Hip Fractures: Clinical, Biomaterial and Biomechanical Insights into a Common Health Challenge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Insights into Hip Fractures
2.1. Clinical Risk Factors and Their Association with Major Fractures
- Demographic Factors
- Bone Health and Medical Conditions
- Lifestyle and Nutrition
- Environmental Factors
2.2. Clinical Assessment Tools Derived from Risk Factors
2.3. Limitations and Challenges of Current Clinical Tools
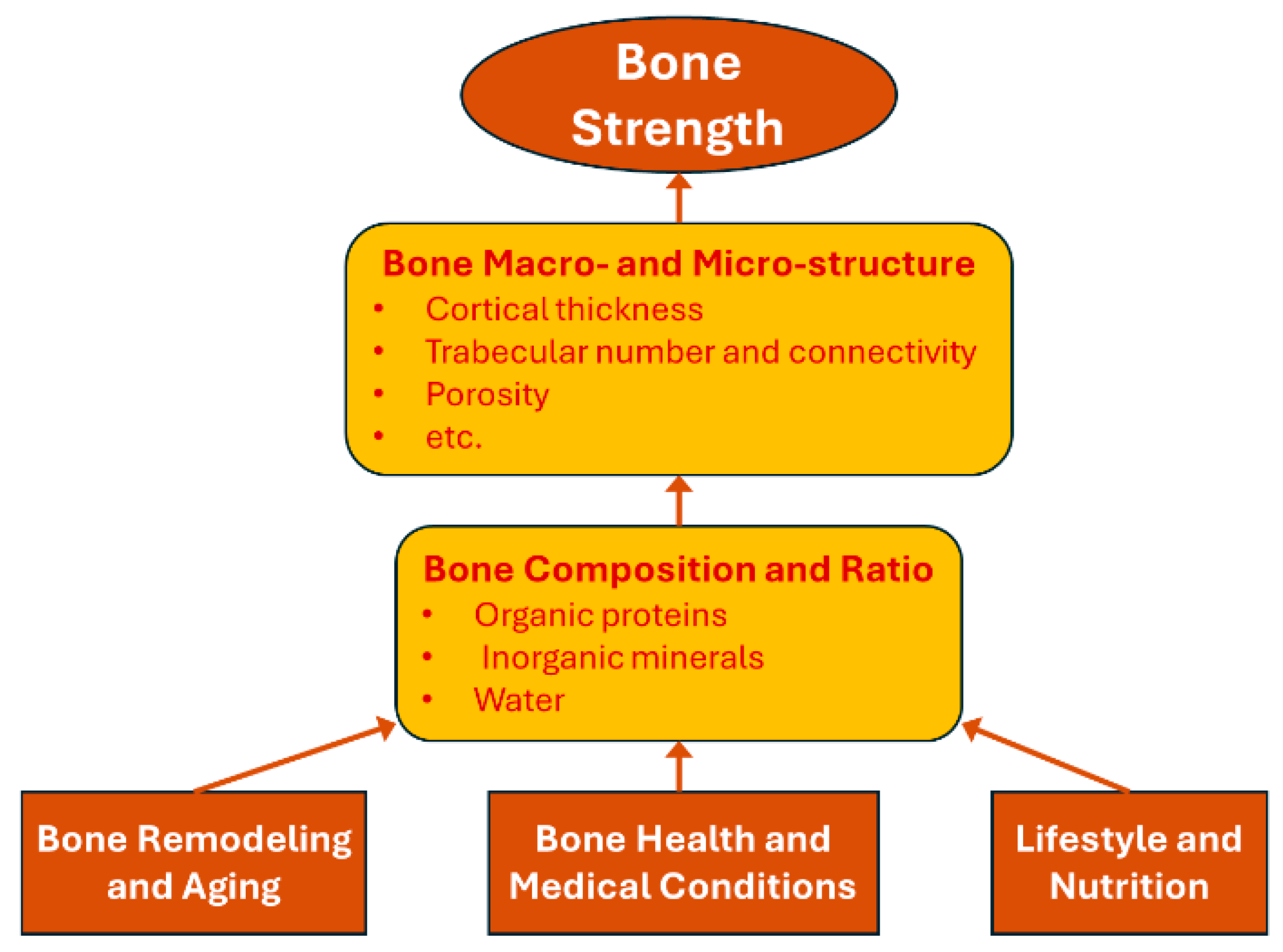
3. Biomaterial Perspectives on Bone Strength
3.1. Bone Composition and Microstructure
3.2. Changes in Bone Composition and Quality During Remodeling and Aging
3.3. Impact of Clinical Risk Factors on Bone Composition and Strength
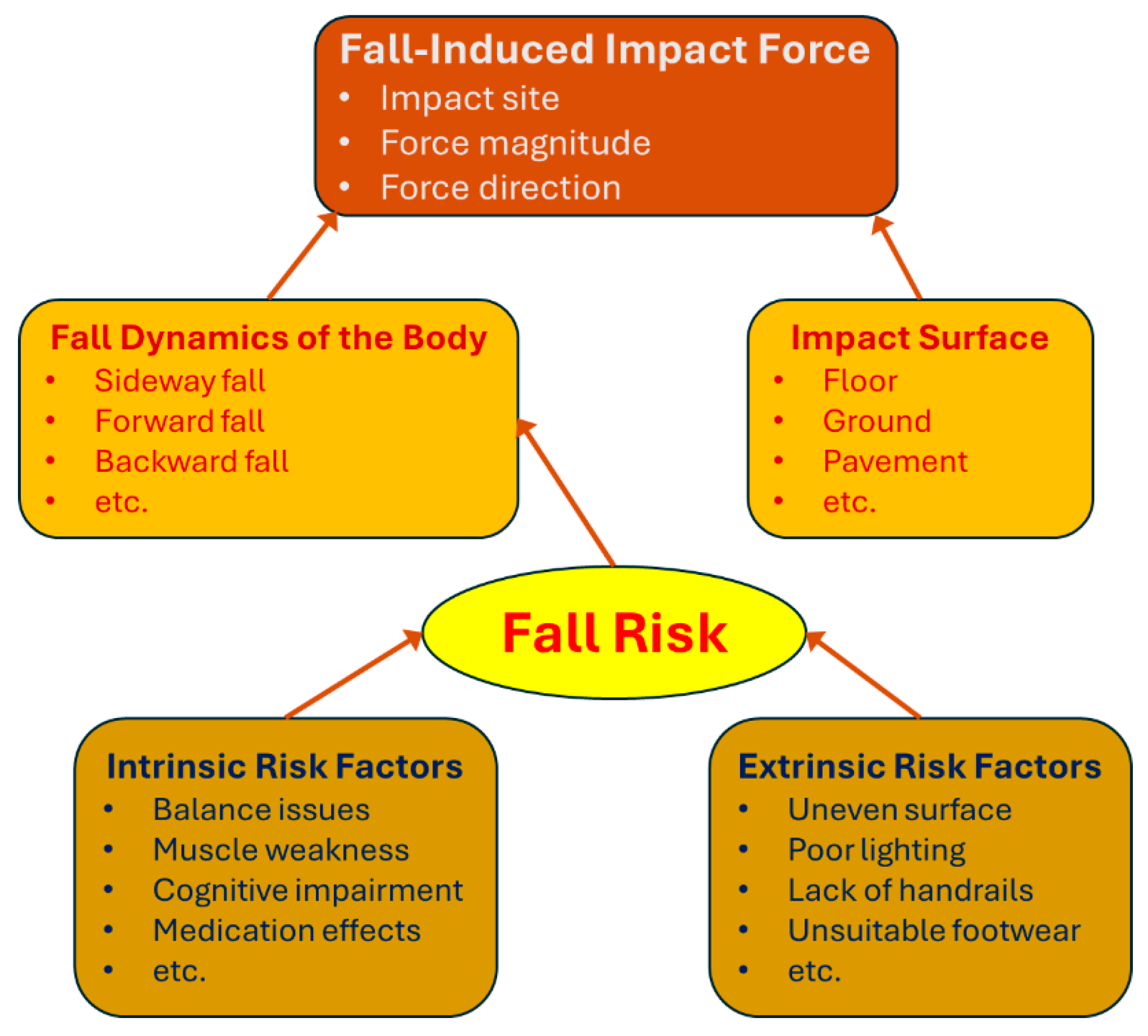
4. Biomechanical Insights into Fall-Induced Impact Force
4.1. Biomechanical Mechanisms of Fall-Induced Hip Fractures
4.2. Biomechanical Factors Affecting Fall-Induced Impact Force
4.3. Fall Risk and Contributing Factors
4.4. Challenges in Predicting Fall Risk and Fall-Induced Impact Force
5. Preventative Strategies for Hip Fractures
5.1. Passive Preventative Strategies
- (1)
- Environmental Modifications to Reduce the Risk of Falling:
- (2)
- Modifications to Reduce the Magnitude of Fall-Induced Impact Force:
- (3)
- Use of Assistive Devices and Protective Equipment:
5.2. Proactive Prevention Strategies
- (1)
- Increasing Cognitive Ability to Judge Fall Risk:
- (2)
- Improving Balance and Coordination:
- (3)
- Increasing Muscle Strength:
- (4)
- Improving Overall Health as a Systemic Approach:
5.3. Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S.; Song, C. Global Burden of Hip Fracture: The Global Burden of Disease Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2024, 35, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Study: Hip Fracture Burden to Nearly Double Worldwide by 2050|Harvard Medical School. Available online: https://hms.harvard.edu/news/study-hip-fracture-burden-nearly-double-worldwide-2050 (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Ebeling, P.R. Hip Fractures and Aging: A Global Problem Requiring Coordinated Global Solutions. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2023, 38, 1062–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swayambunathan, J.; Dasgupta, A.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Hannan, M.T.; Kiel, D.P.; Bhattacharyya, T. Incidence of Hip Fracture Over 4 Decades in the Framingham Heart Study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sociodemographic and Lifestyle Risk Factors Associated with Fragility Hip Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2673-4036/4/2/6 (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Schemitsch, E.; Adachi, J.D.; Brown, J.P.; Tarride, J.-E.; Burke, N.; Oliveira, T.; Slatkovska, L. Hip Fracture Predicts Subsequent Hip Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study to Support a Call to Early Hip Fracture Prevention Efforts in Post-Fracture Patients. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Osteoporosis and Related Fractures in Canada: Report from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System; Public Health Agency of Canada = Agence de la Santé Publique du Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2020.
- Johnell, O.; Kanis, J.A. An Estimate of the Worldwide Prevalence and Disability Associated with Osteoporotic Fractures. Osteoporos. Int. 2006, 17, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, C.; Lin, T.; Bartholomew, S.; Bell, J.S.; Bennett, C.; Beyene, K.; Bosco-Levy, P.; Bradbury, B.D.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Chandran, M.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Hip Fractures: Secular Trends in Incidence Rate, Post-Fracture Treatment, and All-Cause Mortality. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2023, 38, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Levy, A.R.; Lefaivre, K.A.; Guy, P.; Kuramoto, L.; Sobolev, B. Geographic Trends in Incidence of Hip Fractures: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Menyar, A.; El-Hennawy, H.; Al-Thani, H.; Asim, M.; Abdelrahman, H.; Zarour, A.; Parchani, A.; Peralta, R.; Latifi, R. Traumatic Injury among Females: Does Gender Matter? J. Trauma. Manag. Outcomes 2014, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzon-Illescas, O.; Perez Fernandez, E.; Crespí Villarias, N.; Quirós Donate, F.J.; Peña, M.; Alonso-Blas, C.; García-Vadillo, A.; Mazzucchelli, R. Mortality after Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: Incidence, Trends, and Associated Factors. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Schwenk, E.S.; Lev, Y.; Weitz, H. Update on Medical Management of Acute Hip Fracture. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2021, 88, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.M.; Crotty, M.; Fairhall, N.; Magaziner, J.; Beaupre, L.A.; Cameron, I.D.; Sherrington, C.; for the Fragility Fracture Network (FFN) Rehabilitation Research Special Interest Group. A Critical Review of the Long-Term Disability Outcomes Following Hip Fracture. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarride, J.E.; Hopkins, R.B.; Leslie, W.D.; Morin, S.; Adachi, J.D.; Papaioannou, A.; Bessette, L.; Brown, J.P.; Goeree, R. The Burden of Illness of Osteoporosis in Canada. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayeri, A.; Mohamadpour, M.; Mousavi, S.F.; Shirzadpour, E.; Mohamadpour, S.; Amraei, M. Fracture Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Possible Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, L.; Zillikens, M.C.; Dehghan, A.; Buitendijk, G.H.; Castaño-Betancourt, M.C.; Estrada, K.; Stolk, L.; Oei, E.H.; van Meurs, J.B.; Janssen, J.A.; et al. High Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk in Type 2 Diabetes as Skeletal Complications of Inadequate Glucose Control. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulakis, M.; Johansson, L.; Litsne, H.; Axelsson, K.; Lorentzon, M. Type 2 Diabetes and Fracture Risk in Older Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2425106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooven, F.H.; Adachi, J.D.; Adami, S.; Boonen, S.; Compston, J.; Cooper, C.; Delmas, P.; Diez-Perez, A.; Gehlbach, S.; Greenspan, S.L.; et al. The Global Longitudinal Study of Osteoporosis in Women (GLOW): Rationale and Study Design. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, M.; Ettinger, B.; Liang, J.; Pressman, A.R.; Johnston, J. Outcomes of a Disease-Management Program for Patients with Recent Osteoporotic Fracture. Osteoporos. Int. 2006, 17, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauley, J.A.; Robbins, J.; Chen, Z.; Cummings, S.R.; Jackson, R.D.; LaCroix, A.Z.; LeBoff, M.; Lewis, C.E.; McGowan, J.; Neuner, J.; et al. Effects of Estrogen plus Progestin on Risk of Fracture and Bone Mineral Density: The Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, P.M.; Shahnazari, M.; Orwoll, E.S.; Lane, N.E. Osteoporosis in Men: Findings from the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study (MrOS). Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2016, 8, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, D.C.; Hoff, L.S.; Kowalski, S.C.; de Andrade, C.A.F.; Trevisani, V.F.M.; de Melo, A.K.G. Risk Factors for Osteoporotic Hip Fracture among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Real-World Evidence Study. Adv. Rheumatol. 2024, 64, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, R.; Toots, A.; Conradsson, M.; Olofsson, B.; Holmberg, H.; Rosendahl, E.; Gustafson, Y.; Littbrand, H. Risk Factors for Hip Fracture in Very Old People: A Population-Based Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 27, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.; Li, J.J.; Lin, J.; Xing, D.; Dong, S. Multidimensional Characteristics of Musculoskeletal Pain and Risk of Hip Fractures among Elderly Adults: The First Longitudinal Evidence from CHARLS. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnsley, J.; Buckland, G.; Chan, P.E.; Ong, A.; Ramos, A.S.; Baxter, M.; Laskou, F.; Dennison, E.M.; Cooper, C.; Patel, H.P. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Osteoporosis: Challenges for Clinical Practice in Older People. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, J.J.; Kumar, V.; Rohilla, A. Understanding Osteoporosis: Human Bone Density, Genetic Mechanisms, Gut Microbiota, and Future Prospects. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, E.S.; Bondi, D.; Pietrangelo, T.; Fanò-Illic, G.; Fulle, S. Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Sarcopenia, Muscle Healthy Aging and Physical Conditioning in the Elderly. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2020, 2, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petnehazy, N.; Barnes, H.N.; Newman, A.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Cummings, S.R.; Hepple, R.T.; Cawthon, P.M. Muscle Mass, Strength, Power and Physical Performance and Their Association with Quality of Life in Older Adults, the Study of Muscle, Mobility and Aging (SOMMA). J. Frailty Aging 2024, 13, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, T.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y.; Tu, R. Age-Related Differences in the Number of Chronic Diseases in Association with Trajectories of Depressive Symptoms: A Population-Based Cohort Study. BMC Public. Health 2024, 24, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanaeme, C.J.; Ghazi, L.; Akinyelure, O.P.; Wen, Y.; Christenson, A.; Poudel, B.; Dooley, E.E.; Chen, L.; Hardy, S.T.; Foti, K.; et al. Trends in the Prevalence of Multiple Chronic Conditions Among US Adults With Hypertension From 1999–2000 Through 2017–2020. Am. J. Hypertens. 2024, 37, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgadóttir, B.; Laflamme, L.; Monárrez-Espino, J.; Möller, J. Medication and Fall Injury in the Elderly Population; Do Individual Demographics, Health Status and Lifestyle Matter? BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Bartina, Y.; Larti, M.; Kiaei, A.; Hemmati, M.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. Global Prevalence of Osteoporosis among the World Older Adults: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, L.M. Osteocytes and Estrogen Deficiency. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2021, 19, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, J.; Swati, S.; Meeta, M.; Singh, S.H.; Tanvir, T.; Madan, A. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Menopause Hormone Therapy and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators. JOIO 2023, 57, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.J.; Twomey, L.; Sambrook, P.N.; Eisman, J.A. Sex Differences in Peak Adult Bone Mineral Density. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1990, 5, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, B.A.; Kopperdahl, D.L.; Kiel, D.P.; Keaveny, T.M.; Bouxsein, M.L. Mechanical Contributions of the Cortical and Trabecular Compartments Contribute to Differences in Age-related Changes in Vertebral Body Strength in Men and Women Assessed by QCT-based Finite Element Analysis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, E.M.F.; Mendonça, L.M.C.; Paranhos-Neto, F.P.; Vieira Neto, L.; Madeira, M.; Farias, M.L.F. TBS Correlates with Bone Density and Microstructure at Trabecular and Cortical Bone Evaluated by HR-pQCT. J. Bone Min. Metab. 2024, 42, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, S.R.; Eastell, R. Risk and Prevention of Fracture in Patients With Major Medical Illnesses: A Mini-Review. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlborg, H.G.; Nguyen, N.D.; Nguyen, T.V.; Center, J.R.; Eisman, J.A. Contribution of Hip Strength Indices to Hip Fracture Risk in Elderly Men and Women. J. Bone Min. Res. 2005, 20, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapaah, D.; Martel, D.R.; Iranmanesh, F.; Seelemann, C.; Laing, A.C.; Willett, T. Fracture Toughness: Bridging the Gap Between Hip Fracture and Fracture Risk Assessment. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2023, 21, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minisola, S.; Colangelo, L.; Pepe, J.; Diacinti, D.; Cipriani, C.; Rao, S.D. Osteomalacia and Vitamin D Status: A Clinical Update 2020. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.; Berger, D.; Tabatabaie, V. Severe Osteomalacia and Fractures Secondary to Vitamin D Deficiency. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, A221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, S.H.; Corral-Gudino, L.; Cooper, C.; Francis, R.M.; Fraser, W.D.; Gennari, L.; Guañabens, N.; Javaid, M.K.; Layfield, R.; O’Neill, T.W.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Paget’s Disease of Bone in Adults: A Clinical Guideline. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 579–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyles, K.W.; Siris, E.S.; Singer, F.R.; Meunier, P.J. A Clinical Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Paget’s Disease of Bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejnmark, L.; Ejlsmark-Svensson, H. Effects of PTH and PTH Hypersecretion on Bone: A Clinical Perspective. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.; Marini, J.C. Update on the Genetics of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 115, 891–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles Rosa Neto, N.; Pereira, I.A.; Sztajnbok, F.R.; Azevedo, V.F. Unraveling the Genetic Collagen Connection: Clinical and Therapeutic Insights on Genetic Connective Tissue Disorders. Adv. Rheumatol. 2024, 64, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Inflammation Do We Face? Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2673-5261/5/4/30 (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Choy, E. Understanding the Dynamics: Pathways Involved in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, v3–v11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.P.; Shroff, R.C. Disorders of Bone Mineral Metabolism in Chronic Kidney Disease. In Pediatric Kidney Disease; Schaefer, F., Greenbaum, L.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1631–1668. ISBN 978-3-031-11665-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cannata-Andía, J.B.; Martín-Carro, B.; Martín-Vírgala, J.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Bande-Fernández, J.J.; Alonso-Montes, C.; Carrillo-López, N. Chronic Kidney Disease—Mineral and Bone Disorders: Pathogenesis and Management. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, C.P.; Vianna, A.G.D.; Barreto, F.d.C. The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Bone Metabolism. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Liu, T.; Chen, H.; Yang, K. Association of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Bone Mineral Density: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, T.A. Osteoporosis and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Uyl, D.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Tuyl, L.H.; Raterman, H.G.; Lems, W.F. (Sub)Clinical Cardiovascular Disease Is Associated with Increased Bone Loss and Fracture Risk; a Systematic Review of the Association between Cardiovascular Disease and Osteoporosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, S.; Magrey, M.N. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis: Insights for the Clinician. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevention and Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis—UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/prevention-and-treatment-of-glucocorticoid-induced-osteoporosis (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bao, Y.; Alvarez, J.; Gonzales, M.L. Tricyclic Antidepressant Use and Risk of Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies through the Use of Both Frequentist and Bayesian Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risk of Fall-Related Injuries Associated with Antidepressant Use in Elderly Patients: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/4/2298 (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Lespessailles, E.; Toumi, H. Proton Pump Inhibitors and Bone Health: An Update Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hant, F.N.; Bolster, M.B. Drugs That May Harm Bone: Mitigating the Risk. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliano, S.; Poon, S.; Robbins, J.; Bui, M.; Wang, X.; Groot, L.D.; Loan, M.V.; Zadeh, A.G.; Nguyen, T.; Seeman, E. Effect of Dietary Sources of Calcium and Protein on Hip Fractures and Falls in Older Adults in Residential Care: Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ 2021, 375, n2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leser, J.M.; Harriot, A.; Buck, H.V.; Ward, C.W.; Stains, J.P. Aging, Osteo-Sarcopenia, and Musculoskeletal Mechano-Transduction. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2021, 2, 782848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physical Activity and Alterations of Bone Metabolism and Sarcopenia|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-26614-0_13 (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Kim, S.-W.; Seo, M.-W.; Jung, H.-C.; Song, J.-K. Effects of High-Impact Weight-Bearing Exercise on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolism in Middle-Aged Premenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Effects of Exercise on Bone Mineral Density in Middle-Aged and Older Men: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.-C.; Desai, A.B.; Esfahani, P.; Sokolovskaya, T.V.; Bartlett, D.J. Effectiveness of Tai Chi for Health Promotion of Older Adults: A Scoping Review of Meta-Analyses. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2022, 16, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, I.J.; Perkin, O.J.; Williams, S.; McGuigan, P.M.; Thompson, D.; Western, M.J. The Efficacy of 12-Week Progressive Home-Based Strength and Tai-Chi Exercise Snacking in Older Adults: A Mixed-Method Exploratory Randomised Control Trial. J. Frailty Aging 2024, 13, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielson, C.M.; Srikanth, P.; Orwoll, E.S. Obesity and Fracture in Men and Women: An Epidemiologic Perspective. J. Bone Min. Res. 2011, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Yi, S.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Won, Y.J. Association Between Body Mass Index and the Risk of Hip Fracture by Sex and Age: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Fang, W.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Kao, T.-W.; Chang, Y.-W.; Wu, C.-J.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Sun, Y.-S.; Chen, W.-L. Body Fat Has Stronger Associations with Bone Mass Density than Body Mass Index in Metabolically Healthy Obesity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.; Rosenblatt, N.J.; Grabiner, M.D. Obesity as a Factor Contributing to Falls by Older Adults. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2014, 3, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ebeling, P.R.; Scott, D. Body Composition and Falls Risk in Older Adults. Curr. Geri Rep. 2019, 8, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, A.-F.; O’Connor, S.; Morin, S.N.; Gibbs, J.C.; Willie, B.M.; Jean, S.; Gagnon, C. Association between Obesity and Risk of Fracture, Bone Mineral Density and Bone Quality in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinonapoli, G.; Pace, V.; Ruggiero, C.; Ceccarini, P.; Bisaccia, M.; Meccariello, L.; Caraffa, A. Obesity and Bone: A Complex Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, J.M.; Sharieh, F.; Callaci, J.J. Impact of Alcohol on Bone Health, Homeostasis, and Fracture Repair. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2020, 8, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, S.; Kiel, D.P. Smoking, Alcohol, and Bone Health. In Nutrition and Bone Health; Holick, M.F., Nieves, J.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 489–504. ISBN 978-1-4939-2001-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kilim, H.P.; Rosen, H. Optimizing Calcium and Vitamin D Intake through Diet and Supplements. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2018, 85, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, B.; Ahmed, M.; Hussein, N.; Ibrahim, M.E.E.-D. Vitamin D, Calcium and Caffeine Intake Relationship to Bone Mineral Density. Arab. Gulf J. Sci. Res. 2024, 42, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendijk, I.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; Tetens, I.; Grootswagers, P. Discussion on Protein Recommendations for Supporting Muscle and Bone Health in Older Adults: A Mini Review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1394916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P.T.; Witard, O.C.; Højfeldt, G.; Church, D.D.; Breen, L. Dietary Protein Recommendations to Support Healthy Muscle Ageing in the 21st Century and beyond: Considerations and Future Directions. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwerda, A.M.; van Loon, L.J.C. The Impact of Collagen Protein Ingestion on Musculoskeletal Connective Tissue Remodeling: A Narrative Review. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 1497–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Falls Associated with Indoor and Outdoor Environmental Hazards among Community-Dwelling Older Adults between Men and Women. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavy, B.; Byberg, L.; Michaëlsson, K.; Melhus, H.; Åberg, A.C. The Fall Descriptions and Health Characteristics of Older Adults with Hip Fracture: A Mixed Methods Study. BMC Geriatr. 2015, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.J.; Twemlow, T.R.; Pryor, G.A. Environmental Hazards and Hip Fractures. Age Ageing 1996, 25, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, K.M.; Rodriguez, C.A.; Canas, M.A.; Kim, C.; Noroozi, S.; Vis-Dunbar, M.; Komisar, V.; Sakakibara, B.M.; Jakobi, J.M. The Influence of Assistive Technology and Home Modifications on Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review Protocol. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campani, D.; Caristia, S.; Amariglio, A.; Piscone, S.; Ferrara, L.I.; Barisone, M.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Faggiano, F.; Dal Molin, A.; Group, I.W. Home and Environmental Hazards Modification for Fall Prevention among the Elderly. Public. Health Nurs. 2021, 38, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerk, M.; Brovold, T.; Skelton, D.A.; Bergland, A. Associations between Health-Related Quality of Life, Physical Function and Fear of Falling in Older Fallers Receiving Home Care. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensrud, K.E.; Schousboe, J.T.; Crandall, C.J.; Leslie, W.D.; Fink, H.A.; Cawthon, P.M.; Kado, D.M.; Lane, N.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Langsetmo, L. Hip Fracture Risk Assessment Tools for Adults Aged 80 Years and Older. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2418612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Khan, L.; Licata, A.A. DXA and Clinical Challenges of Fracture Risk Assessment in Primary Care. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2021, 88, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.; Edwards, D.L.; Saleh, A.A.; Greenspan, S.L. Performance of Risk Assessment Instruments for Predicting Osteoporotic Fracture Risk: A Systematic Review. Osteoporos. Int. 2014, 25, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schini, M.; Johansson, H.; Harvey, N.C.; Lorentzon, M.; Kanis, J.A.; McCloskey, E.V. An Overview of the Use of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) in Osteoporosis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 47, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.; Stevens, R.; Lix, L.M.; McCloskey, E.V.; Johansson, H.; Harvey, N.C.; Kanis, J.A.; Leslie, W.D. Fracture Prediction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Validation of FRAX with Bone Mineral Density for Incident Major Osteoporotic Fractures. Rheumatology 2023, 64, kead676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenput, L.; Johansson, H.; McCloskey, E.V.; Liu, E.; Åkesson, K.E.; Anderson, F.A.; Azagra, R.; Bager, C.L.; Beaudart, C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; et al. Update of the Fracture Risk Prediction Tool FRAX: A Systematic Review of Potential Cohorts and Analysis Plan. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2103–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, J.; Peterson, M.N.; Crowson, C.S.; Achenbach, S.J.; Atkinson, E.J.; Amin, S.; Khosla, S.; Davis, J.M.; Myasoedova, E. Validating the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool Score in a US Population-Based Study of Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C. Derivation and Validation of Updated QFracture Algorithm to Predict Risk of Osteoporotic Fracture in Primary Care in the United Kingdom: Prospective Open Cohort Study. BMJ 2012, 344, e3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C. Predicting Risk of Osteoporotic Fracture in Men and Women in England and Wales: Prospective Derivation and Validation of QFractureScores. BMJ 2009, 339, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, G.; Brook, S.; Xian, N.Q.Q.; Widekind, S.V.; Freudenthal, B.; Comninos, A.N. Comparison of Fracture Risk Calculators in Elderly Fallers: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e060282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Leslie, W.D.; Nguyen, T.V.; Morin, S.N.; Lix, L.M.; Eisman, J.A. Predictive Performance of the Garvan Fracture Risk Calculator: A Registry-Based Cohort Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Leslie, W.D.; Nguyen, T.V.; Morin, S.N.; Lix, L.M.; Eisman, J.A. Performance of the Garvan Fracture Risk Calculator in Individuals with Diabetes: A Registry-Based Cohort Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2022, 110, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseltine, K.N.; Chukir, T.; Smith, P.J.; Jacob, J.T.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Farooki, A. Bone Mineral Density: Clinical Relevance and Quantitative Assessment. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slart, R.H.J.A.; Punda, M.; Ali, D.S.; Bazzocchi, A.; Bock, O.; Camacho, P.; Carey, J.J.; Colquhoun, A.; Compston, J.; Engelke, K.; et al. Updated Practice Guideline for Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 52, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, D.C.; Lui, L.-Y.; Cawthon, P.M.; Bauer, D.C.; Nevitt, M.C.; Cauley, J.A.; Hillier, T.A.; Lewis, C.E.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Cummings, S.R.; et al. High-Trauma Fractures and Low Bone Mineral Density in Older Women and Men. JAMA 2007, 298, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-Y.; Hwang, H.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, M.-R. Situational Risk Factors for Fall-Related Vertebral Fractures in Older Men and Women. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novel Methods to Evaluate Fracture Risk Models|Journal of Bone and Mineral Research|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jbmr/article-abstract/26/8/1767/7597924?redirectedFrom=fulltext (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Marques, A.; Ferreira, R.J.O.; Santos, E.; Loza, E.; Carmona, L.; da Silva, J. The Accuracy of Osteoporotic Fracture Risk Prediction Tools: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74 (Suppl. S2), 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.T.; Liang, F.W.; Wang, S.T.; Chang, C.M.; Lu, T.H.; Wu, C.H. The Effects of Falls on the Prediction of Osteoporotic Fractures: Epidemiological Cohort Study. Arch. Osteoporos. 2021, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.C.; Odén, A.; Orwoll, E.; Lapidus, J.; Kwok, T.; Karlsson, M.K.; Rosengren, B.E.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Cooper, C.; McCloskey, E.; et al. Falls Predict Fractures Independently of FRAX Probability: A Meta-Analysis of the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, N.; Cohen-Stavi, C.; Leventer-Roberts, M.; Balicer, R.D. External Validation and Comparison of Three Prediction Tools for Risk of Osteoporotic Fractures Using Data from Population Based Electronic Health Records: Retrospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2017, 356, i6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, C.; Moore, L.; Gagné, M.; Bessette, L.; Ste-Marie, L.G.; Brown, J.P.; Jean, S. Performance of Predictive Tools to Identify Individuals at Risk of Non-Traumatic Fracture: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluskiewicz, W.; Werner, A.; Bach, M.; Adamczyk, P.; Drozdzowska, B. Optimal Fracture Prediction Thresholds for Therapy Onset, Established from FRAX and Garvan Algorithms: A Longitudinal Observation of the Population Representative Female Cohort from the RAC-OST-POL Study. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.Y.; Yan, S.; Low, L.L.; Vasanwala, F.F.; Low, S.G. Predictors of Poor Functional Outcomes and Mortality in Patients with Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Pi, H.; Lyu, H.; Gao, Y. Risk Factors for Subsequent Fractures in Hip Fracture Patients: A Nested Case-Control Study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, J.A.; Oden, A.; Johnell, O.; Johansson, H.; De Laet, C.; Brown, J.; Burckhardt, P.; Cooper, C.; Christiansen, C.; Cummings, S.; et al. The Use of Clinical Risk Factors Enhances the Performance of BMD in the Prediction of Hip and Osteoporotic Fractures in Men and Women. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcohol Consumption, Bone Mineral Density, and Risk of Osteoporotic Fractures: A Dose–Response Meta-Analysis. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/3/1515 (accessed on 24 October 2024).
- Lai, B.; Jiang, H.; Gao, R.; Zhou, X. Association between Alcohol Intake and Bone Mineral Density: Results from the NHANES 2005–2020 and Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Arch. Osteoporos 2024, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Shen, Y.; Tan, L.-H.; Fu, S.; Dai, R.-C.; Yuan, L.-Q.; Sheng, Z.-F.; Xie, Z.-J.; Wu, X.-P.; Liao, E.-Y.; et al. Relationship between Bone Mineral Density and Fragility Fracture Risk: A Case-Control Study in Changsha, China. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osteoporotic Fracture Risk Assessment—UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/osteoporotic-fracture-risk-assessment (accessed on 24 October 2024).
- Coutinho, E.S.; Fletcher, A.; Bloch, K.V.; Rodrigues, L.C. Risk Factors for Falls with Severe Fracture in Elderly People Living in a Middle-Income Country: A Case Control Study. BMC Geriatr. 2008, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, E.; Straus, S.; Holroyd-Leduc, J. Risk Factors for Falls in the Elderly. In Medication-Related Falls in Older People: Causative Factors and Management Strategies; Huang, A.R., Mallet, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 91–101. ISBN 978-3-319-32304-6. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Leslie, W.D. Automation of a DXA-Based Finite Element Tool for Clinical Assessment of Hip Fracture Risk. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 155, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, H. Assessment of Hip Fracture Risk by Cross-Sectional Strain-Energy Derived from Image-Based Beam Model. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 63, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L.; Dall’Ara, E.; Eastell, R.; Goertzen, A.L.; McCloskey, E.V.; Leslie, W.D.; Lix, L.M. Comparison of Femoral Strength and Fracture Risk Index Derived from DXA-Based Finite Element Analysis for Stratifying Hip Fracture Risk: A Cross-Sectional Study. Bone 2018, 110, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, W.D.; Luo, Y.; Yang, S.; Goertzen, A.L.; Ahmed, S.; Delubac, I.; Lix, L.M. Fracture Risk Indices from DXA-Based Finite Element Analysis Predict Incident Fractures Independently from FRAX: The Manitoba BMD Registry. J. Clin. Densitom. 2019, 22, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, L.; Väänänen, S.P.; Voss, A.; Nissinen, T.; Sund, R.; Kröger, H.; Isaksson, H. DXA-Based 3D Finite Element Models Predict Hip Fractures Better than Areal BMD in Elderly Women. Bone 2025, 195, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Du, T.; Niu, X.; Fan, Y. Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of the Bone Matrix. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.; Moura, M.F.S.F.; Olhero, S.; Simoes, R.; Magalhães, F.D.; Marques, A.T.; Ferreira, J.P.S.; Reis, A.R.; Carvalho, M.; Parente, M. Bone: An Outstanding Composite Material. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Amromanoh, O. Bone Organic-Inorganic Phase Ratio Is a Fundamental Determinant of Bone Material Quality. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2021, 2021, 4928396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.Y.; Kuhn-Spearing, L.; Zioupos, P. Mechanical Properties and the Hierarchical Structure of Bone. Med. Eng. Phys. 1998, 20, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszta, M.J.; Cheng, X.; Jee, S.S.; Kumar, R.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Kaufman, M.J.; Douglas, E.P.; Gower, L.B. Bone Structure and Formation: A New Perspective. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2007, 58, 77–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.; Kerns, J.G.; Birch, H.L.; Gikas, P.D.; Parker, A.W.; Matousek, P.; Goodship, A.E. Functional Adaptation of Long Bone Extremities Involves the Localized “Tuning” of the Cortical Bone Composition; Evidence from Raman Spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 111602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-G.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Kosel, E.; Agnew, A.M.; McComb, D.W.; Bodnyk, K.; Hart, R.T.; Kim, M.K.; Han, S.Y.; Johnston, W.M. Regional Variation of Bone Tissue Properties at the Human Mandibular Condyle. Bone 2015, 77, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, B.; Greiner, M.; McGlynn, G.; Schmahl, W.W. Anatomical Variation of Human Bone Bioapatite Crystallography. Crystals 2020, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Mouloungui, E.; Castillo Dali, G.; Wang, Y.; Saffar, J.-L.; Pavon-Djavid, G.; Divoux, T.; Manneville, S.; Behr, L.; Cardi, D.; et al. Mineralized Collagen Plywood Contributes to Bone Autograft Performance. Nature 2024, 636, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wallace, R.J.; Callanan, A.; Pankaj, P. From Tension to Compression: Asymmetric Mechanical Behaviour of Trabecular Bone’s Organic Phase. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Sekaran, S.; Dhanasekaran, A.; Warrier, S. Type 1 Collagen: Synthesis, Structure and Key Functions in Bone Mineralization. Differentiation 2024, 136, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguet-Carrin, S.; Garnero, P.; Delmas, P.D. The Role of Collagen in Bone Strength. Osteoporos. Int. 2006, 17, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, D.B. The Contribution of the Organic Matrix to Bone’s Material Properties. Bone 2002, 31, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakbak, S.; Kayacan, R.; Akkuş, O. Effect of Collagen Fiber Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Cortical Bone. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, L.; Bailey, A.J. Collagen Cross-Links in Mineralizing Tissues: A Review of Their Chemistry, Function, and Clinical Relevance. Bone 1998, 22, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, H.; Reyes, M.J.; Dong, X.N.; Wang, X. Effect of Age on Mechanical Properties of the Collagen Phase in Different Orientations of Human Cortical Bone. Bone 2013, 55, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, A.L.; Coleman, R. Aging and Bone. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, F.; Pica, A.; Marinozzi, A.; Marinozzi, F. 3D Random Walk Model of Diffusion in Human Hypo- and Hyper- Mineralized Collagen Fibrils. J. Biomech. 2021, 125, 110586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, T.; Pham, T.-T.; de Leeuw, N.H.; Naili, S. Bone Water at the Nanoscale: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 18 (Suppl. S1), 1982–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowin, S.C. Bone Poroelasticity. J. Biomech. 1999, 32, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonare, L.D.; Giannini, S. Bone Microarchitecture as an Important Determinant of Bone Strength. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2004, 27, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, L.L.; Louis, N.; Zbijewski, W.; Vaishnav, J.; Clark, K.; Nicolella, D.P. Super-Resolution of Clinical CT: Revealing Microarchitecture in Whole Bone Clinical CT Image Data. Bone 2024, 185, 117115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, K.; Váncsa, S.; Agócs, G.; Harnos, A.; Hegyi, P.; Weninger, V.; Baross, K.; Kovács, B.; Soós, G.; Kocsis, G. Anisotropy, Anatomical Region, and Additional Variables Influence Young’s Modulus of Bone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JBMR Plus 2023, 7, e10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner-Frank, M.; Reisinger, A.G.; Andriotis, O.G.; Pahr, D.H.; Thurner, P.J. Cortical and Trabecular Mechanical Properties in the Femoral Neck Vary Differently with Changes in Bone Mineral Density. JBMR Plus 2024, 8, ziae049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jia, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Gu, H.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Z.; Mao, H. Comprehensively Characterizing Heterogeneous and Transversely Isotropic Properties of Femur Cortical Bones. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 151, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.D.; Beaupr?, G.S.; Lang, T.F.; Orwoll, E.S.; Carter, D.R. New QCT Analysis Approach Shows the Importance of Fall Orientation on Femoral Neck Strength. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.M.; Keaveny, T.M.; Hayes, W.C. The Effect of Impact Direction on the Structural Capacity of the Proximal Femur during Falls. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1996, 11, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolamperti, S.; Villa, I.; Rubinacci, A. Bone Remodeling: An Operational Process Ensuring Survival and Bone Mechanical Competence. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; You, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zou, W. Mechanical Regulation of Bone Remodeling. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazzalari, N.L. Bone Remodeling: A Review of the Bone Microenvironment Perspective for Fragility Fracture (Osteoporosis) of the Hip. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurman, C.A.; Kaya, S.; Dole, N.; Luna, N.M.M.; Castillo, N.; Potter, R.; Rose, J.P.; Bons, J.; King, C.D.; Burton, J.B.; et al. Aging Impairs the Osteocytic Regulation of Collagen Integrity and Bone Quality. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, A.L.; Imbert, L. Bone Quality Changes Associated with Aging and Disease: A Review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1410, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, J.S.; Roy, A.; Shen, X.; Acuna, R.L.; Tyler, J.H.; Wang, X. The Influence of Water Removal on the Strength and Toughness of Cortical Bone. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracher, S.; Voumard, B.; Simon, M.; Kochetkova, T.; Pretterklieber, M.; Zysset, P. Bone Collagen Tensile Properties of the Aging Human Proximal Femur. Bone Rep. 2024, 21, 101773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, X. Bone Quality Is Dependent on the Quantity and Quality of Organic–Inorganic Phases. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2020, 40, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, G.; Matsumura, F.; Caporaletti, F.; Micha, D.; Koenderink, G.H.; Ilie, I.M.; Bonn, M.; Woutersen, S.; Giubertoni, G. Water and Collagen: A Mystery Yet to Unfold. Biomacromolecules 2025, 26, 2784–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravazzano, L.; Colaianni, G.; Tarakanova, A.; Xiao, Y.-B.; Grano, M.; Libonati, F. Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Analysis of Aging Processes in Bone. npj Aging 2024, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Deng, Z.; Li, W. The Mechanism of Bone Remodeling After Bone Aging. Clin. Interv. Aging 2022, 17, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Fujita, H.; Onozuka, M.; Kubo, K.-Y. Age-Related Changes in Trabecular and Cortical Bone Microstructure. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 213234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y. Age-Related Periosteal Expansion at Femoral Neck among Elderly Women May Maintain Bending Stiffness, but Not Femoral Strength. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, H.; Moreira-Gonçalves, D.; Coriolano, H.J.; Duarte, J.A. Bone Quality: The Determinants of Bone Strength and Fragility. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Metzger, C.E.; Ahn, J.; Hankenson, K.D. Basic Bone Biology. In Bone Tissue Engineering: Bench to Bedside Using 3D Printing; Guastaldi, F.P.S., Mahadik, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 13–35. ISBN 978-3-030-92014-2. [Google Scholar]
- Runolfsdottir, H.L.; Sigurdsson, G.; Franzson, L.; Indridason, O.S. Gender Comparison of Factors Associated with Age-Related Differences in Bone Mineral Density. Arch. Osteoporos. 2015, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levit, M.; Finn, T.; Sachadava, S.; Matsumura, S.; Shah, J.; Cantos, A.; Yin, M.T.; Wadhwa, S. Menopause-Associated Changes in Mandibular Bone Microarchitecture Are Site-Specific. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 82, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Chen, L.-R.; Chen, K.-H. Osteoporosis Due to Hormone Imbalance: An Overview of the Effects of Estrogen Deficiency and Glucocorticoid Overuse on Bone Turnover. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, P.A.; Siegel, M.I. Bone Biology and the Clinical Implications for Osteoporosis. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. New Insights into Nutrients for Bone Health and Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimann, A.; Misof, B.M.; Fratzl, P.; Fratzl-Zelman, N. Bone Material Properties in Bone Diseases Affecting Children. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2023, 21, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- From Cells to Environment: Exploring the Interplay Between Factors Shaping Bone Health and Disease. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/59/9/1546 (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.; Tu, R.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Z. Associations between Serum Calcium, 25(OH)D Level and Bone Mineral Density in Adolescents. Adv. Rheumatol. 2021, 61, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, W. The Effects of Popular Diets on Bone Health in the Past Decade: A Narrative Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1287140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, P.; Amato, A.; Drid, P.; Korovljev, D.; Vasto, S.; Baldassano, S. The Impact of Diet and Physical Activity on Bone Health in Children and Adolescents. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 704647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.; Sum, M. Nutrition and Lifestyle Approaches to Optimize Skeletal Health. In Osteoporosis: A Clinical Casebook; Cusano, N.E., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 17–29. ISBN 978-3-030-83951-2. [Google Scholar]
- Azzolino, D.; Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Saporiti, E.; Luchetti, C.; Agostoni, C.; Cesari, M. Musculoskeletal Changes Across the Lifespan: Nutrition and the Life-Course Approach to Prevention. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 697954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinovitch, S.N.; McMahon, T.A.; Hayes, W.C. Force Attenuation in Trochanteric Soft Tissues during Impact from a Fall. J. Orthop. Res. 1995, 13, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Kroonenberg, A.J.; Hayes, W.C.; McMahon, T.A. Dynamic Models for Sideways Falls from Standing Height. J. Biomech. Eng. 1995, 117, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.; Deuretzbacher, G.; Heller, M.; Graichen, F.; Rohlmann, A.; Strauss, J.; Duda, G.N. Hip Contact Forces and Gait Patterns from Routine Activities. J. Biomech. 2001, 34, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, P.; Bull, A.M.J. Prediction of in Vivo Hip Contact Forces during Common Activities of Daily Living Using a Segment-Based Musculoskeletal Model. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 995279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliker, E.S.; Laing, A.C.; Ferguson, S.J.; Helgason, B.; Fleps, I. The Influence of Fall Direction and Hip Protector on Fracture Risk: FE Model Predictions Driven by Experimental Data. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 50, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nasiri Sarvi, M.; Sun, P.; Leslie, W.D.; Ouyang, J. Prediction of Impact Force in Sideways Fall by Image-Based Subject-Specific Dynamics Model. Int. Biomech. 2014, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.-C.; Syu, D.-K.; Ho, C.-C.; Lee, T.-S. Associations of Lower-Limb Muscle Strength Performance with Static and Dynamic Balance Control among Older Adults in Taiwan. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1226239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Bok, S.K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Hwang, S.L. Effect of Lower Limb Strength on Falls and Balance of the Elderly. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, W.; Ramadan, A.; Whitall, J.; Alissa, N.; Westlake, K. Age-Related Differences in Lower Limb Muscle Activation Patterns and Balance Control Strategies While Walking over a Compliant Surface. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, S.; Papathanasiou, G.; Chronopoulos, E.; Dontas, I.A.; Baltopoulos, I.P.; Papaioannou, N.A. The Effect of Intensive Abductor Strengthening on Postoperative Muscle Efficiency and Functional Ability of Hip-Fractured Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Indian. J. Orthop. 2019, 53, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, F.; Pica, A.; Marinozzi, A.; Marinozzi, F. Prediction of Stress and Strain Patterns from Load Rearrangement in Human Osteoarthritic Femur Head: Finite Element Study with the Integration of Muscular Forces and Friction Contact. In New Developments on Computational Methods and Imaging in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 49–64. ISBN 978-3-030-23073-9. [Google Scholar]
- Enderlin, C.; Rooker, J.; Ball, S.; Hippensteel, D.; Alderman, J.; Fisher, S.J.; McLeskey, N.; Jordan, K. Summary of Factors Contributing to Falls in Older Adults and Nursing Implications. Geriatr. Nurs. 2015, 36, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, A.F.; Paul, G.; Hausdorff, J.M. Risk Factors for Falls among Older Adults: A Review of the Literature. Maturitas 2013, 75, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welmer, A.-K.; Rizzuto, D.; Laukka, E.J.; Johnell, K.; Fratiglioni, L. Cognitive and Physical Function in Relation to the Risk of Injurious Falls in Older Adults: A Population-Based Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2017, 72, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, G. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Relationship Between Fall Risk and Other Geriatric Syndromes. Available online: https://ejgg.org/articles/a-comprehensive-evaluation-of-the-relationship-between-fall-risk-and-other-geriatric-syndromes/doi/ejgg.galenos.2021.2021-9-4?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Kim, G.S.; Kim, N.; Shim, M.-S.; Lee, J.J.; Park, M.K. Understanding the Home Environment as a Factor in Mitigating Fall Risk among Community-Dwelling Frail Older People: A Systematic Review. Health Soc. Care Community 2023, 2023, 8564397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.S.; Park, M.K.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, L.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, N. Situational and Environmental Risk Factors Associated with Home Falls among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Visualization of Disparities between Actual and Perceived Risks. Geriatr. Nurs. 2025, 62, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E.; Galvin, R.; Keogh, C.; Horgan, F.; Fahey, T. Is the Timed Up and Go Test a Useful Predictor of Risk of Falls in Community Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.; Faisal, A.I.; Deen, M.J. Wearable Sensor Systems for Fall Risk Assessment: A Review. Front. Digit. Health 2022, 4, 921506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Yeung, E.H.K.; Luo, J.; Tsui, K.-L.; Zhao, Y. A Systematic Review of Wearable Sensor-Based Technologies for Fall Risk Assessment in Older Adults. Sensors 2022, 22, 6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachance, C.C.; Jurkowski, M.P.; Dymarz, A.C.; Robinovitch, S.N.; Feldman, F.; Laing, A.C.; Mackey, D.C. Compliant Flooring to Prevent Fall-Related Injuries in Older Adults: A Scoping Review of Biomechanical Efficacy, Clinical Effectiveness, Cost-Effectiveness, and Workplace Safety. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, A.C.; Robinovitch, S.N. Low Stiffness Floors Can Attenuate Fall-Related Femoral Impact Forces by up to 50% without Substantially Impairing Balance in Older Women. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santesso, N.; Carrasco-Labra, A.; Brignardello-Petersen, R. Hip Protectors for Preventing Hip Fractures in Older People. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD001255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, A.-K.; Röder, B.; Zech, A.; Nagel, V.; Hollander, K.; Braumann, K.-M.; Hötting, K. Balance Training Improves Memory and Spatial Cognition in Healthy Adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipardo, D.S.; Tsang, W.W.N. Falls Prevention through Physical and Cognitive Training (Falls PACT) in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.; Schumann, F.; Mostofsky, S.H. Mindful Movement and Skilled Attention. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Layne, C.; Lowder, T.; Liu, J. A Review Focused on the Psychological Effectiveness of Tai Chi on Different Populations. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 678107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Komisar, V.; Shishov, N.; Lo, B.; Korall, A.M.; Feldman, F.; Robinovitch, S.N. The Effect of Fall Biomechanics on Risk for Hip Fracture in Older Adults: A Cohort Study of Video-Captured Falls in Long-Term Care. J. Bone Min. Res. 2020, 35, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisso, J.A.; Kelsey, J.L.; Strom, B.L.; Ghiu, G.Y.; Maislin, G.; O’Brien, L.A.; Hoffman, S.; Kaplan, F. Risk Factors for Falls as a Cause of Hip Fracture in Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviati, N.; Darma, S.; Reagan, M.; Iman, M.B.; Syafira, F.; Indra, B. Relationship between Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength with Bone Density in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Li, X.; Li, Z. Association between Muscle Strength and Mass and Bone Mineral Density in the US General Population: Data from NHANES 1999–2002. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, Y.; An, Y.; Nishita, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Takemura, M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Shimokata, H.; Otsuka, R.; Arai, H.; Ferrucci, L. Longitudinal Association between Muscle and Bone Loss: Results of US and Japanese Cohort Studies. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Meng, Q.; Su, C.-H. Mechanism-Driven Strategies for Reducing Fall Risk in the Elderly: A Multidisciplinary Review of Exercise Interventions. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Faliva, M.A.; Barrile, G.C.; Cavioni, A.; Mansueto, F.; Mazzola, G.; Oberto, L.; Patelli, Z.; Pirola, M.; Tartara, A.; et al. Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Dietary Supplementation to Prevent Bone Mineral Density Loss: A Food Pyramid. Nutrients 2021, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.; Gómez Álvarez, C.B.; Rayman, M.; Lanham-New, S.; Woolf, A.; Mobasheri, A. Strategies for Optimising Musculoskeletal Health in the 21st Century. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Li, X.; Nussler, A.K.; Zhu, S. The Relationship between Healthy Lifestyles and Bone Health: A Narrative Review. Medicine 2021, 100, e24684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Lorente, H.; García-Gavilán, J.F.; Shyam, S.; Konieczna, J.; Martínez, J.A.; Martín-Sánchez, V.; Fitó, M.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Paz-Graniel, I.; Curto, A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Physical Activity, and Bone Health in Older Adults: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e253710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Veronese, N.; Smith, L.; Ragusa, F.S.; Di Bella, G.; Battaglia, G.; Bianco, A.; Barbagallo, M. Nutrition and Physical Activity in Musculoskeletal Health. Endocrines 2025, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassagh, E.Z.; Vatanparast, H. Current Evidence on the Association of Dietary Patterns and Bone Health: A Scoping Review. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazianas, M.; Miller, P.D. Osteoporosis and Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD): Back to Basics. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y. Hip Fractures: Clinical, Biomaterial and Biomechanical Insights into a Common Health Challenge. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060580
Luo Y. Hip Fractures: Clinical, Biomaterial and Biomechanical Insights into a Common Health Challenge. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060580
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yunhua. 2025. "Hip Fractures: Clinical, Biomaterial and Biomechanical Insights into a Common Health Challenge" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060580
APA StyleLuo, Y. (2025). Hip Fractures: Clinical, Biomaterial and Biomechanical Insights into a Common Health Challenge. Bioengineering, 12(6), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060580





