Abstract
Compared to traditional physical and chemical approaches, nanobiotechnology and plant-based green synthesis procedures offer significant advantages, as well as having a greater range of medical and biotechnological applications. Nanoparticles of zinc oxide (ZnO NPs) have recently been recognized as a promising option for many industries, including optics, electrics, packaged foods, and medicine, due to their biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, and cost-effectiveness. Several studies have shown that zinc ions are important in triggering cell apoptosis by promoting the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROSs) and releasing zinc ions (Zn2+), which are toxic to cells. The toxic nature of the chemicals used in the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles limits their clinical utility. An overview of recent developments in green ZnO NP synthesis is presented in this review, emphasizing plant parts as reducing agents and their medical applications, including their antimicrobial, anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as key mechanisms of action for these applications to facilitate further research on the biomedical fields in the future.
1. Introduction
Nanotechnology is a branch of science and technology that deals with synthesizing and manipulating materials over a very small scale (1–100 nm) [1]. In addition to being used in pharmaceuticals and biomedical fields, it can also be used in the synthesis of nanoparticles for the delivery of drugs, treatment of cancer, diagnosis, and the prevention of infection [2,3,4,5,6]. The high surface area-to-volume ratio of these nanomaterials sets them apart from bulk substances with similar compositions in terms of their physicochemical properties [7]. One of the reasons for nanoparticles’ widespread use in biomedicine is their ability to interact well with biological membranes, receptors, nucleic, and protein acids due to their small size (nanoscale) [8]. The biocompatibility, stability, and safety of ZnO nanoparticles make them an excellent choice for use in medical applications [9]. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ZnO-NPs as a pharmaceutical excipient, and it is widely used in prescription formulas and cosmetics [10]. A further property of ZnO is that it has a -OH group that permits it to dissolve at a slow rate in acidic (e.g., cancer cells and tumor microenvironments) as well as strong basic environments, offering the potential to be used in biomedical applications [11]. The use of zinc oxide nanoparticles is widespread in biomedicine against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, anticancer drugs, and therapeutic agents. Furthermore, zinc oxide is used in the manufacture of concrete, photocatalysis, electronics, electrotechnology, and many other industrial applications [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19] as shown in Figure 1.
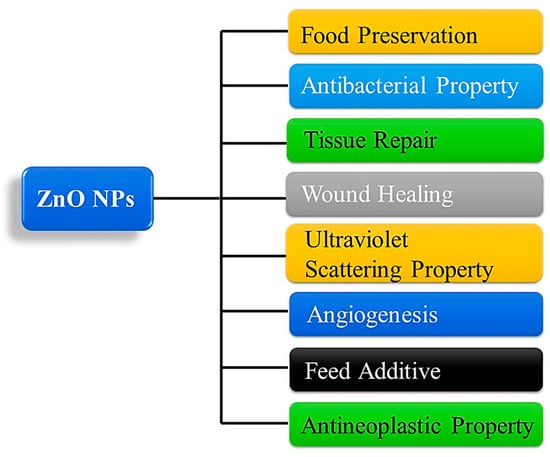
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of common applications of ZnO NP. ZnO, zinc oxide; NPs, nanoparticles.
2. Traditional Method of Producing NPs
Synthesis of NPs can generally be accomplished through a variety of strategies that can be classified as top-down or bottom-up methods. A top-down involves the decomposition of larger molecules into smaller ones, followed by the conversion of these smaller molecules into suitable nanoparticles, this is in contrast to a bottom-up approach in which atomic-sized particles are assembled to produce nanoparticles [20]. In order to manufacture ZnO nanoparticles, several chemical and physical procedures have been employed, such as hydrothermal processes, sol-methods, chemical vapor deposition, precipitations, laser ablations, and physical vapor depositions [21,22,23,24,25,26]. It is important to keep in mind that these methods typically involve the use of organic solvents and hazardous reducing agents, which are in most cases highly reactive and toxic to the environment. In a green synthesis process, microbes and plants are used to create nanoparticles for biomedical applications [27,28,29]. In addition to being environmentally friendly, this process extends the life of nanoparticles, overcoming the limitations of traditional chemical and physical methods for NP synthesis [30]. There are several functional groups in plant phytoconstituents, such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, and amine, that react with metal ions to reduce their size to a nanometer and it is believed that the -OH group in flavonoids is responsible for the reduction of metal ions into NPs. Furthermore, these compounds not only facilitate the biological reduction of ions to nanoscale sizes, but also facilitate the capping of nanoparticles, which are necessary for the stability and biocompatibility of nanoparticles [31,32,33]. The top-down approach can be implemented in several ways such as laser ablation, chemical etching, sputtering, mechanical milling, and so on [34]. In addition to biological techniques, non-biological techniques are also included in the bottom-up strategy, such as spinning, laser pyrolysis, flame spraying, and atomic condensation have been mentioned. Biological strategies are sometimes referred to as green strategies and utilize a variety of biotic resources, including plants, algae, microbes, and other biological components, such as egg albumin, starch, and gelatin, to produce diverse types of nanoparticles [35,36,37,38]. This process used to produce ZnO NPs is safe, environmentally friendly, biocompatible, and simple. Several techniques for producing NP are depicted in Figure 2. The green synthesis approach has grown in significance over the past few years due to its many advantages, including ease of scaling up for large-scale synthesis, low cost, good stability of the nanoparticles produced, and non-toxic byproducts. This makes it the best method for the production of metal oxide nanoparticles such as ZnO NPs compared to other chemical synthesis methods that result in toxic chemical species adsorbed on the surface of nanoparticles. Thus, this study primarily focuses on environmentally sustainable ways to produce ZnO NPs, particularly from plant components, as well as their biomedical applications.
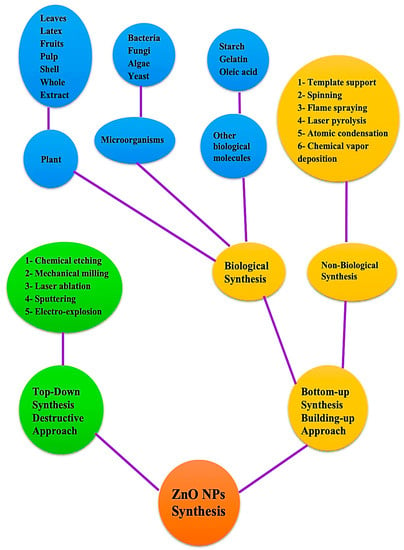
Figure 2.
General methods for creating zinc oxide nanoparticles.
3. Green Synthesis of Nanomaterials
A biosynthesis of nanomaterials is a technique that uses plants and biopolymers to form nanoparticles with a wide range of biomedical applications. It is an expense and environmentally friendly approach because harmful chemicals are not present or a large amount of energy is not required, which explains why this innovative approach is so popular. Further benefit of this process is that the pristine substances are naturally rich in amino, carboxyl, and hydroxyl groups, which are commonly utilized as stabilizing agents or capping agents in aqueous solutions, which lead to the formation of nanoparticles [39,40]. A wide range of plants, bacteria, algae, fungi, as well as other biological components, such as starch and egg, have been employed in the biosynthesis of ZnO NPs, as shown in Figure 3. It is well known that natural compounds, especially phytochemicals, found in plant parts, such as leaves, fruit peels, flowers, and seeds were used in the green synthesis of metal oxide NPs. The plant method has many advantages over the microbe approach because it doesn’t need separate, complicated, or many processes, such as isolation, culture development, and maintenance [41]. The extracted solution may be directly used to synthesize ZnO or may be dried to concentrate solid extracts. Following this, various pH and temperature conditions are applied to react zinc precursors and plant extracts [42]. It is necessary to add zinc precursors to the solution if the extract is used as an aqueous solution [43]. Alternatively, the zinc precursor is mixed with distilled water along with the leaf extract powder [44]. The main mechanism of action is the oxidation and reduction of zinc ions by a phytochemical found in natural extracts [45]. As a result of their considerable antimicrobial activity, photodegradation, and metal ion adsorption process, green synthesized ZnO NPs are being used in many fields including biomedicine and biotechnology [46,47,48]. According to current research investigations, nanoparticles synthesized via the green pathway are more effective at inhibiting bacterial growth because they are coated with functional groups derived from phytochemicals [49]. The green synthesis method also exhibits greater catalytic activity and reduces exposure to and use of hazardous and expensive chemicals, which can help to protect the environment from their toxicity. Throughout this review, we will describe some of the applications of ZnO NPs manufactured from natural extracts.
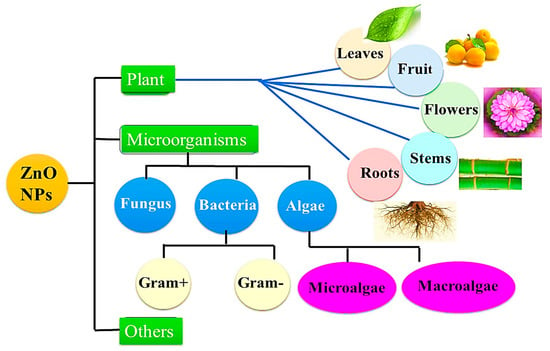
Figure 3.
The typical sources of biosynthesis processes used to produce zinc oxide nanoparticles.
Plant-Based Synthesis of ZnO NPs
Researchers have recently given a lot of attention to plant-based nanoparticle synthesis since it is rapid, inexpensive, and environmentally safe. In relatively recent work, Nazir, Arif, et al. investigated the effect of Rumex dentatus leaf extract on the formation of ZnO nanoparticles using zinc nitrate precursors, and then successfully used it as an efficient antibacterial agent [50]. Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) were created utilizing thyme leaf extract using a green technique, according to ST Karam et al. The formation of the nanoparticles were spherical in shape with an average size in the range of 39.4–51.86 nm [51]. In a study conducted by Droepenu et al., Anacardium occidentale leaf extract was used to produce ZnO NPs with two precursors of zinc salt (zinc acetate dihydrate and zinc chloride) and evaluated against Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Exiguobacterium aquaticum [52]. Zinc nitrate hexahydrate was used as a precursor to producing ZnO nanoparticles from the Vitex negundo plant, which demonstrated bacterial inhibition against pathogenic gram-positive and gram negative bacteria [53]. According to Aldalbahi et al., zinc nitrate hexahydrate was used as a precursor in the green synthesis of ZnO NPs using an aqueous extract of K. blossfeldiana, and its cytotoxicity and anticancer properties were evaluated [54]. Sambucus ebulus leaf extract was used to generate zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs), which were then investigated for a number of potential future applications [55]. There is evidence to suggest that green-generated ZnO NPs utilizing Passiflora caerulea leaf extract may be used to treat urinary tract infections since they are multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles. The obtained ZnO nanoparticles were tested against a pathogenic culture that was extracted from the urine of a patient with a UTI [56]. According to a study, Parkia roxburghii seeds extract used to produce ZnO nanoparticles demonstrated outstanding methylene blue (MB) and Rhodamine B dye degradation, reaching nearly 98% [57]. ZnO NPs isolated from extracts of Allium sativum, Rosmarinus officinalis, and Ocimum basilicum have reportedly shown significant antioxidant activity [58]. Recent studies suggest that the synthetic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs), which were produced using zinc nitrate and an aqueous peel extract from Lagenaria siceraria (L. siceraria), represent an important environmentally friendly alternative to combat malaria parasites and vectors [59]. Examined the performance of ZnO NPs created by Eucalyptus globulus as photocatalysts for. Furthermore, Zinc nitrate and Aloe vera leaf extract were used to produce stable and spherical ZnO nanoparticles. The formed ZnO NPs were examined for their various properties employing UV-Vis spectrophotometers, FTIR, photoluminescence, XRD, FE-SEM, and TEM [60]. There is no doubt that to produce green nanoparticles using metallic ions, plants are most often used as the substrate [61]. In addition, plant parts such as leaves, stems, roots, fruits, and seeds produce a variety of phytochemicals that have been used to synthesize ZnO NPs, which have been used in a variety of potential applications shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
A variety of plant parts were utilized to synthesize zinc nanoparticles.
In theory, one possible reason for this is that other biological sources are perceived as being more dangerous and more complex than vegetable substrates. Furthermore, plants have the potential for large-scale production and the ability to produce NPs of various shapes and sizes. A precise proportion of plant extract is added with zinc precursors such as zinc nitrate, zinc acetate, or zinc chloride. Following the mixing of the ingredients, Whatman paper was used to achieve a transparent solution that would be used as an extract in the next step. ZnO NPs are subsequently produced by calcining the mixture at a higher temperature. Visual confirmation of the ZnO NPs was achieved by using a color change, while further confirmation was obtained using UV-Vis spectroscopy. The key steps of the green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles are shown in Figure 4. Shows the key steps of the green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. It is recognized that plant extracts are used in a green synthesis method to create ZnO NPs an exceptional antibacterial effectiveness against a wider variety of germs than is seen with chemically produced. They are therefore non-toxic and gentle on the skin. appropriate for use in products meant for contact with an animal or human. Given these characteristics, synthesis of green ZnO NP using plant extracts can also be used to give fabrics antimicrobial characteristics, while preserving the development of environmental sensitivity [85].
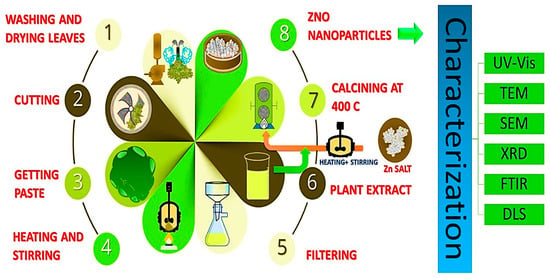
Figure 4.
Key steps of the green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles.
4. Mechanism of “Green” Synthesis for ZnO NPs
In a mechanism based on plants leaf extract to synthesize nanoparticles, the extract is incorporated with metal precursors at various conditions to facilitate the synthesis of nanoparticles [86]. A variety of factors related to the conditions of the leaf extract are acknowledged to influence the rate of nanoparticle formation, its yield, and its stability including kinds of phytochemicals, metal salt concentrations, pH, and temperature [87,88,89]. The phytochemicals included in plant extracts have a remarkable ability to decrease metal ions in a much shorter time than fungi and bacteria, which need a longer incubation duration [90]. It has thus been found that plant leaf extracts are benign sources for the biosynthesis of metal oxide NPs as well as metal ions. Moreover, plant leaf extracts function in the NP synthesis process as both reducing and stabilizing agents to stimulate the production of NPs [91]. Additionally, the plant extract’s composition must be taken into account because different plant extracts contain varying levels of phytochemicals [92,93]. Plants contain an array of phytochemicals such as terpenoids, aldehydes, sugars, flavones, ketones, and amides, which contribute to the bioreduction of NPs [94,95,96]. There are various functional groups present in flavonoids that enhance their capacity to reduce metal ions. When flavonoids are converted from their enol form into their keto form, reactive hydrogen atom is released. Metal ions are converted into metal nanoparticles during this process. The enol-to-keto-transformation is responsible for the production of biogenic silver nanoparticles from sweet basil extracts (Ocimum basilicum) [97]. Sugars that are present in plant extracts, such as glucose and fructose, may also could contribute in the production of metallic NPs [98,99]. An analysis of FTIR spectra of biosynthesized NPs derived from plants revealed that the nascent NPs were repeatedly related to proteins [100]. It is also important to note that amino acids reduce metal ions in various methods. According to Gruen et al. [101], amino acids (namely cysteine, arginine, lysine, and methionine) exhibit excellent affinity for silver ions in solution [102] Recently, Ebrahiminezhad et al., [103]. examined the impact of amino acids on the reduction of magnetic oxide nanoparticles to identify their efficient potential behavior as effective biocompatible coating agents. The biomolecules in plant extracts consist of carbohydrates and proteins, which serve as reductants to assist the production of metallic NPs [104,105]. Further, the amino groups (-NH) in proteins present in the extracts may also play a significant role in the reduction of metal ions.
A variety of phytochemicals, such as flavones, alkaloids, phenols, and anthracenes, contain functional groups (such as –C–O–C–, –C–O–, –C=C–, and –C=O–) that could contribute to the generation of metal nanoparticles [106]. In general, liquid capping ligands are primarily responsible for stabilizing NPs to slow-down their further development and agglomeration [107], silver bromide emulsion was used to cover photographic films. As a result of the light shining on the film, the silver bromide was sensitized. Once the film is immersed in a solution of hydroquinone, the silver ion oxidizes the hydroquinone to quinone. During this process, the silver ions were converted into silver metal, which stayed in the emulsion. Considering the chemistry of photography, hydroquinone, plastohydroquinone or quinol (alcoholic compounds) are the major reduction agents in the process of reducing silver ions to silver nanoparticles by non-cyclic photophosphorylation [108]. Therefore, these results showed that biomolecules and heterocyclic chemicals isolated from plant extracts have a role in the extracellular creation of metallic NPs. Recently, it has been shown that several different phytochemicals found in plants can aid in the reduction of metal salt into metallic NPs. These include alkaloids, terpenoids, phenolic acids, sugars, polyphenols, and proteins [109,110] showed, for example, that terpenoids present in geranium leaf extract contribute to nanoparticle formation. There are several terpenoids found in Cinnamomum zeylanisum (cinnamon) extracts, including eugenol, which is integral to the bioreduction of the metal salts HAuCl4 and AgNO3. As a result of FTIR analysis, it was found that the hydroxyl groups (OH) contained in eugenol dissipate during the growth of Au and Ag NPs. It is also observed that functional groups such as carbonyl, alkenes, and chloride are formed after Au NPs being formed. Additionally, other groups, such as R-CH and -OH (aqueous) have also been reported before and after the generation of Au NPs [111]. Based on these findings, the authors suggested the potential chemical mechanism demonstrated in Figure 5. However, the exact mechanism for the preparation of metal oxide nanoparticles using plants remains unclear. It is generally agreed that, metallic nanoparticles are synthesized from plant extracts in three phases: (1) activation (bioreduction of metal ions/salts and nucleation process of the reduced metal ions), (2) growth (spontaneous combination of small particles with larger ones through a process called Ostwald ripening), and (3) termination (determining the final shape of nanoparticles).
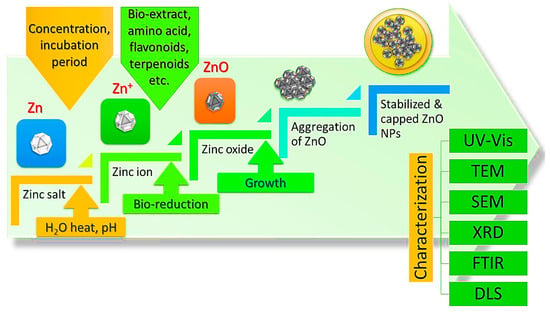
Figure 5.
Potential mechanisms in green synthesis of ZnO NPs.
5. Biomedical Applications
5.1. Antimicrobial Properties
Globally, the emergence of antibiotic resistance is one of the most pressing health issues of the 21st century. In this regard, it is necessary to develop an antibiotic agent that is capable of eradicating pathogenic bacteria that have become resistant to medication. Nanoparticles exhibit strong antibacterial properties because they are small and possess a high surface area compared to larger molecules. In addition, nanoparticles penetrate the membrane at varying levels, disrupting it, inserting themselves inside the cells, and inhibiting bacterial protein production [112,113,114]. It has been demonstrated that different metal nanoparticles (NPs), including gold, silver, iron, as well as metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs), such as iron oxide, copper oxide, and cobalt oxide, exhibit antimicrobial properties [115]. ZnO NPs have a potential to act as antibacterial agents, making them of interest to both the biomedical and food industries [116] as presented in Figure 6. Since traditional antibiotics are becoming increasingly resistant to microbial growth, several experiments have been conducted to improve antimicrobial activity. A series of in vitro antimicrobial tests has shown that metallic nanoparticles inhibit a wide range of bacteria species [117]. Metal nanoparticles are characterized by two factors that determine their antimicrobial effectiveness: (i) the materials used in their production; and (ii) the size of their particles. Throughout history, microbial resistance to antibiotics has increased, posing a serious threat to the health of the public. In addition, methicillin-resistant microorganisms can be found in antimicrobial drug-resistant microorganisms. Based on previous investigations show that ZnO NPs produced through green synthesis utilizing plant extracts had inhibitory effects on a range of pathogens, with excellent antimicrobial properties than ZnO NPs made through chemical synthesis. Furthermore, they have significant activity more than antibiotics and bactericides. Consequently, they are optimistic substances that could help in the effort to overcome antibiotics Using medical antibacterial textiles efficiently contributes to sterilizing by reducing the formation of microorganisms, resistance, and bacterial contamination, including antimicrobial bandages, dressings, and gloves.
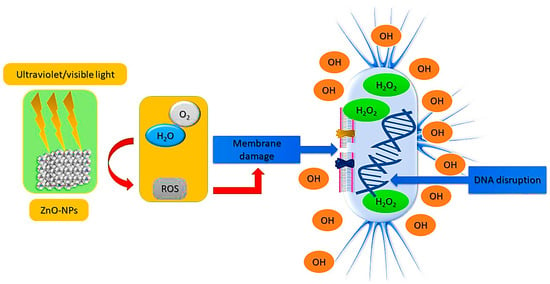
Figure 6.
Mechanism of ROS production from ZnO NPs and their bactericidal effect.
5.2. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Oxidative metabolism plays a crucial role in the survival of cells. During this method, free radicals, and ROS are formed, which can lead to certain unintended consequences. It is possible for these free radicals to overpower certain enzymes, including catalase, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase, and thereby result in lethal impacts on cells via oxidizing proteins, membrane lipids, DNA enzymes, and influencing cell signaling pathways. When excess amounts of these free radicals are produced in the body, cellular respiration ceases. In one hand, oxidation is a critical component of chemical deterioration that can affect food flavor, texture, nutritional value, and safety. On the other hand, antioxidants are available in both natural and synthetic forms to decrease the negative effects of oxidation [110,111]. Additionally, nanoparticles possess powerful antioxidant properties. The leaf extracts of Sageretia thea was used to produce plant-mediated ZnO with cubic structures and an average diameter of 20 nm. A variety of antioxidant assays have been performed along with free radical scavenging, antioxidant capacity, and reducing power evaluations. In addition, biogenic ZnO NPs demonstrated superior radical scavenging properties and overall antioxidant capacities above typical values [112]. ZnO NPs were biosynthesized using Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam leaves aqueous extract, and their antioxidant properties were evaluated, according to Mahdavi et al. [113]. The results of the green-synthesized nanoparticles were outstanding, as they demonstrated their ability to scavenge DPPH free radicals, ZnO NP concentration increases along with scavenging activity in bioinspired ZnO NPs. It has been shown that ZnO NPs derived from Sesbania sesban extract exhibit similar DPPH radical scavenging properties as silver and copper oxide NPs [114].
5.3. Anticancer Properties
It is known that anticancer drugs may damage the mitochondrial electron transport chain and cause significant levels of ROS to develop, since this chain has been implicated in the formation of ROS within cells, as present in Figure 6. Additionally, the presence of excessive ROS will cause mitochondrial damage and impair protein activity, resulting in cell apoptosis [115]. ZnO NPs exhibit some cytotoxicity in cancer cells, primarily due to their ability to release dissolved zinc ions into the cells, cause increased ROS production, and activate the apoptotic signaling pathway [116]. Using human liver cancer cells, HepG2, Sharma et al. [117] evaluated the effects of ZnO NPs and their potential therapeutic mechanisms. It was found that ZnO NPs increased cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in HepG2 cells, which were mediated by ROS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. When the mitochondrial membrane potential is lost, outer membrane pores open, which lead to the release of apoptotic proteins, such as cytochrome C, into the cytosol and the activation of the caspase enzymes. Moghaddam et al. have biosynthesized ZnO NPs and evaluated their anticancer efficacy in breast cancer MCF-7 cells using a novel yeast strain (Pichia kudriavzevii GY1). ZnO NPs have been observed to exhibit moderate to strong cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells, with apoptosis being more likely to be induced than cell cycle arrest as the mechanism causing this cytotoxicity [118]. The expression of antiapoptotic genes, such as Bcl-2, AKT1, and JERK/2, was downregulated during apoptosis induced by ZnO NPs, whereas proapoptotic genes, such as p21, p53, JNK, and Bax, were upregulated [119]. A considerable amount of research has been conducted on the use of ZnO NPs for cancer therapy, and it has been shown that they have a specific cytotoxic effect on the growth of cancer cells. According to Chandrasekaran and Pandurangan’s study [120] on the cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles against cultured C2C12 myoblastoma cancer cells and 3T3-L1 adipocytes found that the nanoparticles were more toxic to the cells of C2C12 than to those of 3T3-L1. It was reported that ZnO NPs inhibited proliferation of cancer cells and induced significant amounts of apoptosis through the pathways p53, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and caspase-3, as well as mitochondrial intrinsic apoptosis, which is mediated by ROS [121]. According to these findings, ZnO NPs can cause cancer cell death specifically, making them a potential target for cancer therapeutics. Additionally, there is evidence that autophagy and ROS contribute to ZnO NP’s cytotoxicity, however the regulatory mechanisms between autophagy and ROS are not fully understood. A study performed by Zhang et al. [122] investigated autophagy regulation and the relationship between autophagy and ROS in lung epithelial cells treated with ZnO NPs. It appears that ZnO nanoparticles may accumulate autophagosomes in A549 cells and hinder their autophagic flux. When zinc ions were released from ZnO NP in lysosomes, this was positively correlated with the induction of autophagy. Furthermore, the zinc ions released may cause damage to lysosomes and disrupt mitochondrial function which may lead to a build-up of ROS resulting in cell death. With these studies, we gained an improved understanding of the mechanisms governing the autophagy-lysosomes-mitochondria-ROS axis, which will contribute to the development of more effective methods of evaluating the toxicity of nanomaterials. A possible anticancer mechanism for zinc oxide nanoparticles derived from plant extracts is illustrated in Figure 7.
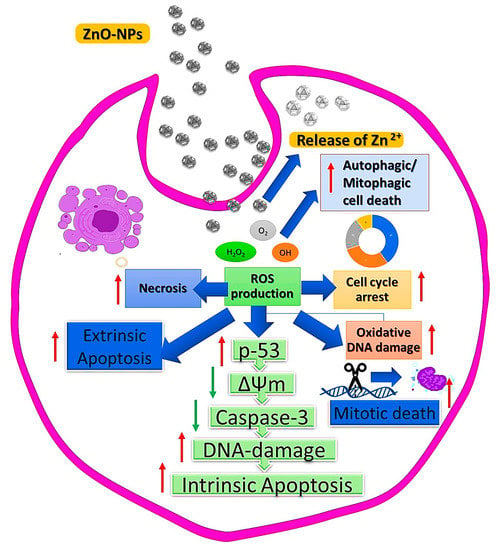
Figure 7.
Anticancer mechanism for zinc oxide nanoparticles produced by plant extracts.
5.4. Other Biomedlogical Applications
Apart from their antibacterial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, hemolytic, and antiviral properties, ZnO NPs have many other biological and medicinal applications [123]. It has been reported that cancer was identified as the second most common cause of dysphoria in humans, after cardiovascular diseases [124]. There is evidence that ZnO NPs possess antitumor properties. Accordingly, Aalami et al. produced ZnO nanoparticles from Saponaria officinalis extract and examined their anti-proliferative effects on MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and HFF cells, using the MTT assay [125]. Additionally, several studies have demonstrated that green-synthesized ZnO NPs have demonstrated a high level of wound healing capacity when used as an ointment [126]. It has been demonstrated that biologically produced ZnO NPs have catalytic properties, enzyme inhibition properties, anti-diabetic efficacy, and anticholinergic properties [127,128,129,130]. In addition to its blue and near-UV emitting properties, ZnO NPs also emit green or yellow fluorescence characteristics of oxygen vacancies. Due to their distinct physicochemical features, zinc oxide nanoparticles in the size range of 20–80 nm are frequently used in commercial products such as doping and catalysis. ZnO NPs would influence particular cells’ and tissues’ functionality [131]. ZnO NPs are highly valuable in numerous sectors, including catalysis, gas sensing, electronics, and environmental remediation, and their unique features encourage their incorporation into a variety of commercial products, biotechnology, and biomedical applications [132]. These properties further increase the effectiveness of ZnO NPs for bioimaging applications.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Several properties of these ZnO nanoparticles make them suitable for biomedical applications, including their ability to treat bacteria, inhibit cancer, combat inflammation, deliver drugs, dress wounds, and perform bioimaging. In light of their inherent toxicity, green-synthesized ZnO NPs have the potential to be useful in treating cancer and bacteria by causing ROS to be generated within the cells and activating apoptotic signals. Both bacteria and malignant cells are believed to be inhibited by these ROS. In addition, these manufactured ZnO NPs have long been recognized for their ability to enhance the bioavailability of medicinal medicines or biomolecules when acting as drug carriers to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Generally, the physical or chemical procedures that are used in the fabrication of nanoparticles are detrimental to the environment and require intensive, costly labor. An environmentally friendly method of producing zinc oxide nanoparticles is by utilizing extracts from a wide variety of plants and plant components, as well as biological molecules such as oleic acid, starch, and gelatin. Compared to traditional ZnO NPs, green synthesized ZnO NPs have several advantages including cost-effectiveness, ease of production, environmental safety, and biocompatibility. Through the use of plant components, such as leaf, stem, root, fruit, and seed, we have evaluated current trends and understandings of greenly synthesized ZnO NPs and their medicinal applications in this review. In a related study, researchers described comprehensive scientific data on recent advancements in the methods used to synthesize and characterize ZnO nanoparticles from plant sources [133]. Another study by Akbar et al. gives a summary of numerous investigations on the creation of zinc oxide nanoparticles by plants and their use as antimicrobial agents [134]. On other hand, a similar study conducted by Agarwal et al. [135] included an investigation and characterization techniques used for the environmentally friendly production of ZnO NPs from various biological sources. Although the widespread involvement of polyphenolic compounds in the plant commonwealth could be used to explain how extracts from various plant species are capable of producing NPs, a precise understanding of the green synthesis process is required to realize the full potential of this process in medical and industrial applications. Obtaining homogeneously dispersed NPs is extremely difficult despite the straightforward synthesis of NPs using a green method because many factors, such as temperature, the pH of the system, the type of capping agent used, the concentration of active compounds, etc., may be crucial in determining the size and morphology. It is crucial to compare ZnO NPs produced using medicinal plant extracts to their chemically or physically manufactured equivalents in order to ascertain whether the bioactivities observed may be related to the presence of capping agents in the ZnO NPs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A., S.A., M.Y. and G.M.S.; Methodology, M.Y., M.K.A.M., H.A.-K., A.A.A., J.A. and F.A.A.; Software, S.A., M.Y., G.M.S. and F.A.A.; Writing—original draft preparation, M.A., M.K.A.M., H.A.-K., A.A.A., J.A. and F.A.A.; Writing—review and editing S.A., M.Y., G.M.S. and F.A.A.; Supervision, M.A., S.A. and G.M.S.; Project administration, M.A., S.A. and G.M.S.; Funding acquisition, M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the university of Warith Al-Anbiyaa, Karbala, Iraq; the University of Technology, Baghdad, Iraq Taif University, Haweiah, Taif; and the University of Bisha, Saudi Arabia for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| UV | Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy |
| FESEM | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| XPS | X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| EDX | Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis |
| MTT | [3-(4.5- dimethylthiazol-2yl)]-2.5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| FE-TEM | Field emission transmission electron microscope |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| Z-P | Zeta potential |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| ZnO NPs | Zinc oxide nanoparticles |
References
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical–Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2020, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albukhaty, S.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Tiraihi, T.; Sakhi Jabir, M. Poly-l-lysine-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles: A novel method for the transfection of pro-BDNF into neural stem cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S125–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabir, M.; Sahib, U.I.; Taqi, Z.; Taha, A.; Sulaiman, G.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Shammari, A.; Alwahibi, M.; Soliman, D.; Dewir, Y.H. Linalool-loaded glutathione-modified gold nanoparticles conjugated with CALNN peptide as apoptosis inducer and NF-κB translocation inhibitor in SKOV-3 cell line. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kaabi, W.J.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Fartosy, A.J.M.; Al-Karagoly, H.K.; Al-Musawi, S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Dewir, Y.H.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Soliman, D.A. Development of Inula graveolens (L.) Plant Extract Electrospun/Polycaprolactone Nanofibers: A Novel Material for Biomedical Application. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurj, A.; Braicu, C.; Pop, L.-A.; Tomuleasa, C.; Gherman, C.D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The new era of nanotechnology, an alternative to change cancer treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2871–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderibigbe, B.A. Metal-Based Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Molecules 2017, 22, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, A.B.; Narain, R. Nanomaterials properties. In Polymer Science and Nanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 343–359. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P. Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Nanoparticle Toxicity in the Biomedical Field. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Singh, N.B.; Afzal, S.; Singh, T.; Hussain, I. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of their biological synthesis, antimicrobial activity, uptake, translocation and biotransformation in plants. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.G.L.; Rodrigues, C.; Valente, S.; Pimenta, C.; Pires, J.R.A.; Alves, M.M.; Santos, C.F.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Fernando, A.L. Eco-Friendly ZnO/Chitosan Bionanocomposites Films for Packaging of Fresh Poultry Meat. Coatings 2020, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, V.N.; Rajeswari, V.D. A review on green synthesis, biomedical applications, and toxicity studies of ZnO NPs. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 3569758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albukhaty, S.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Dragh, M.A. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluated its activity against bacterial isolates. J. Biotech Res. 2020, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Abinaya, M.; Vaseeharan, B.; Divya, M.; Sharmili, A.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Bacterial exopolysaccharide (EPS)-coated ZnO nanoparticles showed high antibiofilm activity and larvicidal toxicity against malaria and Zika virus vectors. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 45, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Wang, X.; Haroon, U.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Kamal, A.; Ali, Q.; Saleem, M.H.; Usman, K.; Alatawi, A.; Ali, S.; et al. Antifungal activity of Zinc nitrate derived nano Zno fungicide synthesized from Trachyspermum ammi to control fruit rot disease of grapefruit. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Jang, N.-Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Park, B.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Cho, N.-H. Application of ZnO-based nanocomposites for vaccines and cancer immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Marzoog, T.R.; Jabir, M.S. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic and anti-cancer activities of aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, T.; Mishra, K.; Khanuja, M.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 32, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, S.W.; James, O.; Sanusi, Y.; Olayinka, O. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using bashful (Mimosa pudica), leaf extract: A precursor for organic electronics applications. SN App. Sci. 2020, 2, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Yusof, H.; Mohamad, R.; Zaidan, U.H.; Abdul Rahman, N.A. Microbial synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential application as an antimicrobial agent and a feed supplement in animal industry: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Khan, A.M.; Shujait, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Ikram, M.; Imran, M.; Haider, J.; Khan, M.; Khan, Q.; Maqbool, M. Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.K.; Srivatava, R.K.; Prakash, S.G.; Yadav, R.S.; Panday, A.C. Photoluminescence and photoconductive characteristics of hydrothermally synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2000, 18, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.-M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.F.; Pedraza, A.J. Synthesis and alignment of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles by laser-assisted chemical vapor deposition. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 045609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoufi, D. Synthesis and microstructural properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viter, R.; Chaaya, A.A.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Kovalevskis, K.; Erts, D.; Miele, P.; Smyntyna, V.; Bechelany, M. Tuning of ZnO 1D nanostructures by atomic layer deposition and electrospinning for optical gas sensor applications. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.K.; Yu, J.S. Growth parameter dependent structural and optical properties of ZnO nanostructures on Si substrate by a two-zone thermal CVD. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 3123–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khane, Y.; Benouis, K.; Albukhaty, S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Al Ali, A.; Aouf, D.; Fenniche, F.; Khane, S.; Chaibi, W.; et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Citrus limon Zest Extract: Characterization and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safat, S.; Buazar, F.; Albukhaty, S.; Matroodi, S. Enhanced sunlight photocatalytic activity and biosafety of marine-driven synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashan, K.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abdulameer, F.A.; Albukhaty, S.; Ibrahem, M.A.; Al-Muhimeed, T.; AlObaid, A.A. Antibacterial Activity of TiO2 Nanoparticles Prepared by One-Step Laser Ablation in Liquid. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Raza, A.; Zafar, M.; Afsheen, S.; Kebaili, I.; Alrobei, H. Plant-mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for novel application to enhance the shelf life of tomatoes. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, M.; Nagashree, K.L.; Yallappa, S.; Manjappa, S.; Manjunath, K.S.; Dharmaprakash, M.S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using pre-hydrolysis liquor of Eucalyptus wood and its effective antimicrobial activity. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 97, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmigid, H.M.; Morsi, M.M.; Hussien, N.A.; Alyamani, A.A.; Alhuthal, N.A.; Albukhaty, S. Green Synthesis of Phosphorous-Containing Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles (nHAP) as a Novel Nano-Fertilizer: Preliminary Assessment on Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagoly, H.; Rhyaf, A.; Naji, H.; Albukhaty, S.; AlMalki, F.A.; Alyamani, A.A.; Albaqami, J.; Aloufi, S. Green synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles using Nigella sativa seed extract. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, G.; Palem, V.V.; Sundaram, T.; Sundaram, V.; Kishore, S.C.; Bellucci, S. Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications in Theranostics. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Mahadevan, S.; Arulmozhi, P.; Sriram, S.; Praseetha, P.K. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Atalantia monophylla leaf extracts: Characterization and antimicrobial analysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 82, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Namvar, F.; Mohamad, R. Green biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using brown marine macroalga Sargassum muticum aqueous extract. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokriwal, A.; Sharma, M.M.; Singh, A. Biological synthesis of nanoparticles using bacteria and their applications. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2014, 4, 38–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Yang, D.; Cui, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L. Egg white-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with excellent biocompatibility and enhanced radiation effects on cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jihad, M.A.; Noori, F.T.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Albukhaty, S.; AlMalki, F.A.; Alyamani, A.A. Polyethylene Glycol Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Nigella sativa Extract: A Smart Antibacterial Therapeutic Drug Delivery System. Molecules 2021, 26, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, A.K.; Verma, N.; Kaushal, P. Role of Biogenic Capping Agents in the Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential. Front. Nanotechnol. 2022, 3, 801620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadiji, A.E.; Babalola, O.O. Metagenomics methods for the study of plant-associated microbial communities: A review. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2020, 170, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Arshad, M.; Chaudhari, K.C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for revolutionizing agriculture: Synthesis and applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 925494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, M.; Aslam, U.; Khalid, B.; Chen, B. Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Chanu, T.I.; Samanta, D.; Chatterjee, S. A review on bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts as reductants and stabilizing agents. J. Photoch. Photobiol. B 2018, 183, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Haw, C.Y.; Zheng, Z.; Kang, J.; Zheng, J.-C.; Wang, H.-Q. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials from Plant Extracts and Future Green Prospects: A Topical Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2000266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abomuti, M.A.; Danish, E.Y.; Firoz, A.; Hasan, N.; Malik, M.A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Salvia Officinalis Leaf Extract and Their Photocatalytic and Antifungal Activities. Biology 2021, 10, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-T.; Thirumavalavan, M.; Jiang, T.-Y.; Lee, J.-F. Synthesis of ZnO/Zn Nano Photocatalyst Using Modified Polysaccharides for Photodegradation of Dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, D.; Verduin, J.J.; Shah, M.; Sharma, S.B.; Poinern, G.E.J. A Review of Current Research into the Biogenic Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles via Marine Algae and Seagrasses. J. Nanosci. 2017, 2017, e8013850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Belely, E.F.; Farag, M.M.S.; Said, H.A.; Amin, A.S.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Fouda, A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) Using Arthrospira platensis (Class: Cyanophyceae) and Evaluation of Their Biomedical Activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Raza, M.; Abbas, M.; Abbas, S.; Ali, A.; Ali, Z.; Younas, U.; Al-Mijalli, S.H.; Iqbal, M. Microwave assisted green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Rumex dentatus leaf extract: Photocatalytic and antibacterial potential evaluation. Z. Phys. Chem. 2022, 236, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, S.T.; Abdulrahman, A.F. Green Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles by Using Thyme Plant Leaf Extract. Photonics 2022, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droepenu, E.K.; Asare, E.A.; Wee, B.S.; Wahi, R.B.; Ayertey, F.; Kyene, M.O. Biosynthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoaggregates using aqueous extract from Anacardium occidentale leaf: Comparative study of different precursors. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika, S.; Sundrarajan, M. Antibacterial behaviour of Vitex negundo extract assisted ZnO nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 146, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldalbahi, A.; Alterary, S.; Ali Abdullrahman Almoghim, R.; Awad, M.A.; Aldosari, N.S.; Fahad Alghannam, S.; Nasser Alabdan, A.; Alharbi, S.; Ali Mohammed Alateeq, B.; Abdulrahman Al Mohsen, A.; et al. Greener Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Characterization and Multifaceted Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Sasani Ghamsari, M.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, J.; Kumar, S.V.; Rajeshkumar, S. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Vadivel, S.; Dhar, S.S.; Debbarma, S.; Kumaravel, M. One-pot green synthesis of zinc oxide nano rice and its application as sonocatalyst for degradation of organic dye and synthesis of 2-benzimidazolederivatives. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 104, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashant, G.K.; Prashant, P.A.; Utpal, B.; Manoj, G.; Nagabhushana, B.M.; Ananda, S.; Krishnaiah, G.M.; Sathyananda, H.M. In vitro antibacterial and cytotoxicity studies of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by combustion assisted facile green synthesis. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2015, 1, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kalpana, V.; Alarjani, K.M.; Rajeswari, V.D. Enhancing malaria control using Lagenaria siceraria and its mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles against the vector Anopheles stephensi and its parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, A.M.; Sivasankarapillai, V.S.; Rahdar, A.; Joseph, J.; Sadeghfar, F.; Anuf, A.R.; Rajesh, K.; Kyzas, G.Z. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and antifungal activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1211, 128107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Huang, Y.; Parsons, J.G.; Zhao, L.; Lopez-Moreno, L.; Hernandez-Viezcas, J.A.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Plant-based green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Scientific curiosity or a realistic alternative to chemical synthesis? Environ. Eng. 2016, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2014, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyamani, A.A.; Albukhaty, S.; Aloufi, S.; AlMalki, F.A.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Sulaiman, G.M. Green Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Phlomis Leaf Extract: Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, H.; Shah, M.; Andleeb, A.; Faisal, S.; Khattak, A.; Rizwan, M.; Drouet, S.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Plant-Based Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Aquilegia pubiflora: Their Antiproliferative Activity against HepG2 Cells Inducing Reactive Oxygen Species and Other In Vitro Properties. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 4786227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siripireddy, B.; Mandal, B.K. Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, G.R.K.S.; Tabrizi, M.H.; Ardalan, T.; Yadamani, S.; Safavi, E. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of anti-angiogenesis, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxicity properties. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, O.; Soto-Robles, C.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, C.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.; Castro-Beltrán, A.; Olivas, A.; Morales, P.L. Fruit peel extract mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1147, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Ullah, W.; Akhtar, N.; et al. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Fruit Extracts of Myristica fragrans: Their Characterizations and Biological and Environmental Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupa, E.J.; Kaliraj, L.; Abid, S.; Yang, D.-C.; Jung, S.-K. Synthesis of a Zinc Oxide Nanoflower Photocatalyst from Sea Buckthorn Fruit for Degradation of Industrial Dyes in Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.M.; Amer, M.W.; Salem, N.M.; Abdeen, A.O. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) using Ailanthus altissima fruit extracts and antibacterial activity. Chem. Int. 2020, 6, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Dhatwalia, J.; Kumari, A.; Chauhan, A.; Mansi, K.; Thakur, S.; Saini, R.V.; Guleria, I.; Lal, S.; Kumar, A.; Batoo, K.M.; et al. Rubus ellipticus Sm. Fruit Extract Mediated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Green Approach for Dye Degradation and Biomedical Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Tahir, R.; Gillani, S.S.A.; Tahir, M.B.; Shakil, M.; Iqbal, T.; Abdellahi, M.O. Plant-mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Syzygium cumini for seed germination and wastewater purification. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghemand, A.; Khaghani, S.; Bihamta, M.R.; Gomarian, M.; Ghorbanpour, M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Nigella sativa L. extract: The effect on the height and number of branches. J. Nanostructures 2018, 8, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Atif, M.; AlQahtani, W.S.; Nicoletti, M.; Serrone, P.D. Therapeutic Potential Assessment of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Derived from Fennel Seeds Extract. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8045–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlzadeh, M.; Khosravi, R.; Zarei, A. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Peganum harmala seed extract, and loaded on Peganum harmala seed powdered activated carbon as new adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, L.F.A.; Jayalakshmy, E. Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using root extract of Zingiber officinale. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Batjikh, I.; Hurh, J.; Han, Y.; Huo, Y.; Ali, H.; Li, J.F.; Rupa, E.J.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from root extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and its photocatalytic degradation activity using methylene blue. Optik 2019, 184, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, P.; Cha, S.J.; Yang, I.J.; Sreekanth, T.; Kim, K.J.; Shin, H.M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Polygala tenuifolia root extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 146, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, A.M.; David Raju, M.; Rama Sekhara Reddy, D. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous root extract of Sphagneticolatrilobata Lin and investigate its role in toxic metal removal, sowing germination and fostering of plant growth. Inorg. Nano Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdagni, P.; Khatri, P.; Rana, J.S. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Flower Extract of Nyctanthes Arbor-Tristis and Their Antifungal Activity. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2016, 30, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeanyichukwu, U.L.; Fayemi, O.E.; Ateba, C.N. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Extracts and Characterization of Their Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Bahadoran, A.; Bayat, S.; Rahim, R.A.; Ariff, A.; Saad, W.Z. Effect of annealing temperature on antimicrobial and structural properties of bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Anchusa italica. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R.; Dlugaszewska, J. Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafey, A.M. Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles from Plant Leaf Extracts and Their pplications: A review. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 304–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.M.; Andrade, S.M.; Grenho, L.; Fernandes, M.H.; Santos, C.; Montemor, M.F. Influence of apple phytochemicals in ZnO nanoparticles formation, photoluminescence and biocompatibility for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Chan, Y.S.; Danquah, M.K. Biosynthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles. ChemBioEng Rev. 2016, 3, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.; El Azab, W.I.; Ali, H.R.; Mansour, M.S. Green synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of anthracene. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 045012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.M.; Ghasemi, N. Influence of temperature and concentration on biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using cherry extract. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2018, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantidos, N.; Horsfall, L.E. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by bacteria, fungi and plants. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1000233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, M.H.; Ibrahim, K.M.; Albukhaty, S. Phytochemical Analysis, and Anti-Microbial Activities of Ethanol Extract of Cordia myxa Fruit: In vitro Study. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 15, 2871–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, Isolation, and Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Bairagi, B.; Banerjee, P.; Ray, A.; Roy, P. Plants for Nanomaterial: Improving the Environmental Sustainability. Sustain. Nanotechnol. Strateg. Prod. Appl. 2022, 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Satapathy, S.; Acharya, D.; Dixit, P.K.; Mishra, G.; Das, J.; Dave, S. Mechanistic aspects and rate-limiting steps in green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles and their potential in photocatalytic degradation of textile dye. In Photocatalytic Degradation of Dyes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 605–630. [Google Scholar]
- Jorepalli, S.; Somala, A.R.; Annavaram, V.; Koduru, J.R. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles for environmental remediation. In Sustainable Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pirtarighat, S.; Ghannadnia, M.; Baghshahi, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum basilicum cultured under controlled conditions for bactericidal application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallappa, S.; Manjanna, J.; Dhananjaya, B.L.; Vishwanatha, U.; Ravishankar, B.; Gururaj, H.; Niranjana, P.; Hungund, B.S. Phytochemically Functionalized Cu and Ag Nanoparticles Embedded in MWCNTs for Enhanced Antimicrobial and Anticancer Properties. Nano-Micro Lett. 2016, 8, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, E.; Tanase, C.; Coman, N.-A.; Berta, L. A Review of Bark-Extract-Mediated Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Pinto, R.; Rocha, S.; Marques, P.; Neto, C.; Silvestre, A.; Freire, C. Unveiling the Chemistry behind the Green Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, L.C. Interaction of amino acids with silver(I) ions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 386, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Lin, Y.W.; Chang, H.T. Growth of various Au–Ag nanocomposites from gold seeds in amino acid solutions. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Amini, S.R.; Davaran, S.; Barar, J.; Ghasemi, Y. Impact of amino-acid coating on the synthesis and characteristics of iron-oxide nanoparticles (IONs). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 3957–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; El-Shabasy, R.M.; Khalifa, S.A.; Saeed, A.; Shah, A.; Shah, R.; Iftikhar, F.J.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Omri, A.; Hajrahand, N.H.; et al. Metal nanoparticles fabricated by green chemistry using natural extracts: Biosynthesis, mechanisms, and applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 24539–24559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; He, N. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, H.; Yasuda, H.; Harada, M.; Taguchi, E.; lida, M. Formation of silver nanoparticles from ionic liquids comprising N-alkylethylenediamine: Effects of dissolution modes of the silver(I) ions in the ionic liquids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, J.; Yoon, K.Y.; Hwang, J.; Rai, M. Phytofabrication of silver nanoparticles by leaf extract of Datura metel: Hypothetical mechanism involved in synthesis. J. Bionanoscience 2009, 3, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Ahmad, A.; Pasricha, R.; Sastry, M. Bioreduction of chloroaurate ions by geranium leaves and its endophytic fungus yields gold nanoparticles of different shapes. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maensiri, S.; Laokul, P.; Klinkaewnarong, J.; Phokha, S.; Promarak, V.; Seraphin, S. Indium oxide (In2O3) nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract: Synthesis and optical properties. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2008, 10, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Burguete, M.I.; García-Verdugo, E.; Luis, S.V.; Restrepo, J.A. Preparation of polymer-supported gold nanoparticles based on resins containing ionic liquid-like fragments: Easy control of size and stability. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 14831–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. ‘Green’synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, B.; Saneei, S.; Qorbani, M.; Zhaleh, M.; Zangeneh, A.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Pirabbasi, E.; Abbasi, N.; Ghaneialvar, H. Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam leaves aqueous extract mediated synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their antibacterial, antifungal, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and cutaneous wound healing properties under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadi, F.E.; Ghara, A.R.; Naeimi, A. Phytochemical fabrication, characterization, and antioxidant application of copper and cobalt oxides nanoparticles using Sesbania sesban plant. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 2859–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, M.; Gogvadze, V.; Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, G.; Rayamajhi, S. ZnO nanoparticles: A promising anticancer agent. Nanobiomedicine 2016, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Anderson, D.; Dhawan, A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2). Apoptosis 2012, 17, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroumand Moghaddam, A.; Moniri, M.; Azizi, S.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Bin Ariff, A.; Navaderi, M.; Mohamad, R. Eco-Friendly Formulated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in the MCF-7 Cancer Cell Line. Genes 2017, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 1062562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Pandurangan, M. In vitro selective anti-proliferative effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles against co-cultured C2C12 myoblastoma cancer and 3T3-L1 normal cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Raja, M.; Ahmad, I.; Siddiqui, M.K.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Alrokayan, S.A. ZnO nanorod-induced apoptosis in human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells via p53, survivin and bax/bcl-2 pathways: Role of oxidative stress. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, J.; Ding, K. Inhibition of cathepsin S induces autophagy and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines through ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and JNK signaling pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabir, M.S.; Rashid, T.M.; Nayef, U.M.; Albukhaty, S.; AlMalki, F.A.; Albaqami, J.; AlYamani, A.A.; Taqi, Z.J.; Sulaiman, G.M. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin production using nanocurcumin capped Au@ZnO nanocomposite. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, L.J. Cardiovascular disease in transgendered people: A review of the literature and discussion of risk. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 8, 2048004019880745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalami, A.H.; Mesgari, M.; Sahebkar, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Green Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Antiproliferative Effects through Apoptosis Induction and MicroRNA Modulation in Breast Cancer Cells. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2020, 2020, 8817110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.A.; Abdel-Hady, A.N.; Haridy, M.A.; Ebnalwaled, K.; Saied, A.A.; Soliman, A.S. Wound healing properties of green (using Lawsonia inermis leaf extract) and chemically synthesized ZnO nanoparticles in albino rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23975–23987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMalki, F.A.; Khashan, K.S.; Jabir, M.S.; Hadi, A.A.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abdulameer, F.A.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Albaqami, J. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Carbon Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Water and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Nanomater. 2022, 7, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrachari, S.; Taslimi, P.; Karaoglanli, A.C.; Uzun, O.; Alp, E.; Jayaprakash, G.K. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) dye in waste water and enzymatic inhibition study using cauliflower shaped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a novel One-pot green synthesis method. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velsankar, K.; Venkatesan, A.; Muthumari, P.; Suganya, S.; Mohandoss, S.; Sudhahar, S. Green inspired synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and its characterizations with biofilm, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-diabetic activities. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1255, 132420. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Luo, Y.; Xie, H.Q.; Chakraborty, S.; Monikh, F.A.; Bu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Intranasal exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces alterations in cholinergic neurotransmission in rat brain. Nano Today 2020, 35, 100977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Darroudi, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Biological synthesis and biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. J. 2017, 43, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbič, A.; Gorjanc, M.; Simončič, B. Zinc Oxide for Functional Textile Coatings: Recent Advances. Coatings 2019, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintelu, S.A.; Folorunso, A.S. A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts and its biomedical applications. BioNanoScience 2020, 10, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Tauseef, I.; Subhan, F.; Sultana, N.; Khan, I.; Ahmed, U.; Haleem, K.S. An overview of the plant-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their antimicrobial potential. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Venkat Kumar, S.; Rajeshkumar, S. A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles—An eco-friendly approach. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).