Sensory Profile, Consumer Preference and Chemical Composition of Craft Beers from Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Craft Beers and Styles
2.2. Chemical Composition of Craft Beers
2.3. Beer Color
2.4. Polyphenols and Antioxidant Analysis
2.5. Determination of Bitterness
2.6. Sensory Analysis of Craft Beers
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Craft Beer Composition and Color
3.2. Bitterness, Antioxidant Activity, and Polyphenols
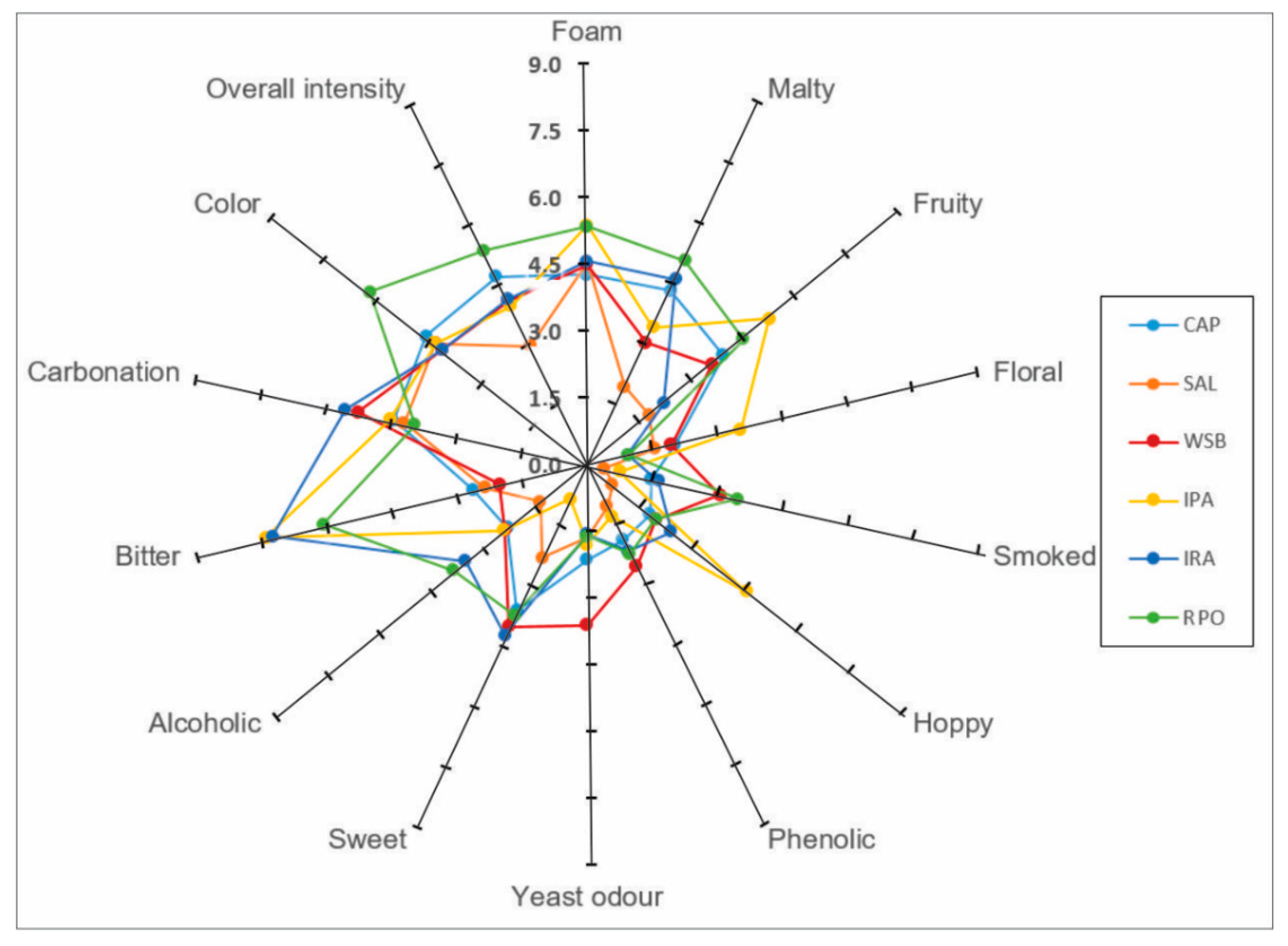
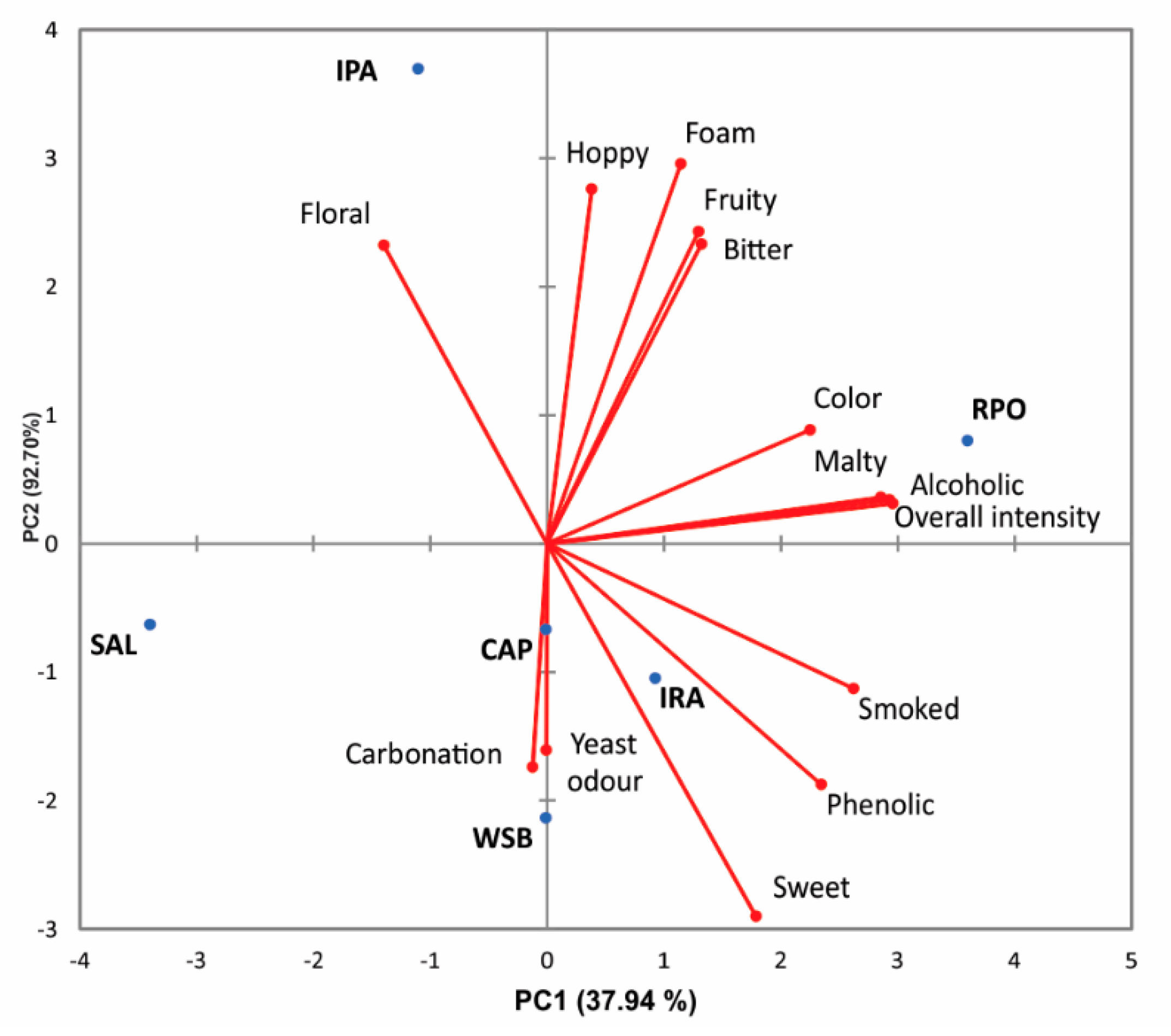
3.3. Sensory Analysis of Beers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaetano, G.; Costanzo, S.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Badimon, L.; Bejko, D.; Alkerwi, A.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Estruch, R.; La Vecchia, C.; Panico, S.; et al. Effect of moderate beer consumption on health and disease: A consensus document. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovas. 2016, 26, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura-Nunes, N.; Brito, T.C.; Fonseca, N.D.; de Aguiar, P.F.; Monteiro, M.; Perrone, D.; Torres, A.G. Phenolic compounds of Brazilian beers from different types and styles and application of chemometrics for modeling antioxidant capacity. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capece, A.; Romaniello, R.; Pietrafesa, A.; Siesto, G.; Pietrafesa, R.; Zambuto, M.; Romano, P. Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii in co-fermentations with S. cerevisiae for the production of craft beers with potential healthy value-added. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 284, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budroni, M.; Zara, G.; Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Saccharomyces and Non-Saccharomyces Starter Yeasts. In Brewing Technology; Kanauchi, M., Ed.; Intechopen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Corona, C.; Lelievre-Desmas, M.; Buendía, H.E.B.; Chollet, S.; Valentin, D. Craft beer representation amongst men in two different cultures. Food Qual. Preferences 2016, 53, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estela-Escalante, W.D.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Moscosa-Santillán, M.; González-Ramírez, J.E. Evaluation of the fermentative potential of Candida zemplinina yeasts for craft beer fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, D.; Ribeiro, L.M.; Frost, M.B. Perception and description of premium beers by panels with different degrees of product expertise. Beverages 2016, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladokun, O.; Tarrega, A.; James, S.; Smart, K.; Hort, J.; Cook, D. The impact of hop bitter acid and polyphenol profiles on the perceived bitterness of beer. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juric, A.; Coric, N.; Odak, A.; Herceg, Z.; Tisma, M. Analysis of total polyphenols, bitterness and haze in pale and dark lager beers produced under different mashing and boiling conditions. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, A.; Forte, M.; Nardini, M. Characterization of phenolics content and antioxidant activity of different beer types. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10677–10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, B.; Zhao, M. Assessment of endogenous antioxidative compounds and antioxidant activities of lager beers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quifer-Rada, P.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Martínez-Huélamo, M.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Jáuregui, O.; Estruch, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R. A comprehensive characterisation of beer polyphenols by high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS). Food Chem. 2015, 169, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilani, B.; Laureti, T.; Poponi, S.; Secondi, L. Beer choice and consumption determinants when craft beers are tasted: An exploratory study of consumer preferences. Food Qual. Preferences 2015, 41, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.H.; Vasconcelos, R.L.; Judice, V.M.M.; Neves, J.T.R. Inovação na fabricação de cervejas especiais na região de Belo Horizonte. Perspect. Ciênc. Inf. 2011, 16, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer Judge Certification Program (BJCP). 2015 Style Guidelines: Beer Style Guidelines. 2015. Available online: https://www.bjcp.org/docs/2015_Guidelines_Beer.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2018).
- Popescu, V.; Soceanu, A.; Dobrinas, S.; Stanicu, G. A study of beer bitterness loss during the various stages of the Romanian beer production process. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamede, M.; Monica, S.; Maria, J.; Cruz, J.; Oliveira, L. Avaliação sensorial e colorimétrica de néctar de uva. Braz. J. Food Nutr. 2013, 24, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Smedley, S.M. Discrimination between beers with small colour differences using the CIELAB colour space. J. Inst. Brew. 1995, 1, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, A.; Lamien, C.; Romito, M.; Millogo, J.; Nacoulma, O. Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci.Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutcosky, S.D. Análise Sensorial de Alimentos, 3rd ed.; Editora Champagnat: Curitiba, Brazil, 2013; Chapter 4; p. 356. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Chapter 4; p. 596. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, G.C.; Abner, A.S.; Silva, L.S.N.; Godoy, R.L.O.; Nogueira, L.C.; Quitério, S.L.; Raices, R.S.L. Method development by GC–ECD and HS-SPME–GC–MS for beer volatile analysis. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marongiu, A.; Zara, G.; Legras, J.; Del Caro, A.; Mascia, I.; Fadda, C.; Budroni, M. Novel starters for old processes: Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains isolated from artisanal sourdough for craft beer production at a brewery scale. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, E.; Ahn, E.; Kim, W.J. Characteristics of beer produced from Korean six-row barley with the addition of adjuncts. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Corona, C.; Valentin, D.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Chollet, S. The role of gender and product consumption in the mental representation of industrial and craft beers: An exploratory study with Mexican consumers. Food Qual. Preferences 2017, 60, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadini, G.; Fumi, M.D.; Newby-Clark, I.R. Consumer’s preference and sensory profile of bottom fermented red beers of the Italian market. Food Res. Int. 2014, 58, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadini, G.; Porretta, S. Uncovering patterns of consumers’ interest for beer: A case study with craft beers. Food Res. Int. 2017, 91, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.F.; Page, J.E. Xanthohumol and related prenylflavonoids from hops and beer: To your good health! Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.B.; Silva, P.H.A.; Minim, V.P.R. Perfil sensorial e composição físico-química de cervejas provenientes de dois segmentos do mercado brasileiro. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 23, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, D.; Frost, M.B.; Bredie, W.L.P.; Pineau, B.; Hunter, D.C.; Paisley, A.G.; Beresford, M.K.; Jaeger, S.R. Situational appropriateness of beer is influenced by product familiarity. Food Qual. Preferences 2015, 39, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Burgos, D.; Zamora, M.C. Exploring the hedonic and incentive properties in preferences for bitter foods via self-reports, facial expressions and instrumental behaviours. Food Qual. Preferences 2015, 39, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Beer Samples | Type | Beer Color | Packing | Packing Volume (mL) | Production City | Purchase Place |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAP | Lager | Yellow | Bottle | 1000 | Porto Alegre | Specialty store |
| SAL | Lager | Yellow | Can | 473 | Caxias do Sul | Supermarket |
| WSB | Lager | Yellow | Bottle | 1000 | Porto Alegre | Specialty store |
| IPA | Ale | Red | Bottle | 500 | Campo Bom | Specialty store |
| IRA | Ale | Red | Bottle | 600 | Porto Alegre | Specialty store |
| RPO | Ale | Brown | Bottle | 600 | Gramado | Specialty store |
| Style/Beer | Turbidity (NTU) | pH | Total Solids (°Brix) | Dry Extract (g/L) | Acidity (g Acetic Acid/L) | Density | Sugars (% w/v) | Ethanol (% w/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAP | 7.27 e | 4.24 c | 6.75 b,c | 4.20 d | 1.84 c | 1.0112 b | 0.9 d,e | 5.1 c |
| SAL | 1.44 f | 4.12 c | 5.75 c | 3.84 e | 1.49 d | 1.0098 b | 0.93 c,d | 5.0 c |
| WSB | 16.78 d | 3.88 d | 7 b | 4.80 c | 1.97 b | 1.0116 b | 0.95 c | 5.0 c |
| IPA | 37.77 b | 4.12 c | 7 b | 4.21 d | 1.97 b | 1.0084 b | 0.86 e | 6.2 b |
| IRA | 29.14 c | 4.33 a,b | 7.75 b | 5.36 b | 1.52 d | 1.0139 a,b | 1.13 b | 6.2 b |
| RPO | 230 a | 4.40 a | 10 a | 7.47 a | 2.19 a | 1.0222 a | 2.08 a | 7.0 a |
| Style/Beer | L* | a* | b* | C* | h* | EBC Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAP | 87.21 c | 1.82 d | 47.39 c | 47.43 c | 1.532 a | 13.37 d |
| SAL | 91.65 a | −0.49 f | 32.73 e | 32.74 e | −1.556 e | 7.50 e |
| WSB | 89.90 b | 1.01 e | 40.87 d | 40.89 d | 1.546a | 9.75 e |
| IPA | 77.12 d | 12.13 c | 71.72 b | 72.74 b | 1.403 b | 16.75 c |
| IRA | 62.46 e | 29.06 b | 89.60 a | 94.19 a | 1.257 c | 44.75 b |
| RPO | 14.02 f | 33.43 a | 24.03 f | 41.17 d | 0.623 d | 157.0 a |
| Style/Beer | Total Polyphenols (mg EAG/mL) | DPPH (μmol Trolox/mL) | Bitterness (IBU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAP | 0.61 d | 3.24 b | 9.52 f |
| SAL | 0.35 e | 1.74 e | 11.57 e |
| WSB | 1.68 a | 5.58 a | 12.55 d |
| IPA | 0.8 c | 2.30 c | 46.15 a |
| IRA | 0.95 b | 2.05 d | 33.45 b |
| RPO | 1.62 a | 3.14 b | 24.72 c |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Da Costa Jardim, C.; De Souza, D.; Cristina Kasper Machado, I.; Massochin Nunes Pinto, L.; De Souza Ramos, R.C.; Garavaglia, J. Sensory Profile, Consumer Preference and Chemical Composition of Craft Beers from Brazil. Beverages 2018, 4, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4040106
Da Costa Jardim C, De Souza D, Cristina Kasper Machado I, Massochin Nunes Pinto L, De Souza Ramos RC, Garavaglia J. Sensory Profile, Consumer Preference and Chemical Composition of Craft Beers from Brazil. Beverages. 2018; 4(4):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4040106
Chicago/Turabian StyleDa Costa Jardim, Carmelita, Daiana De Souza, Isabel Cristina Kasper Machado, Laura Massochin Nunes Pinto, Renata Cristina De Souza Ramos, and Juliano Garavaglia. 2018. "Sensory Profile, Consumer Preference and Chemical Composition of Craft Beers from Brazil" Beverages 4, no. 4: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4040106
APA StyleDa Costa Jardim, C., De Souza, D., Cristina Kasper Machado, I., Massochin Nunes Pinto, L., De Souza Ramos, R. C., & Garavaglia, J. (2018). Sensory Profile, Consumer Preference and Chemical Composition of Craft Beers from Brazil. Beverages, 4(4), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4040106