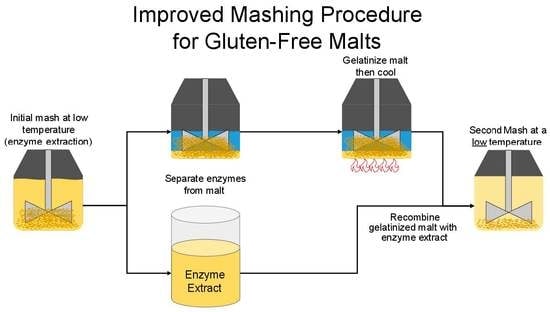
A Modified Brewing Procedure Informed by the Enzymatic Profiles of Gluten-Free Malts Significantly Improves Fermentable Sugar Generation in Gluten-Free Brewing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Teff and Sorghum Malting
2.3. General Enzyme Extraction and Assay Procedure
2.4. Determination of pH Optima of β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase
2.5. Determination of the Temperature Optima of β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase
2.6. Determination of the Thermostability of β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase
2.7. Standardization of Micromashing Experiments
2.8. Micromashing Treatments Overview
2.9. Mashing Procedure
2.10. Measuring Fermentable Sugar Output via High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography with Pulsed Amperometric Detection (HPAEC-PAD)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
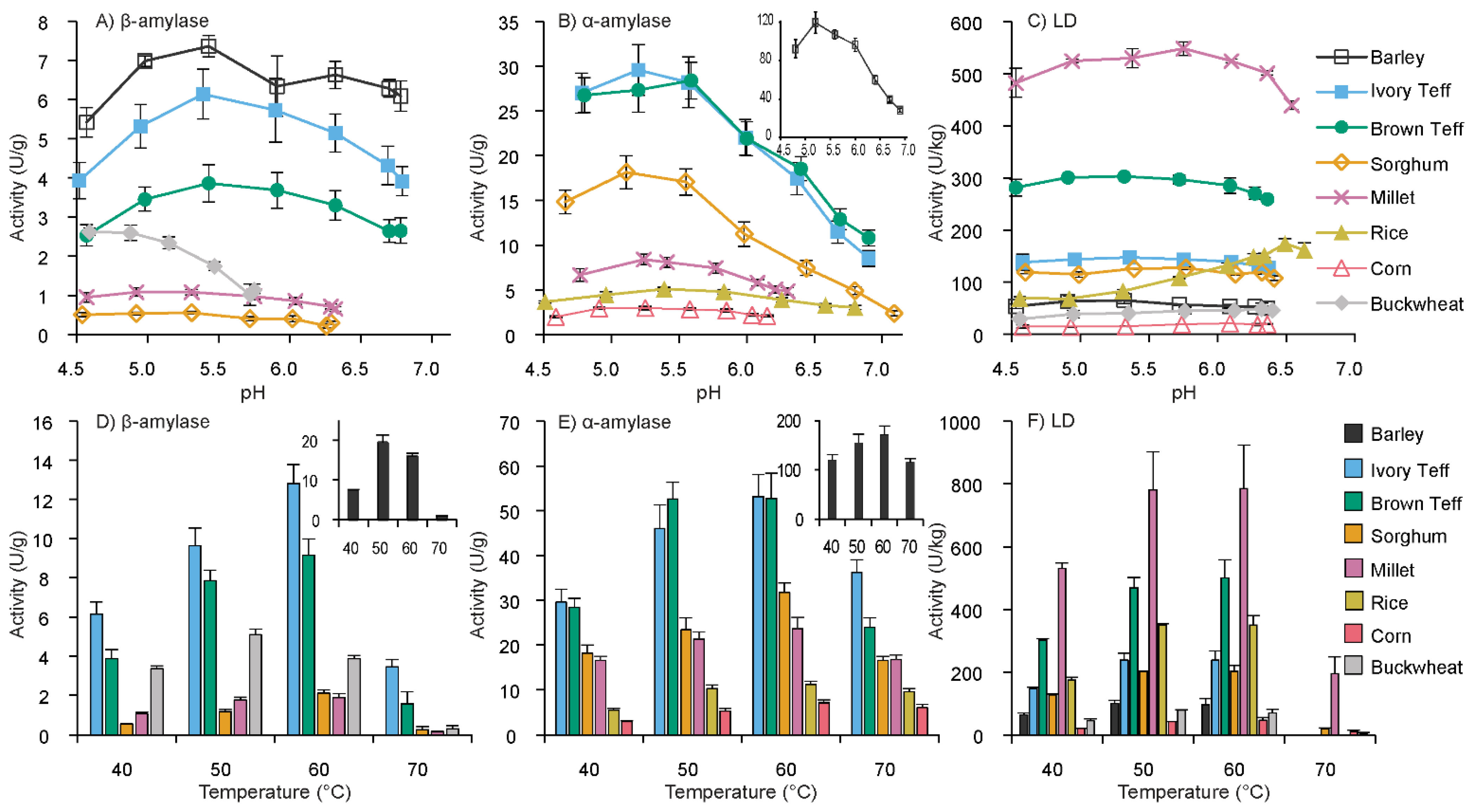
3.1. pH Optima of β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase
3.2. Temperature Optima of β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase
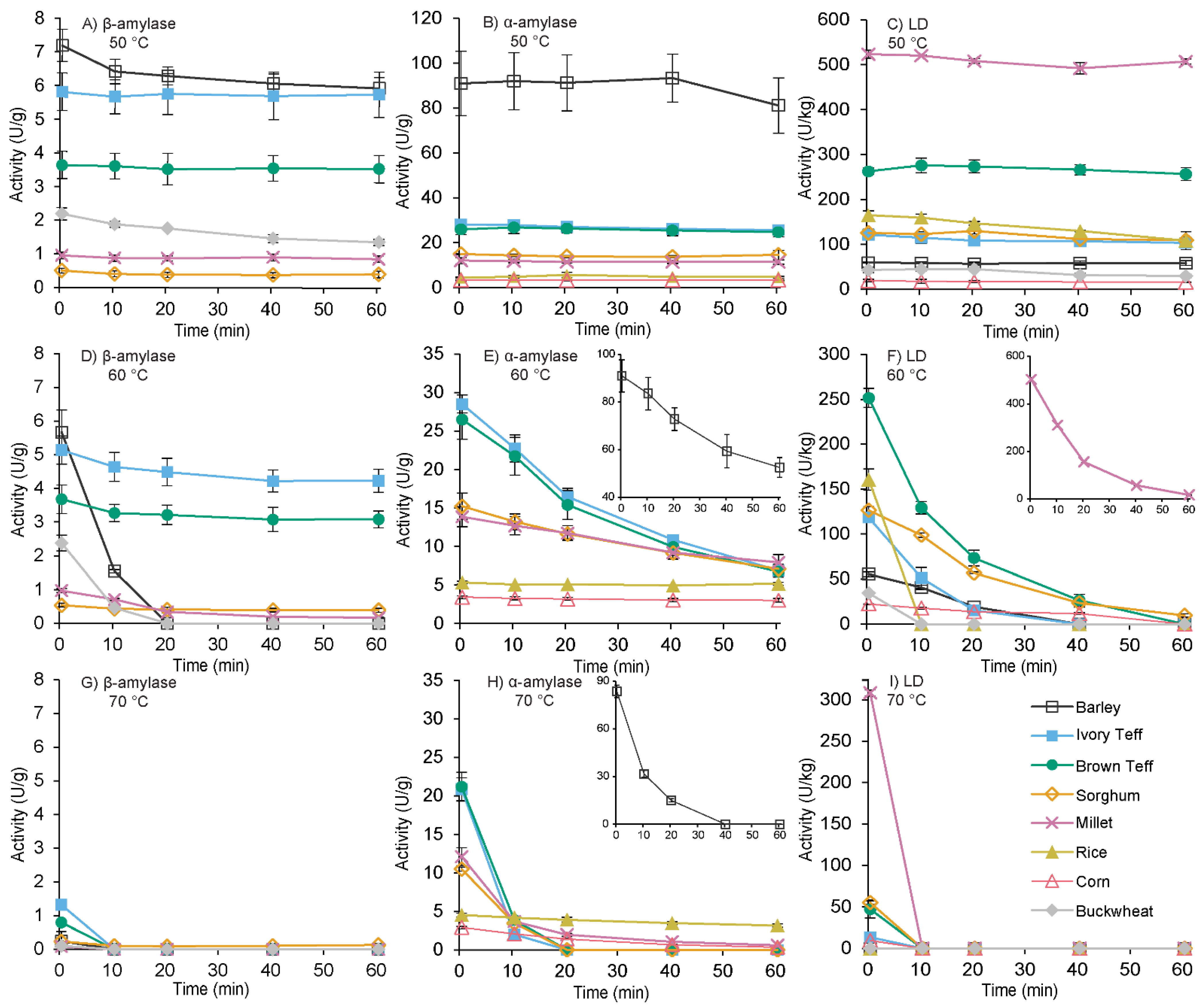
3.3. Thermostability of β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase
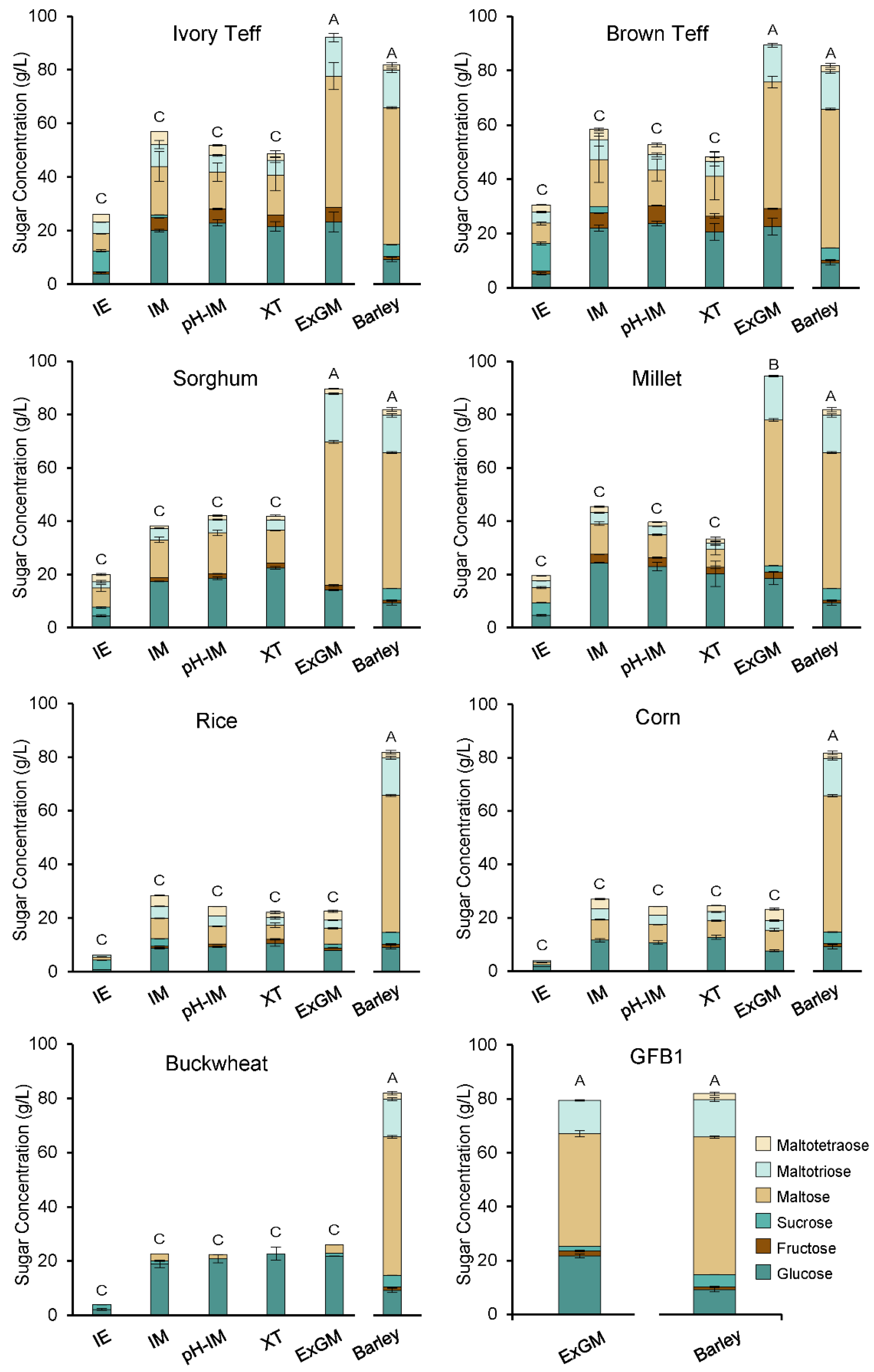
3.4. Mashing Experiments
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Supplementary Methods 1.1. Confirmation of Temperature Optima
Appendix A.2. Supplementary Results 1.1. Specific Gravity Measurements
References
- Fasano, A.; Catassi, C. Celiac Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Chávez, F.; Dezar, G.V.A.; Islas-Zamorano, A.P.; Espinoza-Alderete, J.G.; Vergara-Jiménez, M.J.; Magaña-Ordorica, D.; Ontiveros, N. Prevalence of Self-Reported Gluten Sensitivity and Adherence to a Gluten-Free Diet in Argentinian Adult Population. Nutrients 2017, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, A.-S.; Taylor, J.P.; Waters, D.M.; Arendt, E.K. Gluten free beer—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Flores, M.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O. Technological and Engineering Trends for Production of Gluten-Free Beers. Food Eng. Rev. 2016, 8, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeroyd, M.; Van Zandycke, S.; Hartog, J.D.; Mutsaers, J.; Edens, L.; Berg, M.V.D.; Christis, C. AN-PEP, Proline-Specific Endopeptidase, Degrades All Known Immunostimulatory Gluten Peptides in Beer Made from Barley Malt. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2016, 74, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, H.; Vanderputten, D.; Van Landschoot, A.; Decloedt, A. Applicability of different brewhouse technologies and gluten-minimization treatments for the production of gluten-free (barley) malt beers: Pilot- to industrial-scale. J. Food Eng. 2019, 245, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, G.J.; Colgrave, M.L.; Howitt, C.A. Gluten, Celiac Disease, and Gluten Intolerance and the Impact of Gluten Minimization Treatments with Prolylendopeptidase on the Measurement of Gluten in Beer. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2014, 72, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, K.L.; Panda, R.; Croley, T.R. Analysis of Gluten in a Wheat-Gluten-Incurred Sorghum Beer Brewed in the Presence of Proline Endopeptidase by LC/MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, K.L.; Cao, W.; Zhang, L.; Naziemiec, M.; Bedford, B.; Yin, L.; Smith, N.; Arbuckle, M.; Lopez-Hernandez, A.; Jackson, L.S. Detection of gluten in a pilot-scale barley-based beer produced with and without a prolyl endopeptidase enzyme. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.; van Wegen, B.; Ma, Y.; Eglinton, J. The Impact of the Thermostability of α-Amylase, β-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase on Potential Wort Fermentability. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2003, 61, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enevoldsen, B.S.; Schmidt, F. Dextrins in brewing. J. Inst. Brew. 1974, 80, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaroni, D.; Marconi, O.; Sileoni, V.; Wray, E.; Perretti, G. Rice malting optimization for the production of top-fermented gluten-free beer. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ghionno, L.; Marconi, O.; Lee, E.G.; Rice, C.J.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.I.F. Gluten-Free Sources of Fermentable Extract: Effect of Temperature and Germination Time on Quality Attributes of Teff [Eragrostis tef(zucc.) Trotter] Malt and Wort. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4777–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, M.M.; Zarnkow, M.; Becker, T. Effect of Drying Temperature and Time on Alpha-Amylase, Beta-Amylase, Limit Dextrinase Activities and Dimethyl Sulphide Level of Teff (Eragrostis tef) Malt. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezgebe, A.G.; Abegaz, K.; Taylor, J. Relationship between waxy (high amylopectin) and high protein digestibility traits in sorghum and malting quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nic Phiarais, B.P.; Wijngaard, H.H.; Arendt, E.K. Kilning Conditions for the Optimization of Enzyme Levels in Buckwheat. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2006, 64, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnkow, M.; Keßler, M.; Burberg, F.; Back, W.; Arendt, E.K.; Kreisz, S. The Use of Response Surface Methodology to Optimise Malting Conditions of Proso Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) as a Raw Material for Gluten-Free Foods. J. Inst. Brew. 2007, 113, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousia, Z.; Balkin, R.; Pandiella, S.; Webb, C. The effect of milling parameters on starch hydrolysis of milled malt in the brewing process. Process. Biochem. 2004, 39, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G. Chapter 16—Starch in Brewing Applications. In Starch in Food, 2nd ed.; Sjöö, M., Nilsson, L., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 633–659. [Google Scholar]
- Meo, B.; Freeman, G.; Marconi, O.; Booer, C.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. Behaviour of Malted Cereals and Pseudo-Cereals for Gluten-Free Beer Production. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewale, I.O.; Oladejo, A. Properties of the isoforms of α-amylase from kilned and unkilned malted sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.E. A More Cost- and Labor-Efficient Assay for the Combined Measurement of the Diastatic Power Enzymes β-Amylase, α-Amylase, and Limit Dextrinase. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2008, 66, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornaggia, C.; Evans, D.E.; Draga, A.; Mangan, D.; McCleary, B.V. Prediction of potential malt extract and beer filterability using conventional and novel malt assays. J. Inst. Brew. 2019, 125, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Clerck, J. A Textbook of Brewing; Siebel Institute of Technology: Chicago, IL, USA, 1994; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Langenaeken, N.A.; De Schepper, C.F.; De Schutter, D.P.; Courtin, C.M. Different gelatinization characteristics of small and large barley starch granules impact their enzymatic hydrolysis and sugar production during mashing. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, S.; Husson, F. SensoMineR: A package for sensory data analysis. J. Sens. Stud. 2008, 23, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A. The Advantages of Using Natural Substrate-Based Methods in Assessing the Roles and Synergistic and Competitive Interactions of Barley Malt Starch-Degrading Enzymes. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, C.W. Barley and malt starch in brewing: A general review. Tech. Q. Master Brew. Assoc. Am. 2003, 40, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Stenholm, K.; Home, S. A New Approach to Limit Dextrinase and its Role in Mashing*. J. Inst. Brew. 1999, 105, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schepper, C.; Michiels, P.; Buvé, C.; Van Loey, A.; Courtin, C. Starch hydrolysis during mashing: A study of the activity and thermal inactivation kinetics of barley malt α-amylase and β-amylase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnkow, M.; Keßler, M.; Back, W.; Arendt, E.K.; Gastl, M. Optimisation of the Mashing Procedure for 100% Malted Proso Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) as a Raw Material for Gluten-free Beverages and Beers. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijngaard, H.; Arendt, E. Optimisation of a Mashing Program for 100% Malted Buckwheat. J. Inst. Brew. 2006, 112, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstrepen, K.J.; Derdelinckx, G.; Dufour, J.-P.; Winderickx, J.; Thevelein, J.; Pretorius, I.; Delvaux, F.R. Flavor-active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, O.S.; Stewart, G.G. Sugar uptake and subsequent ester and higher alcohol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Inst. Brew. 1998, 104, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, J.M.; Loureiro-Dias, M.C. Reversible loss of affinity induced by glucose in the maltose-H+ symport of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 856, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernandes, J.R.; Williams, J.W.; Russell, I.; Stewart, G.G. Effect of yeast adaptation to maltose utilization on sugar uptake during the fermentation of brewer’s wort. J. Inst. Brew. 1993, 99, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ghionno, L.; Sileoni, V.; Marconi, O.; De Francesco, G.; Perretti, G.I.F. Comparative study on quality attributes of gluten-free beer from malted and unmalted teff [Eragrostis tef (zucc.) trotter]. LWT 2017, 84, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic Phiarais, B.P.; Mauch, A.; Schehl, B.D.; Zarnkow, M.; Gastl, M.; Herrmann, M.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Processing of a Top Fermented Beer Brewed from 100% Buckwheat Malt with Sensory and Analytical Characterisation. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarni, A.; Miller, K.V.; Block, D.E. A Multi-Parameter, Predictive Model of Starch Hydrolysis in Barley Beer Mashes. Beverages 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inactivated Enzymes (IE) | Infusion Mash (IM) | pH-Adjusted Infusion Mash (pH-IM) | Extended Time Infusion Mash (XT) | ExGM Decoction (ExGM) | |
| Liquor-to-Grist Ratio (3:1) | 15 mL Mashing Water: 5 g Malt Flour | ||||
| Total Volume | 30 mL | ||||
| Mashing Schedule | |||||
| Strike Temperature (°C) | 80 | 80 | 80 | 70 | 70 |
| Initial Mashing Temp (°C) | 65 | 65 | 65 | 55 | 55 |
| pH Adjustment to ~5.3 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Stage 1 | Bring to 99 °C for 1.5 min | 1 h 65 °C | 1 h 65 °C | 2 h 45 min 55 °C | (enzyme extraction) 30 min 55 °C |
| Stage 2 | Cool to 65 °C | - | - | - | Separate enzyme extract from grain Gelatinize and cool grain Recombine extract with gelatinized grain |
| Stage 3 | 1 h 65 °C | - | - | - | 2 h 55 °C |
| End Mash | Bring to 80 °C, centrifuge, and decant 1st wort into sterile 50 mL conical tube | ||||
| Sparge | Sparge remaining water in two batches Hold Sparge water and wort fractions >70 °C Centrifuge each batch sparge and combine 2nd and 3rd fractions with the 1st wort | ||||
| Boil | Bring collected wort to 100 °C for 1.5 min | ||||
| Malt | Reported Gelatinization Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Barley | 56–62 [25] |
| Teff | 66–78 [3] |
| Millet | 64–72 [17] |
| Sorghum | 71–80 [4] |
| Rice | 61–72 [3] |
| Corn | 64–75 [3] |
| Buckwheat | 67–74 [32] |
| Sample | Specific Gravity @20 °C | Glucose (g/L) | Fructose (g/L) | Sucrose (g/L) | Maltose (g/L) | Maltotriose (g/L) | Maltotetraose (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barley | 1.046 ± 0.001 | 9.18 ± 0.78 c | 1.12 ± 0.14 d | 4.42 ± 0.08 a | 51.08 ± 0.41 a | 13.93 ± 0.62 b, c | 2.18 ± 0.68 a |
| Ivory Teff | 1.052 ± 0.001 | 23.13 ± 3.77 a | 5.48 ± 0.03 b | n.d. d | 49.11 ± 5.08 a, b | 14.40 ± 1.55 b, c | n.d. b |
| Brown Teff | 1.049 ± 0.001 | 22.53 ± 3.07 a, b | 6.61 ± 0.23 a | n.d. d | 46.65 ± 2.15 a, b | 13.59 ± 0.73 b, c | n.d. b |
| Sorghum | 1.048 ± 0.001 | 14.09 ± 0.23 b, c | 1.71 ± 0.32 c, d | n.d. d | 53.97 ± 0.57 a | 18.03 ± 0.32 a | 1.93 ± 0.14 a |
| Millet | 1.041 ± 0.000 | 18.54 ± 2.21 a, b | 2.38 ± 0.12 c | 2.35 ± 0.05 b | 54.72 ± 0.52 a | 16.47 ± 0.21 a, b | n.d. b |
| GFB1 | 1.043 ± 0.001 | 21.70 ± 0.64 a, b | 1.87 ± 0.25 c, d | 1.86 ± 0.00 c | 41.74 ± 1.08 b | 12.31 ± 0.26 c | n.d. b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ledley, A.J.; Elias, R.J.; Hopfer, H.; Cockburn, D.W. A Modified Brewing Procedure Informed by the Enzymatic Profiles of Gluten-Free Malts Significantly Improves Fermentable Sugar Generation in Gluten-Free Brewing. Beverages 2021, 7, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030053
Ledley AJ, Elias RJ, Hopfer H, Cockburn DW. A Modified Brewing Procedure Informed by the Enzymatic Profiles of Gluten-Free Malts Significantly Improves Fermentable Sugar Generation in Gluten-Free Brewing. Beverages. 2021; 7(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLedley, Andrew J., Ryan J. Elias, Helene Hopfer, and Darrell W. Cockburn. 2021. "A Modified Brewing Procedure Informed by the Enzymatic Profiles of Gluten-Free Malts Significantly Improves Fermentable Sugar Generation in Gluten-Free Brewing" Beverages 7, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030053
APA StyleLedley, A. J., Elias, R. J., Hopfer, H., & Cockburn, D. W. (2021). A Modified Brewing Procedure Informed by the Enzymatic Profiles of Gluten-Free Malts Significantly Improves Fermentable Sugar Generation in Gluten-Free Brewing. Beverages, 7(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7030053