Characterization of Dadih: Traditional Fermented Buffalo Milk of Minangkabau
Abstract
1. Introduction
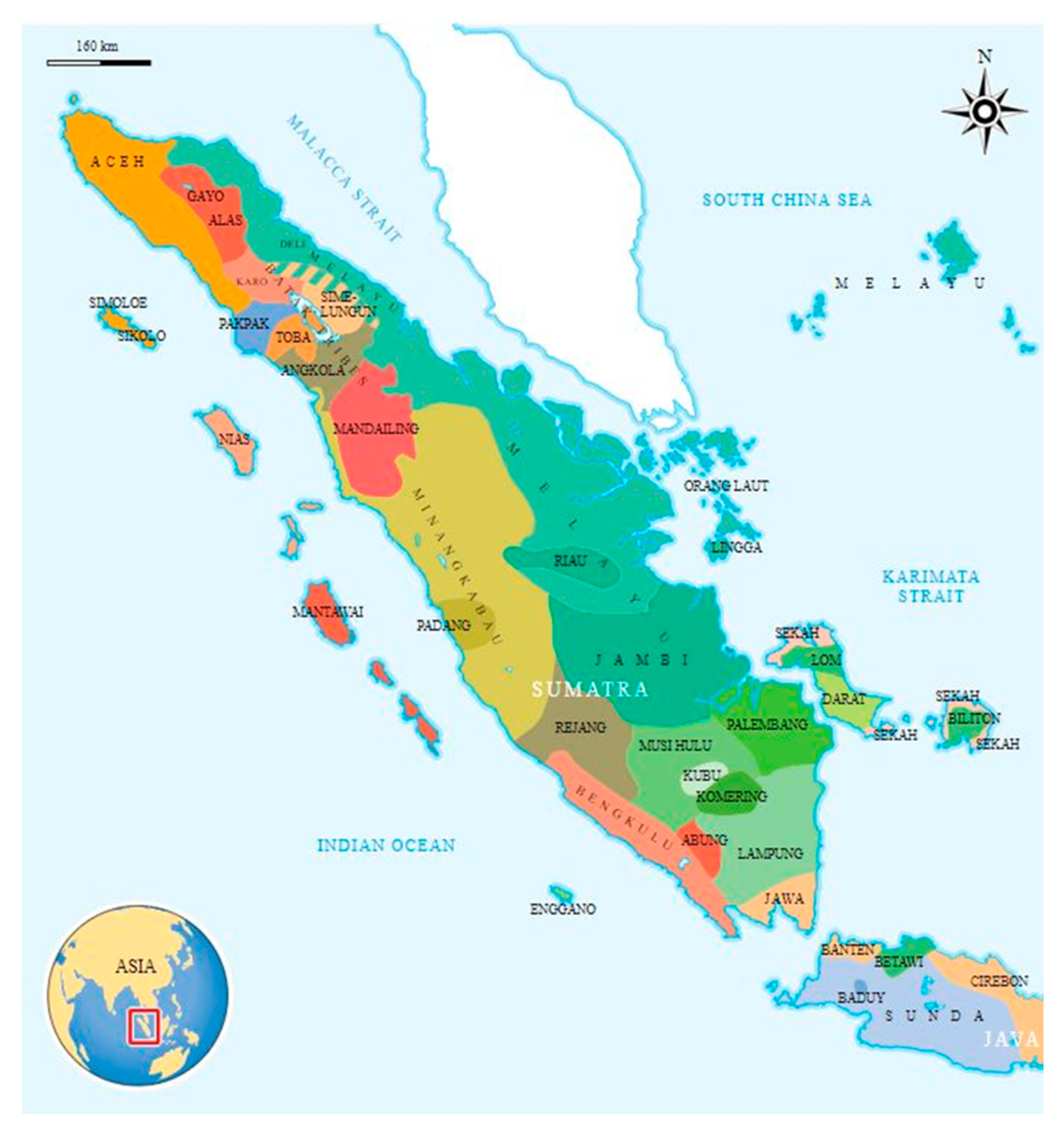
2. Buffalo, Minangkabau, and Dadih
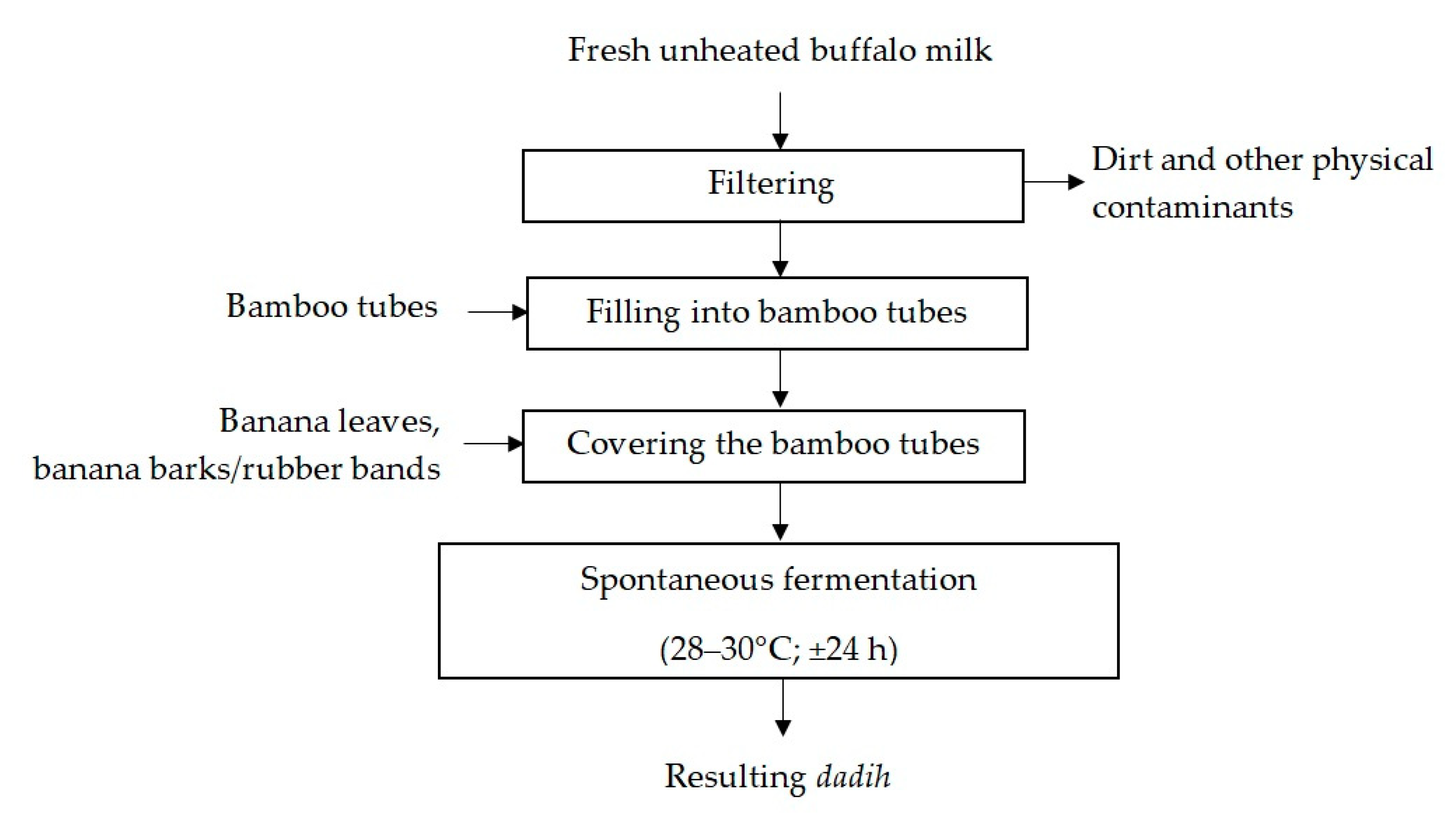
3. Processing of Traditional Dadih
4. Maturation of Dadih
5. Microbiota of Dadih
6. Nutritional Value and Chemical Analysis of Dadih
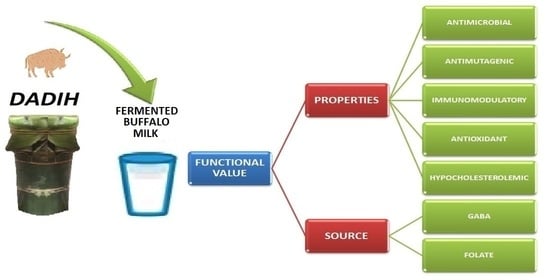
7. The Functional Value of Dadih
7.1. Antimicrobial Properties
7.2. Hypocholesterolemic Properties
7.3. Antimutagenic Properties
7.4. Antioxidant Properties
7.5. Immunomodulatory Properties
7.6. GABA—Source
7.7. Folate—Source
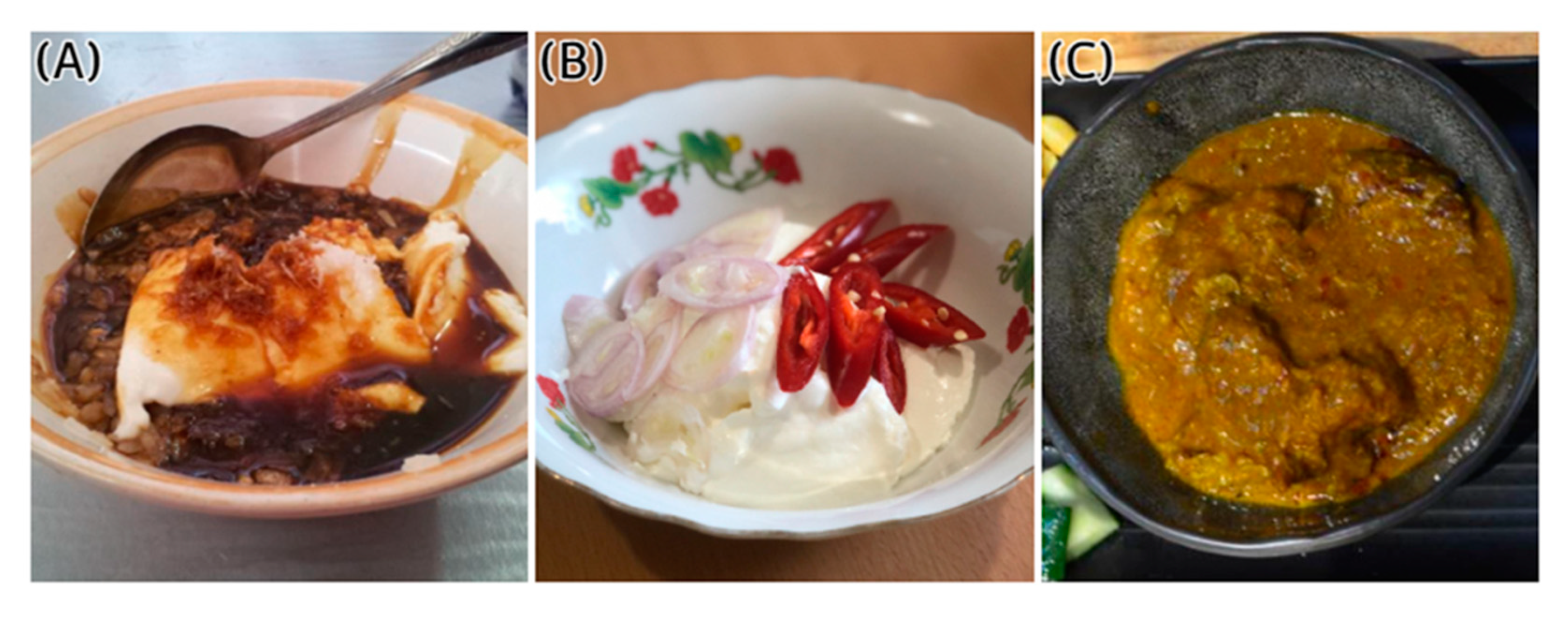
8. Dadih in the Daily Diet
9. Challenges and Future Trends of Dadih
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Statistics Indonesia. Kewarganegaraan, Suku Bangsa, Agama, Dan Bahasa Sehari-Hari Penduduk Indonesia—Hasil Sensus Penduduk 2010; BPS-Statistics Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2011.
- Wahyudi, B.A.; Octavia, F.A.; Hadipraja, M.; Isnaeniah, S.; Viriani, V. Lemang (Rice Bamboo) as a Representative of Typical Malay Food in Indonesia. J. Ethn. Foods 2017, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yovani, T. Lamang Tapai: The Ancient Malay Food in Minangkabau Tradition. J. Ethn. Foods 2019, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmufida, M.; Wangrimen, G.H.; Reinalta, R.; Leonardi, K. Rendang: The Treasure of Minangkabau. J. Ethn. Foods 2017, 4, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianti, A.; Novenia, A.E.; Christopher, A.; Lestari, D.; Parassih, E.K. Ketupat as Traditional Food of Indonesian Culture. J. Ethn. Foods 2018, 5, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S. Indonesian Dadih. In Fermented Milk and Dairy Products; Puniya, A.K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 377–399. [Google Scholar]
- Purwati, E.; Aritonang, S.N.; Melia, S.; Juliyarsi, I.; Purwanto, H. Manfaat Probiotik Bakteri Asam Laktat Dadiah Menunjang Kesehatan Masyarakat; Putra, R.M.S., Ed.; Lembaga Pengembangan Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi, Universitas Andalas: Padang, Indonesia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akuzawa, R.; Miura, T. Asian Fermented Milks. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Science, 2nd ed.; Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Helmizar, H.; Yuswita, E.; Putra, A.E. Analysis of the Nutrients and Microbiological Characteristics of the Indonesian Dadih as a Food Dupplementation. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2019, 11, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, H.; Wirasti, Y.; Purwanto, B.; Purwati, E. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Determination of Antimicrobial Activity in Dadih from Air Dingin Alahan Panjang District, Solok Regency-West Sumatera. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Pato, U. Potensi Bakteri Asam Laktat Yang Diisolasi Dari Dadih Menurunkan Kolesterol Darah. Agritech 2004, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pato, U.; Surono, I.S.; Koesnandar; Hosono, A. Hypocholesterolemic Effect of Indigenous Dadih Lactic Acid Bacteria by Deconjugation of Bile Salts. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 17, 1741–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S. In Vitro Probiotic Properties of Indigenous Dadih Lactic Acid Bacteria. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 16, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Pato, U.; Koesnandar; Hosono, A. In Vivo Antimutagenicity of Dadih Probiotic Bacteria towards Trp-P1. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapsari, A.; Legowo, A.M.; Pramono, Y.B. Total Lactic Acid Bacteria, PH Values, Soluble Protein and Antioxidant Activity of Dadih Using L. casei and L. plantarum with Different Fermentation Time. J. Appl. Food Technol. 2014, 1, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Surono, I.S.; Koestomo, F.P.; Novitasari, N.; Zakaria, F.R.; Yulianasari, K. Novel Probiotic Enterococcus Faecium IS-27526 Supplementation Increased Total Salivary SIgA Level and Bodyweight of Pre-School Children: A Pilot Study. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurliyani; Julia, M.; Harmayani, E.; Ikawati, M.; Baliarti, E. Potency of Lactobacillus plantarum Dad-13 and Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas) Fiber as Immunomodulator in Rats Infected with Salmonella typhimurium. J. Food Res. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnentis, H.; Nurmiati, N.; Marlida, Y.; Adzitey, F.; Huda, N. γ-Aminobutyric Acid Production by Selected Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolate of an Indonesian Indigenous Fermented Buffalo Milk (Dadih) Origin. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, L.; Marlida, Y.; Wizna, W.; Jamsari, J.; Mirzah, M.; Adzitey, F.; Huda, N. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of GABA-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Indigenous Dadih of West Sumatera, Indonesia. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwandhani, S.N.; Utami, T.; Milati, R.; Rahayu, E.S. Isolation, Characterization and Screening of Folate-Producing Bacteria from Traditional Fermented Food (Dadih). Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 566–572. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah; Yulika, F. Perantauan Budaya—Sejarah Minangkabau & Negeri Sembilan; Gunawan, A., Ed.; Institut Seni Indonesia Padangpanjang: Padang Panjang, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harmayani, E.; Santoso, U.; Gardjito, M. Makanan Tradisional Indonesia Seri 1—Kelompok Makanan Fermentasi Dan Makanan Yang Populer Di Masyarakat; Gadjah Mada University Press: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chandan, R.C.; Shahani, K.M. Yogurt. In Dairy Science and Technology Handbook: Product Manufacturing; Hui, Y.H., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Euroka, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Teuber, M. Fermented Milk Products. In Microbial Safety and Quality of Food; Lund, B.M., Baird-Parker, T.C., Gould, G.W., Eds.; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 535–589. [Google Scholar]
- Ginting, N. Dadih Bamboo Ampel (Bambusa vulgaris) and Bamboo Gombong (Gigantochloa verticilata) 2 and 3 Days Fermented: Effect on Salad Dressing Hedonic Quality. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 130, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azria, D. Mikrobiologi Dalam Pembuatan Dadih Susu Sapi (Microbiology of Cow Milk Dadih). Bachelor’s Thesis, Bogor Agricultural University, Bogor, Indonesia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, A.A.; Marlida, Y.; Khasrad, K.; Azhike, S.Y.D.; Wulandari, R. Perkembangan Dan Usaha Pengembangan Dadih: Sebuah Revieiw Tentang Susu Fermentasi Tradisional Minangkabau (Recent Situation and Development Efforts of Dadih: A Review of Minangkabau Traditional Fermentation Milk). J. Peternak. Indones. 2011, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Maslami, V.; Marlida, Y.; Mirnawati, J.; Nur, Y.S.; Adzitey, F.; Huda, N. A Review on Potential of Glutamate Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria of West Sumatera’s Fermented Food Origin, as Feed Additive for Broiler Chicken. J. World’s Poult. Res. 2018, 8, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Surono, I.S. Ethnic Fermented Foods and Beverages of Indonesia. In Ethnic Fermented Foods and Alcoholic Beverages of Asia; Tamang, J.P., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 341–382. [Google Scholar]
- Khedkar, C.D.; Kalyankar, S.D.; Deosarkar, S.S.; Patil, A.M. Dahi. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Finglas, P.M., Toldrà, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 345–351. [Google Scholar]
- Surono, I.S.; Hosono, A. Indigenous Fermented Foods in Indonesia. Jpn. J. Dairy Food Sci. 1995, 44, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jatmiko, Y.D.; Howarth, G.S.; Barton, M.D. Evaluation of Yeast Diversity in Dadih and Dangke Using PCR-RFLP of Internal Transcribed Spacer Region. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 391, 12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarlim, R. Potensi Lactobacillus sp. Asal Dari Dadih Sebagai Starter Pada Pembuatan Susu Fermentasi Khas Indonesia. Bul. Teknol. Pascapanen Pertan. 2009, 5, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Surono, I.S.; Nurani, D. Exploration of Indigenous Lactic Acid Bacteria from Dadih of West Sumatra for Good Starter Cultures and Probiotic Bacteria; Domestic Collaborative Research Grant Program(DCRG), URGE Project, 2000–2001; Research Report; Directorate General of Higher Education, Ministry of Education and Culture: Indonesia, 2001.
- Wirawati, C.U.; Sudarwanto, M.B.; Lukman, D.W.; Wientarsih, I. Karakteristik Dan Pengembangan Dadih Dari Susu Sapi Sebagai Alternatif Dadih Susu Kerbau (Characteristic and Development of Cow’s Milk Dadih as an Alternate of Buffalo’s Milk Dadih). WARTAZOA 2017, 27, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, A.; Wardoyo, R.; Otani, H. Microbial Flora in Dadih, a Traditional Fermented Milk in Indonesia. Leb. Technol. 1989, 22, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nuraida, L. A Review: Health Promoting Lactic Acid Bacteria in Traditional Indonesian Fermented Foods. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, A.; Wardoyo, R.; Otani, H. Binding of Amino Acid Pyrolyzates by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Dadih. Leb. Technol. 1990, 23, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wirawati, C.U.; Sudarwanto, M.B.; Lukman, D.W.; Wientarsih, I.; Srihanto, E.A. Diversity of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Dadih Produced by Either Back-Slopping or Spontaneous Fermentation from Two Different Regions of West Sumatra, Indonesia. Vet. World 2019, 12, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venema, K.; Surono, I.S. Microbiota Composition of Dadih—A Traditional Fermented Buffalo Milk of West Sumatra. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatmiko, Y.D.; Lopes, M.D.B.; Barton, M.D. Molecular Identification of Yeasts Isolated from Dadih by RFLP-PCR and Assessment on Their Ability in Utilizing Lactate. Microbiol. Indones. 2012, 6, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Hernández-Cánovas, J.D.; Guillén-López, I.; Vizcaíno-Milla, P.; Andreo-López, M.I.; Sánchez-Rubio, M.; Taboada-Rodríguez, A.; Marín-Iniesta, F. Antimicrobial Activity of Citrus spp. and Anethum graveolens Components against Candida Metapsilosis in Ranch Sauce. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, L.V.; Pinheiro, L.K.; Miguel, M.G.C.P.; Ramos, C.L.; Vilela, D.M.; Schwan, R.F. Microbial Community and Physicochemical Dynamics during the Production of ‘Chicha’, a Traditional Beverage of Indigenous People of Brazil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elida, M. Profil Bakteri Asam Laktat Dari Dadih Yang Difermentasi Dalam Berbagai Jenis Bambu Dan Potensinya Sebagai Probiotik. Master’s Thesis, Bogor Agricultural University, Bogor, Indonesia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sunaryanto, R.; Marwoto, B. Isolasi, Identifikasi, Dan Karakterisasi Bakteri Asam Laktat Dari Dadih Susu Kerbau. J. Sains dan Teknol. Indones. 2012, 14, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syukur, S.; Rijal, F.; Jamsari; Purwati, E. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria by Using 16s RRNA from Fermented Buffalo Milk (Dadih) in Sijunjung, West Sumatera. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 871–876. [Google Scholar]
- Purwati, E.; Syukur, S.; Husmaini; Purwanto, H.; Pasaribu, R.P. Molekuler Karakterisasi Bakteri Asam Laktat Isolate Dadih Air Dingin Kabupaten Solok Sumatera Barat. J. Penelit. Inov. 2014, 40, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Harlina, D. Isolasi Dan Seleksi Bakteri Asam Laktat Dari Dadih Dalam Menghasilkan Asam Glutamat. Bachelor’s Thesis, Andalas University, Padang, West Sumatra, Indonesia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Usmiati, S.; Risfaheri. Improvement of Dadih as an Indigenous Probiotic Functional Food of West Sumatra. J. Litbang Pertan. 2013, 32, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Usmiati, S.; Broto, W.; Setiyanto, H. Karakteristik Dadih Susu Sapi Yang Menggunakan Starter Bakteri Probiotik. JITV 2011, 16, 140–152. [Google Scholar]
- Taufik, E. Dadih Susu Sapi Hasil Fermentasi Berbagai Starter Bakteri Probiotik Yang Disimpan Pada Suhu Rendah: Karakteristik Kimiawi. Media Peternak. 2004, 27, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Afriani, A. Kualitas Dan Aktivitas Antimikroba Produk Dadih Susu Sapi Pada Penyimpanan Suhu Rendah. Agrinak 2012, 2, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dasril, O.; Putri, G.E.; Amar, S. Comparison of Nutritional Quality and Organoleptic of Dadih(Minangkabau Traditional Yogurt) of Cow Milk and Soy Milk as Functional Food Probiotics. Glob. J. Med. Res. 2019, 19, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayanti, M.; Thohari, I.; Purwadi, P. Manufacture of Goat Milk Dadih Incubated Using Variety of Bambooes. J. Ilmu dan Teknol. Has. Ternak 2016, 11, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnentis, H.; Marlida, Y.; Nur, Y.S.; Wizna, W.; Santi, M.A.; Septiani, N.; Adzitey, F.; Huda, N. Novel Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Indigenous Fermented Foods from West Sumatera, Indonesia. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1922–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syukur, S.; Hermansyah, A.; Fachrial, E. Probiotics and Strong Antimicrobial of Buffalo Milk Fermentation (Dadih) from Different Places in West Sumatera Indonesia. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Retnaningrum, E.; Yossi, T.; Nur’azizah, R.; Sapalina, F.; Kulla, P.D.K. Characterization of a Bacteriocin as Biopreservative Synthesized by Indigenous Lactic Acid Bacteria from Dadih Soya Traditional Product Used in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakomi, H.L.; Skyttä, E.; Saarela, M.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Latva-Kala, K.; Helander, I.M. Lactic Acid Permeabilizes Gram-Negative Bacteria by Disrupting the Outer Membrane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2001–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shouny, W.; Abo-Kamar, A.; El-Shanshoury, A.E.-R.; Ragy, S. Production of Plantarcin by Lactobacillus plantarum SR18. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2012, 1, 1488–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson, T.; Selegård, R.; Musa, A.; Hultenby, K.; Utterström, J.; Sivlér, P.; Skog, M.; Nayeri, F.; Hellmark, B.; Söderquist, B.; et al. Plantaricin NC8 Aβ Exerts Potent Antimicrobial Activity against Staphylococcus spp. and Enhances the Effects of Antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3580. [Google Scholar]
- Pato, U.; Yusuf, Y.; Fitriani, S.; Jonnadi, N.N.; Sri Wahyuni, M.; Feruni, J.A.; Jaswir, I. Inhibitory Activity of Crude Bacteriocin Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Dadih against Listeria monocytogenes. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliana, T.; Hayati, F.; Cahyana, Y.; Rialita, T.; Mardawati, E.; Harahap, B.M.; Safitri, R. Indigenous Bacteriocin of Lactic Acid Bacteria from “Dadih” a Fermented Buffalo Milk from West Sumatra, Indonesia as Chicken Meat Preservative. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 23, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pato, U.; Ali, M.; Parlindungan, A.K. Taurocholate Deconjugation and Cholesterol Binding by Indigenous Dadih Lactic Acid Bacteria. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2005, 12, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Hosono, A. Antimutagenicity of Milk Cultured with Lactic Acid Bacteria from Dadih against Mutagenic Terasi. Milchwissenschaft 1996, 51, 347–363. [Google Scholar]
- Pato, U. Bile and Acid Tolerance of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Dadih and Their Antimutagenicity against Mutagenic Heated Tauco. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 16, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuzawa, R.; Miura, T.; Kawakami, H. Bioactive Components in Caseins, Caseinates, and Cheeses. In Bioactive Components in Milk and Dairy Products; Park, Y.W., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, Iowa, 2009; pp. 217–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumaningtyas, E.; Utami, A. Antioxidant Activity of Soluble Protein from Natural Fermented Buffalo Milk. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 457, 12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Martono, P.D.; Kameo, S.; Suradji, E.W.; Koyama, H. Effect of Probiotic L. plantarum IS-10506 and Zinc Supplementation on Humoral Immune Response and Zinc Status of Indonesian Pre-School Children. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumo, P.D.; Bela, B.; Wibowo, H.; Munasir, Z.; Surono, I.S. Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 Supplementation Increases Faecal SIgA and Immune Response in Children Younger than Two Years. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantis, N.J.; Rol, N.; Corthésy, B. Secretory IgA’s Complex Roles in Immunity and Mucosal Homeostasis in the Gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.W.; Li, G.D. GABA. In Basic Neurochemistry; Brady, S.T., Siegel, G.J., Albers, R.W., Price, D.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 367–376. [Google Scholar]
- Abdou, A.M.; Higashiguchi, S.; Horie, K.; Kim, M.; Hatta, H.; Yokogoshi, H. Relaxation and Immunity Enhancement Effects of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Administration in Humans. BioFactors 2006, 26, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Gao, F.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, W.H.; Song, S.X.; Zhou, G.H. Effects of Dietary Glutamine and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid on Meat Colour, PH, Composition, and Water-Holding Characteristic in Broilers under Cyclic Heat Stress. Br. Poult. Sci. 2012, 53, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, L.; Marlida, Y.; Wizna, W.; Jamsari, J.; Mirzah, M. Optimization of Nutrient Medium for Pediococcus acidilactici DS15 to Produce GABA. J. World’s Poult. Res. 2019, 9, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, L.; Marlida, Y.; Mirzah, M.; Wizna, J.; Huda, N. Isolation and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Producing GABA from Indigenous West Sumatera Fermented Food. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2019, 9, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, R.G.; Martinez, N.R.; Playne, M.J. Synthesis and Utilisation of Folate by Yoghurt Starter Cultures and Probiotic Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 80, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, R.; Tomar, S.K. Folate: A Functional Food Constituent. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, R114–R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardjito, M.; Muliani, L.; Chayatinufus, C. Pusaka Nenek Moyang, Yang Pantas Disayang—Kuliner Minangkabau; Hardiman, I., Ed.; PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wongso, W.W. Ceritarasa William Wongso—Kumpulan Resep Alternatif; PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rezvi, S.; Putra, A.E.; Faadhila, T. In Vivo Antibacterial Activity of Dadih and Dadih Ice Cream toward Salmonella typhimurium Development. Ann. Glob. Health 2017, 83, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Statistics of Sumatera Barat Provinces. Provinsi Sumatera Barat Dalam Angka (Sumatera Barat Provinces in Figures) 2016; BPS-Statistics of Sumatera Barat Provinces: Padang, Indonesia, 2016.
- Statistics of Sumatera Barat Provinces. Provinsi Sumatera Barat Dalam Angka (Sumatera Barat Provinces in Figures) 2019; BPS-Statistics of Sumatera Barat Provinces: Padang, Indonesia, 2019.
- West Sumatra Livestock and Animal Health Department. Inseminasi Buatan, Meningkatkan Populasi Sapi. Available online: https://sumbarprov.go.id/home/news/2014-inseminasi-buatan-meningkatkan-populasi-sapi.html (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Afrizal, A. Pengaruh Pemberian Susu Bubuk Skim Terhadap Kualitas Dadih Susu Kambing (The Influence of Skim Milk Powder to the Goat Milk’s Curd Quality). J. Ilm. Fill. Cendekia 2019, 4, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Febrina, N.N.T.; Bahri, S.; Rasmi, D.A.C. Susu Segar Kambing Etawa Yang Difermentasi Dalam Bambu Betung (Dendrocalamus asper) Dan Bambu Tali (Gigantochloa apus) Sebagai Probiotik Bakteri Asam Laktat. J. Pijar MIPA 2019, 14, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfa, M.; Sugitha, I.M.; Trisna Darmayanti, L.P. Pengaruh Penambahan Skim Terhadap Karakteristik Dadih Susu Sapi Yang Dibuat Dalam Ruas Bambu Wuluh (Schizostachyum silicatum) Di Bali. J. Ilmu Dan Teknol. Pangan 2020, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisriyenni, D.; Zurriyati, Y. Kajian Kualitas Dadih Susu Kerbau Di Dalam Tabung Bambu Dan Tabung Plastik. J. Pengkaj. Dan Pengemb. Teknol. Pertan. 2004, 7, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Delfitriani; Djatna, T. Construction of Business Intelligence in Dadih Product Affective Design. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 230, 12053.
- Helmizar, H.; Surono, I.S.; Saufani, I.A. Development of Dadih Powder as a Complementary Food to Prevent Children from Stunting in West Sumatra, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 583, 12027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidistria, T.R.; Sembiring, L.; Rahayu, E.S.; Haedar, N.; Dwyana, Z. Survival of Lactobacillus plantarum Dad 13 in Probiotic Cheese Making. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 575, 12020. [Google Scholar]
- Amri, K.; Putra, A.A. Introduksi Incubator Buatan Untuk Mempersingkat Waktu Pembuatan Dadih. J. Tek. Mesin 2012, 9, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginting, N. Comparison of Isolate Dadih with Yeast Dadih in Improving Nutrition Quality of Cassava Waste (CW). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 141, 12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mammals | Percent Composition (% w/v) of Mammals’ Milk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | Casein | Whey Protein | Lactose | Ash | Total Solid | Reference | |
| Buffalo | 7.4 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 17.2 | [6,23] |
| Cow | 3.7 | 2.8 | 0.6 | 4.8 | 0.7 | 12.7 | [6,23] |
| Goat | 4.5 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 4.1 | 0.8 | 13.2 | [6,23] |
| Sheep | 7.4 | 4.6 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 1.0 | 19.3 | [6,23] |
| Mare | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 6.2 | 0.5 | 11.2 | [6,23] |
| Camel | 5.4 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 15.0 | [24] |
| Sow | 6.8 | 2.8 | 2.0 | 5.5 | ND | 18.8 | [6,23] |
| Region in West Sumatra | Types of Lactic Acid Bacteria | References |
|---|---|---|
| Bukittinggi and Padang Panjang | Lactobacillus sp., Lactococcus sp., and Leuconostoc sp. | [34] |
| Bukittinggi | Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Levilactobacillus brevis, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum, Lacticaseibacillus casei, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Leuconostoc mesenteroides | [13] |
| Lima Puluh Kota, Agam, Tanah Datar, Solok | Levilactobacillus brevis, Weissella viridescens, Lentilactobacillus buchneri, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Leuconostoc paramesenteroides, Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis, Streptococcus faecium, Streptococcus raffinolactis, Lactococcus piscium | [44] |
| Payakumbuh | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum | [45] |
| Sijunjung | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum | [46] |
| Solok | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum | [47] |
| Payakumbuh | Lactobacillus sp. | [48] |
| Palupuh | Lactobacillus sp., Lactococcus sp., Leuconostoc sp. | [40] |
| Gadut | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis | [39] |
| Kamang | Lactiplantibacillus pentosus, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Pediococcus pentosaceus, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum | [39] |
| Chemical Characteristics of Dadih | Regions of West Sumatra | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agam | Sijunjung | Solok | Tanah Datar | ||
| Protein (%) | 10.89 | 7.06 | 5.01 | 6.91 | 12.41 |
| Fat (%) | 18.00 | 8.17 | 6.50 | 7.98 | 5.70 |
| Carbohydrate (%) | 8.03 | ND | ND | ND | 14.92 |
| Water content (%) | 61.94 | 82.40 | 75.45 | 81.79 | 66.09 |
| Ash content (%) | 1.14 | 0.91 | 0.68 | 0.92 | 0.72 |
| pH | 4.33 | 4.80 | 4.74 | 4.76 | 4.55 |
| Acidity (%) | 1.70 | 1.28 | 1.17 | 1.32 | 0.51 |
| Reference | [9] | [49] | [49] | [49] | [9] |
| Chemical Characteristics of Dadih | Dadih from Other Types of Milk | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow Milk | Goat Milk | Soy Milk | |||
| Starter culture (concentration) | L. plantarum + L. acidophilus + B. bifidum (3% w/v) | L. plantarum + L. acidophilus (3% w/v) | Back-slopping method using dadih from Bukittinggi (4% w/w) | Spontaneous | Back-slopping method using dadih from Bukittinggi (4% w/w) |
| Protein (%) | 3.53 | 4.27 | 9.79 | 3.75 | 4.65 |
| Fat (%) | 10.96 | 7.59 | 7.03 | ND | 2.91 |
| Carbohydrate (%) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Water content (%) | 83.15 | 73.72 | ND | ND | ND |
| Ash content (%) | 0.90 | 0.52 | ND | ND | ND |
| pH | 3.49 | 4.29 | ND | 6.54 | ND |
| Acidity (%) | 3.45 | 0.64 | ND | 0.31 | ND |
| Reference | [51] | [52] | [53] | [54] | [53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arnold, M.; Rajagukguk, Y.V.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Characterization of Dadih: Traditional Fermented Buffalo Milk of Minangkabau. Beverages 2021, 7, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030060
Arnold M, Rajagukguk YV, Gramza-Michałowska A. Characterization of Dadih: Traditional Fermented Buffalo Milk of Minangkabau. Beverages. 2021; 7(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleArnold, Marcellus, Yolanda Victoria Rajagukguk, and Anna Gramza-Michałowska. 2021. "Characterization of Dadih: Traditional Fermented Buffalo Milk of Minangkabau" Beverages 7, no. 3: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030060
APA StyleArnold, M., Rajagukguk, Y. V., & Gramza-Michałowska, A. (2021). Characterization of Dadih: Traditional Fermented Buffalo Milk of Minangkabau. Beverages, 7(3), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030060