Estimation of Three-Dimensional Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking Using a Machine-Learning-Based Markerless Motion Capture System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
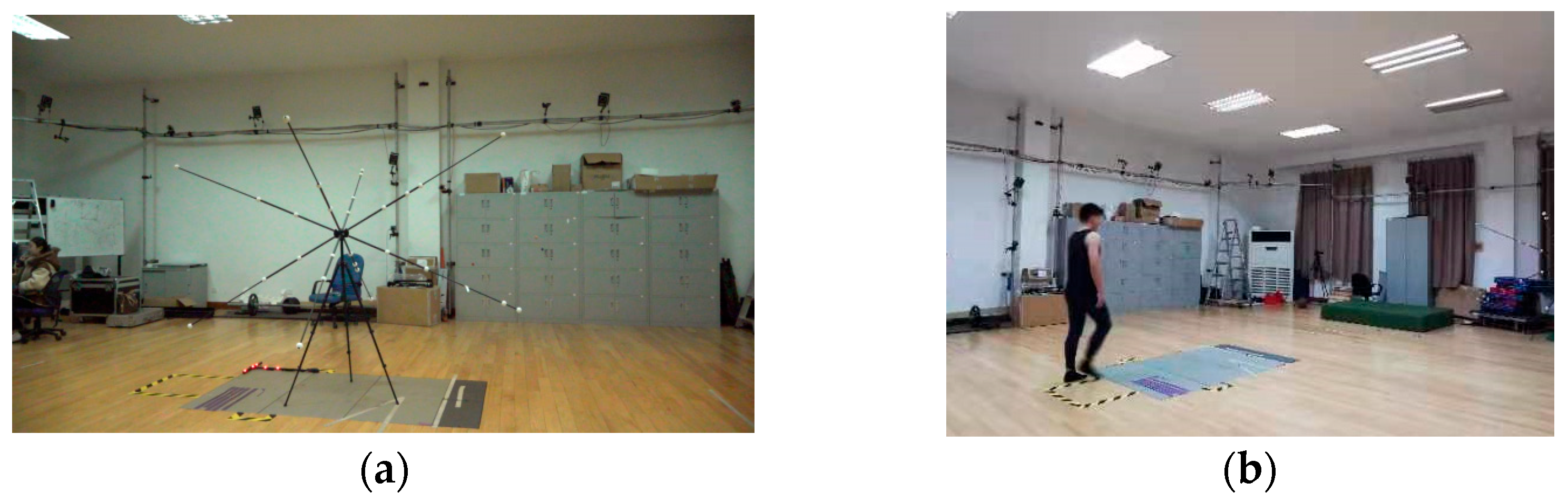
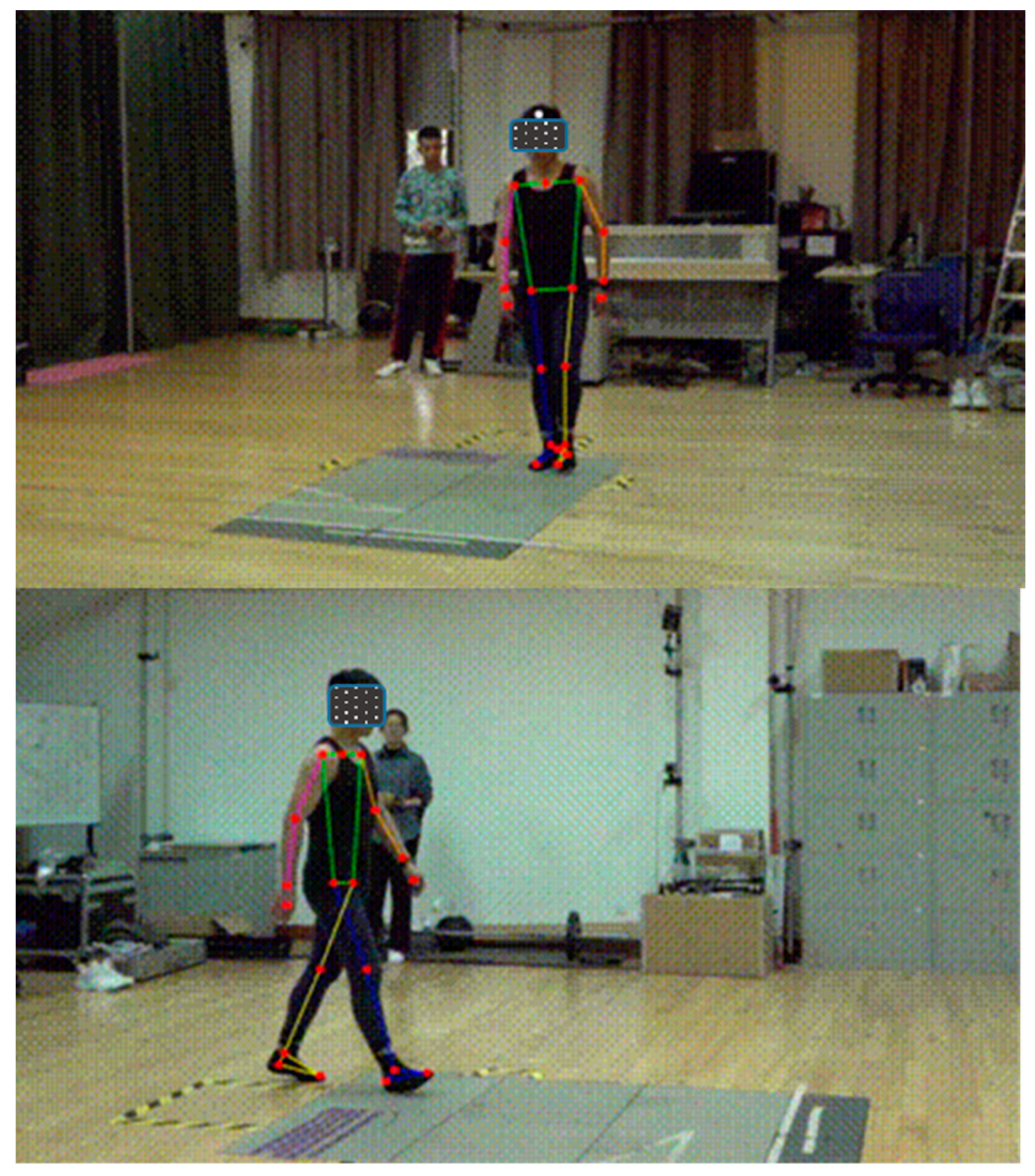
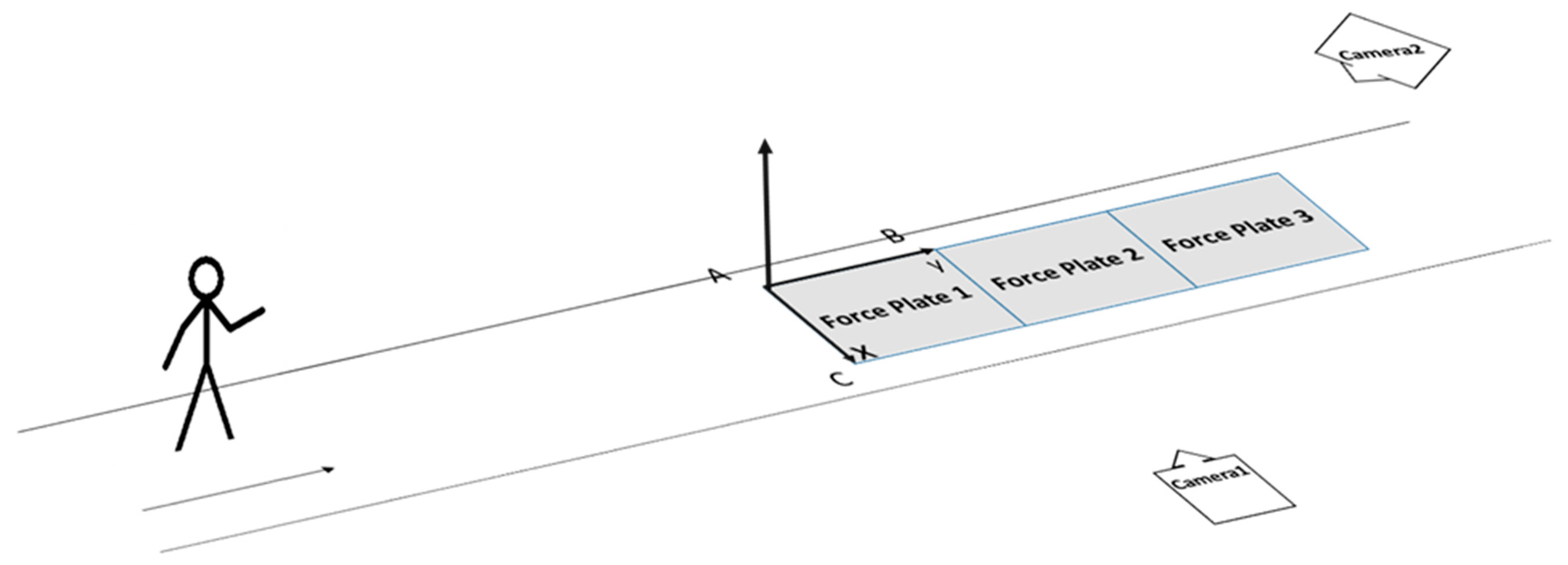
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Processing
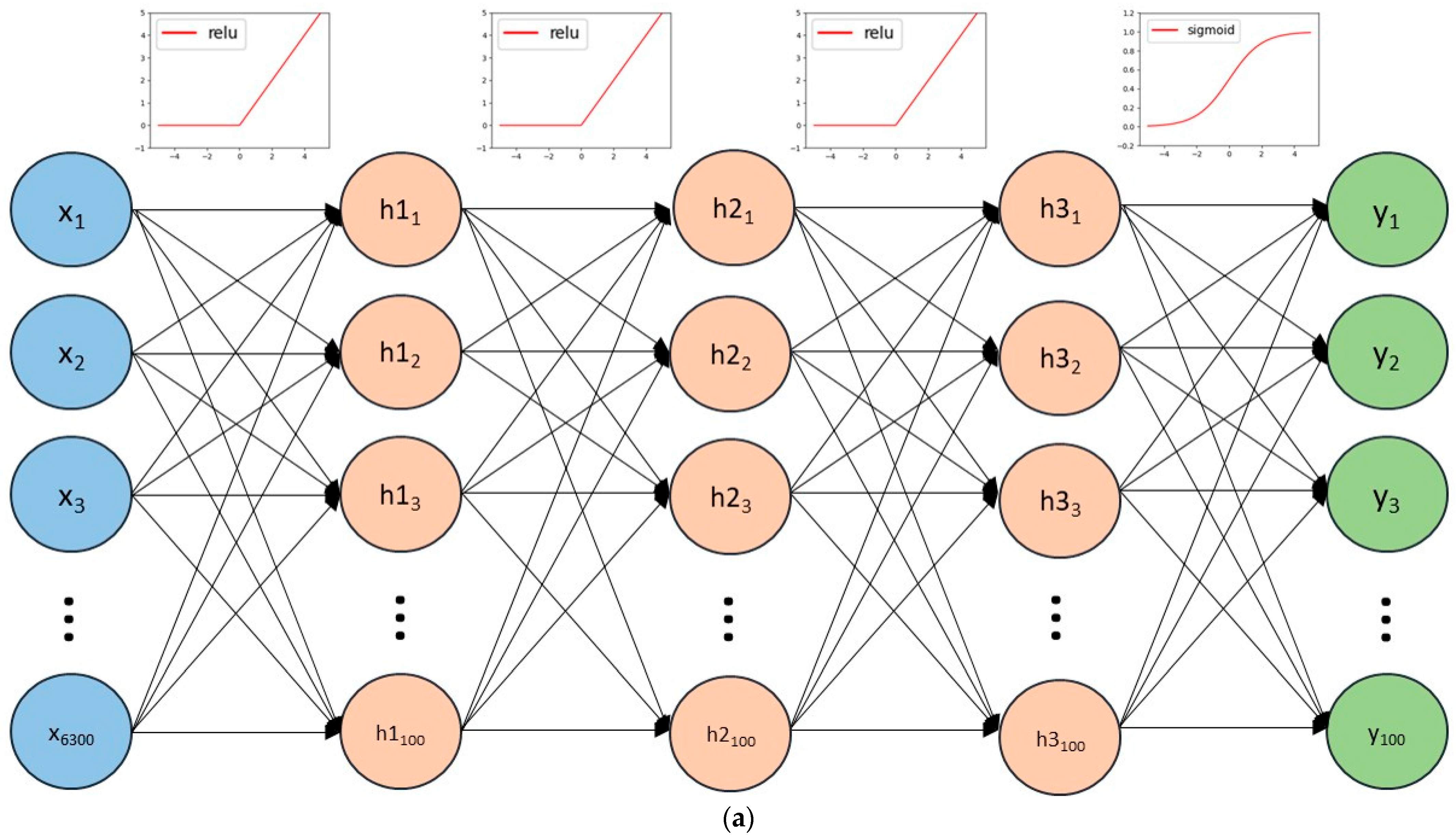
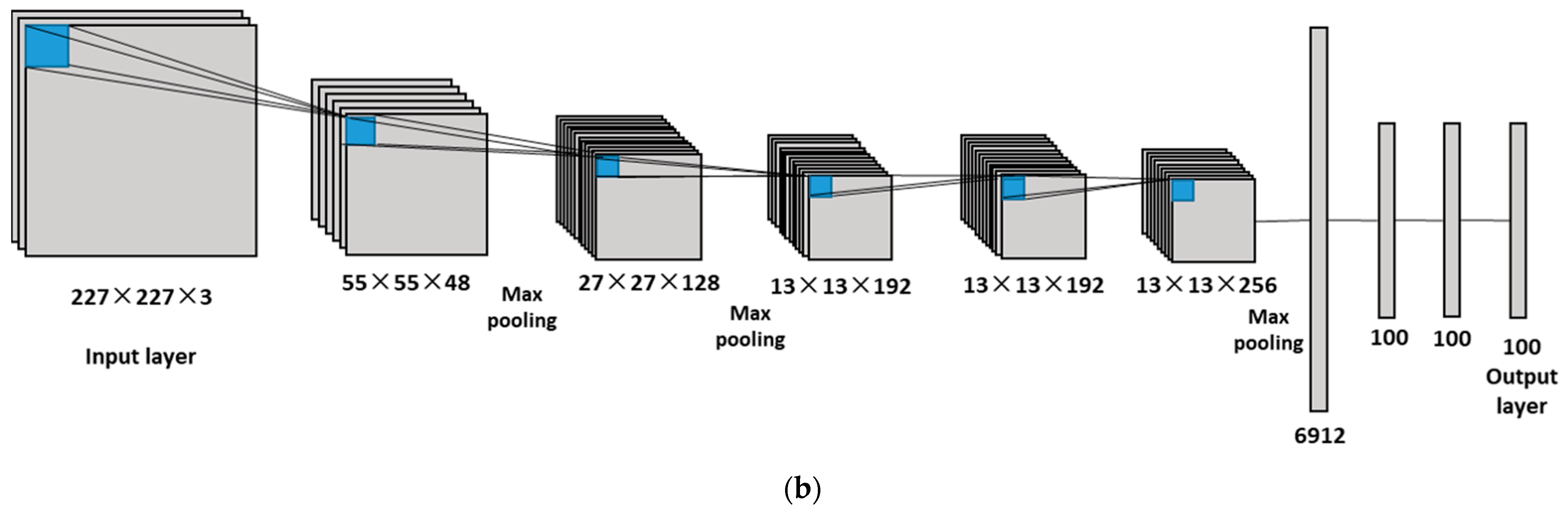
2.4. Model Construction
2.5. Model Assessment
2.6. Statistical Methods
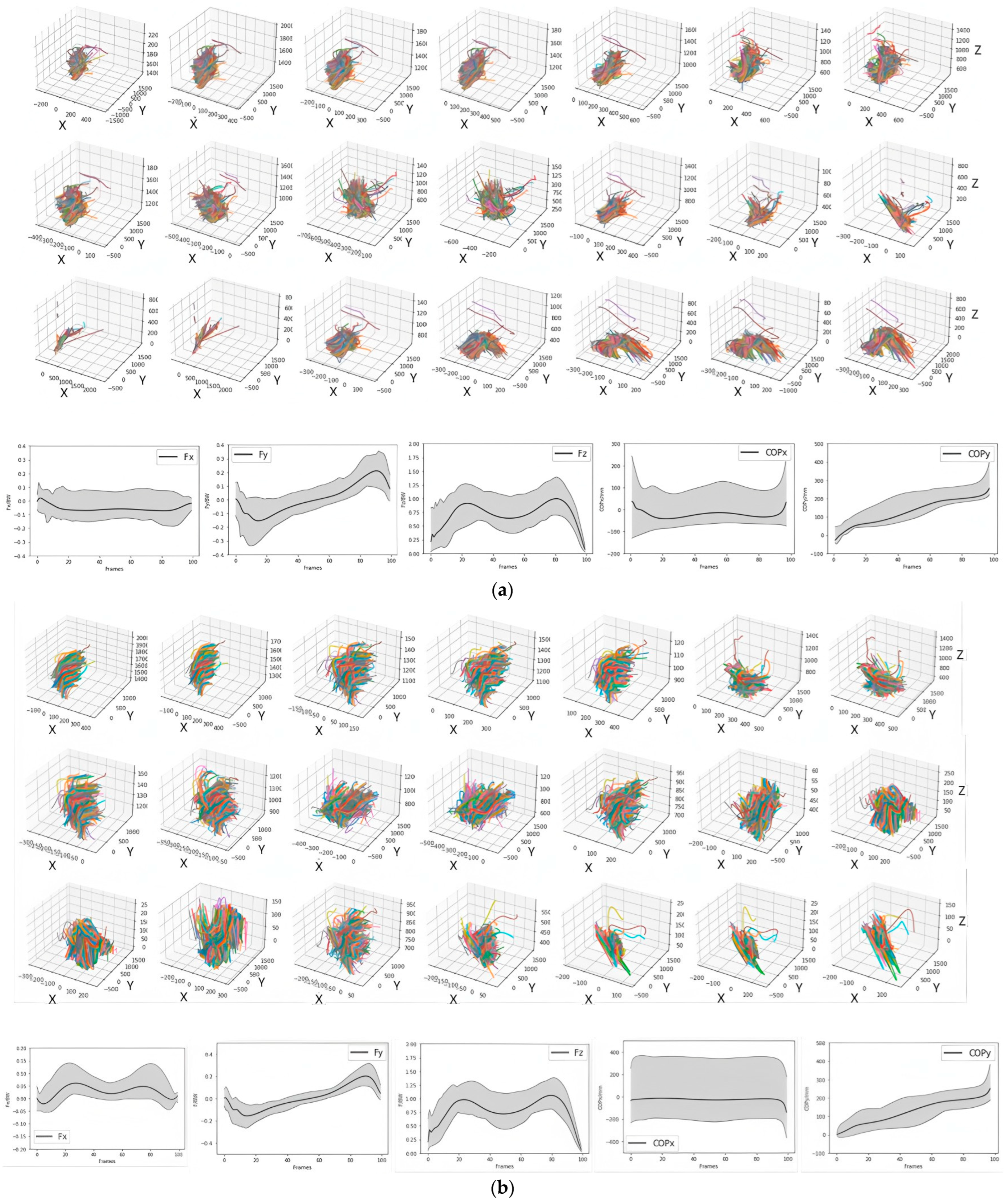
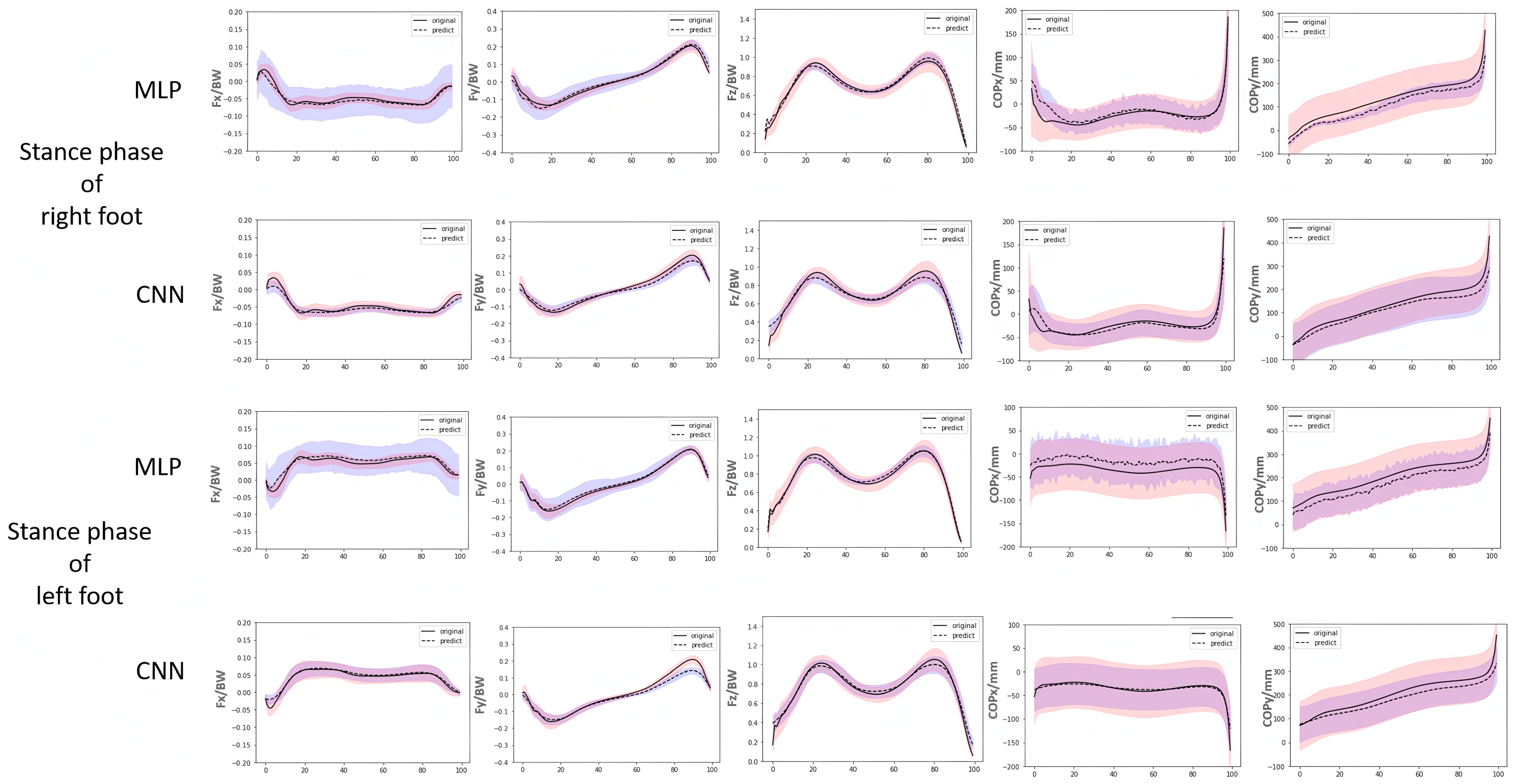
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GRF | Ground reaction force |
| COP | Center of pressure |
| MLP | Multi-layer perceptron |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| rRMSE | Relative root mean square errors |
References
- Visscher, R.M.; Sansgiri, S.; Freslier, M.; Harlaar, J.; Brunner, R.; Taylor, W.R.; Singh, N.B. Towards validation and standardization of automatic gait event identification algorithms for use in paediatric pathological populations. Gait Posture 2021, 86, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, Y.; Powell, D.; Woo, W.L.; Stuart, S.; Godfrey, A. Developing and exploring a methodology for multi-modal indoor and outdoor gait assessment. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 6759–6762. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Lach, J.; Lo, B.; Yang, G.-Z. Toward Pervasive Gait Analysis with Wearable Sensors: A Systematic Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabel, M.; Gilad-Bachrach, R.; Renshaw, E.; Schuster, A. Full Body Gait Analysis with Kinect. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Osis, S.T.; Hettinga, B.A.; Ferber, R. Predicting ground contact events for a continuum of gait types: An application of targeted machine learning using principal component analysis. Gait Posture 2016, 46, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, R.; Yorozu, A.; Fukumoto, T.; Takahashi, M. Estimation of Vertical Ground Reaction Force Using Low-cost Insole with Force Plate-free Learning from Single Leg Stance and Walking. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvinet, E.; Multon, F.; Manning, V.; Meunier, J.; Cobb, J. Validity and sensitivity of the longitudinal asymmetry index to detect gait asymmetry using Microsoft Kinect data. Gait Posture 2017, 51, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Bower, K.J.; Mentiplay, B.F.; Paterson, K.; Pua, Y.-H. Concurrent validity of the Microsoft Kinect for assessment of spatiotemporal gait variables. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2722–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.; Ye, M.; Shapiro, R.; Yang, R.; Noehren, B. Accuracy and repeatability of joint angles measured using a single camera markerless motion capture system. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Yogev Seligmann, G. Validity of the Kinect for Gait Assessment: A Focused Review. Sensors 2016, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.E.; Skubic, M. Passive in-home measurement of stride-to-stride gait variability comparing vision and Kinect sensing. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, FL, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, N.; Sakura, T.; Ueda, K.; Omura, L.; Kimura, A.; Iino, Y.; Fukashiro, S.; Yoshioka, S. Evaluation of 3D Markerless Motion Capture Accuracy Using OpenPose with Multiple Video Cameras. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.J.; Qu, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, B. Validity of an Artificial Intelligence System for Markerless Human Movement Automatic Capture. J. Beijing Sport Univ. 2021, 44, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bastien, G.J.; Gosseye, T.P.; Penta, M. A robust machine learning enabled decomposition of shear ground reaction forces during the double contact phase of walking. Gait Posture 2019, 73, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.R.; Alderson, J.; Lloyd, D.; Mian, A. Predicting Athlete Ground Reaction Forces and Moments from Spatio-temporal Driven CNN Models. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaris, D.-S.; Perez-Valero, E.; Jordan, L.; Barton, J.; Hennessy, L.; O’Flynn, B.; Tedesco, S. Predicting Three-Dimensional Ground Reaction Forces in Running by Using Artificial Neural Networks and Lower Body Kinematics. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 156779–156786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Vujaklija, I. Joint Torque Prediction via Hybrid Neuromusculoskeletal Modelling during Gait Using Statistical Ground Reaction Estimates: An Exploratory Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Park, S. Estimation of Three-Dimensional Lower Limb Kinetics Data during Walking Using Machine Learning from a Single IMU Attached to the Sacrum. Sensors 2020, 20, 6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogson, M.; Verheul, J.; Robinson, M.A.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Lisboa, P. A neural network method to predict task- and step-specific ground reaction force magnitudes from trunk accelerations during running activities. Med Eng. Phys. 2020, 78, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.; Alfieri, D.; Perez-Valero, E.; Komaris, D.-S.; Jordan, L.; Belcastro, M.; Barton, J.; Hennessy, L.; O’flynn, B. A Wearable System for the Estimation of Performance-Related Metrics during Running and Jumping Tasks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouda, F.J.; Giuberti, M.; Bellusci, G.; Maartens, E.; Reenalda, J.; van Beijnum, B.-J.F.; Veltink, P.H. Estimation of Vertical Ground Reaction Forces and Sagittal Knee Kinematics During Running Using Three Inertial Sensors. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillao, A.; Tedesco, S.; Barton, J.; O’flynn, B. Indirect Measurement of Ground Reaction Forces and Moments by Means of Wearable Inertial Sensors: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, R.; Takahashi, M. Insole-Based Estimation of Vertical Ground Reaction Force Using One-Step Learning with Probabilistic Regression and Data Augmentation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Lee, J.-M.; Mun, J.H. Ground reaction forces predicted by using artificial neural network during asymmetric movements. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, M.; David, S.; Koeppe, A.; Bamer, F.; Markert, B.; Potthast, W. Intelligent prediction of kinetic parameters during cutting manoeuvres. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, J.; Kraljić, D.; Zadravec, M.; Munih, M. Centre of Pressure Estimation during Walking Using Only Inertial-Measurement Units and End-To-End Statistical Modelling. Sensors 2020, 20, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.M.; Herzog, W.; Savelberg, H.H. Dynamic muscle force predictions from EMG: An artificial neural network approach. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1999, 9, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporace, G.; Batista, L.A.; Nadal, J. Prediction of 3D ground reaction forces during gait based on accelerometer data. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 34, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billing, D.C.; Nagarajah, C.R.; Hayes, J.P.; Baker, J. Predicting ground reaction forces in running using micro-sensors and neural networks. Sports Eng. 2006, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, D.T.-P.; Chan, Y.-Y.; Hong, Y.; Yung, P.S.-H.; Fung, K.-Y.; Chan, K.-M. Estimating the complete ground reaction forces with pressure insoles in walking. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhani, H.; Favre, J.; Crevoisier, X.; Aminian, K. Ambulatory assessment of 3D ground reaction force using plantar pressure distribution. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporace, G.; Batista, L.A.; Metsavaht, L.; Nadal, J. Residual analysis of ground reaction forces simulation during gait using neural networks with different configurations. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 2812–2815. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, D.; Leadbetter, R.; McKee, K.; Hopper, L.; Wild, C.; O’sullivan, P.; Straker, L.; Campbell, A. An Exploration of Machine-Learning Estimation of Ground Reaction Force from Wearable Sensor Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.E.; Choi, A.; Mun, J.H. Prediction of ground reaction forces during gait based on kinematics and a neural network model. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakas, G.; Baltzopoulos, V. Time and frequency domain analysis of ground reaction forces during walking: An investigation of variability and symmetry. Gait Posture 1997, 5, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanko, R.; Laende, E.; Selbie, S.; Deluzio, K. Inter-session repeatability of Theia3D markerless motion capture gait kinematics. BioRxiv 2020, 2020, 155358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Stance Phase | Training Sets | Test Sets | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects | Samples | Subjects | Samples | |
| Right | 135 | 2710 | 10 | 100 |
| Left | 135 | 1305 | 10 | 100 |
| Stance Phase | Component | MLP | CNN | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | GRFx | 0.918 ± 0.034 | 0.956 ± 0.018 | 49.370 | <0.001 |
| GRFy | 0.984 ± 0.008 | 0.987 ± 0.004 | 5.693 | 0.019 | |
| GRFz | 0.971 ± 0.012 | 0.975 ± 0.012 | 3.247 | 0.074 | |
| COPx | 0.901 ± 0.137 | 0.896 ± 0.054 | 0.056 | 0.813 | |
| COPy | 0.978 ± 0.015 | 0.974 ± 0.016 | 2.356 | 0.128 | |
| Left | GRFx | 0.920 ± 0.030 | 0.967 ± 0.012 | 104.620 | <0.001 |
| GRFy | 0.989 ± 0.004 | 0.988 ± 0.004 | 1.499 | 0.223 | |
| GRFz | 0.966 ± 0.019 | 0.978 ± 0.009 | 17.185 | <0.001 | |
| COPx | 0.727 ± 0.163 | 0.924 ± 0.033 | 70.797 | <0.001 | |
| COPy | 0.982 ± 0.009 | 0.977 ± 0.011 | 6.614 | <0.001 |
| Stance Phase | Component | MLP | CNN | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | GRFx | 12.08 ± 1.49 | 9.44 ± 1.39 | 83.777 | <0.001 |
| GRFy | 6.23 ± 1.42 | 6.49 ± 0.66 | 1.413 | 0.237 | |
| GRFz | 7.06 ± 1.04 | 7.37 ± 0.85 | 2.573 | 0.112 | |
| COPx | 9.33 ± 3.47 | 7.9 ± 2.83 | 5.090 | 0.026 | |
| COPy | 8.28 ± 1.95 | 6.81 ± 1.32 | 19.408 | <0.001 | |
| Left | GRFx | 11.05 ± 1.34 | 7.29 ± 1.17 | 222.221 | <0.001 |
| GRFy | 5.06 ± 0.68 | 8.03 ± 0.89 | 353.561 | <0.001 | |
| GRFz | 7.71 ± 1.39 | 6.03 ± 0.75 | 56.655 | <0.001 | |
| COPx | 27.64 ± 6.12 | 6.41 ± 1.44 | 570.769 | <0.001 | |
| COPy | 6.43 ± 1.8 | 6.52 ± 1.19 | 0.076 | 0.783 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, R.; Ugbolue, U.C.; Yang, C.; Liu, H. Estimation of Three-Dimensional Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking Using a Machine-Learning-Based Markerless Motion Capture System. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060588
Feng R, Ugbolue UC, Yang C, Liu H. Estimation of Three-Dimensional Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking Using a Machine-Learning-Based Markerless Motion Capture System. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060588
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Ru, Ukadike Christopher Ugbolue, Chen Yang, and Hui Liu. 2025. "Estimation of Three-Dimensional Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking Using a Machine-Learning-Based Markerless Motion Capture System" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060588
APA StyleFeng, R., Ugbolue, U. C., Yang, C., & Liu, H. (2025). Estimation of Three-Dimensional Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking Using a Machine-Learning-Based Markerless Motion Capture System. Bioengineering, 12(6), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060588








