Abstract
Flood pulses occur annually along the Tonle Sap River (TSR) due to the large volume of water flowing from Tonle Sap Lake (TSL), its tributaries, and the Mekong River (MR). This study describes the seasonal changes in inundation area and water volume in the floodplain along the TSR over three years. The method employed time series remote sensing images of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) satellite data, the digital elevation model (DEM) of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), bathymetric data, and observed water level data. Adding normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) as a “third band” in the maximum likelihood classification (MLC) provided higher accuracy compared to thresholding NDVI and pure MLC (two bands) only. The results showed that the inundation area ranged from 123.8 to 3251.2 km2 (mean: 1028.5 km2) with overall accuracy of 96.9%. The estimated water volume ranged from 418.3 to 2223.9 million m3 (mean: 917.3 million m3) from the dry to wet season, respectively. Seasonally, the TSR floodplain accounted for up to 5.3% and 3.2% of the mean annual inflow and outflow of the TSR, respectively. In addition to the TSL water reservoir, the TSR and its floodplain exchanged and stabilized the flow of the MR and its downstream delta, respectively. Overall, the obtained results have enhanced our understanding of the TSR, supporting further studies on river connectivity and reversal flow in this study area.
1. Introduction
Flooding is an important cyclic episode in floodplain ecosystems, actively bringing in and exchanging water, sediments, and nutrients [1,2,3]. In Cambodia, the Tonle Sap River (TSR) plays a unique hydrological role by actively exchanging water and materials between Tonle Sap Lake (TSL) and the Mekong River (MR) through reversal flow [4]. During the wet season, the TSR receives a large amount of water, filling up the TSL and its floodplains, and increasing the inundation area six-fold compared to the dry season. During the dry season, the TSL releases water to MR via the TSR, ensuring a sustainable flow to the Mekong Delta. This immutable connectivity of TSL and TSR is crucial for maintaining productivity and biodiversity [4,5,6,7,8]. The annual reversal flow of the TSR is essential for perpetuating ecosystem functions. For example, fish migration from the MR to TSL and its floodplains [9]. A recent study suggested that the TSL ecosystem is relatively healthy, having achieved a certain stage of maturity until at least 2010, albeit with a vulnerable food web structure [10].
The characteristics of the flood pulse in the TSR, including the timing and duration of the different phases, are fundamentally described by the water volume and water levels of MR and TSL. Approximately 53% of the water in TSL originates from MR either through TSR (50%) or overland flow (3%), whereas tributaries account for around 34% and precipitation contributes 13%. The average annual outflow of water from the lake is 81.9 km3, of which around 87% flows to the MR through the TSR (84%) and overland flow (3%), while 13% evaporates directly from the lake [11]. Due to the flat topography of the floodplain along the TSR, the extent of inundation is directly controlled by the water level of the MR [11].
Climate change and water-related infrastructure development, including the construction of hydropower plants upstream on the MR, have had a significant hydrological impact on TSL through alteration of the natural flow [6,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. As a result, the water level of TSL may peculiarly increase and decrease during the dry and wet season, respectively [6]. A reduction of 23% and 11% in water rising and falling rates, respectively, at Prek Kdam provides evidence of a diminished Tonle Sap flood pulse post 1991 [15]. Simulated average and maximum water levels predicted an increase over 2010–2049 as a result of predicted climate change [18]. In addition, a study on flooding in TSL found an increase in the area of open water from 18% to 21% and 2%–21% owing to water-related development and climate change, respectively [6]. These findings clearly show that the flood pulse in the TSR is experiencing disturbances.
As defined by Reid, et al. [19], hydrodynamic connectivity is influenced by three principal mechanisms: hydrological connection (flux), provision of resources (water, sediment, and nutrients), and hydraulics. Disturbance of these mechanisms most likely modifies geomorphology, size and shape, and water depth of the connecting river. Because the TSR serves as the natural medium for reversal flow to TSL and its floodplain, it is an important segment in hydrodynamic connectivity in this area. However, hydrological information on the TSR, such as total water volume storage of the river itself and its floodplain in different seasons, remain scarce. In this context, the TSR should be studied further in order to formulate measures and policies aimed at preserving and managing these precious water resources in a sustainable manner.
An understanding of the hydrology and monitoring of the water resources in this region, especially of the highly dynamic nature of the floodplain along the TSR, is needed if access to and the use of this resource is to be optimized, while minimizing the impact on people and the environment in the region. The vast inaccessible nature of the TSR makes it difficult to carry out in situ observations. However, remote sensing is a powerful and cost-effective method that can help overcome this problem. Remote sensing technology has so far been used to determine the extent of flooding over the TSL area [6,20,21,22,23,24]. Nevertheless, apart from mapping flooding, the results cannot be used to quantify the water volume fully along the TSR because underwater elevation was not considered, even though a digital elevation model (DEM) was used. The lack of underwater elevation information could lead to underestimates in water volume, particularly during the dry season. Although, the water volume in the dry season is relatively small compared with that in the wet season, it cannot be ignored in studies of seasonal change and drought. Combining DEM with bathymetric data can be used to reflect the underwater elevation of TSR fully. Thus, in this study, we use a simple method to extract the inundation area and estimate the volume of water in the floodplain along the TSR in different seasons over three years to determine the seasonal changes. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM)-DEM were combined with bathymetric data and water level observations. The results will help support studies of river connectivity in the TSR region in terms of water resources and flood management. They can be used to calibrate and validate hydrodynamic simulations of inundation.
2. Study Area
The study area included the TSR and its vast peripheral wetland floodplain, as derived from maps of the major flood extent and river catchment area [25] (Figure 1). The defined area covered approximately 4789.2 km2, 30.2% of the total surface area of its catchment (Figure 1). The TSR is approximately 120 km in length and joins the MR near Phnom Penh City. The climate in the study area is characterized by the long rainy season of the southwest monsoon, which lasts from May to October, followed by the dry season of the northeast monsoon from November to April. Average annual precipitation ranges from 1300 to 1500 mm. The flood pulse is an annual event driven by the southwest monsoon, which brings 65% of the total annual precipitation in the MR basin [26,27]. The characteristics of the flood pulse vary annually depending on the volume and water level of the TSR [4,28,29].
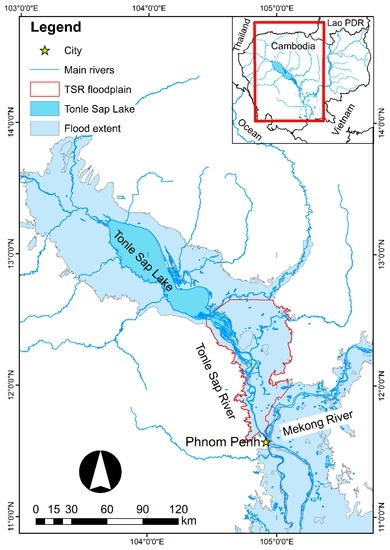
Figure 1.
Tonle Sap River (TSR) and its floodplain. The study area is enclosed by the red line.
3. Materials and Methods
The study consisted of two sequential parts: inundation area mapping and estimation of water volume (Figure 2). The inundation area was extracted from composite satellite images acquired from MODIS Terra product MOD09Q1 followed by an accuracy assessment based on visual interpretation. Water volume was then estimated by using the extracted inundation area and water level over the DEM.
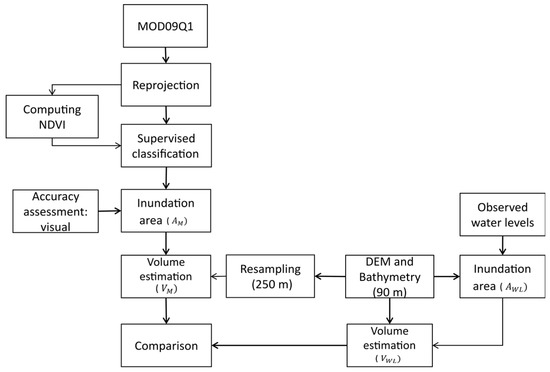
Figure 2.
Flowchart showing the method to estimate inundation area and water volume. DEM, digital elevation model; NDVI, normalized difference vegetation index.
3.1. Inundation Mapping
The inundation area was extracted using a parametric classification method known as supervised classification. The method was based on images obtained using MODIS, a multispectral instrument carried on two polar-orbiting satellites, Terra and Aqua, launched as part of National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)’s Earth Observation Sensor mission. MOD09Q1 is a surface reflectance product of MODIS/Terra. MOD09Q1 provides bands 1 (red) and 2 (near infrared) at 250 m resolution as an eight-day gridded level-3 product in a sinusoidal projection. Each MOD09Q1 pixel contains the best possible higher-order gridded level-2 (L2G) observation during an eight-day period, selected on the basis of high observation coverage, low viewing angle, the absence of clouds or cloud shadow, and aerosol loading. A detailed description of MOD09Q1 can be found in the MODIS algorithm theoretical basis document (ATBD) version 4 [30]. To avoid and minimize cloud cover, MOD09Q1 images were selected and acquired from cloud free days as much as possible in each month from 2003 to 2005.
Inundation area extraction was based on the distinct characteristics of band 2 and the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI). Solar irradiance band 2 (841–876 nm) in MOD09Q1 is highly absorbed by water bodies, making it a useful concept in classifying water and non-water (including cloud) cover. Similarly, although used to assess vegetation, NDVI can also be used to assess water cover, whereas temporal anomalies are efficient in detecting inundation [31]. NDVI uses the near-infrared band to determine water cover, which can then be computed using red and near-infrared band as shown in Equation (1) [32].
here, is the reflectance in the near-infrared band and is the reflectance in the red band. NDIV values range from −1 to 1, with values close to 1 indicating dense vegetation, values around 0 indicating bare soil and rock, and values close to −1 indicating water.
Given the characteristics of MODIS band 2 and NDVI that are sensitive to the presence of water, maximum likelihood classification (MLC) was then applied to distinguish the water and non-water cover. MLC used a combination of three bands consisting of bands 1 and 2 of MOD09Q1 and the computed NDVI. At least 20 regions-of-interest of water and non-water cover were selected based on visual observation for training the MLC.
The satellite images being analyzed were obtained much earlier (2003–2005). As such, ground truth data could no longer be obtained. Ground truth is the basis for computing the user’s accuracy, hence the user’s accuracy which comprises the second part of the overall accuracy could not be determined. Confining the assessment to the producer's accuracy is acceptable in such cases where the subject of study is sometime in the past. In some texts, producer's accuracy is even referred to as “accuracy” (See [33] and [34]). Since there were only two classes (water and non-water), it is implicit that belonging in one class does not lead to another unless there are pixels that were “unclassified”, and in this study there was no pixel left unclassified by MLC. Thus, the water pixels visually presented in MOD09Q1 image were used as reference for the accuracy assessment. Each MOD09Q1 image was visualized and displayed using band 2, 2, 1 as the red, green, and blue (RGB) color composite. In this color composite, water cover appears as light to dark blue depending on depth from shallow to deep. In total, 360 pixels (10 water pixel points for each image) were selected from water pixels as reference points covering deep and shallow water bodies. Accuracy was defined and assessed as the proportion of correctly classified water pixels to the total number of reference points and omission error (equal to 1 minus the accuracy) was used to measure the error of misclassified water pixels as non-water pixels [34]. This accuracy assessment was used and applied to other classification methods, thresholding NDVI (<−0.1) and pure MLC (two bands) for comparison.
3.2. Estimation of Water Volume
Coupled with the inundation map from MODIS classification, SRTM-DEM with 90 m resolution [35] was used to estimate inundation volume. As a pre-processing step, the void cells were removed and filled using the average of the neighboring cells. To be consistent, the resolution of SRTM-DEM was resampled from 90 m to conform to MOD09Q1 250 m. The dataset of hydrographic maps containing bathymetric data was obtained from the Mekong River Commission [36]. Bathymetric data of the TSR was digitized and interpolated based on the hydrographic maps surveyed in 1999. The coordinate system of SRTM-DEM was transformed from WGS84 to Indian 1954 projection and datum to provide a coordinate system consistent with the bathymetric data.
The extracted flood inundation area () consisting of multiple polygons was overlaid on the DEM to estimate the inundation water volume. The maximum elevation along the perimeter of each polygon was considered to be the elevation of the inundation water level in each individual polygon, in which values of all water pixels were set at this water level by assuming a flat water surface. The difference between the water level and DEM was assumed to be the water depth of each water pixel. Volume () was then estimated by summing the products of water depth and the DEM cell size of each water pixel (Equation (2)).
To evaluate the estimated volume results, was also compared with the mean water volume () derived from the water level observations at Kampong Luong (upstream), Prek Kdam (middle stream), and Phnom Penh Port (downstream), respectively. The observed water level of each station was used to mask and generate the inundation area () from the DEM for the same acquisition date as the MOD09Q1 images, assuming that the water surface is uniformly flat in the TSR and its floodplain. Thus, contained pixels of the DEM that have the same as or smaller values than the observed water level. The water volume was then estimated as described above using Equation (2), and the mean estimated from each water level station was compared with .
4. Results and Discussion
Section 4.1 discusses the seasonal changes in the inundated area and Section 4.2 provides the inundation results in terms of water volume. The results showing the seasonal changes in inundation area and water volume of the flood pulse on the floodplain along the TSR are then presented. The implications of these results are then discussed.
4.1. Inundation Area
The spatiotemporal revealed the flood cycle and pattern for the years 2003–2005 (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). ranged from 123.8 to 3251.2 km2 (mean: 1028.5 km2) from the dry to wet season, respectively. Compared to the reference points, achieved an overall accuracy of 96.9% with the omission error of 3.1% (Table 1). This result showed that the addition of NDVI as a “third band” in MLC provided higher accuracy compared to NDVI and pure MLC (two bands) only. According to the processed time series images, the water area of the floodplain increased from June to September. Flooding then extended from September to November with a peak in September, indicating three or four months of flood residence time. The water area gradually shrank from December to February, then dried up almost completely between March to May. This flood regime was the same as that reported by Arias et al. (2013) [26], with four distinct seasons: the rising season (June–August), the wet season (September–November), the receding season (December–February), and the dry season (March–May).
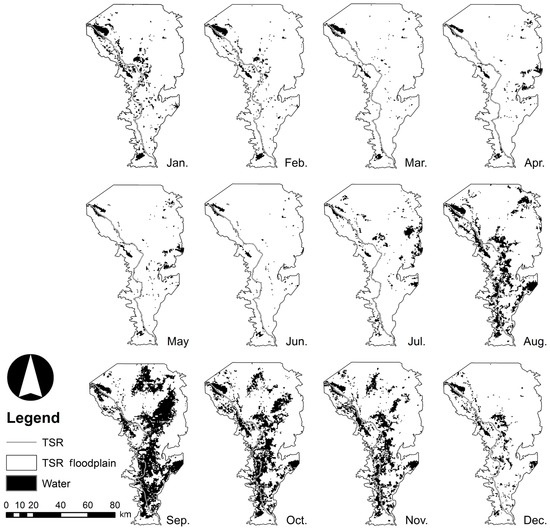
Figure 3.
Monthly changes in inundated area () in the TSR floodplain extracted from MOD09Q1 in 2003.
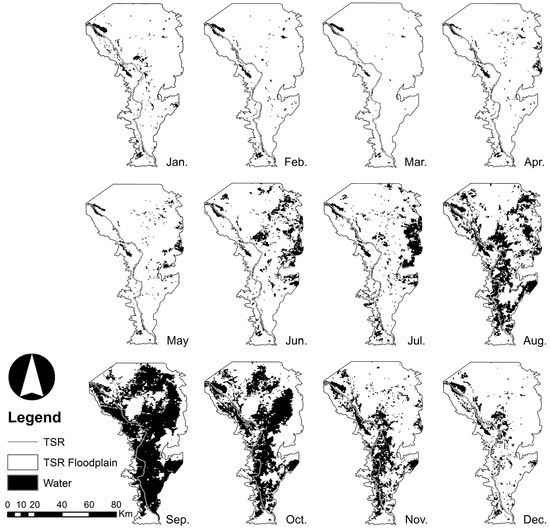
Figure 4.
Monthly changes of inundated area () in the TSR floodplain extracted from MOD09Q1 in 2004.
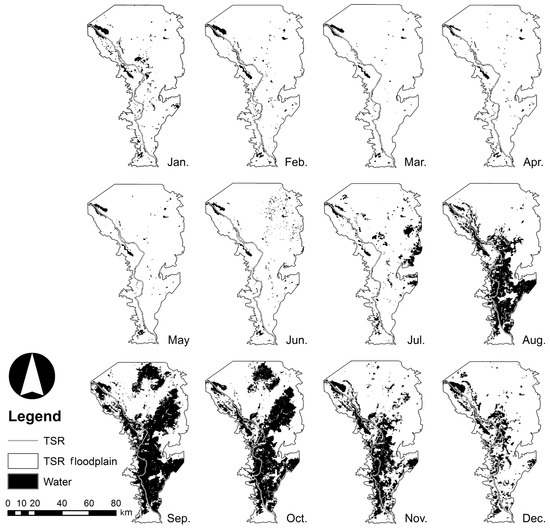
Figure 5.
Monthly changes of inundated area () in the TSR floodplain extracted from MOD09Q1 in 2005.

Table 1.
Comparison the performance of classification methods. MLC, maximum likelihood classification.
Although revealed the overall trend of the flood regime, this method was unable to correctly depict some segments of the TSR during the rising and dry seasons. In the dry season (March–May, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) there were discontinuities in river shape derived from MOD09Q1 in some parts, which may not have been the real case existing along the TSR. One possible reason for this is the coarse resolution of the MOD09Q1. Some parts of the TSR are narrower than the MOD09Q1 resolution (<250 m), and thus, such areas cannot be properly described, giving a disconnected shape of inundation in the resulting images. Another possible reason is the presence of vegetation and bare-soil/suspended sediment along the river. When such factors are dominant within a region, they mix with the water body within a single pixel of the MOD09Q1 images. These mixed pixels make it difficult for supervised classification to classify the pixel correctly as water. The maximum suspended sediment concentration reached 571 mg/L in August 2008, and the mean was 225 mg/L during a study conducted from 2008 to 2010 [37]. Thus, a high concentration of suspended sediment may alter the surface water sufficiently leading to its misclassification in the MOD09Q1 images [38]. Both reasons could result in the underestimation of in the dry season compared with the wet season. Therefore, the method performs better when the sections of the water body are larger than 250 m, which is usually observed during the wet season. In the wet season, was progressively identified as the water level of the TSR increased (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) because the area of the water body gradually increases as the water level rises, leading to an increase in the area ratio of water to non-water cover. Although the overall accuracy was high, a more independent accuracy assessment using higher resolution imagery with greater number of spectral bands, such as images within the Landsat 7 ETM+ data set, would be useful in improving the interpretation of the reference points. In addition, cloud cover (mostly found from April to October) and floodplain vegetation in the area surrounding the TSR possibly contributed to the underestimation of [6,21,22]. These results might be improved by using a combination of remotely sensed products and algorithms [39,40].
4.2. Water Volume in the Floodplain
Similar to the seasonal changes in water inundation area, the temporal MOD09Q1-based inundation volume, , ranged from 418.3 to 2223.9 million m3 (mean: 917.3 million m3), while the water level-based volume, mean , ranged from 409.6 to 1703.6 million m3 (mean: 800.4 million m3). In general, increased or decreased with respect to season and the trend in rising and receding water level. fell within the standard deviation range of , except in the peak flood period in September (Figure 6). The estimated volumes of and were consistent (R = 0.91), whereas the RMSE was estimated to be 176.7 million m3 (Figure 7).
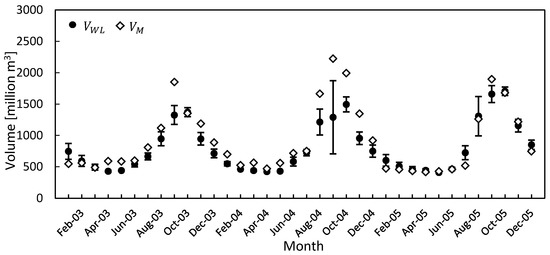
Figure 6.
Temporal changes in water volume estimations of and . The error bar represents the standard deviation of the mean estimated at three water level stations.
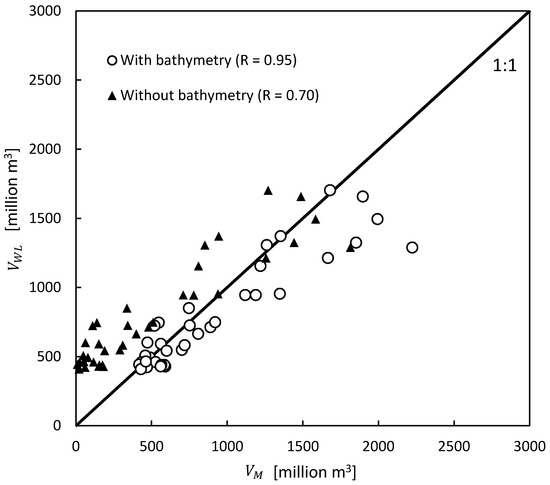
Figure 7.
Comparison of water volume estimations of and .
There was a major difference (volume > 1300 million m3) during the peak flood in September and a minor difference (volume < 1300 million m3) in the estimated volumes during rising, receding, and dry seasons, respectively (Figure 6). One possible cause of the major difference was an underestimation of . The estimated depends on the DEM values, whether they are smaller or equal to the observed water level. During the peak flood (September), the observed water level reached 7.75–8.76 m at all stations from 2003–2005, respectively, while according to the DEM, the floodplain elevation in certain regions was higher than 7.75 m. did not fully cover the actual inundated area seen in MOD09Q1, and thus, and were lower than and , respectively, in September. As stated above, the difference between the estimated volumes during rising, receding, and dry seasons could be due to differences in the spatial resolution of MOD09Q1 and DEM and errors in DEM. As mentioned in the methods, the resolution of DEM was 90 m, and this was then resampled using the resolution of MOD09Q1 (250 m). This resampling may have caused an error in the estimated area as reported previously [41,42]. As a result, the spatial error accumulates, resulting in a discrepancy in the volume estimation. In addition, the estimated 90% vertical errors of SRTM-DEM in the Eurasia region were previously found to be 6.2 m [35], and furthermore, the elevation in DEM is in the integer format metric units. Thus, any analysis associated with SRTM-DEM will have an error of at least 1 m [41,42]. It should be noted that SRTM was launched in February 2000, which was one of the wettest records in TSL [43] and in this study; SRTM-DEM is considered dry floodplain ground. The above-mentioned limitations probably caused errors in the estimation of water volume during receding, dry, and rising seasons (November 2003 to August 2004). The correlation coefficient during each season (excluding September) showed better consistency with the overall water volume estimations (R = 0.95), reducing the RMSE to 118.6 million m3 (Figure 7). Further improvements can also be expected using either the digital terrain model (DTM) derived from the topographic map or with the release of the 1 arc-second (approximately 30 m) version of global SRTM-DEM in the future.
Without bathymetric data incorporated with SRTM-DEM, the volume estimation would have been underestimated, where most of the points lie over the perfect line (Figure 7). During the dry season (April), the estimated volume determined with and without bathymetric data was 418.2 and 8.7 million m3, respectively; a difference of 409.6 million m3 (98%). During the peak flood (September), the estimated volumes with and without bathymetric data were 2223.9 and 1814.3 million m3, respectively, with a difference of 409.6 million m3 (18.4%). As a result, the water volume determined without bathymetric data may have been underestimated by 18.4%–98% from the wet to dry season, respectively. Thus, the method using bathymetric data highlighted in this study provides substantially improved water volume estimations of floodplains than those determined without bathymetric data.
The TSR receives an inflow of 41,800 million m3 from and releases an outflow of 68,800 million m3 to the MR annually [11]. Based on the estimated maximum, , in September 2004, the TSR and its floodplain accounted for 5.3% and 3.2% of this mean annual inflow and outflow of TSR, respectively. This implies that the floodplain of the TSR functions as an important water reservoir for the MR basin as well as TSL, behaving as a natural channel. This active exchange flow stabilizes the flow of the MR, increasing it (20%–50% of the MR flow) during the dry season [11,21]. Thus, the TSR and its floodplain play an important role in storing 5.3% of the mean annual inflow from the MR, thereby reducing flooding from other areas during the wet season, and by providing additional flow to the MR delta during the dry season.
These positive results in water inundation and volume estimation enhance our understanding of the TSR. Satellite-based inundation maps and water volume estimates can be used to validate hydrodynamic modeling of flow reversal. This study also demonstrated the use of remote sensing data as a cost effective and important data source for assessment and monitoring of the TSR where the number of gauge stations could be a limitation. A forthcoming paper is being prepared that describes the subsequent phase of the research, which was to perform hydrologic-hydrodynamic modelling. The results of the satellite-based inundation mapping can then be related and analyzed.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the use of a simple and straightforward method applied to MODIS satellite composite product and SRTM-DEM combined with bathymetric data for estimating inundation and volume in the TSR and its floodplain in different seasons over three years. Although the estimated inundation areas showed marginal errors, the accuracy achieved was 96.9% with the omission error of 3.1%. Adding NDVI as “third band” in MLC provided higher accuracy compared to thresholding NDVI and pure MLC (two bands) only. The estimated inundation areas also adequately described the seasonal pattern and flood cycle in the TSR. The method using bathymetric data highlighted in this study provides substantially better water volume estimations of floodplains than those determined without, leading to improvements in estimates by 18.4%–98% in the wet and dry seasons, respectively. This method could therefore lead to an improvement of at least 18.4% in water volume estimations in other seasonal change studies in which the DEM is not combined with bathymetric data. In addition, the finding suggests that the TSR floodplain functions as an important water reservoir, accounting for 5.3% of the mean annual inflow from the MR basin and TSL. Overall, the results increased our knowledge of hydrological processes governing this region, thereby enhancing our understanding of the TSR and supporting further hydrodynamic modeling of reversal flow and connectivity for flood and water resource management in the area.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank UP-DOST DREAM Program for the additional field equipment and computing resources and Mekong River Commission (MRC) for providing the dataset. This research was funded by AUN-SEED-Net (JICA), SATREPS (JST, JICA), and KAKENHI (15K00592, PI Yoshimura Chihiro).
Author Contributions
Sokly Siev made substantial contributions to data collection, analysis, drafting, and the editing of the manuscripts. Enrico C. Paringit developed the research idea, and supervised and guided this work. Chihiro Yoshimura and Seingheng Hul helped in editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hudson, P.F.; Heitmuller, F.T.; Leitch, M.B. Hydrologic connectivity of oxbow lakes along the lower Guadalupe River, Texas: The influence of geomorphic and climatic controls on the “flood pulse concept”. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tockner, K.; Malard, F.; Ward, J.V. An extension of the Flood pulse concept. Hydrol. Proc. 2000, 14, 2861–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberts, D. The Tonle Sap Lake as a Productive Ecosystem. Int. J. Water Res. Dev. 2006, 22, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Navy, H.; Vuthy, L.; Tiongco, M. Socioeconomic Assessment of Freshwater Capture Fistheries in Cambodia: Report on a Household Survey; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 1998; p. 186. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Piman, T.; Kummu, M.; Caruso, B.S.; Killeen, T.J. Quantifying changes in flooding and habitats in the Tonle Sap Lake (Cambodia) caused by water infrastructure development and climate change in the Mekong Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortle, K.G. Consumption and the Yield of Fish and Other Aquatic Animals from the Lower Mekong Basin; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2007; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Lamberts, D.; Koponen, J. Flood pulse alterations and productivity of the Tonle Sap ecosystem: A model for impact assessment. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2008, 37, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Basin Development Plan Programme Phase 2: Assessment of Basin-Wide Development Scenarios; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2011; pp. 1–254. [Google Scholar]
- Chea, R.; Guo, C.; Grenouillet, G.; Lek, S. Toward an ecological understanding of a flood-pulse system lake in a tropical ecosystem: Food web structure and ecosystem health. Ecol. Model. 2016, 323, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Tes, S.; Yin, S.; Adamson, P.; Józsa, J.; Koponen, J.; Richey, J.; Sarkkula, J. Water balance analysis for the Tonle Sap Lake-floodplain system. Hydrol. Proc. 2014, 28, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, P. The Potential Impacts of Hydropower Developments in Yunnan on the Hydrology of the Lower Mekong. Int. Water Power Dam Constr. 2001, 53, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Laos; Nam Thuen II Power Company Ltd.; EcoLao; Norplan. Cumulative Impact Analysis and Nam Theun 2 Contributions: Final Report; Government of Lao PDR: Vientiane, Laos, 2004; p. 143.
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Holtgrieve, G.W.; Koponen, J.; Piman, T. Impacts of hydropower and climate change on drivers of ecological productivity of Southeast Asia’s most important wetland. Ecol. Model. 2014, 272, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, T.A.; Arias, M.E.; Piman, T. Historical impact of water infrastructure on water levels of the Mekong River and the Tonle Sap system. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4529–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.; Kummu, M. Water Resource Models in the Mekong Basin: A Review. Water Res. Manag. 2012, 26, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Sarkkula, J. Impact of the Mekong River Flow Alteration on the Tonle Sap Flood Pulse. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2008, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Västilä, K.; Kummu, M.; Sangmanee, C.; Chinvanno, S. Modelling climate change impacts on the flood pulse in the Lower Mekong floodplains. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.A.; Reid, M.C.; Thoms, M.C. Ecological significance of hydrological connectivity for wetland plant communities on a dryland floodplain river, MacIntyre River, Australia. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benger, S.N. Remote sensing of ecological responses to changes in the hydrological cycles of the Tonle Sap, Cambodia. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 2007 (IGARSS 2007), Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July, 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 5028–5031.
- Fujii, H.; Garsdal, H.; Ward, P.; Ishii, M.; Morishita, K.; Boivin, T. Hydrological roles of the Cambodian floodplain of the Mekong River. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2003, 1, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Van Nguyen, N.; Kotera, A.; Ohno, H.; Ishitsuka, N.; Yokozawa, M. Detecting temporal changes in the extent of annual flooding within the Cambodia and the Vietnamese Mekong Delta from MODIS time-series imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Ditmar, P.G.; Steele-Dunne, S.C.; Gunter, B.C.; Sutanudjaja, E.H. Assessing total water storage and identifying flood events over Tonlé Sap basin in Cambodia using GRACE and MODIS satellite observations combined with hydrological models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Trung, N.; Choi, J.H.; Won, J.S. A Land cover variation model of water level for the floodplain of Tonle Sap, Cambodia, derived from ALOS PALSAR and MODIS data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2238–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. MRCS/WUP-FIN Model Report: Modelling Tonle Sap Watershed And Lake Processes For Environmental Change Assessment; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2003; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Elliott, V. Modelling future changes of habitat and fauna in the Tonle Sap wetland of the Mekong. Environ. Conserv. 2013, 41, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Overview of the Hydrology of the Mekong Basin; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mekong River Commission/Information and Knowledge Management Programme. Final Report, Detailed Modelling Support Project (DMS); Finnish Environment Institute: Helsinki, Finland; EIA Ltd.: Espoo, Finland; Mekong River Commission (MRC) and Information and Knowledge Management Programme (IKMP): Vientiane, Laos, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- MRCS/WUP-FIN. Final Report—Part 2: Research Findings and Recommendations. WUP-FIN Phase 2—Hydrological, Environmental and Socio-Economic Modelling Tools for the Lower Mekong Basin Impact Assessment; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2007; p. 126. [Google Scholar]
- Vermote, E.F.; Vermeulen, A. Atmospheric Correction Algorithm: Spectral Reflectances (MOD09); NASA: Washington DC, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Landscape-scale Characterization of Cropland in China Using Vegetation and Landsat TM Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3579–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.; Haase, J.A.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS, Proceedings of the 3rd ERTS Symposium, Washington DC, MD, USA, 10–14 December, 1973; NASA SP353: Washington DC, MD, USA, 1973; pp. 309–317.
- Spatial-analyst. Available online: http://spatial-analyst.net/ILWIS/htm/ilwismen/confusion_matrix.htm (accessed on 25 August 2016).
- Congalton, R.G. A Review of Assessing the Accuracy of Classifications of Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Hydrographic Atlas; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Kummu, M.; Oeurng, C. Reappraisal of sediment dynamics in the Lower Mekong River, Cambodia. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2014, 39, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.-R.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Gao, B.-C.; Davis, C.O. Remote Sensing of Suspended Sediments and Shallow Coastal Waters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Huang, X.; Feng, Q.; Ma, X.; Liang, T. Toward Improved Daily Cloud-Free Fractional Snow Cover Mapping with Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6986–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoan, N.T.; Tateishi, R.; Alsaaideh, B.; Ngigi, T.; Alimuddin, I.; Johnson, B. Tropical forest mapping using a combination of optical and microwave data of ALOS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, D.; Goldberg, M.; Stefanidis, A. Derivation of 30-m-resolution water maps from TERRA/MODIS and SRTM. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Liao, J.; Li, X.; Guo, H. Application of the inundation area—Lake level rating curves constructed from the SRTM DEM to retrieving lake levels from satellite measured inundation areas. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Annual-Mekong-Flood-Report-2011; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2015; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).