Co-Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Zein Articular Cartilage Scaffolds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
4. Results
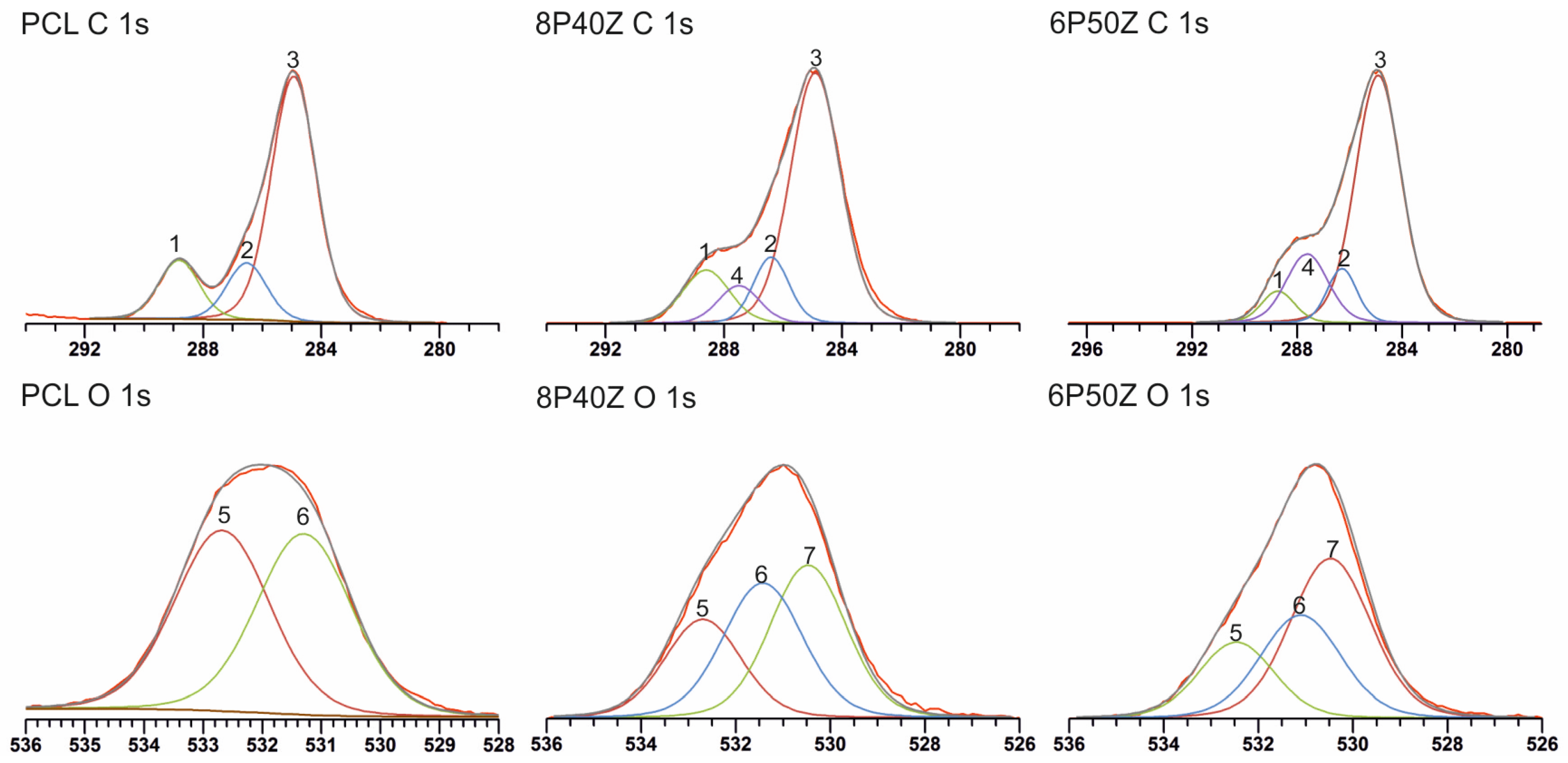
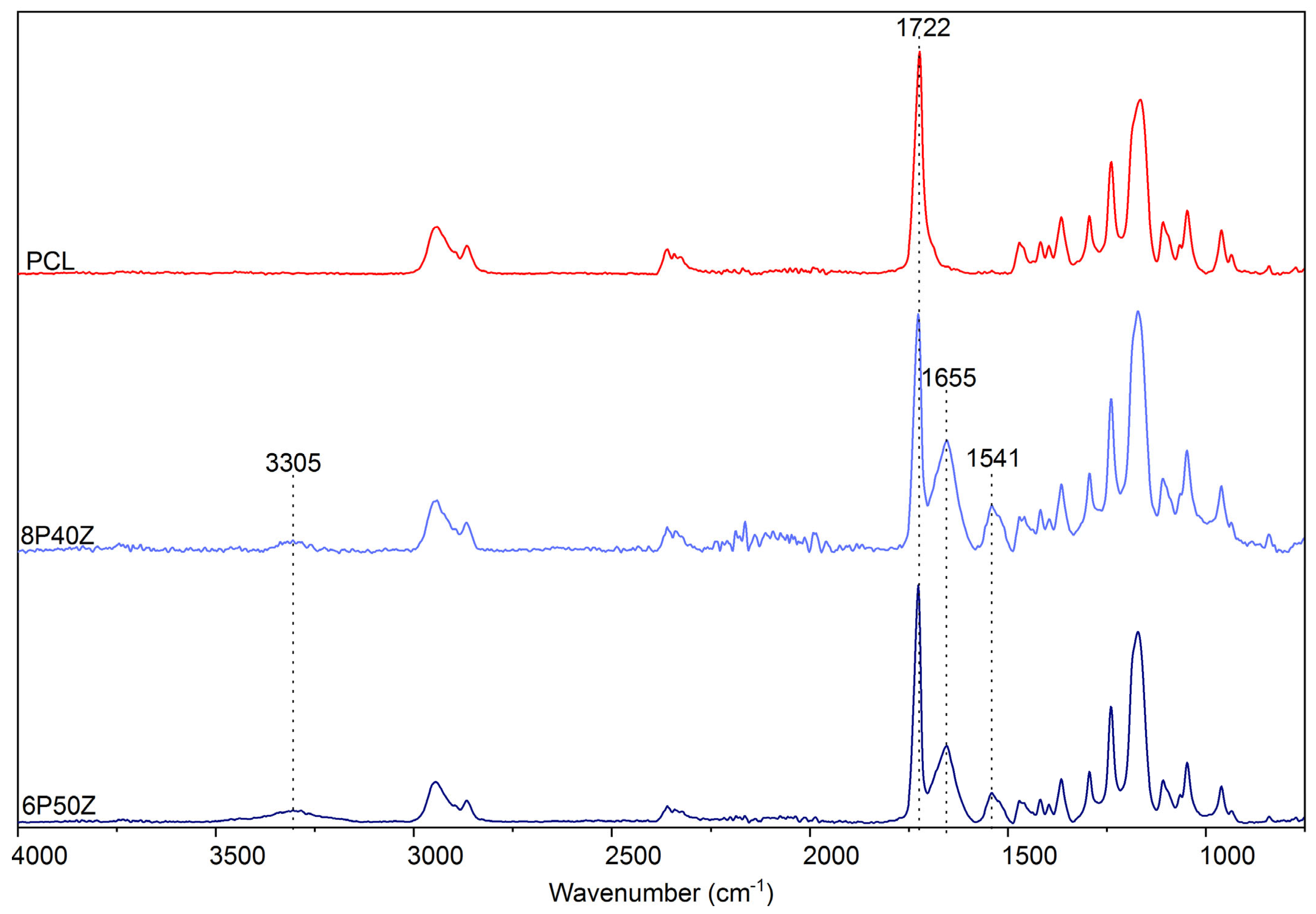
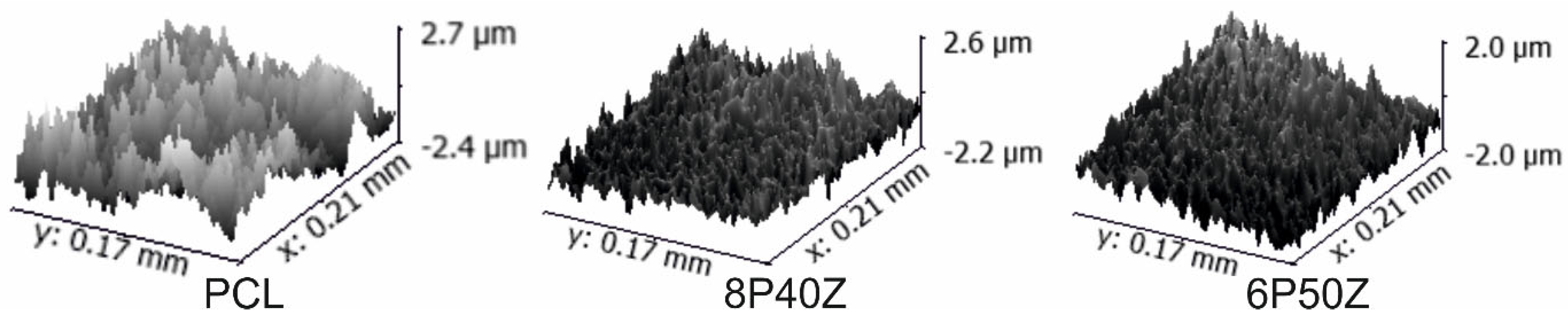
4.1. Nanofiber Mats Characterization
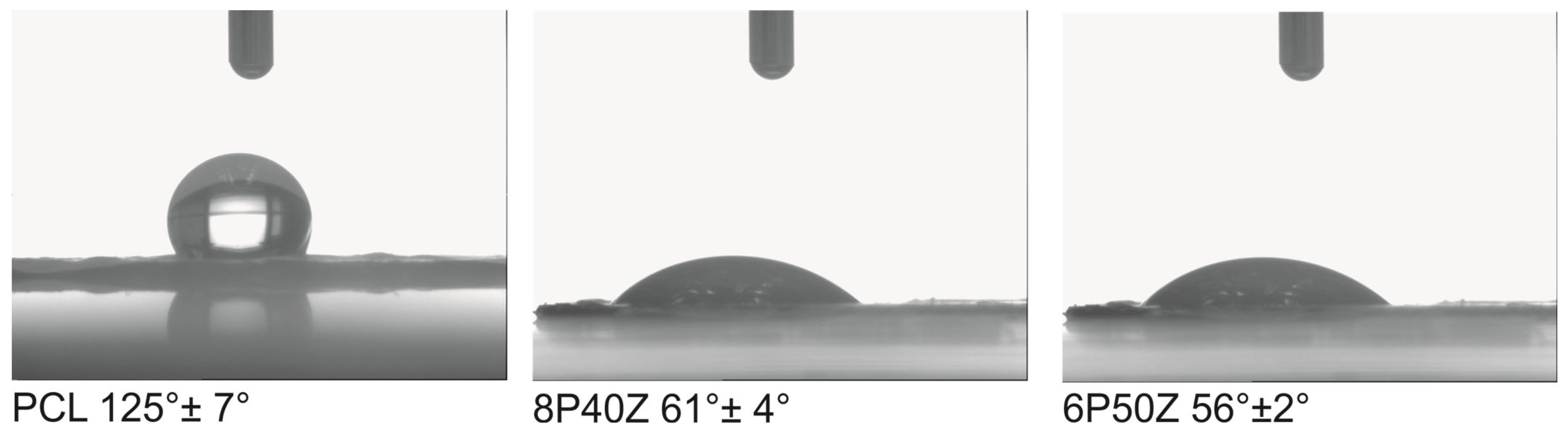
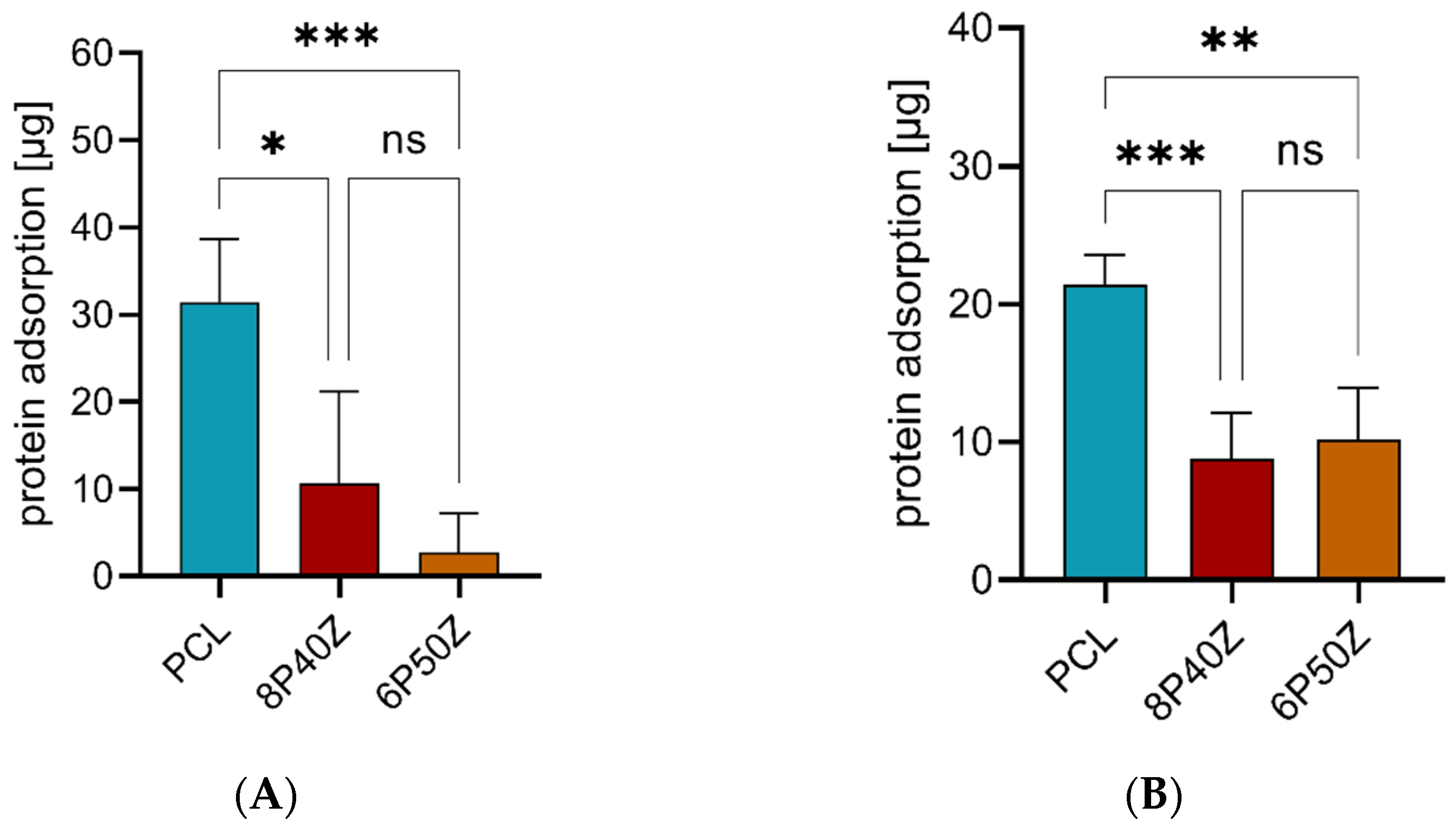
4.2. Protein Adsorption and Cell Cultures
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, F.J. Biomaterials & Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, G.; Clarke, J.; Picard, F.; Riches, P.; Jia, L.; Han, F.; Li, B.; Shu, W. 3D Bioactive Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 278–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, A.; Nain, A.S. ECM in Differentiation: A Review of Matrix Structure, Composition and Mechanical Properties. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 1071–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsara, M.; Agbulut, O.; Kontziampasis, D.; Chen, Y.; Menasché, P. Fibers for Hearts: A Critical Review on Electrospinning for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, K.; Lin, F.; Xiang, L.; Deng, L.; Guan, Z.; Cui, W.; Zhang, H. Pharmaceutical Electrospinning and 3D Printing Scaffold Design for Bone Regeneration. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 504–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armiento, A.R.; Stoddart, M.J.; Alini, M.; Eglin, D. Biomaterials for Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Learning from Biology. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensini, A.; Cristofolini, L. Biofabrication of Electrospun Scaffolds for the Regeneration of Tendons and Ligaments. Materials 2018, 11, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophia Fox, A.J.; Bedi, A.; Rodeo, S.A. The Basic Science of Articular Cartilage: Structure, Composition, and Function. Sport. Health 2009, 1, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.N.; Zeugolis, D.I. Electrospun Polymers in Cartilage Engineering—State of Play. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; March, L.; Chew, M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: A Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 1711–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semitela, Â.; Girão, A.F.; Fernandes, C.; Ramalho, G.; Bdikin, I.; Completo, A.; Marques, P.A. Electrospinning of Bioactive Polycaprolactone-Gelatin Nanofibres with Increased Pore Size for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 35, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, F.; Irani, S.; Azadegan, G.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Zandi, M.; Saeed, M. Co-Electrospun Gelatin-Chondroitin Sulfate/Polycaprolactone Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2020, 22, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuette, H.B.; Kraeutler, M.J.; McCarty, E.C. Matrix-Assisted Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation in the Knee: A Systematic Review of Mid- to Long-Term Clinical Outcomes. Orthop. J. Sport. Med. 2017, 5, 232596711770925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, S.-H.; Goh, B.-T.; Lim, J. Three-Dimensional Printed Polycaprolactone Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration Success and Future Perspective. Tissue Eng. Part A 2019, 25, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wei, J.; Liu, C.; O’Neill, B.; Ngothai, Y. Fabrication and Properties of Porous Scaffold of Zein/PCL Biocomposite for Bone Tissue Engineering. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, D.; Karbasi, S.; Razavi, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Bonakdar, S. Electrospun Poly(Hydroxybutyrate)/Chitosan Blend Fibrous Scaffolds for Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Research Article. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Tavakkoli, S.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Taghavifar, E.; Mohammadali, M.; Daemi, H. Electrospun Nanofibrous Alginate Sulfate Scaffolds Promote Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation to Chondrocytes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Chung, H.J.; Park, T.G. Macroporous and Nanofibrous Hyaluronic Acid/Collagen Hybrid Scaffold Fabricated by Concurrent Electrospinning and Deposition/Leaching of Salt Particles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Yang, T.; Sun, Y.; You, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, B. Composite Poly(l-Lactic-Acid)/Silk Fibroin Scaffold Prepared by Electrospinning Promotes Chondrogenesis for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 30, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga, L.Y.C.; Kipper, M.J. Expanding the Repertoire of Electrospinning: New and Emerging Biopolymers, Techniques, and Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. Hydration Lubrication. Friction 2013, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoor, P.V.; Gearing, B.P.; Muratoglu, O.; Cohen, R.E.; Bellare, A. Wear Reduction of Orthopaedic Bearing Surfaces Using Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanocoatings. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Klein, J. Recent Progress in Cartilage Lubrication. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The Industrial Protein from Corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, G. Overview on Zein Protein: A Promising Pharmaceutical Excipient in Drug Delivery Systems and Tissue Engineering. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plath, A.M.S.; Facchi, S.P.; Souza, P.R.; Sabino, R.M.; Corradini, E.; Muniz, E.C.; Popat, K.C.; Filho, L.C.; Kipper, M.J.; Martins, A.F. Zein Supports Scaffolding Capacity toward Mammalian Cells and Bactericidal and Antiadhesive Properties on Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Zein Electrospun Fibers. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 20, 100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Ding, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.B.; Li, S.T.; Xie, D.M.; Li, Z.Z.; Sun, G.D. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of the Developed PLGA/HAp/Zein Scaffolds for Bone-Cartilage Interface Regeneration. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser, J.; Stok, K.S.; Caversaccio, M.D.; Ferguson, S.J. Direct Electrospinning of 3D Auricle-Shaped Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louette, P.; Bodino, F.; Pireaux, J.-J. Poly(Caprolactone) (PCL) XPS Reference Core Level and Energy Loss Spectra. Surf. Sci. Spectra 2005, 12, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekram, B.; Abdel-Hady, B.M.; El-kady, A.M.; Amr, S.M.; Waley, A.I.; Guirguis, O.W. Optimum Parameters for the Production of Nano-Scale Electrospun Polycaprolactone to Be Used as a Biomedical Material. Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, N.H.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Lotfy, A.; El-Badawy, A.; El-Badri, N. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Growth and Proliferation Enhancement Using PLA vs PCL Based Nanofibrous Scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, C.G.; Hollister, S.J. A Comparison of the Influence of Material on in Vitro Cartilage Tissue Engineering with PCL, PGS, and POC 3D Scaffold Architecture Seeded with Chondrocytes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmerle, J.; Wegel, E.; Schermelleh, L.; Dobbie, I.M. Assessing Resolution in Super-Resolution Imaging. Methods 2015, 88, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Bhushan, B.; Sachdev, A.; Matai, I.; Uday Kumar, S.; Gopinath, P. Silver-Nanoparticle-Incorporated Composite Nanofibers for Potential Wound-Dressing Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, A.; Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Mirjalili, M.; Parsania, M. Argon and Argon–Oxygen Plasma Surface Modification of Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Liu, X.; Miramini, S.; Zhang, L. Influences of Variability and Uncertainty in Vertical and Horizontal Surface Roughness on Articular Cartilage Lubrication. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 148, 105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ferguson, S.J. The Influence of Cartilage Surface Topography on Fluid Flow in the Intra-Articular Gap. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Sathe, S.R.; Yim, E.K.F. From Nano to Micro: Topographical Scale and Its Impact on Cell Adhesion, Morphology and Contact Guidance. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 183001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, M.G.; Otarola, G.A.; Hu, J.C.; Athanasiou, K.A. Cartilage Assessment Requires a Surface Characterization Protocol: Roughness, Friction, and Function. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2021, 27, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.; Weng, L.-T. Surface Characterization of Polymer Blends by XPS and ToF-SIMS. Materials 2016, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurusu, R.S.; Demarquette, N.R. Surface Modification to Control the Water Wettability of Electrospun Mats. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 249–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurusu, R.S.; Demarquette, N.R. Wetting of Hydrophilic Electrospun Mats Produced by Blending SEBS with PEO–PPO–PEO Copolymers of Different Molecular Weight. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeer, M.A.; Yilgor, E.; Yilgor, I. Electrospun Polycaprolactone/Silk Fibroin Nanofibrous Bioactive Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymer 2019, 168, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, B.; Roberto, S.; Bonafé, E.; Camargo, S.; Camargo, C.; Popat, K.; Kipper, M.; Martins, A. Chitosan Imparts Better Biological Properties for Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Electrospun Membranes than Dexamethasone. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, P.; Golas, A.; Vogler, E.A. Role of Proteins and Water in the Initial Attachment of Mammalian Cells to Biomedical Surfaces: A Review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 853–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, S.L.; McKenzie, D.R.; Nosworthy, N.J.; Denman, J.A.; Sezerman, O.U.; Bilek, M.M.M. The Vroman Effect: Competitive Protein Exchange with Dynamic Multilayer Protein Aggregates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Silva, E.A.; Reseland, J.E.; Heyward, C.A.; Haugen, H.J. Biological Responses to Physicochemical Properties of Biomaterial Surface. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5178–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.D.; Sun, Z.Z.; Zhou, M.; Xu, X.X.; Ma, J.Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.M.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Electrospun Chitosan-Graft-PLGA Nanofibres with Significantly Enhanced Hydrophilicity and Improved Mechanical Property. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafahrend, D.; Heffels, K.-H.; Beer, M.V.; Gasteier, P.; Möller, M.; Boehm, G.; Dalton, P.D.; Groll, J. Degradable Polyester Scaffolds with Controlled Surface Chemistry Combining Minimal Protein Adsorption with Specific Bioactivation. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K.; Ploux, L.; Ponche, A. Cell/Material Interfaces: Influence of Surface Chemistry and Surface Topography on Cell Adhesion. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 831–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, H.; Arzaghi, H.; Bayandori, M.; Dezfuli, A.S.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Shafiee, A.; Moradi, L. Controlling Cell Behavior through the Design of Biomaterial Surfaces: A Focus on Surface Modification Techniques. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Khatri, Z.; Oh, K.W.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.H. Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Polycaprolactone/Cellulose Ultrafine Fibers via Electrospinning. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Jiang, Y.J.; Tuan, R.S. Chondrocyte Phenotype in Engineered Fibrous Matrix Is Regulated by Fiber Size. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.J.A.; Mostaço-Guidolin, L.B. Optical Microscopy and the Extracellular Matrix Structure: A Review. Cells 2021, 10, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, S.A.; Zieba, A.; Örnros, J.; Jin, C.; Rolfson, O.; Björkman, L.I.; Eisler, T.; Kalamajski, S.; Kamali-Moghaddam, M.; Karlsson, N.G. Lubricin Binds Cartilage Proteins, Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein, Fibronectin and Collagen II at the Cartilage Surface. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
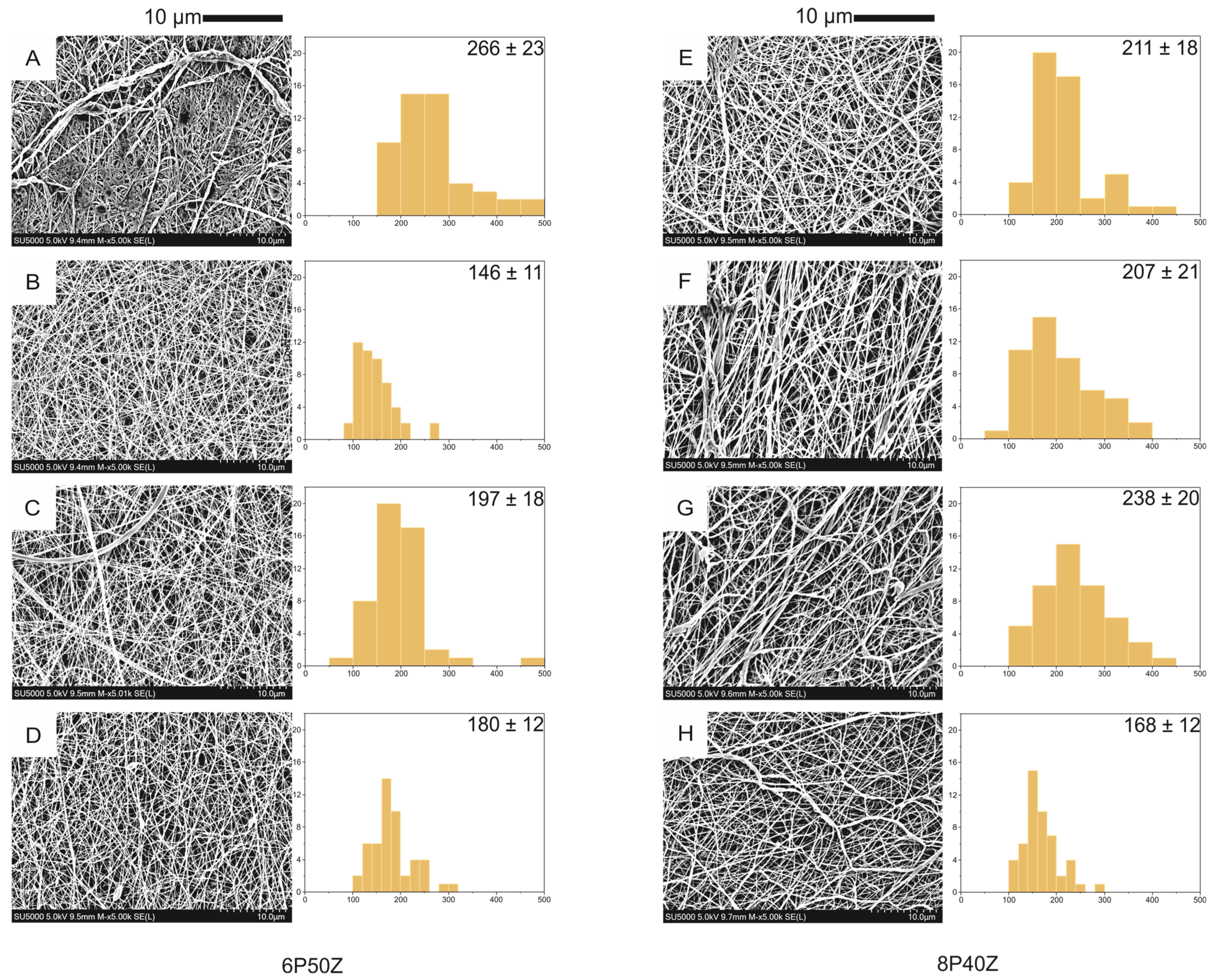

| Sample | Flow Rate (mL·h−1) | Distance (cm) | PCL(g) | Zein (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 06P50Z | A | 0.5 | 12 | 0.240 | 0.120 |
| B | 1 | 12 | 0.240 | 0.120 | |
| C | 0.5 | 16 | 0.240 | 0.120 | |
| D | 1 | 16 | 0.240 | 0.120 | |
| 08P40Z | E | 0.5 | 12 | 0.320 | 0.128 |
| F | 1 | 12 | 0.320 | 0.128 | |
| G | 0.5 | 16 | 0.320 | 0.128 | |
| H | 1 | 16 | 0.320 | 0.128 |
| Atomic Concentration of Surface Detected Elements (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | C1s | O1s | N1s | C/N | C/O |
| PCL | 73.3 | 26.7 | 0 | X | 2.7 |
| 8P40Z | 67.3 | 23 | 9.7 | 6.9 | 2.7 |
| 6P50Z | 66.6 | 21.8 | 11.6 | 5.7 | 2.9 |
| High-Resolution Spectra Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 1s Spectra data | ||||||
| Peak | PCL BE (ev) | PCL Peak Area | 8P40Z BE (eV) | 8P40Z Peak Area (%) | 6P50Z BE (eV) | 6P50Z Peak Area (%) |
| 1 (O=C–O) | 288.8 | 15.2 | 288.7 | 13.2 | 288.7 | 6.2 |
| 2 (C–O) | 286.5 | 14.4 | 286.4 | 12.4 | 286.6 | 9.5 |
| 3 (C–H/C–C) | 284.9 | 70.4 | 284.9 | 66.2 | 284.9 | 67.1 |
| 4 (O=C–N) | 287.5 | 8.3 | 287.6 | 17.1 | ||
| O 1s Spectra data | ||||||
| Peak | PCL BE (ev) | PCL Peak Area | 8P40Z BE (eV) | 8P40Z Peak Area (%) | 6P50Z BE (eV) | 6P50Z Peak Area (%) |
| 5 (O=C–O *) | 532.7 | 50.0 | 532.7 | 25.1 | 532.5 | 21.2 |
| 6 (* O=C–O) | 531.3 | 50.0 | 531.4 | 35.9 | 531.1 | 30.7 |
| 7 (* O=C–N) | 530.5 | 39.0 | 530.5 | 47.9 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plath, A.M.S.; Huber, S.; Alfarano, S.R.; Abbott, D.F.; Hu, M.; Mougel, V.; Isa, L.; Ferguson, S.J. Co-Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Zein Articular Cartilage Scaffolds. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070771
Plath AMS, Huber S, Alfarano SR, Abbott DF, Hu M, Mougel V, Isa L, Ferguson SJ. Co-Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Zein Articular Cartilage Scaffolds. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070771
Chicago/Turabian StylePlath, Andre M. Souza, Stephanie Huber, Serena R. Alfarano, Daniel F. Abbott, Minghan Hu, Victor Mougel, Lucio Isa, and Stephen J. Ferguson. 2023. "Co-Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Zein Articular Cartilage Scaffolds" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070771
APA StylePlath, A. M. S., Huber, S., Alfarano, S. R., Abbott, D. F., Hu, M., Mougel, V., Isa, L., & Ferguson, S. J. (2023). Co-Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Zein Articular Cartilage Scaffolds. Bioengineering, 10(7), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070771






