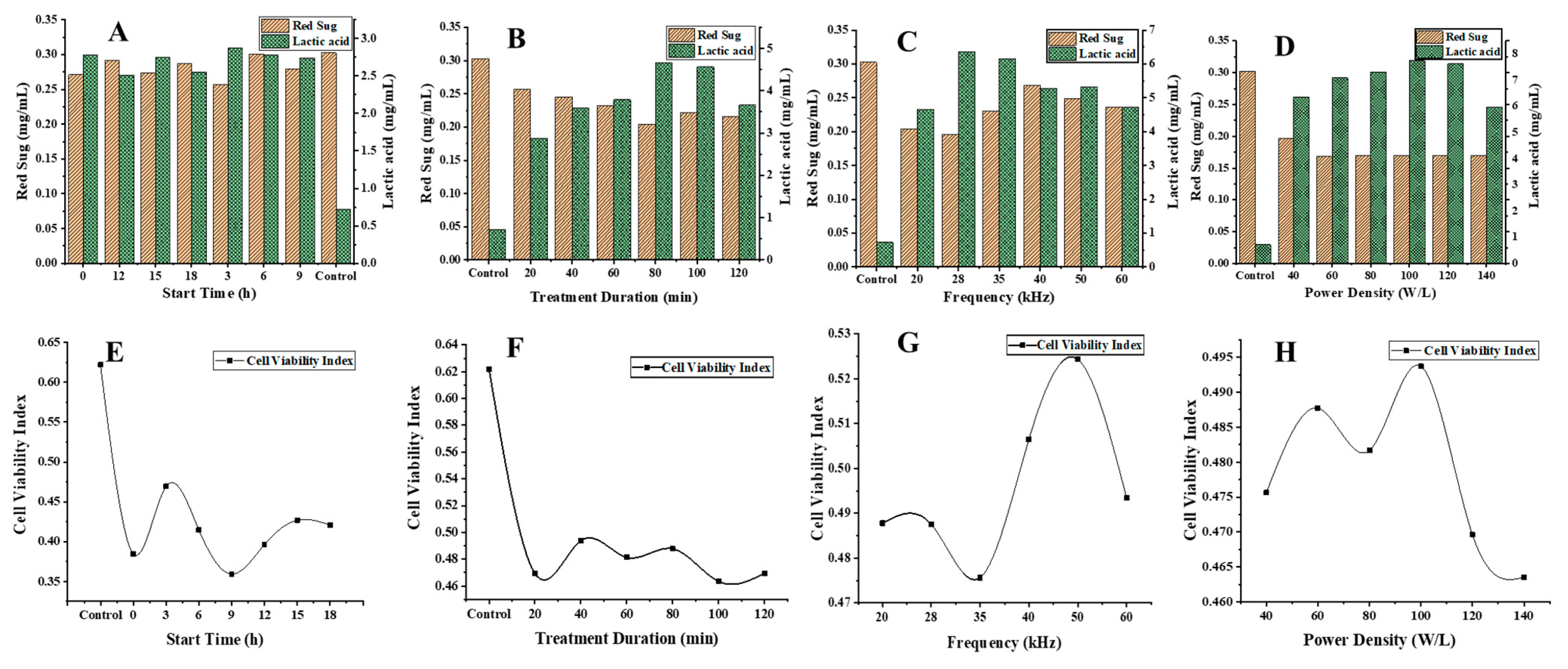
3.2. Influence of Preliminary Ultrasonic Parameters on Reducing Sugar, Lactic Acid, and Cell Viability Index of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei-Fermented Chickpea Beverages
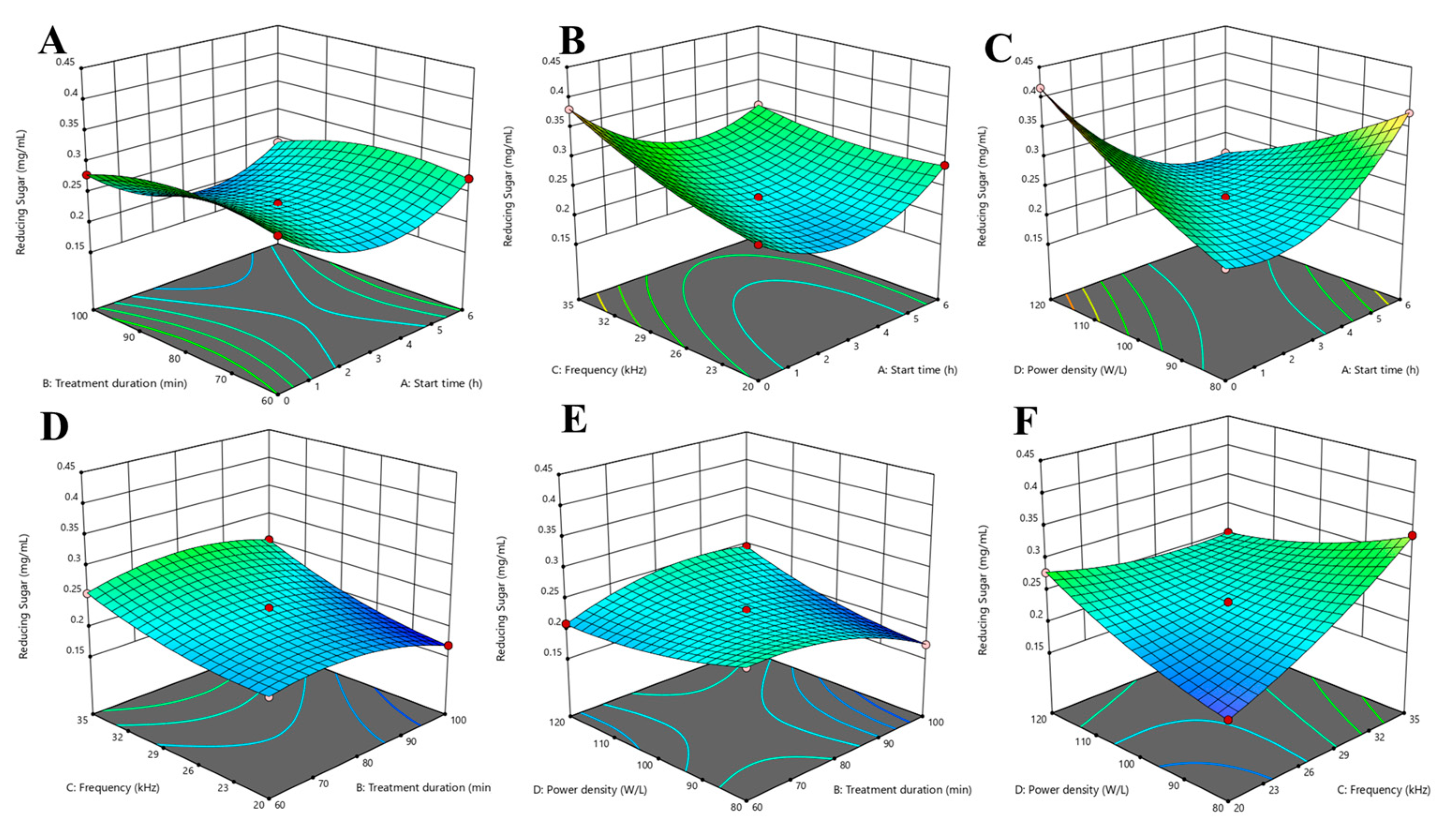
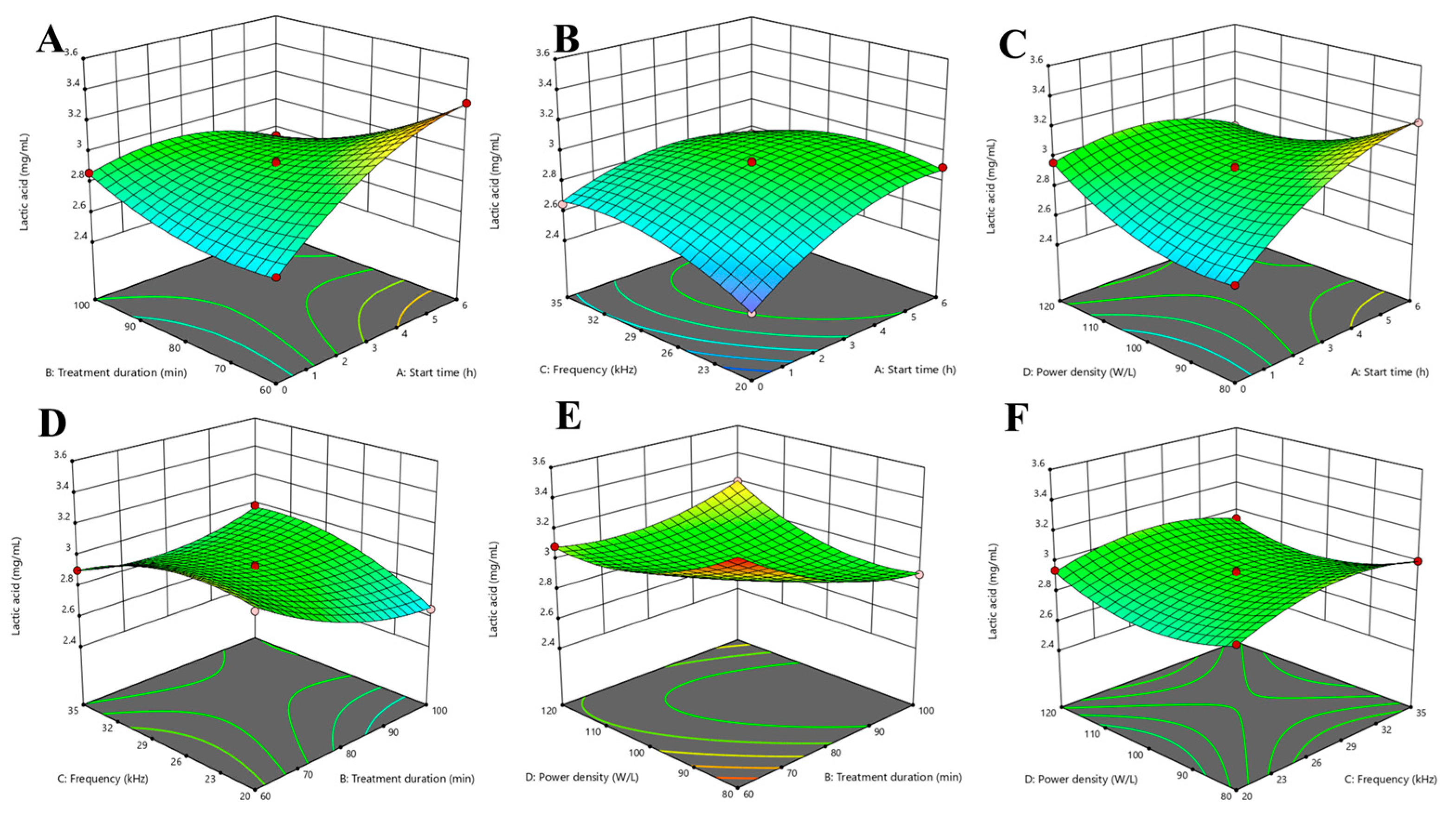
3.3. Optimization of Parameters by RSM Using BBD
3.3.1. Effect of Ultrasonic Parameters on the Reducing Sugar Concentrations of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei-Fermented Chickpea Beverage
3.3.2. Effect of Ultrasonic Parameters on the Lactic Acid Content in Lacticaseibacillus paracasei-Fermented Chickpea Beverage
3.3.3. Effect of Ultrasonic Parameters on the Cell Viability of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei in Fermented Chickpea Beverages
3.4. Optimization and Verification of Model for Producing Ultrasound-Assisted Chickpea Beverage Fermentation
3.5. Influence of Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation on the Phytochemicals Contents of Chickpea Beverages
3.6. Influence of Ultrasonication on the Chemical Structure of Fermented Chickpea Beverage Using FTIR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Fan, Z.; Duan, X.; Cui, D.; Zang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, C. Enhancement of the Transmission Performance of Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasound Transducers by Vibration Mode Optimization. Micromachines 2022, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.-G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, K.S.; Mason, T.J.; O’donnell, C.P.; Kerry, J.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound technology for food fermentation applications. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, L.-H.; Zeng, X.-A.; Han, Z.; Brennan, C.S. Non-thermal technologies and its current and future application in the food industry: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celotti, E.; Stante, S.; Ferraretto, P.; Román, T.; Nicolini, G.; Natolino, A. High power ultrasound treatments of red young wines: Effect on anthocyanins and phenolic stability indices. Foods 2020, 9, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Ma, Y.; Ekumah, J.N.; Osabutey, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, M.; Johnson, N.A.N.; Mintah, B.K. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of bioactive chlorogenic acid from heilong48 soybean variety: Parametric optimization and evaluation of physicochemical and bioactive properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, J.; Ngadi, M. Ultrasound-assisted processing: Science, technology and challenges for the plant-based protein industry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Naviglio, D. Application of Ultrasound in Food Science and Technology: A Perspective. Foods 2018, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, K.S.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’donnell, C.P. Effect of Ultrasound Technology on Food and Nutritional Quality. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 84, 207–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, H.B.; Annapure, U.S.; Deshmukh, R.R. Non-thermal Technologies for Food Processing. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 657090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umego, E.C.; He, R.; Huang, G.; Dai, C.; Ma, H. Ultrasound-assisted fermentation: Mechanisms, technologies, and challenges. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Meullemiestre, A.; Turk, M.; Perino, S.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M. Review of Green Food Processing techniques. Preservation, transformation, and extraction. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, S.; Dai, C.; Sun, L.; Sun, W.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, F.; He, R.; Ma, H. Effects of ultrasound on microbial growth and enzyme activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Dar, A.H.; Bhat, S.A.; Fayaz, J.; Makroo, H.A.; Dwivedi, M. High Intensity Ultrasound Processing in Liquid Foods. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 1123–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, P.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.R.; Mittal, T.C.; Jaiswal, A.K. Application of High-Intensity Ultrasound to Improve Food Processing Efficiency: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astráin-Redín, L.; Alejandre, M.; Raso, J.; Cebrián, G.; Álvarez, I. Direct Contact Ultrasound in Food Processing: Impact on Food Quality. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 633070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Singh, S.; Malani, R.S.; Moholkar, V.S. Ultrasound-assisted bioalcohol synthesis: Review and analysis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65541–65562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewe, J.-A.; Wan-Abdullah, W.-N.; Alias, A.K.; Liong, M.-T. Effects of ultrasound on growth, bioconversion of isoflavones and probiotic properties of parent and subsequent passages of Lactobacillus fermentum BT 8633 in biotin-supplemented soymilk. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Dai, C.; Sun, L.; Ma, H.; He, R. Stimulation of low intensity ultrasound on fermentation of skim milk medium for yield of yoghurt peptides by Lactobacillus paracasei. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Daccache, M.; Koubaa, M.; Salameh, D.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N.; Vorobiev, E. Ultrasound-assisted fermentation for cider production from Lebanese apples. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Luo, J.; Ma, H. Analysis in protein profile, antioxidant activity and structure-activity relationship based on ultrasound-assisted liquid-state fermentation of soybean meal with Bacillus subtilis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.M.; Tarfeen, N.; Mohamed, H.; Song, Y. Fermented Foods: Their Health-Promoting Components and Potential Effects on Gut Microbiota. Fermentation 2023, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Watanabe, K.; Holzapfel, W.H. Review: Diversity of Microorganisms in Global Fermented Foods and Beverages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebo, J.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Gbashi, S.; Oyedeji, A.B.; Ogundele, O.M.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adebo, O.A. Fermentation of Cereals and Legumes: Impact on Nutritional Constituents and Nutrient Bioavailability. Fermentation 2022, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, F.; Cai, W.; Zhao, X.; Shan, C. Evaluating the effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on quality, aroma, and metabolites of chickpea milk. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1069714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xie, B.; Sun, Z. Influence of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Chickpea Yam Milk. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 5523356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.N.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Ekumah, J.-N.; Li, Y.; Betchem, G.; Issaka, E.; Ma, Y. Efficacy of Ultrasound-Assisted Lactic Acid Fermentation and Its Effect on the Nutritional and Sensory Quality of Novel Chickpea-Based Beverage. Fermentation 2023, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, R.S.S.; da Silva, A.S.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.S.; Bon, E.P.d.S. Amino acids interference on the quantification of reducing sugars by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid assay mislead carbohydrase activity measurements. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 363, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borshchevskaya, L.N.; Gordeeva, T.L.; Kalinina, A.N.; Sineokii, S.P. Spectrophotometric determination of lactic acid. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 71, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, T.; Ozcan, T. Effect of steviol glycosides as sugar substitute on the probiotic fermentation in milk gels enriched with red beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) bioactive compounds. LWT 2020, 134, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Ma, Y.; Ekumah, J.N.; Osabutey, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, M.; Johnson, N.A.N. Single-frequency ultrasonic extraction of bioactive chlorogenic acid from heilong48 soybean variety: Parametric optimization and comprehensive evaluation of physicochemical and bioactive properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I.D.; Yang, X.-M.; Li, Y.-Y. Optimization of infrared-drying parameters for Ginkgo biloba L. seed and evaluation of product quality and bioactivity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 160, 113108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseindokht, M.; Khamisabad, A.; Owlia, P.; Zarea, H.; Vahidi, H. Yeast Enriched with Selenium: A Promising Source of Selenomethionine and Seleno-Proteins. Trends Pept. Protein Sci. 2017, 1, 88–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, C.K.M. Optimization of Fermentation Parameters for Maximization of Actinomycin D Production. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Mintah, B.K.; He, R.; Agyekum, A.A.; Dabbour, M.; Golly, M.K.; Ma, H. Edible insect protein for food applications: Extraction, composition, and functional properties. J. Food Process. Eng. 2020, 43, e13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.N.; Ekumah, J.-N.; Ma, Y.; Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Manching, X.; Quaisie, J.; Kwaw, E.; Wang, C. Optimization of fermentation parameters for the production of a novel selenium enriched mulberry (Morus nigra) wine. LWT 2023, 178, 114608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfe, M.D.; Rice, C.J.; Lucchini, S.; Pin, C.; Thompson, A.; Cameron, A.D.S.; Alston, M.; Stringer, M.F.; Betts, R.P.; Baranyi, J.; et al. Lag Phase Is a Distinct Growth Phase That Prepares Bacteria for Exponential Growth and Involves Transient Metal Accumulation. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 686–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X. Enhancing the taste of raw soy sauce using low intensity ultrasound treatment during moromi fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Ge, S.; Cai, L.; Huang, Z.; Van Le, Q.; et al. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on chain elongation of saccharified residue from food waste by anaerobic fermentation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.P.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhou, W. Stimulating fermentative activities of bifidobacteria in milk by highintensity ultrasound. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, E.; Nilsson, M.; Elmståhl, H.L.; Molin, G.; Björck, I. On the Effect of Lactic Acid on Blood Glucose and Insulin Responses to Cereal Products: Mechanistic Studies in Healthy Subjects and In Vitro. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Manickam, S.; Show, P.L. Application of ultrasonication at different microbial growth stages during apple juice fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum: Investigation on the metabolic response. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.A.; Pareek, S.; Sharma, S.; Yahia, E.M.; Lobo, M.G. Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Bioactive Compounds, Their Extraction, and Possible Utilization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, B.; Polachini, T.C.; Augusto, P.E.; Telis-Romero, J. Ultrasound-assisted hydration of wheat grains at different temperatures and power applied: Effect on acoustic field, water absorption and germination. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2020, 155, 108045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhou, C.; Barba, F.J.; Cai, Z.; Liu, L.; Rene, E.R.; Pan, D.; Cao, J.; et al. Strategic thermosonication-mediated modulation of lactic acid bacteria acidification kinetics for enhanced (post)-fermentation performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, I.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, H.S. Characteristics of the Thermal Degradation of Glucose and Maltose Solutions. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 20, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Tan, M.; Øiseth, S.; Buckow, R. An Emerging Segment of Functional Legume-Based Beverages: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 1064–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abesinghe, A.M.N.L.; Islam, N.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Prakash, S.; Silva, K.F.S.T.; Karim, M.A. Effects of ultrasound on the fermentation profile of fermented milk products incorporated with lactic acid bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 90, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Koubaa, M.; Bals, O.; Vorobiev, E. Recent insights in the impact of emerging technologies on lactic acid bacteria: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mettu, S.; Martin, G.J.O.; Ashokkumar, M.; Lin, C.S.K. Ultrasonic pretreatment of food waste to accelerate enzymatic hydrolysis for glucose production. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 53, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, M.; Natarajan, V.; Modupalli, N.; Thangaraj, S.; Rawson, A. Pulsed ultrasound assisted extraction of protein from defatted Bitter melon seeds (Momardica charantia L.) meal: Kinetics and quality measurements. LWT 2022, 155, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Khan, M.K. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, W.G.; Ross, S.A. Ultrasound Increases the Rate of Bacterial Cell Growth. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogate, P.R.; Kabadi, A.M. A review of applications of cavitation in biochemical engineering/biotechnology. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadnia, A.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Ojha, S.; Tiwari, B.K. Exploitation of Ultrasound Technique for Enhancement of Microbial Metabolites Production. Molecules 2020, 25, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dular, M.; Griessler-Bulc, T.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Heath, E.; Kosjek, T.; Klemenčič, A.K.; Oder, M.; Petkovšek, M.; Rački, N.; Ravnikar, M.; et al. Use of hydrodynamic cavitation in (waste)water treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaw, E.; Ma, Y.; Tchabo, W.; Apaliya, M.T.; Xiao, L.; Li, X.; Hu, M. Effect of fermentation parameters and their optimization on the phytochemical properties of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I.D.; Yang, X.-M. Process optimization of intermediate-wave infrared drying: Screening by Plackett–Burman; comparison of Box-Behnken and central composite design and evaluation: A case study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitzmann, C. Characteristics and Health Benefits of Phytochemicals. Complement. Med. Res. 2016, 23, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, A. Control of insect pests in crop plants and stored food grains using plant saponins: A review. LWT 2018, 87, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engmann, F.N.; Ma, Y.; Tchabo, W.; Ma, H. Ultrasonication Treatment Effect on Anthocyanins, Color, Microorganisms and Enzyme Inactivation of Mulberry (Moraceae nigra) Juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.B.; Yusuf, H.L.; Pu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, M.; Liu, D. Ultrasound-assisted adsorption/desorption for the enrichment and purification of flavonoids from baobab (Adansonia digitata) fruit pulp. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 65, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.-H. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on phenyllactic acid production in kimchi. Food Control 2019, 106, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-López, J.; Ruiz-Medina, A.; Ortega-Barrales, P.; Llorent-Martínez, E.J. Phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity of caper berries (Capparis spinosa L.): Evaluation of the influence of the fermentation process. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gallaghar, E. Barley for Brewing: Characteristic Changes during Malting, Brewing and Applications of its By-Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Liu, S.-Q.; Al Mheiri, A.; Aldhaheri, M.; Raeisi, B.; Al-Nabulsi, A.; Osaili, T.; Olaimat, A. In vitro investigation of health-promoting benefits of fermented camel sausage by novel probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum: A comparative study with beef sausages. LWT 2018, 99, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, M.; Lee, J.; Kentish, S.; Grieser, F. Bubbles in an acoustic field: An overview. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlelmoula, A.; Pinho, D.; Carvalho, V.H.; Catarino, S.O.; Minas, G. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy to Analyse Human Blood over the Last 20 Years: A Review towards Lab-on-a-Chip Devices. Micromachines 2022, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhai, X.; Liu, X.; Lian, M.; Liang, G.; Cui, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, W. Effects of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on Structure, Properties, and Enzymolysis of Walnut Protein Isolate. Molecules 2022, 27, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Lei, Y.; Yang, M. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Structure, Functional Properties of Chickpea Protein Isolate and Its Digestibility In Vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimuthu, M.; Gurumoorthi, P. Phytochemical screening and FT-IR studies on wild and common South Indian legumes. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to Read and Interpret FTIR Spectroscope of Organic Material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Run | Independent Variables | Dependent Variables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Time (h) A | Treatment Duration (min) B | Frequency (kHz) C | Power Density (°C) D | Reducing Sugar (mg/mL) Y1 | Lactic Acid (mg/mL) Y2 | Cell Viability Index Y3 | |
| 1 | 3 | 80 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.23 | 2.90 | 0.49 |
| 2 | 3 | 100 | 27.5 | 120 | 0.25 | 3.31 | 0.53 |
| 3 | 6 | 80 | 27.5 | 120 | 0.21 | 2.76 | 0.48 |
| 4 | 3 | 80 | 35 | 80 | 0.34 | 2.27 | 0.50 |
| 5 | 3 | 80 | 20 | 120 | 0.28 | 2.64 | 0.49 |
| 6 | 0 | 60 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.29 | 2.69 | 0.44 |
| 7 | 3 | 80 | 35 | 120 | 0.25 | 2.87 | 0.49 |
| 8 | 3 | 60 | 27.5 | 80 | 0.25 | 3.49 | 0.57 |
| 9 | 3 | 100 | 20 | 100 | 0.17 | 2.75 | 0.44 |
| 10 | 0 | 80 | 27.5 | 120 | 0.42 | 3.05 | 0.49 |
| 11 | 0 | 80 | 35 | 100 | 0.38 | 2.55 | 0.45 |
| 12 | 6 | 80 | 27.5 | 80 | 0.37 | 3.06 | 0.53 |
| 13 | 3 | 60 | 35 | 100 | 0.26 | 2.73 | 0.48 |
| 14 | 6 | 80 | 35 | 100 | 0.30 | 2.25 | 0.46 |
| 15 | 3 | 80 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.23 | 2.92 | 0.49 |
| 16 | 3 | 60 | 20 | 100 | 0.21 | 3.17 | 0.51 |
| 17 | 3 | 80 | 20 | 80 | 0.17 | 3.13 | 0.48 |
| 18 | 3 | 60 | 27.5 | 120 | 0.21 | 3.16 | 0.51 |
| 19 | 3 | 100 | 27.5 | 80 | 0.17 | 2.82 | 0.48 |
| 20 | 3 | 80 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.23 | 2.95 | 0.49 |
| 21 | 3 | 80 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.23 | 2.90 | 0.49 |
| 22 | 6 | 60 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.27 | 3.32 | 0.55 |
| 23 | 0 | 80 | 27.5 | 80 | 0.23 | 2.68 | 0.44 |
| 24 | 6 | 100 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.24 | 2.70 | 0.46 |
| 25 | 3 | 100 | 35 | 100 | 0.25 | 2.60 | 0.50 |
| 26 | 3 | 80 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.23 | 2.95 | 0.49 |
| 27 | 0 | 80 | 20 | 100 | 0.27 | 2.49 | 0.40 |
| 28 | 0 | 100 | 27.5 | 100 | 0.28 | 2.99 | 0.48 |
| 29 | 6 | 80 | 20 | 100 | 0.29 | 2.89 | 0.48 |
| Analysis | Predicted Mean | Predicted Median | Std Dev | SE Pred | 95% PI Low | Observed Mean | 95% PI High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing Sugar | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.001 | 0.0007 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| Lactic acid | 2.93 | 2.93 | 0.050 | 0.0300 | 2.85 | 2.93 | 2.99 |
| Cell viability index | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.001 | 0.0010 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, N.A.N.; Ekumah, J.-N.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Li, Y.; Betchem, G.; Issaka, E.; Ma, Y. Phytochemical and Structural Changes of Chickpea Beverage Prepared Using Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation with Optimized Ultrasound Parameters Modelled by Response Surface Methodology. Beverages 2023, 9, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030062
Johnson NAN, Ekumah J-N, Adade SY-SS, Li Y, Betchem G, Issaka E, Ma Y. Phytochemical and Structural Changes of Chickpea Beverage Prepared Using Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation with Optimized Ultrasound Parameters Modelled by Response Surface Methodology. Beverages. 2023; 9(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Nana Adwoa Nkuma, John-Nelson Ekumah, Selorm Yao-Say Solomon Adade, Yanshu Li, Garba Betchem, Eliasu Issaka, and Yongkun Ma. 2023. "Phytochemical and Structural Changes of Chickpea Beverage Prepared Using Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation with Optimized Ultrasound Parameters Modelled by Response Surface Methodology" Beverages 9, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030062
APA StyleJohnson, N. A. N., Ekumah, J.-N., Adade, S. Y.-S. S., Li, Y., Betchem, G., Issaka, E., & Ma, Y. (2023). Phytochemical and Structural Changes of Chickpea Beverage Prepared Using Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation with Optimized Ultrasound Parameters Modelled by Response Surface Methodology. Beverages, 9(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030062







