Automated Risser Grade Assessment of Pelvic Bones Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
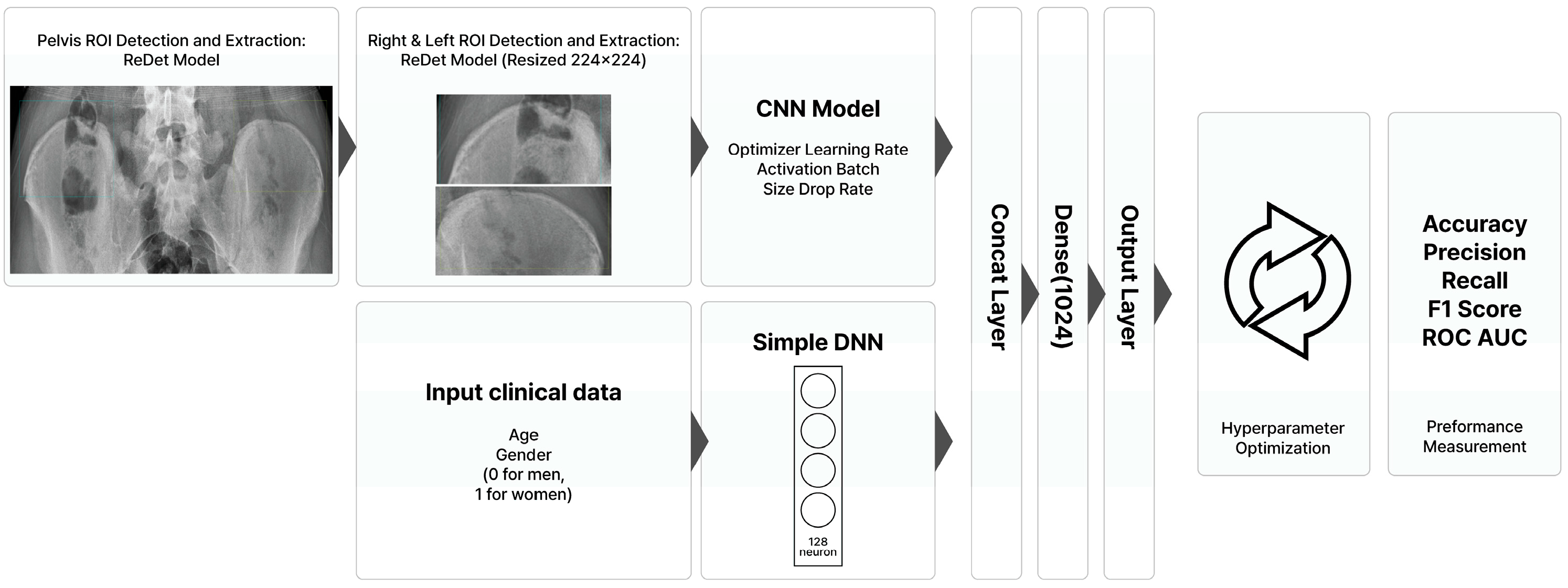
2.2. Deep Learning Model Development
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cavallo, F.; Mohn, A.; Chiarelli, F.; Giannini, C. Evaluation of Bone Age in Children: A Mini-Review. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 580314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.E.; Choi, J.; Kang, C.H.; Kang, W.Y.; Hong, S.J.; Shim, E.; Kim, B.H.; et al. Difference between bone age at the hand and elbow at the onset of puberty. Medicine 2022, 101, e28516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, D.; Chang, M.C. Assessment of Bone Age Based on Hand Radiographs Using Regression-Based Multi-Modal Deep Learning. Life 2024, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimeglio, A.; Canavese, F. Progression or not progression? How to deal with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis during puberty. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacquebord, J.H.; Leopold, S.S. In brief: The Risser classification: A classic tool for the clinician treating adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 2335–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vira, S.; Husain, Q.; Jalai, C.; Paul, J.; Poorman, G.W.; Poorman, C.; Yoon, R.S.; Looze, C.; Lonner, B.; Passias, P.G. The Interobserver and Intraobserver Reliability of the Sanders Classification Versus the Risser Stage. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, e246–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H. Medical image analysis using deep learning algorithms. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1273253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, G.K.; Thakur, A.; Kulkarni, S.; Khan, N.; Khan, S. Deep Learning Approaches for Medical Image Analysis and Diagnosis. Cureus 2024, 16, e59507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Quan, R.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, F. Advances in Medical Image Segmentation: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional, Deep Learning and Hybrid Approaches. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achararit, P.; Bongkaew, H.; Chobpenthai, T.; Nonthasaen, P. Generating accurate sex estimation from hand X-ray images using AI deep-learning techniques: A study of limited bone regions. Leg. Med. 2025, 74, 102612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.E.; Liu, L.; Almeida, L.; Kassick, C.; Makrogiannis, S. Artificial intelligence in pediatric osteopenia diagnosis: Evaluating deep network classification and model interpretability using wrist X-rays. Bone Rep. 2025, 25, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Nijhuis, K.D.; Barvelink, B.; Prijs, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, Z.; Jaarsma, R.L.; FFA, I.J.; Colaris, J.W.; Doornberg, J.N.; Wijffels, M.M.E. An open source convolutional neural network to detect and localize distal radius fractures on plain radiographs. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Trauma Soc. 2025, 51, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaludin, A.; Kadir, T.; Zisserman, A. SpineNet: Automated classification and evidence visualization in spinal MRIs. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 41, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Shan, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, S.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Hybrid transformer convolutional neural network-based radiomics models for osteoporosis screening in routine CT. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsilio, L.; Marzorati, D.; Rossi, M.; Moglia, A.; Mainardi, L.; Manzotti, A.; Cerveri, P. Cascade learning in multi-task encoder-decoder networks for concurrent bone segmentation and glenohumeral joint clinical assessment in shoulder CT scans. Artif. Intell. Med. 2025, 165, 103131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ke, Z.; Cai, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ke, Q.; Ye, Y. Pelvic bone tumor segmentation fusion algorithm based on fully convolutional neural network and conditional random field. J. Bone Oncol. 2024, 45, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, W.-Y.; Mao, B.-H. Borderline-SMOTE: A new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Hefei, China, 23–26 August 2005; pp. 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kuchiba, A.; Koyama, T. Confidence interval for micro-averaged F (1) and macro-averaged F (1) scores. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 4961–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Bai, Y. Solving the class imbalance problem using ensemble algorithm: Application of screening for aortic dissection. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V. Attention Cost-Sensitive Deep Learning-Based Approach for Skin Cancer Detection and Classification. Cancers 2022, 14, 5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.J.A.S. CBF-IDS: Addressing class imbalance using CNN-BiLSTM with focal loss in network intrusion detection system. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, K.E.; Dierckman, B.D.; Burnworth, L.; Meehan, P.L.; Oswald, T.S. Inter-observer and intra-observer reliability of the Risser sign in a metropolitan scoliosis screening program. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2011, 31, e80–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample size and ratio Sample class size and ratio |
| |||||
| Gender ratio Age distribution |
| |||||
| RT model |
| |||||
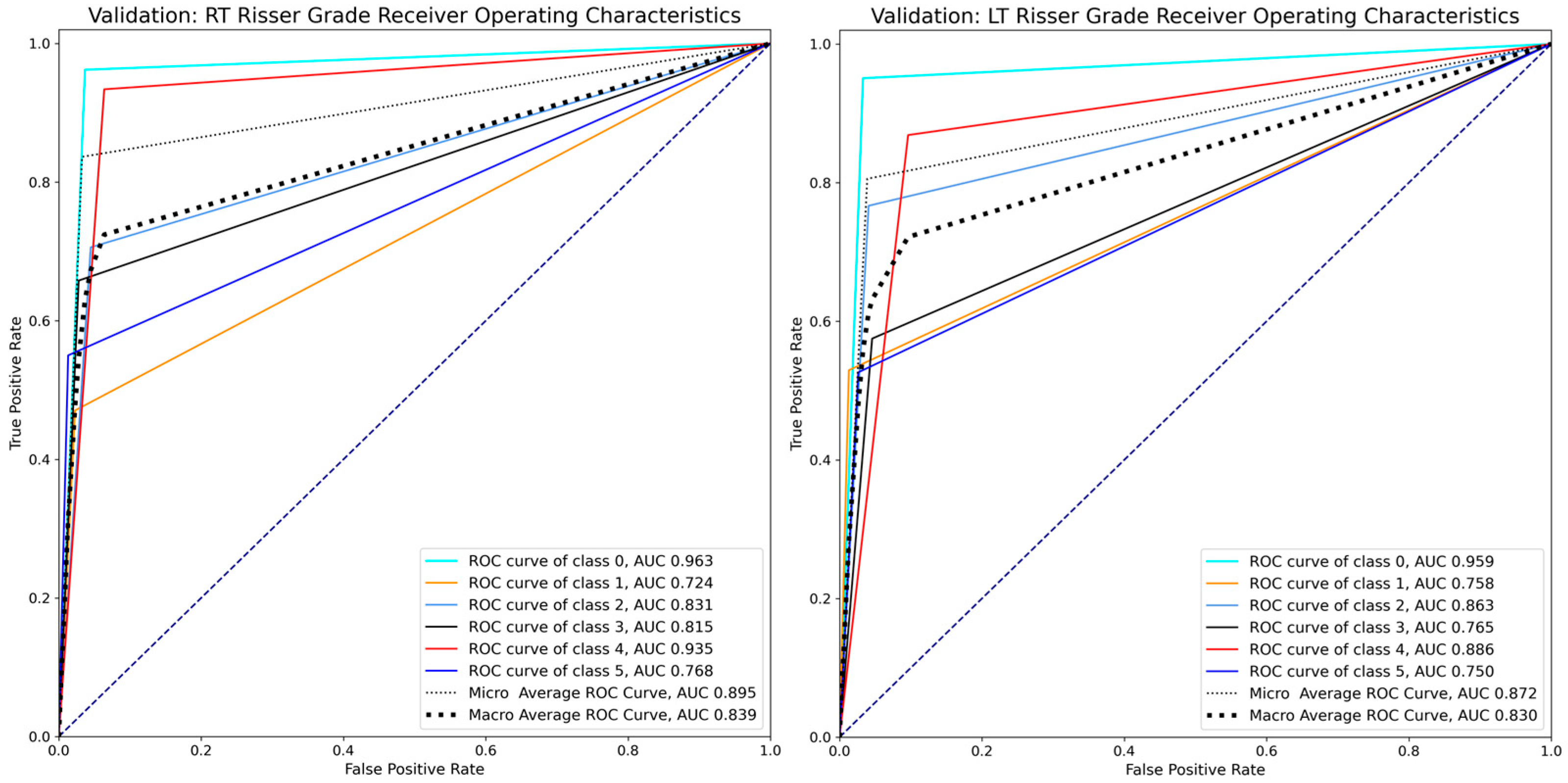
| Model performance | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-score | Support | ROC AUC |
| (Validation data) | 0 | 0.894 | 0.962 | 0.927 | 79 | 0.963 |
| 1 | 0.533 | 0.472 | 0.500 | 17 | 0.724 | |
| 2 | 0.649 | 0.706 | 0.676 | 34 | 0.831 | |
| 3 | 0.758 | 0.658 | 0.704 | 38 | 0.815 | |
| 4 | 0.914 | 0.934 | 0.924 | 136 | 0.935 | |
| 5 | 0.733 | 0.550 | 0.629 | 20 | 0.768 | |
| Microaverage | 0.836 | 0.836 | 0.836 | 324 | 0.895 | |
| Macroaverage | 0.747 | 0.713 | 0.727 | 324 | 0.839 | |
| Sample size and ratio Sample class size and ratio |
| |||||
| Gender ratio Age distribution |
| |||||
| LT model |
| |||||
| Model performance | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-score | Support | ROC AUC |
| (Validation data) | 0 | 0.906 | 0.951 | 0.928 | 81 | 0.959 |
| 1 | 0.692 | 0.529 | 0.600 | 17 | 0.758 | |
| 2 | 0.657 | 0.767 | 0.708 | 30 | 0.863 | |
| 3 | 0.639 | 0.575 | 0.605 | 40 | 0.765 | |
| 4 | 0.869 | 0.869 | 0.869 | 137 | 0.886 | |
| 5 | 0.556 | 0.526 | 0.541 | 19 | 0.750 | |
| Microaverage | 0.806 | 0.806 | 0.806 | 324 | 0.872 | |
| Macroaverage | 0.720 | 0.703 | 0.708 | 324 | 0.830 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.K.; Park, D.; Chang, M.C. Automated Risser Grade Assessment of Pelvic Bones Using Deep Learning. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060589
Kim JK, Park D, Chang MC. Automated Risser Grade Assessment of Pelvic Bones Using Deep Learning. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060589
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeoung Kun, Donghwi Park, and Min Cheol Chang. 2025. "Automated Risser Grade Assessment of Pelvic Bones Using Deep Learning" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060589
APA StyleKim, J. K., Park, D., & Chang, M. C. (2025). Automated Risser Grade Assessment of Pelvic Bones Using Deep Learning. Bioengineering, 12(6), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060589







