Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Beverage Creation
2.3. Physicochemical Characteristics
2.4. Sensory Analysis
2.5. Proximate Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
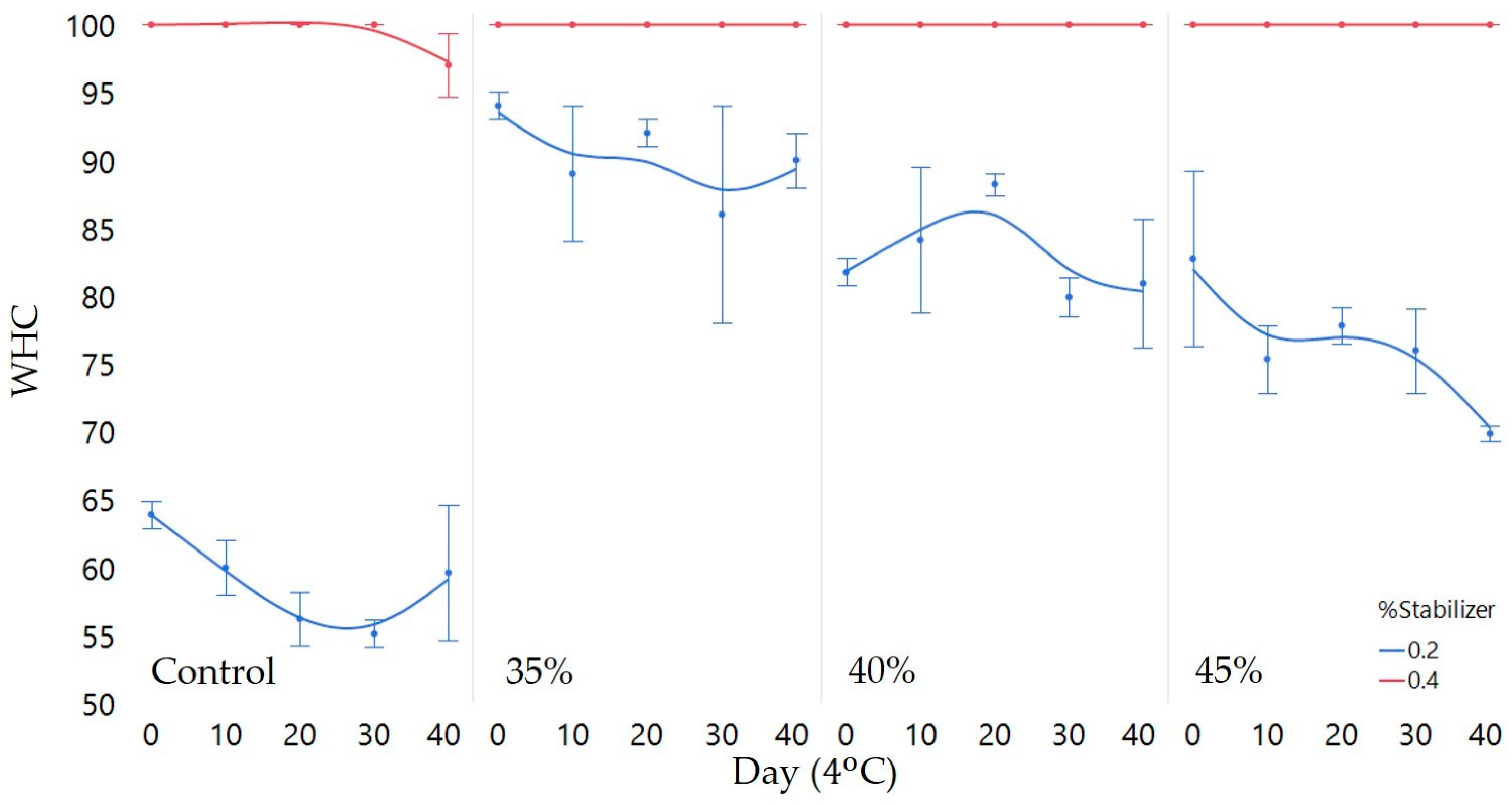
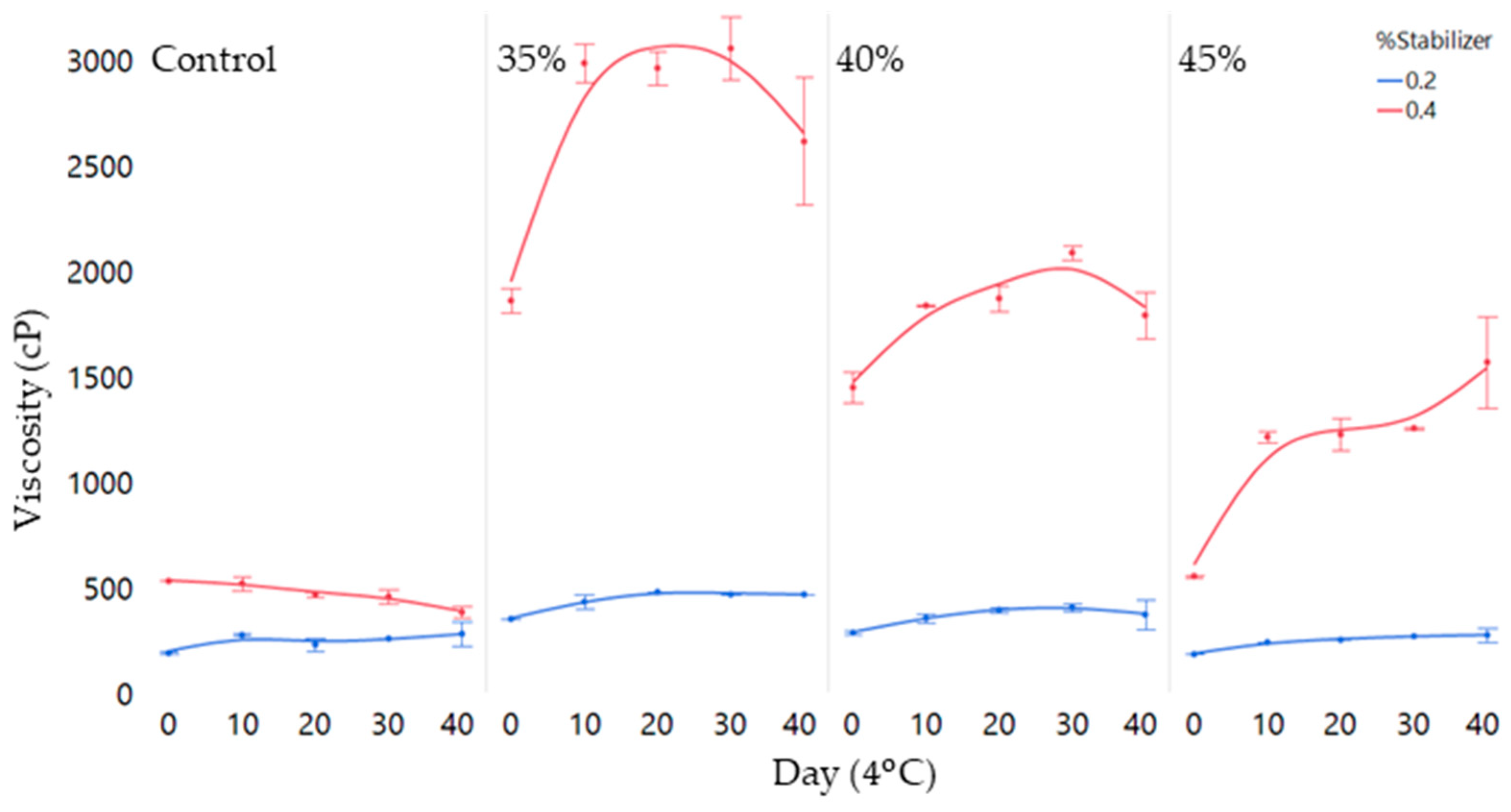
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics
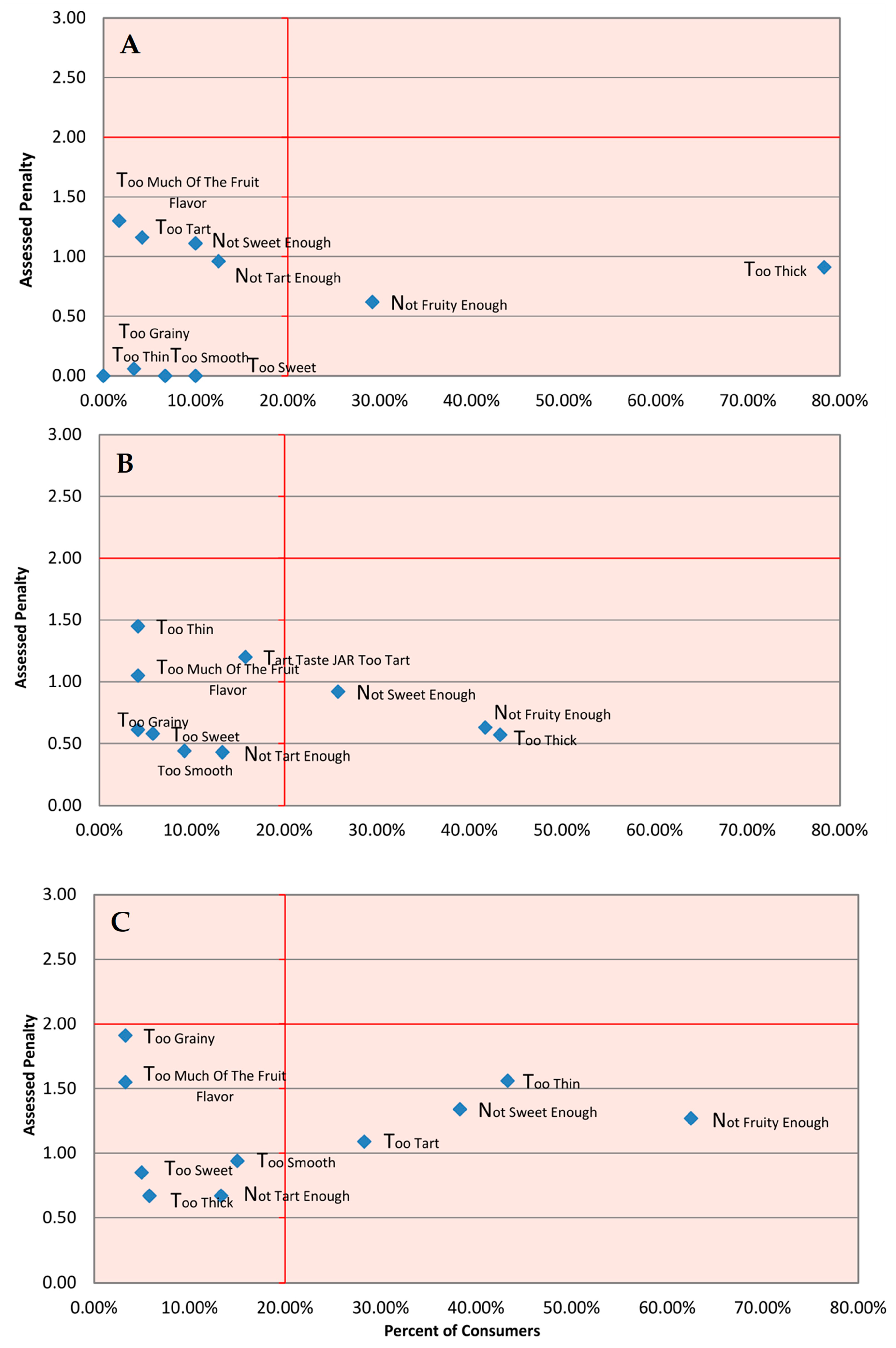
3.2. Sensory Analysis
3.3. Nutrition
4. Discussion
4.1. Sensorial and Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Matrix Stability
4.3. Nutrition
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mintel. Yogurt and Yogurt Drinks US 2022; Mintel Group Ltd.: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tamime, A.Y.; Robinson, R.K. Yoghurt-Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 1999; ISBN 0849317851. [Google Scholar]
- Bolwig, S.; Brekke, A.; Strange, L.; Strøm-Andersen, N. Valorisation of Whey: A Tale of Two Nordic Dairies. In From Waste to Value: Valorisation Pathways for Organic Waste Streams in Circular Bioeconomies; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019; pp. 162–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Smith, T.J.; Drake, M.A. Short Communication: Flavor and Flavor Stability of Cheese, Rennet, and Acid Wheys. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3434–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Kosmerl, E.; Krentz, A.; Zhang, L.; Badiger, S.; Miyagusuku-Cruzado, G.; Mayta-Apaza, A.; Giusti, M.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; García-Cano, I. Invited Review: Acid Whey Trends and Health Benefits. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey-Ing up the Options—Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 48, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, D.; Martindale, W.; Romeih, E.; Hebishy, E. Recent Advances in Whey Processing and Valorisation: Technological and Environmental Perspectives. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchik, P.; Zuber, T.; Zuber, A.; Moraru, C.I. Short Communication: Composition of Coproduct Streams from Dairy Processing: Acid Whey and Milk Permeate. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3978–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurić, M.; Carić, M.; Milanović, S.; Tekić, M.; Panić, M. Development of Whey-Based Beverages. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 219, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinois, J.C.; Dando, R.; Padilla-zakour, O.I. Yogurt Acid Whey Utilization for Production of Baked Goods: Pancakes and Pizza Crust. Foods 2019, 8, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, V.; Chanioti, S.; Xanthou, M.Z.; Katsaros, G. Incorporation of Acid Whey Yogurt By-Product in Novel Sauces Formulation: Quality and Shelf-Life Evaluation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho Flinois, J.; Dando, R.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I. Effects of Replacing Buttermilk with Yogurt Acid Whey in Ranch Dressing. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7874–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skryplonek, K.; Dmytrów, I.; Mituniewicz-Małek, A. Probiotic Fermented Beverages Based on Acid Whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7773–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievore, P.; Simões, D.R.S.; Silva, K.M.; Drunkler, N.L.; Barana, A.C.; Nogueira, A.; Demiate, I.M. Chemical Characterisation and Application of Acid Whey in Fermented Milk. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.K.; O’Kennedy, B.T. Rheology of Stirred Yogurt as Affected by Added Milk Fat, Protein and Hydrocolloids. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, F.; Sherman, P. Identification of Stimuli Controlling the Sensory Evaluation of Viscosity Ii. Oral Methods. J. Texture Stud. 1973, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.; Chinnasamy, B.; Jin, L.; Clark, S. Use of Just-about-Right Scales and Penalty Analysis to Determine Appropriate Concentrations of Stevia Sweeteners for Vanilla Yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, H.T.; Patel, A.A.; Lopez, N.V. Mixed Messages: Ambiguous Penalty Information in Modified Restaurant Menu Items. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 52, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- USDA Milk, Fat Free (Skim). Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1097521/nutrients (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- Gonzalez, N.J.; Adhikari, K.; Sancho-Madriz, M.F. Sensory Characteristics of Peach-Flavored Yogurt Drinks Containing Prebiotics and Synbiotics. LWT 2011, 44, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioui, F.; Ait Saada, D.; Cheriguene, A. Physicochemical and Sensory Quality of Yogurt Incorporated with Pectin from Peel of Citrus Sinensis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubber, S.; Chaturvedi, K.; Thakur, N.; Sharma, N.; Yadav, S.K. Low-Methoxyl Pectin Stabilizes Low-Fat Set Yoghurt and Improves Their Physicochemical Properties, Rheology, Microstructure and Sensory Liking. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobil, M.; Deh, C.Y.; Agbenorhevi, J.K.; Sampson, G.O.; Kpodo, F.M. Effect of Okra Pectin on the Sensory, Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Yoghurt. Food Nutr. Sci. 2020, 11, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mada, T.; Duraisamy, R.; Abera, A.; Guesh, F. Effect of Mixed Banana and Papaya Peel Pectin on Chemical Compositions and Storage Stability of Ethiopian Traditional Yoghurt (Ergo). Int. Dairy J. 2022, 131, 105396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andiç, S.; Boran, G.; Tunçtürk, Y. Effects of Carboxyl Methyl Cellulose and Edible Cow Gelatin on Physico-Chemical, Textural and Sensory Properties of Yoghurt. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2013, 15, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Eze, C.M.; Aremu, K.O.; Alamu, E.O.; Okonkwo, T.M. Impact of Type and Level of Stabilizers and Fermentation Period on the Nutritional, Microbiological, and Sensory Properties of Short-Set Yoghurt. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5477–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzone, F.; Ares, G.; Giménez, A. Temporal Aspects of Yoghurt Texture Perception. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 29, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Olawuyi, I.F.; Lee, W.Y. Pectin Hydrogels: Gel-Forming Behaviors, Mechanisms, and Food Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, A.L.B.; Gurram, S.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Effect of High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing on Rheological and Textural Properties of Probiotic Low-Fat Yogurt Fermented by Different Starter Cultures. J. Food Process Eng. 2006, 29, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelen, P. Whey Processing: Utilization and Products. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Duke, M.C.; Gray, S.R.; Zisu, B.; Weeks, M.; Palmer, M.; Vasiljevic, T. Properties of Acid Whey as a Function of PH and Temperature. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4352–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, B.; Chojnowski, W. Characteristics of Acid Whey Powder Partially Demineralised by Nanofiltration. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2006, 15, 87. [Google Scholar]



| Acid Whey % | Water % | Yogurt % | Stabilizer % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 0 | 64.8 | 0.2 |
| 35 | 0 | 64.6 | 0.4 |
| 40 | 0 | 59.8 | 0.2 |
| 40 | 0 | 59.6 | 0.4 |
| 45 | 0 | 54.8 | 0.2 |
| 45 | 0 | 54.6 | 0.4 |
| 0 | 45 | 54.8 | 0.2 |
| 0 | 45 | 54.6 | 0.4 |
| Acid Whey Addition | Attribute | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Texture | Mouth Feel | Flavor | Overall Liking | |
| 25% | 6.73 a | 6.53 ab | 6.54 ab | 7.08 a | 6.59 a |
| 35% | 6.83 a | 6.93 a | 6.68 a | 6.94 a | 6.74 a |
| 45% | 6.24 b | 6.39 b | 6.13 b | 6.10 b | 5.16 b |
| Yogurt Beverage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient 1 | Unit | Acid Whey | Skim Milk 1 | Yogurt 2 | 35% | 40% | 45% |
| Protein | g/100 g | 2.2 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| Fat | g/100 g | 0.3 | 0.08 | 1.47 | 1.06 | 1.00 | 0.94 |
| Carbohydrate 3 | g/100 g | 2.9 | 4.96 | 19.41 | 13.63 | 12.81 | 11.98 |
| Calcium (Ca) | g/100 g | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| Potassium (K) | g/100 g | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| Sodium (Na) | g/100 g | 0.036 | 0.042 | 0.065 | 0.055 | 0.053 | 0.052 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shukla, V.; Villarreal, M.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I. Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey. Beverages 2024, 10, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010018
Shukla V, Villarreal M, Padilla-Zakour OI. Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey. Beverages. 2024; 10(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleShukla, Viral, Marcela Villarreal, and Olga I. Padilla-Zakour. 2024. "Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey" Beverages 10, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010018
APA StyleShukla, V., Villarreal, M., & Padilla-Zakour, O. I. (2024). Consumer Acceptance and Physicochemical Properties of a Yogurt Beverage Formulated with Upcycled Yogurt Acid Whey. Beverages, 10(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010018







