Comparing Remote Speckle Plethysmography and Finger-Clip Photoplethysmography with Non-Invasive Finger Arterial Pressure Pulse Waves, Regarding Morphology and Arrival Time
Abstract
1. Introduction
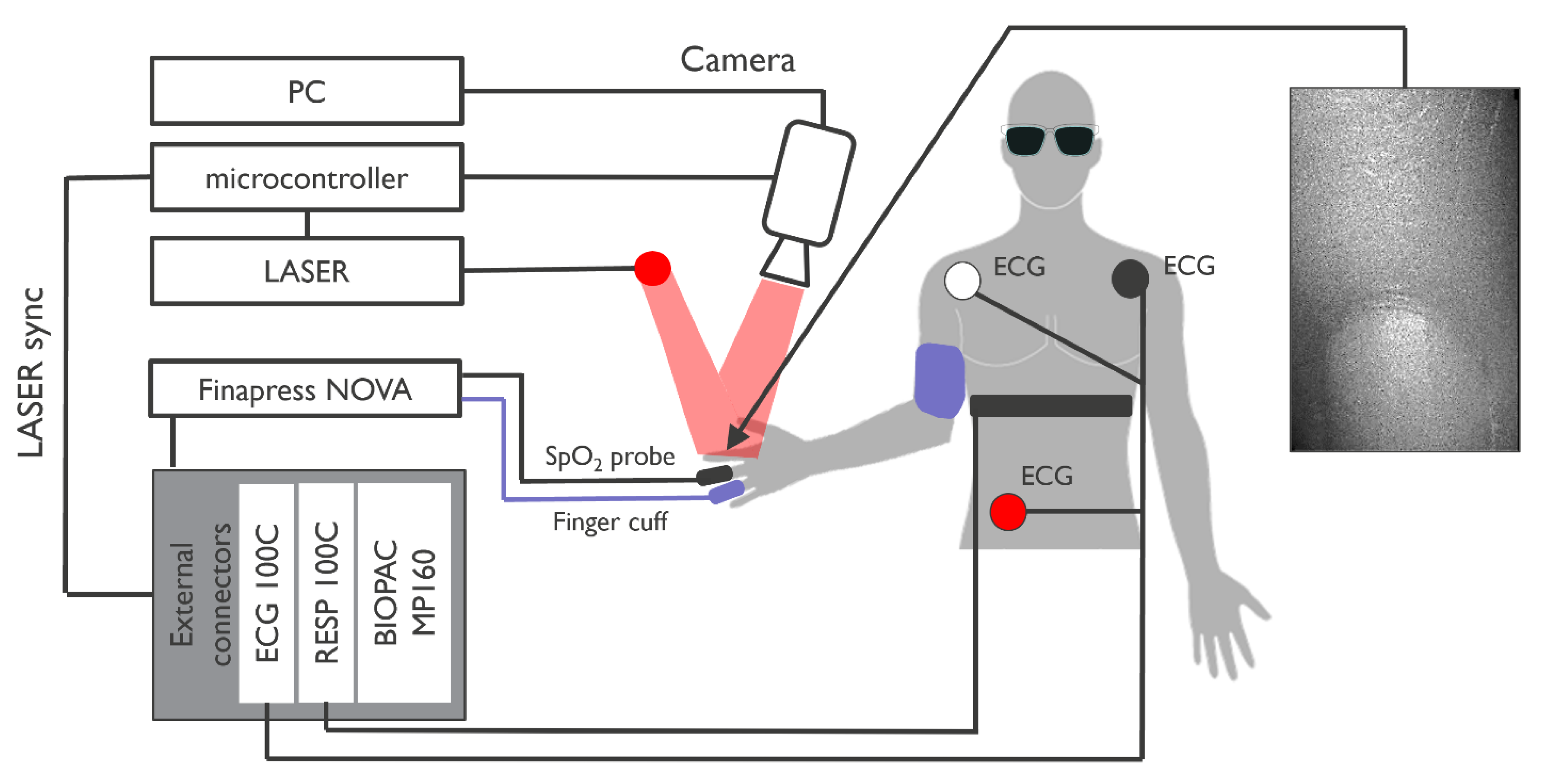
2. Materials and Methods
3. Analysis
3.1. Morphology Analysis
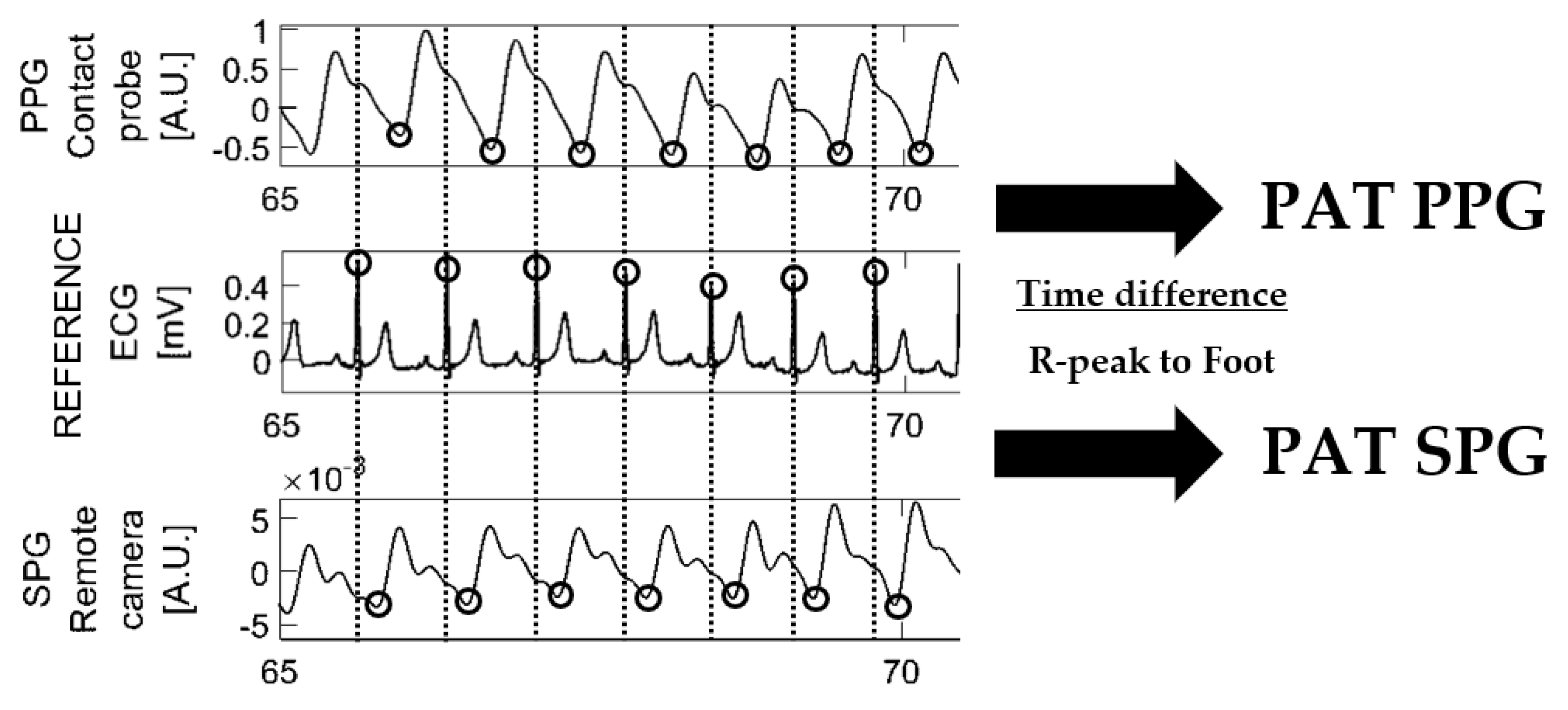
3.2. Pulse Arrival Time Analysis
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Morphology Results: Pulse Waveform
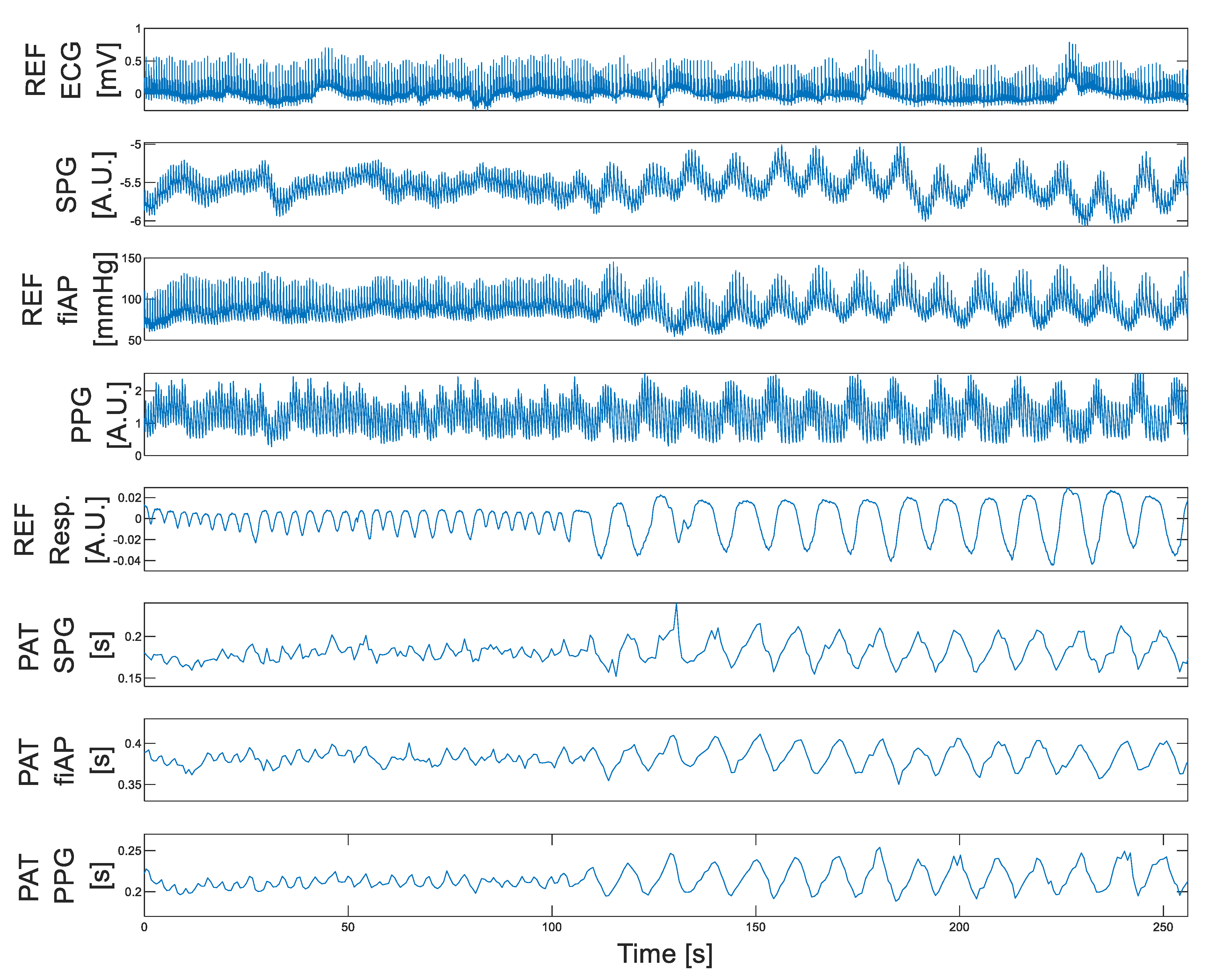
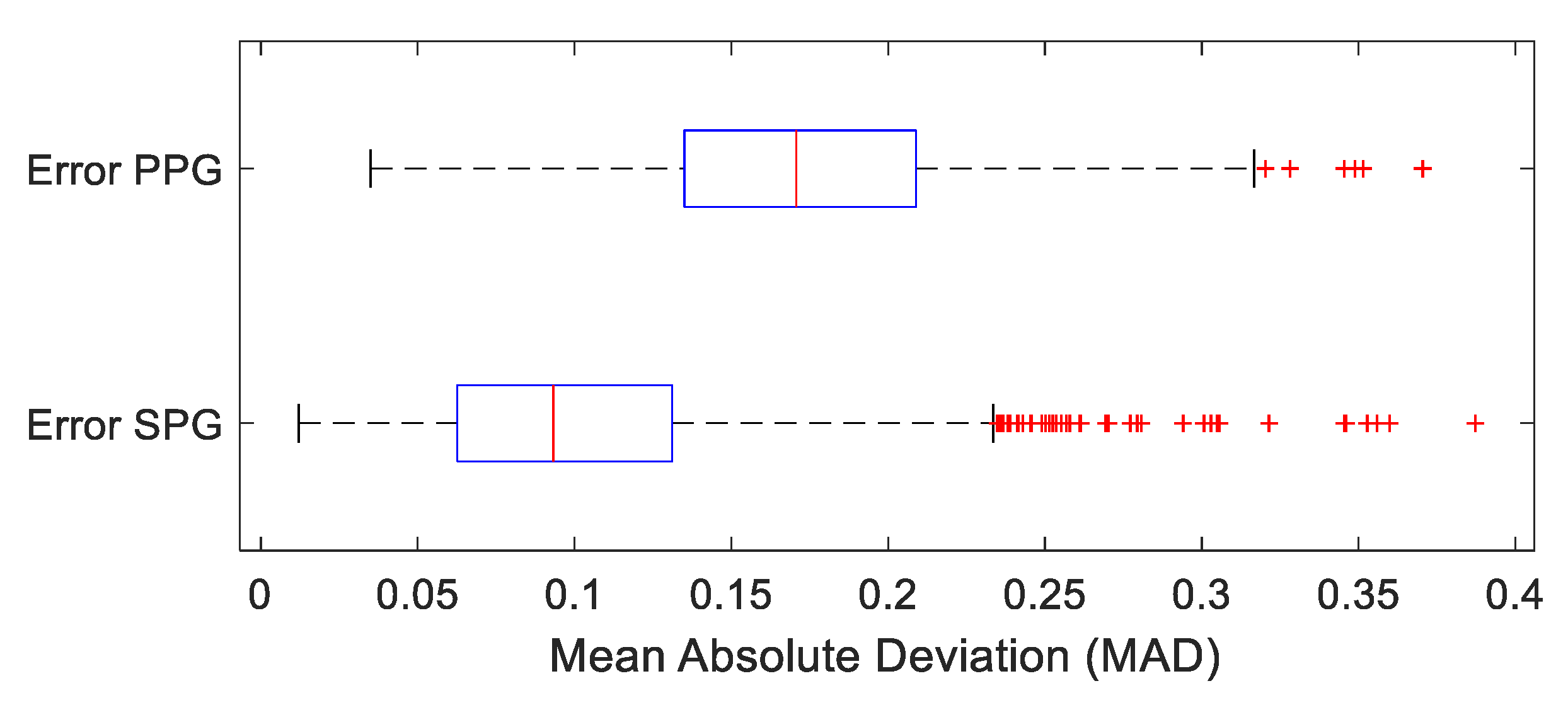
4.2. Temporal Results: Pulse Arrival Time (PAT)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heeman, W.; Steenbergen, W.; van Dam, G.M.; Boerma, E.C. Clinical Applications of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging: A Review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 080901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghijsen, M.; Rice, T.B.; Yang, B.; White, S.M.; Tromberg, B.J. Wearable Speckle Plethysmography (SPG) for Characterizing Microvascular Flow and Resistance. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 3937–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.E.; Monroe, D.C.; Crouzet, C.; Hicks, J.W.; Choi, B. Speckleplethysmographic (SPG) Estimation of Heart Rate Variability During an Orthostatic Challenge. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.E.; Lertsakdadet, B.; Crouzet, C.; Bahani, A.; Choi, B. Comparison of Speckleplethysmographic (SPG) and Photoplethysmographic (PPG) Imaging by Monte Carlo Simulations and in Vivo Measurements. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4306–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugel, B.; Kouz, K.; Meidert, A.S.; Schulte-Uentrop, L.; Romagnoli, S. How to Measure Blood Pressure Using an Arterial Catheter: A Systematic 5-Step Approach. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidert, A.S.; Saugel, B. Techniques for Non-Invasive Monitoring of Arterial Blood Pressure. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.S.; Chapman, N.; Chowienczyk, P.; Clark, C.; Denver, E.; Lacy, P.; Martin, U.; McManus, R.; Neary, A.; Sheppard, J. Oscillometric Measurement of Blood Pressure: A Simplified Explanation. A Technical Note on Behalf of the British and Irish Hypertension Society. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, D.S.; Schultz, M.G.; Otahal, P.; Aakhus, S.; Al-Jumaily, A.M.; Black, J.A.; Bos, W.J.; Chambers, J.B.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, H.M.; et al. Accuracy of Cuff-Measured Blood Pressure: Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, K.H.; Settels, J.J.; de Wit, B. The Measurement of Continuous Finger Arterial Pressure Noninvasively in Stationary Subjects. In Biological and Psychological Factors in Cardiovascular Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, A.P.; Butlin, M.; Walsh, A. Arterial Blood Pressure Measurement and Pulse Wave Analysis-Their Role in Enhancing Cardiovascular Assessment. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 59, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yang, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.C. Analysis of Pulse Arrival Time as an Indicator of Blood Pressure in a Large Surgical Biosignal Database: Recommendations for Developing Ubiquitous Blood Pressure Monitoring Methods. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuke, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nakayama, K.; Tanaka, H.; Minami, S. Blood Pressure Estimation from Pulse Wave Velocity. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6107–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.T. Pulse Transit Time Technique for Cuffless Unobtrusive Blood Pressure Measurement: From Theory to Algorithm. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Xu, D.; Bari Olivier, N.; Mukkamala, R. Pulse Arrival Time Is Not an Adequate Surrogate for Pulse Transit Time as a Marker of Blood Pressure Experimental Data. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imholz, B.P.M.; Wieling, W.; van Montfrans, G.A.; Wesseling, K.H. Fifteen Years Experience with Finger Arterial Pressure Monitoring: Assessment of the Technology. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz Olazábal, J.; Wieringa, F.; Hermeling, E.; van Hoof, C. Camera-Derived Photoplethysmography (RPPG) and Speckle Plethysmography (RSPG): Comparing Reflective and Transmissive Mode at Various Integration Times Using LEDs and Lasers. Sensors 2022, 22, 6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.I.; Struthers, A.D. Beyond Blood Pressure: Pulse Wave Analysis–a Better Way of Assessing Cardiovascular Risk? Future Cardiol. 2005, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieringa, F.P.; Broers, N.J.H.; Kooman, J.P.; van der Sande, F.M.; van Hoof, C. Wearable Sensors: Can They Benefit Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease? Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2017, 14, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Wiles, C.; Parker, B.E.; Clark, B.R.; Sohn, M.W.; Mariani, S.; Hahn, J.O.; Jacobs, D.R.; Stein, J.H.; Lima, J.; et al. Pulse Arrival Time, a Novel Sleep Cardiovascular Marker: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Thorax 2021, 76, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzan, M.; Romem, A.; Koppel, R. Pulse Oximetry: Fundamentals and Technology Update. Med. Devices Evid. Res. 2014, 7, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, I.S.; Romashko, R.V.; Koval, V.T.; Giniatullin, R.; Kamshilin, A.A. Origin of Infrared Light Modulation in Reflectance-Mode Photoplethysmography. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadort, A.; Kalkman, K.; Van Leeuwen, T.G.; Faber, D.J. Quantitative Blood Flow Velocity Imaging Using Laser Speckle Flowmetry. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.N. Arterial Compliance to Stratify Cardiovascular Risk: More Precision in Therapeutic Decision Making. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14 Pt 2, 258S–263S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braverman, I.M. The Cutaneous Microcirculation. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2000, 5, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseling, K.H. Finapres, Continuous Noninvasive Finger Arterial Pressure Based on the Method of Penaz. In Blood Pressure Measurements; Steinkopff: Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz Olazabal, J.; Wieringa, F.; Hermeling, E.; Van Hoof, C. Beat-to-Beat Intervals of Speckle Intensity-Based Optical Plethysmograms Compared to Electrocardiogram. In Proceedings of the 2021 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Brno, Czech Republic, 13–15 September 2021; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.C.; Ma, Y.; Krishnan, S.; Li, Y.; Yoon, S.; Guo, X.; Feng, X.; Shi, Y.; Seidel, M.; Cho, N.H.; et al. Materials Science/Clinical Medi Cine: Epidermal Devices for Noninvasive, Precise, and Continuous Mapping of Macrovascular and Microvascular Blood Flow. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rein, M.; Favrod, V.D.; Hou, C.; Khudiyev, T.; Stolyarov, A.; Cox, J.; Chung, C.C.; Chav, C.; Ellis, M.; Joannopoulos, J.; et al. Diode Fibres for Fabric-Based Optical Communications. Nature 2018, 560, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subject | R PPG PAT | AC PPG | R SPG PAT | AC SPG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.86 | 1.16 | 0.89 | 0.0089 |
| 2 | 0.58 | 1.33 | 0.71 | 0.0088 |
| 3 | 0.21 | 1.51 | 0.18 | 0.0049 |
| 4 | 0.84 | 1.08 | 0.63 | 0.0078 |
| 5 | 0.83 | 1.06 | 0.83 | 0.0086 |
| 6 | 0.65 | 0.99 | 0.35 | 0.0041 |
| 7 | 0.51 | 1.22 | 0.73 | 0.0113 |
| 8 | 0.9 | 1.66 | 0.95 | 0.0129 |
| Average | 0.6725 | 1.25 | 0.65875 | 0.0084 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herranz Olazabal, J.; Wieringa, F.; Hermeling, E.; Van Hoof, C. Comparing Remote Speckle Plethysmography and Finger-Clip Photoplethysmography with Non-Invasive Finger Arterial Pressure Pulse Waves, Regarding Morphology and Arrival Time. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010101
Herranz Olazabal J, Wieringa F, Hermeling E, Van Hoof C. Comparing Remote Speckle Plethysmography and Finger-Clip Photoplethysmography with Non-Invasive Finger Arterial Pressure Pulse Waves, Regarding Morphology and Arrival Time. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerranz Olazabal, Jorge, Fokko Wieringa, Evelien Hermeling, and Chris Van Hoof. 2023. "Comparing Remote Speckle Plethysmography and Finger-Clip Photoplethysmography with Non-Invasive Finger Arterial Pressure Pulse Waves, Regarding Morphology and Arrival Time" Bioengineering 10, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010101
APA StyleHerranz Olazabal, J., Wieringa, F., Hermeling, E., & Van Hoof, C. (2023). Comparing Remote Speckle Plethysmography and Finger-Clip Photoplethysmography with Non-Invasive Finger Arterial Pressure Pulse Waves, Regarding Morphology and Arrival Time. Bioengineering, 10(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010101









