Quality Acceptability, Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method of Preparation of Juice Samples
2.3. Analysis of the Smoothies
2.4. Determination of Vitamin C Content
2.5. Determination of Vitamin A Content
2.6. Determination of Mineral Content
2.7. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content
2.8. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.9. Determination of the Radical Scavenging Ability (DPPH)
2.10. Determination of Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
2.11. Sensory Evaluation
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of the Juice
3.2. The Mineral and Vitamin Compositions of the Juice
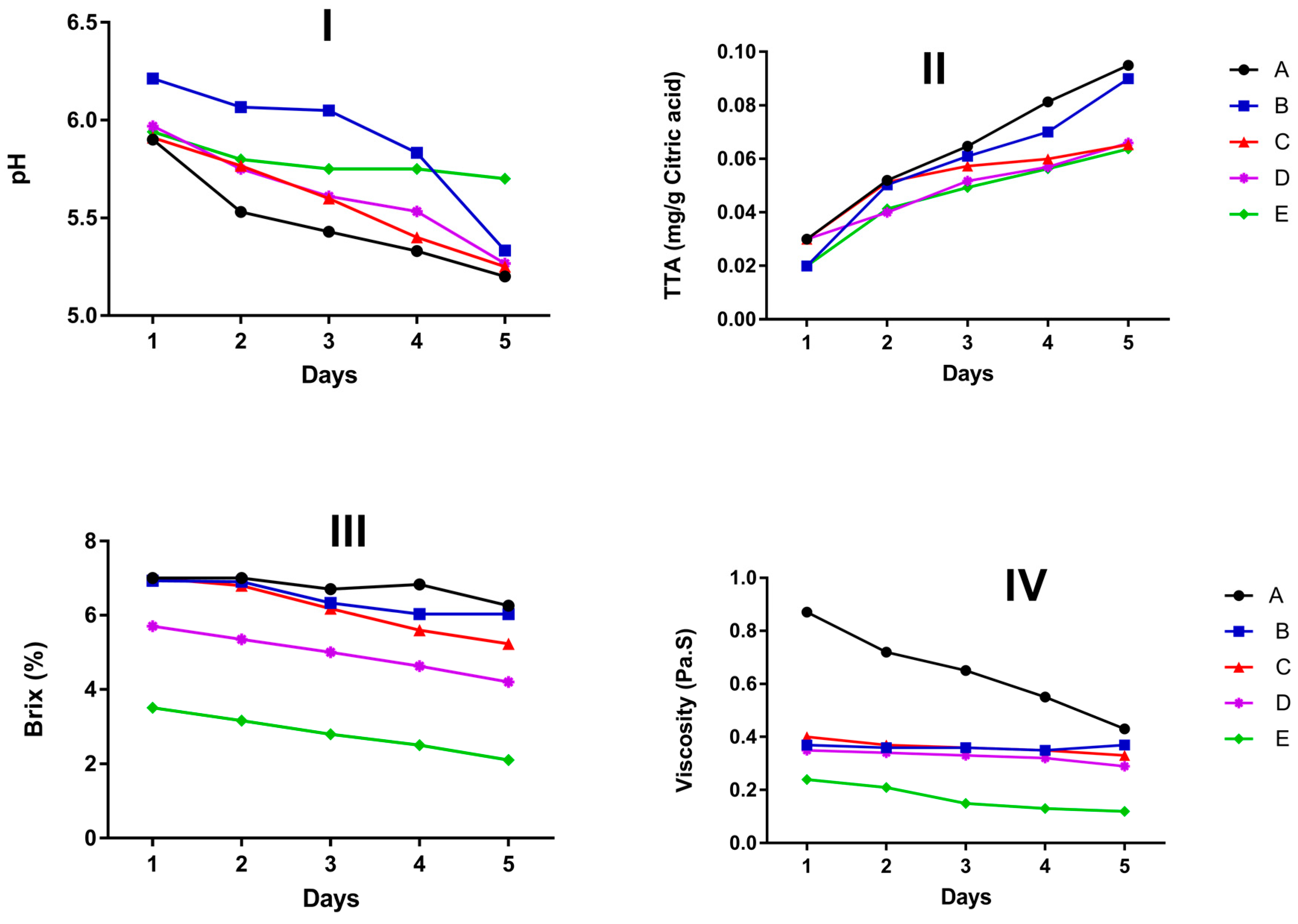
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of the Juice
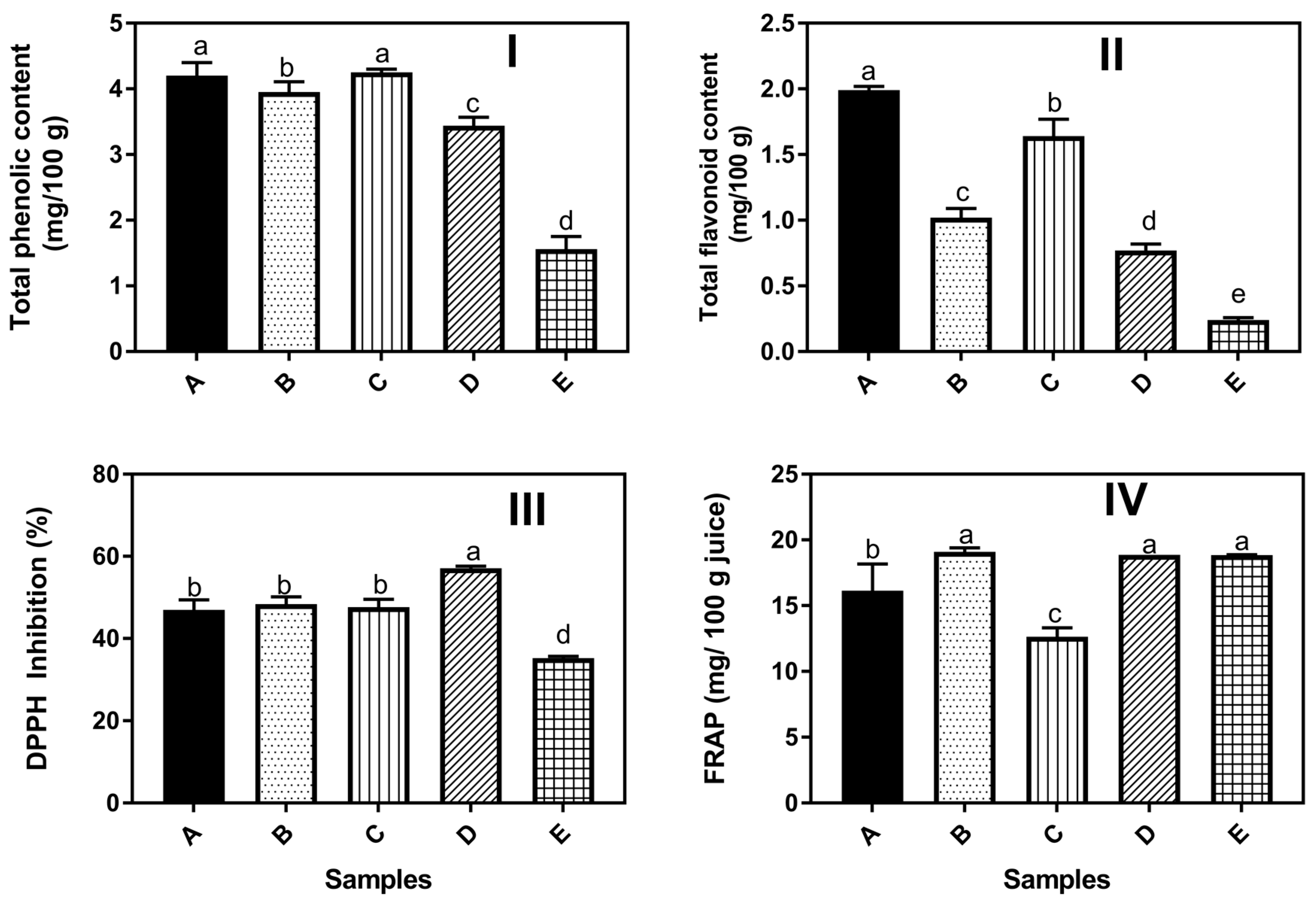
3.4. Phytochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice
3.5. Sensory Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banigo, E.B.; Kiin-Kabari, D.B.; Owuno, F. Physicochemical and sensory evaluation of soy/carrot drinks flavoured with beetroot. Afr. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Aderinola, T.A. Effects of pumpkin leaves on the chemical composition and antioxidant properties of smoothies. In Proceedings of the 4th Regional Food Science and Technology Summit (ReFoSTs), Akure, Nigeria, 6–7 June 2018; pp. 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, J.S. Nutritional Quality and Health Benefits of Vegetables: A. Review. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 1354–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Ji.; Cai, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, G.; Corke, H. Anthocyanins, Flavonols and Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Chinese Bayberry (Myrica rubra) Extracts and Their Color Properties and Stability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2327–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwori, E.; Onu, R.O.; Adamu, M.; Chindo, H.; Dikko, H.; Odunze, I. l.; Baidu, A.L.; Natala, C.; Eze, P. Production and shelf life determination of fruit/vegetable juices using watermelon, cucumber, pineapple and carrot. Afr. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullie, P.; Clarys, P. Association between Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factor Knowledge and Lifestyle. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-abasy, A.E.; Abou-gharbia, H.A.; Mousa, H.M.; Youssef, M.M. Mixes of Carrot Juice and Some Fermented Dairy Products: Potentiality as Novel Functional Beverages. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinola, T.A.; Adeniran, A.E.; Technology, A.; State, O. Effects of storage on physicochemical properties of orange-watermelon juice. Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 16, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, S.; Saghir, A.S.; Saima, M. Role of sodium benzoate as a chemical preservative in extending the shelf life of orange juice. Glob. Adv. Res. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Emelike, N.J.T.; Ebere, C.O. Effect of packaging materials, storage conditions on the vitamin C and pH value of cashew-apple (Anacardium occidentale L.) juice. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 3, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analyticl Chemists International. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC, 19th ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Benderitter, M.; Maupoi, V.; Vergely, C.I.; Dalloz, F.; Briot, F.; Rochette, L. Studies by electron paramagnetic resonance of the importance of iron in the hydroxyl scavenging properties of ascorbic acid in plasma: Effects of iron chelators. Fundam. Clin. Pharcology 1998, 12, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.; Cox, H.E. Chemical Analysis of Foods. In Chemical Analysis of Foods, 7th ed.; Churchill Ligstone: Edinburg, Hidalgo; New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi, S.M.; Ebrahinzadeh, M.A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Jafari, M. Free radical scavenging activity and antioxidant capacity of Eryngium caucasium trautv and Froripia subpinnata. Pharmacologyonline 2008, 25, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Braide, W.; Oranusi, S.U.; Otali, C.C. Nutritional, antinutritional, minerals and vitamin compositions of fourteen brands of fruit juice sold in Onitsha main market. J. Res. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Olalude, C.B.; Oyedeji, F.O.; Adegboyega, A.M. Physico-Chemical Analysis of Daucus Carota (Carrot) Juice for possible industrial applications. J. Appl. Chem. 2015, 8, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Aderinola, T.A. Nutritional, Antioxidant and Quality Acceptability of Smoothies Supplemented with Moringa oleifera Leaves. Beverages 2018, 4, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, F.; Istrati, D.; Garnai, M.; Serea, V. Study on obtaining vegetables juices with high antioxidant potential, preserved by ohmic pasteurization. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2015, 21, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Šic Žlabur, J.; Dobričević, N.; Pliestić, S.; Galić, A.; Bilić, D.; Voća, S. Antioxidant Potential of Fruit Juice with Added Chokeberry Powder (Aronia melanocarpa). Molecules 2017, 22, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderinola, T.A.; Fagbemi, T.N.; Enujiugha, V.N.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E. In vitro antihypertensive and antioxidative properties of trypsin-derived Moringa oleifera seed globulin hydrolyzate and its membrane fractions. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 0, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, B.A.; Milbury, P.E.; Blumberg, J.B. Flavonols, flavonones, flavanones and human health: Epidemological evidence. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, I.C.W.; Hollman, P.C.H. Polyphenols and disease risk in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.D.; Chang, K.S.; Huang, Y.S.; Hsu, C.L.; Lee, S.H.; Su, M.S. Principal phenolic phytochemicals and antioxidant activities of three Chinese medicinal plants. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoviadou, K.G.; Galanakis, C.M.; Brn, M.; Grimi, N.; Boussetta, N.; Mota, M.J.; Saraiva, J.A.; Patras, A.; Tiwari, B.; Barba, F.J. Fruit juice sonication: Implications on food safety and physicochemical and nutritional properties. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Cortés, C.; Esteve, M.J. Study of Antioxidant Capacity and Quality Parameters in An Orange Juice—Milk Beverage After High-Pressure Processing Treatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, P.; Wojdy, A.; Samoticha, J. Sensory attributes and changes of physicochemical properties during storage of smoothies prepared from selected fruit. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, T.; Man, G.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Liao, X. Effects of Anti-browning Combinations of Ascorbic Acid, Citric Acid, Nitrogen and Carbon Dioxide on the Quality of Banana Smoothies. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Carrot | Cucumber |
|---|---|---|
| A | 100 | - |
| B | 80 | 20 |
| C | 70 | 30 |
| D | 50 | 50 |
| E | - | 100 |
| Samples | Crude Fibre | Moisture | Total Ash | Fat | Crude Protein | Carbohydrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.96 ± 0.01 a | 82.03 ± 0.06 e | 0.83 ± 0.01 e | 2.89 ± 0.00 c | 1.75 ± 0.01 e | 10.57 ± 0.01 a |
| B | 1.66 ± 0.01 b | 83.60 ± 0.10 b | 1.98 ± 0.01 a | 1.79 ± 0.01 d | 3.28 ± 0.01 c | 7.69 ± 0.00 c |
| C | 1.65 ± 0.01 b | 83.03 ± 0.06 c | 1.01 ± 0.01 c | 1.59 ± 0.01 e | 2.37 ± 0.01 d | 10.38 ± 0.01 b |
| D | 1.23 ± 0.01 c | 83.85 ± 0.01 a | 0.87 ± 0.01 d | 3.99 ± 0.00 a | 4.80 ± 0.01 a | 5.26 ± 0.01 e |
| E | 1.15 ± 0.01 d | 82.20 ± 0.01 d | 1.59 ± 0.01 b | 3.71 ± 0.01 b | 4.14 ± 0.01 b | 7.21 ± 0.01 d |
| Samples | Calcium | Magnesium | Phosphorous | Potassium | Vit C | Vit A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3.20 ± 0.20 a | 1.10 ± 0.10 b | 4.83 ± 0.21 a | 32.10 ± 0.10 a | 14.48 ± 0.32 | 5.28 ± 0.15 |
| B | 2.15 ± 0.10 b | 0.13 ± 0.03 c | 4.81 ± 0.18 a | 31.10 ± 0.10 b | 21.07 ± 0.26 | 2.7 ± 0.05 |
| C | 1.37 ± 0.06 d | 0.16 ± 0.00 c | 4.81 ± 0.15 a | 26.50 ± 0.10 c | 24.48 ± 1.11 | 2.81 ± 0.07 |
| D | 1.71 ± 0.10 c | 0.17 ± 0.03 c | 3.40 ± 0.10 b | 21.40 ± 0.10 d | 17.71 ± 0.35 | 1.9 ± 0.03 |
| E | 1.60 ± 0.11 c | 1.40 ± 0.10 a | 2.40 ± 0.10 c | 14.70 ± 0.10 e | 15.54 ± 0.42 | 2.8 ± 0.14 |
| Samples | Taste | Appearance | Aroma | Mouthfeel | Overall Acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8.10 ± 0.99 a | 7.60 ± 1.89 a | 7.10 ± 1.52 a | 7.30 ± 1.56 a | 7.53 ± 1.05 a |
| B | 8.10 ± 0.87 a | 7.70 ± 1.76 a | 7.20 ± 1.22 a | 6.00 ± 1.69 a | 7.25 ± 0.99 a |
| C | 7.70 ± 0.94 a | 7.00 ± 1.69 a | 7.10 ± 1.28 a | 6.50 ± 2.32 a | 7.08 ± 1.03 a |
| D | 7.40 ± 0.96 a | 6.80 ± 1.22 a | 6.00 ± 1.82 a | 5.40 ± 1.50 a | 6.4 ± 1.47 a |
| E | 7.80 ± 1.13 a | 6.30 ± 1.82 a | 7.10 ± 2.07 a | 5.80 ± 1.54 a | 6.75 ± 1.22 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aderinola, T.A.; Abaire, K.E. Quality Acceptability, Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice. Beverages 2019, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages5010015
Aderinola TA, Abaire KE. Quality Acceptability, Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice. Beverages. 2019; 5(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages5010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleAderinola, Taiwo Ayodele, and Kemi Elizabeth Abaire. 2019. "Quality Acceptability, Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice" Beverages 5, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages5010015
APA StyleAderinola, T. A., & Abaire, K. E. (2019). Quality Acceptability, Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Carrot-Cucumber Juice. Beverages, 5(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages5010015





