Abstract
Isotope data and major ion chemistry were used to identify aquifer recharge mechanisms and geochemical evolution of groundwaters along the US–Mexico border. Local recharge originates as precipitation and occurs during winter through preferential infiltration pathways along the base of the Gila Range. This groundwater is dominated by Na–Cl of meteoric origin and is highly concentrated due to the dissolution of soluble salts accumulated in the near-surface. The hydrochemical evolution of waters in the irrigated floodplain is controlled by Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl-type Colorado River water. However, salinity is increased through evapotranspiration, precipitation of calcite, dissolution of accumulated soil salts, de-dolomitization, and exchange of aqueous Ca2+ for adsorbed Na+. The Na–Cl-dominated local recharge flows southwest from the Gila Range and mixes with the Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl-dominated floodplain waters beneath the Yuma and San Luis Mesas. Low 3H suggests that recharge within the Yuma and San Luis Mesas occurred at least before the 1950s, and 14C data are consistent with bulk residence times up to 11,500 uncorrected 14C years before present. Either the flow system is not actively recharged, or recharge occurs at a significantly lower rate than what is being withdrawn, leading to aquifer overdraft and deterioration.
1. Introduction
The Colorado River is strictly managed. Water regulatory practices are implemented to provide vital water resources to seven states in the USA and two states in Mexico (Figure 1). In the Lower Colorado River Basin, south of the Utah–Arizona border, more than 27 million people depend on the river for sustenance. Nearly 1.2 million ha of farmland are irrigated with Colorado River water in the fertile and productive fields of the Mexicali and Imperial Valleys [1].
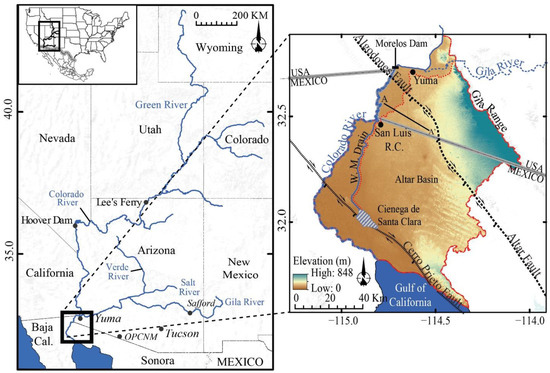
Figure 1.
Colorado River Basin (left). Study area: lower Colorado River, Colorado River Delta and major geographical and geological features (right). The red-dotted line shows the limit of the Yuma and San Luis Mesas. The Wellton-Mohawk Drain (WM Drain) is shown as a solid blue line. OPCNM: Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument. Cross-section A-A’ shown as a supplementary file (Figure S1).
The lower Colorado River basin has seen extensive land-use changes in the last century. Pastures and crops have replaced native vegetation, and surface Colorado River water has been diverted for irrigation. These changes led to a massive loss of natural habitat in the Colorado River Delta (termed “Delta” below). The river no longer reaches the lower part of the Delta today, and riparian, wetland, and estuarine habitats occupy less than 5% of their original 780,000 ha extent [2].
This study aims to establish sources of solutes, sources of aquifer recharge, groundwater residence time, and geographic variation of major ion chemistry in groundwater on the eastern flank of the Colorado River Delta. This is accomplished using environmental isotope data (δ18O, δ2H, 3H, and 14C) and major ion chemistry. In the over-allocated Colorado River system, distinguishing the different sources of water and salt becomes increasingly important for the long-term management and protection of water resources and the natural and seminatural habitats that depend on them.
The results of this investigation are used to evaluate the groundwater dynamics and geochemical process of this transboundary aquifer along the US–Mexico border between the states of Arizona and Sonora. Understanding groundwater flow and its chemical evolution are vital for the effective management and use of groundwater resources in this aquifer vulnerable to overdraft and salinization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geography
The Colorado River Delta lies along the western boundary of the Sonoran Desert and within the Salton Trough geologic region. The Delta extends from the confluence of the Colorado and Gila River near Yuma, Arizona, to the Gulf of California and covers an area of more than 600 km2 (Figure 1; [3]). The lower Colorado River marks the western boundary of this study. The Gran Desierto de Altar is located to the east of the study area and covers an area of 5500 km2 [4]. The Gila River historically flowed around the Gila Range, an arid and rugged, northwest-southeast trending range with its highest elevation at ~960 m above sea level (masl; Figure 1), before joining the Colorado River. Today, the Gila River rarely reaches the area under normal conditions.
2.1.2. Climate
Climate is warm and arid in the area. Records from 1951 to 2010 at Morelos Dam in Baja, California, show maximum temperatures reach 50 °C [5]. Annual evaporation rates range between 1.9 and 3.4 m, evapotranspiration is approximately 1.40 m, and annual precipitation averages only 63 mm [5]. Precipitation occurs as sporadic events during winter and summer seasons as cyclonic and convective events, respectively [6].
2.1.3. Geology
A detailed geological description of the area is provided by [7,8,9,10,11]. In general, the San Luis, Mexicali, and Yuma valleys are part of a graben with an average thickness of 4150 m. The basement consists of igneous and metamorphic rocks of Cretaceous age [7,10]. The valley-fill contains marine sediments deposited during transgressions of the Gulf of California during the Pliocene and Quaternary sedimentary deposits of continental origin [8,11]. Sediment exposed at the surface is of alluvial type (conglomerates, sand, silt, and clays) and represents the most recent deposition cycle from the Colorado River and the Gila River [11]. The study area is bounded by extensive eolian deposits of Pleistocene age to the southeast and igneous and metamorphic rocks of Cretaceous age to the northeast (Gila Range).
An escarpment marks the western boundary of the Altar Basin against the Delta. Two faults pass through the study area. The Cerro Prieto fault, which passes southeast into the Gulf of California, is the active southernmost segment of the San Andreas fault system and has strike-slip movement as high as 60 mm/year [12,13]. The Altar fault is an inactive strike-slip fault, running parallel to the Cerro Prieto fault. Both faults dip to the west, have dextral offset and displace the southwestern side downwards.
2.1.4. Colorado and Gila River Discharge
Before developing major river engineering projects (the 1930s–1960s), such as Hoover Dam and Glen Canyon Dam, the Colorado River flowed along its natural course and discharged into the Gulf of California. Natural annual flows ranged between 1.6 × 1010 m3 and 1.8 × 1010 m3 at Lee’s Ferry [14]. Peak flows occurred from April to June when late-spring snowmelt from higher elevations entered the area (Figure 2). The Gila River contributed an estimated 0.16 × 1010 m3 per year to Colorado River discharge at its confluence near Yuma before upstream diversions dewatered the river [15]. Construction of dams along the Colorado River, particularly the Hoover Dam in 1936, has increased the evaporation of river water and greatly influenced δ18O and δ2H in surface water below Hoover Dam. Pre-dam and post-dam river water are, consequently, distinctive in isotope composition [16].
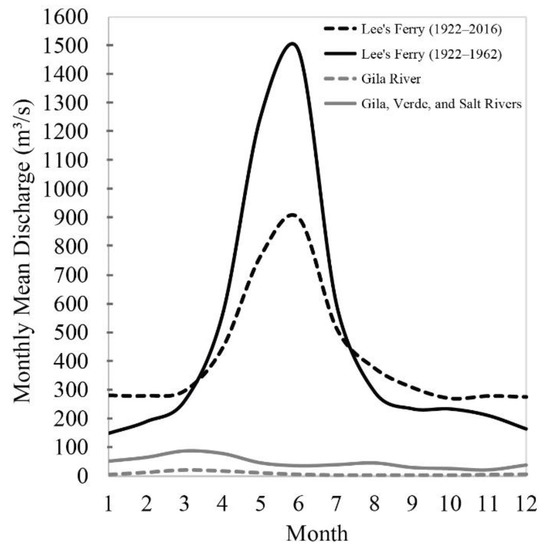
Figure 2.
Monthly mean discharge in m3/s for Colorado River at Lee’s Ferry (USGS Station 09380000), and Gila River as combining the Gila (USGS Station 09474000), Verde (USGS Station 09510000) and Salt River (USGS Station 09497500). All data are available online from [17].
The entire flow of the Colorado River is now captured and used before reaching the river’s mouth. South of the USA–Mexico border, no water flows, except during unusually wet years and engineered environmental flows resulting from water treaties between the USA and Mexico [18,19]. Climatic anomalies arise from El Niño Southern Oscillation and affect the entire Colorado River catchment. When upstream storage reservoirs are full, high precipitation during El Niño years can increase river discharge. This was observed at the USA–Mexico border, where daily discharges peaked at 935 m3/s during the mid-1980s [3].
2.1.5. Hydrogeology
Water-bearing units in the area are described in great detail by [9,10]. These are divided based on age: Tertiary rocks with poor transmissive properties and Pliocene to Holocene deposits yield a significant amount of water. For this study, we focus on the upper ~300 m of the younger water-bearing sediments where most of the production wells in the study area are found. This part of the aquifer is formed by the upper fine-and medium-grained sediment of the younger alluvium [9,20,21].
Direct infiltration from the Colorado River and overbank flooding were the main source of recharge to the aquifer before major agricultural development [10,22]. Today, the aquifer has an annual recharge of 755 × 106 m3 by infiltration from unlined irrigation canals supplied with Colorado River water and groundwater from the Colorado River Basin upstream of Yuma, Arizona [7,23]. Pre-development, regional groundwater flowed in a northeast-southwest direction from the junction of the Colorado River and Gila River near Yuma, Arizona, to the northern Gulf of California (Figure 3A; [21]).
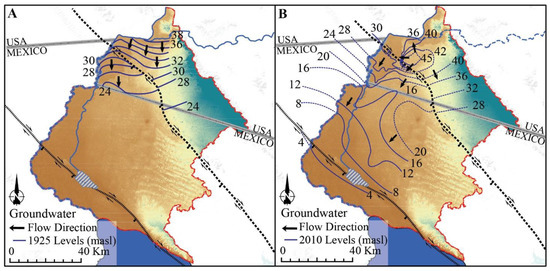
Figure 3.
(A) Groundwater levels in 1925. (B) Groundwater levels in 2010. Contours represent water table elevation in meters above sea level. Based on data from [9,11,25].
Unlined canals and groundwater pumping have disturbed the source and sink patterns of water movement to and from the aquifer within the Delta [10]. Groundwater flow direction has remained constant, but in areas where long-term surface irrigation has occurred (e.g., Yuma Valley), groundwater levels are higher now than during pre-development time (Figure 3B). Several reaches along the river now act as drains for groundwater where groundwater levels are high, but less than 3.5 × 107 m3 (4.6%) of the yearly Colorado River flow discharges as groundwater into the Gulf of California [11,24].
2.1.6. Ciénega de Santa Clara
The Ciénega de Santa Clara (Ciénega) is a brackish wetland along an old course of the Colorado River in Mexico. The Ciénega lies along a shallow depression on the eastern edge of the Delta and covers an area of 6000 ha dominated by Typha dominguensis (Figure 1; [26]). It is an “off-channel” wetland; its water does not come directly from the Colorado River. The most important source of water for the Ciénega is brackish groundwater (TDS > 2.6 ppt) derived from the Wellton-Mohawk Irrigation Drainage District of Arizona (irrigated with Colorado River water). Excess agricultural runoff is transported to the Ciénega by a concrete-lined canal, the Wellton-Mohawk Drain, which delivers 1.3 × 108 m3/y. The Riito Drain (Figure 4), which transports wastewater from Mexican agriculture, supplies approximately 1.4 × 107 m3 to the Ciénega [27].
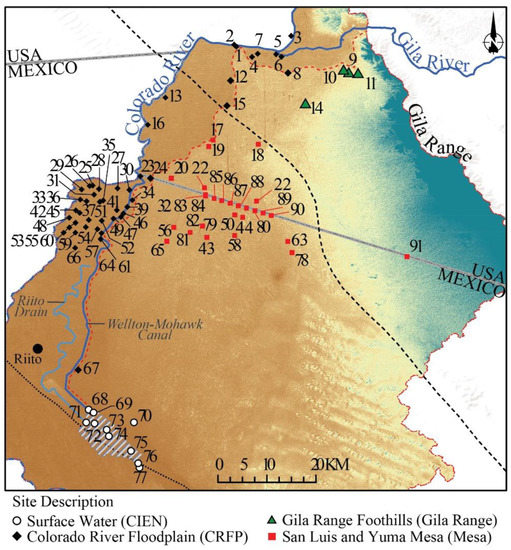
Figure 4.
Location of sampling sites in the study area. Symbols for adjacent locations overlap in some cases. The red-dotted line shows the western limit of the San Luis and Yuma Mesas.
2.2. Field Methods
Surface water samples were collected from the Ciénega, Wellton-Mohawk Drain, and Colorado River at Yuma, Arizona during May 2013, October 2013, and July 2014 (Figure 4). These surface water samples were used to establish the evaporation trend of Colorado River water. Groundwater samples were collected from the Minute 242 well field along the Arizona–Sonora border in October 2016. These groundwater samples were used to evaluate potential water sources besides Colorado River water. Additionally, two bulk sediment samples from the San Luis Mesa were analyzed for δ13CCaCO3 to correct 14C ages.
Temperature, pH, dissolved O2, and electrical conductivity (EC) levels were measured in the field after each parameter had stabilized. Samples for oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon (DIC) stable isotopes were filtered with a 0.45 μm nylon filter and kept in capped glass vials with no headspace. Unfiltered water samples were collected for 3H and 14C analysis in rinsed 1-L HDPE and amber borosilicate glass bottles, respectively. Samples for ions and alkalinity were filtered with a 0.45 μm nylon filter and kept in HDPE bottles. Cation samples were preserved with concentrated, optima grade HNO3. All samples were kept on ice while in the field and then refrigerated at 4 °C before analysis. Alkalinity was determined by the Gran alkalinity titration method [28] within 12 h of collection. This is expressed as HCO3−, assuming dominance of this anion at the observed pH values and consistent with units used in previous studies.
2.3. Laboratory Methods
Values of δ18O and δ2H were measured at the Environmental Isotope Laboratory, Department of Geosciences, University of Arizona, using a Finnigan Delta-S mass spectrometer with automated CO2 equilibration and Cr-reduction attachments. Analytical precisions (1σ) for these techniques are 0.08% for δ18O and 0.9% for δ2H. δ18O and δ2H data are reported in delta notation:
where R is the ratio of the heavier over, the lighter isotope in the sample, and Rstd is the isotope ratio of Vienna standard mean ocean water (VSMOW).
δ = (R/Rstd − 1) × 1000 (‰)
δ13CDIC values were measured on a ThermoQuest Finnigan Delta Plus XL continuous-flow gas-ratio mass spectrometer coupled with a Gasbench automated sampler. Samples were reacted for >1 h with phosphoric acid at room temperature in Exetainer vials previously flushed with He gas. Standardization was based on NBS-19 and NBS-18, and precision was ± 0.30‰ or better (1σ). All δ13C values were expressed in delta notation relative to the Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite (VPDB) standard.
Tritium values were measured by liquid scintillation counting on electrolytically enriched water in a Quantulus 1220 spectrophotometer with a detection limit of 0.7 tritium units (TU) for 8-fold enrichment and 1500 min of counting. Carbon-14 was measured as liberated CO2 reduced to graphite at the NSF-Arizona Accelerator facility. These results are reported as percent modern carbon (pMC) relative to NBS standards oxalic acid I and II.
Anion concentrations were determined in the Department of Hydrology and Atmospheric Sciences at the University of Arizona using a Dionex ion chromatograph model 3000 with an AS23 analytical column (precision ± 2%). The analyses for cations were performed by the Arizona Laboratory for emerging contaminants (ALEC) at the University of Arizona using a PerkinElmer Elan-II inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometer (precision ± 2%).
2.4. Data
The final dataset for this study (Table S1) contains published and unpublished results for water samples from agricultural wells in the San Luis Valley [29,30], Yuma and San Luis Mesa [10,17,30], and the lower Colorado River floodplain [7,31]. The saturation indices of water samples were calculated using the hydrogeochemical equilibrium model of PHREEQC [32].
Average δ18O, δ2H, and solute chemistry values for the different potential water sources in the area were determined from other existing databases or publications and are used for comparison with individual values in the study area (Table 1; Figure 5). These endmembers include pre-dam Colorado River water (water recharging before Hoover Dam completion in 1936), post-dam Colorado River water (evaporated, while stored in upstream reservoirs), agricultural discharge, and Gila River. Pre-dam Colorado River water ion concentration and δ18O and δ2H values were approximated using data from USGS station 9380000 at Lee’s Ferry [17]. This station was used because it is located upstream from Lake Mead, where enrichment by evaporation occurs. Colorado River water near Lee’s Ferry is assumed to represent water reaching the Delta before major development along the lower Colorado River. For post-dam Colorado River water δ18O, δ2H, and ion values were calculated using data from USGS station 9522000 at Morelos Dam [17].

Table 1.
Average composition of waters in the study area.
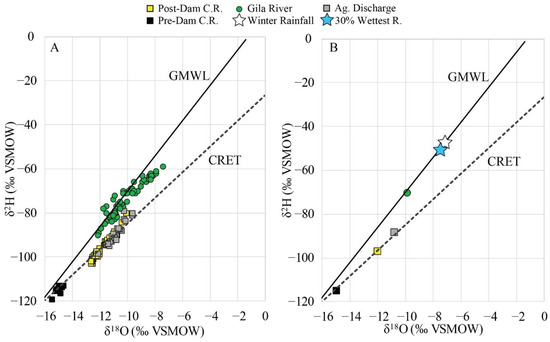
Figure 5.
(A) δ18O and δ2H values for the water endmembers in the area [17,33,34] compared to the Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL; [35]), and the Colorado River evaporation trend (CRET, dashed line). (B) Average values for each endmember. This figure also includes winter rainfall and the largest 30% of precipitation events at Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument [30].
For agricultural discharge, δ18O, δ2H, and ion values were calculated using data from USGS station 9529300 at the Wellton-Mohawk Drain [17] and [7,33]. Values of δ18O and δ2H, and ion concentrations in the upper Gila River, near Safford, Arizona (Figure 1) were calculated using well data from [34].
Multiyear rainfall isotope data collected at Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument (OPCNM; Figure 1) in Arizona were used to estimate long-term δ18O and δ2H values of winter precipitation representing local recharge in the area [30]. OPCNM is located 175 km east of the study area at an elevation of 515 masl, which is similar to the average elevations in the Gila Range.
Individual and mean δ18O and δ2H values for the different endmembers are shown in Figure 5A,B. For rainwater, the means are weighted for precipitation amount.
Evaporated Colorado River Water
The (δ18O, δ2H) values of Colorado River water at different degrees of evaporation were modeled using a method described by [36]. Average pre-dam Colorado River water is used as a starting point (δ18O = −15‰ and δ2H = −115‰). A displacement of data to the right of the GMWL reflects evaporative loss. Average humidity is assumed to be 60% to obtain an evaporation slope between 5 and 6, which is characteristic of evaporated Colorado River water in the area [16,37]. This evaporation trend is referred to as the Colorado River evaporation trend (CRET) in several isotope plots (e.g., Figure 5). Equilibrium (α) and kinetic fractionation (ΔƐ) factors for 18O and 2H are calculated using the following equations [38,39]:
103lnα18Ol−v = 1.137 × (106/T2) − 0.4156 × (103/T) − 2.0667
103lnα2Hl−v = 24.844 × (106/T2) − 76.248 × (103/T) − 52.612
ΔƐ18Ol−v = 14.2 × (1 − h)
ΔƐ2Hl−v = 12.5 × (1 − h)
In Equations (1) and (2), T is the mean annual temperature (K), and α is the fractionation factor. A temperature of 298 Kelvin is assumed for calculation purposes. This temperature is nearly identical to the average temperature at Yuma, Arizona (296 K; [40]). In Equations (3) and (4), h is the relative humidity (0.60).
The enrichment factor ε is calculated using Equation (5):
Ɛ18Ol−v = [α − 1] × 103
The evaporative enrichment for δ18O and δ2H values can be modeled, according to a Rayleigh distillation, by assuming different residual water fractions (f) in the following Equation (6):
Ɛ18Ototal × ln(f) = evaporative enrichment
Ɛ18Ototal is the overall enrichment for 18O in this case. The overall enrichment for evaporation under the specified conditions is +15.06‰ for 18O and +84.51‰ for 2H. The result of Equation (6) is added to the average (δ18O, δ2H) values of pre-dam Colorado River water to model the evolution of Colorado River water under different degrees of evaporation (Figure 6).
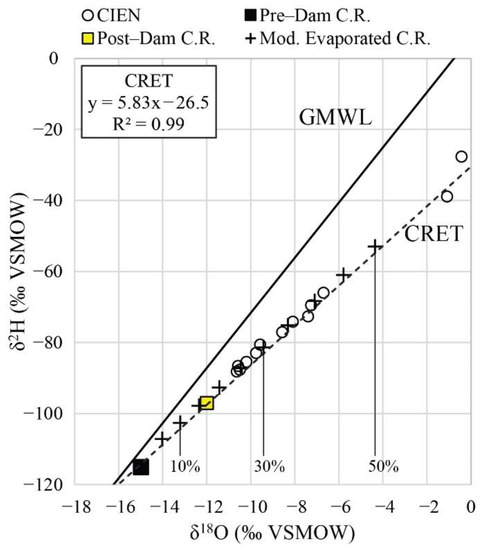
Figure 6.
δ2H vs. δ18O showing modeled evolution of Colorado River water evaporating under 60% relative humidity (mod. evaporated Colorado River). Also shown: data for surface water from the Ciénega (labeled CIEN), average pre-dam Colorado River water, average post-dam Colorado River water, the GMWL, and the CRET. Percentages indicate the degree of evaporation relative to pre-dam river water.
3. Results
3.1. Major Ion Trends
The distribution of predominant anions and cations shows that surface Colorado River water evolves from a Ca–HCO3-dominated water type in its headwaters into Na–Ca–Cl-SO4-dominated waters as it travels downstream and reaches the international border with Mexico (Figure 7A). Groundwater samples from the Colorado River floodplain consist of mixed Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl water types. Samples belonging to the Yuma and San Luis Mesas and Gila Range foothills groups show Na+ and Cl− as the predominant ions (Na–Cl-type; Figure 7B).
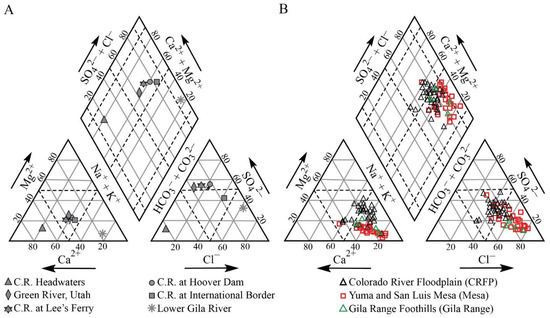
Figure 7.
(A) Piper diagram showing data for surface waters in the Colorado River Basin including data for headwaters (USGS Station 09196500), Green River, Utah (USGS Station 09315000), Lee’s Ferry (USGS Station 09380000), Hoover Dam (USGS Station 09421500), US–Mexico border (USGS Station 09522000), and Gila River near Dome, Arizona (USGS Station 09520500). All USGS data are available online from [17]. (B) Piper diagram showing data for groundwaters in the study area, including Colorado River Floodplain, Yuma and San Luis Mesas, and Gila Range.
All groundwater samples in the floodplain, Yuma and San Luis Mesas, and Gila Range foothills are undersaturated concerning halite, gypsum, and anhydrite (SI < 0). This allows Na+, Cl−, Ca2+, and SO42− concentrations to increase along the flow paths. Most of the groundwater samples are supersaturated or close to saturation concerning dolomite, calcite, or both (SI between −1 and 1), indicating a strong presence of these two minerals in the aquifer system.
3.2. Stable Isotopes
3.2.1. Endmembers and Evaporation Calculation
Endmember isotope compositions were calculated as means of the data shown in Figure 5A. Pre-dam Colorado River water (δ18O, δ2H) values are −15‰ and −115‰, post-dam Colorado River water values are −12‰, and −97‰, agricultural discharge values are −10.8‰ and −89‰, and Gila River water values are −9.9‰ and −71‰ (Table 1; Figure 5B). Rainfall isotope data (δ18O, δ2H) yielded average values of −7.2‰ and −47‰ for winter, and −7.5‰ and −50‰ for the 30% wettest events (Table 1; Figure 5B). Although the study area is close to the coast, seawater from the Gulf of California (Figure 8) is not required as an endmember for the present dataset.
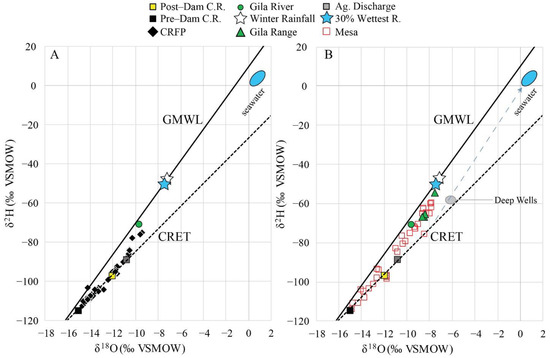
Figure 8.
(A) δ18O and δ2H values of surface water and groundwater from the Colorado River floodplain (CRFP). (B) δ18O and δ2H values of waters from the San Luis and Yuma Mesas, Gila Range relative to the GMWL and the CRET. Deep well data from [41]. Dashed gray line shows hypothetical mixing between seawater in the Gulf of California [42] and evaporated Colorado River water.
Surface water samples from the Ciénega (labeled CIEN in Figure 6) have δ18O values between −10.6‰ and +6.0‰, and δ2H values between −88‰ and +8‰. The highest δ18O and δ2H values are located in the southern part of the Ciénega near the tidal flats (sites 76 and 77). All water samples fall to the right of the GMWL (Figure 6). Some of the samples in the Ciénega have lost more than 50% of volume by evaporation relative to the pre-dam Colorado River endmember (Figure 6).
3.2.2. Surface and Groundwater Data
Stable isotope data for the study area are shown in Figure 8A,B. The (δ18O, δ2H) values of Colorado River collected at Yuma, Arizona were −11.8‰ and −95‰, respectively (Table S1). Wellton-Mohawk Drain discharge (WMD) had (δ18O, δ2H) values of −10.6‰ and −87‰. Groundwater samples from wells in the Colorado River floodplain (CRFP), on both sides of the border, have δ18O values between −9.4‰ and −14.7‰, and δ2H values between −75‰ and −112‰, and plot mainly on the CRET. Groundwater samples from wells in the Yuma and San Luis Mesas (Mesa) have δ18O values between −7.9‰ and −14.9‰, and δ2H values between −60‰ and −114‰. These fall mainly along a linear mixing trend between the pre-dam Colorado River and local winter precipitation endmembers.
Groundwater samples from four wells near the Gila Range have δ18O values between −7.6‰ and −8.7‰, and δ2H values between −55‰ and −67‰.
3.2.3. H and 14C
Tritium and 14C activities for Colorado River water at Yuma were ~5 TU in 2017 and ~101 pMC in 2009, respectively (Table S1; [43]). However, values for 3H and 14C were higher during the previous decades when more bomb-pulse 3H and 14C were present in the atmosphere [44]. Colorado River water measured near the USA–Mexico border contained 716 TU in 1967 and 12–17 TU between 1993 and 1998 [16]. Post-bomb-pulse precipitation in the Kofa Mountains, 90 km northeast of Yuma, averaged 3.4 TU in 2008–2009 [44]. Colorado River floodplain groundwater samples range between 5 and 16 TU, and San Luis Mesa samples range between <0.1 and 15 TU. The high values, 10–16 TU, all occur close to the Colorado River (Figure 9); they cannot be explained by the recharge of river water since 1993 but must include some recharge from the bomb pulse. With one exception, tritium is below detection level in groundwater from the San Luis and Yuma Mesas, indicating pre-bomb recharge.
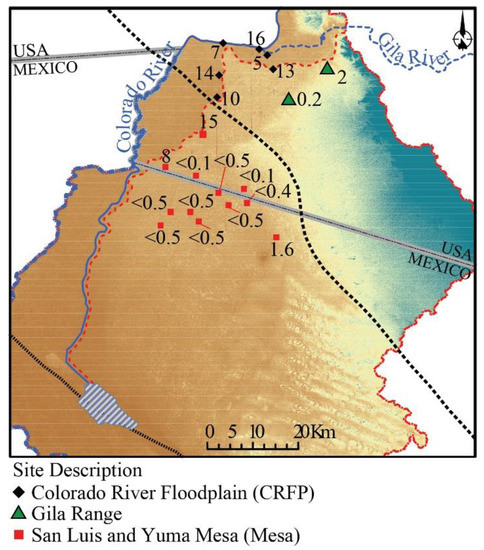
Figure 9.
Tritium (TU) data for groundwater samples. Shading indicates topography (see Figure 1). The red-dotted line indicates the extent of the San Luis and Yuma Mesa.
Three 14C measurements from the San Luis Mesa have 59, 29, and 26 pMC, corresponding to uncorrected 14C ages between 4800 and 11,500 14C years before present.
Most Colorado River floodplain groundwater samples consist of mixed Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl, but a few samples fall exclusively within Na–Cl facies. The opposite is true for the Yuma and San Luis Mesas and Gila Range foothills where groundwater samples are Na–Cl-dominated, but a few samples fall within the Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl mix (Figure 7B). The influence of SO42−-rich Colorado River water in the floodplain is evident in Figure 10. While most of the groundwaters in the floodplain have SO42− values >200 mg/L, those in the Mesa and Gila Range foothills have SO42− values <200 mg/L.
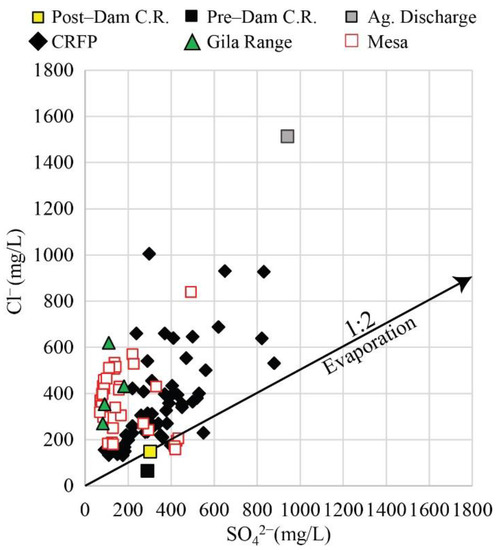
Figure 10.
Cross-plot of Cl− and SO42− concentrations (mg/L) for surface and groundwater in the study area. Arrow indicates hypothetical evaporation trajectory for Cl−/SO42− = 1:2.
4. Discussion
4.1. General Patterns
Colorado River headwaters are initially Ca–HCO3-dominated due to the dissolution of silicate and carbonate minerals. These waters evolve into Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl type in the upper Colorado River in part due to the interaction with the local geology, anthropogenic activities (e.g., mining and farming), and evaporative concentration where extensive irrigation of land occurs (Figure 7A). Salts (halite and gypsum) dissolved from the Eagle Valley Evaporite, Paradox Formation, Mancos Shale, Chinle Formation, and their associated soils account for approximately half of the total solutes in this part of the river [45,46].
Agriculture dominates the floodplain in the lower Colorado River area. Here, the proportion of Cl− and Na+ in Colorado River water increases due to irrigation return flows, marine salt input, and/or halite evaporites in the lower Colorado River basin. Evaporation at Lake Mead and mixing with return flow is evident from Figure 5A, where post-dam Colorado River waters plot to the right of the GMWL and overlap agricultural discharge in some cases. Nearly 30% of the total river surface discharge has been lost to evapotranspiration when Colorado River water enters Morelos Dam, as suggested by the (δ18O, δ2H) values of post-dam Colorado River water (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
Evaporated Colorado River water would fall along the 1:2 line in Figure 10, representing the Cl/SO4 mass ratio in post-dam Colorado River water. There is an excess of Cl−, relative to SO42−, in virtually every water sample plotted. Bacterial SO42− reduction could drive water samples to plot to the left of the evaporation line, creating an excess of Cl−. However, SO42− concentrations are relatively high, oxic conditions prevail in the unconfined aquifer, and SO42− reduction has only been noted in a few wells within the floodplain where organic matter is more readily available [9]. Thus, evaporation by itself does not explain the observed relationship between Cl− and SO42−, and there are additional sources of Cl−. These additional sources of Cl− result in a wide range of Cl− concentrations, which tend to be lower near the Colorado River floodplain than in the Mesa (Figure 11A).
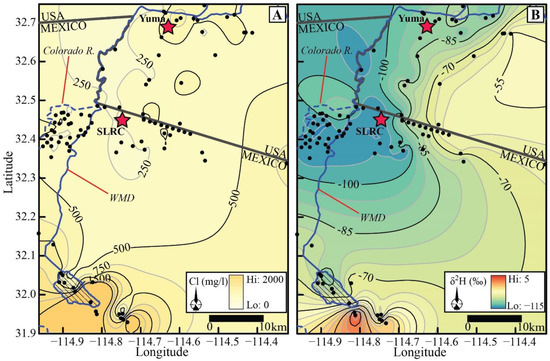
Figure 11.
(A). Contour map showing spatial patterns for Cl−. (B) Contour map showing spatial patterns for δ2H. Black-filled circles represent control points. SLRC: San Luis Rio Colorado, Mexico. WMD: Wellton-Mohawk Drain.
The (δ18O, δ2H) values for groundwater in the study area are also variable. Figure 11B shows the differences in δ2H in groundwaters. Within the floodplain, the observed range of δ2H corresponds to mixtures of average pre-dam river water with δ2H values near −114‰ and post-dam river water with average values near −97‰ (compare Figure 8A). Mixtures with a high proportion of pre-dam water (<−105‰) dominate groundwater beneath a broad area of the floodplain in Mexico. The area is poorly constrained to the south, and this pattern may extend further south than indicated in Figure 11B.
The (δ18O, δ2H) values of groundwaters derived from local precipitation (−7.6‰ and −51%; [30]) are slightly lower than the average winter precipitation (δ18O and δ2H) values (−7.2‰ and −47‰), but are consistent with the isotope composition of the largest 30% of rain events (−7.5‰ and −50‰, Figure 5B; [30,47,48,49]). The extensive alluvial fans observed at the base of the Gila Range suggest that mountain system recharge and focused recharge in ephemeral streams are likely to occur at the mountain front, as in other semi-arid basins in southern Arizona [50,51,52]. This occurs during winter when precipitation exceeds evapotranspiration. Groundwater flows from these recharge zones in the mountain front of the Gila Range west into the Yuma and San Luis Mesas. Mountain system recharge is present in at least one of the samples located at the base of the Gila Range (Figure 8B, −7.6‰ and 55‰).
Clearly, many such samples are Colorado River water or mixtures that are predominantly local recharge (Figure 8B). Infiltration of river water beneath the mesas is physically difficult to occur as far east as the pediment of the Gila Range (Figure 3). Three floodplain groundwater samples clearly contain mixtures of local recharge with river water (Figure 8A). Precise estimation of ratios in each case is problematic because of the difficulty of specifying a river water end member on the river evaporation trend, which intersects the mixing trend at a small angle.
The groundwater levels (Figure 3), location of the samples (Figure 4) and chemical and isotopic composition (Figure 7 and Figure 8) suggest that Na–Cl-dominated groundwaters from the Yuma and San Luis Mesas and the Gila Range (mountain system recharge) are moving westward, and mixing with Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl waters from the floodplain (Colorado River). This idea is illustrated in Figure 11, which shows higher Cl− and δ2H over the eastern side of the study, relative to groundwaters in the floodplain and intermediate values between them. Previous studies in the area [7,31] suggested that the Na–Cl-dominated waters along the border represent Gila River water. The presence of Gila River water cannot be discounted from isotope data alone; however, water with higher (δ18O and δ2H) values than the floodplain waters also occurs at the mountain front, where recharge from the Gila River is not possible. Therefore, such water is attributed here to local recharge.
Before major development, Gila River water in Yuma likely had (δ18O and δ2H) values consistent with the evaporation of high-elevation precipitation in the headwaters originating on the GMWL at δ18O = −12 to −10‰ (Figure 5A). There is an evaporation trend in the Gila River samples that overlaps with the Gila Range data (compare Figure 5A and Figure 8B). However, this is likely influenced by modern irrigation and the infiltration and percolation of evaporated agricultural return, which did not occur before major development in the floodplain.
Evaporation of Gila River surface water in pre-development times certainly occurred, as it occurs in the river upstream of dams [53]. Historical hydrochemical data along the lower Gila River are scant, and recent data show that today groundwater up to 90 km upstream from the Colorado and Gila River confluence is dominated by Colorado River chemistry [33]. Peak flows in the Colorado River occurred from April to June when late-spring snowmelt arrived in the area and replenished the aquifer. Historical Colorado River streamflow was at least two orders of magnitude larger than the Gila River during high flow season. It is very likely that the two rivers mixed, even before their confluence, resulting in waters dominated by Colorado River chemistry, and a pure Gila River endmember would be hard to find west of the Gila Range.
Independently of the origin of groundwaters in the eastern side of the study area, the low 3H levels indicate that recharge within the Yuma and San Luis Mesas occurred at least before the 1950′s, before the detonation of thermonuclear devices for most groundwater samples (Figure 9), and the 14C data are consistent with bulk residence times of thousands of (uncorrected 14C) years before present (between 4800 and 11,500). Combining old water and limited modern recharge across the Mesa suggests that the aquifer is vulnerable to overdraft.
4.2. Source of Solutes
4.2.1. Na+ and Cl−
Most waters from the Colorado River floodplain, Yuma and San Luis Mesas, and Gila Range foothills have a Na/Cl equivalent ratio close to the trends corresponding to halite dissolution and seawater dilution (Figure 12A). A Na/Cl equivalent ratio higher than one indicates the release of Na+ from silicate weathering reactions [54] in the Delta sediments.
Halite beds likely exist in the Delta due to marine transgression/regression cycles and seawater evaporation, but within the study area, there is no evidence of them in the available well-log data [9]. Partial dissolution of evaporite deposits explains high salinity in groundwaters in the western part of the Colorado River Delta [55]. There, halite and sylvite associated with lacustrine clayey sediments have been identified by X-ray diffraction and severely affect Cl− concentrations in groundwater. These clays are also likely found in the study area.
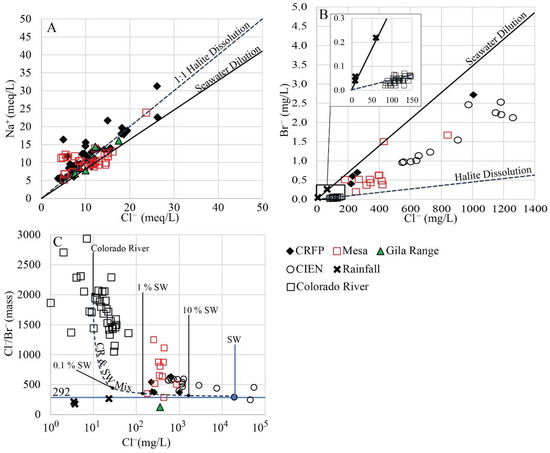
Figure 12.
(A) Na+ vs. Cl− (meq/L). Lines show 1:1 halite dissolution and seawater dilution trajectories. (B) Cl− (mg/L) vs. Br− (mg/L). Inset shows samples with low concentrations. (C) Cl−/Br− (mass) vs. Cl− (mg/L) with seawater/Colorado River water mixing trend. The horizontal line shows the seawater (SW) Cl/Br ratio [56]. Graphs include data for floodplain (CRFP), Mesa, Gila Range, surface water from the Ciénega (CIEN), local rainfall, and Colorado River. Colorado River data obtained from USGS Station 09404200. See text for further explanation.
Groundwater levels in the sampled areas are several meters higher than the high tide levels in the nearby coastline of the Gulf of California (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Isotope data for the Mesa could be interpreted as indicating mixing of Colorado River water and seawater (Figure 8B). Based on the elevation of the water table and the location of the groundwater samples, this is physically impossible. However, this is a possibility for groundwater samples obtained from deeper wells (>1200 m) at Riito (Figure 8B; [41]).
Since no halite-bearing strata are known within the study area, and no evidence exists for seawater intrusion (excluding deep wells), the possible sources of Cl− are (1) Salt-bearing clays, (2) irrigation water, (3) precipitation, and (4) dry deposition and eventual dissolution of marine-derived salts. The ions Cl− and Br− provide a useful tracer combination to identify the source of salinity in groundwater. Bromide is rejected during the process of halite precipitation, and the Cl/Br mass ratio of solid NaCl is usually 2–3 orders of magnitude higher than in the original waters (~5000; [57]). The Cl/Br mass ratio of seawater is about 290 and is preserved in precipitation occurring near the sea [58].
The Cl/Br mass ratio of post dam Colorado River water upstream of Lake Mead (USGS Station 09404200) appears consistent with a trend line resulting from halite dissolution. This line plots very close to the Cl− axis because of the low Br− content in the mineral (Figure 12B, inset). Closer inspection of Cl/Br data in the study area (Figure 12C) provides an alternative explanation of Br− content in the river water. Figure 12C indicates large ranges in both Cl− (1–60 mg/L) and Cl/Br (1000–3000) in river water. The figure shows a mixing line for seawater with a river water composition chosen as 10 mg/L Cl−, and a Cl/Br = 2000. Other mixing lines are possible for alternative choices of river water composition. The range of Cl− could be explained in part by changes in the dilution of salt input from upstream evaporites. However, the prominent linear data array to the right of the mixing line is better explained by very small additions of sea salt to river water. The Cl/Br mass ratio of local precipitation follows a trend line resulting from the dilution of seawater (Figure 12B). The Cl/Br mass ratio in local precipitation ranges between 150 and 274, similar to the marine Cl/Br mass ratio and is consistent with marine-derived aerosols (Figure 12C). A single sample from the Gila Range and a few samples from the floodplain and the Yuma and San Luis Mesas plot near the marine Cl/Br mass ratio (Figure 12C). Most of the samples have intermediate Cl/Br equivalent ratios. This indicates mixing between Colorado River water having irrigation and halite-derived Cl−, and local recharge having Na+ and Cl− originating from seawater aerosols.
Groundwaters within the floodplain and the Yuma and San Luis Mesas have Cl− concentrations between 132 and 1000 mg/L (Table S1). It is important to emphasize that some of the variability in Cl− concentration is likely explained by the spatial and temporal distribution of the sample collection. Water samples were obtained from wells with depths between 40 and 242 m from the surface. Shallower wells are more likely to be disturbed by anthropogenic activity, such as irrigation. The historical data used in this study are for samples collected between 1962 and 2016. Older samples could reflect a chemical composition more closely related to pre-dam Colorado River water with evaporation and less anthropogenic sources of solutes, and newer samples could be more similar to post-dam Colorado River water.
4.2.2. Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42−, and HCO3−
The dissolution of calcite, dolomite, and gypsum results in waters dominated by Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42−, and HCO3− [59]. There is an approximate 1:1 relationship for groundwaters in the study area with a slight deficiency of (Ca2+ + Mg2+) relative to (SO42− + HCO3−), particularly in groundwater samples from the floodplain (Figure 13). The excess negative charge is balanced by Na+ likely derived from old groundwater discharging into the river through the exchange of Ca2+ or Mg2+ for Na+ with clay minerals. Cation exchange also explains the excess Na+ relative to Cl− observed in Figure 12A and causes floodplain groundwaters to plot above the 1:1 halite dissolution trend.
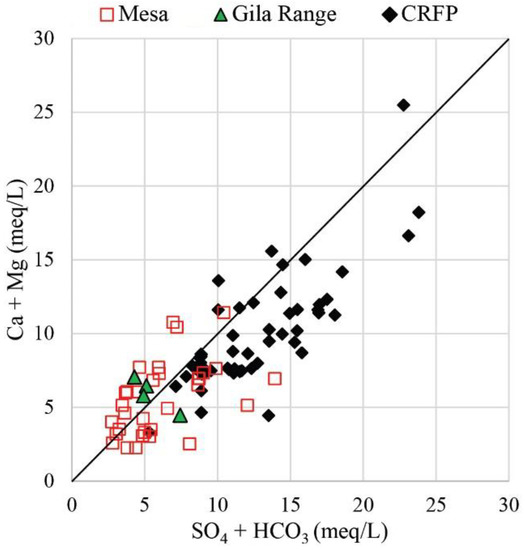
Figure 13.
Ca + Mg vs. SO4 + HCO3 (meq/L) for groundwater from Yuma–San Luis Mesas (MESA), Gila Range, and Colorado River floodplain (CRFP). The solid line represents 1:1 plotting location.
The highest Cl/SO4 mass ratio in the Gila Range samples (~6) approaches the ratio in seawater (~7.4, Figure 14). This further supports the idea that local recharge contains marine salts transported to the mountains either as marine aerosol or dust. As locally recharged groundwaters having a high Cl/SO4 molar ratio move westward, they mix with an SO42−-dominated endmember (Colorado River water), as illustrated by the Mesa samples in Figure 14A,B (dashed line).
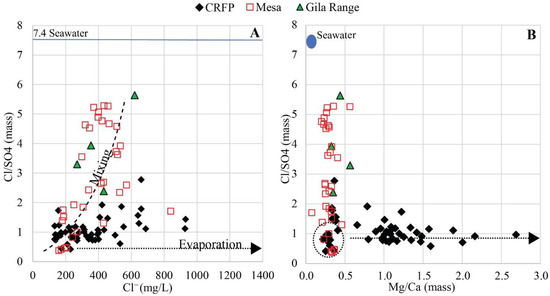
Figure 14.
(A) Cl− (mg/L) vs. Cl−/SO42− (mass ratio) values for floodplain (CRFP), Yuma–San Luis Mesas (Mesa), and Gila Range. The dashed line represents a hypothetical mixing trend. The dotted line represents the potential evaporation trajectory. (B) Mg/Ca vs. Cl−/SO42− (mass ratio) values for floodplain (CRFP), Mesa, and Gila Range samples. The dashed line represents potential evaporation trajectories. Solid blue lines show ratios of seawater in A and B [56].
The Mg/Ca mass ratio for the Gila Range samples varies between 0 and 0.6 (Figure 14B). Samples 43 and 82, both located in the Mesa, have the lowest δ18O and δ2H values of all the samples (−14.9 and −114, and −14.8‰ and −111, respectively), and characterize pre-dam Colorado River water. We assume that the Mg/Ca mass ratio range (0.2–0.5) of these samples represents pre-dam Colorado River water. Within the floodplain, Mg/Ca molar ratios range between 0.2 and ~3. Some degree of evaporation is observed in floodplain samples (Figure 8A and Figure 14A), but the Mg/Ca mass ratios would remain constant if this were the only process occurring in the floodplain and would plot in the dashed circle in Figure 14B. Three additional processes are believed to affect Colorado River floodplain groundwaters 1) precipitation of solid phases, such as calcium carbonate, 2) de-dolomitization of Mg-bearing carbonates, and 3) exchange of Ca2+ or Mg2+ for Na+ in the vadose zone, as previously discussed.
4.3. Hydrochemical Evolution
Features of the regional flow system, the relations between major solutes, and stable isotope data suggest that the following set of reactions is responsible for the hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in the study area:
Ca2+ + CO32− ←→ CaCO3
CaSO4 → Ca2+ +SO42−
Ca(Mg)CO3 → Ca2+ + Mg2+ + CO32−
Ca2+ + 2Na–X = Ca–X + 2Na+
In reaction (10), X represents an ion exchange site occupied by two monovalent cations or one divalent cation.
The evolution of groundwaters in the study area is described in the following paragraphs. Recharge having ionic ratios similar to those of seawater enters the aquifer along the Gila Range. Most rainwater is concentrated by evaporation and transpiration by water-efficient native vegetation, leading to the accumulation of meteoric salts near the surface. These readily soluble salts are dissolved during the most intense and infrequent events, and contribute with Na+, Ca2+, Cl−, and SO42− to groundwater when excess precipitation reaches the aquifer. Average local recharge in the region plots near the GMWL. This suggests that infiltration occurs during winter as the mountain system recharge when evaporation is low and through preferential pathways along the major washes draining the Gila Range. The concentration of range-front groundwater is remarkably higher than the rainfall it was derived from, as observed in the Gila Range samples, and is dominated by Na–Cl. This groundwater flows towards the southwest and mixes with Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl Colorado River water along the Yuma and San Luis Mesas (Figure 8).
Mineral–water equilibria suggest that dissolution–precipitation of calcite and dolomite, dissolution of halite and gypsum, and exchange of aqueous Ca2+ for adsorbed Na+ control the concentrations of solutes in the floodplain. Groundwater pumping draws sulfate-rich groundwater used for flood irrigation in the Yuma and San Luis Valley. Soil water is subjected to evapotranspiration, and Ca2+ and dissolved inorganic carbon are removed by precipitation of calcium carbonate. Precipitation of calcium carbonate allows the further dissolution of gypsum by the common ion effect. In the special case where groundwater is in equilibrium with calcite and dolomite, the dissolution of dolomite (de-dolomitization) increases Mg2+ concentrations, as observed in Figure 14B [60].
Montmorillonite is the most abundant clay in the study area and has considerable capacity for cation exchange [9]. As soil water moves through the soil, Na+ is released for Ca2+ during the cation exchange process. This affects the Mg/Ca ratio in floodplain samples (Figure 14) and explains the deficit of Ca2+ + Mg2+ relative to SO42− and HCO3 (Figure, balanced by the excess Na+ observed in Figure 12A. The groundwater produced by this set of reactions is enriched in readily soluble salts left behind by evapotranspiration of irrigation water and contributes to the salinization of the aquifer when excess irrigation infiltrates and reaches the water table [60]. Once in the aquifer, the enriched solution mixes with Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl groundwater and Na–Cl groundwaters derived from local recharge (Figure 15).
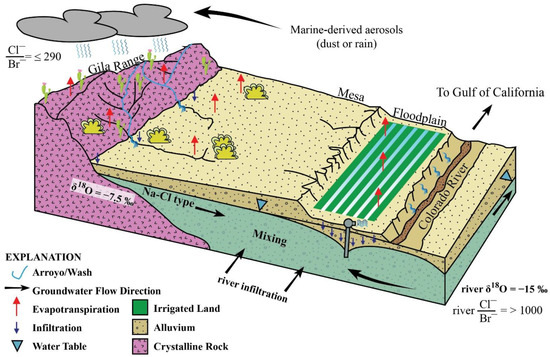
Figure 15.
Conceptual model of the study area.
5. Conclusions
Stable isotopes (δ18O and δ2H) distinguish four potential water endmembers in the Colorado River Delta: post-dam river water, pre-dam river water, Gila River water, and local recharge. Evaporation effects are prominent in the dataset; Colorado River samples form a single evaporation trend of slope 5.8. Groundwater from the Delta floodplain and water from the Ciénega de Santa Clara plot on the river evaporation trend. Seawater cannot intrude on the shallow aquifers examined in this study.
In the Gila Range, local mountain system recharge results from the largest 30% of winter rainfall events. Recharge occurs through preferential infiltration pathways along the major washes draining the Gila Range. Water from smaller rainfall events is lost to evaporation and transpiration, which causes the accumulation of meteoric salts with seawater ion ratios near the surface. Accumulated salts are dissolved during the large and infrequent precipitation events, yielding infiltration more concentrated than rainwater; these solutions infiltrate into the water table. Solutes are dominated by Na–Cl and contribute Na+, Ca2+, Cl−, and SO42− to the aquifer.
In the irrigated floodplain of the Colorado River Delta, hydrochemical evolution is mostly controlled by the original Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl-type Colorado River water, with small (<1%) additions of marine salt. Mineral saturation states, ionic relations, and stable isotopes indicate that salinity is augmented by evapotranspiration, precipitation of calcite that leads to the dissolution of gypsum by the common ion effect, dissolution of accumulated soil salts, de-dolomitization, and exchange of aqueous Ca2+ for adsorbed Na+. Pre-dam Colorado River water is common in floodplain groundwater.
In the Yuma and San Luis Mesas, values of δ18O and δ2H indicate mixing between local recharge at the Gila Range and Colorado River water. Na–Cl-dominated groundwater flows southwest from the Gila Range and mixes with the Ca–Mg–Cl/Na–Cl-dominated floodplain waters. Low 3H indicates that groundwater within the Yuma and San Luis Mesas infiltrated before the 1950′s, and 14C data are consistent with bulk residence times of thousands of years (4800 and 11,500 uncorrected 14C years before present).
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/hydrology8020080/s1, Figure S1: General geology and cross-section A–A’. Table S1: Isotopic and chemical composition of waters in the study area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.A.Z. and C.J.E.; methodology, H.A.Z., C.J.E. and J.C.M.; validation, H.A.Z., C.J.E. and J.C.M.; formal analysis, H.A.Z., C.J.E. and J.C.M.; investigation, H.A.Z.; resources, K.W.F., J.C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.A.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.J.E., J.C.M. and K.W.F.; visualization, H.A.Z., C.J.E.; supervision, K.W.F. and J.C.M.; project administration, H.A.Z. and K.W.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Grant (DGE-1143953), a University of Arizona Water Sustainability Program Fellowship, and a University of Arizona Geosciences Department R. Wilson Thompson Scholarship (H.A.Z.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this study are available at https://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis (accessed on 28 April 2021) and other sources provided in Table S1.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their suggestions and comments to improve this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barnett, T.P.; Pierce, D.W. Sustainable water deliveries from the Colorado River in a changing climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7334–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Arroyo, F.; Flessa, K.W. Nature’s fair share: Finding and allocating water for the Colorado River delta. In Conservation of Shared Environments: Learning from the United States and Mexico; Lopez-Hoffman, L., McGovern, E.D., Varady, R., Flessa, W.K., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2009; pp. 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés-Casillas, C.; Hinojosa-Huerta, O.; Muñoz-Viveroz, M.; Zamora-Arroyo, F.; Carrillo-Guerrero, Y.; Delgado-Garcia, S.; Lopez-Camacho, M.; Glenn, E.P.; Garcia, J.; Riley, J.; et al. Information Database and Local Outreach Program for the Restoration of the Hardy River Wetlands, Lower Colorado River delta, Baja California and Sonora. Available online: http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/salton/InfoDatabaseRioHardy.html (accessed on 1 November 2016).
- Lancaster, N.; Greeley, R.; Christensen, P.R. Dunes of the Gran Desierto Sand-Sea, Sonora, Mexico. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 1987, 12, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA: Comisión Nacional del Agua: Normas Climatológicas por Estado—Baja California (Presa Morelos). Available online: https://smn.conagua.gob.mx/es/informacion-climatologica-por-estado?estado=bc (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Álvarez-Borrego, S.; Flores- Báez, B.P.; Galindo-Bect, L.A. Hidrología del Alto Golfo de California II. Condiciones durante invierno, primavera y verano. Cienc. Mar. 1975, 2, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, B.R.; Quijano, L.; Carlos, L.D. Environmental isotopes in a study of the origin of salinity of groundwater in the Mexicali Valley. J. Hydrol. 1979, 41, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kamp, P.C. Holocene continental sedimentation in the Salton Basin, California: A reconnaissance. G.S.A. Bull. 1973, 84, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmsted, F.; Loeltz, O.; Irelan, B. Geohydrology of the Yuma Area, Arizona and California, Water Resources of Lower Colorado River-Salton Sea Area. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1973, 486–H, 1–273. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, J.; Land, M.; Faunt, C.; Leake, S.; Richard, E.; Fleming, J.B.; Pool, D.R. Hydrologic Framework Refinement, Ground-Water Flow and Storage, Water-Chemistry Analyses and Water-Budget Components of the Yuma Area, Southwestern Arizona, and Southeastern California. USGS Sci. Investig. Rep. 2006, 5135, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- CONAGUA: Comisión Nacional del Agua: Actualización de la Disponibilidad Media Anual de agua en el Acuífero Valle de San Luis Río Colorado (2601), Estado de Sonora. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/104293/DR_2601.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Curray, J.R.; Moore, D.G. Geologic history of the mouth of the Gulf of California. In Tectonics and Sedimentation along the California Margin; Crouch, J.K., Bachman, S.B., Eds.; Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1984; Volume 38, pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gastil, R.G.; Phillips, R.P.; Allison, E.C. Reconnaissance geology of the state of Baja California. GSA Mem. 1975, 140, 1–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meko, D.M.; Woodhouse, C.A.; Baisan, C.A.; Knight, T.; Lukas, J.J.; Hughes, M.K.; Salzer, M.W. Medieval Drought in the Upper Colorado River Basin. Geoph. Res. Let. 2007, 34, L10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, H.; Harris, K. Consumptive use of water rates in the lower Colorado River Basin: Report on water supply of the lower Colorado River basin: Project plan. U.S.B.R. 1952, 1, 1–427. [Google Scholar]
- Guay, B.; Eastoe, C.; Basset, R.; Long, A. Identifying sources of groundwater in the lower Colorado River valley, USA with δ18O, δ2H, and 3H: Implications for river water accounting. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.G.S.: Water-Quality Data for the Nation. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Morrison, J.I.; Postel, S.L.; Gieck, P.H. The Sustainable Use of Water in the Lower Colorado River Basin; Pacific Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 1996; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Flessa, K.W.; Glenn, E.P.; Hinojosa-Huerta, O.; de la Parra-Renteria, C.A.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Schmidt, J.C.; Zamora-Arroyo, F.A. Flooding of the Colorado River delta: A Landscape-Scale Experiment. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel Construcciones, S.A. Estudio Hidrogeológico Preliminar de los Acuíferos del Valle de Mexicali, B.C. y Mesa Arenosa de San Luis, Sonora; S.R.H.: Mexicali, México, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz Cabrera, P. Simulación Numérica del Acuífero Superior del Valle de Mexicali, Baja California, México. Master’s Thesis, Centro de Investigación Científica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada, Ensenada, México, December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Hernández, J.; Hinojosa-Huerta, O.; Peregrina-Llanes, M.; Calvo-Fonseca, A.; Carrera-Villa, E. Groundwater responses to controlled water releases in the Limitrophe Region of the Colorado River: Implications for management and restoration. Eco Eng. 2013, 59, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Duran, A.; Daessle, L.W.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Ortiz-Campos, E.; Barth, J.A.C. Turnover and release of P-, N-, Si-nutrients in the Mexicali Valley (Mexico): Interactions between the lower Colorado River and adjacent ground- and surface water systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CONAGUA: Comisión Nacional del Agua: Actualización de la Disponibilidad de Agua en el Acuifero del Valle de Mexicali (0210), Estado de Baja California. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/103411/DR_0210.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- ADEQ: Arizona Department of Water Resources Well Registry. Available online: https://gisweb.azwater.gov/waterresourcedata/wellregistry/ (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Glenn, E.P.; Lee, C.; Felger, R.; Zengel, S. Effects of water management on the wetlands of the Colorado River Delta, Mexico. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monitoring Program for the Ciénega de Santa Clara. Available online: https://www.ibwc.gov/Files/Exec_Summary_FR_Mon_Prog_Cienegad.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Gieskes, J.; Rogers, W. Alkalinity determinations in interstitial waters of marine sediments. J. Sediment. Res. 1973, 43, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares-Ramírez, R.B. Identificación de los Componentes Hidrogeoquimicos que Contaminan el Acuífero del Módulo de Riego I del Valle de San Luis, R.C. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California, Mexicali, México, December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, H.A.; Wilder, T.W.; Eastoe, C.J.; McIntosh, J.C.; Welker, J.; Flessa, K.W. Evaluation of Groundwater Sources, Flow Paths, and Residence Time of the Gran Desierto Pozos, Sonora, Mexico. Geosciences 2019, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makdisi, R.S.; Truesdell, A.H.; Thompson, J.M.; Coplen, T.B.; Sanchez, R. Geochemical evolution of Mexicali Valley groundwaters. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Cerro Prieto Geothermal Field, Guadalajara, Mexico, 10 August 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst, D.; Appelo, C. User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. USGS Water Resour. Investig. Rep. 1999, 99, 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Towne, D. Ambient groundwater of the Lower Gila Basin: A 2013–2016 baseline study. Ariz. Dep. Environ. Qual. Rep. 2017, 17-01, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Towne, D. Ambient groundwater quality of the Gila Valley Sub-Basin of the Safford Basin: A 2004 baseline study. Ariz. Dep. Environ. Qual. Rep. 2009, 9–12, 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; pp. 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, F.N. Geochemistry of groundwater in alluvial basins of Arizona and adjacent parts of Nevada, New Mexico, and California. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1991, 1406-C, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Majoube, M. Fractionnement en oxygene-18 et en deuterium entre l’eau et sa vapeur. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 197, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. Environmental isotopes in lake studies. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Chemistry. The Terrestrial Environment; Fritz, P., Fontes, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 113–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AZMET: The Arizona Meteorological Network. Available online: https://cals.arizona.edu/azmet/ (accessed on 8 July 2019).
- Barragán, R.M.; Birkle, P.; Portugal, E.; Arellano, V.M.; Álvarez, J. Geochemical survey of medium temperature geothermal resources from the Baja California Peninsula and Sonora, Mexico. J. Volc. Geoth. Res. 2001, 110, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettman, D.L.; Flessa, K.W.; Roopnarine, P.D.; Schöne, B.R.; Goodwin, D.H. The use of oxygen isotope variation in the shells of estuarine mollusks as a quantitative record of seasonal and annual Colorado River discharge. Geoch. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.A. Isotopes of Helium, Hydrogen, and Carbon as Groundwater Tracers in Aquifers along the Colorado River. Master’s Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Eastoe, C.J.; Watts, C.J.; Ploughe, M.; Wright, W.E. Future use of tritium in mapping pre-bomb groundwater. Ground Water 2012, 50, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, M.L.W.; Fahy, J.; Grauch, R.I.; Ball, B.A.; Chong, W.; Elliott, J.G.; Kosovich, J.J.; Livo, K.E.; Stillings, L.L. Results of the Chemical Analyses of Soil, Shale, and Soil Shale Extract from the Mancos Shale Formation in the Gunnison Gorge National Conservation Area, Southwestern Colorado, and at Hanksville, Utah. USGS Open-File Rep. 2007, 2007-1002D, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Repenning, C.A.; Cooley, M.E.; Akers, J.P. Stratigraphy of the Chinle and Moenkopi Formations, Navajo and Hopi Indian Reservations Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1969, 521-B, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, H.A.; Eastoe, C.J.; Wilder, B.T.; McIntosh, J.C.; Meixner, T.; Flessa, K.W. Groundwater Isotopes in the Sonoyta River Watershed, USA-Mexico: Implications for Recharge Sources and Management of the Quitobaquito Springs. Water 2020, 12, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastoe, C.J.; Towne, D. Regional zonation of groundwater recharge mechanisms in alluvial basins of Arizona: Interpretation of isotope mapping. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 194, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Taylor, R. Intensive rainfall recharges tropical groundwaters. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, A.; Hogan, J.; Ekwurzel, B.; Baillie, M.; Eastoe, C. Geochemical Quantification of Semiarid Mountain Recharge. Ground Water 2008, 46, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixner, T.; Manning, A.H.; Stonestrom, D.A.; Allen, D.M.; Ajami, H.; Blasch, K.W.; Brookfield, A.E.; Castro, C.L.; Clark, J.F.; Gochis, D.J.; et al. Implications of projected climate change for groundwater recharge in the western United States. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovich, K.H.; Manning, A.H.; Condon, L.E.; McIntosh, J.C. A mountain-front recharge component characterization approach combining groundwater age distributions, noble gas thermometry, and fluid and energy transport modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR027743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Kendall, C. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Ratios for Selected Sites in the U.S. Geological Survey’s NASQAN and Benchmark Surface-water Networks. USGS Open-File Rep. 2000, 00-160, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Meybeck, M. Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am. J. Sci. 1987, 287, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, E.; Izquierdo, G.; Truesdell, A.; Alvarez, J. The geochemistry and isotope hydrology of the Southern Mexicali Valley in the area of the Cerro Prieto, Baja California (Mexico) geothermal field. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Conditioning & Purification Magazine: Water Desalinization Processes and Associated Health and Environmental Issues. Available online: http://wcponline.com/2005/01/31/water-desalination-processes-associated-health-environmental-issues/ (accessed on 15 February 2016).
- Braitsch, O. Salt Deposits, their Origin and Composition; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.N.; Whittemore, D.O.; Fabryka-Marin, J. Uses of chloride/bromide ratios in studies of potable water. Ground Water 1998, 36, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Mullican, W.F., III. Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulfate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the Northern Chihuahuan Desert, Trans-Pecos, TX, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 1997, 5, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; A.A. Balkema Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 201–204. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).