Abstract
Iran has different climatic and geographical zones (mountainous and desert areas), mostly arid and semi-arid, which are suffering from land degradation. Desertification as a land degradation process in Iran is created by natural and anthropogenic driving forces. Meteorological drought is a major natural driving force of desertification and occurs due to the extended periods of low precipitation. Scarcity of water, as well as the excessive use of water resources, mainly for agriculture, creates negative water balances and changes in plant cover, and accelerates desertification. Despite various political measures having been taken in the past, desertification is still a serious environmental problem in many regions in Iran. In this study, drought and aridity indices derived from long-term temperature and precipitation data were used in order to show long-term drought occurrence in different climatic zones in Iran. The results indicated the occurrence of severe and extremely severe meteorological droughts in recent decades in the areas studied. Moreover, the De Martonne Aridity Index (IDM) and precipitation variability index (PVI) showed an ongoing negative trend on the basis of long-term data and the conducted regression analysis. Rapid population growth, soil salinization, and poor water resource management are also considered as the main anthropogenic drivers. The percentage of the rural population in Iran is decreasing and the urban area is growing fast. Since the 1970s, the usage of groundwater in Iran has increased around fourfold and the average annual decrease in the groundwater table has been around 0.51 m. The results of the study provide a better ex-post and ex-ante understanding of the occurrence of droughts as key driving forces of the desertification in Iran. Additionally, they can enable policymakers to prepare proper regional-based strategic planning in the future. Desertification cannot be stopped or managed completely, but could be mitigated by the adoption of some proposed sustainable land management strategies.
1. Introduction
Desertification is a land degradation process that affects dryland areas. More than 250 million people directly suffer from the effects of desertification and more than 70% of drylands are currently subject to desertification [1,2]. Moreover, approximately one billion people around the world are at risk of the consequences of desertification [3]. Large areas of land in marginal areas of the world’s deserts have been degraded and it is estimated that desertification is now taking place on around 12 million hectares per year [4]. Desertification results in a seriously undesirable situation for farmland and settlement and it is a critical environmental threat worldwide e.g., [5,6,7], as well as for Iran [8]. In Iran, approximately 0.33 million km2 (20% of Iran’s total land) is covered by desert [8,9] and around one million km2 of land is also at risk of desertification [10]. In the mid-1950s, projects to combat desertification were established and since 1958, more than 2300 km2 of sand dune areas have been stabilized by oil mulch and about 21,000 km2 has been improved through afforestation and sowing programs [11,12]. Regardless of the many anti-desertification projects that have been implemented during the past six decades, desertification is still an important environmental issue in many parts of the country and costs around one billion U.S. dollars annually [3,13]. Overgrazing, and the conversion of rangelands into farmland and residential areas on the one hand, and poor irrigation practice on the other, are the major anthropogenic driving forces of desertification in many parts of Iran [9], which are accelerating the effects of natural driving forces such as climate variability and drought.
Desertification is strongly associated with drought. According to Mishra and Singh [14], droughts and their effects are classified as meteorological, agricultural, hydrological, and socioeconomic. Drought as a main driving force of desertification occurs due to the effects of extended periods of low precipitation, so that its impact is mostly manifested as hydrological and agricultural droughts following meteorological phenomena [15]. The main purpose of this study is to identify the spatial and temporal variation of drought, as well as its specific effects in the context of Iran.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Database
In terms of its physiography, Iran can be divided into four regions: Caspian, Central Plateau (Kavir and Lut deserts), Zagros, and the Southern coastal plain [16]. Iran is located in the arid belt and comprises around 1.6 million km2. More than 50 percent of the land area is mountainous and around 30 percent of the total land area (situated in the central plateau) receives low annual precipitation (50–250 mm). Only the Caspian Plain in the north receives more than 1000 mm per year (Table 1). The average annual potential evaporation is estimated to be more than 4000 mm in the central part of Iran [17].

Table 1.
The De Martonne Aridity Index (IDM), annual precipitation, and mean temperature for the 12 synoptic stations over long periods.
Monthly precipitation and temperature data used in this study were collected from 12 synoptic stations distributed in Iran (Table 1; Figure 1) and were obtained from the Iranian Meteorological Organization (https://irimo.ir/eng/index.php). Groundwater discharge data were obtained from the Iranian Water Resource Management Company [18].
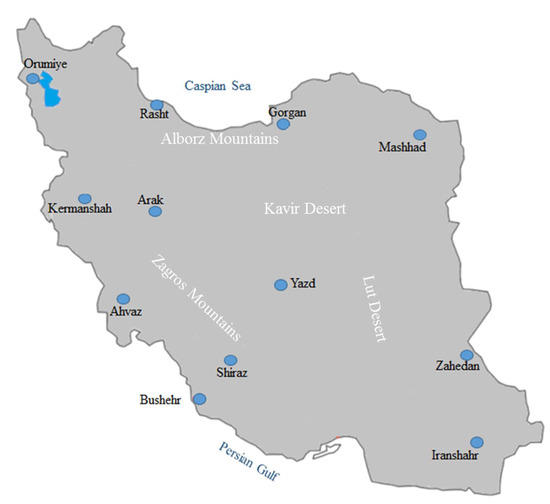
Figure 1.
Location of the synoptic stations which are considered in this study.
2.2. Drought Index
A large number of drought indices are used to monitor meteorological drought [19,20,21,22], but in this study, the precipitation variability index (PVI) or standardized precipitation index is considered because, according to Sivandi and Gharehdaghi [20], it provides more suitable results for Iran. The precipitation variability index (PVI) was calculated based on the following formula to show a normal distribution of the annual (twelve months) meteorological drought situation:
where:
PVIi = (Pi − µ)/σ
- PVIi is the precipitation variability index for year i;
- Pi is the annual precipitation for year i; and
- µ and σ are the mean annual precipitation in a selected period and standard deviation, respectively.
- Precipitation time series are classified into different climatic regimes as follows [21,22]:
- Extremely dry: P < µ − 2 × σ;
- Dry: µ − 2 × σ < P < µ − σ;
- Normal: µ – σ < P < µ + σ;
- Wet: P > µ + σ
- P is annual precipitation
A drought year is considered to occur if the PVIi is negative. Extremely severe drought occurs when the PVIi is between −0.84 and −1.28 [20].
2.3. Aridity Index
The de Martonne aridity index (IDM) is one of the best known and widely used aridity indices [23]. IDM was calculated based on the following equation [24]:
where:
IDM = P/T + 10
- P is the annual precipitation (mm) and
- T is the annual mean air temperature (°C).
- The type of climate according to the de Martonne aridity index is shown in Table 2.
 Table 2. Type of climate according to the de Martonne aridity index (IDM).
Table 2. Type of climate according to the de Martonne aridity index (IDM). - Linear regression is also used to compute the magnitude of trends.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Drought
Drought is a complex natural event that has serious destructive consequences for agriculture, industry, and the human environment. Droughts may be classified into four types: meteorological, hydrological, agricultural, and socioeconomic [25]. The frequency and severity of drought in many areas of the world are increasing due to the influences of natural and anthropogenic climate changes e.g., [26,27]. Drought is a major natural driving force of desertification in Iran. The multi-decadal average annual precipitation in Iran is 247 mm. There is also high spatial variability in the rainfall distribution: approximately 70% of the total precipitation falls in only 40% of the area of the country. According to Javari [28], a long-term analysis of annual precipitation in Iran shows significant variability in the spatial and temporal distributions, as well as in the frequency and intensity.
The de Martonne Aridity Index (IDM), long term average annual precipitation, and mean temperature for the 12 synoptic stations over long periods are presented in Table 1. The results show considerable differences in annual precipitation amounts between the recording stations. The regions of highest precipitation are found in the Mediterranean and humid zones, as well as the mountainous area in the west. The regions of lowest precipitation are located in the central plateau. In Yazd (centre), Zahedan (east), and Iranshahr (south east), the annual precipitation levels are relatively low. However, the annual precipitation in the other stations are all above 200 mm. Rasht located in the Caspian Plain in the north receives around 1334 mm of precipitation per year on average. In contrast, Yazd in the desert area receives approximately 57 mm of precipitation per year on average.
The long-term averages of the annual PVI values for each observed synoptic station are presented in Figure 2. According to the classification of different climatic regimes, as mentioned above, evidence shows that there have been severe meteorological droughts for all stations in recent decades. All the recording stations experienced at least two main periods that were characterized by long and extremely severe drought. In Kermanshah and Orumiye (west and north-west of the country), long periods of severe droughts occurred during 1999–2017. The stations, which are located in the Central Plateau, including Yazd and Shiraz, show extremely severe drought in the past decade. Moreover, the number of extremely severe drought years at Yazd was higher than for the other stations. Gorgan synoptic station, which is located in north Iran, and has a Mediterranean climate, also shows aridification according to the de Martonne aridity index. Furthermore, an extremely severe drought condition was indicated in 2008 and 2014 for this station. There was a severe drought in Zahedan station from 1999 to 2005 (Figure 2).
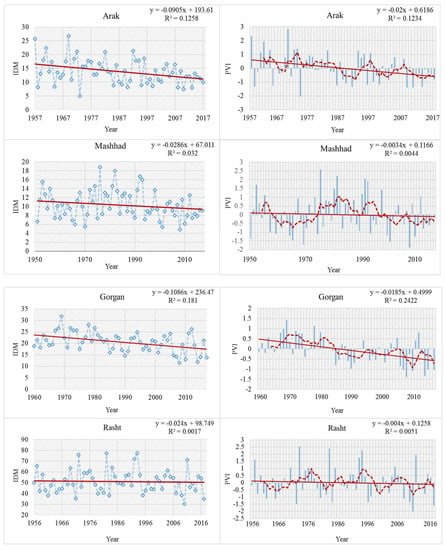
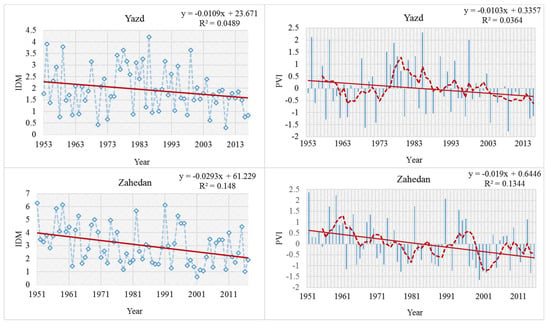
Figure 2.
Annual precipitation variability indices (PVI) for the six selected synoptic stations from four different climate types. The dashed red lines (right) show the five-year moving average. The solid red lines (left and right) denote a simple regression analysis. Source: Iranian Meteorological Organization (https://irimo.ir/eng/index.php).
The de Martonne Aridity Index (IDM) calculated for the recording stations shows a negative trend (Figure 2). The spatial distribution of IDM shows a high variability, with the lowest values in Yazd for the driest conditions in the center, and the highest values in the Caspian Plain in the north (Figure 2; Table 1). IDM varied from 1.9 at the Yazd station to 20.5 and 51 at the Gorgan and Rasht stations, respectively. The Yazd station is arid, while Goragn and Rasht stations are Mediterranean and very humid. The reduction of IDM at the Yazd station was greater than for the other stations (Figure 2). This negative trend could also indicate aridification in all study areas. The trend of the aridity index in Mashhad station (north east of the country) shows the change of climate type from semi-arid to arid (Table 2).
Drought has negative influences on agriculture. The central plateau, which is considered to be the major area of the country, is characterized by having IDM values of 1.9 to 13.7. The main agricultural activity in this area is the production of wheat, barley, cotton, and canola, which are all at risk of water scarcity. Regarding the severe drought that has been shown in this study, high yields cannot be achieved without using irrigation. Therefore, overexploitation of ground water will continue in the future and will also accelerate the impacts of meteorological drought. Therefore, there is a need to formulate effective water management for agriculture in this region. The results of this study may therefore be useful in terms of raising awareness among decision makers in order to ensure the better management of water resources in arid and semi-arid lands with regard to the prediction of drought occurrence.
One of the main negative environmental impacts of drought is the reduction in groundwater recharge due to the shortage of surface water. In addition, the overexploitation of water resources by human activities leads to a severe water deficit and this has impacts on both natural vegetation cover and the production of agriculture crops e.g., [29]. According to Linsley et al. [30], a hydrological drought occurs when groundwater and surface water availability is not sufficient to supply the demand. Moreover, it should also be pointed out that different types of drought, including meteorological, agricultural, and hydrological droughts, have significant effects on local economies and businesses, and thereby cause socioeconomic drought [25,31]. According to Guo et al. [25], socioeconomic drought will take place when the water supply cannot meet various human demands and related sectors. Despite the importance of socioeconomic drought, it has generally received little attention [25,31].
3.2. Overexploitation of Groundwater
The water shortage worldwide is considered a key threat for the twenty-first century [32]. The issue of water scarcity in Iran is long-term and it has become a chronic environmental problem. Iran has been facing increasingly severe water scarcity, especially in recent decades, mainly in the central part of the country. Inadequate precipitation is the main cause of water scarcity, but anthropogenic drivers, such as rapid population growth and poor water resource management, also play an important role. Approximately 89.5 billion cubic meters per year of fresh water are consumed by human activities in Iran and around 93% of this amount is used for agricultural purposes [33]. Farmlands under irrigation are estimated to comprise around 8 million hectares. Water use for irrigation is supplied from both surface water and groundwater resources, in proportions of 45% and 55%, respectively. Groundwater plays a very important role in Iran’s agricultural operations; every year, an average of approximately 44 billion cubic meters of water is supplied for agricultural purposes from around 363,000 deep (>50 m) and semi-deep (<50 m) wells [33,34]. According to the Iranian Water Resource Management Company [18], the exploitation of groundwater in Iran has increased from around 16,517 million cubic meters in 1972 to about 61,093 million cubic meters in 2014 due to increased human consumption, land use change, and the irrigation of farmland, especially so following the rapid population growth and urbanization that has occurred since 1975 (Figure 3). Therefore, the exploitation usage of groundwater in Iran has been increased around fourfold and the average annual decrease in the groundwater table has been around 0.51 m [34]. The mean yearly decrease in the level of the groundwater table is around 50 cm in central Iran [8]. Therefore, pumping of the groundwater urgently needs to be regulated.
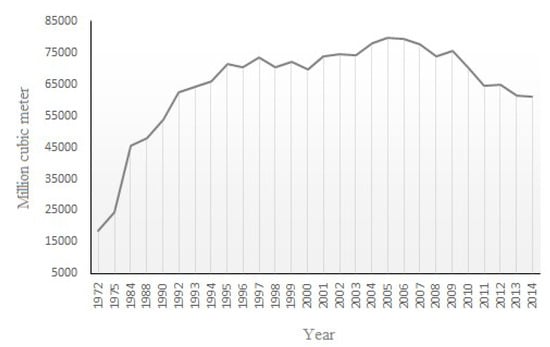
Figure 3.
The annual amounts of extracted ground water in Iran. Source: Iranian Water Resource Management Company [18].
3.3. Salinization
Areas with saline soils are expanding in Iran and now cover 25% of the total area of the country [35]. Salinization is an important factor of soil degradation in the central plateau of Iran and is also considered a challenge in terms of land management activities [36]. High salinity can reduce the conversion of ammonium salts to nitrate by soil organisms, thereby reducing soil fertility [5]. Farmlands in Iran are suffering from salinization as a result of anthropogenic activities and natural processes [17]. Overexploitation of the groundwater from saline aquifers is considered to be an important man-made driving force of salinity [37] (Table 3). Salinization effectively reduces the capacity of groundwater-connected habitats [38] and hence, it reduces the productivity of land and accelerates desertification. Around 50% of the irrigated lands in Iran are facing various rates of salinity, which normally causes a loss of soil health and quality [39].

Table 3.
Soil salinity level in irrigated lands in Iran.
According to Qadir et al. [17], extreme saline soils are located in the Central part, Southern Coastal Plains, and the Caspian Coastal Plain of Iran. The annual economic losses due to salinization are estimated to be around US $1 billion for the whole country.
3.4. Economic and Socio-Political Implications of Desertification
Desertification is not only an environmental problem, but it is also an important economic problem that has direct impacts on incomes in rural areas [40]. According to Sivakumar and Stefanski [41], the worldwide decrease in income related to desertification in farmland is calculated to be around 42 billion US dollars annually. Population and economic growth as socio-political and economic drivers are increasing pressure on natural ecosystems globally [35,42,43]. Urbanization and urban-sprawl directly or indirectly cause the main changes in environmental qualities and functions with great pressure on natural resources [5]. Moreover, both impact climate dynamics and accelerate desertification and aridification e.g., [44,45,46]. Therefore, anthropogenic climate change and environmental change could also be considered as the major driving force of migration [47,48] (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
An abandoned village as a consequence of the long-term drought and water scarcity near the city of Qom in Qom Province, north central Iran (Photo: Emadodin).
The total land area of Iran is 1.65 million km2 and the population is around 82 million. Population growth and urbanization are the main driving forces of environmental stresses. Since the late 1950s, there has been rapid population growth in Iran. Between 1956 and 2018, the population increased from about 19 million to more than 82 million. The rural population, as a proportion of the total in Iran, is decreasing and the size of the urban area shows growth over the past six decades e.g., [49,50] (Figure 5). Around 21 million people (about 25.6% of the total population) live in rural areas and approximately one-fourth are engaged in agriculture [34]. Economic progress and population growth are the basic and primary driving forces of unsustainable land-use changes and overexploitation of natural resources and subsequent desertification in Iran. As an example, since the 1950s, Iran’s farmland has increased by more than five times and deforestation has also occurred at a significant rate [51].
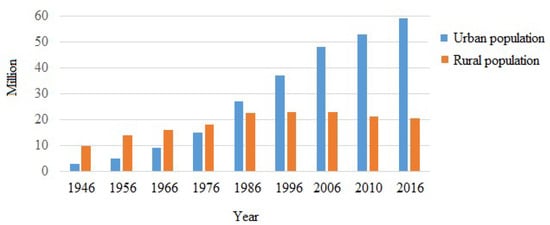
Figure 5.
Iran’s population growth in urban and rural areas. Source: Statistical Centre of Iran [42].
Poverty is also an important and controversial implication of desertification. According to Cleaver and Schreiber [52], poverty is a driving force of desertification and also contributes to its acceleration through land-use intensification, thus creating more environmental problems, as well as greater poverty. Poverty and its environmental impacts are unlikely to be mitigated in the dryland areas unless there is a sustainable management of natural resources and notable investment in plant, soil, and water conservation, as well as in training and education.
Rapid population growth and an unsuitable population distribution, the over use of land, and poor water resource management are recognized as three major causes of water crisis in Iran [53] that are exacerbating the effects of climate change, as well as droughts. Therefore, a good awareness of drought is important in order to provide early warnings of the threats to environmental resources [54,55].
4. Conclusions
The main purpose of this study was to show the interactions between the annual aridity trends and drought behavior in Iran over a long period, on the one hand, and the consequences for the dimension of desertification of agricultural land, on the other hand. Therefore, monthly precipitation and temperature data from 12 synoptic stations with different climatic conditions were analyzed. The reduction of IDM during the selected period was greater at stations in arid areas than other stations. This negative trend could also indicate aridification in these regions, especially in recent decades. According to the main issues mentioned above, drought as a natural driving force plays an important role in desertification in Iran, especially in arid and semi-arid areas. Evidence shows extreme natural events such as droughts and floods that could be related to climate change in general and to local climate perturbations. The use of the de Martonne aridity index to assess aridification confirms that there has been a long-term increase in all selected synoptic stations, which is mainly due to the increased annual temperature and shortage of precipitation. The long-term precipitation variability index (PVI) also shows severe meteorological droughts for all stations in recent decades. The trend of de Martonne Aridity Index (IDM) during selected periods indicated a negative trend for all selected stations, especially in the central plateau with arid and semi-arid climate. This negative trend will lead to increased aridity in the future and a worsening of its present extreme drought situation in arid and semi-arid areas. The total use of groundwater has also increased around fourfold since 1970 and this plays an important role as an anthropogenic driving force of desertification in Iran. The findings of this study also show that the people in the Iranian Central Plateau are at greater risk of extreme drought and desertification than those in other parts of the country. Therefore, it is assumed that an increase in the duration and magnitude of droughts will result in increased migrations.
It should also be pointed out that desertification in Iran cannot be stopped or managed completely, but it could be mitigated by sustainable land management strategies. This requires:
- An ecological-economic approach as a basis for ensuring an integrated and coordinated approach to find various policy alternatives;
- A logical balance and management between the needs of society and the exploitation of natural resources;
- Participation of local non-governmental organizations in water-management decisions to achieve sustainable watershed management;
- Investigation of best water supply and storage methods and modified irrigation systems to enhance the water use efficiency;
- Adaptive and proper management frameworks in rural development projects to provide an appropriate basis for accelerating the process of combating desertification;
- Multidisciplinary works to combine modern scientific findings with indigenous knowledge;
- Assessing the opportunities that can be achieved through controlling desertification and land restoration attempts as pilot projects through an optimal policy;
- Improving information for decision-makers about environmental policy and their responsibilities for the monitoring of environmental impacts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.E.; methodology, I.E.; formal analysis, I.E., T.R.; investigation, I.E., T.R.; data curation and analysis, I.E.; writing—original draft preparation, I.E.; reviewing and editing, I.E., T.R. and F.T.; funding acquisition, F.T.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank anonymous reviewers for their invaluable comments and constructive suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Evans, R.D.; Johansen, J.R. Microbiotic crusts and ecosystem processes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 183–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, C.J. Environmental Management for Sustainable Development; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP. Iran and UNDP Strengthen Efforts to Combat Desertification. 2017. Available online: http://www.ir.undp.org/content/iran/en/home/presscenter/articles/2017/06/17/iran-and-undp-strengthen-efforts-to-combat-desertification.html (accessed on 17 June 2017).
- Brauch, H.S.; Spring, U. Securitizing the Ground, Grounding Security; UNCCD Issue Paper No. 2; UNCCD: Bonn, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, C.J. Land Degradation: Development and Breakdown of Terrestrial Environments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Pan, X.; Wang, D.; Shen, C.; Lu, Q. Combating desertification in China: Past, present and future. Land Use Policy 2013, 31, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S.; Stringer, L.C. Land Degradation, Desertification and Climate Change: Anticipating, Assessing and Adapting to Future Change; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, R.; Hasheminasab, S. Assessing the effects of dam building on land degradation in central Iran with Landsat LST and LULC time series. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadodin, I.; Bork, H.R. Degradation of soils as a result of long-term human-induced transformation of the environment in Iran: An overview. J. Land Use Sci. 2012, 7, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Bakhshandehmehr, L. Quantitative mapping and assessment of environmentally sensitive areas to desertification in central Iran. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiraslani, F.; Dragovich, D. Combating desertification in Iran over the last 50 years: An overview of changing approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Tavili, A.; Panahi, F.; Zandi Esfahan, E.; Ghorbani, M. Reclamation of Arid Lands; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhtesasi, M.R. Investigating Morphometric and Morphodynamic Characteristics of Wind Erosion in Yazd Plain and Determining their Indices for Desertification Models. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agana, N.A.; Homaifar, A. EMD-Based Predictive Deep Belief Network for Time Series Prediction: An Application to Drought Forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2018, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M. The Economic Geology of Iran; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Qureshi, A.S.; Cheraghi, S.A.M. Extent and characterization of salt-affected soils in Iran and strategies for their amelioration and management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranian Water Resource Management Company. 2018. Available online: http://wrbs.wrm.ir/SC.php?type=static&id=179 (accessed on 6 August 2019). (In Persian).
- Quiring, S.M. Monitoring Drought: An Evaluation of Meteorological Drought Indices. Geogr. Compass 2009, 3, 64–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandi, A.; Gharehdaghi, H. Performance evaluation of some Metrological Drought Indices in south of khuzestan Province and zoning it using geographic information system (GIS). Indian J. Fundam. Appl. Life Sci. 2014, 4, 730–737. [Google Scholar]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of precipitation and drought data in Serbia over the period 1980–2010. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Liu, K. Analysis of Changes in Precipitation and Drought in Aksu River Basin, Northwest China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, A.; Toros, H.; Incecik, S. Spatial variations of climate indices in Turkey. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martonne, E. Aréisme et indice artidite. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie Des Sciences. Paris 1926, 182, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Fang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L. Assessing socioeconomic drought based on an improved Multivariate. J. Hydrol. 2019, 268, 904–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Van Der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Barichivich, J.; Briffa, K.R.; Sheffield, J. Global warming and changes in drought. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javari, J. Trend and Homogeneity Analysis of Precipitation in Iran. Climate 2016, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Beck, H.E.; Crosbie, R.S.; Jeu, R.A.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Podger, G.M.; Timbal, B.; Viney, N.R. The millennium drought in southeast Australia (2001–2009): Natural and human causes and implications for water resources, ecosystems, economy, and society. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1040–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, R.K., Jr.; Kohler, M.A.; Paulhus, J.L.H. Hydrology for Engineers; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, B.; Gray, M.; Hunter, B. The Social and Economic Impacts of Drought; CSRM Working Papers; The Australian National University: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; No: 5. [Google Scholar]
- Bodner, G.; Nakhforoosh, A.; Kaul, H.P. Management of crop water under drought: A review. Agron. Sustain Dev. 2015, 35, 401–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati, M.H.; Boustani, F. An assessment of groundwater crisis in Iran, case study: Fars province. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 70, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Emadodin, I.; Narita, D.; Bork, H.R. Soil degradation and agricultural sustainability: An overview from Iran. J. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2012, 14, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesgaran, M.B.; Madani, K.; Hashemi, H.; Azadi, P. Iran’s land suitability for agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichels, D.; Qadir, M. Achieving sustainable irrigation requires effective management of salts, soil salinity, and shallow groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 157, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kath, J.; Powell, S.; Reardon-Smith, K.; Sawah, S.E.; Jakeman, A.J.; Croke, B.F.W.; Dyer, F.J. Groundwater salinization intensifies drought impacts in forests and reduces refuge capacity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, S.A.M. Institutional and scientific profiles of organizations working on saline agriculture in Iran. In Prospects of Saline Agriculture in the Arabian Peninsula: Proceedings of the International Seminar on Prospects of Saline Agriculture in the GCC Countries 18–20 March 2001, Dubai, United Arab Emirates; Taha, F.K., Ismail, S., Jaradat, A.A., Eds.; Amherst Scientific Publishers: Amherst, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 399–412. [Google Scholar]
- Moameni, A. An appraisal of land resources of Iran; FAO Report: Tehran, Iran, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, B.; Quaas, M.; Frank, K.; Baumgärtner, S. Pitfalls and Potential of Institutional Change: Rain-Index Insurance and the Sustainability of Rangeland Management; University of Lüneburg Working Paper Series in Economics. No. 149; University of Lüneburg: Lüneburg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, M.V.K.; Stefanski, R. Climate and land degradation—An overview. In Climate and Land Degradation; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007; pp. 105–135. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, J.; Binswanger, H.P. Natural resource degradation effects of poverty are largely policy-induced: The case of Colombia. Environ. Dev. Econ. 1996, 1, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Synthesis Report. Chapter 4; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 66–68.
- Wang, F.; Ge, Q.S. Estimation of urbanization bias in observed surface temperature change in China from 1980 to 2009 using satellite land-use data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadodin, I.; Taravat, A.; Rajaei, M. Effects of urban sprawl on local climate: A case study, north central Iran. Urban Clim. 2016, 17, 230–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadodin, I.; Reinsch, T. Assessing the impact of land use change on aridification in semi-arid land. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3423–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requier-Desjardins, M. Social costs of desertification in Africa: The case of migration. In Future of Drylands; Lee, C., Schaaf, T., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2008; pp. 569–581. [Google Scholar]
- Klepp, S. Climate change and migration. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Climate Science; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Taravat, A.; Rajaei, M.; Emadodin, I. Urbanization dynamics of Tehran city (1975–2015) using artificial neural networks. J. Maps 2017, 13, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Centre of Iran. Population Estimation, Country’s Population, Urban and Rural Areas. Available online: https://www.amar.org.ir. 2018 (accessed on 6 August 2019).
- Bahrami, A.; Emadodin, I.; Atashi, M.R.; Bork, H.R. Land-use change and soil degradation: A case study, North of Iran. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. (ABJNA) 2010, 4, 600–605. [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver, K.M.; Schreiber, G.A. Reversing the Spiral: The Population, Agriculture and Environment Nexus in Sub-Saharan Africa; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Madani, K. Water management in Iran: What is causing the looming crisis? J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2014, 4, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X. Spatial-temporal variation and impacts of drought in Xinjiang (Northwest China) during 1961–2015. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wilhite, D.A. An Operational Agricultural Drought Risk Assessment Model for Nebraska, USA. Natl. Hazards 2004, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).