Abstract
There is an increasing demand for non-dairy probiotic carriers such as fruit and vegetable juices. Probiotic Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis is predominantly used in the bakery industry, and its efficacy in fruit juices has not been studied sufficiently. Additionally, support from the carrier matrices for maintaining probiotic viability and gastrointestinal tolerance is important in selecting suitable vehicles for probiotic delivery. Three different non-dairy carrier juices (apple, orange and tomato) were tested for their ability to maintain L. sanfranciscensis viable during four weeks of refrigerated storage (4 °C). Their potential protection of L. sanfranciscensis against in vitro gastrointestinal digestion was also evaluated. Results indicated that the probiotics viability in all three juice samples met the recommended level for probiotic food (>106–107 cfu/mL) at the end of storage. However, all three juice samples showed a comparatively lower protective effect (p < 0.05) on the viability of L. sanfranciscensis when exposed to simulated gastric juice (pH = 2) at the end of 60 min and simulated intestinal juice with 0.3% (w/v) bile salt (pH = 8) at the end of 240 min exposure. In general, the three tested juices can be regarded as the potential non-dairy based carriers for L. sanfranciscensis. The future research is needed to improve the modification of the probiotic carriers in order to prolong the viability of L. sanfranciscensis during the gastrointestinal digestion.
1. Introduction
Probiotics are living microorganisms that can benefit host’s health when consumed in adequate amounts [1]. Due to the adhesion and aggregation ability of probiotic bacteria, they can also assist in a build-up of protective barriers in the human gastrointestinal track (GIT) against pathogens and regulate the composition of gut microflora contributing to better gut health [2,3]. Over the past few decades, probiotics have been reported to have therapeutic effects on a variety of intestinal problems such as diarrhea, digestive disorders, inflammatory bowel disease and some other related diseases [4,5]. In addition to improving gastrointestinal health, probiotics have also been associated with enhancing immune function, reducing blood pressure and preventing urogenital infections [3,6,7]. Probiotics were also associated with playing a major role in bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain by significant lowering of depressive symptoms [8].
Due to the potential health benefits of probiotic consumption, development of probiotic food products has been a focus for food scientists, manufacturers and consumers in recent decades. Probiotic food products are defined as functional foods that have the ability to enhance the health status of the consumer or reduce the risk of certain diseases [9]. At present, the common probiotic foods on the market include various dairy and several fermented fruits and vegetable products, which have taken a large share of the global market [10]. The worldwide probiotics market value was estimated to be around $36.6 billion in 2015 and is expected to grow to $64 billion by 2023 [11]. Moreover, it was reported that the annual growth rate of probiotic products increased rapidly in North America and Eastern Europe by 25% and 18%, respectively [12]. The most commonly used probiotic species for commercial products are lactobacilli, which accounted for more than 60% of the world probiotic food market in 2007 [13].
While there is a plethora of probiotic foods developed and sold currently, non-dairy probiotic foods still have a relatively small market share. However, the demand for non-dairy-based probiotic products has been growing widely as an alternative for dairy probiotic foods [14]. Recent studies have indicated that fruit and vegetable juices are suitable carriers for probiotics [15,16,17]. This is primarily due to the fruit juice contains high amount of sugars (providing energy sources for probiotics), relatively low pH (suitable environmental medium) and relatively high total antioxidant content prolonging product shelf life [18]. Furthermore, the taste of fruit juices (sweet/sour) also improves the consumer acceptance of the products as a method of probiotic delivery [16]. Moreover, the treatment of vegetables during juice production can potentially increase the release of nutrients and antioxidants [19] creating an ideal environment for probiotics growth [20]. This is also supported by the juices relatively short transit time through the GIT, which can greatly reduce the adverse effects of gastric environment on probiotics [10]. At present, several fruit and vegetable-based juices have been developed to incorporate the probiotics formulations, including apple [21,22], carrot [23], tomato [15], pineapple [17] and plum juices [24].
Despite a variety of different probiotic foods currently available, maintaining a high survival rate of probiotics during processing, storage and ingestion is still a concern for food scientists and manufacturers [9]. According to a study by Boylston et al. [25], in order to achieve the potential health effects, active probiotic food is required to contain a recommended minimum viability level (106 log cfu/mL or g of food carriers) at the time of consumption. Although the buffering effect of fruit and vegetable juices is capable to alleviate the negative impacts of adverse environmental changes (temperature, gastric juices, bile salts), there are also differences that will be impacted by the types of juices included as a carrier medium and differences in probiotic species and strains [18]. Therefore, studies are required to investigate the effects that can be imposed on the final product prior to the large-scale product development containing probiotics that will remain active on the “site of action” in the GIT.
The Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis is an autochthonous species exclusively detected in sourdoughs, which plays an essential role in the fermentation of rye and wheat sourdoughs [26]. In addition, L. sanfranciscensis also contributes to the sourdough rheology and flavor properties predominately due to the strong acidification via optimized carbohydrate metabolism and the catabolism of the specific amino-acids [26,27,28]. These activities lead to the formation of exopolysaccharides and enhance the shelf life and nutritional value of the product [29]. Recent studies have indicated that the exopolysaccharides produced by L. sanfranciscensis had prebiotic activity that can enhance the growth of bifidobacteria, which was an important component of gut microflora in healthy humans [30]. L. sanfranciscensis LBH1068 previously demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects and a greater potential as a novel probiotic to treat IBD [31]. However, the studies of probiotic food containing L. sanfranciscensis are scarce and mainly focused on the sourdough. To the best of our knowledge, L. sanfranciscensis was not previously investigated for its effectiveness in the non-dairy beverages. Taking into consideration that there is a globally increasing demand for novel functional beverages and functional foods overall, investigations on applicability of these non-traditional probiotic strains in beverage manufacturing are important. Consequently, an increasing interest in the therapeutic properties of the probiotic L. sanfranciscensis via other functional foods is progressing. The aim of this study was to investigate the functional efficacy of probiotic L. sanfranciscensis in terms of viability and gastrointestinal survival in apple, orange and tomato juices as a beverage carrier matrix of probiotic delivery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Probiotics
The probiotic bacteria (Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis) was provided by the culture collection of Faculty of Veterinary and Agricultural Sciences, the University of Melbourne (Melbourne, VIC, Australia). The probiotic culture was isolated and purified by streaking on MRS agar plates (Oxoid, VIC, Australia). The purified colonies were introduced to MRS broth and incubated in an anaerobic jar at 37 °C for 36–48 h. The grown culture was then centrifuged at (2000× g, 10 min, 4 °C) and harvested cells were suspended in 200 mL 2% (w/v) sterile peptone water (Oxoid, VIC, Australia).
2.2. Probiotics Juice Prepararion
All juices used in this study; apple juice (AJ, Nudie®, VIC, Australia), orange juice (OJ, BERRI®, VIC, Australia) and tomato juice (TJ, Golden Circle™, VIC, Australia) were ultra-high temperature processed and were purchased from the local commercial source (Coles Supermarket, Melbourne, VIC, Australia). The probiotics suspension obtained in Section 2.1 was washed twice with sterile peptone water followed by centrifugation at 4 °C (2000× g, 10 min) using a laboratory-scale centrifuge (Thermoline, Wetherill Park, NSW, Australia) [32]. The pellet was collected and added to 40 mL 2% (w/v) sterile peptone water (Oxoid, VIC, Australia). This mixture was then gently shaken using a vortex mixer (Ratek, Boronia, Victoria, Australia). The obtained probiotic suspension (10 mL) was aseptically transferred to each 220 mL of the three tested juices AJ, OJ and TJ. The probiotic-fortified samples were stored in sterile containers, mixed up until there was an even distribution of probiotic culture observed and stored in refrigerator (4 °C) for 4 weeks. All analysis of the samples was conducted at least in duplicates.
2.3. The Viability of Probiotics
The viability of L. sanfranciscensis in three juices was conducted weekly during the storage of 4 weeks using serial dilution and spread plating method with MRS agar plates (Oxoid, VIC, Australia). The viability results were expressed as log cfu/mL.
2.4. pH Value and Titratable Acidity
The pH value of each sample was recorded weekly over the storage using a digital pH meter (HANNA Instruments, Vinsokite, RI, USA). The titratable acidity was performed by titrating each sample mixture (6 g of sample in 50 mL MilliQ water) with 0.1 N NaOH to pH 8.2 and expressed as a percentage of respective acid (% acid), malic for AJ and citric for OJ and TJ [33].
2.5. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Transit Tolerance Assay
Simulated gastric and small intestinal juice tolerance of three probiotic-fortified juices was measured at the end of the storage following the methods of Ranadheera et al. [32] with some modifications. Briefly, simulated gastric juice was prepared by adding pepsin (Sigma-Aldrich, Castle Hill, NSW, Australia) to 0.5% (w/v) sterile saline solution to the concentration of 3 g/L. This solution was then adjusted pH to 2.0 using 0.1 N HCl. Simulated small intestinal juice was made by adding pancreatin (Sigma-Aldrich, Castle Hill, NSW, Australia) to 0.5% (w/v) sterile saline solution to the concentration of 1 g/L, with or without 0.3% bile salt (Fluka, Castle Hill, NSW, Australia). Both types of small intestinal juices were adjusted the pH value to 8.0 with 0.1 N NaOH. Then 1 mL from each probiotic-fortified juice samples was taken and mixed with 9 mL of either gastric or small intestinal juices and the mixtures were blend evenly and stored at 37 °C. Aliquots (1 mL) of each reaction mixture were plated on MRS agar plates at 1 and 60 min for gastric juice or at 1 and 240 min for intestinal juices with all incubations performed at 37 °C. The viability of probiotics was expressed as log cfu/mL.
2.6. Data Analysis
All collected data were analyzed using Minitab statistical software (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA). The differences between the treatments, juices and storage times were analyzed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA). The differences between means were classified by Fisher’s least significance difference (LSD) test and p-value < 0.05 was used to represent statistical significance for all results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in pH Value and Titratable Acidity during Storage
The titratable acidity and pH value of AJ, OJ and TJ were presented in Figure 1. Orange juice demonstrated significantly higher (p < 0.05) acidity compared to other two types of juices throughout the storage (Figure 1a). All juices showed some reduction in pH value during the 4 weeks of storage under 4 °C, ranging from 0.2 to 0.3 (Figure 1b). As the pH value decreased, the titratable acidity of OJ and TJ was found to increase, which can potentially indicate that the amount of acid in both samples increased during 4 weeks of storage.
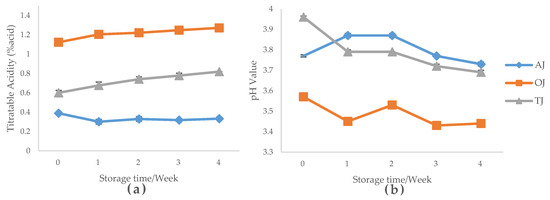
Figure 1.
The pH and titratable acidity of probiotic-fortified apple, orange and tomato juices during 4 weeks of storage under 4 °C. (a) titratable acidity changes; (b) pH value changes. AJ, probiotic-fortified apple juice; OJ, probiotic-fortified orange juice; TJ, probiotic-fortified tomato juice.
According to Tieking et al. [34], L. sanfranciscensis was able to metabolize fructose through microbial metabolism, which reduced the pH level and increased the titratable acidity of samples. This could be due to the by-products of fructose degradation caused by Lactobacillus such as acetic acid, lactic acid and carbon dioxide [35]. All these products positively contribute to the total acid content in juice samples. Similar findings were reported in a study by Kumar et al. [16] where mango and sapota juices enriched with L. plantarum showed an increase of acid content during incubation. In addition to organic acid production, another reason for the acidity increase may be due to the hydrolyzing of juice sugar induced by the released enzymes from dead probiotic cells [21].
The pH level of AJ was observed to have an increase in the first storage week and then showed a decreasing trend (p > 0.05), probably due to post-acidification. In the literature, with respect to probiotic enriched fruit juices different results were reported. For example, a study by Ding and Shah [21] reported that apple juice fortified with free probiotic lactobacilli and bifidobacteria showed a significant decreasing trend in pH during 6 weeks of storage. One possible reason of the pH changes of these juices during storage can be due to microbial metabolism such as conversion of malic acid to lactic acid that can be induced by probiotics [36].
3.2. The Viability of Probiotics during Storage
The viability of L. sanfranciscensis in all three juices (Figure 2) were observed to significantly decrease (p < 0.05) at the end of the 4 weeks of storage at 4 °C. The difference in viable numbers of probiotics between the start and at the end of the 4 weeks of storage were 0.52, 0.18 and 0.53 log cfu/mL for AJ, OJ and TJ, respectively. These findings were further supported with the research of Ding and Shah [21] where probiotic lactobacilli were added to apple and orange juice and reported a significant decreasing trend in their numbers in both juices during 5 weeks of storage at 4 °C. Our findings indicate that there was a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in the probiotic viability of AJ and TJ after the second week of storage. One possible reason was that the increasing content of lactic acid due to probiotic growth in the first 2 weeks lowered the acidity of juices, which influenced the subsequence viability of the probiotics. Furthermore, the most stable viability was found in OJ, with only a significant decline (p < 0.05) between the first and second storage week, which was in contrast to the findings from Ding and Shah [21] study. This may be due to the lower initial pH level of OJ, which can potentially increase the tolerance of L. sanfranciscensis to acidic environments [37]. Therefore, the production of organic acids in this case appeared not to have the adverse effect on the growth of probiotic bacteria. Nevertheless, this result will require more in-depth analysis and verification before these statements can be considered as potential mechanisms of action. Despite the reduction in probiotics numbers, all three juice samples met the recommended viability level (>106 cfu/mL) of probiotic food after 4 weeks storage. Therefore, all three juices (AJ, OJ and TJ) can be regarded as the suitable food carriers for L. sanfranciscensis while OJ has shown to be the most effective substrate for L. sanfranciscensis delivery.
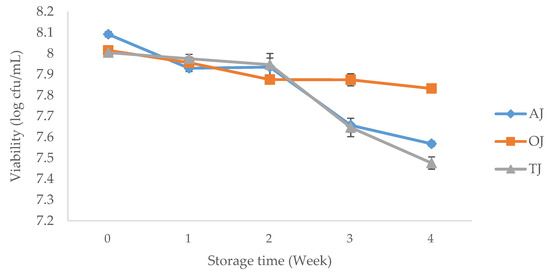
Figure 2.
The viability of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis during 4 weeks of storage under 4 °C. AJ, probiotic-fortified apple juice; OJ, probiotic-fortified orange juice; TJ, probiotic-fortified tomato juice.
3.3. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Transit Tolerance Assay
The results of in vitro simulated gastric juice tolerance assay were shown in Table 1. All three juice samples showed a significant reduction (All p’s < 0.05) in the viability of probiotics after 60 min of exposure to simulated gastric juice. Interestingly, there was no significant decrease in the probiotic viability in AJ between 0 and 1 min (p > 0.05). Furthermore, after 60 min of digestion, the reduction in viable number in AJ (5.39 log cfu/mL) was the smallest while the largest was in TJ (5.92 log cfu/mL). These reductions are potentially caused by the harsh condition of simulated gastric juice. The acidic environment activates digestive enzymes such as pepsin [37]. This enzyme can destroy the peptide bond between amino acids and potentially degrade the cell membrane of probiotics and effectively destroy them. Moreover, according to a study by Ganzle et al. [38], the most suitable pH for the growth of L. sanfranciscensis was 5.5, indicating that this probiotic bacteria has a low acid resistance. Although the initial juices had a relatively lower pH level, the acid tolerance of L. sanfranciscensis did not show an effective increase, resulting in a significant decrease in viable number (All p’s < 0.05).

Table 1.
The change of viability of probiotics in fruit and vegetable juice samples in the digestion of simulated gastric juice (pH = 2).
The viability of probiotics in the absence of bile salt groups were relatively stable during 240 min of exposure to simulated small intestinal juice (Table 2). However, the viability of probiotics in the 0.3% bile salt group significantly reduced (p < 0.05) throughout 240 min exposure. These results are very similar to the findings by Ranadheera et al. [32] where it was demonstrated that the probiotics viability in goat’s milk ice cream and yogurt were significantly lower in the group with 0.3% bile salt than that without bile salts in vitro. The major component of simulated small intestinal juice is pancreatin, which can only continue to digest the small molecular protein that are degraded by pepsin. Therefore, in this assay, pancreatin’s damage to probiotics was not significant. In addition, the reason for the viability reduction under 0.3% bile salt can also be potentially explained by bile acid composition. As surfactants, bile acids can emulsify the fats and oils into micelles and separate them from the rest part of food and waiting for the further digestion. This function can also pose an effect on probiotic’s cell membrane and degrade them. The findings of our study indicate that the lowest reduction of viability was noted in OJ (decrease of 3.8 log cfu/mL), followed by TJ (decrease by 4.06 log cfu/mL). This can indicate that OJ had a better protective effect than other juices on L. sanfranciscensis against simulated intestinal juice digestion. As fruit juices are highly popular among consumers as non-dairy products [39,40], selection of most suitable fruit juice carriers in terms of probiotic efficacy would be highly beneficial for both consumers and the beverage industry.

Table 2.
The change of viability of probiotics in fruit and vegetable juice samples in the digestion of simulated small intestinal juice (with and without bile salt) (pH = 8).
4. Conclusions
In this study, the ability of apple, orange and tomato juices as probiotic carriers during 4 weeks of storage at 4 °C as well as their potential protective effects on probiotics during in vitro gastrointestinal environment were evaluated. The pH value of juices indicated a decrease at the end of the 4 weeks of storage while the titratable acidity in OJ and TJ demonstrated a clear increasing trend over the storage time. Although there was a decline observed in probiotics viability in all three samples, the viable number of probiotics in each juice at the end of storage was still enough to meet the recommended viability level for probiotic food. Furthermore, all samples were found to have lower protective effects on the survival rate of L. sanfranciscensis during 60 min of exposure to simulated gastric juice and 240 min of digestion in the simulated small intestinal juice with 0.3% bile salt. In general, apple, orange and tomato juices can be regarded as the potential non-dairy food carriers for L. sanfranciscensis, which is not a typical beverage probiotic strain. However, further research is required to enhance their viability in the gastrointestinal environment and any potential health effects that these combinations might have after the consumption of products in healthy individuals.
Author Contributions
C.S.R. conceived and designed the experiments; W.Z. performed the experiments; C.S.R. and S.A. contributed reagents and materials; W.Z. and F.L. conducted the statistical analysis; C.S.R., W.Z. and F.L. wrote the first draft; C.S.R., N.N. and S.A. revised and edited the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The Research Initiatives Fund (2018), Faculty of Veterinary and Agricultural Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Australia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rijkers, G.T.; De Vos, W.M.; Brummer, R.-J.; Morelli, L.; Corthier, G.; Marteau, P. Health benefits and health claims of probiotics: Bridging science and marketing. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.U. Clinical uses of probiotics. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián Domingo, J.J. Review of the role of probiotics in gastrointestinal diseases in adults. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Engl. Ed. 2017, 40, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Martinez, E.G.; Gregorio, G.V.; Dans, L.F. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Lara, M.J.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. The role of probiotic lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and other related diseases: A systematic review of randomized human clinical trials. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, G.W.; McFarland, L.V.; McFarland, M.; Russo, E.B. The Power of Probiotics: Improving Your Health with Beneficial Microbes; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 1-317-82496-2. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, R.A.; Versalovic, J. Probiotics and Gastrointestinal Infections. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, K.; Hu, J. Effect of probiotics on depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 2016, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarao, L.K.; Arora, M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and microencapsulation: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 344–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.V.; Vijayendra, S.V.N.; Reddy, O.V.S. Trends in dairy and non-dairy probiotic products—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6112–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Market Insights Inc. Probiotics Market Size to Exceed USD 64 Billion by 2023. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/probiotics-market-size-to-exceed-usd-64-billion-by-2023-global-market-insights-inc-578769201.html (accessed on 22 June 2019).
- Meybodi, N.M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Sohrabvandi, S.; da Cruz, A.G.; Mohammadi, R. Probiotic Supplements and Food Products: Comparison for Different Targets. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2017, 4, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Food Processing Modest Growth for Probiotic Ingredients. Available online: https://www.foodprocessing.com/articles/2008/383/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Prado, F.C.; Parada, J.L.; Pandey, A.; Soccol, C.R. Trends in non-dairy probiotic beverages. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.Y.; Woodams, E.E.; Hang, Y.D. Probiotication of tomato juice by lactic acid bacteria. J. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.V.; Sreedharamurthy, M.; Reddy, O.V.S. Probiotication of mango and sapota juices using Lactobacillus plantarum NCDC LP 20. Nutrafoods 2015, 14, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.G.M.; Fonteles, T.V.; de Jesus, A.L.T.; Rodrigues, S. Sonicated pineapple juice as substrate for L. casei cultivation for probiotic beverage development: Process optimisation and product stability. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shori, A.B. Influence of food matrix on the viability of probiotic bacteria: A review based on dairy and non-dairy beverages. Food Biosci. 2016, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouws, C.A.; Georgouopoulou, E.; Mellor, D.D.; Naumovski, N. The Effect of Juicing Methods on the Phytochemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of the Purple Prickly Pear (Opuntia ficus indica)—Preliminary Findings on Juice and Pomace. Beverages 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.A.; de Souza, V.M.; Bergamini, A.M.M.; Martinis, E.C.P.D. Microbiological quality of ready-to-eat minimally processed vegetables consumed in Brazil. Food Control 2011, 22, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.K.; Shah, N.P. Survival of Free and Microencapsulated Probiotic Bacteria in Orange and Apple Juice. Int. Food Res. J. 2008, 2, 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, T.C.; Madrona, G.S.; Garcia, S.; Prudencio, S.H. Probiotic viability, physicochemical characteristics and acceptability during refrigerated storage of clarified apple juice supplemented with Lactobacillus paracasei ssp. paracasei and oligofructose in different package type. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Sada, A.; Orlando, P. Synbiotic potential of carrot juice supplemented with Lactobacillus spp. and inulin or fructooligosaccharides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 2271–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, T.; Suganya, R.S. Studies on anti-diarrhoeal activity of synbiotic plums juice. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Boylston, T.D.; Vinderola, C.G.; Ghoddusi, H.B.; Reinheimer, J.A. Incorporation of bifidobacteria into cheeses: Challenges and rewards. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Corsetti, A. Lactobacillus sanfranciscoa key sourdough lactic acid bacterium: A review. Food Microbiol. 1997, 14, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Smacchi, E.; Corsetti, A. The proteolytic system of Lactobacillus sanfrancisco CB1: Purification and characterization of a proteinase, a dipeptidase, and an aminopeptidase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Mariotti, L.; Rossi, J.; Servili, M.; Fox, P.F.; Rollán, G.; Gobbetti, M. Arginine catabolism by sourdough lactic acid bacteria: Purification and characterization of the arginine deiminase pathway enzymes from Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis CB1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 6193–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.F.; Pavlovic, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Wiezer, A.; Liesegang, H.; Offschanka, S.; Voget, S.; Angelov, A.; Böcker, G.; Liebl, W. Genomic analysis reveals Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis as stable element in traditional sourdoughs. Microbial Cell Factories 2011, 10, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.M.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Caplice, N.M.; Stanton, C. Sugar-coated: Exopolysaccharide producing lactic acid bacteria for food and human health applications. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Maravilla, E.; Lenoir, M.; Mayorga-Reyes, L.; Allain, T.; Sokol, H.; Langella, P.; Sánchez-Pardo, M.E.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Identification of novel anti-inflammatory probiotic strains isolated from pulque. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranadheera, C.S.; Evans, C.A.; Adams, M.C.; Baines, S.K. In vitro analysis of gastrointestinal tolerance and intestinal cell adhesion of probiotics in goat’s milk ice cream and yogurt. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, G. Application of ultrasound and high-pressure homogenization against high temperature-short time in peach juice. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieking, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F.; Gänzle, M.G. Molecular and functional characterization of a levansucrase from the sourdough isolate Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis TMW 1.392. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 66, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, W.H.; Fred, E.B. Fermentation of fructose by Lactobacillus pentoaceticus, n. sp. J. Biol. Chem. 1920, 41, 431–450. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, A.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Jazaeri, S. Viability of probiotic bacteria and some chemical and sensory characteristics in cornelian cherry juice during cold storage. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 21, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C.P.; Gardner, N.J. Effect of storage in a fruit drink on subsequent survival of probiotic lactobacilli to gastro-intestinal stresses. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Ehmann, M.; Hammes, W.P. Modeling of growth of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis and Candida milleri in response to process parameters of sourdough fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2616–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranadheera, C.; Prasanna, P.H.P.; Vidanarachchi, J.K. Fruit juices as probiotic carriers. In Fruit Juices: Types, Nutritional Composition and Health Benefits; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 253–267. ISBN 978-1-63321-134-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ranadheera, C.; Vidanarachchi, J.; Rocha, R.; Cruz, A.; Ajlouni, S. Probiotic delivery through fermentation: Dairy vs. non-dairy beverages. Fermentation 2017, 3, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).