Contactless Camera-Based Sleep Staging: The HealthBed Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Protocol
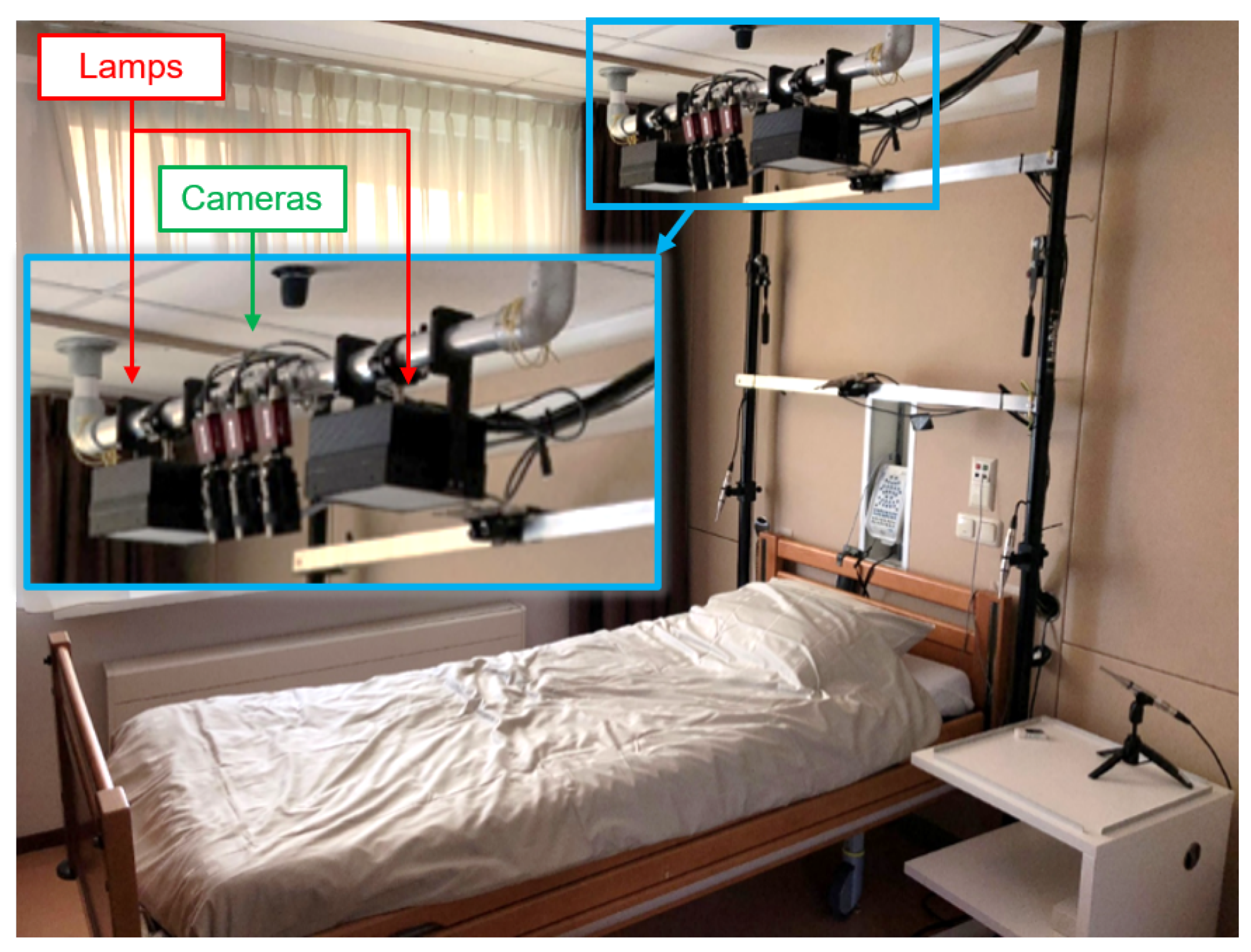
2.2. Measurement Setup
2.3. Camera-Based Remote PPG, Pulse Extraction and Inter-Pulse Interval Detection
2.4. Sleep Stage Classifier
2.5. Sleep Staging Performance
2.6. ECG Benchmark-Sleep Staging and Pulse Detection Performance
3. Results
3.1. Questionnaire Results on Experienced Obtrusiveness
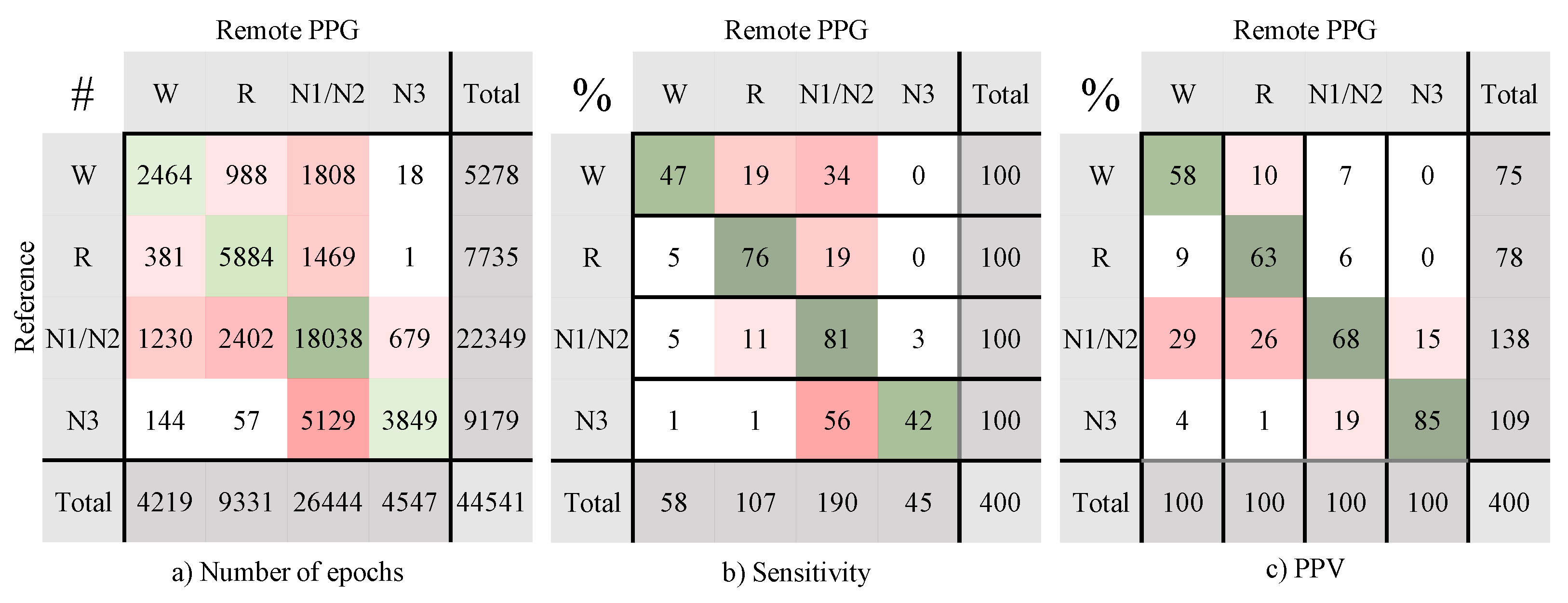
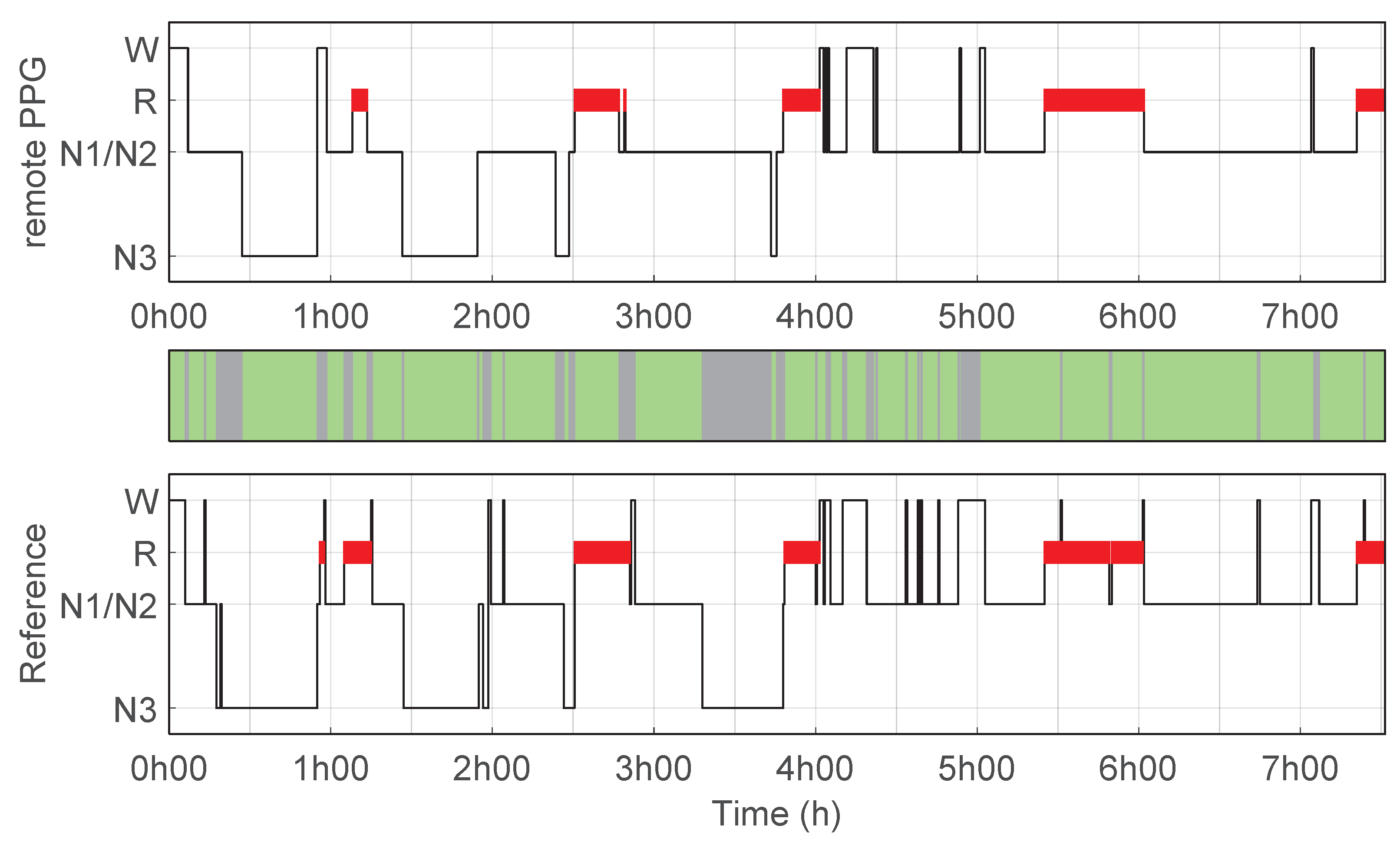
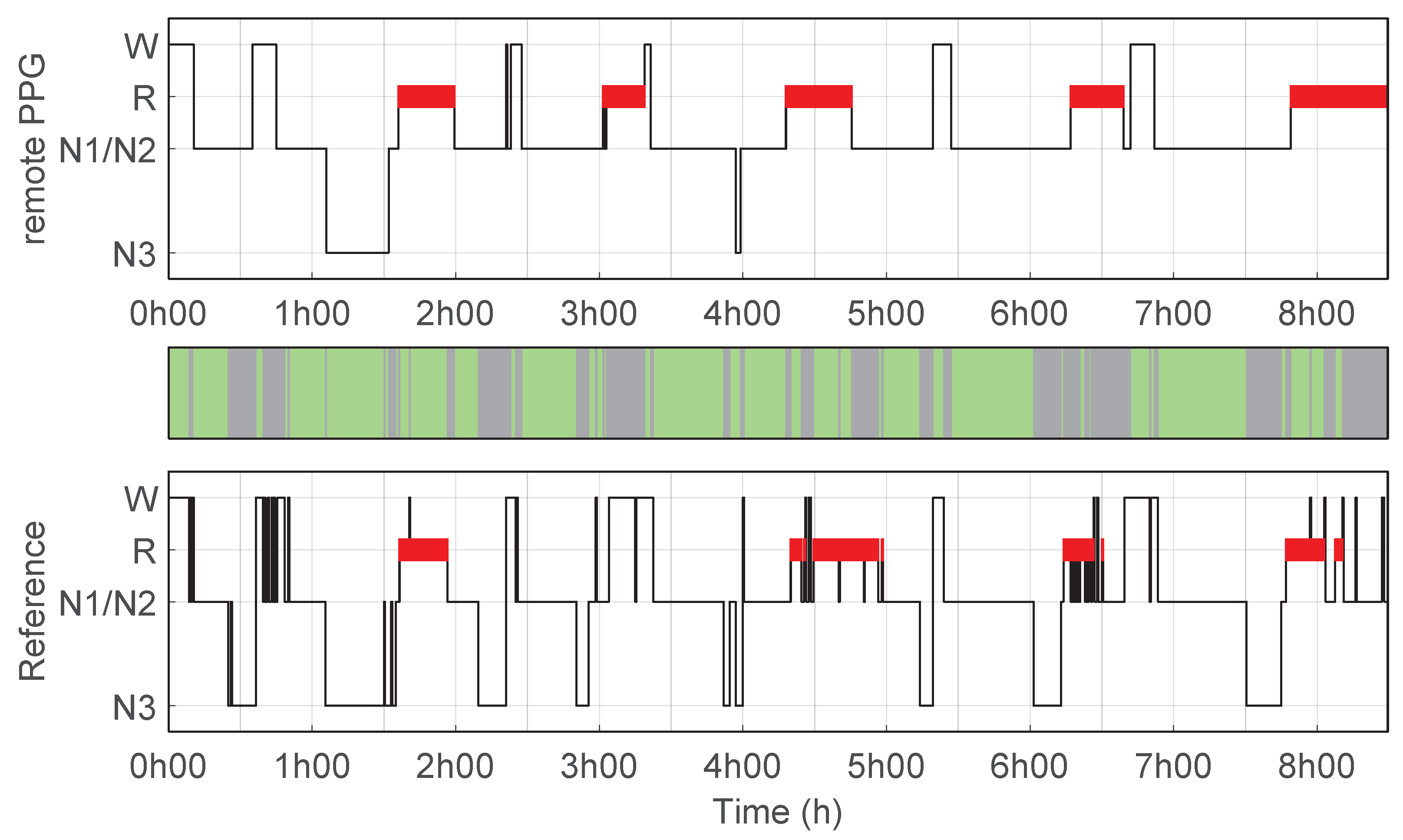
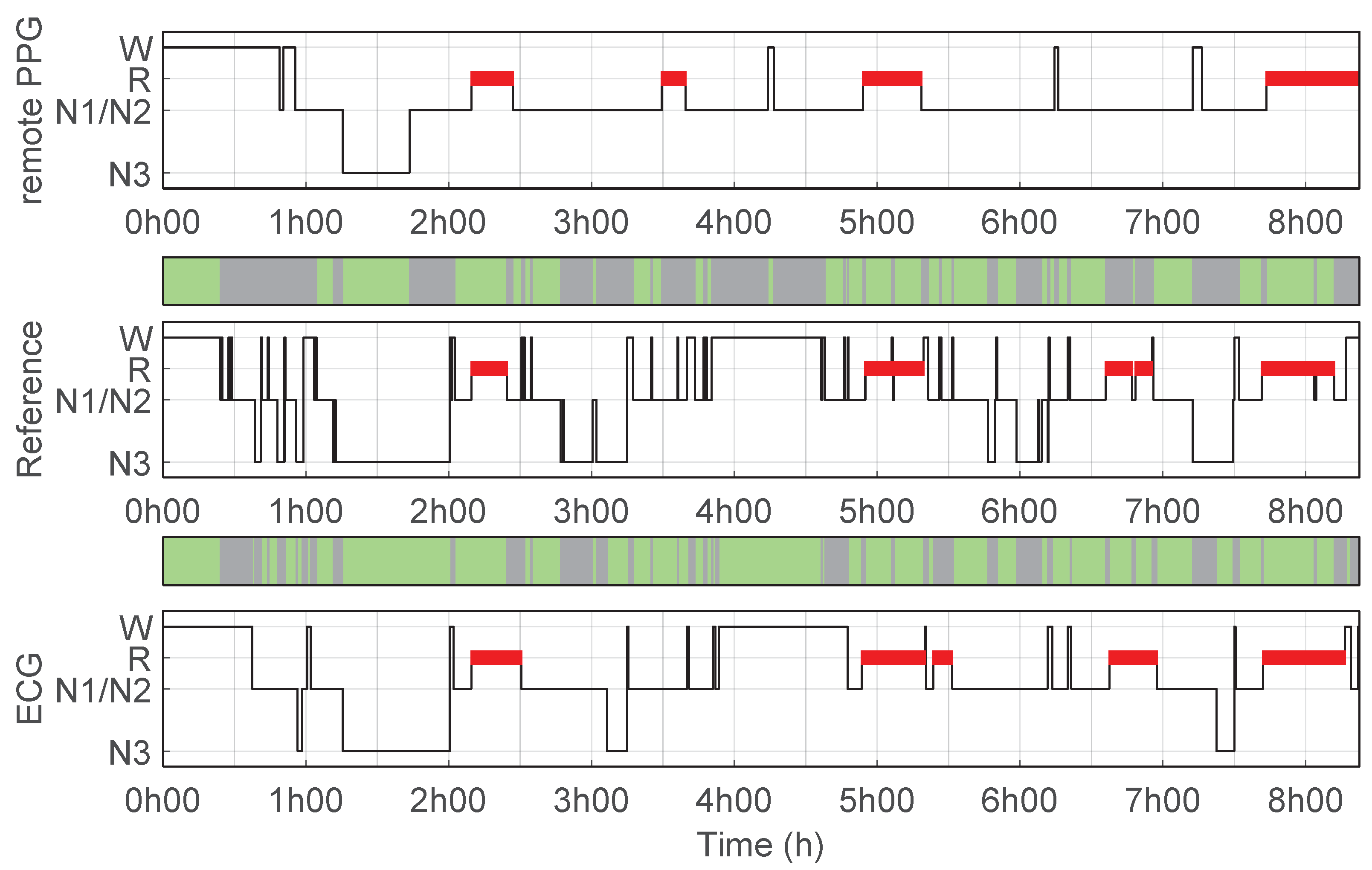
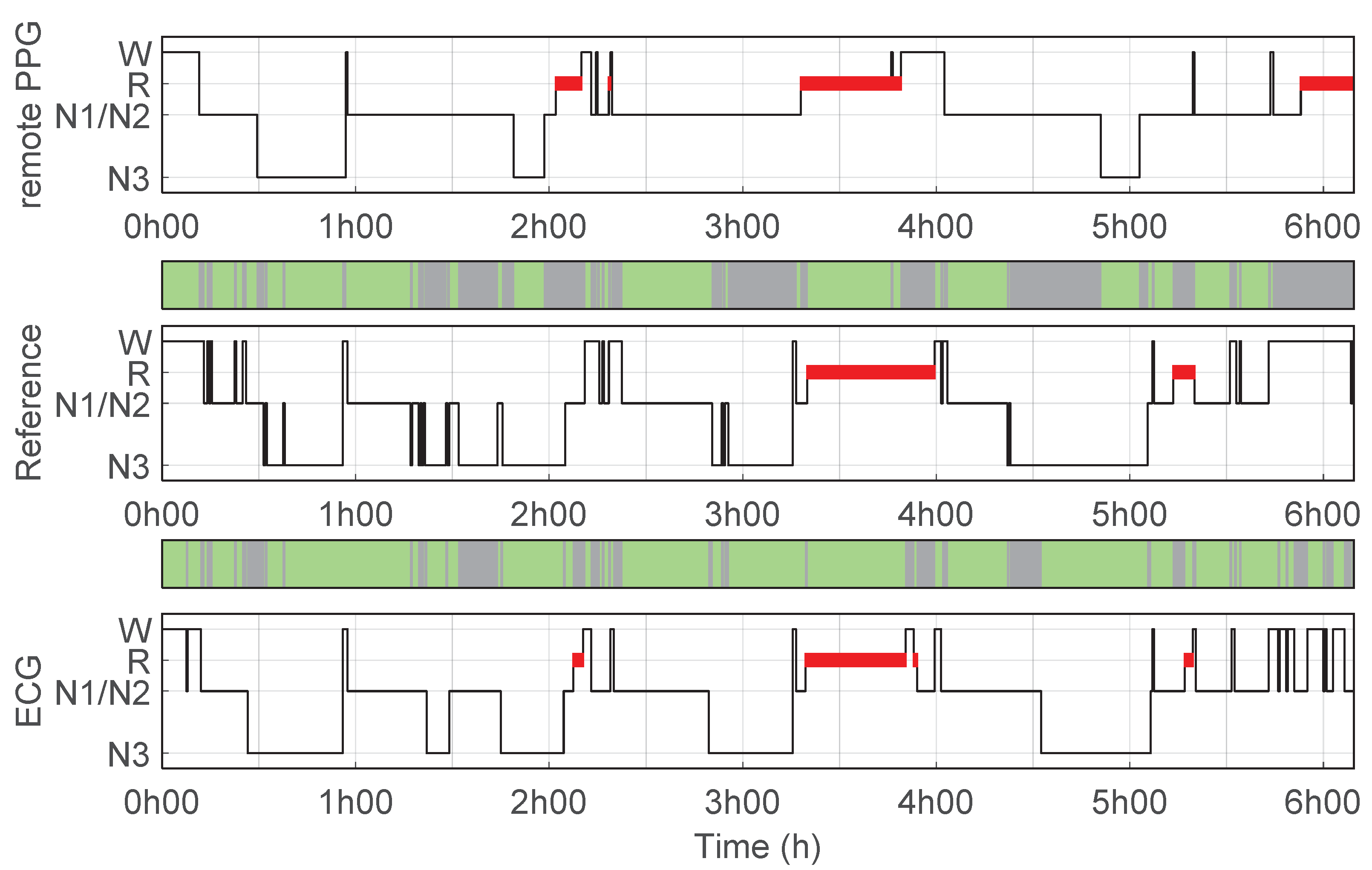
3.2. Sleep Stage Classifier and Performance
3.3. ECG Benchmark-Sleep Staging and Pulse Detection Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AASM | American Academy of Sleep Medicine |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram / Electrocardiography |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| IBI | Inter Beat Interval |
| IPI | Inter Pulse Interval |
| N1/2/3 | Sleep stages 1, 2 and 3 with No Rapid Eye Movements |
| PPG | Photoplethysmography |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| PSG | Polysomnography |
| QRS | QRS-complex, the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical ECG |
| REM | Sleep stage with Rapid Eye Movement |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| TP | True Positive |
| Cohen’s kappa coefficient of agreement | |
| Agreement between the predicted sleep stages using the ECG setup and the reference | |
| Agreement between the predicted sleep stages using the remote PPG setup and the reference |
Appendix A. Questionnaire Results
- Did the presence of the remote PPG measurement setup influence your consideration to participate in this study?
- Did the presence of the camera influence your sleep?
- Did the presence of the additional light-source, of the remote PPG setup, influence your sleep?
| 1: Very Much | 2: A Lot | 3: A Little Bit | 4: Hardly | 5: Not at All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Question 1 | - | - | 3 | 7 | 33 |
| Question 2 | - | - | 6 | 10 | 27 |
| Question 3 | - | 1 | 1 | 8 | 33 |
Appendix B. Confusion Matrices Remote PPG Setup
Appendix C. ECG Performance

| Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 classes | |||||
| Wake | 0.70 (0.13) | 93.9 (2.7) | 79.3 (16.2) | 95.9 (3.4) | 72.9 (17.1) |
| N1/N2 | 0.56 (0.12) | 78.4 (6.1) | 83.7 (7.0) | 72.8 (9.3) | 74.8 (8.8) |
| N3 | 0.61 (0.15) | 89.6 (4.2) | 56.0 (18.1) | 98.5 (1.9) | 89.7 (14.9) |
| REM | 0.73 (0.10) | 93.1 (4.0) | 84.0 (12.8) | 95.1 (3.1) | 77.4 (12.0) |
| 3 classes | 0.74 (0.10) | 87.6 (4.3) | |||
| 4 classes | 0.65 (0.10) | 77.5 (6.5) |
References
- Austin, D.; Beattie, Z.T.; Riley, T.; Adami, A.M.; Hagen, C.C.; Hayes, T.L. Unobtrusive classification of sleep and wakefulness using load cells under the bed. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5254–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, J.; Mairesse, O.; Verbanck, P.; Neu, D. Is a one-night stay in the lab really enough to conclude? First-night effect and night-to-night variability in polysomnographic recordings among different clinical population samples. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 200, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surtees, A.D.; Oliver, C.; Jones, C.A.; Evans, D.L.; Richards, C. Sleep duration and sleep quality in people with and without intellectual disability: A meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.K.; Pu, Y. Heart rate variability, sleep and sleep disorders. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.; Gao, S. The relationship of HRV to sleep EEG and sleep rhythm. Int. J. Neurosci. 2005, 115, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P.; van Gilst, M.M.; Radha, M.; Ross, M.; Moreau, A.; Cerny, A.; Anderer, P.; Long, X.; van Dijk, J.P.; Overeem, S. Automatic sleep staging using heart rate variability, body movements, and recurrent neural networks in a sleep disordered population. Sleep 2020, 43, zsaa048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, S.A. A systematic review of sensing technologies for wearable sleep staging. Sensors 2021, 21, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P.; Weysen, T.; Goelema, M.S.; Møst, E.I.; Radha, M.; Lunsingh Scheurleer, C.; van den Heuvel, L.; Aarts, R.M. Validation of photoplethysmography-based sleep staging compared with polysomnography in healthy middle-aged adults. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulterkens, B.M.; Fonseca, P.; Hermans, L.W.; Ross, M.; Cerny, A.; Anderer, P.; Long, X.; van Dijk, J.P.; Vandenbussche, N.; Pillen, S.; et al. It is all in the wrist: Wearable sleep staging in a clinical population versus reference polysomnography. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2021, 13, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zamboti, M.; Cellini, N.; Goldstone, A.; Colrain, I.M.; Baker, F.C. Wearable Sleep Technology in Clinical and Research Settings. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2019, 51, 1538–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Li, Y.; Rueschman, M.N.; Winkelman, J.W.; Ellenbogen, J.M.; Solet, J.M.; Dulin, H.; Berkman, L.F.; Buxton, O.M. Measuring Sleep: Accuracy, Sensitivity, and Specificity of Wrist Actigraphy Compared to Polysomnography. Sleep 2013, 36, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekedulegn, D.; Andrew, M.E.; Shi, M.; Violanti, J.M.; Knox, S.; Innes, K.E. Actigraphy-Based Assessment of Sleep Parameters. Ann. Work. Exp. Health 2020, 64, 350–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, V.; Spicher, N.; Wang, J.; Ganapathy, N.; Warnecke, J.M.; Leonhardt, S.; Swaminathan, R.; Deserno, T.M. Continuous Monitoring of Vital Signs Using Cameras: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakkaew, P.; Onoye, T. Non-Contact Respiration Monitoring and Body Movements Detection for Sleep Using Thermal Imaging. Sensors 2020, 20, 6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.M.; Alnowami, M.; Khan, S.; Dijk, D.J.; Hilton, A.; Wells, K. Sleep Posture Classification using a Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gastel, M.; Stuijk, S.; Overeem, S.; van Dijk, J.P.; van Gilst, M.M.; de Haan, G. Camera-based vital signs monitoring during sleep—A proof of concept study. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vosters, L.; den Brinker, A.C. Modified Camera Setups for Day-and-Night Pulse-rate Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, C.; Wiesmeyr, C.; Garn, H.; Kohn, B.; Wimmer, M.; Mandl, M.; Glos, M.; Penzel, T.; Klösch, G.; Stefanic-Kejik, A.; et al. 3D camera and pulse oximeter for respiratory events detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorato, I.; Stuijk, S.; Meftah, M.; Kommers, D.; Andriessen, P.; van Pul, C.; de Haan, G. Automatic Separation of Respiratory Flow from Motion in Thermal Videos for Infant Apnea Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochino, T.; Ohno, Y.; Kato, T.; Taniike, M.; Okada, S. Sleep stage estimation method using a camera for home use. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falie, D.; Ichim, M. Sleep monitoring and sleep apnea event detection using a 3D camera. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th International Conference on Communications, Bucharest, Romania, 10–12 June 2010; pp. 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Brooks, R.; Lloyd, R.M.; Vaughn, B.V.; Marcus, C.L. AASM scoring manual version 2.2 updates: New chapters for scoring infant sleep staging and home sleep apnea testing. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 1253–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, T.; Van Gastel, M.; Wang, W.; De Haan, G. Fully-automatic camera-based pulse-oximetry during sleep. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gastel, M.; Stuijk, S.; de Haan, G. Motion robust remote-PPG in infrared. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Boss, J.; Wolf, M. An efficient algorithm for automatic peak detection in noisy periodic and quasi-periodic signals. Algorithms 2012, 5, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, M.; Fonseca, P.; Moreau, A.; Ross, M.; Cerny, A.; Anderer, P.; Long, X.; Aarts, R.M. Sleep stage classification from heart-rate variability using long short-term memory neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klosh, G.; Kemp, B.; Penzel, T.; Schlogl, A.; Rappelsberger, P.; Trenker, E.; Gruber, G.; Zeithofer, J.; Saletu, B.; Herrmann, W.; et al. The SIESTA project polygraphic and clinical database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Alste, J.A.; Van Eck, W.; Herrmann, O. ECG baseline wander reduction using linear phase filters. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1986, 19, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P.; Aarts, R.M.; Foussier, J.; Long, X. A novel low-complexity post-processing algorithm for precise QRS localization. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, S.; Piek, M.; Tulevski, I.; Somsen, G.; Winter, M. The accuracy of heartbeat detection using photoplethysmography technology in cardiac patients. J. Electrocardiol. 2021, 67, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochstadt, A.; Havakuk, O.; Chorin, E.; Schwartz, A.L.; Merdler, I.; Laufer, M.; Lubman, N.; Ghantous, E.; Viskin, S.; Rosso, R. Continuous heart rhythm monitoring using mobile photoplethysmography in ambulatory patients. J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 60, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gilst, M.; Wulterkens, B.; Fonseca, P.; Radha, M.; Ross, M.; Moreau, A.; Cerny, A.; Anderer, P.; Long, X.; van Dijk, J.; et al. Direct application of an ECG-based sleep staging algorithm on reflective photoplethysmography data decreases performance. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, M.; Fonseca, P.; Moreau, A.; Ross, M.; Cerny, A.; Anderer, P.; Long, X.; Aarts, R.M. A deep transfer learning approach for wearable sleep stage classification with photoplethysmography. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turppa, E.; Kortelainen, J.M.; Antropov, O.; Kiuru, T. Vital Sign Monitoring Using FMCW Radar in Various Sleeping Scenarios. Sensors 2020, 20, 6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (−) | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 classes | |||||
| Wake | 0.42 (0.21) | 89.7 (7.6) | 44.7 (21.7) | 95.4 (7.2) | 59.2 (23.1) |
| N1/N2 | 0.43 (0.15) | 71.5 (7.4) | 80.8 (9.3) | 62.3 (10.6) | 68.1 (10.1) |
| N3 | 0.48 (0.15) | 86.4 (4.6) | 43.7 (18.1) | 98.1 (2.2) | 85.5 (17.4) |
| REM | 0.61 (0.16) | 88.2 (5.1) | 76.8 (16.0) | 90.8 (5.7) | 64.0 (17.6) |
| 3 classes | 0.58 (0.14) | 81.0 (7.5) | |||
| 4 classes | 0.49 (0.13) | 67.9 (8.7) |
| Parameter (Unit) | Mean | SD | Min. | Max. | Correlation with |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage (%) | 83.1 | 6.9 | 63.3 | 92.4 | = −0.32, p = 0.028 |
| Pulse detection | |||||
| Sensitivity (%) | 84.3 | 7.3 | 61.9 | 94.2 | = −0.45, p = 0.002 |
| PPV (%) | 96.6 | 3.9 | 82.5 | 99.6 | = −0.21, p = 0.156 |
| Pulse timing | |||||
| Bias (ms) | 35.4 | 26.7 | −20.0 | 108.7 | = 0.24, p = 0.113 |
| Trigger jitter (ms) | 54.9 | 8.8 | 37.7 | 75.0 | = 0.33, p = 0.025 |
| Pulses within 50 ms of QRS (%) | 68.3 | 7.4 | 49.3 | 84.2 | = −0.25, p = 0.092 |
| Pulses within 100 ms of QRS (%) | 94.0 | 3.6 | 86.2 | 99.0 | = −0.32, p = 0.029 |
| Pulse interval | |||||
| RMSE (ms) | 70.6 | 23.6 | 36.2 | 156.4 | = 0.30, p = 0.040 |
| (−) | 0.75 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.94 | = −0.52, p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Meulen, F.B.; Grassi, A.; van den Heuvel, L.; Overeem, S.; van Gilst, M.M.; van Dijk, J.P.; Maass, H.; van Gastel, M.J.H.; Fonseca, P. Contactless Camera-Based Sleep Staging: The HealthBed Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010109
van Meulen FB, Grassi A, van den Heuvel L, Overeem S, van Gilst MM, van Dijk JP, Maass H, van Gastel MJH, Fonseca P. Contactless Camera-Based Sleep Staging: The HealthBed Study. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010109
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Meulen, Fokke B., Angela Grassi, Leonie van den Heuvel, Sebastiaan Overeem, Merel M. van Gilst, Johannes P. van Dijk, Henning Maass, Mark J. H. van Gastel, and Pedro Fonseca. 2023. "Contactless Camera-Based Sleep Staging: The HealthBed Study" Bioengineering 10, no. 1: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010109
APA Stylevan Meulen, F. B., Grassi, A., van den Heuvel, L., Overeem, S., van Gilst, M. M., van Dijk, J. P., Maass, H., van Gastel, M. J. H., & Fonseca, P. (2023). Contactless Camera-Based Sleep Staging: The HealthBed Study. Bioengineering, 10(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010109









