First Flush Stormwater Runoff in Urban Catchments: A Bibliometric and Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
2.2. Comprehensive Review
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bibliometric Review
3.1.1. Publication Journals and Contingency Matrix
3.1.2. Network Mapping and Evolution of Keywords and Terms
3.2. Comprehensive Review
3.2.1. Definitions of ‘First Flush’
3.2.2. Characteristics of the Study Sites
3.2.3. Characteristics of Monitored Storm Events
3.2.4. Monitoring and Sampling Methodologies
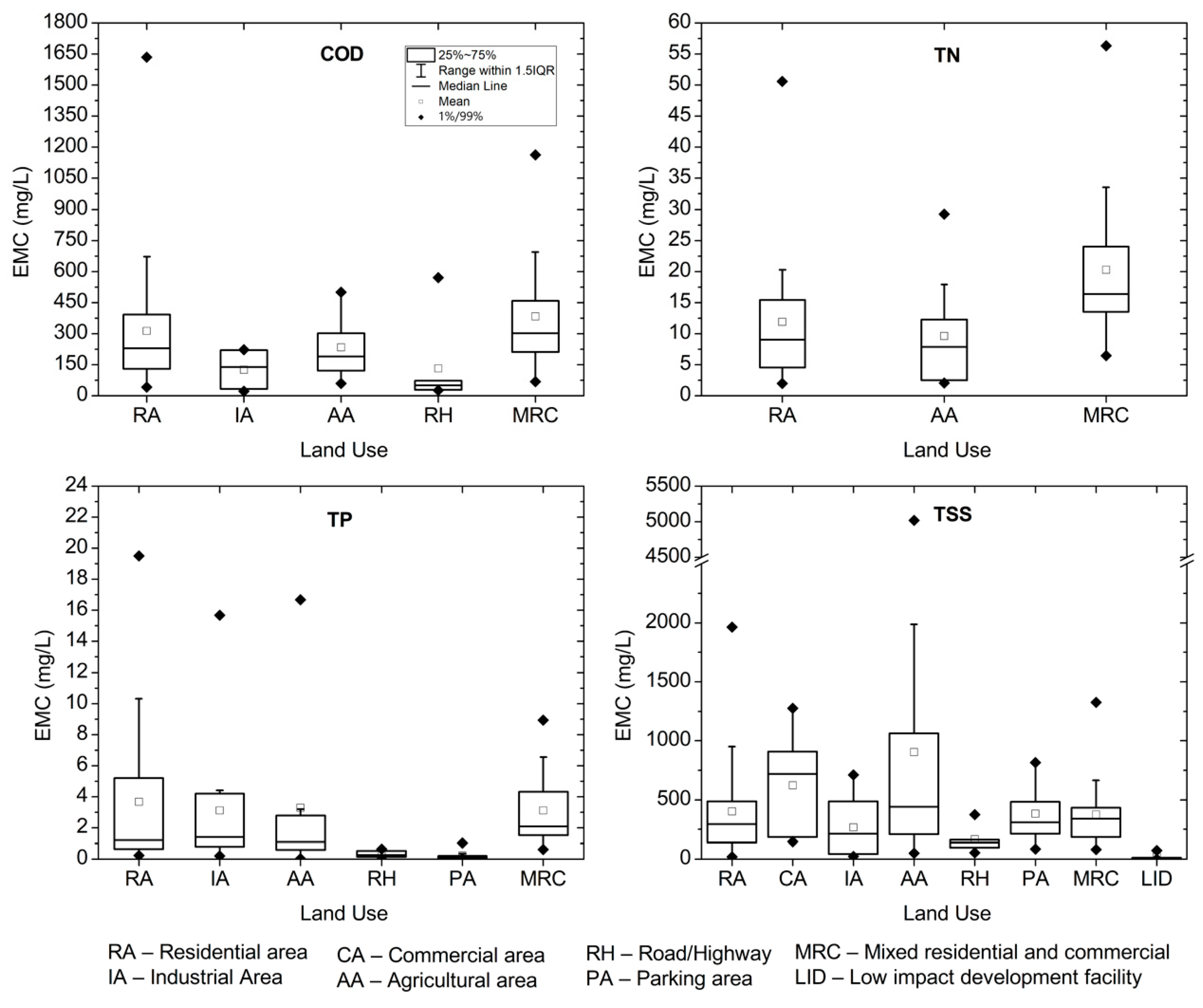
3.2.5. Water Quality Parameters
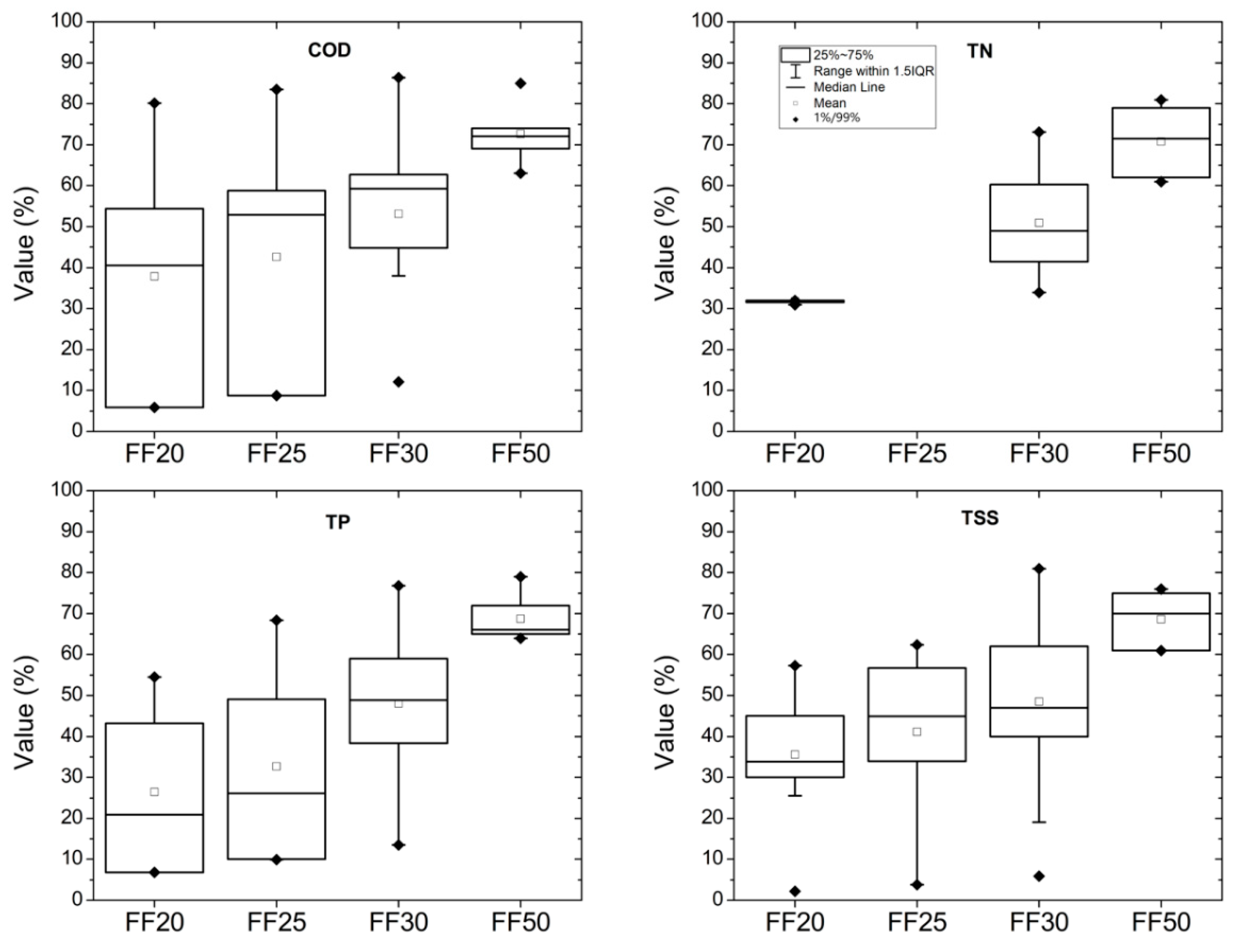
3.2.6. Event Mean Concentration (EMC) and First Flush Values
3.2.7. Application to the Design of BMPs/LID Technologies
4. Challenges and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Global Projections of Future Urban Land Expansion under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Güneralp, B.; Reba, M.; Hales, B.U.; Wentz, E.A.; Seto, K.C. Trends in Urban Land Expansion, Density, and Land Transitions from 1970 to 2010: A Global Synthesis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, J. Direct and Indirect Loss of Natural Area from Urban Expansion. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Ren, G.; Feng, Y. Analysis of the Environmental Behavior of Farmers for Non-Point Source Pollution Control and Management: An Integration of the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Protection Motivation Theory. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 237, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrissou, M.; Diekkrüger, B.; Tischbein, B.; Op de Hipt, F.; Näschen, K.; Poméon, T.; Yira, Y.; Ibrahim, B. Modeling the Impact of Climate and Land Use/Land Cover Change on Water Availability in an Inland Valley Catchment in Burkina Faso. Hydrology 2022, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, H. Estimating the Effect of Urban Growth on Annual Runoff Volume Using GIS in the Erbil Sub-Basin of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Hydrology 2017, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obahoundje, S.; Diedhiou, A.; Ofosu, E.A.; Anquetin, S.; François, B.; Adounkpe, J.; Amoussou, E.; Kouame, Y.M.; Kouassi, K.L.; Nguessan Bi, V.H.; et al. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Changes of Land Use and Land Cover over South-Western African Basins and Their Relations with Variations of Discharges. Hydrology 2018, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christian, L.; Epps, T.; Diab, G.; Hathaway, J. Pollutant Concentration Patterns of In-Stream Urban Stormwater Runoff. Water 2020, 12, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeung, M.; Baek, S.; Beom, J.; Cho, K.H.; Her, Y.; Yoon, K. Evaluation of Random Forest and Regression Tree Methods for Estimation of Mass First Flush Ratio in Urban Catchments. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M. First-flush characterization for stormwater runoff treatment. Stormwater 2008, 9, 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ringler, S. First Flush Characterization of Storm Water Runoff. Master’s Thesis, University of New Orleans, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2007. Available online: https://scholarworks.uno.edu/td/537 (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Flint, K.R.; Davis, A.P. Pollutant Mass Flushing Characterization of Highway Stormwater Runoff from an Ultra-Urban Area. J. Environ. Eng. 2007, 133, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, T.; McGree, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Taxonomy of Influential Factors for Predicting Pollutant First Flush in Urban Stormwater Runoff. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fai, C.M.; Yusop, Z. Determination of Stromwater First Flush Treatment Strategies at Tropical Urban Catchments. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 79, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.S.; Choi, D.H.; Jung, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.; Yoon, K.S.; Cho, K.H. Optimizing Low Impact Development (LID) for Stormwater Runoff Treatment in Urban Area, Korea: Experimental and Modeling Approach. Water Res. 2015, 86, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q. A Review of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems Considering the Climate Change and Urbanization Impacts. Water 2014, 6, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, P.J.; Argue, J.R.; Kuczera, G. Figtree Place: A Case Study in Water Sensitive Urban Development (WSUD). Urban Water 2000, 1, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier. Scopus. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- IFRIS; INRAE. CorTexT Platform. Available online: https://www.cortext.net/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- OriginLab Corporation. OriginPro 8.5. Northampton, MA, 2022. Available online: https://www.originlab.com/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Che, W. Pollutant First Flush Identificatio n and Its Implications for Urban Runoff Pollution Control: A Roof and Road Runoff Case Study in Beijing, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun, A.; Shams, S.; Nuruzzaman, M. Review on Uncertainty of the First-Flush Phenomenon in Diffuse Pollution Control. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M.K. First Flush Phenomenon and Its Application for Stormwater Runoff Management. J. Water Wastewater 2021, 31, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, M.; Nnadi, F.N.; Chasar, L.S. Characterizing Dry Deposition of Mercury in Urban Runoff. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2007, 185, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, S.L.; Webster-Brown, J.G. Stormwater Runoff Quality from Copper Roofing, Auckland, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2008, 42, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berndtsson, J.C.; Bengtsson, L.; Jinno, K. First Flush Effect from Vegetated Roofs during Simulated Rain Events. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, W.F. Flushing Effects in Combined Sewer Systems. In Proceedings of the 4th InternationalConference on Urban Storm Drainage, Lausanne, Switzerland, 31 August–4 September 1987; pp. 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Barco, J.; Papiri, S.; Stenstrom, M.K. First Flush in a Combined Sewer System. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deletic, A. The First Flush Load of Urban Surface Runoff. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, P.M.; McCarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A. Redefining the Stormwater First Flush Phenomenon. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; Chebbo, G.; Saget, A. Distribution of Pollutant Mass vs Volume in Stormwater Discharges and the First Flush Phenomenon. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, T.; McGree, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Goonetilleke, A. New Conceptualisation of First Flush Phenomena in Urban Catchments. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 281, 111820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, G. Rainwater Utilization and Storm Pollution Control Based on Urban Runoff Characterization. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, F.J.; Cochrane, T.A.; O’Sullivan, A.D. Characterising Urban Zinc Generation to Identify Surface Pollutant Hotspots in a Low Intensity Rainfall Climate. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Chen, Y. Stormwater Runoff Pollutant Loading Distributions and Their Correlation with Rainfall and Catchment Characteristics in a Rapidly Industrialized City. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenmueller, E.A.; Criss, R.E. Multiple Sources of Boron in Urban Surface Waters and Groundwaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, K.R.; Garcia-Chevesich, P.A.; Slinski, K.M.; Sharp, J.O.; McCray, J.E. Quantifying the Effects of Residential Infill Redevelopment on Urban Stormwater Quality in Denver, Colorado. Water 2021, 13, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Asal, S.; Toor, G.S. Residential Catchments to Coastal Waters: Forms, Fluxes, and Mechanisms of Phosphorus Transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, D.M.; Petts, G.E.; Foster, I.D.L.; Harper, S. Turbidity Dynamics during Spring Storm Events in an Urban Headwater River System: The Upper Tame, West Midlands, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 360, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E. Pollutant Concentrations of Stormwater and Captured Sediment in Flood Control Sumps Draining an Urban Watershed. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Samrani, A.G.; Lartiges, B.S.; Ghanbaja, J.; Yvon, J.; Kohler, A. Trace Element Carriers in Combined Sewer during Dry and Wet Weather: An Electron Microscope Investigation. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bang, K.W. Characterization of Urban Stormwater Runoff. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helness, H.; Sun, C.; Damman, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Raspati, G.; Bjerkelund, V.; Moldestad, G.; Hattori, K.; Kato, T.; Ando, N. High Rate Filtration for Local Treatment of Combined Sewer Overflow. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Ge, X.; Tian, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Z. Variations of Concentration Characteristics of Rainfall Runoff Pollutants in Typical Urban Living Areas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soller, J.; Stephenson, J.; Olivieri, K.; Downing, J.; Olivieri, A.W. Evaluation of Seasonal Scale First Flush Pollutant Loading and Implications for Urban Runoff Management. J. Environ. Manage. 2005, 76, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamoon, A.; Jahan, S.; He, X.; Joergensen, N.E.; Rahman, A. First Flush Analysis Using a Rainfall Simulator on a Micro Catchment in an Arid Climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ali, S.; Bonhomme, C.; Chebbo, G. Evaluation of the Performance and the Predictive Capacity of Build-up and Wash-off Models on Different Temporal Scales. Water 2016, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Ali, S.; Bonhomme, C.; Dubois, P.; Chebbo, G. Investigation of the Wash-off Process Using an Innovative Portable Rainfall Simulator Allowing Continuous Monitoring of Flow and Turbidity at the Urban Surface Outlet. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, H.K.; Hasenmueller, E.A. Transport of Road Salt Contamination in Karst Aquifers and Soils over Multiple Timescales. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Dai, M. Influence of Rainfall Characteristics on Pollutant Wash-off for Road Catchments in Urban Shanghai. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Modugno, M.; Gioia, A.; Gorgoglione, A.; Iacobellis, V.; la Forgia, G.; Piccinni, A.F.; Ranieri, E. Build-up/Wash-off Monitoring and Assessment for Sustainable Management of First Flush in an Urban Area. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5050–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, B.P.; Kerkez, B. Adaptive Measurements of Urban Runoff Quality. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 8986–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Qu, X.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Gui, C. Effect of Urban Stormwater Road Runoff of Different. Water 2019, 11, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Che, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y. Discussion about Initial Runoff and Volume Capture Ratio of Annual Rainfall. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, F.J.; Cochrane, T.A.; O’Sullivan, A.D. Untreated Runoff Quality from Roof and Road Surfaces in a Low Intensity Rainfall Climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beom, J.; Jeung, M.; Choi, W.; Her, Y.; Yoon, K. Characteristics of Chloride Loading from Urban and Agricultural Watersheds during Storm and Non-Storm Periods. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.T.; Edward Beighley, R.; VanHoven, D.; Watkins, K. Dynamic Stormwater Management to Mitigate Phosphorous Export. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Liu, J.; Aini, G.; Gong, Y. A Comparative Study of the Grain-Size Distribution of Surface Dust and Stormwater Runoff Quality on Typical Urban Roads and Roofs in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shen, Z.; Tian, T.; Liu, R.; Qiu, J. Temporal Variation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Stormwater Runoff. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2012, 6, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Luo, L.; Huang, G.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, F.; Xu, R.; Huang, X. Total Pollution Effect of Urban Surface Runoff. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Q.; Yin, C.Q.; He, Q.C.; Kong, L.L. First Flush of Storm Runoff Pollution from an Urban Catchment in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirpak, A.; Winston, R.J.; Feliciano, M.; Dorsey, J.D. Stormwater Quality Performance of Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavement Receiving Run-on from an Asphalt Traffic Lane in a Cold Climate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21716–21732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, D.; Aryal, R.; Hasan Johir, M.A.; Loganathan, P.; Bush, C.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Interrelationship among the Pollutants in Stormwater in an Urban Catchment and First Flush Identification Using UV Spectroscopy. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zou, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, X. Role of Low-Impact Development in Generation and Control of Urban Diffuse Pollution in a Pilot Sponge City: A Paired-Catchment Study. Water 2018, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nosrati, K. Identification of a Water Quality Indicator for Urban Roof Runoff. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L. Urban Stormwater Forecasting Model and Drainage Optimization Based on Water Environmental Capacity. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, P.; Wan, W.; Ren, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, L. The Temporal Changes in Road Stormwater Runoff Quality and the Implications to First Flush Control in Chongqing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9763–9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecco, I.; Palla, A.; Lanza, L.G.; La Barbera, P. The Role of Green Roofs as a Source/Sink of Pollutants in Storm Water Outflows. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4715–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shan, B.; Yin, C. Stormwater Runoff Pollution Loads from an Urban Catchment with Rainy Climate in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2012, 6, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Guo, B.; Hao, F.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Gong, Y. Modeling Urban Storm Rainfall Runoff from Diverse Underlying Surfaces and Application for Control Design in Beijing. J. Environ. Manage. 2012, 113, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowny, J.G.; Stewart, J.R. Characterization of Nonpoint Source Microbial Contamination in an Urbanizing Watershed Serving as a Municipal Water Supply. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6143–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hathaway, J.M.; Tucker, R.S.; Spooner, J.M.; Hunt, W.F. A Traditional Analysis of the First Flush Effect for Nutrients in Stormwater Runoff from Two Small Urban Catchments. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5903–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecco, I.; Berretta, C.; Lanza, L.G.; La Barbera, P. Storm Water Pollution in the Urban Environment of Genoa, Italy. Atmos. Res. 2005, 77, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.P.; Khu, S.T.; Yu, X.Y. Spatial Variations of Storm Runoff Pollution and Their Correlation with Land-Use in a Rapidly Urbanizing Catchment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4613–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Yur, J.; Kim, J. Diffuse Pollution Loading from Urban Stormwater Runoff in Daejeon City, Korea. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Maniquiz, M.C.; Gorme, J.B.; Kim, L.H. Determination of Cost-Effective First Flush Criteria for BMP Sizing. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 19, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Johnston, P.; Osei, K.; Gill, L. The Influence of Particle Size on the First Flush Strength of Urban Stormwater Runoff. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.; Koo, Y. Development of Integrated Management System (ISTORMS) for Efficient Operation of First Flush Treatment System for Urban Rivers. Water Pract. Technol. 2017, 12, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, K.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y. Mapping the Scientific Research on Non-Point Source Pollution: A Bibliometric Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4352–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule-Mercado, M.C.A.; Salim, I.; Lee, B.-Y.; Memon, S.; Sajjad, R.U.; Sukhbaatar, C.; Lee, C.-H. Monitoring and Quantification of Stormwater Runoff from Mixed Land Use and Land Cover Catchment in Response to Land Development. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

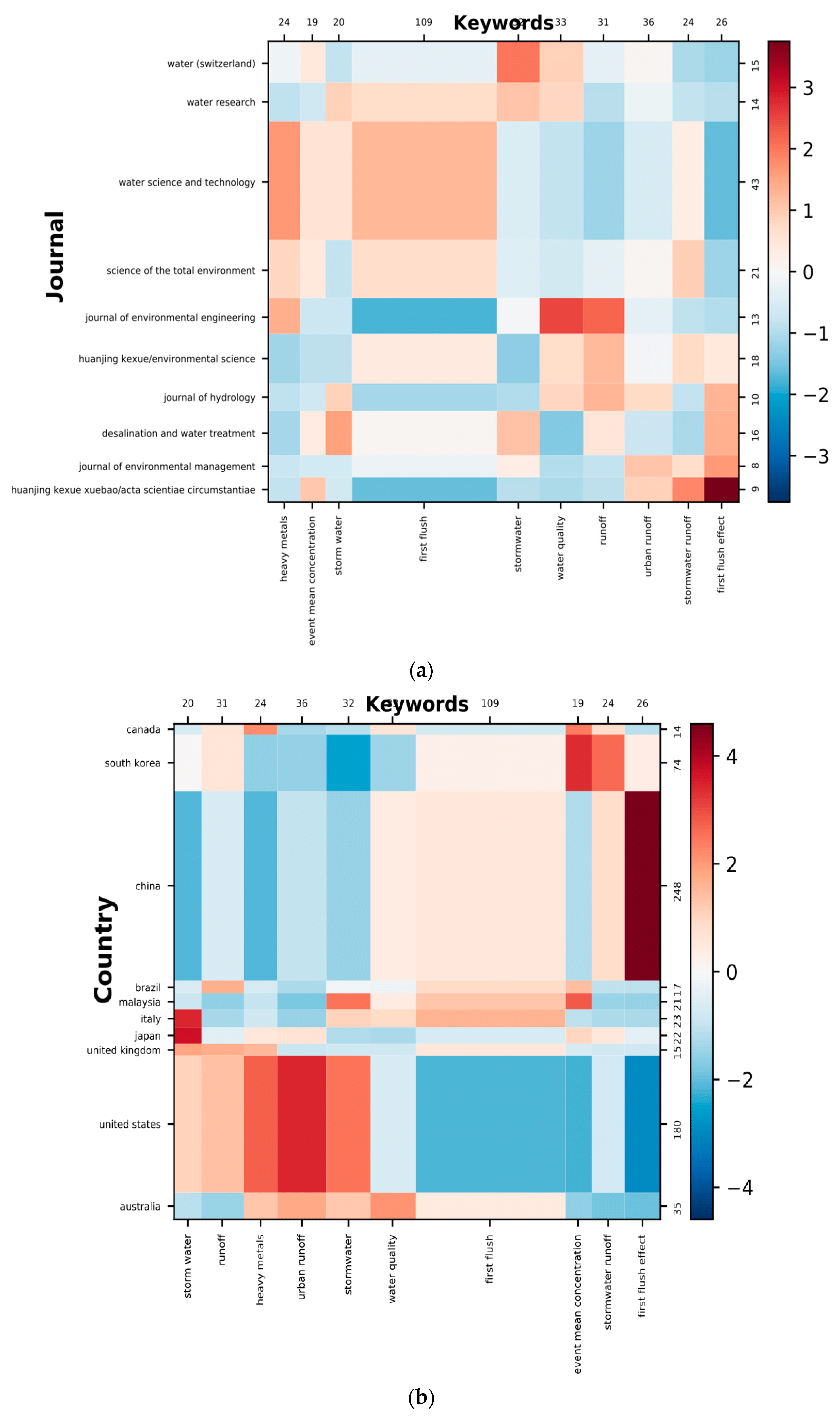

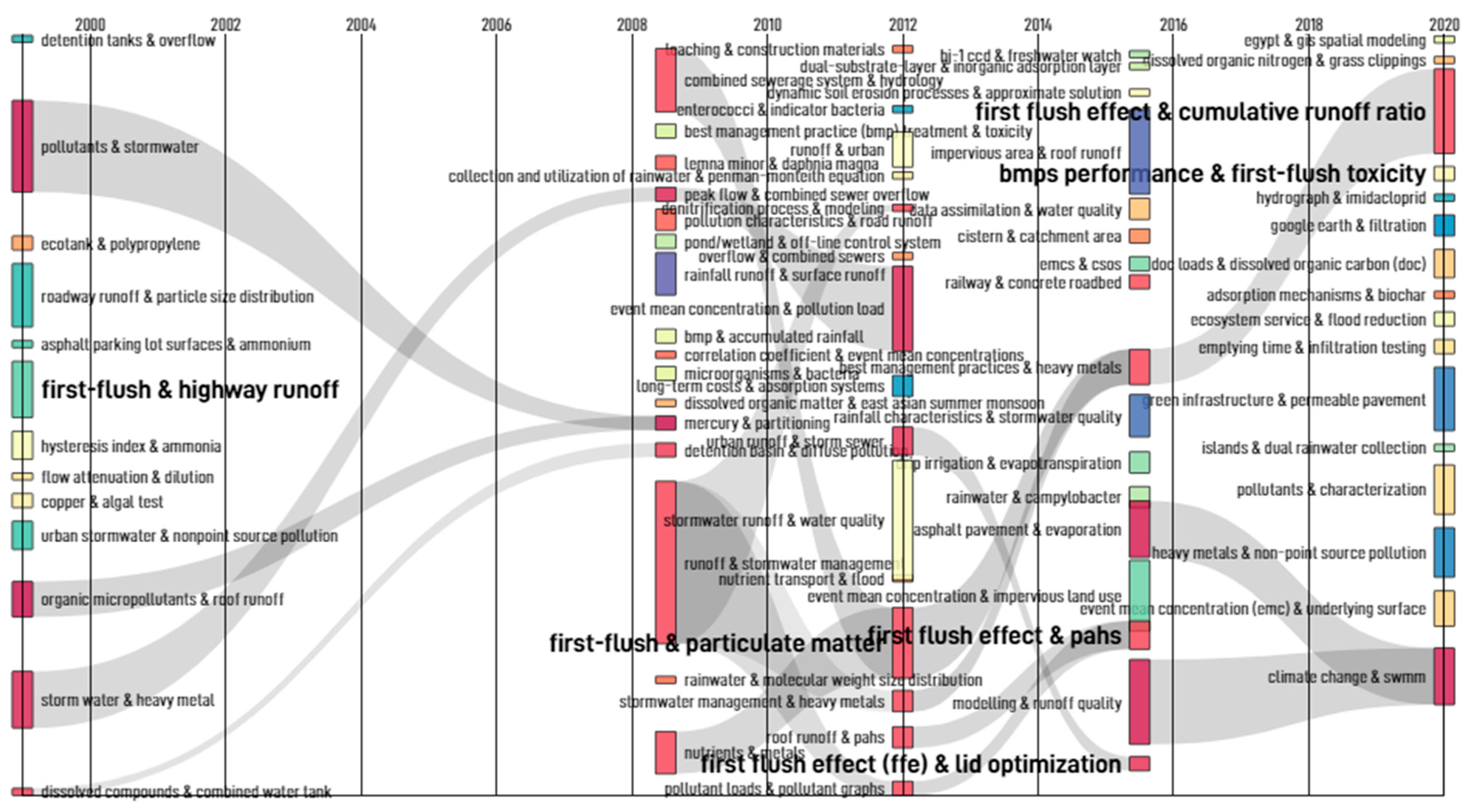
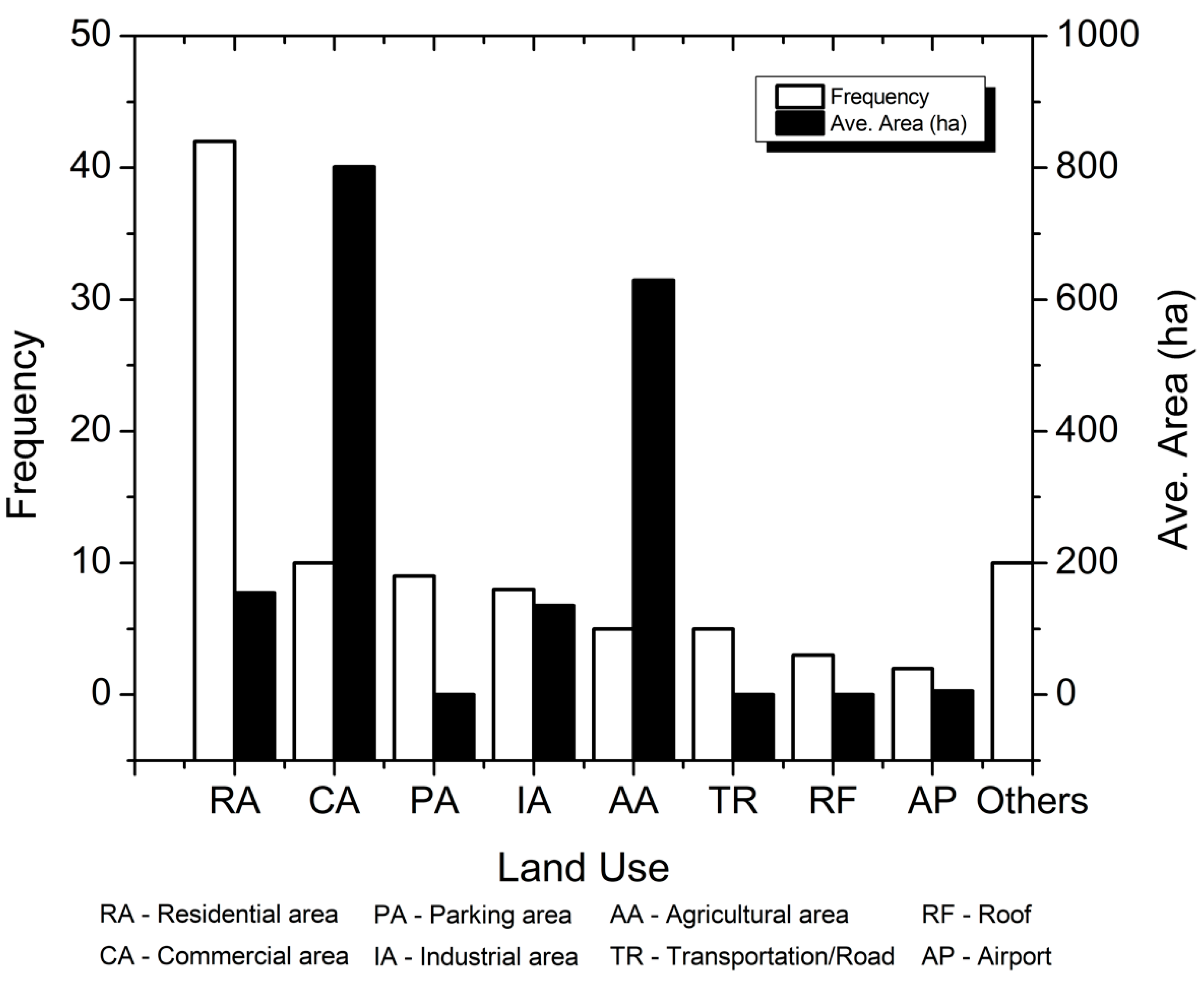
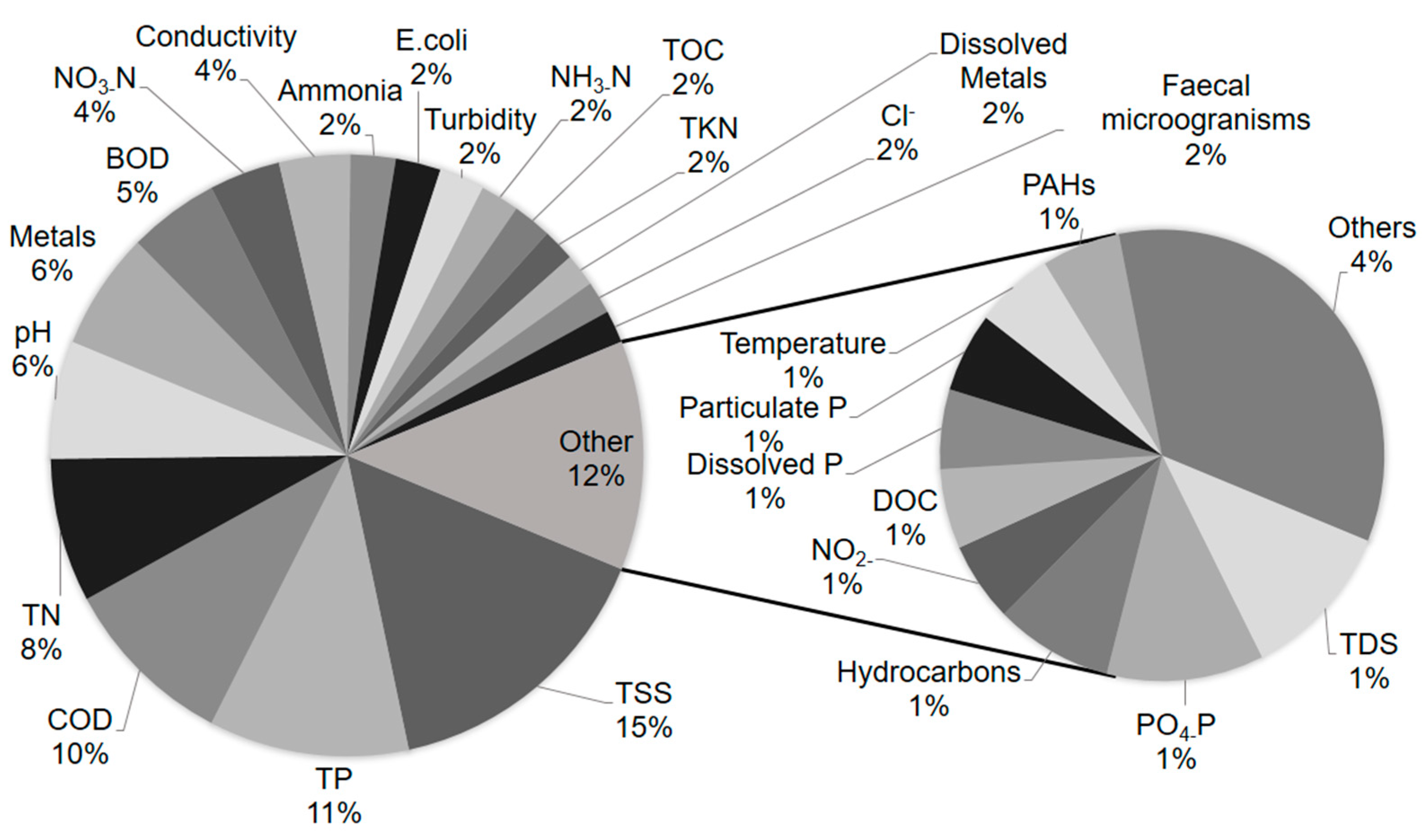
| Rank | Journal Name | Number of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water Science and Technology | 43 |
| 2 | Science of the Total Environment | 21 |
| 3 | Huanjin Kexue/Environmental Science | 18 |
| 4 | Desalination and Water Treatment | 16 |
| 5 | Water (Switzerland) | 15 |
| 6 | Water Research | 14 |
| 7 | Journal of Environmental Engineering | 13 |
| 8 | Journal of Hydrology | 10 |
| 9 | Huanjing Kexue/Acta Scientiae Circumstanciae | 9 |
| 10 | Journal of Environmental Management | 8 |
| 11 | Water Environment Research | 7 |
| 12 | Journal of Environmental Engineering (United States) | 6 |
| 13 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 6 |
| 14 | Chemosphere | 6 |
| 15 | Journal of Environmental Sciences | 6 |
| 16 | Water, Air, and Soil Pollution | 5 |
| 17 | Environmental Earth Sciences | 5 |
| 18 | Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry | 4 |
| 19 | Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering | 4 |
| 20 | Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering in China | 4 |
| 21–156 | Others | 136 |
| Number of Rainfall Events | Rainfall Depth (mm) | Mean Rainfall Intensity (mm/h) | Peak Rainfall Intensity (mm/h) | Rainfall Duration (h) | ADD (Days) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| na | 67 | 39 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 30 |
| Mean | 9.6 | 20.1 | 9.8 | 28.5 | 5.4 | 6.9 |
| Median | 6.0 | 14.2 | 5.9 | 13.2 | 3.8 | 4.8 |
| Minimum | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Maximum | 68 | 141 | 126 | 252 | 45.3 | 56 |
| Standard Deviation | 11.8 | 20.2 | 15.8 | 33.8 | 5.4 | 7.7 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| Skewness | 3.5 | 2.2 | 4.7 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| Country | Specified Land Use | Storm Event Duration (min) | Succeeding | Type of Sampling | Reference | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 90 | |||||
| China | Residential | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | - | - | x | Every 1 h | Grab | Xu et al., 2021 [45] |
| United States | Residential | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | Every 10 min | Automatic (ISCO (3700C) | Gustafson et al., 2021 [38] |
| Korea | Mixed | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | - | Every 6 h | Automatic (ISCO 570) | Beom et al., 2021 [57] |
| United States | Mostly residential | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Automatic (ISCO 6712FR) | Khan et al., 2021 [58] |
| China | Commercial | x | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | - | Grab | Chen et al., 2020 [2] |
| China | Residential | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | Every 10 min | Grab | Liu et al., 2019 [54] | |||||
| Australia | Urban | - | - | - | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | x | Every 30 min | Automatic (ISCO Avalanche) | Ekanayake et al., 2019 [64] |
| South Korea | Commercial | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | Every 1 to 2 h | Automatic (ISCO Portable Sampler 6712) | Jeung et al., 2019 [10] |
| China | Residential | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | - | - | x | - | - | - | x | - | - | >40 min: every 20 min | Grab | Zhao et al., 2018 [65] |
| Iran | Roof | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | - | >30 min: every 20 min | Not identified | Nosrati, K., 2017 [66] |
| China | Mostly residential | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | - | - | - | x | Every 30 min | Grab | Peng et al., 2016 [67] |
| China | Road; residential; roof | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | - | - | x | - | - | Every 30 min | Grab | Shen et al., 2016 [59] |
| China | Residential; commercial | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | x | - | x | - | >2 h: every 1 h | Automatic | Zhang et al., 2013 [68] |
| Italy | Green roof | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | Maximum of 120 samples | Grab | Gnecco et al., 2013 [69] |
| China | Parking lot; road; roof | x a | x a | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | Every 15 min | Grab | Li et al., 2012 [60] |
| China | Urban | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | Every 15 min | Grab | Li, Shan and Yin, 2012 [70] |
| China | Cement roof; asphalt road; parking area; grassland | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | Grab | Ouyang et al., 2012 [71] |
| United States | Multiple | x b | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 sample between hours 2 and 4; 1 sample between hours 5 and 12; 1 sample between hours 12 and 36 | Grab | Rowny & Stewart, 2012 [72] |
| China | Multiple | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | >3 h: every 1 h | Grab | Luo et al., 2009 [61] |
| China | Urban | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | - | x | Every 10 min | Grab | Li et al., 2007 [62] |
| Title | Authors List | Country | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stormwater quality performance of permeable interlocking concrete pavement receiving run-on from an asphalt traffic lane in a cold climate | Tirpak et al., 2020 [63] | United States | Environmental Science and Pollution Research |
| Quantifying the Effects of Residential Infill Redevelopment on Urban Stormwater Quality in Denver, Colorado | Gustafson et al., 2021 [38] | United States | Water |
| Dynamic stormwater management to mitigate phosphorous export | Khan et al., 2021 [58] | United States | Science of the Total Environment |
| Sustainable Urban Drainage Designing Approach for São Paulo and Humid Sub-tropical Climates | Castañer et al., 2020 [17] | Brazil | Springer Geography |
| Role of Low-Impact Development in Generation and Control of Urban Diffuse Pollution in a Pilot Sponge City: A Paired-Catchment Study | Zhao et al., 2018 [65] | China | Water |
| Development of integrated management system (ISTORMS) for efficient operation of first flush treatment system for urban rivers | Seo et al., 2017 [79] | Korea | Water Practice & Technology |
| The influence of particle size on the first flush strength of urban stormwater runoff | Morgan et al., 2017 [78] | Ireland | Water Science & Technology |
| A comparative study of the grain-size distribution of surface dust and stormwater runoff quality on typical urban roads and roofs in Beijing, China | Shen et al., 2016 [59] | China | Environmental Science and Pollution Research |
| Optimizing low impact development (LID) for stormwater runoff treatment in urban area, Korea: Experimental and modeling approach | Baek et al., 2015 [16] | Korea | Water Research |
| Determination of cost-effective first flush criteria for BMP sizing | Lee et al., 2010 [77] | Korea | Desalination and Water Treatment |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniquiz-Redillas, M.; Robles, M.E.; Cruz, G.; Reyes, N.J.; Kim, L.-H. First Flush Stormwater Runoff in Urban Catchments: A Bibliometric and Comprehensive Review. Hydrology 2022, 9, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9040063
Maniquiz-Redillas M, Robles ME, Cruz G, Reyes NJ, Kim L-H. First Flush Stormwater Runoff in Urban Catchments: A Bibliometric and Comprehensive Review. Hydrology. 2022; 9(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiquiz-Redillas, Marla, Miguel Enrico Robles, Gil Cruz, Nash Jett Reyes, and Lee-Hyung Kim. 2022. "First Flush Stormwater Runoff in Urban Catchments: A Bibliometric and Comprehensive Review" Hydrology 9, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9040063
APA StyleManiquiz-Redillas, M., Robles, M. E., Cruz, G., Reyes, N. J., & Kim, L.-H. (2022). First Flush Stormwater Runoff in Urban Catchments: A Bibliometric and Comprehensive Review. Hydrology, 9(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9040063







