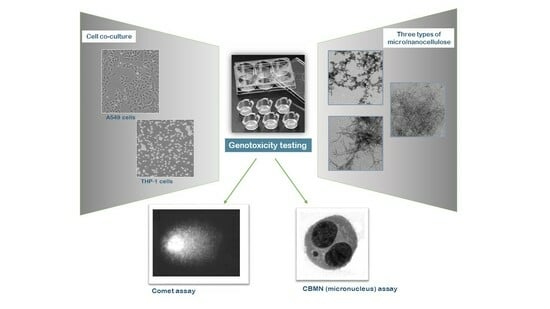
Assessing the Genotoxicity of Cellulose Nanomaterials in a Co-Culture of Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibrils and Nanocrystals
2.2. Cell Culture and Exposure to Nanofibers
2.3. Cytokinesis-Blocked Micronucleus (CBMN) Assay
2.4. Comet Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossi, B.R.; Pellegrini, V.O.; Cortez, A.A.; Chiromito, E.M.; Carvalho, A.J.; Pinto, L.O.; Rezende, C.A.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Polikarpov, I. Cellulose nanofibers production using a set of recombinant enzymes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 256, 117510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moohan, J.; Stewart, S.A.; Espinosa, E.; Rosal, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; Domínguez-Robles, J. Cellulose Nanofibers and Other Biopolymers for Biomedical Applications. A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Tarchoun, A.F.; Derradji, M.; Hamidon, T.S.; Masruchin, N.; Brosse, N.; Hussin, M.H. Nanocellulose: From Fundamentals to Advanced Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Jin, T.; He, H.; Liu, L. Preparation of nanocellulose and its potential in reinforced composites: A review. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 919–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Al Rashid, A.; Arif, Z.U.; Ahmed, W.; Arshad, H. Recent advances in nanocellulose-based different biomaterials: Types, properties, and emerging applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2601–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanthong, P.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Hao, X.; Xu, G.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Nanocellulose: Extraction and application. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2018, 1, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrega, M.; Orelma, H. Cellulose Nanofibril (CNF) Films and Xylan from Hot Water Extracted Birch Kraft Pulps. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Salvador, J.L.; Campano, C.; Lopez-Exposito, P.; Tarrés, Q.; Mutjé, P.; Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Monte, M.C.; Blanco, A. Enhanced Morphological Characterization of Cellulose Nano/Microfibers through Image Skeleton Analysis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Emerging technologies for the production of nanocellulose from lignocellulosic biomass. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 285, 119258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rol, F.; Belgacem, M.N.; Gandini, A.; Bras, J. Recent advances in surface-modified cellulose nanofibrils. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 88, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Gao, W. Cellulose nanofibrils manufactured by various methods with application as paper strength additives. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.; Zhao, H.; Mo, Q.; Pan, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, H.; Hu, B.; Song, H. From Cellulose to Cellulose Nanofibrils—A Comprehensive Review of the Preparation and Modification of Cellulose Nanofibrils. Materials 2020, 13, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errokh, A.; Magnin, A.; Putaux, J.-L.; Boufi, S. Morphology of the nanocellulose produced by periodate oxidation and reductive treatment of cellulose fibers. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3899–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Tian, P.; Xie, R.; Duan, Z.; Lv, Q.; Tao, Y. The Application Status of Nanoscale Cellulose-Based Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Biomedicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 732513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, X.-R.; Chen, A.X.; Li, N.; Yang, Y.Y.; Luo, H.-K. Nanocellulose: Recent Advances Toward Biomedical Applications. Small Sci. 2022, 3, 2200076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smole, M.S.; Hribernik, S.; Kurečič, M.; Krajnc, A.U.; Kreže, T.; Kleinschek, K.S. Surface Properties of Non-Conventional Cellulose Fibres; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Lei, H.; Xu, H. Cellulose nanocrystals prepared from wheat bran: Characterization and cytotoxicity assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibolla, H.; Pelissari, F.; Martins, J.; Lanzoni, E.; Vicente, A.; Menegalli, F.; Cunha, R. Banana starch nanocomposite with cellulose nanofibers isolated from banana peel by enzymatic treatment: In vitro cytotoxicity assessment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 207, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, A.B.; Seehra, M.S.; Fix, N.R.; Leonard, S.S. Lung biodurability and free radical production of cellulose nanomaterials. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, A.B.; Bernardes, J.S.; Fávaro, W.J.; Paula, A.J.; Durán, N. Cellulose nanocrystals as carriers in medicine and their toxicities: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Lourenço, A.F.; Sousa-Uva, A.; Ferreira, P.J.; Silva, M.J. Evaluating the genotoxicity of cellulose nanofibrils in a co-culture of human lung epithelial cells and monocyte-derived macrophages. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 291, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoudmann, N.; Schmutz, M.; Hirsch, C.; Nowack, B.; Som, C. Human hazard potential of nanocellulose: Quantitative insights from the literature. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endes, C.; Camarero-Espinosa, S.; Mueller, S.; Foster, E.J.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Weder, C.; Clift, M.J.D. A critical review of the current knowledge regarding the biological impact of nanocellulose. J. Nanobiotechnology 2016, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Pinto, F.; Lourenço, A.F.; Ferreira, P.J.T.; Louro, H.; Silva, M.J. On the toxicity of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils in animal and cellular models. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5509–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Knudsen, K.B.; Berthing, T.; Wolff, H.; Bengtson, S.; Kofoed, C.; Espersen, R.; Højgaard, C.; Winther, J.R.; Willemoës, M.; et al. Pulmonary effects of nanofibrillated celluloses in mice suggest that carboxylation lowers the inflammatory and acute phase responses. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 66, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, J.; Rydman, E.; Aimonen, K.; Hannukainen, K.-S.; Suhonen, S.; Vanhala, E.; Moreno, C.; Meyer, V.; Perez, D.d.S.; Sneck, A.; et al. Genotoxic and inflammatory effects of nanofibrillated cellulose in murine lungs. Mutagenesis 2016, 32, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.M.; Raposo, N.R.; Brayner, R.; Teixeira, E.M.; Oliveira, V.; Quintão, C.C.; Camargo, L.S.; Mattoso, L.H.; Brandão, H.M. Cytotoxicity and expression of genes involved in the cellular stress response and apoptosis in mammalian fibroblast exposed to cotton cellulose nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 075103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menas, A.L.; Yanamala, N.; Farcas, M.T.; Russo, M.; Friend, S.; Fournier, P.M.; Star, A.; Iavicoli, I.; Shurin, G.V.; Vogel, U.B.; et al. Fibrillar vs crystalline nanocellulose pulmonary epithelial cell responses: Cytotoxicity or inflammation? Chemosphere 2017, 171, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Marques, C.; Cadete, J.; Vilar, M.; Pedrosa, J.F.S.; Pinto, F.; Fernandes, S.N.; da Rosa, R.R.; Godinho, M.H.; Ferreira, P.J.T.; et al. Genotoxicity of Three Micro/Nanocelluloses with Different Physicochemical Characteristics in MG-63 and V79 Cells. J. Xenobiotics 2022, 12, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunasee, R.; Araoye, E.; Pyram, D.; Hemraz, U.D.; Boluk, Y.; Ckless, K. Cellulose nanocrystal cationic derivative induces NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1β secretion associated with mitochondrial ROS production. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despres, H.W.; Sabra, A.; Anderson, P.; Hemraz, U.D.; Boluk, Y.; Sunasee, R.; Ckless, K. Mechanisms of the immune response cause by cationic and anionic surface functionalized cellulose nanocrystals using cell-based assays. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 55, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, M.J.D.; Foster, E.J.; Vanhecke, D.; Studer, D.; Wick, P.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Weder, C. Investigating the Interaction of Cellulose Nanofibers Derived from Cotton with a Sophisticated 3D Human Lung Cell Coculture. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3666–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; Grootaers, G.; van der Does, A.M.; Krul, C.A.; Kooter, I.M. Human lung epithelial cell cultures for analysis of inhaled toxicants: Lessons learned and future directions. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 47, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.; Brown, R.; Shakesheff, K. Engineering tissue alternatives to animals: Applying tissue engineering to basic research and safety testing. Regen. Med. 2009, 4, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vis, M.A.M.; Ito, K.; Hofmann, S. Impact of Culture Medium on Cellular Interactions in in vitro Co-culture Systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Kim, D.; Soundharrajan, I.; Hwang, I.; Choi, K.C. Adipose and Muscle Cell Co-Culture System: A Novel In Vitro Tool to Mimic the In Vivo Cellular Environment. Biology 2020, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodson, M.; Vierck, J.; Hossner, K.; Byrne, K.; McNamara, J. The development and utility of a defined muscle and fat co-culture system. Tissue Cell 1997, 29, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wottrich, R.; Diabaté, S.; Krug, H.F. Biological effects of ultrafine model particles in human macrophages and epithelial cells in mono- and co-culture. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2004, 207, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Matos, P.; Marques, B.; Jordan, P.; Sousa-Uva, A.; Silva, M.J. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of MWCNT-7 and crocidolite: Assessment in alveolar epithelial cells versus their coculture with monocyte-derived macrophages. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 479–503, Erratum in Nanotoxicology 2022, 16, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfuhler, S.; van Benthem, J.; Curren, R.; Doak, S.H.; Dusinska, M.; Hayashi, M.; Heflich, R.H.; Kidd, D.; Kirkland, D.; Luan, Y.; et al. Use of in vitro 3D tissue models in genotoxicity testing: Strategic fit, validation status and way forward. Report of the working group from the 7th International Workshop on Genotoxicity Testing (IWGT). Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 850–851, 503135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfuhler, S.; Downs, T.R.; Allemang, A.J.; Shan, Y.; Crosby, M.E. Weak silica nanomaterial-induced genotoxicity can be explained by indirect DNA damage as shown by the OGG1-modified comet assay and genomic analysis. Mutagenesis 2016, 32, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolić, M.; Tomić, S.; Bekić, M. Immunological aspects of nanocellulose. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 222, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, Y.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Mariussen, E.; Hesler, M.; El Yamani, N.; Longhin, E.M.; Dusinska, M. Genotoxicity of Nanomaterials: Advanced In Vitro Models and High Throughput Methods for Human Hazard Assessment—A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Collins, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A.; Stone, V.; Dusinska, M. Mechanisms of genotoxicity. A review of in vitro and in vivo studies with engineered nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Karlsson, H.L. Primary and Secondary Genotoxicity of Nanoparticles: Establishing a Co-Culture Protocol for Assessing Micronucleus Using Flow Cytometry. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 845987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, P.; Bürkle, A.; Wick, P.; Hirsch, C. Exploring Flow Cytometry-Based Micronucleus Scoring for Reliable Nanomaterial Genotoxicity Assessment. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2538–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.; Lourenço, A.F.; Pedrosa, J.F.S.; Gonçalves, L.; Ventura, C.; Vital, N.; Bettencourt, A.; Fernandes, S.N.; da Rosa, R.R.; Godinho, M.H.; et al. Analysis of the In Vitro Toxicity of Nanocelluloses in Human Lung Cells as Compared to Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 487: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Louro, H.; Pinhão, M.; Santos, J.; Tavares, A.; Vital, N.; Silva, M.J. Evaluation of the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of benchmark multi-walled carbon nanotubes in relation to their physicochemical properties. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 262, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals 487-In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Catalán, J.; Ilves, M.; Järventaus, H.; Hannukainen, K.-S.; Kontturi, E.; Vanhala, E.; Alenius, H.; Savolainen, K.M.; Norppa, H. Genotoxic and immunotoxic effects of cellulose nanocrystals in vitro. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2014, 56, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanamala, N.; Farcas, M.T.; Hatfield, M.K.; Kisin, E.R.; Kagan, V.E.; Geraci, C.L.; Shvedova, A.A. In Vivo Evaluation of the Pulmonary Toxicity of Cellulose Nanocrystals: A Renewable and Sustainable Nanomaterial of the Future. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanamala, N.; Kisin, E.R.; Menas, A.L.; Farcas, M.T.; Khaliullin, T.O.; Vogel, U.B.; Shurin, G.V.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Fournier, P.M.; Star, A.; et al. In Vitro Toxicity Evaluation of Lignin-(Un)coated Cellulose Based Nanomaterials on Human A549 and THP-1 Cells. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3464–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.R.; Sanchez-Martinez, C.; Strømme, M.; Ferraz, N. In vitro biological responses to nanofibrillated cellulose by human dermal, lung and immune cells: Surface chemistry aspect. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimonen, K.; Suhonen, S.; Hartikainen, M.; Lopes, V.R.; Norppa, H.; Ferraz, N.; Catalán, J. Role of Surface Chemistry in the In Vitro Lung Response to Nanofibrillated Cellulose. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisin, E.; Yanamala, N.; Rodin, D.; Menas, A.; Farcas, M.; Russo, M.; Guppi, S.; Khaliullin, T.; Iavicoli, I.; Harper, M.; et al. Enhanced morphological transformation of human lung epithelial cells by continuous exposure to cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryston, T.B.; Georgiev, A.B.; Pissis, P.; Georgakilas, A.G. Role of oxidative stress and DNA damage in human carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2011, 711, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, K.A.; Mena, J.A.; Male, K.B.; Hrapovic, S.; Kamen, A.; Luong, J.H. Effect of Surface Charge on the Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Fluorescent Labeled Cellulose Nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2924–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazali, N.A.H.; Zaidi, N.E.; Ariffin, H.; Abdullah, L.C.; Ghaemi, F.; Abdullah, J.M.; Takashima, I.; Rahman, N.M.A.N.A. Characterization and Cellular Internalization of Spherical Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNC) into Normal and Cancerous Fibroblasts. Materials 2019, 12, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Hirani, A.A.; Colacino, K.R.; Lee, Y.W.; Roman, M. Cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of cellulose nanocrystals. Nano Life 2012, 2, 1241006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Nanocellulose Sample | Yield (%) | CCOOH (μmoL/g) | DP | [η] (mL/g) | Fibril Diameter 1 (nm) | z-Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | CM | PBS | CM | |||||
| CNF-TEMPO | 100 | 1332 | 309 | 130 | 10.7 ± 1.9 | - | −24.6 ± 1.0 | −19.7 ± 1.5 |
| CMF-ENZ | 4.9 | 143 | 1591 | 618 | 29.7 ± 7.3 | 85.2 ± 41.2 | −11.6 ± 1.0 | −9.4 ± 0.6 |
| CNC | - | - | - | - | 19.7 ± 6.1 | 36.0 ± 9.0 | −17.3 ± 0.8 | −13.9 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ventura, C.; Pinto, F.; Lourenço, A.F.; Pedrosa, J.F.S.; Fernandes, S.N.; da Rosa, R.R.; Godinho, M.H.; Ferreira, P.J.T.; Louro, H.; Silva, M.J. Assessing the Genotoxicity of Cellulose Nanomaterials in a Co-Culture of Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080986
Ventura C, Pinto F, Lourenço AF, Pedrosa JFS, Fernandes SN, da Rosa RR, Godinho MH, Ferreira PJT, Louro H, Silva MJ. Assessing the Genotoxicity of Cellulose Nanomaterials in a Co-Culture of Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(8):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080986
Chicago/Turabian StyleVentura, Célia, Fátima Pinto, Ana Filipa Lourenço, Jorge F. S. Pedrosa, Susete N. Fernandes, Rafaela R. da Rosa, Maria Helena Godinho, Paulo J. T. Ferreira, Henriqueta Louro, and Maria João Silva. 2023. "Assessing the Genotoxicity of Cellulose Nanomaterials in a Co-Culture of Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages" Bioengineering 10, no. 8: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080986
APA StyleVentura, C., Pinto, F., Lourenço, A. F., Pedrosa, J. F. S., Fernandes, S. N., da Rosa, R. R., Godinho, M. H., Ferreira, P. J. T., Louro, H., & Silva, M. J. (2023). Assessing the Genotoxicity of Cellulose Nanomaterials in a Co-Culture of Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Bioengineering, 10(8), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080986