Chemical, Physicochemical, Microbiological, Bioactive, and Sensory Characteristics of Cow and Donkey Milk Kefir during Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Kefir Manufacture
2.3. Physicochemical and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.5.1. Extraction
2.5.2. ABTS Test
2.5.3. DPPH Test
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
2.6.1. Bacterial Strains
2.6.2. Disc Diffusion Test
2.7. Sensory Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical and Chemical Analyses
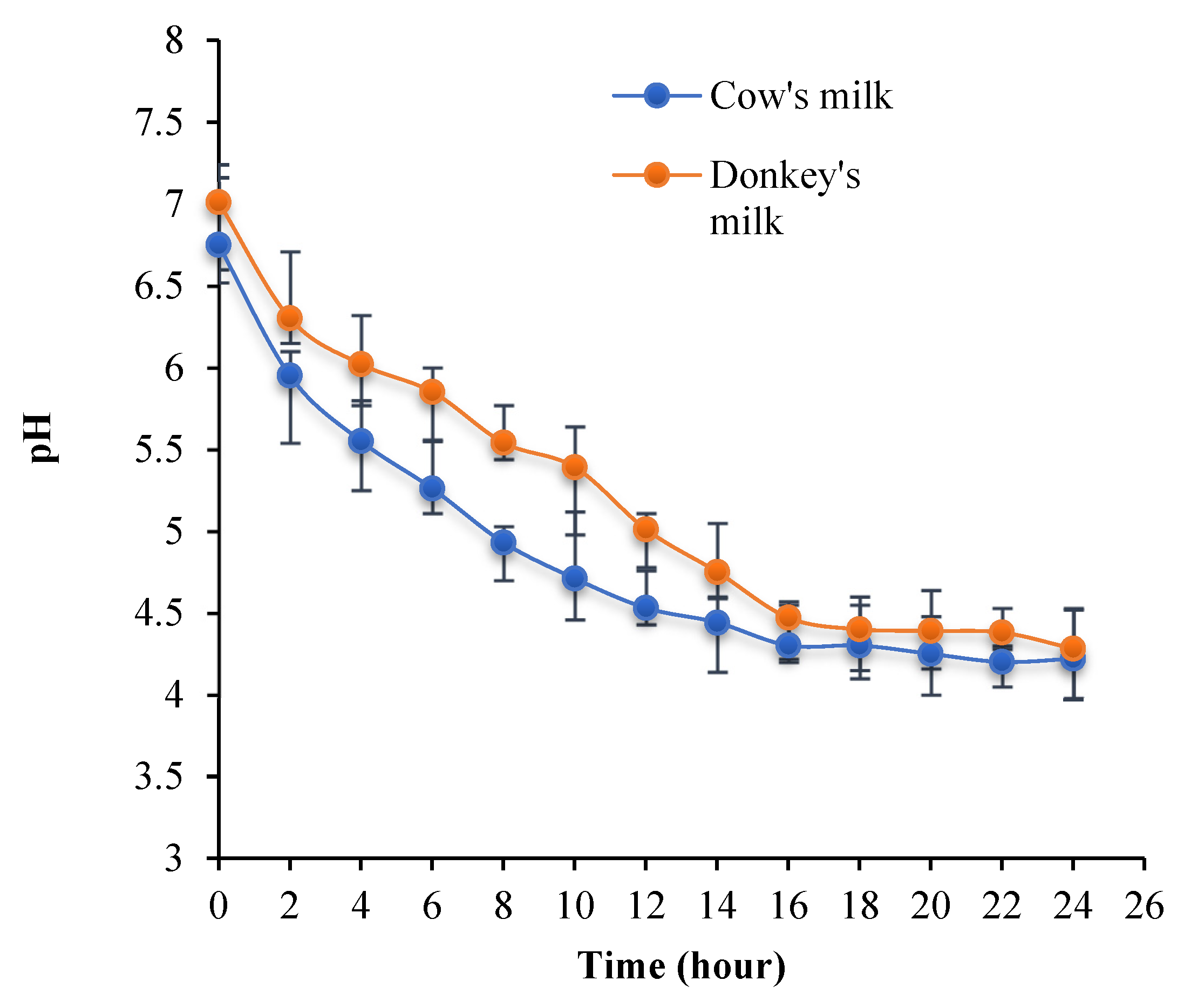
pH Variation during the Fermentation
3.2. Evolution of Physicochemical Parameters during Storage
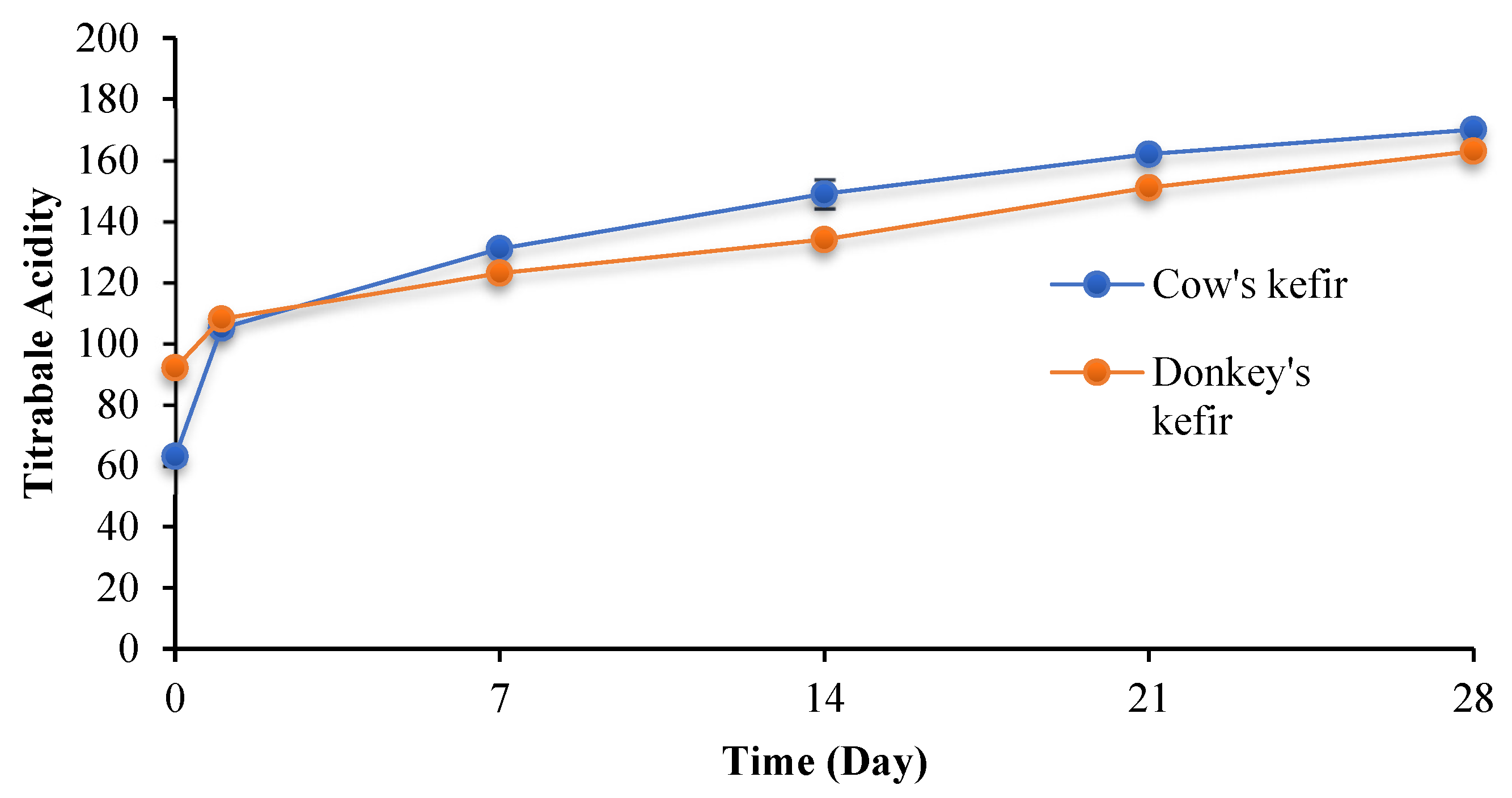
3.2.1. Dornic Acidity Evolution during Storage
3.2.2. Biochemical Composition Evolution during Storage Time at 4 °C
3.3. Microbial Profile of Kefirs
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
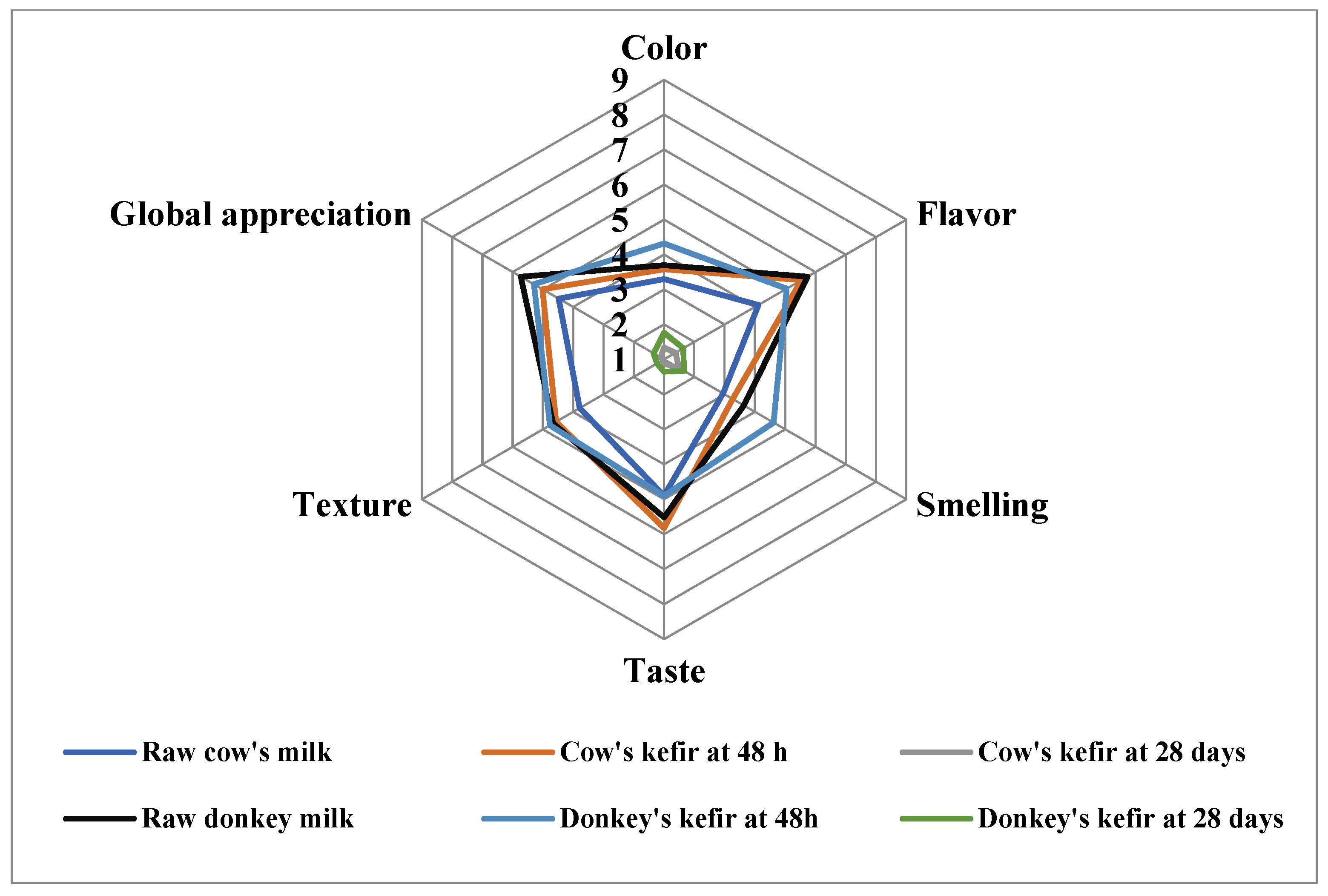
3.6. Consumer Acceptability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | donkey milk |
| CM | cow milk |
| TS | total solids |
| TAMB | total aerobic mesophile bacteria |
| TC | total coliforms |
| FC | fecal coliforms |
| Y | yeasts |
| LAB | lactic acid bacteria |
References
- Hitch, T.C.; Hall, L.J.; Walsh, S.K.; Leventhal, G.E.; Slack, E.; de Wouters, T.; Walter, J.; Clavel, T. Microbiome-based interventions to modulate gut ecology and the immune system. J. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1095–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroua, M. Caractérisation Morpho-Biométrique, Génétique et du Potentiel Laitier des Ressources Asines en Tunisie. Bachelor’s Thesis, Ecole Doctorale Sciences et Techniques de L’Agronomie et de l’Environnement, Aubière, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, A.G.; Tesse, R.; Montagna, C.; De Leo, V.; Addante, N.; Armenio, L.; Martemucci, G.J. Production of donkey milk for human feeding: Changes of the gross composition and energetic value during lactation in Martina Franca breed. Maced. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 1, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Pang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, S.; Dong, M.; Ren, F. Composition, physiochemical properties, nitrogen fraction distribution, and amino acid profile of donkey milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polidori, P.; Vincenzetti, S. The Therapeutic, Nutritional and Cosmetic Properties of Donkey Milk; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Donkey. Encycl. Dairy Sci. 2022, 108, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdak, R.; Sakoui, S.; Pop, O.L.; Muresan, C.I.; Vodnar, D.C.; Addoum, B.; Vulturar, R.; Chis, A.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A. Insights on health and food applications of Equus asinus (Donkey) milk bioactive proteins and peptides—An Overview. Foods 2020, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroccio, A.; Cavataio, F.; Montalto, G.; D’amico, D.; Alabrese, L.; Iacono, G. Intolerance to hydrolyzed cow’s milk proteins in infants: Clinical characteristics and dietary treatment. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 1598–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavita, G.; Amadoro, C.; Rossi, F.; Fantuz, F.; Salimei, E. Hygienic characteristics and microbiological hazard identification in horse and donkey raw milk. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Villoslada, F.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J. The balance between caseins and whey proteins in cow’s milk determines its allergenicity. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papademas, P.; Aspri, M.; Malissiova, E.; Fantuz, F.; Salimei, E. Donkey Milk. Encycl. Dairy Sci. 2022, 5, 522–529. [Google Scholar]
- Aroua, M.; Jemmali, B.; Ben Said, S.; Touati, I.; Mokhtar, M. Milk composition Comparison between donkey, goat and cow breeds. J. New Sci. 2018, 9, 202–206. [Google Scholar]
- Aroua, M.; Jemmali, B.; Said, S.B.; Kbaier, H.B.H.; Mahouachi, M.J.E.J.N. Physicochemical properties of north African donkey milk. Agric. Res. Technol. Open Access J. 2019, 57, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Equid milk for human consumption. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 24, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F.; Coppola, R.; Chiofalo, B.; Polidori, P.; Varisco, G. Composition and characteristics of ass’s milk. Anim. Res. 2004, 53, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Pal, Y.; Legha, R.A.; Sharma, P.; Nayan, V.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, H.; Tripathi, B. Donkey milk composition and its therapeutic applications. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 90, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Peñas, E. Fermented Foods in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780128023099. [Google Scholar]
- Ganatsios, V.; Nigam, P.; Plessas, S.; Terpou, A. Kefir as a functional beverage gaining momentum towards its health promoting attributes. Beverages 2021, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.L.; Caputo, L.R.G.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Evangelista, J.; Schneedorf, J.M. Antimicrobial and healing activity of kefir and kefiran extract. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, R.S.; Shami, A.; Ali, M.A.; Almohawes, Z.N.; Mohammed, A.E.; Bin-Meferij, M.M. Kefir: A protective dietary supplementation against viral infection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.F.; Kumar, M.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdullah, J.O.; Khalid, M.; Omar, A.R.; Osman, M.A.; Mortadza, S.A.S.; Alitheen, N.B. Kefir and its biological activities. Foods 2021, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorda, F.A.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Rakshit, S.K.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Soccol, C.R. Microbiological, biochemical, and functional aspects of sugary kefir fermentation-A review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensmira, M.; Jiang, B. Effect of some operating variables on a novel Kefir formulation’s microstructure and physical properties. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biadała, A.; Adzahan, N.M. Storage Stability of Antioxidant in Milk Products Fermented with Selected Kefir Grain Microflora. Molecules 2021, 26, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Aquilanti, L.; De Filippis, F.; Stellato, G.; Di Mauro, S.; Turchetti, B.; Buzzini, P.; Ercolini, D. Bacteria and yeast microbiota in milk kefir grains from different Italian regions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesenkaş, H.; Gürsoy, O.; Özbaş, H. Kefir. In Fermented Foods in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 339–361. [Google Scholar]
- Nejati, F.; Junne, S.; Neubauer, P. A big world in small grain: A review of natural milk kefir starters. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessas, S.; Nouska, C.; Mantzourani, I.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Alexopoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Microbiological exploration of different types of kefir grains. Fermentation 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, A.; Simonetti, A.; Gambacorta, E. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of donkey milk kefir fortified with sulla honey and rosemary essential oil during refrigerated storage. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis. In Ash of Milk (Gravimetric Method); No. 945.46; Association of Official Analytical Chemists Inc.: Washington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasempour, Z.; Alizadeh, M.; Bari, M.R. Optimisation of probiotic yoghurt production containing Zedo gum. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2012, 65, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, A.; Plessas, S.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Stefanis, C.; Vavias, S.; Voidarou, C.; Mantzourani, I.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Experimental effect of ozone upon the microbial flora of commercially produced dairy fermented products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 246, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachtarzi, N.; Amourache, L.; Dehkal, G. Qualité du lait cru destiné à la fabrication d’un fromage à pâte molle type Camembert dans une laiterie de Constantine (Est algérien) [Quality of raw milk for the manufacture of a Camembert-type soft cheese in a dairy of Constantine (eastern Algeria)]. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2015, 17, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tzavaras, D.; Papadelli, M.; Ntaikou, I. From Milk Kefir to Water Kefir: Assessment of Fermentation Processes, Microbial Changes and Evaluation of the Produced Beverages. Fermentation 2022, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbandari, J.; Golkar, A.; Taghavi, S.M.; Amiri, A. Effect of storage period on physicochemical, textural, microbial and sensory characteristics of stirred soy yogurt. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2016, 5, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Grønnevik, H.; Falstad, M.; Narvhus, J.A. Microbiological and chemical properties of Norwegian kefir during storage. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontán, M.C.G.; Martínez, S.; Franco, I.; Carballo, J. Microbiological and chemical changes during the manufacture of Kefir from cows’ milk, using a commercial starter culture. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler-Akın, M.B.; Akın, M.S. Effects of cysteine and different incubation temperatures on the microflora, chemical composition and sensory characteristics of bio-yogurt made from goat’s milk. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz-Ersan, L.; Ozcan, T.; Akpinar-Bayizit, A.; Sahin, S. Comparison of antioxidant capacity of cow and ewe milk kefirs. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3788–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouacida, S.; Koubaier, H.B.H.; Snoussi, A.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Bouzouita, N. Glucosinolate profiles by HPLC-DAD, phenolic compositions and antioxidant activity of Eruca vesicaria longirostris: Impact of plant part and origin. Mediterr. J. Chem. 2016, 5, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Han, Z.; Ji, R.; Xiao, Y.; Si, R.; Guo, F.; He, J.; Hai, L.; Ming, L.; Yi, L. Antibacterial activity of trypsin-hydrolyzed camel and cow whey and their fractions. Animals 2020, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 22935-2:2009; Milk and Milk Products—Sensory Analysis. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Cosentino, V.; Fratter, A.; Cosentino, M. Anti-inflammatory effects exerted by Killox®, an innovative formulation of food supplement with curcumin, in urology. Eur Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Hazebrouck, S. Laits de chèvre, d’ânesse et de chamelle: Une alternative en cas d’allergie au lait de vache. Innov. Agron. 2016, 52, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Aroua, M.; Ben Said, S.; Bayrem, J.; Selmi, H.; Touati, I.; Mahouachi, M. Typology and influence of the asinine breeding system on milk composition. SYLWAN 2021, 165, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Bornaz, S.; Guizani, N.; Sammari, J.; Allouch, W.; Sahli, A.; Attia, H. Physicochemical properties of fermented Arabian mares’ milk. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız-Akgül, F.; Yetişemiyen, A.; Şenel, E.; Yıldırım, Z. Microbiological, physicochemical, and sensory characteristics of kefir produced by secondary fermentation. Mljekarstvo 2018, 68, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochirkhuyag, B.; Chobert, J.-M.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Haertlé, T. Characterization of mare caseins. Identification of αS1- and αS2-caseins. Dairy J. 2000, 80, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Irigoyen, A.; Arana, I.; Castiella, M.; Torre, P.; Ibanez, F. Microbiological, physicochemical, and sensory characteristics of kefir during storage. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, O.; Mortas, M.; Atalar, I.; Dervisoglu, M.; Kahyaoglu, T. Manufacture and characterization of kefir made from cow and buffalo milk, using kefir grain and starter culture. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egito, A.; Miclo, L.; Lopez, C.; Adam, A.; Girardet, J.-M.; Gaillard, J.-L. Separation and characterization of mares’ milk αs1-, β-, κ-caseins, γ-casein-like, and proteose peptone component 5-like peptides. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawardani, T.; Sumarmono, J. Chemical and microbiological characteristics of goat milk kefir during storage under different temperatures. J. Indones. Trop. Anim. Agric. 2015, 40, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonetto, B.; Nidelet, T.; Guezenec, S.; Perez, M.; Segond, D.; Sicard, D. Interactions between Kazachstania humilis yeast species and lactic acid bacteria in sourdough. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, M.d.S.F.; da Silva, R.A.; da Silva, M.F.; da Silva, P.A.B.; Costa, R.M.P.B.; Teixeira, J.A.C.; Porto, A.L.F.; Cavalcanti, M.T.H. Brazilian Kefir-Fermented Sheep’s Milk, a Source of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Peptides. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 10, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Jeong, D.; Kim, H.; Kang, I.-B.; Chon, J.-W.; Song, K.-Y.; Seo, K.-H. Antimicrobial activity of kefir against various food pathogens and spoilage bacteria. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Orlando, P.; Fratianni, F.; Coppola, R. Isolation of components with antimicrobial property from the donkey milk: A preliminary study. Open Food Sci. J. 2010, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannot, K.; Sobel, M.L.; El Garch, F.; Poole, K.; Plésiat, P. Induction of the MexXY efflux pump in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on drug-ribosome interaction. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5341–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, P. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. R. Soc. Med. 2002, 95, 22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| g/100 g | Storage Time (Day) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | Significance | ||
| TS | Cow | 11.70 ± 0.21 | 10.42 ± 0.16 | 10.86 ± 0.04 | 9.83 ± 0.02 | 10.84 ± 0.01 | 9.75 ± 0.02 | ** |
| Donkey | 8.55 ± 0.04 | 8.27 ± 0.08 | 8.90 ± 0.09 | 8.36 ± 0.12 | 8.27 ± 0.04 | 8.14 ± 0.04 | * | |
| Significance | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| Protein | Cow | 3.07 ± 0.02 | 3.06 ± 0.06 | 3.39 ± 0.03 | 3.43 ± 0.10 | 3.37 ± 0.04 | 3.15 ± 0.09 | NS |
| Donkey | 1.52 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 0.02 | 1.53 ± 0.02 | 1.64 ± 0.02 | 1.55 ± 0.01 | 1.56 ± 0.05 | NS | |
| Significance | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| Lactose | Cow | 4.10 ± 0.65 | 3.54 ± 0.01 | 3.46 ± 0.10 | 3.44 ± 0.13 | 3.37 ± 0.19 | 3.34 ± 0.23 | * |
| Donkey | 6.13 ± 0.05 | 5.54 ± 0.15 | 4.93 ± 0.06 | 3.72 ± 0.06 | 3.71 ± 0.04 | 3.68 ± 0.01 | *** | |
| Significance | *** | *** | *** | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Fat | Cow | 3.63 ± 0.02 | 3.55 ± 0.01 | 3.54 ± 0.02 | 3.53 ± 0.01 | 3.52 ± 0.01 | 3.51 ± 0.02 | NS |
| Donkey | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 1.31 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.02 | 1.31 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.01 | NS | |
| Significance | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| Storage Time (Day) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log CFU/mL | 0 | 1 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | Significance | |
| LAB | Cow | 8.96 | 7.96 | 7.75 | 7.10 | 6.90 | 6.80 | * |
| Donkey | 8.12 | 7.67 | 7.42 | 7.2 | 6.87 | 6.80 | * | |
| Significance | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| FC | Cow | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | NS |
| Donkey | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | NS | |
| Significance | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| TC | Cow | 4.02 | 4.33 | 4.34 | 4.43 | 4.50 | 4.51 | NS |
| Donkey | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | NS | |
| Significance | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| TAMB | Cow | 4.80 | 4.85 | 4.85 | 4.86 | 4.96 | 4.97 | * |
| Donkey | 4.18 | 4.12 | 4.22 | 4.39 | 4.67 | 4.71 | * | |
| Significance | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||
| Y | Cow | 6.60 | 6.94 | 6.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ** |
| Donkey | 6.67 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.00 | *** | |
| Significance | NS | *** | *** | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Storage Time (Day) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | Significance | ||
| DPPH | Cow | 56.04 ± 7.62 | 58.7 ± 4.45 | 72.27 ± 2.55 | 76.99 ± 7.71 | 78.76 ± 5.3 | 84.95 ± 0.88 | ** |
| Donkey | 58.7 ± 7.72 | 63.71 ± 6.19 | 66.96 ± 4.87 | 68.43 ± 1.02 | 75.22 ± 6.13 | 78.76 ± 7.56 | ** | |
| Significance | NS | * | * | * | NS | * | ||
| ABTS | Cow | 88.31 ± 1.77 | 88.3 ± 0.42 | 87.32 ± 2.61 | 91.59 ± 0.88 | 91.59 ± 0.24 | 92.73 ± 0.42 | ** |
| Donkey | 86.6 ± 0.88 | 89.31 ± 1.7 | 89.74 ± 2.26 | 92.02 ± 2.1 | 93.3 ± 2.43 | 94.01 ± 2.26 | ** | |
| Significance | NS | NS | NS | * | * | * | ||
| Time (Day) | E. coli | S. aureus | A. hydrophila | P. aeruginosa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow | 0 | 5 ± 0.01 | 5 ± 0.012 | 6 ± 0.03 | 5 ± 0.01 |
| 1 | 5.5 ± 0.002 | 5 ± 0.016 | 6 ± 0.05 | 5 ± 0.029 | |
| 7 | 5.75 ± 0.04 | 6 ± 0.031 | 6 ± 0.036 | 5.5 ± 0.012 | |
| 14 | 6 ± 0.012 | 6.5 ± 0.012 | 6.5 ± 0.062 | 5.5 ± 0.023 | |
| 21 | 6 ± 0.01 | 6.5 ± 0.042 | 6.5 ± 0.031 | 5.5 ± 0.064 | |
| 28 | 6 ± 0.03 | 7 ± 0.096 | 7 ± 0.042 | 5.75 ± 0.012 | |
| Donkey | 0 | 5.5 ± 0.014 | 6 ± 0.036 | 6 ± 0.026 | 5 ± 0.012 |
| 1 | 5.75 ± 0.012 | 6.5 ± 0.031 | 6 ± 0.043 | 5 ± 0.041 | |
| 7 | 5.5 ± 0.025 | 7 ± 0.056 | 6 ± 0.082 | 5 ± 0.065 | |
| 14 | 5.5 ± 0.034 | 6.5 ± 0.011 | 6 ± 0.017 | 5 ±0.22 | |
| 21 | 6± 0.036 | 6.5 ±0.046 | 6± 0.042 | 5 ±0.036 | |
| 28 | 6.75 ± 0.012 | 6.5 ± 0.022 | 7 ± 0.016 | 5 ± 0.092 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aroua, M.; Ben Haj Koubaier, H.; Bouacida, S.; Ben Saïd, S.; Mahouachi, M.; Salimei, E. Chemical, Physicochemical, Microbiological, Bioactive, and Sensory Characteristics of Cow and Donkey Milk Kefir during Storage. Beverages 2023, 9, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010002
Aroua M, Ben Haj Koubaier H, Bouacida S, Ben Saïd S, Mahouachi M, Salimei E. Chemical, Physicochemical, Microbiological, Bioactive, and Sensory Characteristics of Cow and Donkey Milk Kefir during Storage. Beverages. 2023; 9(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleAroua, Mohamed, Hayet Ben Haj Koubaier, Saoussen Bouacida, Samia Ben Saïd, Mokhtar Mahouachi, and Elisabetta Salimei. 2023. "Chemical, Physicochemical, Microbiological, Bioactive, and Sensory Characteristics of Cow and Donkey Milk Kefir during Storage" Beverages 9, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010002
APA StyleAroua, M., Ben Haj Koubaier, H., Bouacida, S., Ben Saïd, S., Mahouachi, M., & Salimei, E. (2023). Chemical, Physicochemical, Microbiological, Bioactive, and Sensory Characteristics of Cow and Donkey Milk Kefir during Storage. Beverages, 9(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010002







