Cardiovascular Complications of Energy Drinks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
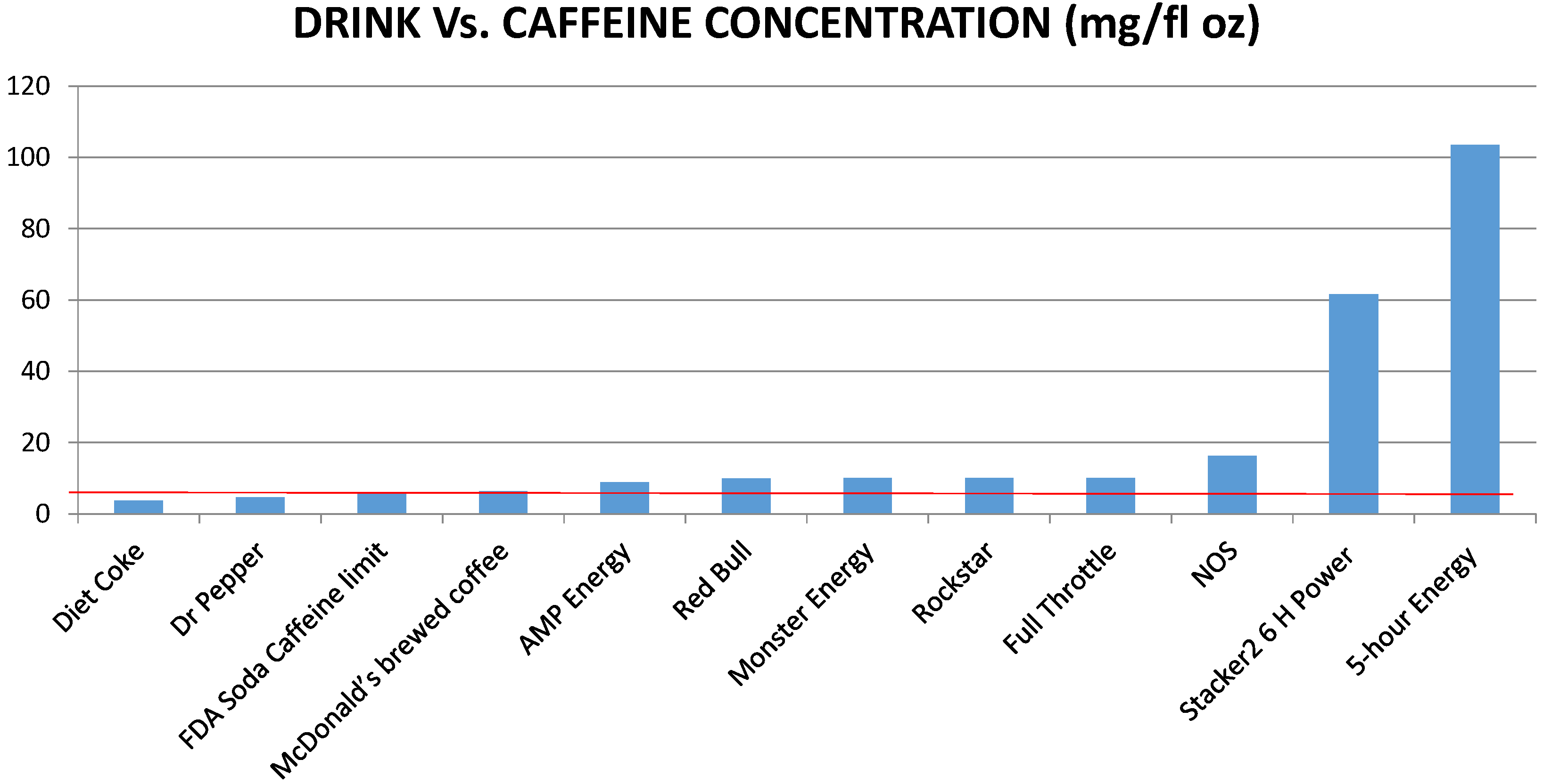
2. Cardiovascular Complications
| Acute Effects | Potential Chronic Effects |
|---|---|
| Elevated Blood Pressure | Hypertensive Heart Disease |
| Increased Heart Rate | Coronary Artery Disease |
| Increased Corrected QT (QTc) Interval | Atherosclerosis |
| Supraventricular Arrythmia | Cerebrovascular Disease |
| Ventricular Arrythmia | Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Coronary Artery Spasm | |
| Coronary Artery Thrombosis | |
| Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy | |
| ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) | |
| Aortic Dissection | |
| Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome | |
| Sudden Cardiac Death | |
| Endothelial Dysfunction |
2.1. Acute Effects
2.1.1. Elevated Blood Pressure
2.1.2. Increased Heart Rate
2.1.3. Increased Corrected QT (QTc) Interval
2.1.4. Supraventricular Arrhythmia
2.1.5. Ventricular Arrhythmia
2.1.6. Coronary Artery Spasm
2.1.7. Coronary Artery Thrombosis
2.1.8. Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
2.1.9. ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
2.1.10. Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
2.1.11. Aortic Dissection
2.1.12. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
2.1.13. Sudden Cardiac Death
- A 14 year-old girl, in Hagerstown, MD, who died after drinking two, 24-ounce Monster EDs in 24 h; an autopsy concluded she died of cardiac arrhythmia due to caffeine toxicity [80].
- A healthy 18 year-old man, died while playing basketball after drinking two cans of Red Bull® ED [81].
- A healthy 16- year-old girl, an athletic teenage softball player, died after consuming several Red Bull® EDs [82]. The beverages were consumed while at the beach; later that day she reported malaise and shortness of breath. She was rushed to a hospital and was pronounced dead after suffering cardiac arrest.
2.1.14. Endothelial Dysfunction
2.2. Chronic Effects
3. Suggestions
| Age and medical condition | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| <18 years old | Do not consume EDs |
| ≥18 years old–healthy, non-pregnant, and taking no medications | No more than 1 regular can of ED per day at rest (avoid if any symptoms related to consumption) |
| Do not consume ED prior to exercise | |
| Do not consume ED with alcohol | |
| ≥18 years old and pregnant | Do not consume EDs |
| ≥18 years old and caffeine sensitivity | Do not consume EDs |
| ≥18 years old and history of cardiovascular condition: Elevated blood pressure, Increased heart rate, Increased QTc interval, Supraventricular arrhythmia, Ventricular arrhythmia, Coronary artery spasm, Coronary artery thrombosis, Takasubu cardiomyopathy, ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI), Sudden cardiac death, or Endothelial dysfunction | Do not consume EDs |
| ≥18 years old and any other medical condition/taking medications | Do not consume EDs and discuss with health care provider |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higgins, J.P.; Tuttle, T.D.; Higgins, C.L. Energy beverages: Content and safety. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, S.M.; Schaechter, J.L.; Hershorin, E.R.; Lipshultz, S.E. Health effects of energy drinks on children, adolescents, and young adults. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlivan, A.; Irwin, C.; Grant, G.D.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Skinner, T.; Leveritt, M.; Desbrow, B. The Effects of Red Bull® Energy Drink Compared with Caffeine on Cycling Time Trial Performance. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.A.; Marczinski, C.A. Acute effects of a glucose energy drink on behavioral control. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 18, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Park, S.; Onufrak, S. Perceptions about energy drinks are associated with energy drink intake among U.S. youth. Am. J. Health Promot. 2015, 29, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Energy drinks fuel the obesity epidemic. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 218, 345. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Ortiz, B.L. Energy drink ingredients and their effect on endothelial function: A Review. Int. J. Clin. Cardiolol. 2014, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Babu, K.M. Caffeine reduces myocardial blood flow during exercise. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 730.e1–730.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Science in the Public Interest. Caffeine Content of Food & Drugs. Available online: http://www.cspinet.org/new/cafchart.htm (accessed on 12 April 2014).
- Goldfarb, M.; Tellier, C.; Thanassoulis, G. Review of published cases of adverse cardiovascular events after ingestion of energy drinks. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckman, M.A.; Weil, J.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) in foods: A comprehensive review on consumption, functionality, safety, and regulatory matters. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R77–R87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.K.; Iftikhar, R. Energy drinks: Getting wings but at what health cost? Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACOG. Committee Opinion No. 462: Moderate caffeine consumption during pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 116, 467–468. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Bell, E.M.; Browne, M.L.; Druschel, C.M.; Romitti, P.A. Exploring maternal patterns of dietary caffeine consumption before conception and during pregnancy. Matern. Child Health J. 2014, 18, 2446–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Cervellin, G.; Lippi, G.; Earnest, C.P. Energy Drink Overconsumption in Adolescents: Implications for Arrhythmias and Other Cardiovascular Events. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emond, J.A.; Sargent, J.D.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. Patterns of Energy Drink Advertising over US Television Networks. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2015, 47, 120–126.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, N.; Laska, M.N.; Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Sports and energy drink consumption are linked to health-risk behaviours among young adults. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.K.; Kim, K.M. Energy drink consumption patterns and associated factors among nursing students: A descriptive survey study. J. Addict. Nurs. 2015, 26, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, E.R.; Marmorstein, N.R. Energy drink consumption and later alcohol use among early adolescents. Addict. Behav. 2015, 43, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulos, N.S.; Pasch, K.E. Energy drink consumption is associated with unhealthy dietary behaviours among college youth. Perspect. Public Health 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verster, J.C.; Benjaminsen, J.M.; van Lanen, J.H.; van Stavel, N.M.; Olivier, B. Effects of mixing alcohol with energy drink on objective and subjective intoxication: Results from a Dutch on-premise study. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonar, E.E.; Cunningham, R.M.; Polshkova, S.; Chermack, S.T.; Blow, F.C.; Walton, M.A. Alcohol and energy drink use among adolescents seeking emergency department care. Addict. Behav. 2015, 43, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapp, G.S.; Allen, K.L.; O’Sullivan, T.; Robinson, M.; Jacoby, P.; Oddy, W.H. Energy drink consumption among young Australian adults: Associations with alcohol and illicit drug use. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 134, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKetin, R.; Coen, A.; Kaye, S. A comprehensive review of the effects of mixing caffeinated energy drinks with alcohol. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 151, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striley, C.W.; Khan, S.R. Review of the energy drink literature from 2013: Findings continue to support most risk from mixing with alcohol. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2014, 27, 263–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spierer, D.K.; Blanding, N.; Santella, A. Energy drink consumption and associated health behaviors among university students in an urban setting. J. Community Health 2014, 39, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Murphy, T.; Roberts, R.; Cooksley, W.G.; Halliday, J.W.; Powell, L.W. Influence of alcohol and caffeine consumption on caffeine elimination. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1986, 13, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, B.V.; Jackson, D.A.; Merchant, R.C.; Babu, K.M.; Baird, J.R.; Nirenberg, T.; Linakis, J.G. Energy drink and other substance use among adolescent and young adult emergency department patients. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2013, 29, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunja, N.; Brown, J.A. Energy drinks: Health risks and toxicity. Med. J. Aust. 2012, 196, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, S.M.; Seifert, S.A.; Schaechter, J.L.; Bronstein, A.C.; Benson, B.E.; Hershorin, E.R.; Arheart, K.L.; Franco, V.I.; Lipshultz, S.E. An analysis of energy-drink toxicity in the National Poison Data System. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 2013, 51, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, B.D.; Okuda, D.T. Pontine myelinolysis following excessive consumption of commercial energy drinks. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2015, 2, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, R.S.; Italiano, D.; Gervasi, G.; Bramanti, P. Single tonic-clonic seizure after energy drink abuse. Epilepsy Behav. 2012, 23, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordt, S.P.; Vilke, G.M.; Clark, R.F.; Lee Cantrell, F.; Chan, T.C.; Galinato, M.; Nguyen, V.; Castillo, E.M. Energy drink use and adverse effects among emergency department patients. J. Community Health 2012, 37, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabulo, D.; Marques, S.; Pedroso, E. Caffeinated energy drink intoxication. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasser, E.K.; Yepuri, G.; Dulloo, A.G.; Montani, J.P. Cardio- and cerebrovascular responses to the energy drink Red Bull in young adults: A randomized cross-over study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elitok, A.; Oz, F.; Panc, C.; Sarikaya, R.; Sezikli, S.; Pala, Y.; Bugan, Ö.S.; Ateş, M.; Parıldar, H.; Ayaz, M.B.; et al. Acute effects of Red Bull energy drink on ventricular repolarization in healthy young volunteers: A prospective study. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, D.; Frolich, J.C.; Carr, R.K.; Watson, J.T.; Hollifield, J.W.; Shand, D.G.; Oates, J.A. Effects of caffeine on plasma renin activity, catecholamines and blood pressure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 298, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, T.G.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Ioakeimidis, N.; Alexopoulos, N.; Stefanadis, C. Nonlinear dynamics of blood pressure variability after caffeine consumption. Clin. Med. Res. 2006, 4, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.L.; Townsend, R.R. Does consumption of high-caffeine energy drinks affect blood pressure? J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 2006, 8, 744–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.; Weiss, M. The influence of a taurine containing drink on cardiac parameters before and after exercise measured by echocardiography. Amino Acids 2001, 20, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, L.; Lanfear, D.E.; Dhanapal, V.; Kalus, J.S. Effect of “energy drink” consumption on hemodynamic and electrocardiographic parameters in healthy young adults. Ann. Pharmacother. 2009, 43, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, A.M.; Schmidt, J.M.; McCain, K.R.; Fraer, M. Comparison of the effects of energy drink vs. caffeine supplementation on indices of 24-h ambulatory blood pressure. Ann. Pharmacother. 2012, 46, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerner, J.M.; Kuetting, D.L.; Luetkens, J.A.; Naehle, C.P.; Dabir, D.; Homsi, R.; Nadal, J.; Schild, H.H.; Thomas, D.K. Caffeine and taurine containing energy drink increases left ventricular contractility in healthy volunteers. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 31, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.; Jawaid, A. Hypertension in a young boy: An energy drink effect. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H. Elecropharmacology of taurine on the hyperpolarization-activated inward current and the sustained inward current in spontaneously beating rat sino-atrial nodal cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 91, 229–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottlaender, D.; Motloch, L.J.; Reda, S.; Larbig, R.; Hoppe, U.C. Cardiac arrest due to long QT syndrome associated with excessive consumption of energy drinks. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 158, e51–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufendach, K.A.; Horner, J.M.; Cannon, B.C.; Ackerman, M.J. Congenital type 1 long QT syndrome unmasked by a highly caffeinated energy drink. Heart Rhythm: Off. J. Heart Rhythm Soc. 2012, 9, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidance for Industry: E14: Clinical Evaluation of QT/QTc Interval Prolongation and Proarrhythmic Potential for Non-antiarrhythmic Drugs. 2005. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm073153.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2015).
- Artin, B.; Singh, M.; Richeh, C.; Jawad, E.; Arora, R.; Khosla, S. Caffeine-related atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Ther. 2010, 17, e169–e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turagam, M.K.; Velagapudi, P.; Kocheril, A.G.; Alpert, M.A. Commonly Consumed Beverages in Daily Life: Do They Cause Atrial Fibrillation? Clin. Cardiol. 2015, 38, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rocco, J.R.; During, A.; Morelli, P.J.; Heyden, M.; Biancaniello, T.A. Atrial fibrillation in healthy adolescents after highly caffeinated beverage consumption: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo Fos, I.; Vazquez Gomis, R.M.; Vazquez Gomis, C.; Piernas, R.; Climent Forner, E.; Llaguno Salvador, M.D.; Vargas Torcal, F. Atrial fibrillation after ingestion of a high energy drink. An. Pediatr. (Barc.) 2012, 77, 417–419. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagajothi, N.; Khraisat, A.; Velazquez-Cecena, J.L.; Arora, R.; Raghunathan, K.; Patel, R.; Parajuli, R. Energy drink-related supraventricular tachycardia. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaoukis, A.; Panagopoulou, V.; Mojibian, H.R.; Jacoby, D. Reverse Takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with the consumption of an energy drink. Circulation 2012, 125, 1584–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, S.T.; Mehta, P.A.; Dubrey, S.W. Atrial fibrillation-related cardiomyopathy: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2007, 1, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.E.; Lipshultz, S.E.; Fisher, S.D. Energy drink-induced near-fatal ventricular arrhythmia prevented by an intracardiac defibrillator decades after operative “repair” of tetralogy of Fallot. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1124–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, S.; Sarikaya, R.; Buyukcam, F. Death of a young man after overuse of energy drink. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 1624.e3–1624.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, M.E.; Cooke, C.T.; McCarthy, J.S. Caffeine-induced cardiac arrhythmia: An unrecognised danger of healthfood products. Med. J. Aust. 2001, 174, 520–521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.J.; Alford, K. Cardiac arrest in a young man following excess consumption of caffeinated “energy drinks”. Med. J. Aust. 2009, 190, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rutledge, M.; Witthed, A.; Khouzam, R.N. It took a RedBull to unmask Brugada syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 161, e14–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanan Israelit, S.; Strizevsky, A.; Raviv, B. ST elevation myocardial infarction in a young patientafter ingestion of caffeinated energy drink and ecstasy. World J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 3, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.J.; El-Hassan, M.; Khan, A.A. Myocardial infarction in a young adult following the consumption of a caffeinated energy drink. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, P.; Norden-Pettersson, L.; Ahlner, J. Caffeine fatalities—Four case reports. Forensic Sci. Int. 2004, 139, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.E.; Kado, H.S.; Samson, R.; Miller, A.B. A case of caffeine-induced coronary artery vasospasm of a 17-year-old male. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2012, 12, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjo, A.M.; Pineda, A.M.; Nascimento, F.O.; Zamora, C.; Lamas, G.A.; Escolar, E. Left main coronary artery acute thrombosis related to energy drink intake. Circulation 2012, 125, 1447–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomin, D.; Borron, S.W.; Watts, S.H. STEMI Associated with Overuse of Energy Drinks. Case Rep. Emerg. Med. 2015, 2015, 537689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissig, C.J.; Strain, E.C.; Griffiths, R.R. Caffeinated energy drinks—A growing problem. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverio, A.; Prota, C.; di Maio, M.; Polito, M.V.; Cogliani, F.M.; Citro, R.; Gigantino, A.; Iesu, S.; Piscione, F. Aortic dissection in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: A series of two cases and a review of the Literature. Nephrology (Carlton) 2015, 20, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonjev, Z.S.; Bala, G. High-energy drinks may provoke aortic dissection. Coll. Antropol. 2013, 37, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Schwartz, M.A.; Tellides, G.; Milewicz, D.M. Role of Mechanotransduction in Vascular Biology: Focus on Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1448–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlizzi, R.; Rocchi, C.; Serra, M.; Solieri, L.; Cortelli, P. Reversible postural tachycardia syndrome due to inadvertent overuse of Red Bull. Clin. Auton. Res. 2008, 18, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxtable, R.J. Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 101–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.P.; Lin, M.T. Amino acids injected into the cerebroventricular system induce an enhancement of reflex bradycardia in the rat. Neuropharmacology 1983, 22, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, C.; Cox, H.; Wescott, R. The effects of red bull energy drink on human performance and mood. Amino Acids 2001, 21, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichler, A.; Swenson, A.; Harris, M.A. A combination of caffeine and taurine has no effect on short term memory but induces changes in heart rate and mean arterial blood pressure. Amino Acids 2006, 31, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NINDS. Postural Tachycardia Syndrome Information Page. Available online: http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/postural_tachycardia_syndrome/postural_tachycardia_syndrome.htm (accessed on 15 May 2015).
- Higgins, J.P.; Yang, B.; Ortiz, B.; Herrin, N.; Doolittle, J.; Kahlden, K.; Dayah, T.; Cassel, D.; Ali, A. Consumption Of Energy Beverage Is Associated With An Attenuation Of Arterial Endothelial Flow-mediated Dilatation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, A519. [Google Scholar]
- Worthley, M.I.; Prabhu, A.; de Sciscio, P.; Schultz, C.; Sanders, P.; Willoughby, S.R. Detrimental effects of energy drink consumption on platelet and endothelial function. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CFSAN Adverse Event Reporting System. Voluntary and Mandatory Reports on 5-Hour Energy, Monster Energy, and Rockstar Energy Drink. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AboutFDA/CentersOffices/OfficeofFoods/CFSAN/CFSANFOIAElectronicReadingRoom/UCM328270.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2015).
- Teen Girl Dies of ‘Caffeine Toxicity’ after Downing 2 Energy Drinks. Available online: http://www.today.com/health/teen-girl-dies-caffeine-toxicity-after-downing-2-energy-drinks-506441 (accessed on 16 April 2015).
- Red Bull, Alcohol and Drugs ‘Can Spark Violence’. Available online: http://www.independent.ie/irish-news/red-bull-alcohol-and-drugs-can-spark-violence-26276918.html (accessed on 12 April 2014).
- Jackson, C. Teenage Girl Is Dead after Consuming Red Bull Energy Drink. Available online: http://guardianlv.com/2014/06/teenage-girl-is-dead-after-consuming-red-bull-energy-drink/ (accessed on 12 April 2014).
- Ernest, D.; Chia, M.; Corallo, C.E. Profound hypokalaemia due to Nurofen Plus and Red Bull misuse. Crit. Care Resusc.: J. Australas. Acad. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 12, 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Ananaba, I.E.; Higgins, C.L. Sudden cardiac death in young athletes: Preparticipation screening for underlying cardiovascular abnormalities and approaches to prevention. Phys. Sportsmed. 2013, 41, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, B.J.; Ganetsky, M.; Babu, K.M. Toxicity of energy drinks. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2012, 24, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deanfield, J.E.; Halcox, J.P.; Rabelink, T.J. Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical relevance. Circulation 2007, 115, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blanch, N.; Clifton, P.M.; Keogh, J.B. A systematic review of vascular and endothelial function: Effects of fruit, vegetable and potassium intake. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis.: NMCD 2015, 25, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashor, A.W.; Lara, J.; Siervo, M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Oggioni, C.; Jakovljevic, D.G.; Mathers, J.C. Exercise modalities and endothelial function: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerasamy, M.; Bagnall, A.; Neely, D.; Allen, J.; Sinclair, H.; Kunadian, V. Endothelial dysfunction and coronary artery disease: A state of the art review. Cardiol. Rev. 2015, 23, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwaidi, J.A.; Hamasaki, S.; Higano, S.T.; Nishimura, R.A.; Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Lerman, A. Long-term follow-up of patients with mild coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 2000, 101, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.J.; Kuo, L.; Davis, M.J.; DeFily, D.V.; Chilian, W.M. Role of nitric oxide in the coronary microvascular responses to adenosine and increased metabolic demand. Circulation 1995, 91, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looi, K.L.; Grace, A.; Agarwal, S. Coronary artery spasm and ventricular arrhythmias. Postgrad. Med. J. 2012, 88, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P. Endothelial function acutely worse after drinking energy beverage. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, e47–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabas, I.; Garcia-Cardena, G.; Owens, G.K. Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.A.; Lacey, C.S.; Bergendahl, T.; Kolasa, M.; Riddock, I.C. QTc interval prolongation with high dose energy drink consumption in a healthy volunteer. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 172, e336–e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, J. ADVERSE DRUG EVENTS: Substantial Problem but Magnitude Uncertain; United States General Accounting Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. Available online: http://www.gao.gov/new.items/he00053t.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2015).
- Goel, V.; Manjunatha, S.; Pai, K.M. Effect of red bull energy drink on auditory reaction time and maximal voluntary contraction. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 58, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pai, K.M.; Kamath, A.; Goel, V. Effect of Red Bull energy drink on muscle performance: An electromyographic overview. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Eckerson, J.M.; Bull, A.J.; Baechle, T.R.; Fischer, C.A.; O’Brien, D.C.; Moore, G.A.; Yee, J.C.; Pulverenti, T.S. Acute ingestion of sugar-free red bull energy drink has no effect on upper body strength and muscular endurance in resistance trained men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.T.; Biltz, G.R.; Dengel, D.R. Cardiovascular and ride time-to-exhaustion effects of an energy drink. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagba, S.; Langille, D.; Asbridge, M. An emerging adolescent health risk: Caffeinated energy drink consumption patterns among high school students. Prev. Med. 2014, 62, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arria, A.M.; Caldeira, K.M.; Kasperski, S.J.; O’Grady, K.E.; Vincent, K.B.; Griffiths, R.R.; Wish, E.D. Increased alcohol consumption, nonmedical prescription drug use, and illicit drug use are associated with energy drink consumption among college students. J. Addict. Med. 2010, 4, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sports drinks and energy drinks for children and adolescents: Are they appropriate? Pediatrics 2011, 127, 1182–1189.
- MEDICINE IO. Caffeine in Food and Dietary Supplements: Examining Safety-Workshop Summary; The National Academies Press Washington, DC: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; La Bounty, P.; Taylor, L.; Nelson, M.T.; Greenwood, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Lopez, H.L.; Hoffman, J.R.; Stout, J.R.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Energy drinks. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2013, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, R.D. Caffeinated energy drinks in children. Can. Fam. Phys. Med. Fam. Can. 2013, 59, 947–948. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higgins, J.P.; Yarlagadda, S.; Yang, B. Cardiovascular Complications of Energy Drinks. Beverages 2015, 1, 104-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages1020104
Higgins JP, Yarlagadda S, Yang B. Cardiovascular Complications of Energy Drinks. Beverages. 2015; 1(2):104-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages1020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiggins, John P., Santi Yarlagadda, and Benjamin Yang. 2015. "Cardiovascular Complications of Energy Drinks" Beverages 1, no. 2: 104-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages1020104
APA StyleHiggins, J. P., Yarlagadda, S., & Yang, B. (2015). Cardiovascular Complications of Energy Drinks. Beverages, 1(2), 104-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages1020104





