Fresh and Recirculated Submarine Groundwater Discharge Evaluated by Geochemical Tracers and a Seepage Meter at Two Sites in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
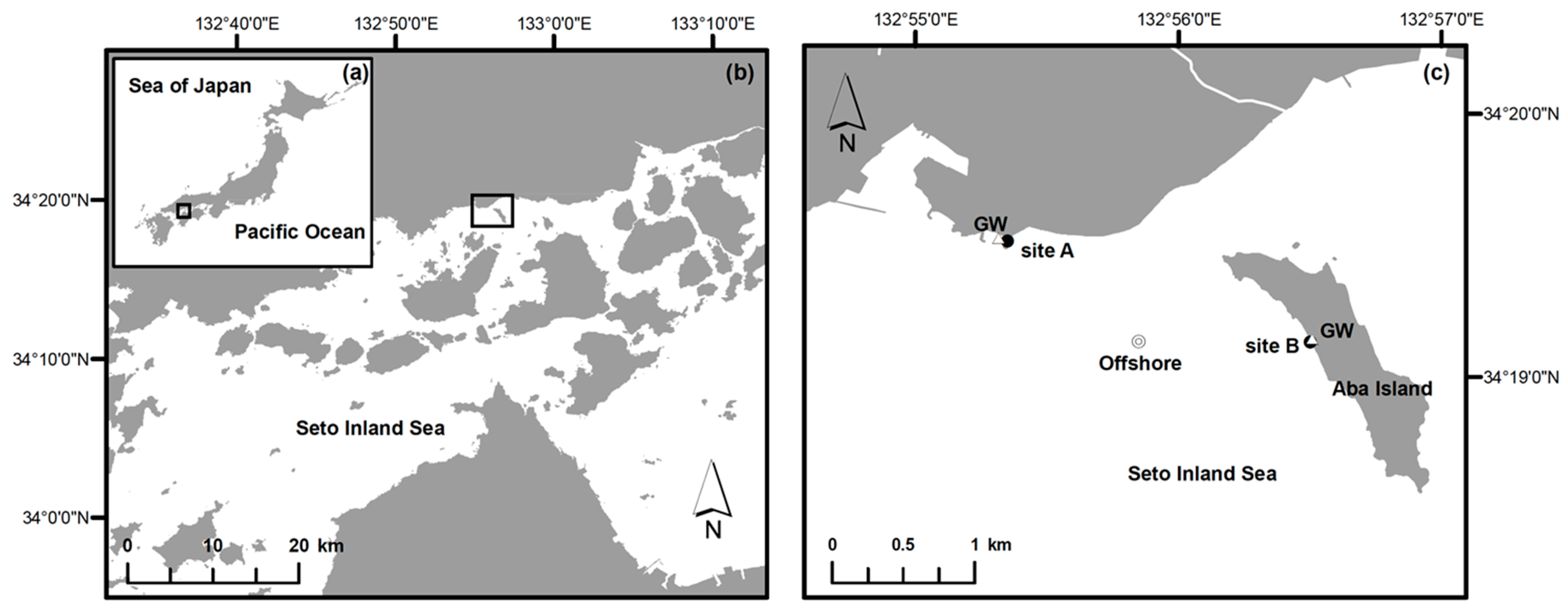
2.1. Field Survey
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Estimates of SGD Rates by Seepage Meters and Radioisotopes
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Groundwater and Offshore Seawater
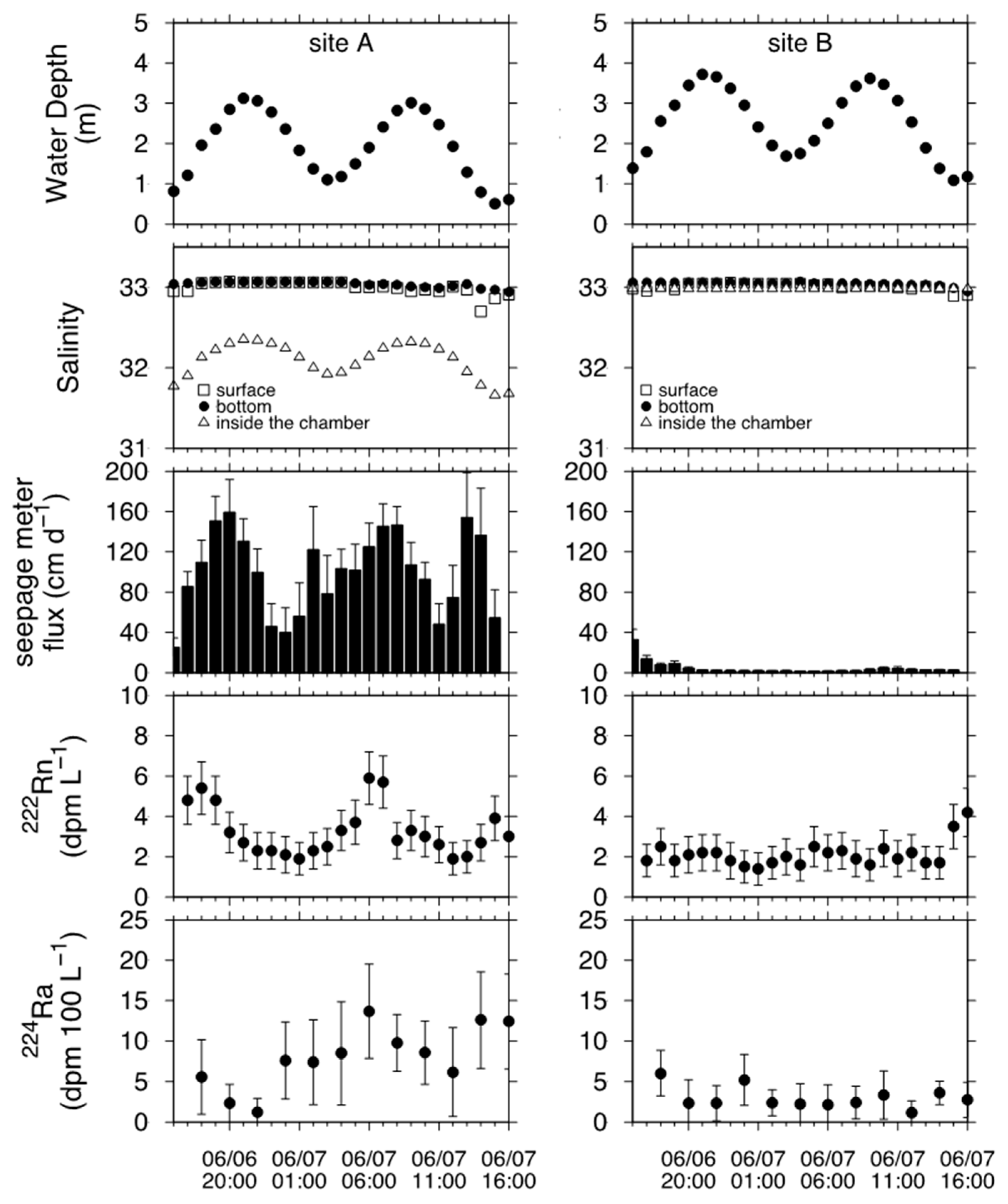
3.2. Temporal Changes in Total SGD Rates and Activities of Geochemical Tracers
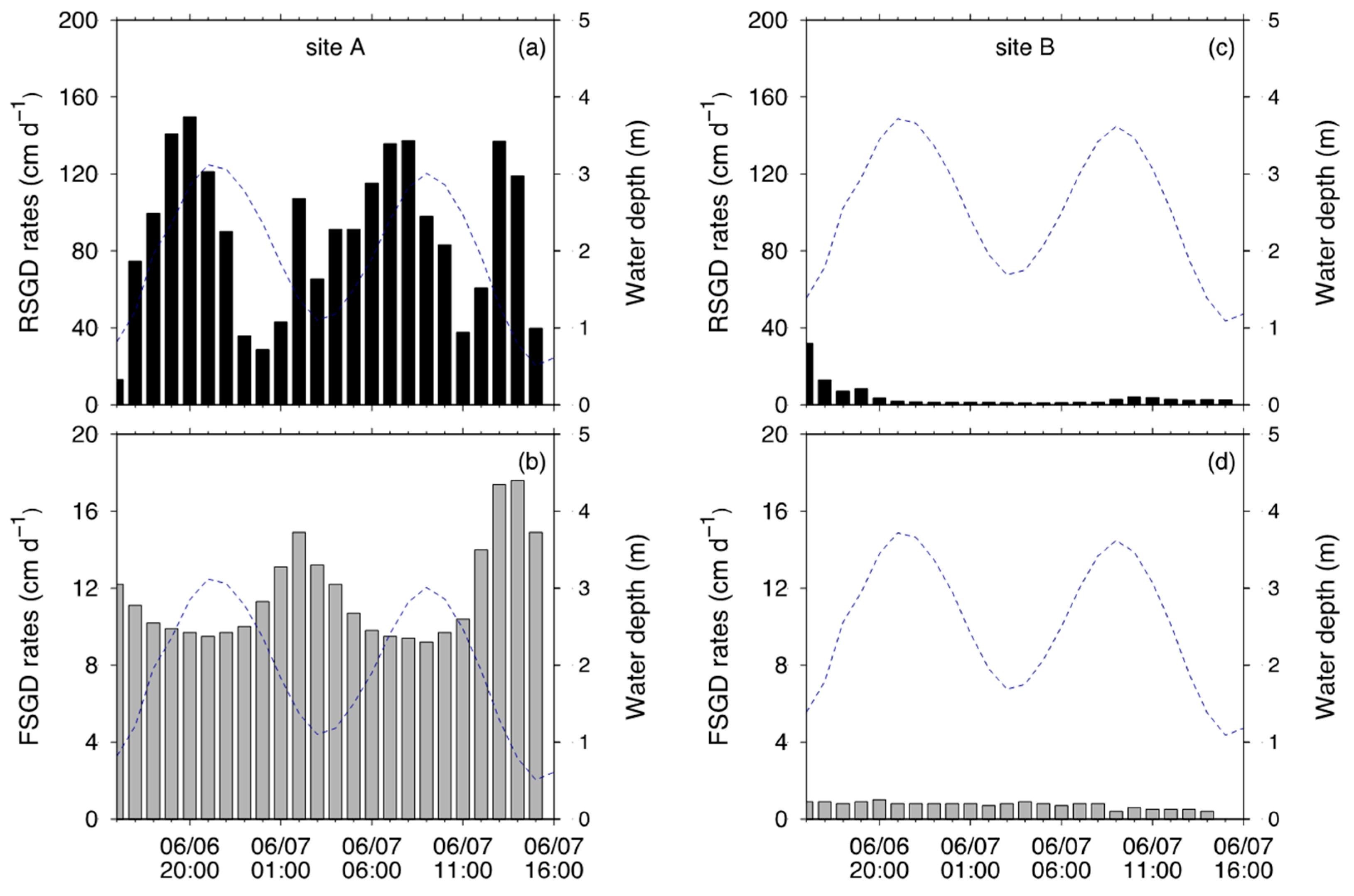
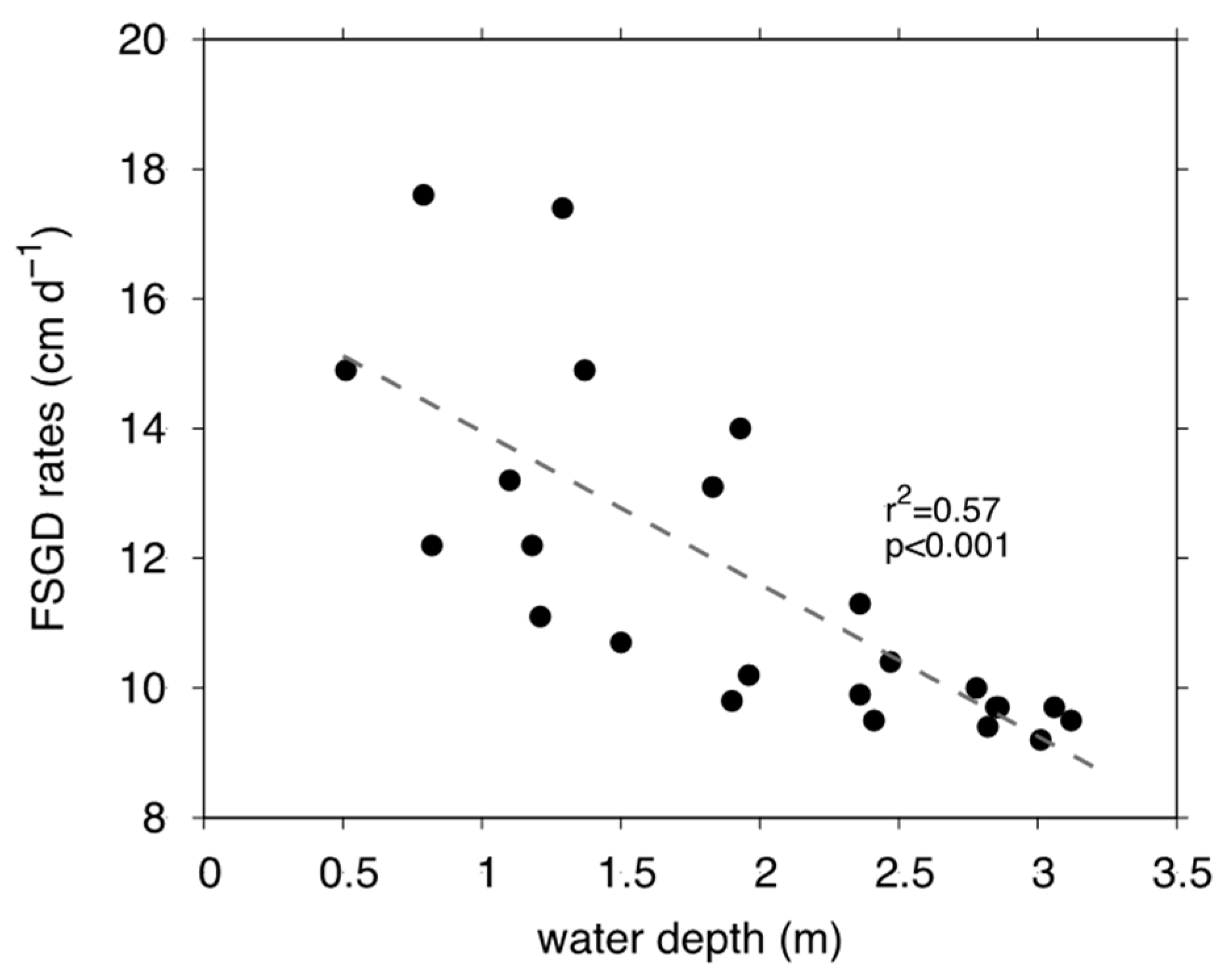
3.3. FSGD and RSGD Quantified via Seepage Meter
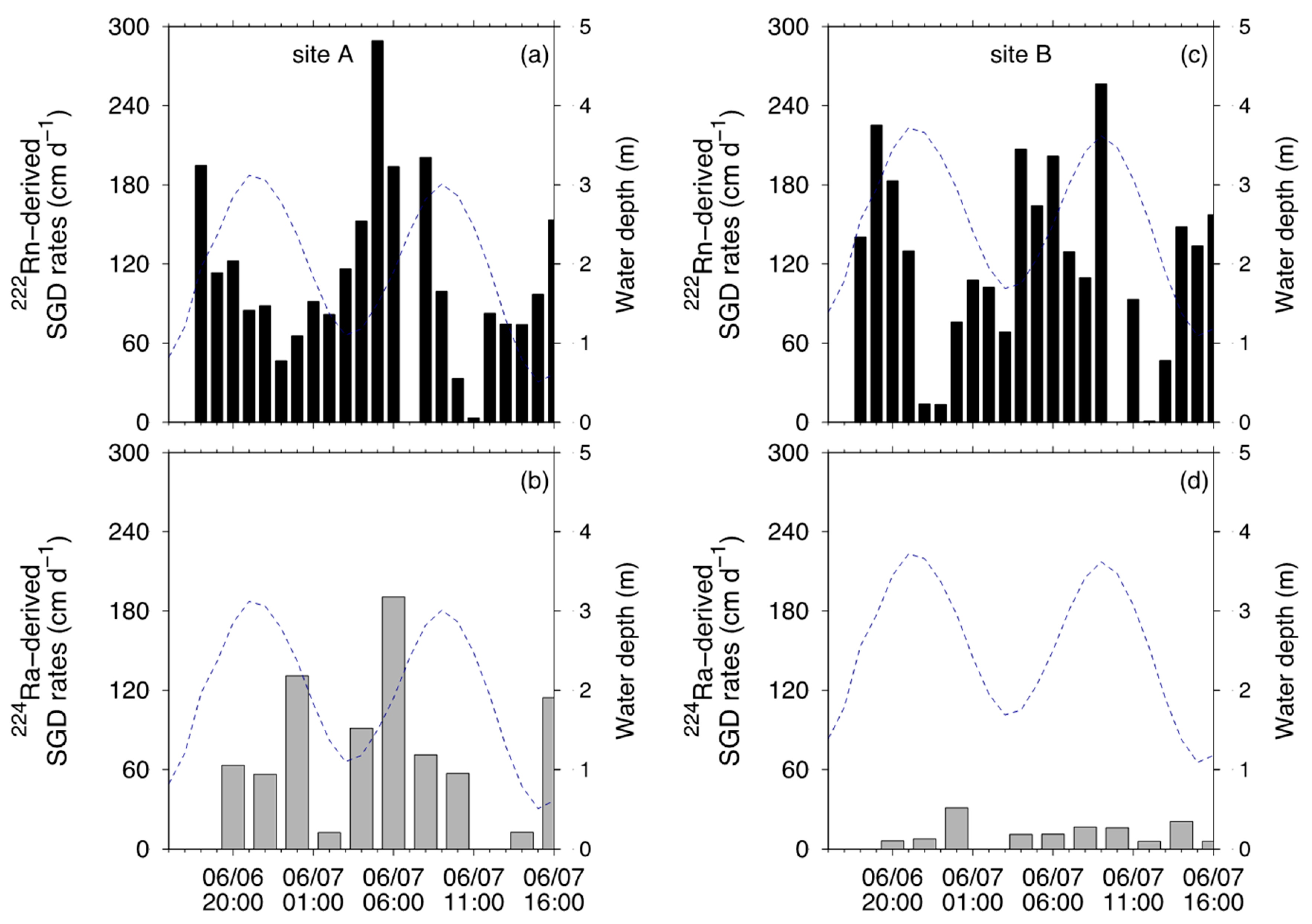
3.4. SGD Rates Quantified by 222Rn and 224Ra Mass Balance Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Controlling Temporal Changes in SGD Rates
4.2. Comparison of SGD Rates Estimated using Geochemical Tracers and Seepage Meters
4.3. Uncertainties in SGD Rates Determined using Geochemical Tracers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Slomp, C.P.; Van Cappellen, P. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: controls and potential impact. J. Hydrol. 2004, 295, 64–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Cable, J.E.; Turner, J.V. Investigations of submarine groundwater discharge. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Eyre, B.D.; Huettel, M. The driving forces of porewater and groundwater flow in permeable coastal sediments: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 98, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R. A device for measuring seepage flux in lakes and estuaries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Iwakawa, H. Measurements of submarine groundwater discharge rates by a continuous heat-type automated seepage meter in Osaka Bay, Japan. J. Groundw. Hydrol. 2001, 43, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberry, D.O.; Morin, R.H. Use of an electromagnetic seepage meter to investigate temporal variability lake seepage. Groundwater 2004, 42, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Ishitobi, T.; Shimada, J. Dynamics of submarine groundwater discharge and freshwater-seawater interface. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Sugimoto, R.; Honda, H.; Miyata, Y.; Tahara, D.; Tominaga, O.; Shoji, J.; Yamada, M.; Nakada, S.; Taniguchi, M. High-resolution mapping and time-series measurements of 222Rn concentrations and biogeochemical properties related to submarine groundwater discharge along the coast of Obama Bay, a semi-enclosed sea in Japan. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.A.; Lubetsky, J.S.; Harvey, C.F. Characterizing submarine groundwater discharge: A seepage meter study in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, J.E.; Bugna, G.C.; Burnett, W.C.; Chanton, J.P. Application of 222Rn and CH4 for assessment of groundwater discharge to the coastal ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature 1996, 380, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Eyre, B.D. Radon tracing of groundwater discharge into an Australian estuary surrounded by coastal acid sulphate soils. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Burnett, W.C.; Maclntyre, H.L.; Liefer, J.D.; Peterson, R.N.; Viso, R. Natural radon and radium isotopes for assessing groundwater discharge into Little Lagoon, AL: Implications for harmful algal blooms. Estuar. Coast. 2014, 37, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat-Noori, M.; Santos, I.R.; Sanders, C.J.; Sanders, L.M.; Maher, D.T. Groundwater discharge into an estuary using spatially distributed radon time series and radium isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Aureli, A.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Cable, J.E.; Charette, M.A.; Kontar, E.; Krupa, S.; Kulkarni, K.M.; Loveless, A.; et al. Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci. Total. Environ. 2006, 367, 498–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H. Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 69, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Burnett, W.C.; Chanton, J.; Mwashote, B.; Suryaputra, I.G.; Dittmar, T. Nutrient biogeochemistry in a Gulf of Mexico subterranean estuary and groundwater-derived fluxes to the coastal ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charette, M.A.; Buesseler, K.O.; Andrews, J.E. Utility of radium isotopes for evaluating the input and transport of groundwater-derived nitrogen to a Cape Cod estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, R.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Takao, T.; Tahara, D.; Tominaga, O.; Taniguchi, M. Seasonal Changes in Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Associated Nutrient Transport into a Tideless Semi-enclosed Embayment (Obama Bay, Japan). Estuar. Coast. 2016, 39, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, G.; Primeau, F.; Moore, W.S.; Cho, H.-M.; DeVries, T.; Cho, Y.-K. Global estimate of submarine groundwater discharge based on an observationally constrained radium isotope model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8433–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.M.; Kim, G.; Kwon, E.Y.; Moosdorf, N.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Santos, I.R. Radium tracing nutrient inputs through submarine groundwater discharge in the global ocean. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarzenski, P.W. U/Th series radionuclides as coastal groundwater tracers. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Chan, L.H. Desorption of Ba and 226Ra from river-borne sediments in the Hudson estuary. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 43, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, H. Geology of the Mitsu District with Geological Sheet Map at 1:50,000; Geological Survey of Japan: Okayama, Japan, 2001; 58p, (In Japanese with English abstract 4p).
- Onodera, S.I.; Saito, M.; Shimizu, Y. Visit to valuable water springs (102) Valuable waters of coastal area in western part of Hiroshima prefecture. J. Groundw. Hydrol. 2013, 55, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Hori, M.; Tomiyama, T.; Shoji, J. Occurrence, distribution and prey items of juvenile marbled sole Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae around a submarine groundwater seepage on a tidal flat in southwestern Japan. J. Sea Res. 2016, 111, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Moore, W.S. Measurement of 224Ra and 226Ra activities in natural waters using a radon-in-air monitor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4680–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimova, N.; Burnett, W.C.; Horwitz, E.P.; Lane-Smith, D. Automated measurement of 224Ra and 226Ra in water. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007, 65, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, T.; Ono, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Tokunaga, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Akimichi, T. Spatial distribution of submarine groundwater discharge and associated nutrients within a local coastal area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5319–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanninkhof, R. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7373–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, S.; Wanninkhof, R.; Chanton, J.P. Trace gas exchange across the air-water interface in freshwater and coastal marine environments. In Biogenic Trace Gases: Measuring Emissions from Soil Water; Matson, P.A., Harris, R.C., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 52–97. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.; Malin, G.; Nightingale, P.D.; Liss, P.S. Seasonal variation of dimethyl sulphide in the North Sea and an assessment of fluxes to the atmosphere. Mar. Chem. 1996, 54, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat-Noori, M.; Tait, D.R.; Maher, D.T.; Holloway, C.; Santos, I.R. Greenhouse gases and submarine groundwater discharge in a Sydney Harbour embayment (Australia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Hwang, D.W. Tidal pumping of groundwater into the coastal ocean revealed from submarine 222Rn and CH4 monitoring. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M. Tidal effects on submarine groundwater discharge into the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Iwakawa, H. Submarine groundwater discharge in Osaka Bay, Japan. Limnology 2004, 5, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.E.; Xin, P.; Santos, I.R.; Charette, M.A.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Groundwater dynamics in subterranean estuaries of coastal unconfined aquifers: Controls on submarine groundwater discharge and chemical inputs to the ocean. Adv. Water Resour. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, T.; Mogolló, J.M.; Moosdorf, N.; Winkler, A.; Kopf, A.; Pichler, T. Submarine groundwater discharge within a landslide scar at the French Mediterranean coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H.; Siringan, F.; Foronda, J.; Wattayakorn, G.; Rungsupa, S.; Kontar, E.A.; Ishitobi, T. Groundwater discharge as an important land-sea pathway into Manila Bay, Philippines. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitobi, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Saeki, K.; Ono, K. Quantitive evaluations of submarine groundwater discharge in Suruga Bay, Japan. Geochemistry 2005, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.N.; Burnett, W.C.; Taniguchi, M.; Chen, J.; Santos, I.R.; Ishitobi, T. Radon and radium isotopes assessment of submarine groundwater discharge in the Yellow River delta, China. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Burnett, W.C.; Chanton, J.; Dimova, N.; Peterson, P.N. Land or Ocean? Assessing the driving forces of submarine groundwater discharge at a coastal site in the Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarzenski, P.W.; Izbicki, J.A. Coastal groundwater dynamics off Santa Barbara, California: Combining geochemical tracers, electromagnetic seepmeters, and electrical resistivity. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, A.E.; Charette, M.A. Intercomparison of submarine groundwater discharge estimates from a sandy unconfined aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Santos, I.R.; Weinstein, Y.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Herut, B. Remaining uncertainties in the use of Rn-222 as a quantitative tracer of submarine groundwater discharge. IAHS Publ. 2007, 312, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Santo, I.R.; Erler, D.; Tait, D.; Eyre, B.D. Breathing of a coral cay: Tracing tidally driven seawater recirculation in permeable coral reef sediments. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.G.; Rodellas, V.; Stieglitz, T.C. Quantifying Surface Water, Porewater, and Groundwater Interactions Using Tracers: Tracer Fluxes, Water Fluxes, and End-member Concentrations. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 2452–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Masqué, P.; Font-Muñoz, J.S. The influence of sediment sources on radium-derived estimates of Submarine Groundwater Discharge. Mar. Chem. 2015, 171, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Distance from the Low Tide Mark(m) | Salinity | 222Rn (dpm L−1) | 224Ra (dpm 100 L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| site A | ||||
| GW1 | 1 | 33.8 | 1.2 ± 1.1 | 260 ± 85.0 |
| GW2 | 10 | 21.8 | 17.9 ± 6.0 | 150.6 ± 47.7 |
| GW3 | 19 | 13.8 | 42.9 ± 5.1 | 114.8 ± 59.4 |
| site B | ||||
| GW4 | 0 | 33.7 | 14.6 ± 6.5 | 449.3 ± 118.4 |
| GW5 | 20 | 33.6 | 16.1 ± 2.3 | 1080.2 ± 116.5 |
| GW6 | 25 | 31.1 | 17.7 ± 4.5 | 1598.7 ± 150.0 |
| Offshore seawater | ||||
| OS | − | 33.0 | 3.3 ± 2.3 | 0.0 ± 1.3 |
| Seepage Meter | Geochemical Tracers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm d−1) | (%) | (cm d−1) | (%) | |
| Site A | ||||
| SGD | 99.8 ± 39.3 | (100) | 106.9 ± 65.8 * | (100) |
| RSGD | 88.1 ± 39.4 | (88.3) | 72.7 ± 54.3 ** | (68.1) |
| FSGD | 11.6 ± 2.5 | (11.7) | – | (31.9) |
| Site B | ||||
| SGD | 4.9 ± 6.5 | (100) | 117.8 ± 70.8 * | (100) |
| RSGD | 4.2 ± 6.4 | (85.6) | 12.0 ± 8.3 ** | (10.2) |
| FSGD | 0.7 ± 0.2 | (14.4) | – | (89.8) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakajima, T.; Sugimoto, R.; Tominaga, O.; Takeuchi, M.; Honda, H.; Shoji, J.; Taniguchi, M. Fresh and Recirculated Submarine Groundwater Discharge Evaluated by Geochemical Tracers and a Seepage Meter at Two Sites in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Hydrology 2018, 5, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5040061
Nakajima T, Sugimoto R, Tominaga O, Takeuchi M, Honda H, Shoji J, Taniguchi M. Fresh and Recirculated Submarine Groundwater Discharge Evaluated by Geochemical Tracers and a Seepage Meter at Two Sites in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Hydrology. 2018; 5(4):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5040061
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakajima, Toshimi, Ryo Sugimoto, Osamu Tominaga, Masaru Takeuchi, Hisami Honda, Jun Shoji, and Makoto Taniguchi. 2018. "Fresh and Recirculated Submarine Groundwater Discharge Evaluated by Geochemical Tracers and a Seepage Meter at Two Sites in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan" Hydrology 5, no. 4: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5040061
APA StyleNakajima, T., Sugimoto, R., Tominaga, O., Takeuchi, M., Honda, H., Shoji, J., & Taniguchi, M. (2018). Fresh and Recirculated Submarine Groundwater Discharge Evaluated by Geochemical Tracers and a Seepage Meter at Two Sites in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Hydrology, 5(4), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5040061





