Abstract
Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) is a global and well-studied geological process by which groundwater of varying salinities enters coastal waters. SGD is known to transport bioactive solutes, including but not limited to nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorous, silica), gases (methane, carbon dioxide), and trace metals (iron, nickel, zinc). In addition, physical changes to the water column, such as changes in temperature and mixing can be caused by SGD. Therefore SGD influences both autotrophic and heterotrophic marine biota across all kingdoms of life. This paper synthesizes the current literature in which the impacts of SGD on marine biota were measured and observed by field, modeling, or laboratory studies. The review is grouped by organismal complexity: bacteria and phytoplankton, macrophytes (macroalgae and marine plants), animals, and ecosystem studies. Directions for future research about the impacts of SGD on marine life, including increasing the number of ecosystem assessment studies and including biological parameters in SGD flux studies, are also discussed.
1. Introduction
Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) encompasses all manner of groundwater flow to the ocean, including point source discharge from springs, and diffuse seepage from coastal aquifers [1,2,3]. SGD may consist of seawater that has circulated through the coastal aquifer before returning to the ocean, fresh groundwater from inland sources, or a mixture of both of these waters [3,4,5]. The magnitude of SGD is a function of both land (hydraulic gradient, aquifer permeability) and marine (wave set up, tidal range) site characteristics; for example, SGD is enhanced in areas with large tides due to tidal pumping [6,7]. Yet, even when discharge is small, it can still have an effect on coastal systems [8]. Often hidden from the naked eye, SGD rivals river discharge globally in terms of volume discharge to the ocean, and it is known to occur in every ocean basin [1,9,10]. Not only a source of freshwater to the ocean, SGD also transports bioactive solutes to the coastal ocean when it discharges, including but not limited to nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), silica (Si), iron (Fe), methane (CH4), and mercury (Hg) [1,3,5,6,11,12]. The impacts of SGD can extend into society as well, as a freshwater resource and a process that exerts a positive influence on fisheries [13].
A topic of much study since the late 20th century, several methods have been developed to detect and quantify SGD. Seepage meters can be deployed in shallow and calm conditions to quantify the flux (volume discharge normalized to area and time) of SGD by observations of changing water volume in attached bags, dilution of dye in an attached chamber, or the change in temperature caused by groundwater convection [14,15,16]. Natural tracers, such as radon (Rn) and radium (Ra), can be used to quantify the flux of SGD to coastal systems across a wide variety of conditions [17,18,19,20]. Additionally, radon and methane surveys have been used to identify SGD hotspots, areas of relatively high discharge [21,22]. Mixing models of isotopic tracers and other water quality parameters can indicate how much nutrient content of a coastal water body is attributed to SGD [23,24]. More recently, satellite imagery has been used to identify SGD hotspots from noting the locations of temperature anomalies as the temperature of discharging groundwater often differs from surficial ocean water [25]. Whatever the method of quantification, SGD-associated solute transport to the coastal ocean is most often determined by multiplying the concentration of that solute in the coastal aquifer by the calculated SGD flux. Such studies have become common, spanning sites across the globe in recent years. Less well observed are the actual impacts of SGD on marine biota.
Marine organisms are subject to various physical and chemical gradients that can affect their growth and physiology, and SGD is one factor that contributes to these environmental gradients in coastal waters. The most commonly studied impact of SGD impacts on biota is the delivery of dissolved nutrients, principally nitrogen, e.g., [6,8,26,27,28]. Nitrogen is a growth-limiting nutrient for many phytoplankton and macrophytes that form the base of the marine food web. As an aggregate, marine phytoplankton require nitrogen and phosphorus at a ratio of 16N:1P for balanced growth; hence, if SGD delivery of nitrogen relieves nutrient limitation, phytoplankton may replicate faster, show shifts in species composition, and/or potentially accumulate more biomass [29,30,31]. The outcome of these changes is varied and depends strongly on the location, species present, nutrient content of the groundwater, and the SGD flux, among other factors [30,32,33,34]. Eutrophication from SGD has been observed in some regions, which can lead to anoxic conditions when blooms decline [7,35,36]. SGD nutrient loading has also been linked to the occurrence of harmful algal blooms [29,36,37,38]. However, the effect of SGD on organisms is not limited to nutrient loading. In regions with substantial SGD flux, organisms may respond to changes in salinity, light penetration into the water column, turbulence, and/or pH [30,39,40,41,42]. Fresh SGD has even been proposed to aid in the removal of parasites from fish, a common aquaculture practice [43]. As with nutrient loading, the specific effects that these factors will cause are strongly site-specific and depend on the species present.
Various approaches have been used to assess the effects of SGD on organisms. In field campaigns in which SGD is measured in situ, organisms may be enumerated or their physiologies assessed over transects that run alongshore and offshore, thus capturing the natural gradients caused by SGD [26,32]. In contrast, experiments seeking to understand the dose response of organisms to groundwater, such as mesocosm experiments and bottle incubation studies, make additions of groundwater to ambient seawater at pre-determined percentages and observe how the organisms respond over time [29,30,31]. The effects of SGD can also be predicted based on simple models that account for the SGD flux and chemical composition. For example, the flux of nitrogen at a site can be used to predict how much additional phytoplankton growth may occur in response to SGD over time [44].
Methods that directly assess biological responses to SGD depend on the physiological or ecological trait of interest, and as with any scientific study, the hypothesis should inform which methods are appropriate. In the case of phytoplankton, growth is generally monitored via chlorophyll a analysis, cell counts via microscopy, or flow cytometry; however, phytoplankton blooms can also be monitored using satellite remote sensing analysis [29,31,45,46]. In contrast, macroalgae and benthic organisms are typically enumerated by counting the number of organisms or measuring their percent cover in a pre-determined area (quadrat), or by measuring changes in their size or biomass [26,28,47]. Microbes, including phytoplankton, can also be enumerated and identified via genetic barcoding of their deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) [39,48].
Physiological parameters, such as nutrient uptake kinetics, changes in protein expression, and other physiological changes are monitored in many different ways. A complete discussion of all methods is outside the scope of this review. However, the most common types of analyses include uptake of labeled tracers (e.g., 15N), enzyme activity assays (e.g., for alkaline phosphatase activity), and gene expression metrics (e.g., transcriptomics) [28,49,50]. The rate of photosynthesis in phytoplankton and macroalgae can be assessed experimentally by measuring the incorporation of radiocarbon (14C) into biomass, dissolved oxygen production, and pulse-amplitude-modulation fluorometry [51,52,53].
The purpose of this review is to expose and discuss the commonalities of how SGD influences marine organisms. The studies discussed here span a variety of coastal systems and kingdoms of life (Figure 1, Table 1). As the diversity of species and genera in some kingdoms is large, and physiological similarities do not necessarily correspond with kingdoms (e.g., macroalgae are considered by some more similar to marine plants than phytoplankton), the paper is divided into the following sections: Section 2. Phytoplankton and Bacteria; Section 3. Macrophytes (macroalgae and marine plants); Section 4. Marine Animals; and Section 5. Ecosystem Studies (studies which explore effects beyond a single other section). Only studies that made observations of actual changes in marine organisms attributed to SGD were included in the review. Therefore, studies that only estimated an effect from calculated SGD and associated solute fluxes were excluded.
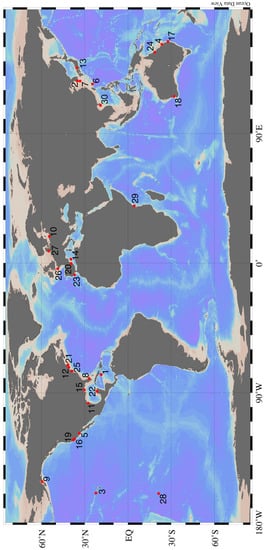
Figure 1.
Locations of studies reviewed in this paper. All studies measured the effects of SGD on marine biota. Numbers correspond to locations in Table 1. Figure made with Ocean Data View [54].

Table 1.
Summary of the studies reviewed in this paper.
2. Phytoplankton and Bacteria
By far the most frequently studied organisms with respect to SGD impacts are bacteria and phytoplankton. Approximately 40% of the studies reviewed in this paper contained analyses of phytoplankton and/or bacteria. This focus is warranted, as these organisms provide the base of many marine ecosystems, both as a food and as an oxygen source. Indeed, the importance of phytoplankton is profound, because through photosynthesis, they generate over 50% of atmospheric oxygen [111]. The simplest method to identify how SGD impacts these organisms is through analysis of the photosynthetic pigment, chlorophyll a. Mesocosm experiments with natural seawater have consistently shown increases in chlorophyll a in response to local groundwater additions [29,30,32,45]. The increase in chlorophyll a is typically attributed to the addition of nutrients from SGD, which relieves nutrient limitation. Once the phytoplankton take up all of the nutrients supplied by the groundwater treatments, chlorophyll a ceases to increase, and it may begin to decline [30]. Field surveys of bays and lagoons that combine chlorophyll a concentrations with radon, a natural tracer associated with SGD, have shown the chlorophyll a and radon activities can correlate at these sites, or that elevated chlorophyll a in a particular area is often associated with higher radon activities [81,84,89]. Covariance of these two parameters can occur throughout the water column as well. For example, Honda et al. [81] showed that chlorophyll a concentrations increased near the bottom of Obama Bay, where higher radon activities indicated that SGD was occurring. A modeling study on the coast of Perth, Australia also indicated that SGD could induce higher chlorophyll a concentrations by relieving nutrient limitation [87].
Some of the primary types of phytoplankton in coastal waters to be influenced by SGD are diatoms, a genus characterized by cells with silica-based frustules. Diatoms tend to react favorably to the input of SGD due to their ability to more easily take up and process dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP), compared to many other phytoplankton [112]. DIN (as nitrate, NO3, and ammonium, NH4) and DIP (as phosphate, PO4) are often the dominant forms of nitrogen and phosphorous in SGD [5], and the presence of these nutrients in SGD has been observed to induce diatom blooms or to sustain seed populations of diatoms, due to its lack of seasonality [23,29,38,70]. In addition to nitrogen and phosphorous loading, nutrients required by all phytoplankton, SGD has consistently been shown to be a substantial source of dissolved silica as silicate SiO4 to coastal systems [6,12,88,113]. Unlike other photosynthetic phytoplankton that do not require silica, diatoms require silica in a one-to-one ratio with nitrogen to build their frustules [114]. Frustules act as a defense mechanism against predation [115]. SGD is enriched in dissolved silicate due to rock–water interactions in the coastal aquifer that dissolve aquifer substrates [23,116,117]. Increases specifically in diatom abundance due to SGD has been shown in mesocosm experiments, where diatoms reacted similarly to additions of SGD and SGD-like treatments composed of inorganic nutrients, including silicate [29,30,31]. Noting the importance of silicate, treatments containing DIN and silicate together showed a greater increase in diatom abundance with time, than treatments containing DIN alone [29,30,31]. Such findings suggest that SGD is a preferential source of nutrients to diatoms, compared to nutrient sources that do not contain silicate in abundance. The mesocosm results agree with field studies that show increases in diatom abundance after pulses of groundwater discharge [32,38], and higher abundances of diatoms at groundwater-influenced sites compared to nearby sites lacking SGD influence [57,70,93]. However, the response among diatom genera are not uniform and seem to be dependent on factors other than nutrient contribution alone.
One genus that responds favorably to SGD is Pseudo-nitzschia. Pseudo-nitzschia is a chain-forming pennate diatom, with some species in the genus capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid [118,119]. However, Pseudo-nitzschia only creates domoic acid when stressed, such as under phosphate or silica limiting conditions after a bloom [118,119]. Blooms of Pseudo-nitzschia can impact ecosystems and fisheries, but on the whole, the genus contributes positively to the base of ecosystems [118,120]. It has been hypothesized from a field study that Pseudo-nitzschia responds better to SGD than river discharge because SGD provides nitrate without simultaneously lowering salinity, if the SGD is comprised mostly of brackish or recirculated seawater [38]. Pseudo-nitzschia prefer higher salinities [118,120]. This hypothesis was supported by a mesocosm experiment containing treatments of groundwater and river water, where groundwater additions led to a higher relative abundance of Pseudo-nitzschia compared to river-water additions [30]. Field studies have also shown shifts away from higher abundances of Pseudo-nitzschia in areas influenced by rivers compared to SGD alone [38,121].
Cascading effects of initial diatom blooms to other types of phytoplankton and bacteria have also been observed. Typically, the diatoms influence these other organisms by transforming inorganic nutrients into organic nutrients that are more readily utilized by those other genera [59,78,122]. However, this effect is difficult to parse out from SGD-enriched water being transported offshore, which could also directly influence those genera [37,56,84]. Such cascading effects have been proposed to influence dinoflagellate red tide blooms in the Southern Sea of Korea and the Gulf of Mexico, although much of the data is corollary and needs confirmation via further study [56,73]. Evidence in support of the cascading effect has been shown during brown tide blooms of the pelagophyte Aureococcus anophaegefferens in a New York embayment, which are spurred by both the organic nutrients transformed by diatoms, and the low light levels created by diatom blooms [36,78]. Considered a harmful species, A. anophaegefferens has devastated the scallop industry in that area, indicating the cascade of effects continues to other trophic levels [36].
Cyanobacteria are another example of unicellular organisms that are influenced by the cascading effects of SGD [32,37,70]. These photosynthetic bacteria are also commonly referred to as blue-green algae, as they are influenced by many of the same environmental variables as autotrophic phytoplankton. Cyanobacteria have been shown to increase in abundance due to the cascading effects of SGD-influenced diatom blooms on a fringing reef off the coast of Japan [32]. Cyanobacteria have also been shown to increase in abundance away from shore, as diatom abundances decline in both the coastal waters of Japan and a lagoon adjacent to the Gulf of Mexico [37,70]. It is not fully understood whether diatom-mediated nutrient transformation alone caused the increasing cyanobacteria abundance with distance, or if other factors such as higher salinity or alternate nutrient sources were also implicated [84].
The last group of phytoplankton that has been shown to be subject to the cascading effects of SGD nutrient loading is cryptophytes [32,59]. Cryptophytes are near-flat, oval-shaped, plastid-containing algae with two unequal flagella [123]. With some members of this class exhibiting mixotrophic behavior, they can be influenced by SGD indirectly in two ways: (1) they can take up nutrients supplied by SGD directly or indirectly via diatom nutrient transformation, or (2) they can graze on other phytoplankton, like diatoms, that increase in abundance in response to SGD [32,59].
SGD also directly affects non-diatom phytoplankton through nutrient loading. The pico-cyanobacterium Synechococcus exhibited a response to groundwater additions in a mesocosm experiment conducted in the Western Mediterranean, but the response was not repeated in a later experiment in coastal California [29,31]. SGD loading of anthropogenic ammonium can induce an increase in dinoflagellates, as has been shown off the coast of New York [33], the Yucatan Peninsula [40,93], and Korea [7]. However, the response of the dinoflagellate community overall was not uniform across these studies. Gobler and Boneillo [33] observed a dinoflagellate-dominated community, whereas the other studies observed diatoms increasing in concert with the dinoflagellates, due to nutrients (nitrate and silicate) being supplied by the SGD. The effects of nutrients from SGD on phytoplankton and bacteria are summarized in Figure 2A.

Figure 2.
Summary of the effects of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) on phytoplankton and bacteria. In (A), loading of high nitrate and dissolved silica groundwater induces the growth of diatoms that take up nitrate and phosphate from the water column. The diatoms transform the inorganic nutrients into organic nitrogen and phosphorous, which are taken up by dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria or brown tides. Cryptophytes graze the dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria. Loading of groundwater that is high in ammonium and phosphate aids in the development of dinoflagellates in addition to diatoms. In (B), discharge of fresh groundwater increases the abundance of freshwater-preferring and pennate diatoms. Saline SGD from seawater that has circulated through the coastal aquifer spurs the growth of Pseudo-nitzschia. Vertical mixing from high discharge submarine springs suspends benthic diatoms and dinoflagellates. In (C), fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) and enteric viruses enter the groundwater system from anthropogenic waste sources. The FIB are diluted as salinity increases, until FIB and viruses are output to the coastal ocean via SGD. Concentrations of FIB abundance decrease faster than viruses, due to their faster degradation time in seawater. Viruses and FIB negatively affect corals, in addition to causing beach closures.
Aside from nutrients, SGD also affects phytoplankton and bacteria by altering salinity. Pseudo-nitzschia is unique in its affinity for high salinity SGD, as the presence of low salinity SGD or rivers has corresponded with higher relative abundances of other diatom species. A study of the Yucatan Peninsula that explored differences in diatom species across sites receiving different types of SGD hypothesized that the thick frustules of some pennate diatoms, such as Synedra gailloni and Striatella interrupta, allowed these diatoms to withstand low salinity SGD that was high in nitrate and dissolved silica [93]. Similarly, the abundance of Chaetoceros, a chain-forming centric diatom genera that also has a relatively complex frustule structure, increased in response to low salinity river water treatments, more so than higher salinity groundwater additions in the Gulf of Alaska [30]. The influence of low salinity SGD can be so extreme that it can support the presence of benthic freshwater diatom species (Anorthoneis dulcis, Karayevia oblongella, Planothidium delicatulum, and Stauroneis spp.) around the submarine springs off the coast of Brisbane, Australia [85]. However, low salinity associated with SGD from submarine springs has also been thought to limit the primary productivity of phytoplankton in some cases, although temperature differences also caused by the springs could not be ruled out [34]. Salinity effects can extend to other members of the planktonic community. For example, bacteria communities at a SGD seepage face on Jeju Island, Korea shifted to freshwater-preferring-bacteria at low tide, when salinity decreased, and returned to seawater-preferring bacteria at high tide [39]. However, it is unknown whether this shifting population was the result of changes in salinity itself, or an indicator of physical processes that transported the bacteria [39].
Physical processes associated with SGD can transport both bacteria and phytoplankton to the water column, as well as re-suspend organisms already present. It has been proposed that groundwater flow from fresh aquifers can flush bacteria from fractured coastal aquifer substrate into the water column [39]. Sediment-filled column tests of bacteria-laden water have also shown that bacteria can be transported through a coastal aquifer, as sand does not act as a bacterial filter [67]. Tidal flushing of the coastal aquifer has also been proposed to transport bacteria into the water column [39]. In karst environments, vertical mixing due to high rates of SGD at submarine springs can suspend benthic diatoms and dinoflagellates in the water column [40]. The physical presence of water in seepage face sediments compared to the surrounding areas promotes benthic diatom persistence at low tide, which has cascading effects for predators of the diatoms [57]. The physical and salinity effects of SGD on phytoplankton and bacteria are summarized in Figure 2B.
SGD can also play a role in transporting allochthonous bacteria and viruses from anthropogenic sources to the coastal ocean. Examples include fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) such as Escherichia coli and enterococci, as well as human enteric viruses [45,48,62,67]. Sequencing of surface proteins can specifically link the presence of enterococci and enteric viruses to human sewage [48,62]. Enteric viruses and bacteria enter the groundwater system through septic systems, cesspools, and injection wells of treated sewage [48,62]. Coastal aquifers may provide an ideal conduit for the replication and transportation of FIB, as the bacteria are protected from exposure to sunlight, which can kill them [67]. Once in the groundwater system, these viruses and bacteria can be transported to coastal waters via SGD [48,62]; although, in a clastic aquifer, human-sourced bacteria did not discharge due to dilution or filtering of the bacteria within the aquifer [45]. High degradation rates of FIB in marine waters may also cause lower concentrations of FIB in coastal aquifer water as salinity increases [48]. Degradation rates of some enteric viruses can be much longer than for FIB, which supports observations of their abundance remaining relatively constant with distance from the shore [48]. Implications of SGD transport of enteric bacteria and viruses to the ocean include beach closures, as has occurred in California [45,67], Hawaii [62], and the Florida Keys [48]. Other marine organisms can also be affected by the presence of FIB and enteric viruses, such as corals that develop white pox disease as a result of exposure to FIB [124]. A study of the abundance of corals and enteric viruses and bacteria sourced from SGD also found that concentrations of bacteria and viruses were higher in coastal water where coral was present, indicating there may be some longer term interplay between these organisms once the bacteria and viruses are transported to the ocean [48]. Solutes associated with waste, such as methane, can also impact bacteria as well. This was shown in the Baltic Sea where areas of methane and sulfate transport through SGD resulted in increased bacterial activity through aerobic methane oxidation and sulfate reduction [107]. The effects of SGD on FIB and enteric viruses are summarized in Figure 2C.
Recently, molecular methods have been applied to examine the effects of SGD on the diversity of microbial communities in coastal aquifers, where salinity, oxygen, and nutrient gradients have been found to directly influence the diversity of microbes involved in the nitrogen cycle. In Huntington Beach, California, the nitrite reductase gene fragments nirK and nirS showed that unique communities of taxonomically diverse denitrifiers existed in close spatial proximity along steep salinity and nitrate gradients [68]. Similarly, the composition of betaproteobacterial ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (β-AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) was assessed using the gene for the ammoniamono-oxygenase subunit A (amoA) [69]. They found that salinity, oxygen, and nutrient levels drove the relative proportions of the two groups. Specifically, seasonal shifts in the location of the brackish mixing zone had a large influence on where the transition between β -AOB- and AOA-dominated communities occurred, suggesting a strong link between coastal hydrology and microbial community composition. Different AOA communities have also been shown to exist at different depths within coastal sediment influenced by groundwater. A study in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts, Rogers and Casciotti [91] showed that genetically distinct AOA populations occurred in the ventilated top meter of sediment compared to deeper communities in a region of fresh and salt water mixing with gradients of oxygen, nitrate, and ammonium. These studies demonstrate how molecular methods can reveal the microdiversity of microbial populations, and shed light on how physical and chemical gradients influence their distributions and biogeochemical activity.
3. Macrophytes
SGD has also been shown to affect oceanic macrophytes. Macrophytes encompass both macroalgae, such as kelp, and marine plants, such as turtle grass. Although comprising members of different kingdoms, macrophytes contain many anatomical similarities, and they often react similarly when exposed to SGD [26,72,75,90]. The benthic nature of many macrophytes, which use holdfasts or root-like structures that anchor them to the sea floor, means they can be anchored at the location of discharging groundwater, giving them the first opportunity to take advantage of nutrient loading via SGD [7,27,72,75]. Macrophytes may uptake nutrients from the water column through their leaves and blades, or from sediment pore water through roots and root-like structures, allowing some species to access SGD-laden nutrients before the groundwater discharges to the water column [27,71,72].
Macrophytes on the whole are particularly sensitive to SGD with high DIN associated with anthropogenic activities, and macrophyte blooms have become common in areas where DIN pollutes SGD. One of the first studies to make this link used groundwater flow maps paired with DIN data to show transport of DIN from cesspools and septic systems outside of Perth, Australia to a neighboring estuary that experienced blooms of the green macroalgae Cladophora albida. These blooms were unobserved prior to the 1960s, but were common at the time of study in the 1970s [86]. With the advent of technology that allows for evaluating δ15N in macrophyte tissues, several subsequent studies have directly linked the nitrogen found in algal and plant tissues to anthropogenic sources, including wastewater and agriculture. Not limited to one region, this link has been established in various areas surrounding Hawaii [26,60], Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts [90], the Atlantic coast of Florida [72], coastal Kenya and Zanzibar Island [109], and the west coast of the main island of Japan [80] in various macrophyte species. Macrophyte tissues that mirror the δ15N of SGD tend to coincide with higher nitrogen concentrations, higher N:P ratios, larger leaf and blade area, reduced macrophyte biodiversity, and higher macrophyte biomass [26,28,72,109]. Moving away from SGD sources, these effects are less pronounced as δ15N in macrophyte tissues assume oceanic values [26,28,72]. Lacking δ15N data, higher concentrations of nitrogen and N:P ratios, along with larger leaf/blade area and biomass closer to known SGD areas, have also been observed [27,47,55]. Changes in the δ15N of macrophyte tissues due to SGD loading can propagate through the ecosystem via trophic transfer [90].
The most commonly studied macrophyte that has shown these trends is the green macroalgae in the genus Ulva, commonly referred to as sea lettuce. Lacking roots, this genus uptakes nutrients directly from the water column through its blades, and is therefore sensitive to water column nutrient concentrations, even thriving in high nutrient conditions that would inhibit other organisms [125]. Ulva spp. respond positively to nitrogen-loading via SGD, and SGD has been implicated in the development of green tides caused by Ulva spp. [7,71]. Supporting these field observations, a mesocosm experiment where Ulva spp. were exposed to local SGD laden with DIN, growth rates increased by 160% on average [71]. Even in non-bloom conditions, SGD has been shown to contribute 15.5 to 42.8% of nitrogen to Ulva spp. in areas of known SGD influence, and where agriculture is a common land use [80]. Furthermore, areas of increased Ulva spp. abundance due to anthropogenic nitrogen inputs via SGD also have lower diversity and species richness, as Ulva spp. outcompete other local organisms or stress them via other biochemical pathways [26]. A genus common to coastal waters, δ15N of Ulva spp. tissue can give an estimate of the importance of nitrogen-loading via SGD across a wide variety of ecosystems [125].
However, the presence of nitrogen loading via SGD does not always positively influence macrophytes, as demonstrated by a case study of eelgrass (Zostera marina), a flowering marine plant in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. SGD in Waquoit Bay is heavily influenced by anthropogenic nitrogen, which is reflected in the δ15N of DIN in SGD [90]. Yet, as nutrient loading through SGD increased as the area developed, eelgrass cover decreased rapidly, and eelgrass beds became fragmented [41]. Eelgrass was not the only organism to be influenced by nitrogen loading via SGD, as phytoplankton and epiphytes increased in abundance as well, shading the eelgrass, stressing the macrophyte through light limitation, which ultimately led to decline of the macrophyte [41,89].
SGD can affect macrophytes in ways other than increasing or decreasing abundance caused by nitrogen loading, as has repeatedly been shown with turtle grass (Thalassia testudinum), a marine plant that is capable of taking up nutrients from the water column through the leaves and from pore water through the roots [27]. As shown in a study of turtle grass in Laguna Madre, on the Texas coast, nitrogen loading of turtle grass through pore water resulted not only in significantly higher nitrogen concentrations in turtle grass tissue and larger leaf size, but also lead to a significant decline in flower production [27]. An adaptation to move offspring to more favorable conditions, flowering is not needed when nutrient limitation is lifted by SGD; instead the turtle grass invested more energy in growth than reproduction [27]. Nitrogen loading through SGD has also been shown to push turtle grass toward phosphorous-limitation in Discovery Bay, Jamaica. Herbivores began to prefer turtle grass with a lower N:P ratio, due to lack of exposure to SGD [47]. SGD was shown also to influence phosphorous in turtle grass tissue in a Yucatán lagoon with known SGD points [92]. In this case, phosphorous concentrations increased in turtle grass tissue that was closer to the SGD source, but not nitrogen [92]. This change in phosphorous concentration was attributed to either high phosphorous concentrations in the SGD, or high concentrations of iron in the SGD, which can enhance the uptake of phosphorous [92]. Therefore, as with phytoplankton and bacteria, SGD can affect macrophytes in a variety of ways other than just by enhancing macrophyte primary productivity or increasing biomass.
4. Animals
While there is evidence that SGD impacts a wide variety of animal taxa, most of the studies that assessed those impacts focused on invertebrates. One of the most commonly studied invertebrates in this respect are corals. Sometimes the impact of SGD on corals causes no apparent physical stress, but it can affect the isotopic signature, such as by altering the δ18O and δ15N signatures or rare earth element ratios of corals on century to Holocene scales [101,108,110]. More often, the presence of SGD in a coral ecosystem results in a reduction of coral cover and coral species diversity [26,74,94]. However, the reasons for these decreases vary site-to-site. In the case of Biscayne Bay, Florida areas of lower salinity due to SGD and runoff had less coral extent and diversity overall. Furthermore, the lower salinity areas displayed an absence of reef-building species, and lower growth rates among one of the only corals to inhabit lower salinity areas Siderastrea radians [74]. The oligotrophic-preferring nature of corals can also be at odds with nutrient loading from SGD. In Hawaii, lower coral diversity and abundance was associated with nitrogen loading through SGD [26]. Lastly, as a calcifying organism, corals can be negatively impacted by low pH and low aragonite/calcite saturation, often associated with water discharging from submarine springs, as is the case on the Yucatan peninsula. Changes to the carbon chemistry of the coastal waters off the Yucatan due to SGD has been linked to lower coral cover, smaller coral size, and reduced species richness, with no reef-building species present in the SGD-impacted areas [94]. Indeed, only scleractinian corals were observed close to the SGD springs [94]. However, even scleractinian corals that could withstand the low pH/saturation waters experienced negative consequences of lower tissue density and higher erosion from burrowing animals [42]. Similar impacts of low pH/saturation waters at this site have also been found in calcifying benthic foraminifera. Areas closer to springs had lower absolute abundances of these organisms, and a shift in relative abundance was observed from heterotrophic foraminifera to symbiont-bearing foraminifera [95]. This observed trend of calcifying corals and foraminifera suffering under low pH/saturation SGD suggests that other calcifying animals could similarly find such conditions taxing.
Another organismal group that has been much studied with respect to SGD impacts is the meiofaunal community. Meiofauna are animals that live in the pore spaces between shallow sediments, extending no more than 500 µm in length, and consisting of segmented worms, nematodes, and other small animals [126]. These animals may be the first to interact with SGD, as they live within the sediment through which SGD must pass before discharging. Like corals, the response of meiofauna across SGD study sites differed with the biogeochemical changes caused by SGD at each site. In coastal Portugal, SGD impacted sites were associated with higher meiofaunal species richness and diversity than non-SGD-impacted sites [97]. The increase was attributed to the presence of finer grain sizes at the SGD-impacted site, possibly due to SGD transporting finer grains to the water–sediment interface, although an increase in primary production due to SGD nutrient transport could not be ruled out [97]. In contrast, studies of coastal Poland and France observed a decrease in abundance of the meiofaunal community at SGD-impacted sites as a result of lower salinity that most meiofauna could not tolerate [76,105]. When studying the impacts of SGD on the meiofaunal community, special consideration must be given to nematodes, as this phylum is a large component of the meiofaunal community, dominating the community structure in some areas [76,79]. Not all nematodes react similarly to the presence of SGD. Even considering studies where a change in salinity due to SGD was the driving factor, nematode abundances decreased in coastal Poland and increased in coastal Long Island, New York [76,79]. These different responses of nematodes in different areas may be due to the genera present at each site, as opportunistic genera increase in abundance when exposed to lower salinity caused by SGD, even as nematode diversity decreases [79].
Benthic macrofauna, including but not limited to large marine worms, bivalves, and crabs, are similarly impacted by the presence of SGD. The presence of SGD can alter the δ15N and δ13C signature of benthic macrofauna to mirror terrestrial sources [90,104]. The consistency of effects has also been observed in marine worms, with general shifts towards the class Polychaeta (bristled segmented worms), due to their ability to withstand a wider range of salinities than their competitors [98,99,102,103,104,106]. Several Polychaeta species have specifically been identified as increasing in abundance with SGD influence, but only Nereis diversicolor has been observed to be more abundant in areas of SGD influence across multiple locations [104,106]. Outside of the Polychatae class, SGD can also impact flatworms (Symsagittifera roscoffensis) that contain symbiotic algae, as the flatworms assimilate nitrate from SGD when light is present for their symbionts [96]. Yet, consistency in response of marine animals to SGD influence are not limited to marine worms. Locations of SGD also tend to see shifts towards omnivores and carnivores [57,82,98,104]. Such shifts are associated with increased food supply due to increased primary productivity and stabilized environmental conditions, such as temperature and sediment moisture content, and include such animals as isopods [98], snails [57,82,100], and crabs [57,82]. Although not benthic species, the fish Japanese temperate bass (Lateolabrax japonicas), black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii), and juvenile marbled sole (Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae) have also been observed to dominate areas under the influence of SGD, due to these same reasons [82,83].
However when considering other parts of the coastal ecosystem, the effects of SGD on the benthic macrofaunal community as a whole vary across sites, even contradicting each other. Species richness and diversity of benthic macrofauna can be reduced in some areas due to stress from changing salinities [105], while in other locations, the stabilizing temperature and food supply caused by SGD can increase benthic macrofaunal diversity, species richness, and biomass [82]. Indeed, contradictory studies on the changes in bivalve community have been completed, even though the underlying mechanism of nutrient loading was the same in all cases [89,98,100]. Nutrient loading through SGD increased primary production and increased the abundance of mussels and barnacles in south Portugal [98,100]. In contrast, nutrient loading in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts, induced a shift from eelgrass to macroalgae, and was associated with a decline in the bay scallop Argopecten irradians [89].
Due to these varying results of nutrient loading from SGD on marine animals, it cannot always be assumed that SGD has a positive impact on marine ecosystems. The benefits of nutrient input may be outweighed by salinity swings that local marine fauna cannot tolerate, lowered pH, and calcite/aragonite saturation that stresses calcifying organisms, or nutrient loading that causes a reduction in corals or bivalves. Indeed, these negative effects of SGD on marine organisms are the only negative outcomes that are currently known to occur. More negative consequences may be identified in future literature.
5. Ecosystem Studies
Determining the extent to which SGD influences and alters the biota of coastal ecosystems as a whole has been approached historically via two methods. The first method involves utilizing geochemical parameters (such as DIC concentration, pH, total alkalinity, and δ13-DIC) of the coastal water to determine net community production (NCP) and net community calcification (NCC). SGD has been shown to increase NCP through nutrient loading [66,77]. However, the NCP may actually be reduced in areas where SGD supplies oxygen to the water column continuously, allowing respiration to continue unheeded through the nighttime when photosynthesis is reduced from light limitation [61]. Also, an increase in NCP due to SGD-influence is not necessarily followed by an increase in respiration, if other solutes in the SGD inhibit respiration. For example, high methane concentrations from SGD may reduce dissolved oxygen concentrations through aerobic methane oxidation, or labile dissolved organic carbon (DOC) may be replaced in the water column by refractive SGD-sourced DOC [77]. Like NCP, NCC can also be positively or negatively influenced by SGD. Nutrients supplied by SGD can induce an increase in NCC [66]. However, if SGD increases respiration to the point that carbon dioxide concentration in the water column increase substantially, the ecosystem may experience conditions that cause dissolution of calcareous shells and skeletons [61]. By calculating an increase or decrease in NCP and NCC from geochemical tracers, researchers can look into how SGD influences biota in an ecosystem as a whole.
The second method of determining net ecosystem changes from SGD include quantifying the abundances of various organisms, and inferring the interplay between them. Amato et al. [26] is one such study by which surveys of benthic marine biota were conducted at sites with known SGD influences. The surveys, combined with biogeochemical analyses of water and marine life, were able to show how areas impacted by large nitrogen-loading through SGD experienced lower diversity and species richness, in addition to an overall shift away from coral and turf algae to macroalgae [26]. Such a decrease in diversity due to macroalgal proliferation caused by SGD was also observed in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts [89]. Such decreases in diversity can still be accompanied by increases in benthic metabolism and primary productivity, as [105] showed in Roscoff Aber Bay, France. This study highlights the need for conservative interpretations when ascertaining the influence of SGD on productivity. Increased productivity due to SGD may not benefit the health of an ecosystem if it is accompanied by decreased biodiversity or loss of indigenous biota. In contrast, SGD can induce overall positive changes at the ecosystem level as shown by [57], in two Korean bays. In this study, the presence of SGD seepage faces in mudflats allowed for the proliferation of diatoms by keeping the sediment moist and providing nutrients, which in turn led to a proliferation of grazers such as the mud snail (Batillaria cumingi) and the ghost crab (Scopimera sp.). Additionally, the moist seepage faces created a haven for all benthic species to prevent desiccation during low tide [57]. Therefore, whether SGD exudes a positive or negative effect on an ecosystem requires actual measurement of the fauna and flora reactions, rather than simply calculating primary productivity that might be supported by SGD nutrient loading, and presuming a positive or negative impact.
6. Research Priorities
Despite the numerous studies described in this paper that ascertained an effect of SGD on marine biota, they are still vastly outnumbered by studies that solely determine the flux of solutes via SGD in coastal systems. Yet, without determining the biological effects of SGD quantifiably, the flux studies are incomplete in their interpretation of the system. An overall shift towards including marine biota assessment in future SGD studies is needed to create the context through which SGD solute fluxes can be assessed. Depending on the research approach, the data created may result in two complementary studies (e.g., [61] and [127], [6] and [30], or [26] and [128]) or a single cohesive study (e.g., [29,37]). Even adding one biological parameter among the existing sampling plan of a traditional SGD flux study will provide insight into how SGD influences local biota. One such parameter that may be easily implemented in a tracer study of SGD (such as radon or radium) is the collection of chlorophyll a concentration samples. The tracer and chlorophyll a concentrations can be analyzed in concert to infer a relationship between SGD and phytoplankton, and this is useful because of the bottom up effects of nutrients from SGD on marine food webs.
Aside from integrating biological indicators into standard SGD studies, there is also a need to conduct comprehensive ecosystem studies across a variety of coastal environments. Studies that assess how SGD influences the entire ecosystem, beyond phytoplankton or macrophytes, are the least common and they are most insightful (e.g., [26,105]). Such studies are the only way to know if SGD truly supports an ecosystem through solute loading, or whether it has negative consequences such as reducing species richness, biodiversity, and calcification. To date, these studies have only been completed in a handful of environments. As SGD is a common hydrological process in many environments worldwide, ecosystem studies of representative coastal environments are needed to fully know the effect of SGD on marine biota worldwide.
7. Conclusions
In summary, SGD has been shown to influence marine biota across a variety of coastal ecosystems. Nutrient loading through SGD supports the primary productivity of uni- and multicellular algae and plants. As SGD is often a more constant source of nutrients to coastal systems than episodic inputs like runoff, upwelling, or atmospheric deposition, it can sustain an ecosystem consistently over time. Increased primary productivity can further support higher trophic levels. In some cases, SGD can even allow for freshwater organisms to survive in coastal systems.
However helpful in some ecosystems, SGD can also act as a conduit of anthropogenic pollution to coastal regions, which negatively influences coastal ecosystems. The cascading effects of increased primary production may include the growth of harmful algae, increased light limitation of benthic fauna, eutrophication, blooms of opportunistic species, and decreased biodiversity. Additionally, the lower salinity associated with some types of SGD can stress local fauna and flora, allowing opportunistic species to dominate systems. Furthermore, the low pH and calcite/aragonite saturation state of some SGD springs have proven to be a metabolic obstacle for calcifying marine organisms. More study is needed for the comprehensive assessment of SGD’s impact on marine systems globally.
Author Contributions
A.L.L. and K.R.M.M. wrote and revised the manuscript.
Funding
Article Processing Charges was sponsored by MDPI.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Robert Stote for proofreading the manuscript and providing comments for its improvement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lecher, A.L. Groundwater Discharge in the Arctic: A Review of Studies and Implications for Biogeochemistry. Hydrology 2017, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Cable, J.E.; Turner, J.V. Investigation of submarine groundwater discharge. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the ocean. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, W.S. The subterranean estuary: A reaction zone of ground water and sea water. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomp, C.P.; Van Cappellen, P. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: Controls and potential impact. J. Hydrol. 2004, 295, 64–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecher, A.L.; Chien, C.; Paytan, A. Submarine groundwater discharge as a source of nutrients to the North Pacific and Arctic coastal ocean. Mar. Chem. 2016, 186, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.W.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, G. Large submarine groundwater discharge and benthic eutrophication on Bangdu Bay on volcanic Jeju Island, Korea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellenbarger, G.; Monismith, S.; Genin, A.; Paytan, A. The importance of submarine groundwater discharge to the nearshore nutrient supply in the Gulf of Aqaba (Israel). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.; Kim, G.; Primeau, F.; Moore, W.; Cho, H.-M.; DeVries, T.; Sarmiento, J.; Charette, M.; Cho, Y.-K. Global Estimate of Submarine Groundwater Discharge Based on an Observationally Constrained Radium Isotope Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8438–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Key, R.M. Submarine groundwater discharge revealed by 228Ra distribution in the upper Atlantic Ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, F.J.; Paytan, A.; Knee, K.L.; De Sieyes, N.R.; Ganguli, P.M.; Gray, E.; Flegal, A.R. Submarine groundwater discharge of total mercury and monomethylmercury to central California coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5652–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georg, R.B.; West, A.J.; Basu, A.R.; Halliday, A.N. Silicon fluxes and isotope composition of direct groundwater discharge into the Bay of Bengal and the effect on the global ocean silicon isotope budget. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 283, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosdorf, N.; Oehler, T. Societal use of fresh submarine groundwater discharge: An overlooked water resource. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.D.; Prepas, E.E. Groundwater-lake interactions: I. Accuracy of seepage meter estimates of lake seepage. J. Hydrol. 1990, 119, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Herbold, C.W.; Charette, M.A. An automated dye-dilution based seepage meter for the time-series measurement of submarine groundwater discharge. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2011, 1, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Smith, C.F.; Paulsen, R.J.; O’Rourke, D.; Krupa, S.L.; Christoff, J.L. Spatial and temporal distributions of submarine groundwater discharge rates obtained from various types of seepage meters at a site in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Fifteen years experience in measuring 224Ra and 223Ra by delayed-coincidence counting. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Peterson, R.; Moore, W.S.; de Oliveira, J. Radon and radium isotopes as tracers of submarine groundwater discharge—Results from the Ubatuba, Brazil SGD assessment intercomparison. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, T.; Mogollón, J.M.; Moosdorf, N.; Winkler, A.; Kopf, A.; Pichler, T. Submarine groundwater discharge within a landslide scar at the French Mediterranean coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.G.; Rodellas, V.; Andrisoa, A.; Stieglitz, T.C. Exchange across the sediment-water interface quantified from porewater radon profiles. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaiova, H.; Camilli, R.; Henderson, P.B.; Charette, M.A. Coupled radon, methane and nitrate sensors for large-scale assessment of groundwater discharge and non-point source pollution to coastal waters. J. Environ. Radioact. 2010, 101, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paytan, A.; Lecher, A.L.; Dimova, N.; Sparrow, K.J.; Kodovska, F.G.-T.; Murray, J.; Tulaczyk, S.; Kessler, J.D. Methane transport from the active layer to lakes in the Arctic using Toolik Lake, Alaska, as a case study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3636–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecher, A.L.; Fisher, A.T.; Paytan, A. Submarine groundwater discharge in Northern Monterey Bay, California: Evaluation by mixing and mass balance models. Mar. Chem. 2016, 179, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.B.; Gonneea, M.E.; Fong, D.A.; Moore, W.S.; Herrera-Silveira, J.; Paytan, A. Characterizing sources of groundwater to a tropical coastal lagoon in a karstic area using radium isotopes and water chemistry. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Rocha, C. Regional scale assessment of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Ireland combining medium resolution satellite imagery and geochemical tracing techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, D.W.; Bishop, J.M.; Glenn, C.R.; Dulai, H.; Smith, C.M. Impact of submarine groundwater discharge on marine water quality and reef biota of Maui. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, K.M.; Dunton, K.H. Plasticity in turtle grass (Thalassia testudinum) flower production as a response to porewater nitrogen availability. Aquat. Bot. 2017, 138, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, Y.; Miyajima, T.; Yamamuro, M.; Kayanne, H.; Koike, I. Fine-scale mapping of land-derived nitrogen in coral reefs by δ15N in macroalgae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecher, A.L.; Mackey, K.; Kudela, R.; Ryan, J.; Fisher, A.; Murray, J.; Paytan, A. Nutrient loading through submarine groundwater discharge and phytoplankton growth in Monterey bay, CA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecher, A.L.; Mackey, K.R.M.; Paytan, A. River and submarine groundwater discharge effects on diatom phytoplankton abundance in the Gulf of Alaska. Hydrology 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, E.; Basterretxea, G.; Tovar-Sánchez, A. Changes in microbial communities in response to submarine groundwater input. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 438, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.C.; Nadaoka, K.; Yamamoto, T. Planktonic and benthic microalgal community composition as indicators of terrestrial influence on a fringing reef in Ishigaki Island, Southwest Japan. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobler, C.J.; Boneillo, G.E. Impacts of anthropogenically influenced groundwater seepage on water chemistry and phytoplankton dynamics within a coastal marine system. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 255, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, R.; Kitagawa, K.; Nishi, S.; Honda, H.; Yamada, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Shoji, J.; Ohsawa, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Tominaga, O. Phytoplankton primary productivity around submarine groundwater discharge in nearshore coasts. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 563, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: Importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as “new” nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, J.; Nuzzi, R.; Waters, R.; Wyman, K.; Falkowski, P.; Wallace, D. Brown Tide blooms in Long Island’s coastal waters linked to interannual variability in groundwater flow. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1997, 3, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Burnett, W.C.; Eller, K.T.; MacIntyre, H.L.; Mortazavi, B.; Leifer, J.; Novoveska, L. Radon and radium isotopes, groundwater discharge and harmful algal blooms in Little Lagoon, Alabama. In Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; Volume 6, pp. 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Liefer, J.D.; MacIntyre, H.L.; Novoveská, L.; Smith, W.L.; Dorsey, C.P. Temporal and spatial variability in Pseudo-nitzschia spp. in Alabama coastal waters: A “hot spot” linked to submarine groundwater discharge? Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Shin, D.; Hyun, S.P.; Ko, K.-S.; Moon, H.S.; Koh, D.-C.; Ha, K.; Kim, B.-Y. Periodic change in coastal microbial community structure associated with submarine groundwater discharge and tidal fluctuation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troccoli-Ghinaglia, L.; Herrera-Silveira, J.A.; Comín, F.A.; Díaz-Ramos, J.R. Phytoplankton community variations in tropical coastal area affected where submarine groundwater occurs. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Burdick, D.M. Quantifying Eelgrass Habitat Loss in Relation to Housing Development and Nitrogen Loading in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Estuaries 1996, 19, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, E.D.; Cohen, A.L.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Hernandez, L.; Paytan, A. Reduced calcification and lack of acclimatization by coral colonies growing in areas of persistent natural acidification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11044–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironet, F.N.; Jones, J.B. Treatments for ectoparasites and diseases in captive Western Australian dhufish. Aquac. Int. 2000, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qi, Z.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X. Submarine groundwater discharge as an important nutrient source influencing nutrient structure in coastal water of Daya Bay, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 225, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sieyes, N.; Yamahara, K.; Layton, B.; Joyce, E.; Boehm, A. Submarine discharge of nutrient-enriched fresh groundwater at Stinson Beach, California is enhanced during neap tides. Limnol. Ocean. 2008, 53, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.P.; Gower, J.F.R.; King, S.A.; Bissett, W.P.; Fischer, A.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Kolber, Z.; Mazzillo, F.; Rienecker, E.V.; Chavez, F.P. A coastal ocean extreme bloom incubator. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L12602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Stubler, A.D.; Wall, C.C.; Gobler, C.J. Nitrogen-rich groundwater intrusion affects productivity, but not herbivory, of the tropical seagrass thalassia testudinum. Aquat. Biol. 2012, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futch, J.C.; Griffin, D.W.; Lipp, E.K. Human enteric viruses in groundwater indicate offshore transport of human sewage to coral reefs of the Upper Florida Keys. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, M.J. Alkaline phosphatase activity in subtropical Central North Pacific waters using a sensitive fluorometric method. Mar. Biol. 1972, 15, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichard, S.L.; Paul, J.H. Detection of gene expression in genetically engineered microorganisms and natural phytoplankton populations in the marine environment by mRNA analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, E.S. The use of radio-active carbon (c14) for measuring organic production in the sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1952, 18, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, K.D.; Williams, P.J.L.; Marra, J.; Purdie, D.A.; Heinemann, K.; Eppley, R.W.; Bender, M.L. Primary production in the North Pacific gyre: A comparison of rates determined by the 14C, O2 concentration and 18O methods. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1989, 36, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.; Ribeiro, L.; Jesus, B.; Cartaxana, P.; Silva, J.M. Da Photosynthesis assessment in microphytobenthos using conventional and imaging pulse amplitude modulation fluorometry. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. 2018. odv.awi.de.
- Lapointe, B.E. Nutrient thresholds for bottom-up control of macroalgal blooms on coral reefs in Jamaica and southeast Florida. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-W.; Kim, G.; Lim, W.-A.; Hwang, D.-W. A relationship between submarine groundwater borne nutrients traced by Ra isotopes and the intensity of dinoflagellate red-tides occurring in the southern sea of Korea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waska, H.; Kim, G. Differences in microphytobenthos and macrofaunal abundances associated with groundwater discharge in the intertidal zone. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 407, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waska, H.; Kim, G. Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) as a main nutrient source for benthic and water-column primary production in a large intertidal environment of the Yellow Sea. J. Sea Res. 2011, 65, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Kim, G. Linking groundwater-borne nutrients and dinoflagellate red-tide outbreaks in the southern sea of Korea using a Ra tracer. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derse, E.; Knee, K.L.; Wankel, S.D.; Kendall, C.; Berg, C.J.; Paytan, A. Identifying sources of nitrogen to Hanalei Bay, Kauai, utilizing the nitrogen isotope signature of macroalgae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5217–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, C.M.; Dulai, H.; Popp, B.N.; Ruttenberg, K.; Fackrell, J.K. Submarine groundwater discharge drives biogeochemistry in two Hawaiian reefs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, S348–S363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knee, K.L.; Layton, B.A.; Street, J.H.; Boehm, A.B.; Paytan, A. Sources of Nutrients and Fecal Indicator Bacteria to Nearshore Waters on the North Shore of Kaua`i (Hawai`i, USA). Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubarsky, K.A.; Silbiger, N.J.; Donahue, M.J. Effects of submarine groundwater discharge on coral accretion and bioerosion on two shallow reef flats. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouty, N.G.; Cohen, A.; Yates, K.K.; Storlazzi, C.D.; Swarzenski, P.W.; White, D. Vulnerability of Coral Reefs to Bioerosion From Land-Based Sources of Pollution. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 9319–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouty, N.G.; Yates, K.K.; Smiley, N.; Gallagher, C.; Cheriton, O.; Storlazzi, C.D. Carbonate system parameters of an algal-dominated reef along West Maui. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2467–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, A.; Santos, I.R. Nitrogen enrichment and speciation in a coral reef lagoon driven by groundwater inputs of bird guano. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7218–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Shellenbarger, G.G.; Paytan, A. Groundwater discharge: Potential association with fecal indicator bacteria in the surf zone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.E.; Boehm, A.B.; Francis, C.A. Denitrifier community composition along a nitrate and salinity gradient in a coastal aquifer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.E.; Francis, C.A.; De Sieyes, N.R.; Boehm, A.B. Shifts in the relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across physicochemical gradients in a subterranean estuary. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, A.C.; Watanabe, A.; Nadaoka, K.; Motooka, S.; Herrera, E.C.; Yamamoto, T. Estimation of nearshore groundwater discharge and its potential effects on a fringing coral reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.K.; Kang, H.; Oh, Y.H.; Park, S.R.; Kim, G. Green tide development associated with submarine groundwater discharge in a coastal harbor, Jeju, Korea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Barile, P.J.; Littler, M.M.; Littler, D.S. Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: II. Cross-shelf discrimination of nitrogen sources indicates widespread assimilation of sewage nitrogen. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Swarzenski, P.W. Hurricanes, submarine groundwater discharge, and Florida’s red tides. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirman, D.; Orlando, B.; Maciá, S.; Manzello, D.; Kaufman, L.; Biber, P.; Jones, T. Coral communities of Biscayne Bay, Florida and adjacent offshore areas: Diversity, abundance, distribution, and environmental correlates. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2003, 13, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohout, F.A.; Kolipinski, M.C. Biological zonation related to groundwater discharge along the shore of Biscayne Bay, Miami, Florida. In Estuaries; Lauff, G., Ed.; AAAS: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; pp. 488–499. [Google Scholar]
- Kotwicki, L.; Grzelak, K.; Czub, M.; Dellwig, O.; Gentz, T.; Szymczycha, B.; Böttcher, M.E. Submarine groundwater discharge to the Baltic coastal zone: Impacts on the meiofaunal community. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 129, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donis, D.; Janssen, F.; Liu, B.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Dellwig, O.; Escher, P.; Spitzy, A.; Böttcher, M.E. Biogeochemical impact of submarine ground water discharge on coastal surface sands of the southern Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 189, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Sañudo-Wilhelmy, S.A. Temporal variability of groundwater seepage and brown tide blooms in a Long Island embayment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 217, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelak, K.; Tamborski, J.; Kotwicki, L.; Bokuniewicz, H. Ecostructuring of marine nematode communities by submarine groundwater discharge. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 136, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Tominaga, O.; Sugimoto, R.; Kitagawa, K.; Yamanda, M.; Honda, H.; Shoki, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Ikuta, K.; Taniguchi, M. Evaluation of the environmental condition of Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) by using nitrate stable isotope ratio recorded in sea lettuce (Ulva sp.). In Proceedings of the JSFS 85th Anniversary-Commemorative International Symposim “Fisheries Science for Future Generations”, Tokyo, Japan, 22–24 September 2017; p. 5005. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, H.; Sugimoto, R.; Kobayashi, S. Submarine Groundwater Discharge and its Influence on Primary Production in Japanese Coasts: Case Study in Obama Bay. In The Water-Energy-Food Nexus; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya, T.; Hata, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Miyata, Y.; Yamada, M.; Tominaga, O.; Shoji, J.; Taniguchi, M. Higher species richness and abundance of fish and benthic invertebrates around submarine groundwater discharge in Obama Bay, Japan. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Hori, M.; Tomiyama, T.; Shoji, J. Occurrence, distribution and prey items of juvenile marbled sole Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae around a submarine groundwater seepage on a tidal flat in southwestern Japan. J. Sea Res. 2016, 111, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Burnett, W.C.; MacIntyre, H.L.; Liefer, J.D.; Peterson, R.N.; Viso, R. Natural Radon and Radium Isotopes for Assessing Groundwater Discharge into Little Lagoon, AL: Implications for Harmful Algal Blooms. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welti, N.; Gale, D.; Hayes, M.; Kumar, A.; Gasparon, M.; Gibbes, B.; Lockington, D. Intertidal diatom communities reflect patchiness in groundwater discharge. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, P.L. Urban groundwater as a possible nutrient source for an estuarine benthic algal bloom. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1982, 15, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.A.; Imberger, J. Modeling the impact of natural and anthropogenic nutrient sources on phytoplankton dynamics in a shallow coastal domain, Western Australia. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2014, 14, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sospedra, J.; Niencheski, L.F.H.; Falco, S.; Andrade, C.F.F.; Attisano, K.K.; Rodilla, M. Identifying the main sources of silicate in coastal waters of the Southern Gulf of Valencia (Western Mediterranean Sea). Oceanologia 2018, 60, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiela, I.; Foreman, K.; LaMontagne, M.; Hersh, D.; Costa, J.; Peckol, P.; DeMeo-Andreson, B.; D’Avanzo, C.; Babione, M.; Sham, C.-H.; et al. Couplings of Watersheds and Coastal Waters: Sources and Consequences of Nutrient Enrichment in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Estuaries 1992, 15, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.W.; Valiela, I.; Michener, R.H. Nitrogen-stable isotope signatures in estuarine food webs: A record of increasing urbanization in coastal watersheds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.R.; Casciotti, K.L. Abundance and diversity of archaeal ammonia oxidizers in a coastal groundwater system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7938–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, T.J.B.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Dennison, W.C. Influence of submarine springs and wastewater on nutrient dynamics of Caribbean seagrass meadows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Góngora, C.; Herrera-Silveira, J.A. Variations of phytoplankton community structure related to water quality trends in a tropical karstic coastal zone. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crook, E.D.; Potts, D.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Hernandez, L.; Paytan, A. Calcifying coral abundance near low-pH springs: Implications for future ocean acidification. Coral Reefs 2012, 31, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Hernandez-Terrones, L.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Paytan, A. Impact of carbonate saturation on large Caribbrean benthic foraminifera assemblages. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.F.; Rocha, C.; Fleming, A.; Veiga-Pires, C.; Aníbal, J. Interception of nutrient rich submarine groundwater discharge seepage on European temperate beaches by the acoel flatworm, Symsagittifera roscoffensis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encarnação, J.; Leitão, F.; Range, P.; Piló, D.; Chícharo, M.A.; Chícharo, L. The influence of submarine groundwater discharges on subtidal meiofauna assemblages in south Portugal (Algarve). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, J.; Leitão, F.; Range, P.; Piló, D.; Chícharo, M.A.; Chícharo, L. Local and temporal variations in near-shore macrobenthic communities associated with submarine groundwater discharges. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.F.; Tavares, P.; Shapouri, M.; Stigter, T.Y.; Monteiro, J.P.; Machado, M.; Cancela da Fonseca, L.; Ribeiro, L. Estuarine biodiversity as an indicator of groundwater discharge. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 97, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piló, D.; Barbosa, A.B.; Teodósio, M.A.; Encarnação, J.; Leitão, F.; Range, P.; Krug, L.A.; Cruz, J.; Chícharo, L. Are submarine groundwater discharges affecting the structure and physiological status of rocky intertidal communities? Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 136, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagan, M.K.; Ayliffe, L.K.; Opdyke, B.N.; Hopley, D.; Scott-Gagan, H.; Cowley, J. Coral oxygen isotope evidence for recent groundwater fluxes to the Australian Great Barrier Reef. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 43-1–43-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.C.; Ullman, W.J. Ecological Consequences of Ground Water Discharge to Delaware Bay, United States. Ground Water 2004, 42, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.K.; Miller, D.C. Hydrologic interactions of infaunal polychaetes and intertidal groundwater discharge. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 363, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouisse, V.; Riera, P.; Migné, A.; Leroux, C.; Davoult, D. Freshwater seepages and ephemeral macrolagae proliferation in an intertidal bay: I Effect on benthic community structure and food web. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migné, A.; Ouisse, V.; Hubas, C.; Davoult, D. Freshwater seepages and ephemeral macroalgae proliferation in an intertidal bay: II. Effect on benthic biomass and metabolism. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipperle, A.; Reise, K. Freshwater springs on intertidal sand flats cause a switch in dominance among polychaete worms. J. Sea Res. 2005, 54, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussmann, I.; Dando, P.R.; Niven, S.J.; Suess, E. Groundwater seepage in the marine environment: Role for mass flux and bacterial activity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 178, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erler, D.V.; Shepherd, B.O.; Linsley, B.K.; Lough, J.M.; Cantin, N.E. Coral skeletons record increasing agricultural related groundwater nitrogen inputs to a South Pacific reef over the past century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamermans, P.; Hemminga, M.A.; Tack, J.F.; Mateo, M.A.; Marbà, N.; Mtolera, M.; Stapel, J.; Verheyden, A.; Van Daele, T. Groundwater effects on diversity and abundance of lagoonal seagrasses in Kenya and on Zanzibar Island (East Africa). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 231, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, K.; Song, Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Feng, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S. Coral geochemical record of submarine groundwater discharge back to 1870 in the northern South China Sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 507, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekerci, Y.; Petrovskii, S. Mathematical Modelling of Plankton–Oxygen Dynamics Under the Climate Change. Bull. Math. Biol. 2015, 77, 2325–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomas, M.W.; Gilbert, P.M. Comparisons of nitrate uptake, storage, and reduction in marine diatoms and flagellates. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ryu, J.W.; Yang, H.S.; Yun, S.T. Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) into the Yellow Sea revealed by228Ra and226Ra isotopes: Implications for global silicate fluxes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M.A. The Si:C:N of marine diatoms: Interspecific variability and the effect of some environmental variables. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillane, T. Diatom Frustules as a Mechanical Defense against Predation by Heterotrophic Dinoflagellates. Master’s Thesis, Western Washington University, Bellingham, WA, USA, February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anschutz, P.; Smith, T.; Mouret, A.; Deborde, J.; Bujan, S.; Poirier, D.; Lecroart, P. Tidal sands as biogeochemical reactors. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tréguer, P.J.; De La Rocha, C.L. The World Ocean Silica Cycle. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainer, V.L.; Bates, S.S.; Lundholm, N.; Thessen, A.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Adams, N.G.; Trick, C.G. Pseudo-nitzschia physiological ecology, phylogeny, toxicity, monitoring and impacts on ecosystem health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.; Garrison, D.; Horner, R. Bloom dynamics and physiology producing pseudo-nitzschia species. In Physioligical Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 267–292. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, R.M.; Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Thomson, R.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trainer, V.L. An unprecedented coastwide toxic algal bloom linked to anomalous ocean conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10366–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnetzer, A.; Miller, P.E.; Schaffner, R.A.; Stauffer, B.A.; Jones, B.H.; Weisberg, S.B.; DiGiacomo, P.M.; Berelson, W.M.; Caron, D.A. Blooms of Pseudo-nitzschia and domic acid in the San Pedro Channel and Low Angeles harbor areas of the Southern California Bight, 2003–2004. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, K.R.M.; Mioni, C.E.; Ryan, J.P.; Paytan, A. Phosphorus cycling in the red tide incubator region of monterey bay in response to upwelling. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibberd, D.J.; Greenwood, A.D.; Bronwen Griffiths, H. Observations on the ultrastructure of the flagella and periplast in the cryptophyceae. Br. Phycol. J. 1971, 6, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, K.L.; Porter, J.W.; Ritchie, K.B.; Polson, S.W.; Mueller, E.; Peters, E.C.; Santavy, D.L.; Smith, G.W. The etiology of white pox, a lethal disease of the Caribbean elkhorn coral, Acropora palmata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8725–8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichberg, M.; Fox, S.E.; Olsen, Y.S.; Valiela, I.; Martinetto, P.; Iribarne, O.; Muto, E.Y.; Petti, M.A.V.; Corbisier, T.N.; Soto-Jiménez, M.; et al. Eutrophication and macroalgal blooms in temperate and tropical coastal waters: Nutrient enrichment experiments with Ulva spp. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 2624–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giere, O. Meiobenthology: The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9783540686613. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C.M.; Dulai, H.; Whittier, R.B. Sources and spatial variability of groundwater-delivered nutrients in Maunalua Bay, O‘ahu, Hawai‘i. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.M.; Glenn, C.R.; Amato, D.W.; Dulai, H. Effect of land use and groundwater flow path on submarine groundwater discharge nutrient flux. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 194–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).