Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
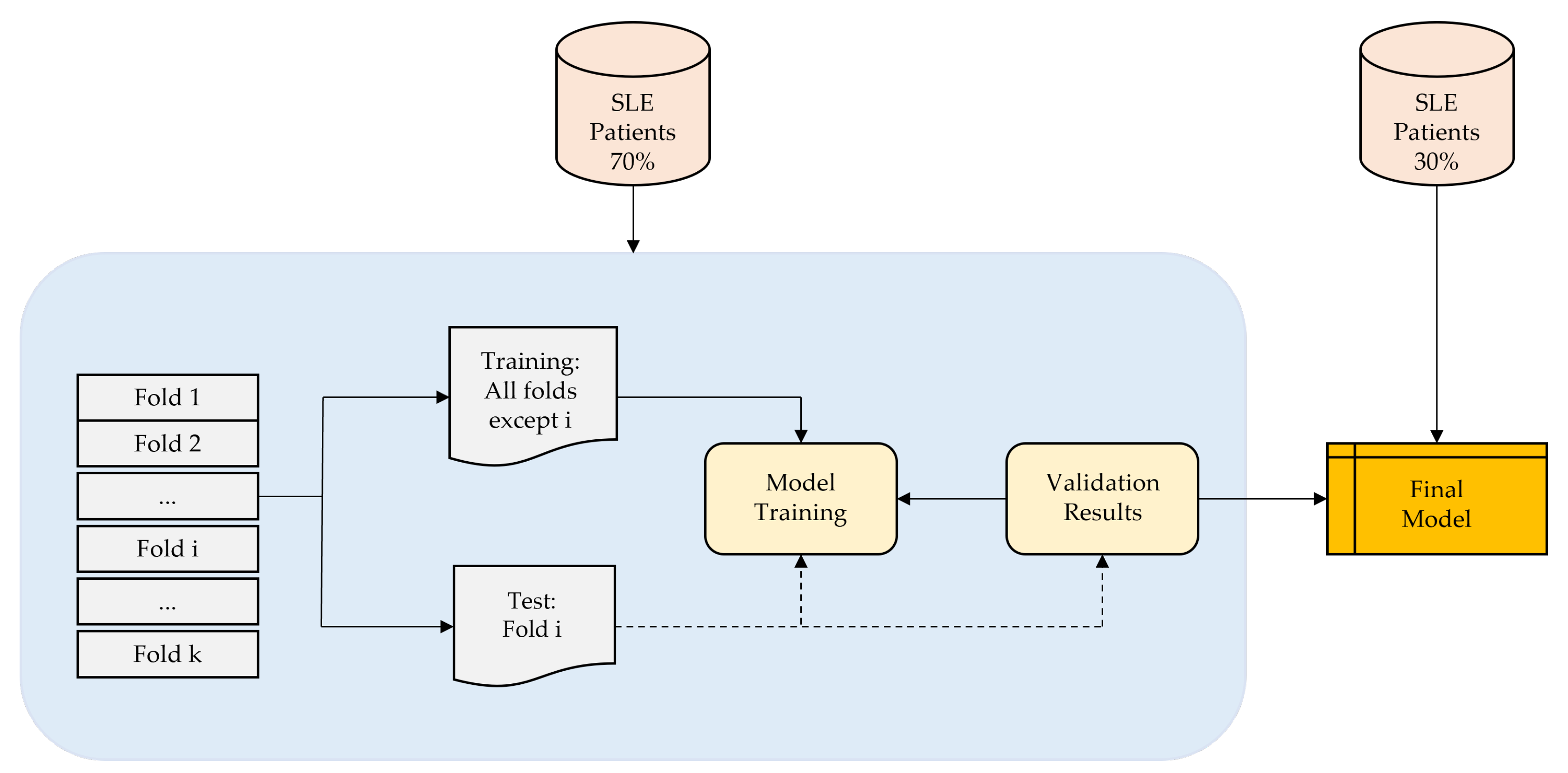
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method
- Draw a bootstrap sample of size N from the training data.
- Grow a decision tree to the bootstrapped data by recursively repeating the following steps for each terminal node of the tree, until the minimum node size is reached:
- (a)
- Select m variables at random from the p variables.
- (b)
- Pick the best variable/split-point among the m variables.
- (c)
- Split the node into two daughter nodes.
2.3. Performance Evaluation
3. Results
- 17 patients were hospitalized due to lower respiratory infections.
- 4 patients were hospitalized for upper respiratory infections.
- 9 patients were treated for urinary infections.
- 10 patients had soft tissue infections.
- 4 patients suffered from digestive infections.
- 1 patient was diagnosed with tuberculous lymphadenitis.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortés Verdú, R.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Seoane-Mato, D.; Morcillo Valle, M.; Palma Sánchez, D.; Moreno Martínez, M.J.; Mayor González, M.; Atxotegi Sáenz de Buruaga, J.; Urionagüena Onaindia, I.; Blanco Cáceres, B.A.; et al. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in Spain: Higher than previously reported in other countries? Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.E.; Grimbacher, B.; Witte, T. Autoimmunity and primary immunodeficiency: Two sides of the same coin? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandinelli, F.; Bombardieri, S.; Matucci, M.; Delle Sedie, A. Systemic lupus erythematosus joint involvement—What does musculoskeletal ultrasound provide Us? Eur. Musculoskelet. Rev. 2012, 7, 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kariburyo, F.; Xie, L.; Sah, J.; Li, N.; Lofland, J.H. Real-world medication use and economic outcomes in incident systemic lupus erythematosus patients in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2020, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piga, M.; Arnaud, L. The main challenges in systemic lupus erythematosus: Where do we stand? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, F.; Doherty, M.; Grainge, M.; Davenport, G.; Lanyon, P.; Zhang, W. The incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in the UK, 1999–2012. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamichou, C.; Bertsias, G. Flares in systemic lupus erythematosus: Diagnosis, risk factors and preventive strategies. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Yan, Y. Machine Learning for Diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7167066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelman, G.; Kok, H.; Chandra, R.; Razavi, A.; Lee, M.; Asadi, H. eDoctor: Machine learning and the future of medicine. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamichou, C.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Genitsaridi, I.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Fanouriakis, A.; Papastefanakis, E.; Kalogiannaki, E.; Gergianaki, I.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Boumpas, D.T.; et al. In an early SLE cohort the ACR-1997, SLICC-2012 and EULAR/ACR-2019 criteria classify non-overlapping groups of patients: Use of all three criteria ensures optimal capture for clinical studies while their modification earlier classification and treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Martínez, R.; Torres, A.M.; Ramón, A.; Blasco, P.; Mateo, J. Personalized Risk Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis after Cholecystectomy in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Machine Learning Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillas, N.; Ramón, A.; Torres, A.M.; Blasco, P.; Mateo, J. Predictive Model for Mortality in Severe COVID-19 Patients across the Six Pandemic Waves. Viruses 2023, 15, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, C.; Arroyo, Y.; Torres, A.M.; Redondo, M.Á.; Basar, C.; Mateo, J. Method for Classifying Schizophrenia Patients Based on Machine Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, Q.; Wang, B.; Duan, P.; Zhang, B.; Hong, Z. Privacy-Preserving Multi-Class Support Vector Machine Model on Medical Diagnosis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 3342–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, M.; Ahuja, S.; Rani, S.; Bawa, P.; Zaguia, A. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease using Gaussian-based Bayesian parameter optimization for deep convolutional LSTM network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 4186666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahfouz, M.A.; Shoukry, A.; Ismail, M.A. EKNN: Ensemble classifier incorporating connectivity and density into kNN with application to cancer diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 111, 101985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reges, O.; Krefman, A.E.; Hardy, S.T.; Yano, Y.; Muntner, P.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Allen, N.B. Decision tree-based classification for maintaining normal blood pressure throughout early adulthood and middle age: Findings from the coronary artery risk development in young adults (CARDIA) study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Song, Z.; Ni, B.; You, Y. Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated bioinformatics analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Shao, M.; Dai, X.; Pan, Z.; Liu, D. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus based on bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 865559. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, A.M.; Smith, D.; Wu, Z.; Chowdhury, T.; Costenbader, K.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, H.K.; Feldman, C.H.; Zhao, Y. Exploration of machine learning methods to predict systemic lupus erythematosus hospitalizations. Lupus 2022, 31, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Du, Y. Three hematologic/immune system-specific expressed genes are considered as the potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis through bioinformatics analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicalese, P.A.; Mobiny, A.; Shahmoradi, Z.; Yi, X.; Mohan, C.; Van Nguyen, H. Kidney level lupus nephritis classification using uncertainty guided Bayesian convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Aringer, M.; Brinks, R.; Dörner, T.; Daikh, D.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. European League against Rheumatism (EULAR)/American College of Rheumatology (ACR) SLE classification criteria item performance. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Machine Learning 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Williamson, B.D.; Fong, Y. Improving random forest predictions in small datasets from two-phase sampling designs. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 322. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.; Zhou, W. BLDA Approach for Classifying P300 Potential. In Proceedings of the 7th Asian-Pacific Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering, Beijing, China, 22–25 April 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 341–343. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M. Theory and Implementation of linear regression. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL), Chongqing, China, 10–12 July 2020; pp. 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchibhotla, A.K.; Brown, L.D.; Buja, A.; Cai, J. All of Linear Regression. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.06386. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Kamber, M. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, I.N.; O’Keeffe, A.G.; Farewell, V.; Hanly, J.G.; Manzi, S.; Su, L.; Gladman, D.D.; Bae, S.C.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; et al. Factors associated with damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) Inception Cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Liossis, S.N.; Staveri, C. What is New in the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 655100. [Google Scholar]
- Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Mendoza-Pinto, C.; Reátegui-Sokolova, C.; Pons-Estel, G.J.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Bertsias, G.; Alarcon, G.S.; Pons-Estel, B.A. Achieving remission or low disease activity is associated with better outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic literature review. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, S.; Lipsky, P.E. Current Status of the Evaluation and Management of Lupus Patients and Future Prospects. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 682544. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, E.E.; Barr, S.G.; Clarke, A.E. The global burden of SLE: Prevalence, health disparities and socioeconomic impact. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Soto, M.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Alarcón-de-la Lastra, C. An update on diet and nutritional factors in systemic lupus erythematosus management. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tselios, K.; Gladman, D.; Touma, Z.; Su, J.; Anderson, N.; Urowitz, M. Disease course patterns in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2019, 28, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhil, A.; Bansal, R.; Anupam, K.; Ankit, T.; Bhatnagar, A. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Latest insight into etiopathogenesis. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larosa, M.; Iaccarino, L.; Gatto, M.; Punzi, L.; Doria, A. Advances in the diagnosis and classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Johnson, S.R. Classifying and diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus in the 21st century. Rheumatology 2020, 59, v4–v11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inês, L.; Silva, C.; Galindo, M.; López-Longo, F.J.; Terroso, G.; Romão, V.C.; Rúa-Figueroa, I.; Santos, M.J.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Nero, P.; et al. Classification of systemic lupus erythematosus: Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics versus American College of Rheumatology criteria. A comparative study of 2055 patients from a real-life, international systemic lupus erythematosus cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamichou, C.; Genitsaridi, I.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Nikoloudaki, M.; Repa, A.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Fanouriakis, A.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Boumpas, D.T.; Bertsias, G.K. Lupus or not? SLE Risk Probability Index (SLERPI): A simple, clinician-friendly machine learning-based model to assist the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 758–766. [Google Scholar]
- Donner-Banzhoff, N. Solving the diagnostic challenge: A patient-centered approach. Ann. Fam. Med. 2018, 16, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Asano, Y.; Mohsin, A.; Henry, C.; Abraham, R.; Chang, A.; Labno, C.; Wilson, P.C.; Clark, M.R. Machine learning to quantify in situ humoral selection in human lupus tubulointerstitial inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 593177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usategui, I.; Barbado, J.; Torres, A.M.; Cascón, J.; Mateo, J. Machine learning, a new tool for the detection of immunodeficiency patterns in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Investig. Med. 2023, 71, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lei, X.; Chakrabortty, R.; Pal, S.C.; Sahana, M.; Janizadeh, S. Evaluation of different boosting ensemble machine learning models and novel deep learning and boosting framework for head-cut gully erosion susceptibility. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics of Patients with Immunodeficiency Patterns | |
|---|---|
| N | 77 |
| Median age (years) | 52 |
| Female/Male | 68/9 |
| SLE evolution time (years) | 14 |
| Corticosteroids (n) | 50 (64.9%) |
| Immunosuppressants (n) | 25 (32.4%) |
| Hydroxychloroquine (n) | 37 (48%) |
| Severe infections (n) | 51 |
| Immunodeficiency patterns (n) | |
| Leucocytes (<4000 cL/μL) | 9 |
| Lymphocytes (<1500 cL/μL) | 28 |
| Neutrophils (<1800 cL/μL) | 9 |
| CD3 (<700 cL/μL) | 10 |
| CD4 (<300 cL/μL) | 6 |
| CD8 (<200 cL/μL) | 3 |
| CD19 (<100 cL/μL) | 23 |
| NK (<90 cL/μL) | 13 |
| IgG (<870 mg/dL) | 17 |
| IgG1 (<383 mg/dL) | 3 |
| IgG2 (<242 mg/dL) | 36 |
| IgG3 (<22 mg/dL) | 16 |
| IgG4 (<4 mg/dL) | 7 |
| IgA (117 mg/dL) | 8 |
| IgM (<60 mg/dL) | 20 |
| C3 (<90 mg/dL) | 13 |
| C4 (<10 mg/dL) | 6 |
| IgG. | |||||
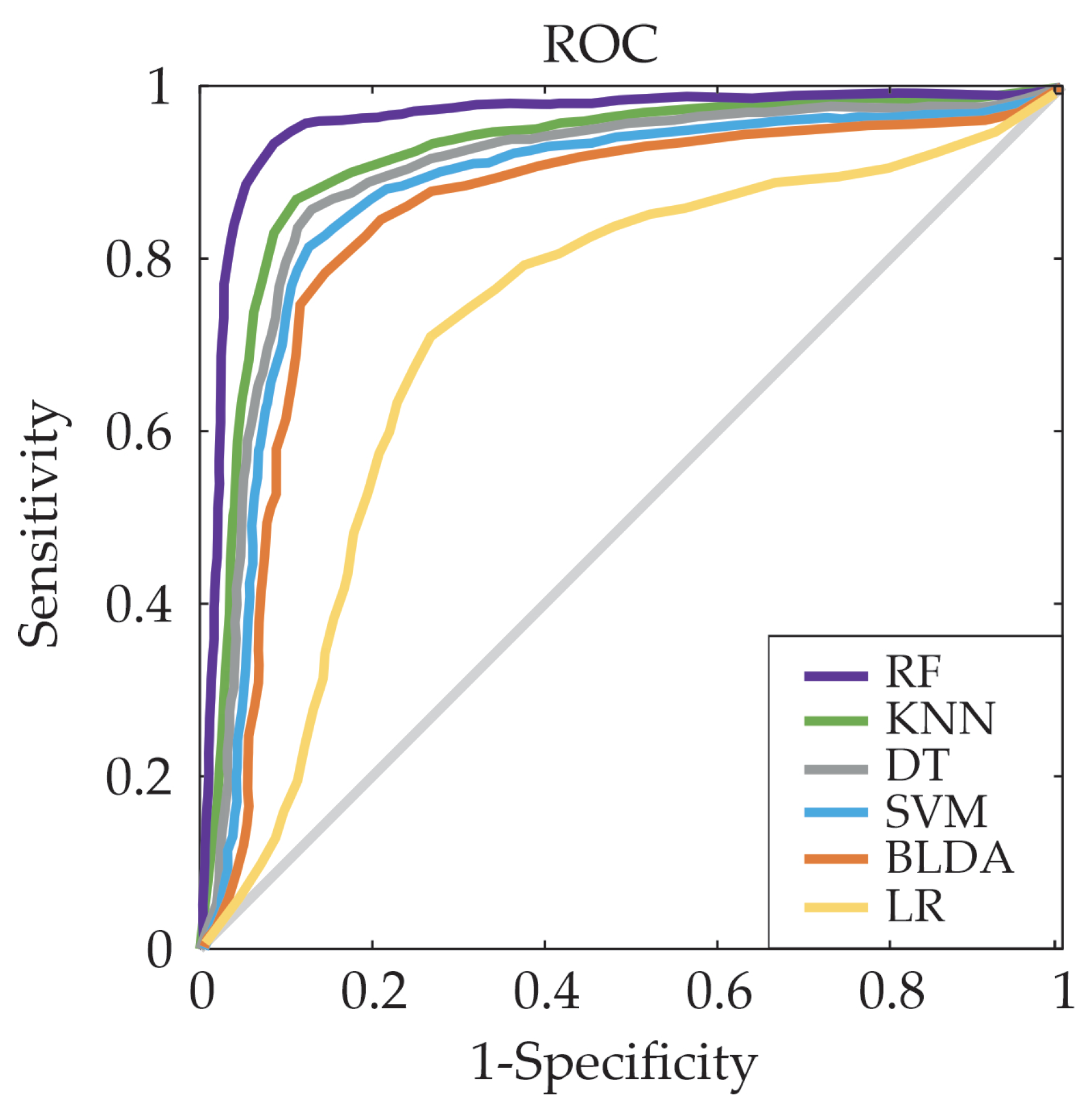
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 80.85 | 80.95 | 80.76 | 80.28 | 80.00 |
| BLDA | 78.11 | 78.20 | 78.02 | 77.55 | 78.00 |
| DT | 83.85 | 83.95 | 83.75 | 83.25 | 83.00 |
| LR | 70.02 | 69.75 | 68.84 | 68.95 | 68.42 |
| RF | 93.96 | 94.07 | 93.85 | 93.29 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 86.38 | 86.48 | 86.28 | 85.76 | 86.00 |
| IgG2. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 81.85 | 81.95 | 81.76 | 81.27 | 81.00 |
| BLDA | 77.37 | 77.46 | 77.28 | 76.82 | 77.00 |
| DT | 83.16 | 83.26 | 83.06 | 82.57 | 83.00 |
| LR | 69.51 | 69.24 | 68.33 | 68.44 | 68.42 |
| RF | 94.58 | 94.69 | 94.47 | 93.90 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 85.99 | 86.09 | 85.89 | 85.38 | 86.00 |
| IgG3. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 81.56 | 81.66 | 81.47 | 80.98 | 81.00 |
| BLDA | 79.16 | 79.25 | 79.06 | 78.59 | 79.00 |
| DT | 83.82 | 83.92 | 83.72 | 83.22 | 83.00 |
| LR | 69.44 | 69.17 | 68.27 | 68.38 | 68.42 |
| RF | 94.42 | 94.53 | 94.31 | 93.75 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 86.57 | 86.67 | 86.47 | 85.95 | 86.00 |
| IgG4. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 81.35 | 81.45 | 81.26 | 80.77 | 81.00 |
| BLDA | 78.93 | 79.02 | 78.83 | 78.36 | 78.00 |
| DT | 83.26 | 83.36 | 83.16 | 82.67 | 83.00 |
| LR | 70.15 | 69.88 | 68.97 | 69.08 | 68.42 |
| RF | 94.50 | 94.61 | 94.39 | 93.83 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 86.07 | 86.17 | 85.97 | 85.46 | 86.00 |
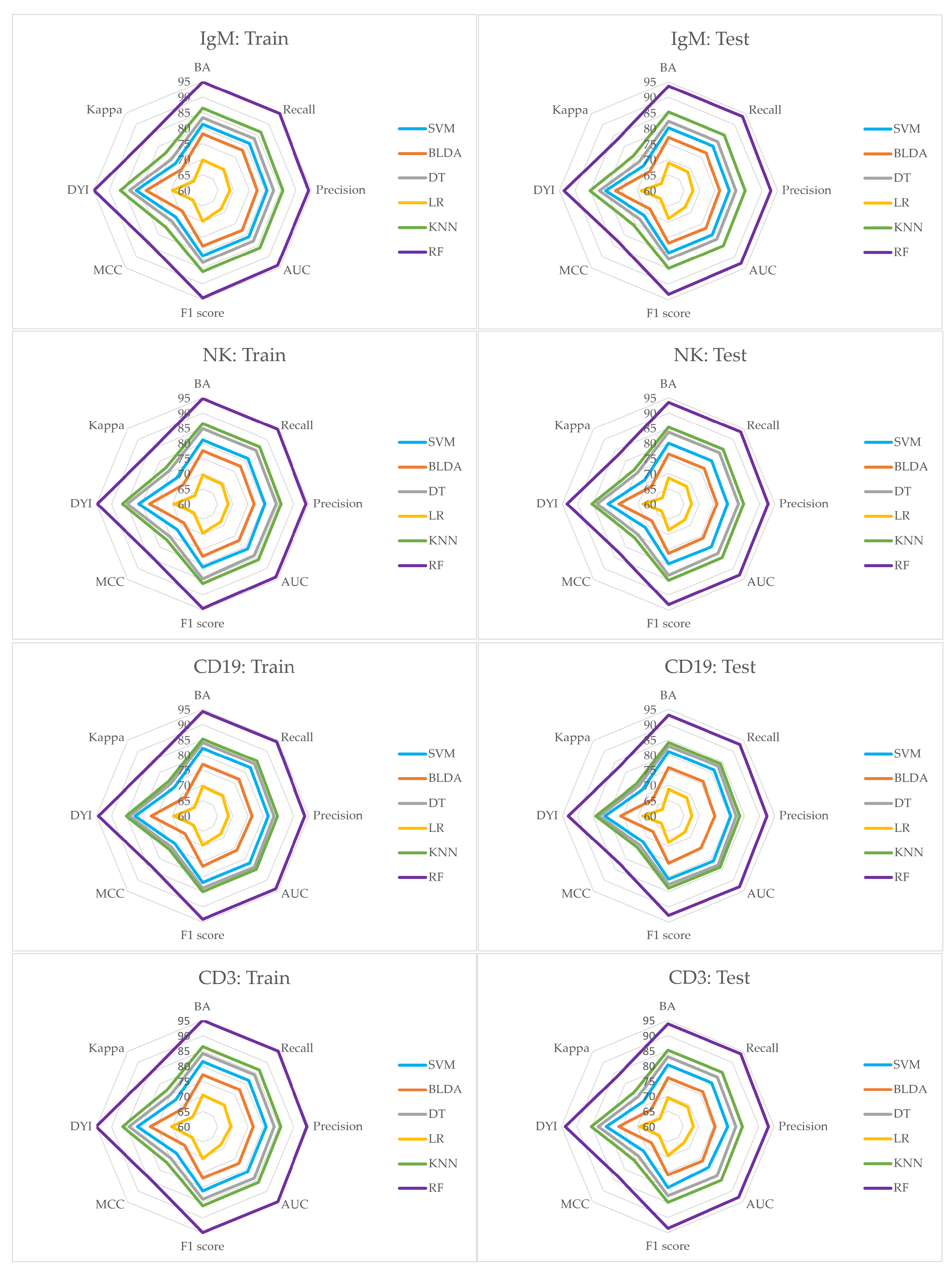
| IgM. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 81.24 | 81.34 | 81.15 | 80.67 | 81.00 |
| BLDA | 78.11 | 78.20 | 78.02 | 77.55 | 78.00 |
| DT | 83.35 | 83.45 | 83.25 | 82.76 | 83.00 |
| LR | 69.86 | 69.59 | 68.68 | 68.79 | 68.42 |
| RF | 94.80 | 94.91 | 94.69 | 94.12 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 86.38 | 86.48 | 86.28 | 85.76 | 86.00 |
| NK. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 81.06 | 81.16 | 80.97 | 80.49 | 81.00 |
| BLDA | 77.52 | 77.61 | 77.43 | 76.97 | 77.00 |
| DT | 84.84 | 84.94 | 84.74 | 84.24 | 84.00 |
| LR | 69.51 | 69.24 | 68.33 | 68.44 | 68.42 |
| RF | 94.75 | 94.86 | 94.64 | 94.07 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 86.51 | 86.61 | 86.41 | 85.89 | 86.00 |
| CD19. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 82.21 | 82.31 | 82.12 | 81.63 | 82.00 |
| BLDA | 76.89 | 76.98 | 76.80 | 76.34 | 76.00 |
| DT | 84.04 | 84.14 | 83.94 | 83.44 | 84.00 |
| LR | 69.65 | 69.38 | 68.47 | 68.58 | 68.42 |
| RF | 94.34 | 94.45 | 94.23 | 93.67 | 94.00 |
| KNN | 85.24 | 85.34 | 85.14 | 84.63 | 85.00 |
| CD3. | |||||
| Methods | BA | Recall | Specificity | Precision | AUC |
| SVM | 81.46 | 81.56 | 81.37 | 80.88 | 81.00 |
| BLDA | 77.21 | 77.30 | 77.12 | 76.66 | 77.00 |
| DT | 84.16 | 84.26 | 84.06 | 83.56 | 84.00 |
| LR | 70.41 | 70.14 | 69.22 | 69.33 | 68.42 |
| RF | 95.12 | 95.23 | 95.01 | 94.44 | 95.00 |
| KNN | 86.38 | 86.48 | 86.28 | 85.76 | 86.00 |
| IgG. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 80.61 | 71.74 | 80.85 | 71.98 |
| BLDA | 77.87 | 69.31 | 78.11 | 69.54 |
| DT | 83.60 | 74.40 | 83.85 | 74.65 |
| LR | 70.06 | 64.59 | 69.83 | 64.23 |
| RF | 93.68 | 83.37 | 93.96 | 83.65 |
| KNN | 86.12 | 76.65 | 86.38 | 76.90 |
| IgG2. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 81.61 | 72.63 | 81.85 | 72.87 |
| BLDA | 77.14 | 68.65 | 77.37 | 68.88 |
| DT | 82.91 | 73.79 | 83.16 | 74.04 |
| LR | 69.54 | 64.12 | 69.32 | 63.76 |
| RF | 94.30 | 83.92 | 94.58 | 84.20 |
| KNN | 85.73 | 76.30 | 85.99 | 76.55 |
| IgG3. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 81.32 | 72.37 | 81.56 | 72.61 |
| BLDA | 78.92 | 70.24 | 79.16 | 70.47 |
| DT | 83.57 | 74.38 | 83.82 | 74.62 |
| LR | 69.48 | 64.06 | 69.25 | 63.70 |
| RF | 94.14 | 83.78 | 94.42 | 84.06 |
| KNN | 86.31 | 76.81 | 86.57 | 77.07 |
| IgG4. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 81.11 | 72.19 | 81.35 | 72.43 |
| BLDA | 78.69 | 70.03 | 78.93 | 70.27 |
| DT | 83.01 | 73.88 | 83.26 | 74.13 |
| LR | 70.19 | 64.72 | 69.96 | 64.35 |
| RF | 94.22 | 83.85 | 94.50 | 84.13 |
| KNN | 85.81 | 76.37 | 86.07 | 76.62 |
| IgM. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 81.00 | 72.09 | 81.24 | 72.33 |
| BLDA | 77.87 | 69.31 | 78.11 | 69.54 |
| DT | 83.10 | 73.96 | 83.35 | 74.21 |
| LR | 69.90 | 64.45 | 69.67 | 64.08 |
| RF | 94.51 | 84.12 | 94.80 | 84.40 |
| KNN | 86.12 | 76.65 | 86.38 | 76.90 |
| NK. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 80.82 | 71.93 | 81.06 | 72.17 |
| BLDA | 77.29 | 68.78 | 77.52 | 69.01 |
| DT | 84.59 | 75.28 | 84.84 | 75.53 |
| LR | 69.54 | 64.12 | 69.32 | 63.76 |
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| RF | 94.46 | 84.07 | 94.75 | 84.35 |
| KNN | 86.25 | 76.76 | 86.51 | 77.02 |
| CD19. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 81.97 | 72.95 | 82.21 | 73.19 |
| BLDA | 76.66 | 68.23 | 76.89 | 68.45 |
| DT | 83.79 | 74.57 | 84.04 | 74.82 |
| LR | 69.68 | 64.25 | 69.45 | 63.89 |
| RF | 94.06 | 83.71 | 94.34 | 83.99 |
| KNN | 84.98 | 75.63 | 85.24 | 75.89 |
| CD3. | ||||
| Methods | F1 score | MCC | DYI | Kappa |
| SVM | 81.22 | 72.28 | 81.46 | 72.52 |
| BLDA | 76.98 | 68.51 | 77.21 | 68.74 |
| DT | 83.91 | 74.68 | 84.16 | 74.93 |
| LR | 70.45 | 64.96 | 70.22 | 64.59 |
| RF | 94.83 | 84.40 | 95.12 | 84.68 |
| KNN | 86.12 | 76.65 | 86.38 | 76.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usategui, I.; Arroyo, Y.; Torres, A.M.; Barbado, J.; Mateo, J. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010090
Usategui I, Arroyo Y, Torres AM, Barbado J, Mateo J. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsategui, Iciar, Yoel Arroyo, Ana María Torres, Julia Barbado, and Jorge Mateo. 2024. "Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares" Bioengineering 11, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010090
APA StyleUsategui, I., Arroyo, Y., Torres, A. M., Barbado, J., & Mateo, J. (2024). Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares. Bioengineering, 11(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010090









