Production and Application of Pectinases from Aspergillus niger Obtained in Solid State Cultivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
2.2. Culture Media
2.3. Experimental Conditions
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
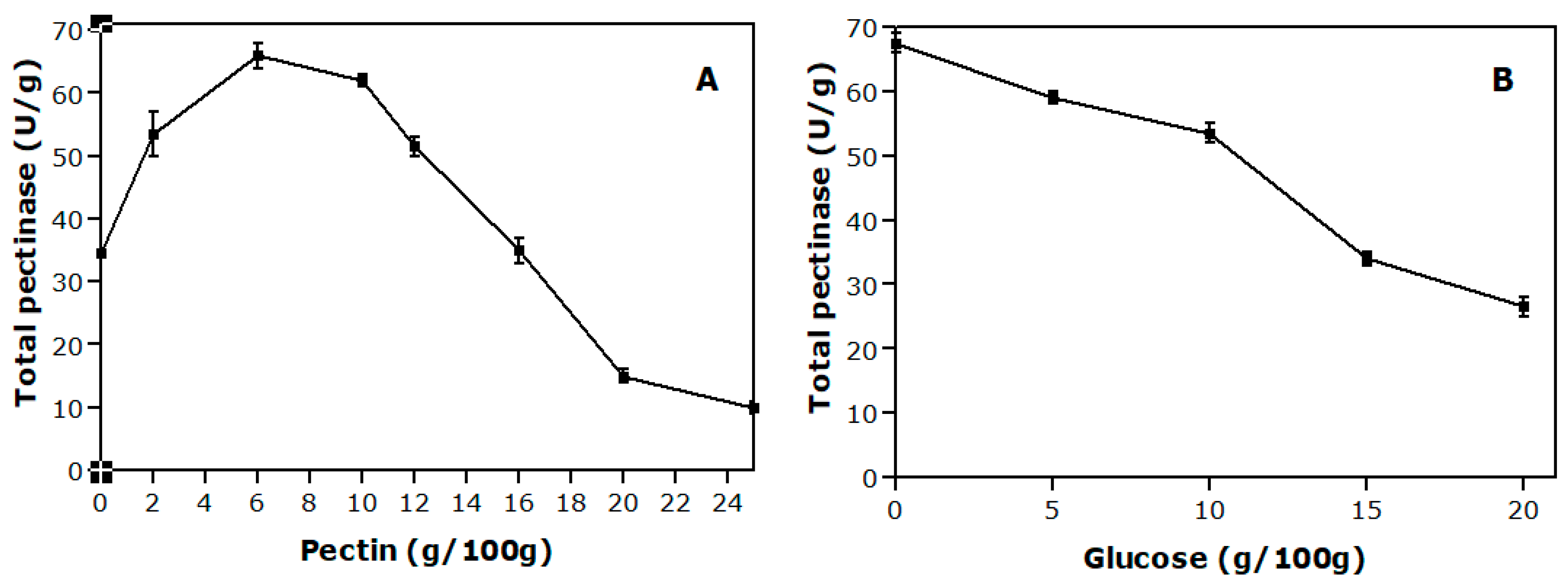
3.1. Effect of Pectin and Glucose Concentrations on the Solid-State Process
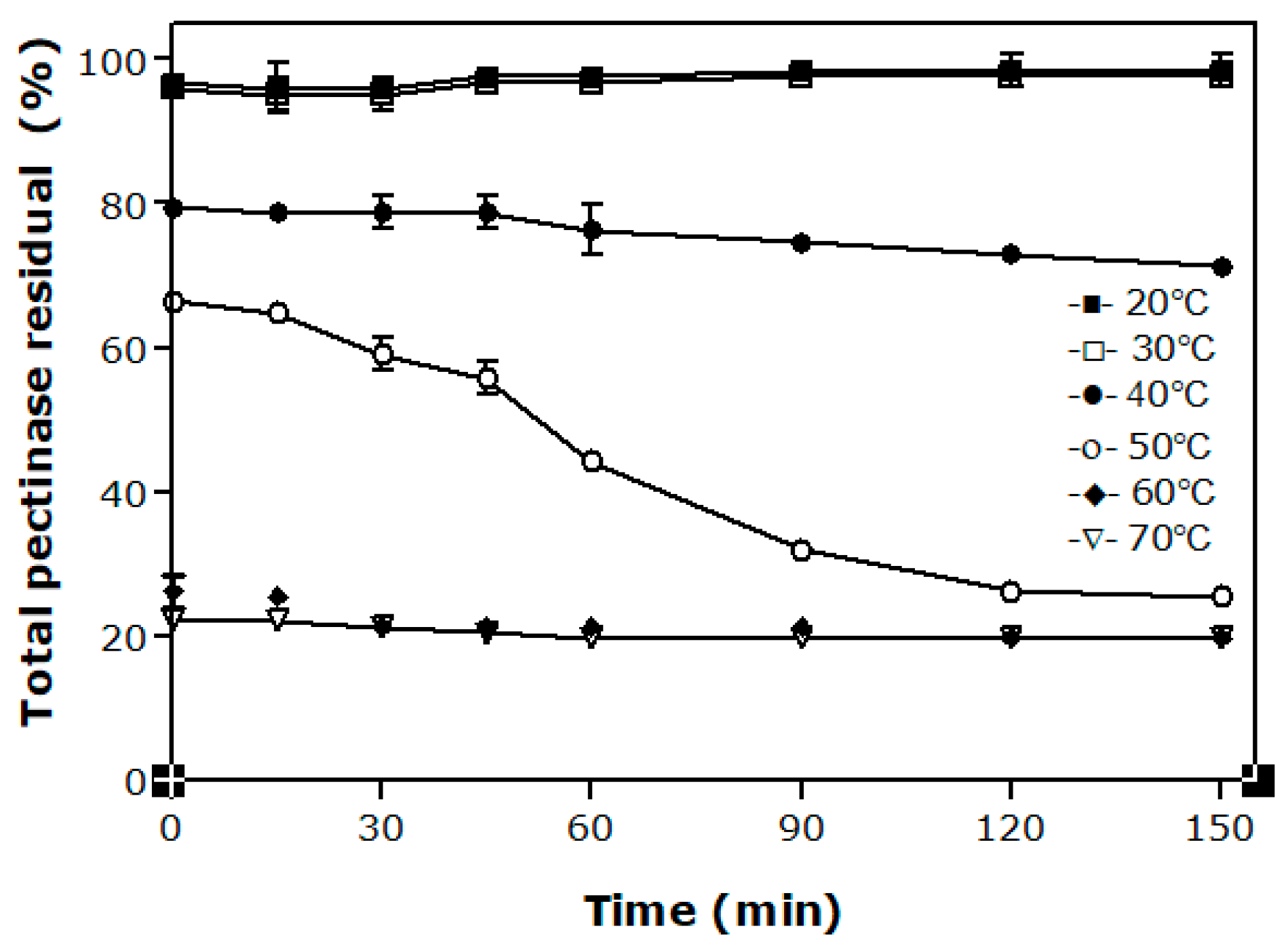
3.2. Effect of the Temperature on the Stability of Pectinases
3.3. Application of the Enzyme Extract in Strawberry Juice Treatment and Characterization of the Enzyme Complex
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandri, I.G.; Fontana, R.C.; Barfknecht, D.M.; Silveira, M.M. Clarification of fruit juices by fungal pectinases. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, I.G.; Lorenzoni, C.M.T.; Fontana, R.C.; Silveira, M.M. Use of pectinases produced by a new strain of Aspergillus niger for the enzymatic treatment of apple and blueberry juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.-L.; Li, P.-J. Pectic Enzymes. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, H.A.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Rodríguez, R.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Aguilar, C.N. Pectinase production from lemon peel pomace as support and carbon source in solid-state fermentation column-tray bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 65, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.M.; da Rosa, A.S.; Dal’Boit, S.; Mitchell, D.A.; Krieger, N. Thermal denaturation: Is solid-state fermentation really a good technology for the production of enzymes? Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 93, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, R.C.; Salvador, S.; Silveira, M.M. Influence of pectin and glucose on growth and polygalacturonase production by Aspergillus niger in solid-state cultivation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 32, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.F.S.; Lima-Filho, J.L.; Durán, N. Carbon sources effect on pectinase production from Aspergillus Japonicus 586. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummadi, S.M.; Panda, T. Purification and biochemical properties of microbial pectinases: Review. Process Biochem. 2003, 38, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, P.; Renosto, D.R.; Baldasso, C.; Zeni, M.; Silveira, M.M. Activated charcoal and microfiltration as pretreatment before ultrafiltration of pectinases produced by Aspergillus niger in solid-state cultivation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainvors, A.; Nedjaoum, N.; Gognies, S.; Muzart, M.; Nedjma, M.; Belarbi, A. Purification and characterization of acidic endo-polygalacturonase encoded by the PGLI-I gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 183, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albersheim, P. Pectin lyase from fungi. Methods Enzymol. 1966, 8, 628–631. [Google Scholar]
- Duvetter, T.; Loey, A.V.; Smout, C.; Verlent, I.; Nguyen, L.B.; Hendrickx, M. Effect of temperature and pressure on the activity of purified tomato polygalacturonase in the presence of pectins with different patterns of methyl esterification. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2005, 6, 293–303. [Google Scholar]
- Camassola, M.; Dillon, A.J.P. Cellulase determination: Modifications to make the filter paper assay easy, fast, practical and efficient. J. Anal. Bioanal. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, T.K. Measurement of cellulose activities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1987, 59, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, D.S. Solid-state fermentation with Trichoderma reesei for cellulose production. Appl Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.J.; Biely, P.; Poutanen, K. Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J. Biotechnol. 1992, 23, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Tewari, R.; Gupta, J.K.; Soni, R.; Soni, S.K. A novel strain of Aspergillus niger producing a cocktail of industrial depolymerising enzymes for the production of second generation biofuels. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 6, 552–569. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicilic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagent. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Giusti, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Characterization and measurement of anthocyanins by UV-visible spectroscopy. In Current Protocols in Food Analytical Chemistry; Wrolstad, R.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. F1.2.13. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Biochem. Eng. J. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A. Solid-state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 13, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Tari, C. Valorization of wheat bran for the production of polygalacturonase in SSC of Aspergillus sojae. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 54, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, P.; Polidoro, T.A.; Zeni, M.; Silveira, M.M. Evaluation of the operating conditions for the solid-state production of pectinases by Aspergillus niger in a bench-scale, intermittently agitated rotating drum bioreactor. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendges, D.H.; Montanari, Q.; Malvessi, E.; Silveira, M.M. Production and characterization of endo-polygalacturonase from Aspergillus niger in solid-state fermentation in double-surface bioreactor. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, N.; Diego, S.; Perez-Mateos, M.; Busto, M.D. Kinetic properties and thermal behavior of polygalacturonase used in fruit juice clarification. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, C.A.A.; Martins, M.L.L. Production of a polygalacturonase by thermophilic Bacillus sp. and some properties of the enzyme. Ciênc. Tecnol. Aliment. 2009, 29, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, I.G.; Piemolini-Barreto, L.T.; Fontana, R.C. Enzymes in Food Processing. In Biotechnology in Agriculture and Food Processing: Opportunities and Challenges, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 329–353. [Google Scholar]
- Echavarría, A.P.; Torras, C.; Pagán, J.; Ibarz, A. Fruit juice processing and membrane technology application. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maktouf, S.; Neifar, M.; Drira, S.J.; Baklouti, S.; Fendri, M.; Châabouni, S.E. Lemon juice clarification using fungal pectinolytic enzymes coupled to membrane ultrafiltration. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. A Critical Review on Polyphenols and Health Benefits of Black Soybeans. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tulipani, S.; Mezzetti, B.; Capocasa, F.; Bompadre, S.; Beekwilder, J.; De Vos, C.R.; Battino, M. Antioxidants, phenolic compounds, and nutritional quality of different strawberry genotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Yusof, S.; Hamid, N.S.A.; Baharin, B.S. Effects of fining treatment and storage temperature on the quality of clarified banana juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, T.J.; Howard, L.R.; Prior, R.L. Processing and storage effects on monomeric anthocyanins, percent polymeric color, and antioxidant capacity of processed blackberry products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.N.; Mazlina, M.K.S.; Taip, F.S. Impact of commercial pectolytic enzymes on selected properties of white dragon fruit juice. J. Inst. Eng. Malays. 2010, 71, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cerreti, M.; Liburdi, K.; Benucci, I.; Spinelli, S.E.; Esti, M. Optimization of pectinase and protease clarification treatment of pomegranate juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velderrain-Rodríguez, G.R.; Quirós-Sauceda, A.E.; González Aguilar, G.A.; Siddiqui, M.W.; Ayala Zavala, J.F. Technologies in fresh-cut fruit and vegetables. In Minimally Processed Foods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 79–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, D.B.; Putnik, P.; Dragović-Uzelac, V.; Vahčić, N.; Babojelić, S.M.; Levaj, B. Influences of organically and conventionally grown strawberry cultivars on anthocyanins content and color in purees and low-sugar jams. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.; Tokuioshi, K.; da Silva Martins, E.; Da Silva, R.; Gomes, E. Production of pectinase by solid-state fermentation with Penicillium viridicatum RFC3. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2885–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, S.S.; Garg, G.; Sharma, J.; Mahajan, R.; Methoxy. Characterization of statistically produced xylanase for enrichment of fruit juice clarification process. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
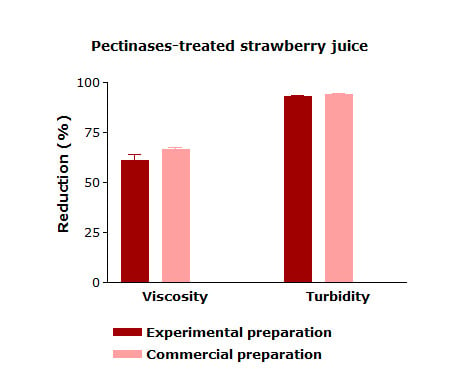
| Parameters | Untreated Juice | Pectinases-Treated Juice | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Commercial Preparation | Experimental Preparation | |
| Viscosity (mPa.s) | 2898.67 ± 263.44 a | 999.34 ± 110.40 b | 1133.33 ± 47.25 b |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 2360 ± 378.02 a | 145.36 ± 16.69 b | 156.67 ± 33.26 b |
| pH value | 3.50 ± 0.00 b | 3.48 ± 0.02 b | 3.64 ± 0.03 a |
| Total soluble solids (°Brix) | 5.10 ± 0.26 b | 5.47 ± 0.29 ab | 6.00 ± 0.20 a |
| Titratable acidity (meq. NaOH/100 mL juice) | 7.66 ± 0.57 ab | 8.25 ± 0.46 a | 7.13 ± 0.31 b |
| TA (mg Pel3Glu/100 mL juice) | 18.44 ± 1.61 a | 16.84 ± 1.76 a | 17.76 ± 1.83 a |
| TP (mg GAE/100 mL juice) | 140.10 ± 4.13 a | 134.4 ± 3.89 a | 137.13 ± 2.55 a |
| AC (µmol TE/mL juice) | 1030.44 ± 15.47 a | 1022.34 ± 15.65 a | 1027.00 ± 17.39 a |
| Enzymes | Commercial Preparation (U/mL) | Experimental Preparation (U/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| TP | 919 a | 865 a |
| PME | 3.3 a | 3.7 a |
| PL | 828 a | 361 b |
| FPase | 3.39 a | 0.15 b |
| Endoglucanases | 78 a | 53 b |
| β-glucosidases | 21 a | 18 a |
| Xylanases | 1411 a | 1224 a |
| Amylases | 45 a | 38 a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandri, I.G.; Silveira, M.M.d. Production and Application of Pectinases from Aspergillus niger Obtained in Solid State Cultivation. Beverages 2018, 4, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030048
Sandri IG, Silveira MMd. Production and Application of Pectinases from Aspergillus niger Obtained in Solid State Cultivation. Beverages. 2018; 4(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandri, Ivana Greice, and Mauricio Moura da Silveira. 2018. "Production and Application of Pectinases from Aspergillus niger Obtained in Solid State Cultivation" Beverages 4, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030048
APA StyleSandri, I. G., & Silveira, M. M. d. (2018). Production and Application of Pectinases from Aspergillus niger Obtained in Solid State Cultivation. Beverages, 4(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030048